Itching skin early pregnancy sign
Itching and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
Itching is common in pregnancy. Usually it's thought to be caused by raised levels of certain chemicals in the blood, such as hormones.
Later, as your bump grows, the skin of your tummy (abdomen) is stretched and this may also feel itchy.
However, itching can be a symptom of a liver condition called intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP), also known as obstetric cholestasis (OC).
ICP needs medical attention. It affects around 1 in 140 pregnant women in the UK.
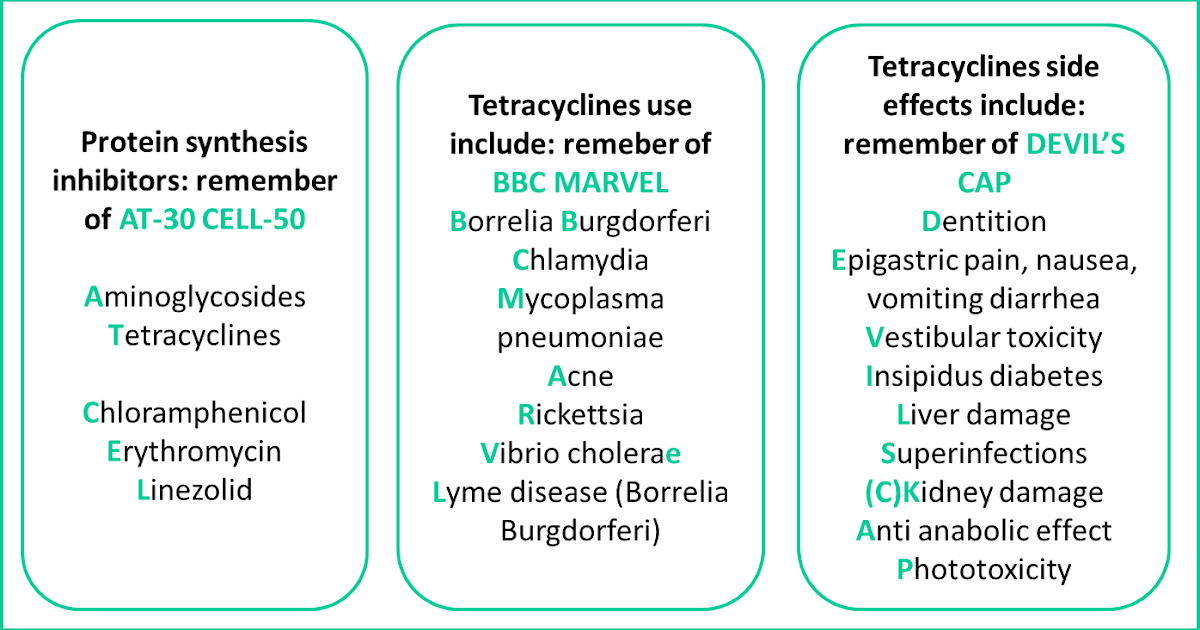
Symptoms of ICP
The main symptom is itching, usually without a rash. For many women with ICP, the itching is often:
- more noticeable on the hands and feet, but can be all over the body
- worse at night
Other symptoms can include:
- dark urine
- pale poo
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), but this is less common
Symptoms of ICP typically start from around 28 weeks of pregnancy, but it's possible to develop the condition earlier.
Non-urgent advice: Call your midwife or GP if you have itching that's:
- mild or distressing, possibly worse at night
- anywhere on your body, but may be worse on the palms of your hands and soles of your feet
Feeling itchy like this can be a sign of ICP and needs to be checked.
Mild itching
Wearing loose clothes may help prevent itching, as your clothes are less likely to rub against your skin and cause irritation.
You may also want to avoid synthetic materials and opt for natural ones, such as cotton, instead. These are "breathable" and allow the air to circulate close to your skin.
You may find having a cool bath or applying lotion or moisturiser can help soothe the itching.
Some women find that products with strong perfumes can irritate their skin, so you could try using unperfumed lotion or soap.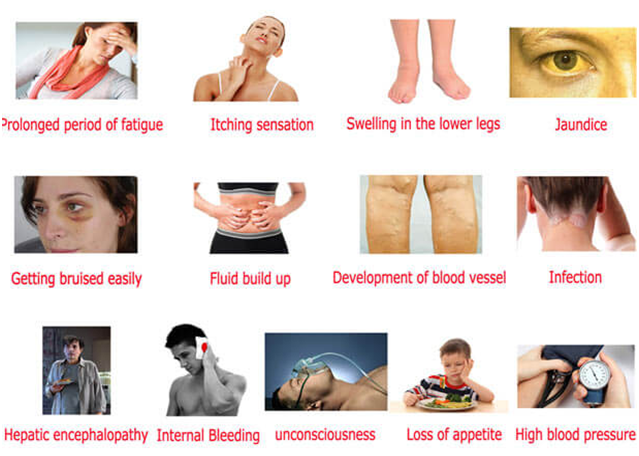
Mild itching is not usually harmful to you or your baby, but it can sometimes be a sign of a more serious condition, particularly if you notice it more in the evenings or at night.
