Hcg level ranges
HCG blood test - quantitative Information | Mount Sinai
Serial beta HCG; Repeat quantitative beta HCG; Human chorionic gonadotropin blood test - quantitative; Beta-HCG blood test - quantitative; Pregnancy test - blood - quantitative
A quantitative human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) test measures the specific level of HCG in the blood. HCG is a hormone produced in the body during pregnancy.
Other HCG tests include:
- HCG urine test
- HCG blood test -- qualitative
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed. This is most often taken from a vein. The procedure is called a venipuncture.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Why the Test is Performed
HCG appears in the blood and urine of pregnant women as early as 10 days after conception.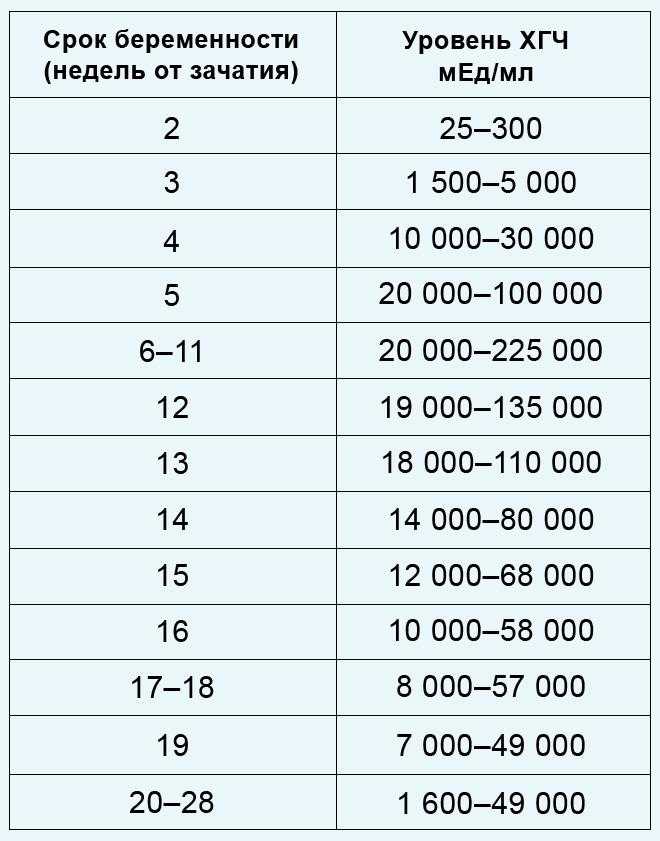 Quantitative HCG measurement helps determine the exact age of the fetus. It can also assist in the diagnosis of abnormal pregnancies, such as ectopic pregnancies, molar pregnancies, and possible miscarriages. It is also used as part of a screening test for Down syndrome.
Quantitative HCG measurement helps determine the exact age of the fetus. It can also assist in the diagnosis of abnormal pregnancies, such as ectopic pregnancies, molar pregnancies, and possible miscarriages. It is also used as part of a screening test for Down syndrome.
This test is also done to diagnose abnormal conditions not related to pregnancy that can raise HCG level.
Normal Results
Results are given in milli-international units per milliliter (mUI/mL).
Normal levels are found in:
- Non-pregnant women: less than 5 mIU/mL
- Healthy men: less than 2 mIU/mL
In pregnancy, HCG level rises rapidly during the first trimester and then declines slightly. The expected HCG ranges in pregnant women are based on the length of the pregnancy.
The expected HCG ranges in pregnant women are based on the length of the pregnancy.
