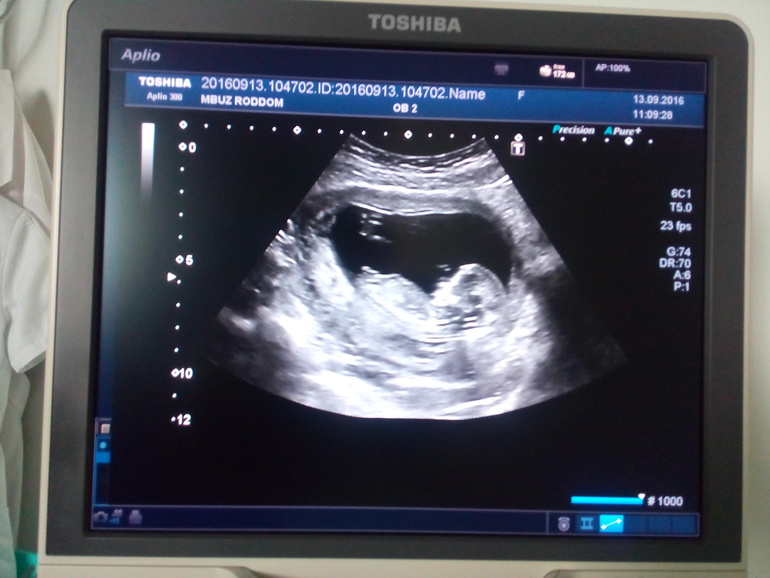
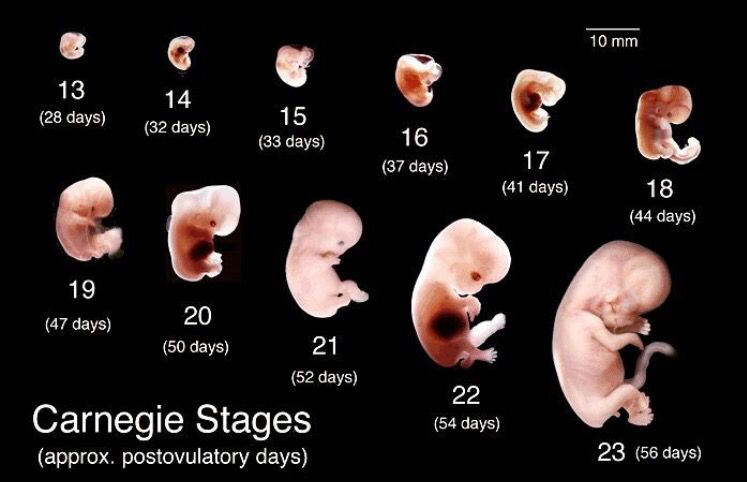
Migraines 13 weeks pregnant
Headaches during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Headaches during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content9-minute read
Listen
If you have a severe headache during pregnancy that is not usual for you, seek medical help immediately.
Key facts
- It’s common to get mild headaches in the first few months of pregnancy because of hormonal changes.
- If you usually suffer from migraines, they may get better, worse, change or stay the same when you’re pregnant.
- Headaches during pregnancy may be triggered by poor sleep, stress, dehydration, low blood sugar or eye strain.
- If your headache doesn’t settle with simple measures (for example, rest and rehydration), you can take paracetamol.
- A headache after 20 weeks can be a sign of pre-eclampsia, which is a serious pregnancy condition that needs medical attention – see your doctor or midwife.
Does pregnancy cause headaches?
Many people get mild headaches when they are pregnant. Headaches can often be triggered by a change in hormones. They are more common in the first few months of pregnancy.
If you usually suffer from migraines, you might notice a change when you’re pregnant. There’s a good chance that your migraines will improve after the first trimester. This may be because your oestrogen level starts to stabilise. However, some people don’t notice a change, or may get worse migraines during pregnancy. You also might notice different changes from one pregnancy to the next.
Headaches can develop for many different reasons — it’s not always because of pregnancy hormones.