Let your midwife or doctor know if you are experiencing itching so they can decide whether you need to have any further investigations.
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) is a potentially serious liver disorder that can develop in pregnancy.
Normally, bile acids flow from your liver to your gut to help you digest food.
In ICP, the bile acids do not flow properly and build up in your body instead. There's no cure for ICP, but it should go once you've had your baby.
ICP seems to run in families, but it can happen even if there is no family history.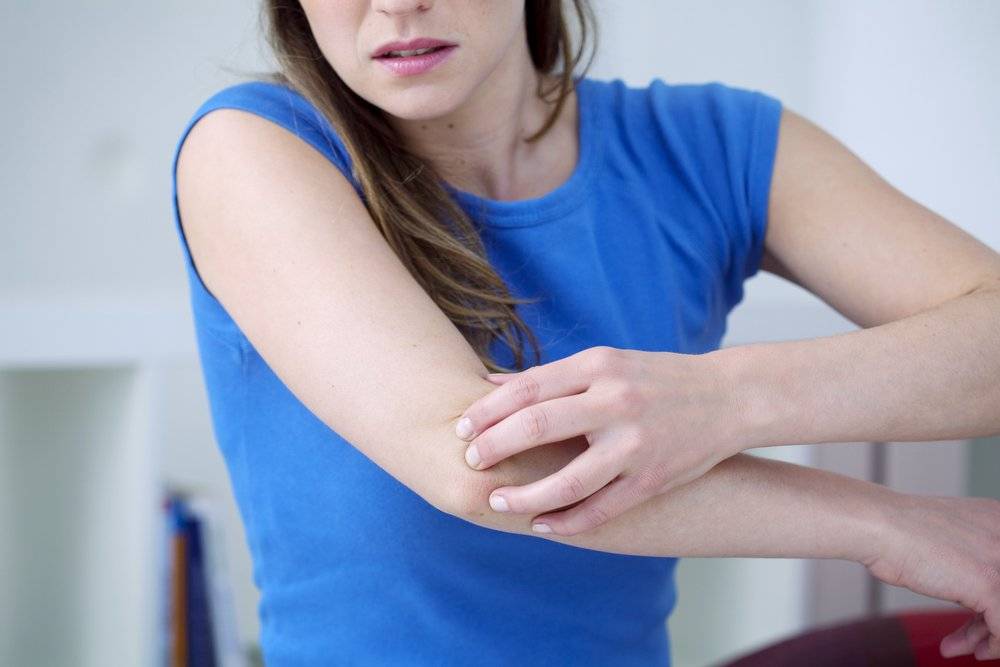 It is more common in women of south Asian origin, affecting around 1 in 70 to 80 pregnancies.
It is more common in women of south Asian origin, affecting around 1 in 70 to 80 pregnancies.
If you have had ICP in a previous pregnancy, you have a high chance of developing it again in another pregnancy.
Some studies have found that babies whose mothers have ICP have a higher chance of being born prematurely or stillborn.
Because of the link with stillbirth, you may be offered induction of labour. This could be any time from 35 weeks, depending on the level of bile acids in your blood.
If you have ICP, you will probably be advised to give birth in hospital under a consultant-led maternity team.
Diagnosis and treatment of ICPICP is diagnosed by excluding other causes of the itch. Your doctor will probably talk to you about your medical and family history and advise you to have some blood tests.
These will include tests to check your liver function (LFT) and measure your bile acid levels (BA).
If you are diagnosed with ICP, you will have regular liver blood tests (LFTs) and bile acid measurement tests so your doctor can monitor your condition.
Initially, you may be given these tests every week. You may then be given more, or less, frequent tests depending on the results and your symptoms.
Creams and medicines for ICPCreams, such as aqueous cream with menthol, are safe to use in pregnancy and can provide some relief from itching.
A medicine called ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) can be prescribed to try to relive itching. But recent evidence suggests it may not be effective in reducing bile acids and easing itching.
UDCA is considered safe to take in pregnancy, although it is prescribed on what is known as an "informed consent" basis as it has not been properly tested in pregnancy. It is usually only prescribed by a hospital doctor.
It is usually only prescribed by a hospital doctor.
A possible alternative, which can be helpful if itchiness is keeping you awake at night, is antihistamine medicine, such as chlorphenamine. Chlorphenamine tends to cause drowsiness so it can also help with sleep problems as well as itchiness. If you do feel drowsy do not drive or operate machinery.
You may also be offered a vitamin K supplement. This is because ICP can affect your absorption of vitamin K, which is important for healthy blood clotting.