- 3 weeks: 5 - 72 mIU/mL
- 4 weeks: 10 -708 mIU/mL
- 5 weeks: 217 - 8,245 mIU/mL
- 6 weeks: 152 - 32,177 mIU/mL
- 7 weeks: 4,059 - 153,767 mIU/mL
- 8 weeks: 31,366 - 149,094 mIU/mL
- 9 weeks: 59,109 - 135,901 mIU/mL
- 10 weeks: 44,186 - 170,409 mIU/mL
- 12 weeks: 27,107 - 201,165 mIU/mL
- 14 weeks: 24,302 - 93,646 mIU/mL
- 15 weeks: 12,540 - 69,747 mIU/mL
- 16 weeks: 8,904 - 55,332 mIU/mL
- 17 weeks: 8,240 - 51,793 mIU/mL
- 18 weeks: 9,649 - 55,271 mIU/mL
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test result.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Higher than normal level may indicate:
- More than one fetus, for example, twins or triplets
- Choriocarcinoma of the uterus
- Hydatidiform mole of the uterus
- Ovarian cancer
- Testicular cancer (in men)
During pregnancy, lower than normal levels based on the gestational age may indicate:
- Fetal death
- Incomplete miscarriage
- Threatened spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)
- Ectopic pregnancy
Risks
Risks of having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Blood accumulating under the skin (hematoma)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Jain S, Pincus MR, Bluth MH, McPherson RA, Bowne WB, Lee P.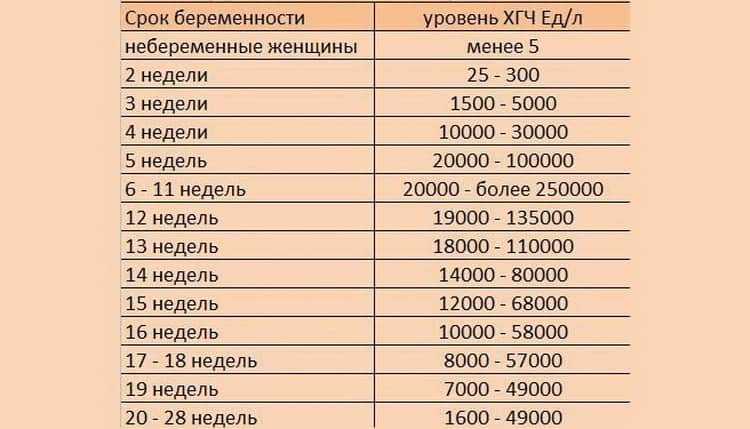 Diagnosis and management of cancer using serological and other body fluid markers. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 74.
Diagnosis and management of cancer using serological and other body fluid markers. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 74.
Jeelani R, Bluth MH. Reproductive function and pregnancy. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 25.
University of Iowa Diagnostic Laboratories. Test directory: HCG - serum, quantitative. www.healthcare.uiowa.edu/path_handbook/rhandbook/test446.html. Updated February 10, 2022. Accessed March 11, 2022.
Yarbrough ML, Stout M, Gronowski AM. Pregnancy and its disorders. In: Rifai N, ed. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics. 6th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2018:chap 69.
Last reviewed on: 12/3/2020
Reviewed by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 03/11/2022.
Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 03/11/2022.
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone normally produced by the placenta. If you are pregnant, you can detect it in your urine. Blood tests measuring hCG levels can also be used to check how well your pregnancy is progressing.
Confirming pregnancy
After you conceive (when the sperm fertilises the egg), the developing placenta begins to produce and release hCG.
It takes about 2 weeks for your hCG levels to be high enough to be detected in your urine using a home pregnancy test.
A positive home test result is almost certainly correct, but a negative result is less reliable.
If you do a pregnancy test on the first day after your missed period, and it’s negative, wait about a week. If you still think you might be pregnant, do the test again or see your doctor.
hCG blood levels by week
If your doctor needs more information about your hCG levels, they may order a blood test. Low levels of hCG may be detected in your blood around 8 to 11 days after conception. hCG levels are highest towards the end of the first trimester, then gradually decline over the rest of your pregnancy.
The average levels of hCG in a pregnant woman’s blood are:
| 3 weeks | 6 – 70 IU/L |
| 4 weeks | 10 - 750 IU/L |
| 5 weeks | 200 - 7,100 IU/L |
| 6 weeks | 160 - 32,000 IU/L |
| 7 weeks | 3,700 - 160,000 IU/L |
| 8 weeks | 32,000 - 150,000 IU/L |
| 9 weeks | 64,000 - 150,000 IU/L |
| 10 weeks | 47,000 - 190,000 IU/L |
| 12 weeks | 28,000 - 210,000 IU/L |
| 14 weeks | 14,000 - 63,000 IU/L |
| 15 weeks | 12,000 - 71,000 IU/L |
| 16 weeks | 9,000 - 56,000 IU/L |
| 16 - 29 weeks (second trimester) | 1,400 - 53,000 IU/L |
| 29 - 41 weeks (third trimester) | 940 - 60,000 IU/L |