Why else might I get headaches during pregnancy?
Besides hormonal changes, there are many triggers that cause headaches in general, but might occur more often when you’re pregnant, such as:
- not getting enough sleep
- withdrawal from caffeine — such as in coffee, tea or cola drinks
- low blood sugar from not eating regularly
- dehydration
- feeling stressed, anxious or depressed
- eye strain — especially as your eye muscles relax during pregnancy
Many of these triggers can cause tension headaches, which are very common.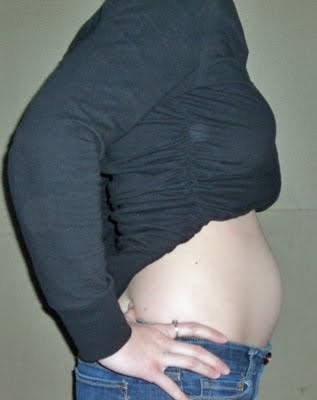 The pain is usually mild and on both sides of your head.
The pain is usually mild and on both sides of your head.
Some of these triggers can cause migraines, which are more severe and mostly occur on one side of your head. If you have migraines, you might also feel sick or vomit and be sensitive to light or sound.
Pre-eclampsia
If you start getting frequent headaches after 20 weeks of pregnancy, this could be a sign of a more serious pregnancy condition called pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is when you have high blood pressure that affects your kidneys and sometimes other parts of your body. If you have a pre-eclampsia headache, you may find that simple pain-relieving medicines like paracetamol don’t help.
It’s very important to tell your doctor or midwife if you are getting headaches in the second half of pregnancy, or if your headaches are very severe.
If you have a severe headache during pregnancy, call your doctor or midwife. It could be something more serious.
Health conditions
Just like when you’re not pregnant, a headache can sometimes be a sign of other health conditions, including:
- infections, such as an ear infection or flu
- sinusitis
- problems with your teeth
- an aneurysm or stroke
What can I do to treat a headache when I’m pregnant?
If you have a headache, you could try:
- having a nap, or resting with your eyes closed
- drinking water
- having something to eat
- putting a cold or heat pack on your forehead or the back of your neck
- asking someone to give you a gentle neck massage
If you need to take medicine for pain relief, paracetamol is safe during pregnancy. Pain-relieving medicines can actually cause headaches if you take them too often, so don’t take paracetamol more than 3 times a week.
Pain-relieving medicines can actually cause headaches if you take them too often, so don’t take paracetamol more than 3 times a week.
When you’re pregnant, avoid anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen or aspirin and medicines that contain caffeine.
What can I do to prevent headaches during pregnancy?
If you find you are getting mild headaches often, it’s a good idea to:
- getting more sleep
- drink at least 8 cups of water a day
- go to pregnancy yoga classes or do some other type of exercise
- learn relaxation or stress management techniques
- don't go more than 4 hours without eating
- avoid processed foods
- see an optometrist for an eye check
What can I do if I suffer from migraines during pregnancy?
If you suffer from migraines, try to avoid things that may trigger migraines for you. People have different triggers for migraines, so it’s important to learn what your personal triggers are.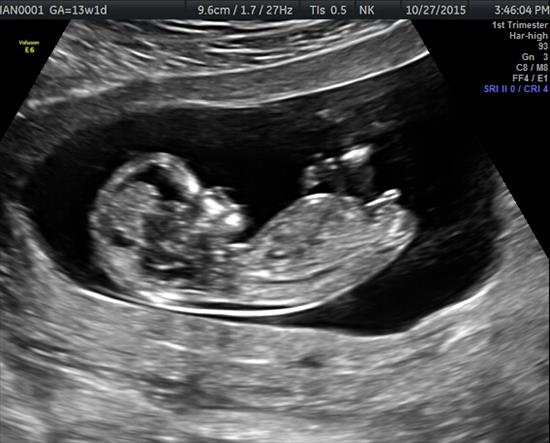 Keep a headache diary, and see if your triggers include:
Keep a headache diary, and see if your triggers include:
- specific foods such as chocolate, or food additives such as caffeine or MSG
- bright or flickering lights, strong smells and loud sounds
- not enough sleep, or too much sleep
- skipping meals
- computer or movie screens
- strenuous exercise
- emotional triggers such as arguments or stress
Check with your doctor, pharmacist or midwife before you take a medicine for your migraine, to make sure it’s safe during pregnancy.