Most experts on ICP only prescribe vitamin K if the mother-to-be reports pale poo, has a known blood clotting problem, or has very severe ICP from early in pregnancy.
If you are diagnosed with ICP, your midwife and doctor will discuss your health and your options with you.
Further information
There is information about obstetric cholestasis on the Royal College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RCOG) website, including what it means for you and your baby, and the treatment that's available.
You can also get information about intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) on the British Liver Trust website.
The charity ICP Support provides information about ICP. You can also watch a video about living with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) on the ICP support website featuring mums and clinical experts.
Community content from HealthUnlockedPregnancy Symptoms: 19 Early Signs of Pregnancy
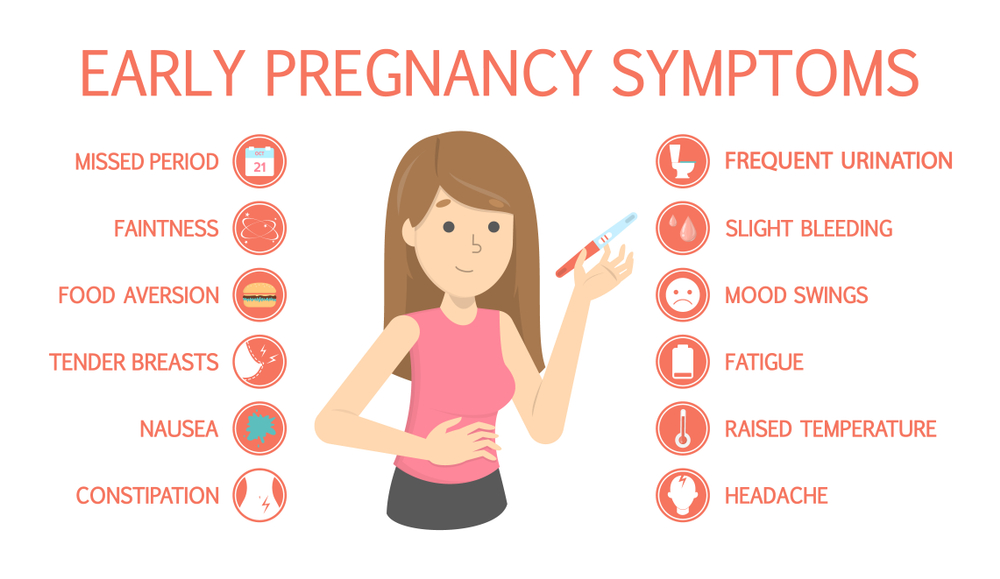
Sometimes it's hard to interpret the signals your body is sending you. If you suspect you might be experiencing the first signs of pregnancy, you're probably eager to know for sure. Here we list some of the early signs of pregnancy as well as symptoms you may experience throughout your pregnancy. Keep in mind that every pregnancy and every mom-to-be is different, so you may not notice every single sign and symptom listed.
First Signs of Pregnancy
Did you miss your period, and are starting to ask yourself “Am I pregnant”? Or, maybe there's a gut feeling that you can’t shake. It's normal and understandable to wonder what are the early signs of pregnancy as you mentally cross off the different feelings you’ve been experiencing in the past few days.
You may start experiencing specific signs and symptoms of pregnancy early on even before you know for sure that you’re pregnant. Of course, either a home pregnancy test or a test through your healthcare provider will be the best way to determine if you’re pregnant.
In the meantime, take this “Am I Pregnant?” quiz and read up on some of the early pregnancy signs and symptoms you may start feeling about one to two weeks after a missed period and within the first month of being pregnant:
It's normal and understandable to wonder what are the early signs of pregnancy as you mentally cross off the different feelings you’ve been experiencing in the past few days.
You may start experiencing specific signs and symptoms of pregnancy early on even before you know for sure that you’re pregnant. Of course, either a home pregnancy test or a test through your healthcare provider will be the best way to determine if you’re pregnant.
In the meantime, take this “Am I Pregnant?” quiz and read up on some of the early pregnancy signs and symptoms you may start feeling about one to two weeks after a missed period and within the first month of being pregnant:
Missing a period. One of the very early signs of pregnancy is a missed period, though if you have an irregular menstrual cycle, this sign can be misleading.
Spotting. Very light spotting known as implantation bleeding, can be an early sign of pregnancy. It happens when the fertilized egg attaches itself to the lining of the uterus.
Cramping. Some moms-to-be experience mild uterine cramps during the first trimester. To soothe your lower abdomen, place a hot water bottle, wrapped in a towel, on your belly or take a warm bath.
Hot flashes. Elevated pregnancy hormone levels early in your pregnancy and a metabolism that has sped up can both lead to a feeling of hot flashes resulting from an increase in your core body temperature. Your body compensates for this hot feeling by sweating more to help cool you down.