The amount of hCG in your blood can give some information about your pregnancy and the health of your baby.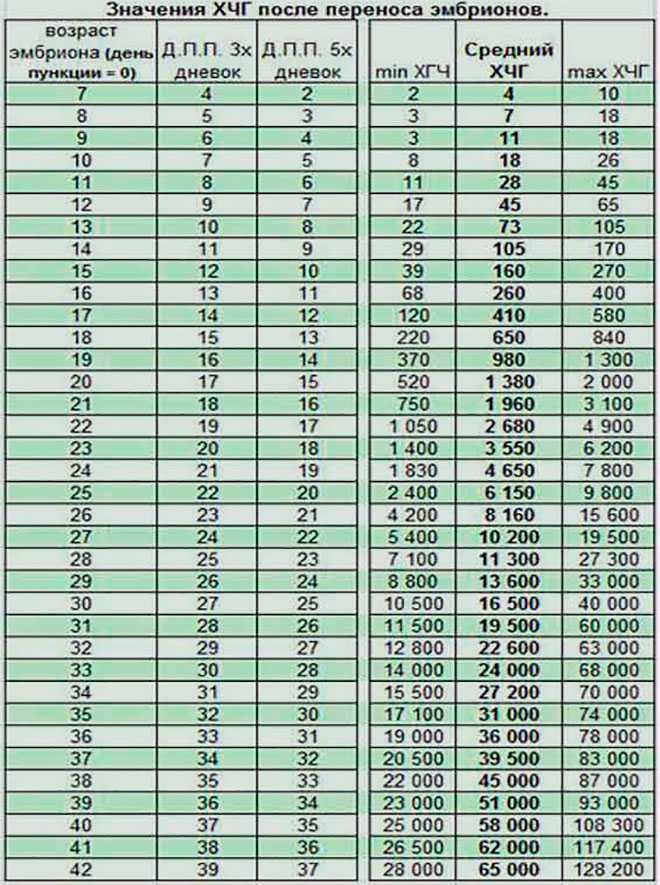
- Higher than expected levels: you may have multiple pregnancies (for example, twins and triplets) or an abnormal growth in the uterus
- Your hCG levels are falling: you may be having a loss of pregnancy (miscarriage) or risk of miscarriage
- Levels that are rising more slowly than expected: you may have an ectopic pregnancy – where the fertilised egg implants in the fallopian tube
hCG levels and multiple pregnancies
One of the ways of diagnosing a multiple pregnancy is by your hCG levels. A high level may indicate you are carrying multiple babies, but it can also be caused by other factors. You will need an ultrasound to confirm that it’s twins or more.
Levels of hCG in your blood don’t provide a diagnosis of anything. They can only suggest that there are issues to look into.
If you have any concerns about your hCG levels, or wish to know more, speak to your doctor or maternity healthcare professional. You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436.
Sources:
UNSW Embryology (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin), Elsevier Patient Education (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin test), SydPath (hCG (human Chorionic Gonadotrophin), Pathology Tests Explained (Human chorionic gonadotropin), NSW Government Health Pathology (hCG factsheet)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: December 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Due date calculator
- Pregnancy tests
- Early signs of pregnancy
Need more information?
Human chorionic gonadotropin - Pathology Tests Explained
Why and when to get tested for hCG
Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website
Pregnancy testing - MyDr.
 com.au
com.au Pregnancy testing can be done from around the time that your period is due, and involves testing your urine for the pregnancy hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Read more on myDr website
Pregnancy tests
Find out how a home pregnancy test works.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy testing - Better Health Channel
Sometimes, a home pregnancy test may be positive when a woman isn’t pregnant.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Molar pregnancy
A molar pregnancy is a type of pregnancy where a baby does not develop. A molar pregnancy can be either complete or partial.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Beta HCG Test | HealthEngine Blog
A Beta HCG (BHCG or Blood Pregnancy Test) May Be Performed by Your Doctor If They Suspect That You May Be Pregnant, or if You Suspect Pregnancy Yourself!
Read more on HealthEngine website
5 weeks pregnant: Changes for mum
Week 5 of pregnancy is probably when you’ll know that you’re pregnant because your period is missing. There are also subtle changes in your body which are symptoms of pregnancy such as changes to your breasts, and pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and pregnancy heartburn. These changes are caused by pregnancy hormones, like hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, produced by the placenta) which is the hormone detected by a pregnancy test.
Read more on Parenthub website
4 weeks pregnant: Key points
When you are 4 weeks pregnant your body and your new baby are undergoing rapid changes. The placenta forms and begins producing a hormone called human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), which is the substance a pregnancy test detects to confirm you are pregnant. The cells which are growing into your new baby establish membranes which connect them to the placenta and prepare themselves for differentiation into different types of cells, which will occur next week when you are 5 weeks pregnant. These developments may cause you to experience unusual emotions and also cause changes in your body such as darkening of the areolas of your nipples.