Paracetamol is the safest option for pain relief. If paracetamol doesn’t help and you need something stronger, ask your doctor about if you can take codeine. Try not to take codeine often, as you could become dependent on it and your baby could have withdrawal symptoms after they are born.
Most triptans (migraine medicines) are not considered safe in pregnancy. If you don’t get relief from paracetamol and codeine, you may be able to take sumatriptan occasionally. This medicine is available from a pharmacist and requires a prescription. Speak with your doctor or pharmacist before using it to help you understand the risks and the benefits of this medicine during pregnancy.
This medicine is available from a pharmacist and requires a prescription. Speak with your doctor or pharmacist before using it to help you understand the risks and the benefits of this medicine during pregnancy.
You can take metoclopramide if you suffer from nausea or vomiting with migraines.
Acupuncture can help treat migraines. Talk to your doctor or midwife first to check it’s safe for you. Make sure to tell your acupuncturist that you’re pregnant, so they can avoid certain points that shouldn’t be used in pregnancy.
When should I see a doctor?
See your doctor or midwife if you have symptoms of pre-eclampsia, including:
- a headache that doesn’t get better with paracetamol
- severe pain below your ribs
- heartburn that doesn’t disappear after taking antacids
- sudden swelling in your face, hands or feet
- blurred vision
Headaches can sometimes be a sign of other serious health conditions. Contact your doctor straightaway if you have:
- a sudden severe headache
- a change in your usual headaches
- your first-ever migraine
- a headache together with fever, neck stiffness, sensitivity of your eyes to light, drowsiness or weakness of your arm or leg
- a recent head injury
CHECK YOUR SYMPTOMS — If you are feeling unwell and not sure what to do next, check your symptoms using the healthdirect Symptom Checker tool.
- Speak with your doctor or midwife, particularly if you have any concerns about pre-eclampsia.
- For more information about headaches, visit Migraine and Headache Australia.
- For more information about medicines you can take during pregnancy, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Tommy’s (Headaches in pregnancy – should I be worried?), NSW Government (Having a baby), Migraine & Headache Australia (Adults and headache), Migraine & Headache Australia (Migraine), Migraine & Headache Australia (Headache triggers), Migraine & Headache Australia (Headache treatment – no absolute cure), Migraine & Headache Australia (What is headache?), Migraine & Headache Australia (Tension headache), RANZCOG (Pre-eclampsia and high blood pressure in pregnancy), Royal Women's Hospital (Medicines in pregnancy), NSW Health (Migraine in pregnancy and breastfeeding), RANZCOG (Q&A: severe headache in the third trimester), Migraine & Headache Australia (Self-Care & Trigger Management)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: September 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Common discomforts during pregnancy
Need more information?
Treatment of Headache - Migraine & Headache Australia
There is no absolute cure for headache, but many effective treatments exist which can prevent and treat different headache types.
Read more on Migraine and Headache Australia website
Common discomforts during pregnancy
Your body has a great deal to do during pregnancy. Sometimes the changes taking place will cause irritation or discomfort, and on occasions they may seem quite alarming.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Adults and Headache - Headache Australia
Studies confirm that tension-type headache and migraine are more common in women while cluster headache, a rare form of headache, is more common in men.
Read more on Migraine and Headache Australia website
Tension-type Headache - Migraine & Headache Australia
Tension-type headache is one of the most common everyday headaches. It causes a dull, non-throbbing pain and can be caused by stress.
Read more on Migraine and Headache Australia website
Migraine Management Tips - Headache Australia
It’s important to be organized and informed about your migraine attacks and how they impact your life. Here are some migraine management tips to assist.