Racing heart. Hormonal changes can also cause heart palpitations, but if they last more than a few seconds, or if they happen frequently, contact your healthcare provider for a checkup to make sure everything is OK.
Mood swings. Finding out you’re pregnant is a big milestone, and it’s natural to feel everything from joy and excitement to anxiety and confusion. It may help to speak to your loved ones about your feelings.

Bloating and constipation. As the digestive system slows, you may also feel bloated (similar to what it can feel like at the start of your period) and constipated. Eat high-fiber foods, drink lots of water, and—if you can—add some exercise to your day.
Heartburn. During pregnancy the muscles that keep digestive acids out of the esophagus tend to relax, which can lead to acid reflux, commonly known as heartburn. Eat small, frequent meals, and avoid fried foods, citrus fruits, chocolate, and spicy or fried foods to help prevent heartburn.
Acne. The overproduction of sebum (oil) in the skin can cause pimple outbreaks during pregnancy. Gently cleanse your skin each day, use non-greasy cosmetics, and consult your healthcare provider about anti-acne medications that are safe.
Dizziness. Low blood sugar levels, stress, and fatigue can make you feel dizzy or faint. To prevent dizziness in pregnancy, try to eat small, regular meals, and try to keep stress under control.
Weight gain. Some women gain between 1 to 4 pounds in the first few months of pregnancy, but your doctor will be able to advise you on healthy pregnancy weight gain that is right for you.
Congestion. Early in pregnancy, the mucous membranes in your nose swell, dry out, and bleed easily. To help relieve congestion, consider using a humidifier, or try saline drops or a saline rinse, and remember to stay hydrated.
Headaches. These can be an early sign of pregnancy as estrogen levels rise. You may also experience tension headaches, which may be caused by stress or fatigue. Check with your healthcare provider about possible medications; for most pregnant women, acetaminophen is considered safe to treat the odd headache.
Frequent urination. If you find that you’re peeing a lot more than usual, it could be a sign of pregnancy as your kidneys are processing more fluid, which end up in your bladder.
 Don’t drink less water, though, as keeping hydrated is very important.
Don’t drink less water, though, as keeping hydrated is very important.
Tender, swollen breasts. Early on, your breasts may feel more tender and become larger, but as your body adjusts to the hormonal changes, the discomfort may decrease.
Nausea. With or without vomiting, nausea is a classic pregnancy symptom more commonly called morning sickness. So, how soon does morning sickness start? It often appears around a month after you become pregnant. For some women, morning sickness occurs at other times of the day, not just in the morning, while other women won’t experience it at all. Eat something before getting out of bed, like crackers, and then have small, regular meals throughout the day to keep your blood sugar levels stable.
Food cravings and aversions/smell sensitivity. Early signs of pregnancy also include changes in taste, smell, and cravings. Keep up a balanced diet and talk to your doctor if you crave non-food items (like chalk or dirt).

Fatigue. It’s natural to feel tired while pregnant, particularly early on when the hormone progesterone is in overdrive, making you feel tired. Your body is working hard to support your baby, so give yourself plenty of time to rest and relax.
Skin changes. You may notice skin pigmentation changes, such as the darkening of the skin around your nipples, dark patches on your face, or the appearance of a dark line from your navel to your pubic bone.
Do All Women Experience Early Signs and Symptoms of Pregnancy?
Each mom-to-be and each pregnancy is unique, so you may only notice some of these early signs of pregnancy. For example, the first signs and symptoms of pregnancy could occur before a missed period; alternatively, missing a period may be your first clue that you’re pregnant. What’s more, the symptoms you notice in a second pregnancy may be different from what you experienced the first time around.
When Do Pregnancy Symptoms Start?
You may be wondering when pregnancy symptoms start. Once again, it’s different for every woman. Some may experience early signs of pregnancy in the first few weeks after conception. Others may be pregnant and not experience any symptoms at all for a while.
How Do You Know You’re Pregnant?
You may be asking yourself “How do I know if I’m pregnant?” If you think you may be pregnant, a home pregnancy test will confirm it. There’s no way to know that you are pregnant without taking a test.
If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms of pregnancy and take a home pregnancy test but the test comes out negative, there’s still a chance you may be pregnant. Wait until your period is a week late (or more), and then take the test again.
If the test comes out positive, make an appointment with your healthcare provider to confirm the pregnancy. Once your pregnancy is confirmed, check out our go-to pregnancy guide, which includes lots of pertinent information and tools you'll need to navigate your pregnancy, including infographics, checklists, trackers, and more!
If you like, use our due date calculator to find out how far along you are in your pregnancy:
Once your pregnancy is confirmed, check out our go-to pregnancy guide, which includes lots of pertinent information and tools you'll need to navigate your pregnancy, including infographics, checklists, trackers, and more!