Read more on Parenthub website
Week by week pregnancy- 6 weeks pregnant
6 weeks pregnant is a time when embryo development is occurring rapidly and pregnant women often start experiencing pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness.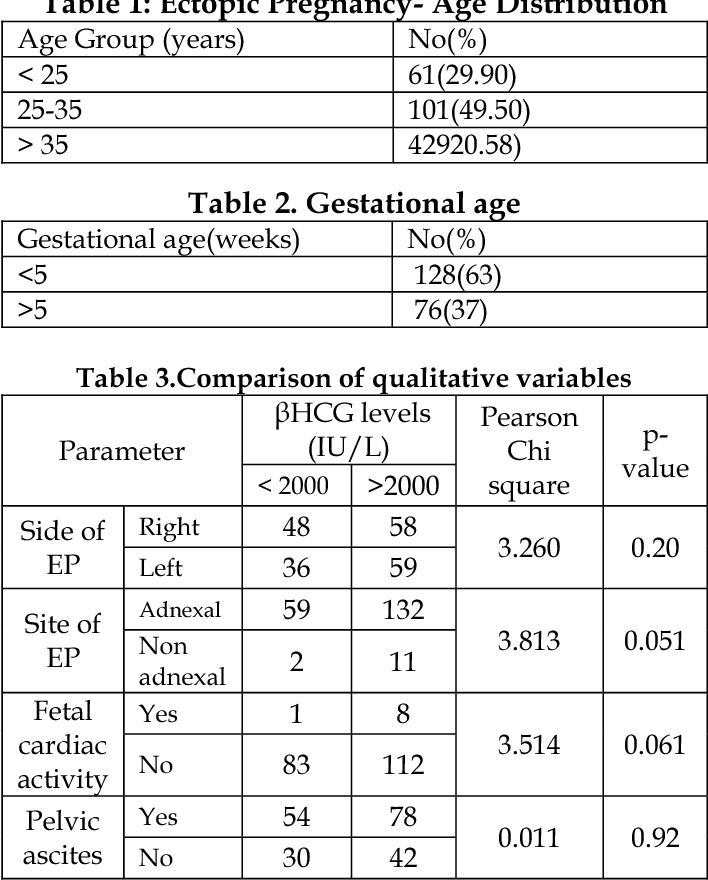 Pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), the hormone a pregnancy test detects, is usually evident in the woman’s blood in the sixth week of pregnancy. Antenatal care should be provided at a doctor appointment for women who have not already checked their pregnancy health. Find out more about the pregnancy changes which occur this week.
Pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), the hormone a pregnancy test detects, is usually evident in the woman’s blood in the sixth week of pregnancy. Antenatal care should be provided at a doctor appointment for women who have not already checked their pregnancy health. Find out more about the pregnancy changes which occur this week.
Read more on Parenthub website
5 weeks pregnant: Key points
The fifth week of pregnancy begins around the time your menstrual bleeding is due and is a good time to take a pregnancy test to confirm that you are pregnant. You are also likely to begin experiencing pregnancy symptoms like fatigue, morning sickness and changes to your breasts this week. Your baby is still only about 1.5mm long but it is developing rapidly and taking on a more human form. If you have not already visited your doctor the 5th week of pregnancy is a good time to do so.
Read more on Parenthub website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Sign in
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
HCG norms by weeks of pregnancy
HCG norms by weeks of pregnancy - Private maternity hospital Ekaterininskaya Clinics
Content
- Table of average hCG norms
- Table of average hCG norms for carrying twins
- Table of average hCG values after IVF with engrafted twins
- Guidelines for free β-hCG subunit
- Norm РАРР-А
- What if I am at high risk?
- How to confirm or deny the results of screening?
- The doctor says I need an abortion.
 What to do?
What to do?
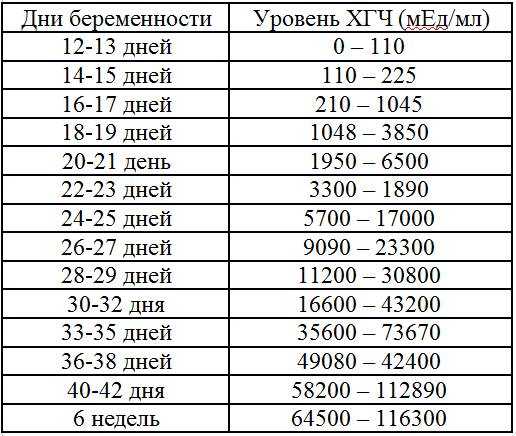
One of the main tests during pregnancy is the study of the level of pregnancy hormone - hCG or human chorionic gonadotropin. If expectant mothers want to know if the hormone level is normal, we made a summary table of values
Table of average hCG rates:
| Gestational age | HCG in mU/ml | HCG in mIU/ml | HCG in ng/ml |
| 1-2 weeks | 25-156 | 5-25 (doubtful result) | - |
| 2-3 weeks | 101-4870 | 5-25 (doubtful result) | - |
| 3-4 weeks | 1100 – 31500 | 25-156 | - |
| 4-5 weeks | 2560 – 82300 | 101-4870 | - |
| 5-6 weeks | 23100 – 151000 | 1110 -31500 | - |
| 6-7 weeks | 27300 – 233000 | 2560 -82300 | - |
| 7-11 weeks | 20900 – 291000 | 23100 -233000 | 23.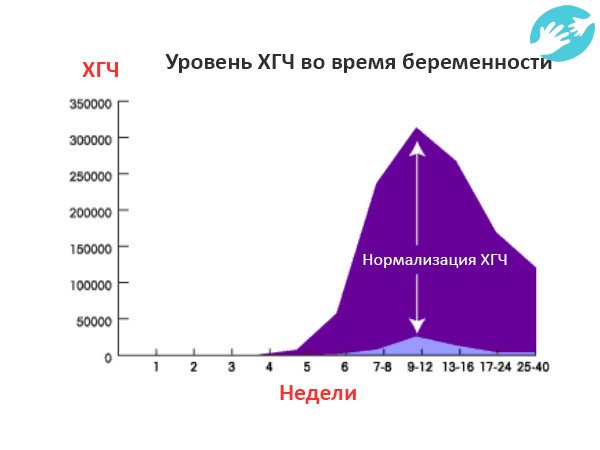 7 - 130.4 7 - 130.4 |
| 11-16 weeks | 6140 – 103000 | 20900 -103000 | 17.4 - 50.0 |
| 16-21 weeks | 4720 – 80100 | 6140 – 80100 | 4.67 - 33.3 |
| 21-39 weeks | 2700 – 78100 | 2700 -78100 | - |
Table of average hCG norms for carrying twins:
| Gestation period, weeks | Average range of hCG concentration (mU/ml) |
| 1-2 weeks | 50 – 112 |
| 2-3 weeks | 209 – 9740 |
| 3-4 weeks | 2220 – 63000 |
| 4-5 weeks | 5122 – 164600 |
| 5-6 weeks | 46200 – 302000 |
| 6-7 weeks | 54610 – 466000 |
| 7-11 weeks | 41810 – 582000 |
| 11-16 weeks | 12280 – 206000 |
| 16-21 weeks | 9440 – 160210 |
| 21-39 weeks | 5400 – 156200 |
Table of average values of hCG after IVF with accustomed twins:
| Gestational age, weeks | HCG range, mU/ml |
| 1-2 weeks | 50 – 600 |
| 2-3 weeks | 3000 - 10000 |
| 3-4 weeks | 20000 – 60000 |
| 4-5 weeks | 40000 – 200000 |
| 5-6 weeks | 100000 – 400000 |
| 6-7 weeks | 100000 – 400000 |
| 7-11 weeks | 40000 – 200000 |
| 11-16 weeks | 40000 – 120000 |
| 16-21 weeks | 20000 – 70000 |
| 21-39 weeks | 20000 – 120000 |
Free hCG β-subunit limits
Measuring free hCG β-subunit levels can more accurately determine the risk of Down syndrome in an unborn child than measuring total hCG.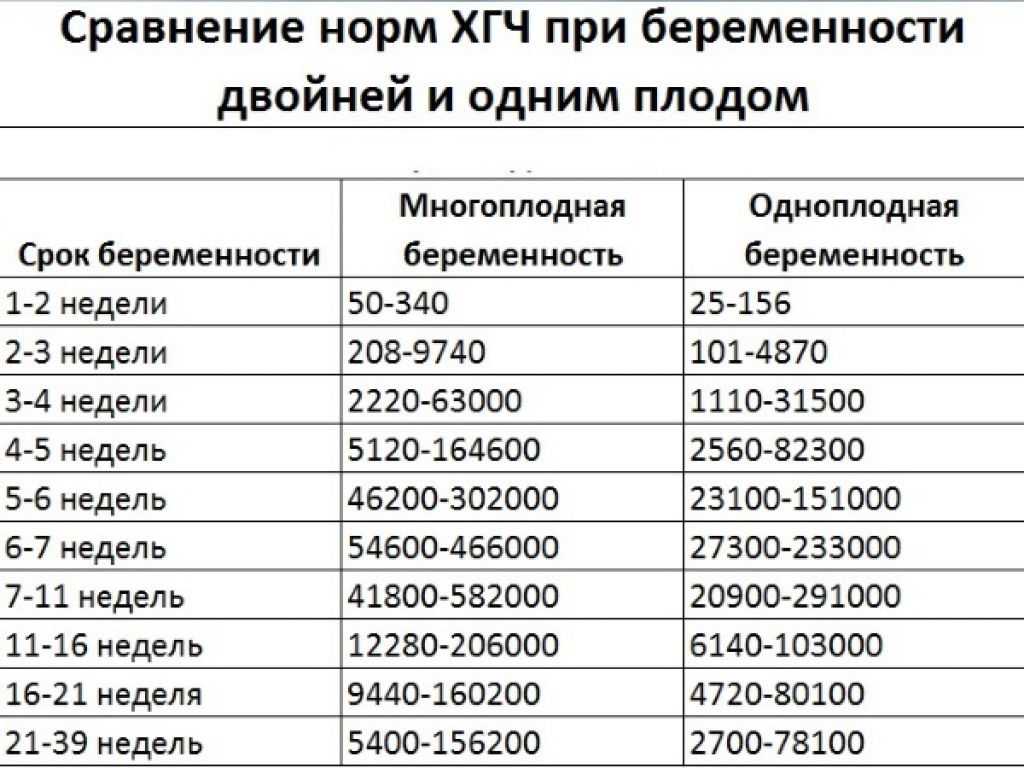
Norms for free β-hCG subunit in the first trimester:
| Gestational period, weeks | HCG in ng/ml |
|---|---|
| 9 weeks | 23.6 - 193.1 ng / ml, or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 10 weeks | 25.8 - 181.6 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 11 weeks | 17.4 - 130.4 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 12 weeks | 13.4 - 128.5 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 13 weeks | 14.2 - 114.7 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
Norms in ng / ml may vary in different laboratories, therefore the data indicated is not final, and in any case you should consult your doctor. If the result is indicated in MoM, then the norms are the same for all laboratories and for all analyzes: from 0.5 to 2 MoM.