Read more on Migraine and Headache Australia website
Six ways to manage migraine without drugs | The George Institute for Global Health
We’ve all heard of the crushing headache pain that comes with migraine but did you know that one in every seven people experience them, three in every four people with migraine are females, and migraine is the number one cause of disability in young people? With so many people affected worldwide, you’d think modern medicine would have developed a solution by now but unfortunately there’s still no definite cure for migraine.![]()
Read more on The George Institute for Global Health website
Stress and pregnancy
Stress is a normal response to major life changes but you can reduce pregnancy-related stress. Learn more about causes and strategies to help.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Mumps and pregnancy
Find out about mumps and its symptoms, how it spreads, how to manage it at home, and how to avoid mumps if you’re planning a pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Toxaemia of pregnancy (pre-eclampsia) - MyDr.com.au
Pre-eclampsia, also known as pre-eclamptic toxaemia, or just toxaemia, occurs in pregnancy, causing problems for the baby and mother.
Read more on myDr website
Experiences of pregnancy - Healthtalk Australia
The parents we spoke with found pregnancy life-changing and exciting, and described at length its physical and emotional dimensions.
Read more on Healthtalk Australia website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Sign in
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Pregnancy and Headaches: When Should I Worry?
Pregnancy is a beautiful thing to be celebrated, but few people fill you in on the not-so-great symptoms that may occur during the journey. Namely, heartburn, gas, constipation and, for some pregnant mamas, headaches.
Namely, heartburn, gas, constipation and, for some pregnant mamas, headaches.
While headaches can be just another normal symptom of pregnancy, should they ever be a cause for concern?
“Headaches are common in women both in and outside of pregnancy,” said Kelley Saunders, MD, an OBGYN with Banner – University Medicine Women’s Institute. “But whether they are normal or not should always be discussed with your doctor."
Here is some insight into what causes headaches during pregnancy, some remedies to treat them and why your doctor should be kept in the loop.
Is it a headache or something else?
It isn’t always easy to tell what kind of headache you’re having, but the most common types of headaches during pregnancy are tension-type headaches, migraines and cluster headaches.
Tension headaches are the most common kind of headache in pregnant women. It can feel like someone is trying to squish your head like a watermelon. If you carry your stress in your shoulders and neck, you may be more susceptible to this kind of headache.
Migraines are a particular type of headache that occur on one side of the head. For some women, migraine headaches can get worse the first few months and then improve in later stages of pregnancy. For others, they may experience no change, decrease or difference in their migraines.
Cluster headaches are less common but can occur during pregnancy. You’ll suddenly have severe pain around your eyes or temples usually about the same time every day.
The good news is that there are plenty of pregnancy-safe things you can do to prevent and relieve the most common pregnancy headaches.
Tips for relieving mild headaches
- Get plenty of rest. Sleep is especially hard later in your pregnancy but is so important to physical and mental health. Find yourself a comfy prenatal pillow and snuggle away.
- Drink plenty of water. Pregnant moms require more water than the average person. While you may want to avoid extra trips to the bathroom, adequate fluid intake is important for you and baby.

- Eat regular, well-balanced meals. To prevent low blood sugar, eat small meals throughout the day. Avoid sugar, like soda and candy.
- Get a prenatal massage. A full-body massage can release tension in the muscles of your neck, shoulders and back.
- Use warm or cool compresses on head, neck and shoulders.
- Avoid triggers. Keep a journal to help identify specific triggers so you can learn what to avoid. Some common headache triggers include strong odors and nitrites or nitrates.
- Try exercise and relaxation techniques. There’s evidence that regular exercise can reduce stress and boost overall mood. Check with your doctor first before starting any new fitness routines.
- Take acetaminophen to relieve symptoms (as approved by doctor).
- Take caffeine in doses less than 200mg in a day (as approved by doctor).
If you have a history of migraines, however, your doctor may treat them differently during pregnancy. Discuss with your doctor what medications are safe to take during pregnancy.