If you like, use our due date calculator to find out how far along you are in your pregnancy:
Other Signs and Symptoms You May Experience During Pregnancy
Throughout your pregnancy, your body will do some unique and wonderful things. Some of these physical changes (like morning sickness) may subside, while others (like nasal congestion and heartburn) may continue over the course of your pregnancy.
These are some of the changes you may experience during the second and third trimesters of your pregnancy:
Discharge. A sticky, clear, or white vaginal discharge is a normal symptom during pregnancy not necessarily an early sign but contact your healthcare provider if it becomes strong smelling or is accompanied by a sore, itchy vagina.
Cramps or pain in the lower abdomen. In later pregnancy, you may experience a cramping sensation, which may be a result of round ligament pain or Braxton Hicks “practice” contractions.
Back pain. Backaches can be caused by hormonal changes, weight gain, and changes in your posture due to your growing belly. Practicing good posture, sleeping on your side, and getting some physical activity in each day may help relieve the pain.
Frequent urination. Although the more frequent urination that you may have experienced early in pregnancy probably subsides in the second trimester, by the third trimester, it may return. This is because your growing baby moves deeper into the pelvis, putting pressure on your bladder, so you may feel the urge to pee more often.
Itchy Skin. Wherever your skin stretches during pregnancy (for example, the abdomen and thighs), it could start to feel itchy.
 Avoid scratching, use a good moisturizer, and shower or bathe in lukewarm water, as hot water can dry out skin.
Avoid scratching, use a good moisturizer, and shower or bathe in lukewarm water, as hot water can dry out skin.
Stretch marks. As your skin stretches during pregnancy, you may notice stretch marks forming on areas like your belly, thighs, buttocks, and breasts. Gaining a healthy amount of weight slowly over the pregnancy may help minimize these streaks.
Shortness of breath. Your growing baby pushing against your lungs may cause that out-of-breath feeling. Good posture may give your lungs more room to expand.
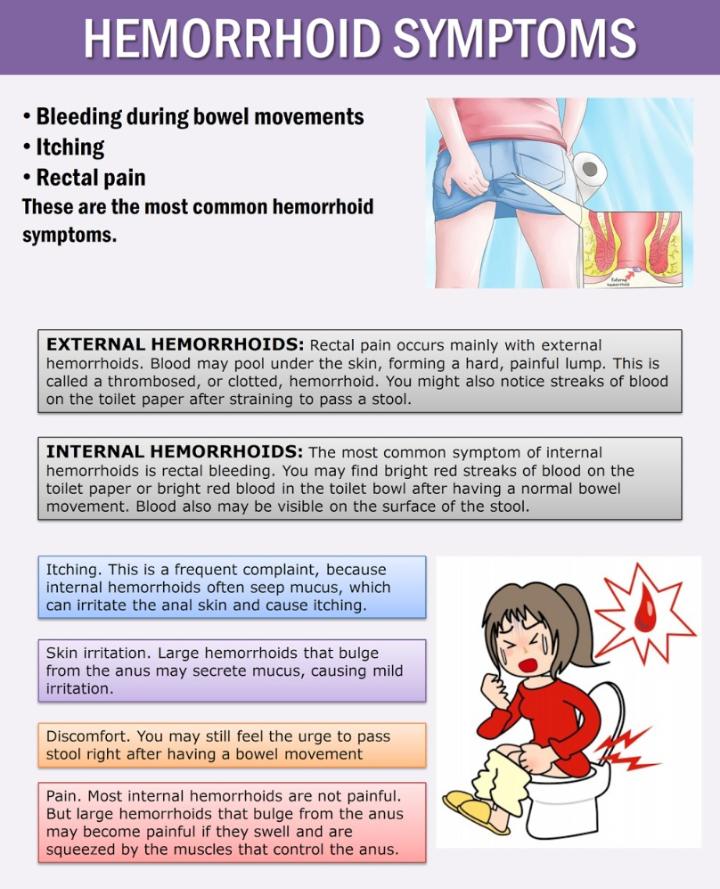
Various aches and pains. You may encounter different symptoms at different points throughout pregnancy, such as dental pain or sensitivity, varicose veins or hemorrhoids, and swollen ankles or leg cramps. Read more about some of these aches and pains along with tips here.
Watch the following video to find out how your partner can be more involved during your pregnancy:
When to Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Most of the time, the aforementioned physical discomforts and changes are completely normal, but there are some signs you should not ignore, including severe headaches, changes in eyesight, or sudden swelling (edema). If you notice anything that just doesn’t seem right, consult your healthcare provider.
If you notice anything that just doesn’t seem right, consult your healthcare provider.