If hCG is not normal, then:
- If the free β-hCG subunit is higher than normal for your gestational age, or more than 2 MoM, then the child has an increased risk of Down syndrome.
- If the free hCG β-subunit is below normal for your gestational age, or is less than 0.5 MoM, then the baby is at increased risk of Edwards syndrome.
PAPP-A norm
PAPP-A, or "pregnancy-associated plasma protein A" as it is called, is the second indicator used in biochemical screening of the first trimester. The level of this protein constantly increases during pregnancy, and deviations in the indicator may indicate various diseases in the unborn child.
Norm for PAPP-A depending on the duration of pregnancy:
| Gestational period, weeks | HCG in ng/ml |
|---|---|
| 8-9 weeks | 0.17 - 1.54 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 9-10 weeks | 0.32 - 2.42 mU/ml or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 10-11 weeks | 0.46 - 3.73 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 11-12 weeks | 0.79– 4.76 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 12-13 weeks | 1. 03 - 6.01 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM 03 - 6.01 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
| 13-14 weeks | 1.47 - 8.54 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM |
Norms in ng / ml may vary in different laboratories, therefore the data indicated is not final, and in any case you should consult your doctor. If the result is indicated in MoM, then the norms are the same for all laboratories and for all analyzes: from 0.5 to 2 MoM.
If PAPP-A is abnormal:
- If PAPP-A is lower for your gestational age, or less than 0.5 MoM, your baby is at increased risk of Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome.
- If PAPP-A is higher than normal for your gestational age, or more than 2 MoM, but other screening values are normal, then there is no cause for concern.
Studies have shown that women with elevated PAPP-A levels during pregnancy are not at greater risk of fetal disease or pregnancy complications than other women with normal PAPP-A.
What if I am at high risk?
If your screening reveals an increased risk of having a baby with Down syndrome, then this is not a reason to terminate the pregnancy.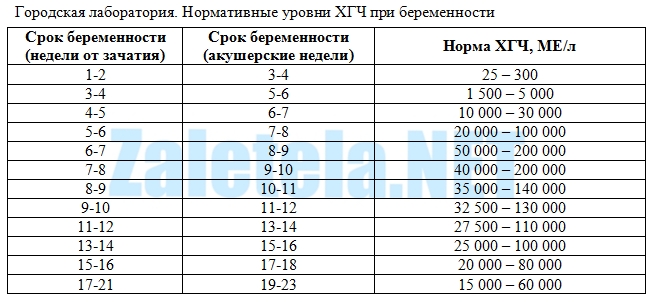 You will be referred for a consultation with a geneticist who, if necessary, will recommend examinations: chorionic villus biopsy or amniocentesis
You will be referred for a consultation with a geneticist who, if necessary, will recommend examinations: chorionic villus biopsy or amniocentesis
How to confirm or refute the screening results?
If you think that the screening was not done correctly, then you should be re-examined at another clinic, but for this you need to retake all the tests and undergo an ultrasound. This method is possible only if the gestational age at the time of the examination does not exceed 13 weeks and 6 days.
The doctor says I need an abortion. What to do?
Unfortunately, there are times when a doctor strongly recommends or even forces an abortion based on the screening results. Remember: no doctor has the right to such actions. Screening is not a definitive method for diagnosing Down syndrome and, based on poor results alone, a pregnancy should not be terminated.