Is my headache a cause for concern?
Sometimes. Headaches tend to be more common in the first and third trimesters, but they can occur in the second trimester as well. While there are common causes for headaches during pregnancy, it’s important to note that headaches during the second and third trimester can also be due to high blood pressure, called preeclampsia.
“Preeclampsia is a pregnancy-related condition that requires prompt evaluation and management with an obstetrician or maternal fetal medicine specialist,” Dr. Saunders said. “Elevated blood pressure prior to pregnancy puts a woman at increased risk for preeclampsia.”
When should I call my doctor?
Whether you experience headaches or not, it’s always important to discuss your pre-pregnancy history, obstetrical history and concerns with your doctor for an individualized assessment and management plan. However, if none of the above treatments resolve your mild headache or your headaches become more frequent and severe, talk to your doctor to determine the cause.
However, if none of the above treatments resolve your mild headache or your headaches become more frequent and severe, talk to your doctor to determine the cause.
“This includes new headaches that present after 20 weeks, a sudden onset of severe headaches, headaches associated with a fever, mental health changes, elevated blood pressure and vision changes,” Dr. Saunders said. “It’s important to keep an open line of communication with your physician and let them know about any changes in your health so they can rule out anything serious."
Got questions? We can help!
If a headache is keeping you up at night and your doctor isn’t available, call the Banner Nurse Now line, a free health care service that offers advice 24-hours a day, seven days a week. Call 844-259-9494.
Check out other pregnancy articles on our Banner Health blog
Pregnancy is an exciting, but also a bit scary time (especially if this is your first baby). Here are some other reads to help guide you through the trimesters and welcoming baby:
- 5 Tips for Having a Happy, Healthy Pregnancy
- Expect the Unexpected: How Your Body Changes During Pregnancy
- What To Expect In The Second Trimester
- Understanding Pulmonary Embolism Risk During Pregnancy
Women's Health Pregnancy
Join the Conversation
Migraine during pregnancy: what to do
Migraine is a benign disease, it does not affect the course of pregnancy and fetal development. However, migraine and pregnancy is a combination that requires a responsible attitude. Especially with frequent migraines (more than 2 times a week) and migraines with aura, because:
However, migraine and pregnancy is a combination that requires a responsible attitude. Especially with frequent migraines (more than 2 times a week) and migraines with aura, because:
-
medicines approved for use, few,
-
and the approach to the treatment and prevention of migraine during this period is extremely individual: it depends on the frequency, severity and duration of headache, the degree of impact on life.
Our neurologist Daria Korobkova conducted a live broadcast on the clinic's Instagram account, where she told how migraine and pregnancy are connected, why attacks become more frequent or disappear, and answered subscribers' questions. The ether was saved, see “Air recording: migraine during pregnancy and GV.
We will tell about migraine during breastfeeding separately.
The statistics of clinical observations of migraine during pregnancy looks like this:
In 60-70% of pregnant women with migraine, headache attacks become less frequent, milder, or even completely disappear in the second and third trimesters. This is due to the stabilization of estrogen levels. By the beginning of the second trimester, it rises 6 times and its fluctuations stop.
This is due to the stabilization of estrogen levels. By the beginning of the second trimester, it rises 6 times and its fluctuations stop.
In other women, migraines during pregnancy either remain unchanged or worsen. But as the duration of pregnancy increases, the proportion of such women gradually decreases:
If at the end of the first trimester the frequency and intensity of attacks persist, then it is most likely that migraine will disturb the woman throughout the entire period of pregnancy and after childbirth too.
How to manage migraine during pregnancy?
The main thing here is to learn how to control seizures and, if necessary, seek medical help.
-
Follow lifestyle advice:
-
get enough sleep;
-
drink enough fluids;
-
eat fractionally and without long breaks;
-
rest;
-
avoid stressful situations.
 This is one of the main provocateurs of migraine. Psychotherapy, relaxation and stress management are here to help you.
This is one of the main provocateurs of migraine. Psychotherapy, relaxation and stress management are here to help you.