The Bottom Line
Early signs of pregnancy can be as subtle as a food craving or an aversion, or more noticeable like spotting or tender breasts. As your pregnancy progresses some of these signs and symptoms will likely return, such as heartburn, cramping, and frequent urination. If you’re unsure whether you’re pregnant but have been experiencing some of the early signs of pregnancy, take a home pregnancy test or visit your healthcare provider. The signs and symptoms of pregnancy can be tiresome, especially if you’re experiencing several simultaneously, but sooner than you know it, you'll be giving birth and taking your baby home. This is just the beginning of an amazing journey! See our Pregnancy Calendar for a more detailed description of everything that happens during each week, month, and trimester.
Why does the skin itch during pregnancy?
Skin itching during pregnancy is not a very common phenomenon.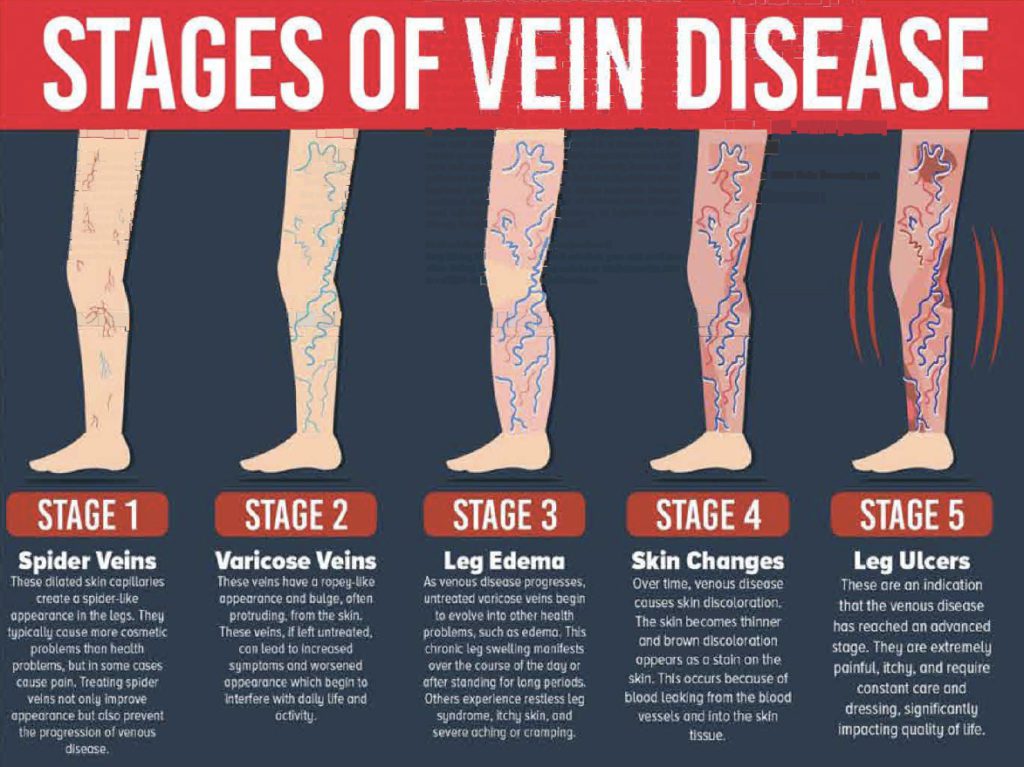 Most often, the skin begins to itch unbearably (as after mosquito bites) in the evening, closer to night, which can provoke insomnia and generally worsen a woman’s mood. Usually itching does not harm the baby and goes away after childbirth. However, it is still worth consulting with a gynecologist and dermatologist.
Most often, the skin begins to itch unbearably (as after mosquito bites) in the evening, closer to night, which can provoke insomnia and generally worsen a woman’s mood. Usually itching does not harm the baby and goes away after childbirth. However, it is still worth consulting with a gynecologist and dermatologist.
What does it come from? nine0005
The cause of itching during pregnancy in most cases is a violation of the liver: the production and outflow of bile, a general increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood. This is due to a hormonal failure in the body of the future mother - a violation of the synthesis of estrogens, as well as due to fetal pressure on the bile ducts. The fatty acids produced in large quantities enter the woman's skin with the bloodstream and irritate the nerve endings, causing excruciating itching. Similar phenomena associated with stagnation of bile in the body can make themselves felt in the third trimester of pregnancy. Sometimes itching is accompanied by such dangerous diseases as diabetes mellitus. nine0003
nine0003
Who is predisposed?
Itching during pregnancy is usually observed in women with chronic diseases of the biliary tract and with high levels of cholesterol in the blood. Such future mothers need to regularly (at least once a month) do a biochemical blood test to exclude toxic effects on liver cells.
How to fight?