Say that you want to consult a geneticist and undergo diagnostic procedures for Down syndrome (or other disease): chorionic villus biopsy (if you are 10-13 weeks pregnant) or amniocentesis (if you are 16-17 weeks pregnant).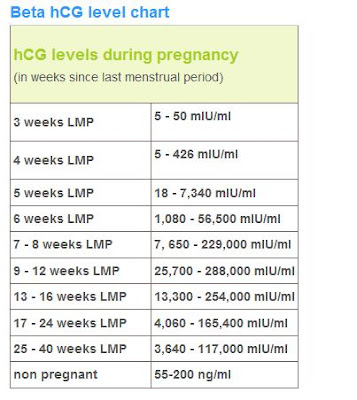
The author of the article:
Ananyina Anna Alexandrovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Work experience since 2010
Sign up
Eat more foods rich in iron: beef tongue, liver, buckwheat and oatmeal, prunes, dried apricots, green apples, etc. But diet alone will not work to raise hemoglobin.
Medical therapy with iron supplements is required. If the problem is associated with insufficient intake of iron into the body, one set of drugs is needed, if with absorption, another. The doctor must select drugs.
Injection therapy may be required for more severe anemia.
If there are no contraindications, natural childbirth is possible. Only an obstetrician-gynecologist should decide on the possibility of EP.
Get tested
- Chest X-ray
- KSR
- Hepatitis B HBsAg
- Hepatitis C Anti-HCV
- Rubella IgM
- Rubella IgG
- HIV
- B/P for flora and senses.
 - from throat
- from throat
Specialist consultation:
- General practitioner consultation
With an increase in the duration of pregnancy and the growth of the baby, the uterus increases - this can lead to increased tone. Sometimes tension arises in response to the movements of the child. Strong physical exertion, stress, overwork of a pregnant woman can also lead to increased tone.
In early pregnancy, uterine tone may be associated primarily with reduced progesterone production. In this case, the doctor prescribes the patient treatment with progesterone preparations.
Symptoms of increased tone
All pregnant women experience tone differently. Someone - like heaviness and tension in the lower abdomen. Others - as a pulling pain in the lumbar region. In the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy, a woman can feel the tone by putting her hand on her stomach: the uterus becomes "stone", then relaxes.
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the first category
Specify the cost of admission
in the Call-center
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the first category
Admission fee
2500 ₽
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Candidate of Medical Sciences
Check the cost of admission
in the Call-center
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the first category
Check the cost of admission
in Call-center
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Specify the cost of admission
in the Call-center
Obstetrician-gynecologist / Gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Candidate of Medical Sciences
Cost of admission
2500 ₽
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Admission fee
2500 ₽
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the second category
Check the cost of admission
in Call-center
Mobile application of the clinic
You can make an appointment with a doctor, get tests
and much more. ..
Fill out the form to make an appointment or order a call back
I agree with personal data processing policy and user agreement I also give my consent to the processing of personal data.
Sign up for a consultation
I agree with personal data processing policy and user agreement I also give my consent to the processing of personal data.
By continuing to use rd.clinic23.ru, you agree to the use of cookies. How to ban the use of certain cookies can be found in Politics
hCG during pregnancy - analysis, norm
Human chorionic gonadotropin, the abbreviation of which is hCG, is a hormone that is secreted by the membranes of a conceived child. An analysis of hCG during pregnancy shows how the physiological processes proceed in the body of a pregnant woman, and what is the condition of the fetus in the womb. It can be performed from the first days of delayed menstruation.
What is human chorionic gonadotropin
Chemically, human chorionic gonadotropin is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of forty-six thousand daltons. The hCG molecule consists of two subunits -α and β. α-particle identical in three hormones of the anterior pituitary - luteinizing (LH), follicle-stimulating (FSH) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The uniqueness of hCG lies in the structure of its β-subunit. Thanks to the beta particle, the biological activity inherent in this chemical substance and the immunochemical specificity are realized.
The biological activity of hCG is manifested in relation to the ovaries and adrenal glands, which begin the synthesis of their own hormones that maintain pregnancy, immediately after an increase in the level of hCG in the blood serum. Immunological specificity is expressed in the fact that antibodies are obtained to the β-subunit, and this makes it possible to determine hCG immunochemically. Antigen-specific monoclonal antibodies are the basis of all modern methods for determining this hormone in blood and urine.
The developing embryo synthesizes hCG immediately after conception. Then it is produced by syncytiotrophoblast. The presence of the hCG hormone is a prerequisite for the successful progression of pregnancy. It supports corticosteroid hormones and other growth factors in the corpus luteum, promotes the development of blood vessels in the uterus, better immunological adaptation during pregnancy. HCG, due to its high negative charge, repels the mother's immune cells from the fetus and protects it. Some scientists believe that hCG is a link in the development and maintenance of immune tolerance during pregnancy.