-
Keep a headache diary. This will help you take control of migraine triggers.
Yes, these simple recommendations are sometimes enough to make seizures less frequent! Pregnancy is a special state of a woman. If in other periods of life we do not take such recommendations so seriously, then in this situation it is worth trying to change the philosophy of life and attitude towards ourselves =)
How to relieve an attack?
-
Favor non-drug methods. Sometimes, in order to relieve an attack, it is enough to eliminate an unfavorable factor:
-
dry biscuits, ginger, or applesauce may help with nausea;
-
for dehydration - diluted juice or other liquid;
-
sleep, walking or breathing exercises can also help to cope;
-
If the attacks are severe, interfere with your life, then under the supervision of a specialist, you can resort to drug therapy.

PARACETAMOL is considered the safest and can be taken throughout pregnancy.
All other drugs have nuances. For example:
-
ibuprofen can be taken in the second trimester, and in the first trimester it is better to limit, in the third trimester the drug is contraindicated for use;
-
aspirin is prohibited in the 3rd trimester and is undesirable for taking in the first two, as it can cause extremely undesirable consequences;
-
It is strictly forbidden to use ergotamine and opioid analgesics;
-
triptans are not officially approved for use during pregnancy as no controlled studies have been conducted. However, clinical observations of women around the world who took them on their own showed no adverse effects on the fetus. We discussed this issue in more detail on the air.
!Other than paracetamol, we do not recommend the use of any drug without a doctor's prescription.
When to see a doctor:
-
migraine occurred for the first time during pregnancy;
-
if migraine attacks suddenly become more frequent and stronger;
-
if the aura became longer or appeared for the first time;
-
if the headache is rapidly increasing and has an unusual character;
-
if the pressure rises during the headache.
Read more articles about headaches in our Telegram channel.
How do doctors diagnose headaches? Answering questions about Ajovi and Irinex If you are pregnant and suffer from migraines
Migraine during pregnancy: description of the disease, causes, symptoms, cost of treatment in Moscow
Migraine during pregnancy is a fairly common phenomenon that should not be ignored and treated. There are many reasons for the appearance of the problem during this period. After childbirth, the disease usually disappears completely. In the next pregnancy, there is a risk of recurrence of the violation, but it will not necessarily appear again. Since the pain negatively affects not only the condition of the woman, but also the child, it is necessary to take drugs to eliminate the attack, but only those that are allowed for pregnant women.
There are many reasons for the appearance of the problem during this period. After childbirth, the disease usually disappears completely. In the next pregnancy, there is a risk of recurrence of the violation, but it will not necessarily appear again. Since the pain negatively affects not only the condition of the woman, but also the child, it is necessary to take drugs to eliminate the attack, but only those that are allowed for pregnant women.
Migraine in pregnant women occurs not infrequently, since, in addition to hormonal changes in the body, there are also changes in the psycho-emotional state, which often also act as a trigger for the development of pathology. Depending on the duration of pregnancy, a woman's well-being may improve or worsen. The peak of migraines in most cases occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy, when a woman's body undergoes especially rapid hormonal changes. In the later stages, headaches may begin to disturb due to changes in the spine that appear against the background of a shift in the center of gravity.
Reasons
Migraine attacks during pregnancy are usually triggered by specific factors. Migraines during early pregnancy can be caused by the following reasons:
-
specific stresses for the body, which are associated with the process of implantation of the egg and the beginning of the development of the embryo;
-
a sharp change in hormonal levels;
-
dehydration due to changes in metabolic processes in the body and a woman's lack of attention to herself;
-
the appearance of food intolerance against the background of early toxicosis.
Also, a number of women in the first trimester of pregnancy often experience migraine-provoking nervous strain due to constant concern about their condition, the development of the child and the upcoming birth.