A pregnant woman should tell her gynecologist about the discomfort associated with skin itching. In some cases, itching can be a sign of the development of such a dangerous disease as hepatitis. The doctor will conduct appropriate examinations. If, according to an objective examination, itching does not pose any danger, it is often possible to get rid of discomfort simply by following a diet aimed at lowering cholesterol levels, limiting the intake of fatty, spicy and salty foods that prevent the liver from coping with the function of bile secretion, as well as drinking plenty of water - it is necessary to eliminate dry skin. If the diet does not help, the doctor may prescribe choleretic drugs suitable for pregnant women. nine0003
If the diet does not help, the doctor may prescribe choleretic drugs suitable for pregnant women. nine0003
It is important to find the cause of the bothersome itching, eliminating a whole group of skin diseases that can occur during pregnancy.
Itching in the abdomen and chest
This itch is worth mentioning separately. As a rule, the skin on the abdomen or chest itches in the second and third trimesters due to its stretching, because it is these parts of the body that increase in volume during pregnancy. In this case, it is very important not to scratch the skin - this will lead to the appearance of stretch marks, which, unlike itching, will not go away after childbirth. Regularly use moisturizing creams, special products for stretch marks, do a light massage of the chest and abdomen with circular movements of your fingers and do not take hot showers. nine0003
You can get answers to any questions about pregnancy and childbirth from leading EMC experts in the classes of the School of Moms.
Subscribe to our Instagram. You will find useful information about pregnancy and childbirth from leading EMC obstetricians and gynecologists.
Itchy skin during pregnancy: causes and remedies
Itching of the skin during pregnancy can be psychogenic. In this case, itching is a consequence of stress, an early symptom of multiple sclerosis. nine0003
In the early stages, itching occurs due to loss of skin elasticity caused by hormonal changes and excessive dryness of the skin. In the second and third trimester, the reasons may be the rapid weight gain of the expectant mother, the developing stretching of the skin of the abdomen as it increases.
Some expectant mothers experience intimate itching. It is provoked by genital infections, urological and proctological diseases.
The causes of skin itching also include dermatoses of pregnant women (atopic dermatitis, cholestasis of pregnancy). They are provoked by hereditary predisposition, decreased immunity, physiological changes (stretching of the skin with damage to the connective tissue).
Atopic dermatitis is the most common cause of itching during pregnancy. A specific condition is caused by hormonal immune restructuring of the whole organism. In 80% of cases, the disease manifests itself exclusively during pregnancy, and all signs disappear after childbirth without specific treatment. nine0003
Atopic dermatitis is more common in nulliparous women in the early stages and in the second trimester. Itching is caused by papular and exametic rashes localized on the face, neck, limbs, elbows, palms.
Atopic dermatitis is the most benign form of dermatosis of pregnancy and usually does not adversely affect the fetus. However, children born to mothers who suffered from this disease at the stage of gestation are also prone to allergic skin diseases. nine0003
Itching of the skin, as a symptom of cholestasis, is provoked by intrahepatic stagnation of bile as a reaction to increased estrogen production. The disease occurs at the end of the second - beginning of the third trimester, closer to the date of birth. A pregnant woman experiences severe itching in the abdomen, back, palms, legs.
A pregnant woman experiences severe itching in the abdomen, back, palms, legs.
Cholestasis is dangerous for the health of the mother and unborn child in severe cases of the disease. There is a risk of fetal hypoxia, delayed development and even premature birth. nine0003
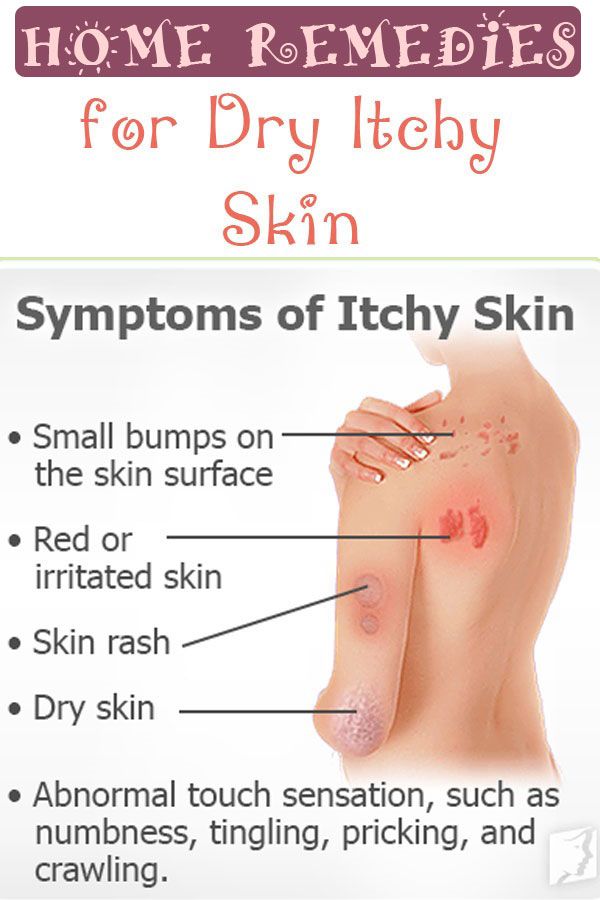
Symptoms
The main sign of pathological changes is the appearance of irritating-itchy sensations in different parts of the body. Locally, a woman may also feel a tingling and burning sensation.