Presence and levels of the hormone hCG during pregnancy can be determined in the blood or urine. Many immunological methods that detect hCG in biological fluids are based on the "sandwich" principle. In diagnostics, monoclonal antibodies to human chorionic hormone are used, which are labeled with an enzyme or a luminescent dye. Pregnancy tests are based on the lateral flow technique.
The level of hCG during pregnancy in the urine is determined using immunochromatography. The range of threshold values depends on the test system. Serum is subjected to research by chemiluminescence or fluorometry. With the help of enzyme immunoassay, hCG can be detected at its level of five milliinternational units per milliliter.
HCG during pregnancy. Norm
The level of the hCG hormone during pregnancy is used to judge how it proceeds, whether there is a threat of abortion, miscarriage, or ectopic pregnancy, and whether the fetus has frozen. The level of hCG during pregnancy can be determined in the urine or blood. With the help of pregnancy test systems, the presence of hCG in a woman's body is detected.
In order for the results of the analysis of hCG during pregnancy to be true, it is necessary to prepare for donating blood for the study. It is better to donate blood on an empty stomach in the morning. If this is not possible, then do not eat for six hours before donating blood.
During the three days preceding the blood test for hCG, the woman's physical and emotional stress is limited. She must refrain from drinking alcohol during this period of time. The analysis of hCG during pregnancy is best performed before the delay, about seven days before the possible implantation of the egg.
The maximum level of hCG in non-pregnant women should not exceed 15 mU / ml. In men, it ranges from zero to five milliunits. In the first days of a delay in menstruation, an hCG analysis may be unreliable. Particularly sensitive test systems show an increase in the level of hCG in the presence of pregnancy before the expected period.
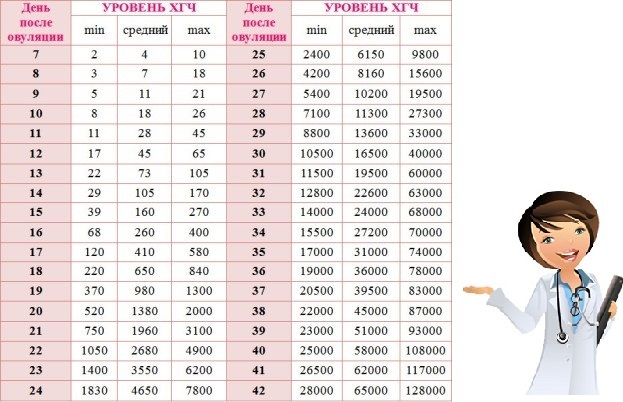
HCG rate is not the same in different weeks of pregnancy. So, in the first week of pregnancy, the hCG level is in the range of 25-155 mU / ml. In the second week, it rises to 103-4870 mU / ml. HCG in the fourth and fifth weeks is at the level of 2500-82300 mU / ml. From the fifth to the sixth week, the concentration of the pregnancy hormone is 23,000-150,000 mU / ml. The peak concentration of hCG occurs in the seventh week of pregnancy. Subsequently, its level begins to gradually decrease and by the end of pregnancy does not exceed 2700 to 78100 mU / ml.
Changes in hCG levels
Changes in hCG levels may indicate more than just pregnancy. It also changes in other conditions of the male and female body. A decrease or increase in the concentration of hCG often occurs during pathological processes. The discrepancy between the level of hCG and the expected gestational age indicates that the woman has problems with bearing a child.
Chorionic gonadotropin may cease to be produced if fetal development is arrested. This is a signal that there is a risk of spontaneous abortion. In the event that the death of the fetus in the womb is confirmed by ultrasound data, the woman is treated with curettage of the uterine cavity.
A decrease in the level of hCG during pregnancy indicates the following pathology:
- location of the fetus outside the uterine cavity;
- beginning detachment of the chorion;
- dishormonal disorders;
- diabetes mellitus.
An abnormal increase in the level of hCG occurs in such cases:
- multiple pregnancy;
- preeclampsia or toxicosis of pregnant women;
- the fetus has Down syndrome;
- prolongation of pregnancy.
The concentration of hCG in the serum of a non-pregnant woman may be elevated with malignant neoplasms of the ovaries or uterus, cancer of other organs, in the first week after an abortion. In the male body, the level of hCG increases with malignant neoplasms of the testicles (seminoma or teratoma). When taking certain hormonal drugs, the concentration of hCG in the blood serum also increases.
HCG in ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is defined when a fertilized egg is implanted not in the wall of the uterus, but outside the organ. The most common is tubal pregnancy. Until some time, it proceeds in the same way as a normal pregnancy.
However, the fallopian tube is not suitable for carrying a fetus.