In the second trimester, a woman has a significant improvement in her condition. The frequency of seizures is reduced, and because of the ability to use more drugs, they become less painful. The main provocateurs of the appearance of headaches in this period are the following factors:
The main provocateurs of the appearance of headaches in this period are the following factors:
-
physical overload - it occurs if a woman does not reduce physical activity, continuing to lead the same lifestyle as before pregnancy. As a result, an attack occurs as a protest of the body against what is happening;
-
strong emotional experience;
-
sudden changes in the weather - they affect a woman if she suffered from meteorological dependence before pregnancy;
-
inhalation of very sweet heavy odours.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, the intensity of migraine increases. Due to the ongoing changes in the spine, blood circulation begins to deteriorate to a large extent, due to which even a slight vascular spasm is enough for a migraine attack. The main reasons that can cause it are:
-
drinking a large amount of liquid at once - in order not to provoke an attack, you need to drink often, but little by little, thereby not causing a sharp influx of water into the blood;
-
staying in an uncomfortable position, which significantly worsens blood circulation in the lower extremities;
-
prolonged stay in the supine position, which also worsens blood circulation;
-
eating spicy or spicy foods;
-
great excitement or prolonged nervous tension.

Migraines may persist for some time after childbirth due to hormonal changes in the body. However, this phenomenon is not always the case and is considered the exception rather than the rule for migraine during pregnancy.
Is an aura possible
Migraine with aura occurs in pregnant women with the same frequency as the classical one. In a quarter of cases, a few minutes before an attack or a maximum of an hour before it, a woman develops previous neurological disorders. If they do not appear strongly, then the patient has time to take medications, thereby relieving an attack, or to return home. When the symptoms of the aura are strong, they can cause no less torment than the pain attack itself.
You can talk about the presence of an aura in a woman if any of the following symptoms are present before a migraine attack:
-
visual disturbances - these may cause loss of visual fields, temporary loss of vision in one or both eyes, flickering flies before the eyes or flashes of light;
-
severe weakness - it can spread to the whole body, but more often it is felt only in the limbs of the side from which the head will hurt in the future.
 The opposite side of the body suffers much less often;
The opposite side of the body suffers much less often; -
tingling in the limbs and upper half of the body, even affecting the tongue and lips;
-
goosebumps;
-
complete loss or significant reduction in the sensation of limbs;
-
various speech disorders such as confusion or slurring.
Quite often, in pregnant women with migraine with aura, such a phenomenon is noted that if during this period the effect of the negative factor is eliminated, a further attack does not develop, even if medications are not taken. Because of this, in such a situation, a woman needs to fix as accurately as possible what caused the deterioration.
Is an attack dangerous for the fetus
Today, thanks to numerous studies, doctors have been able to find out whether a migraine attack affects the fetus. The unborn child is able to feel the emotions of the mother and her pain, which is why there is a negative change in his condition at the time of the attack. Also, against the background of pain, a spasm of the vessels supplying the placenta often occurs. As a result, the fetus begins to receive significantly less oxygen, which causes hypoxia in it, which, with frequent repetitions of migraine attacks, can cause mental development disorders against the background of brain damage.
Also, against the background of pain, a spasm of the vessels supplying the placenta often occurs. As a result, the fetus begins to receive significantly less oxygen, which causes hypoxia in it, which, with frequent repetitions of migraine attacks, can cause mental development disorders against the background of brain damage.
Medicines prescribed for pregnant women must be taken during an attack without fail. They will not harm the child, as they do not penetrate the placental barrier and effectively relieve pain, eliminating its negative impact. It is unacceptable to prescribe such funds on your own, since mistakes can be too dangerous for the fetus. All drugs are correctly selected taking into account the duration of pregnancy only by a doctor.
Prophylaxis
Preventive measures against migraine during pregnancy greatly help to reduce the risk of this problem. Additionally, it will help improve well-being and a proper lifestyle. The main preventive measures during pregnancy include:
-
full sleep at least 9 hours a day;
-
taking light sedatives when nervous tension appears;
-
providing a comfortable temperature in the room;
-
drinking frequently and in small amounts;
-
eating food that does not cause a burning sensation in the mouth.