Other symptoms include:
- blistering or eruption of blistering character;
- peeling, irritation and redness of the skin;
- formation of scaly spots;
- sores and sores caused by scratching; nine0057
- deterioration in general condition caused by sleep disorders and emotional depression.
In most cases, itching of the skin during pregnancy does not pose a real danger to the intrauterine development of the fetus, but significantly worsens the quality of life of the expectant mother, acts depressingly on the state of her nervous system and general well-being.
Diagnostics
In order to successfully deal with itching, it is necessary to establish the cause that causes it. The choice of diagnostic methods is determined based on the degree of intensity and localization of itching, the presence of concomitant symptoms and chronic diseases, the duration of pregnancy, and the individual characteristics of the health of the expectant mother. nine0003
Treatment is prescribed only after the exact cause of the itching is established.
At the initial examination, the doctor listens to the patient's complaints, examines the condition of the skin, paying attention to the appearance of rashes or spots. This allows you to draw a preliminary conclusion and determine what laboratory tests and instrumental studies will be needed.
The main diagnostic measures for itchy skin in pregnant women include: nine0003
- general urine and blood tests;
- biochemical blood test;
- studies of hormone levels - if endocrine pathologies are suspected;
- analysis of vaginal smear for microflora;
- skin scraping examination;
- allergy testing;
- Ultrasound of the digestive tract, liver and kidneys;
- histological examination;
- analysis of feces for the detection of helminth eggs.
 nine0057
nine0057
The choice of research methods is determined individually. In some cases, a pregnant woman is shown a consultation with an endocrinologist, urologist, gastroenterologist, venereologist.
Identification of atopic dermatitis is usually not difficult. In addition to the general examination, such types of diagnostics as dermatoscopy and examination under the Voodoo lamp are carried out.
If itching in a pregnant woman is allergic in nature, a mandatory diagnostic measure is the determination of the allergen (pathogen). nine0003
Treatment of itching
Although itching during pregnancy is not dangerous in many cases, it should not be tolerated either. You need to tell the gynecologist about unpleasant sensations, who will determine the diagnostic methods and, if necessary, give a referral to other specialists. Treatment of itching during pregnancy is carried out by the attending gynecologist together with a dermatologist.
You can not self-medicate and use medicines without the approval of a doctor. Many of them have contraindications and can cause severe side effects. A pregnant woman should remember the prohibition of scratching itchy places. This leads to a violation of the integrity of the skin, the appearance of wounds and abrasions, which will become sites of infection. nine0003
Many of them have contraindications and can cause severe side effects. A pregnant woman should remember the prohibition of scratching itchy places. This leads to a violation of the integrity of the skin, the appearance of wounds and abrasions, which will become sites of infection. nine0003
The treatment regimen depends on the disease that causes itching. When choosing drug therapy, the risks of negative effects on the fetus are taken into account. This is especially true in the case of the appointment of antibiotics, hormonal and antifungal drugs. Self-medication is unacceptable!
In the treatment of itching during pregnancy, the following types of drugs can be prescribed:
- antihistamines - to eliminate itching caused by dermatitis, urticaria; nine0057
- glucocorticoids - used to treat dermatitis;
- emollients - have a moisturizing and regenerating effect in case of excessive dryness and dehydration of the skin;
- adsorbents and hepatoprotectors - to normalize the liver;
- choleretic preparations - for the correction of the state of the digestive tract;
- sedatives - to normalize the state of the nervous system, if a pregnant woman has signs of increased anxiety and sleep disturbances.
 nine0057
nine0057
With moderate itching, a pregnant woman is shown taking baths with a decoction of a string or oatmeal. An oatmeal bath is effective for itching caused by stretch marks, eczema, or psoriasis. To prepare it, crushed oatmeal is mixed with baking soda and a little milk is added, the mixture is poured into a warm bath.
Lotions on herbal decoctions can be applied to itchy areas of the skin. Chamomile, succession or St. John's wort is poured with boiling water and insisted. After a few hours, the decoction for lotions is ready for use. nine0003
To eliminate itching of the genital organs, medicinal suppositories with local action are prescribed. Of great benefit are sitz baths of decoctions of sage or chamomile.
Itching in the abdomen, caused by skin tension, can cause stretch marks. To prevent aesthetic imperfections, it is necessary to moisturize the skin with special means.
To reduce itching, a pregnant woman should only wear clothes made from natural fabrics, preferably cotton.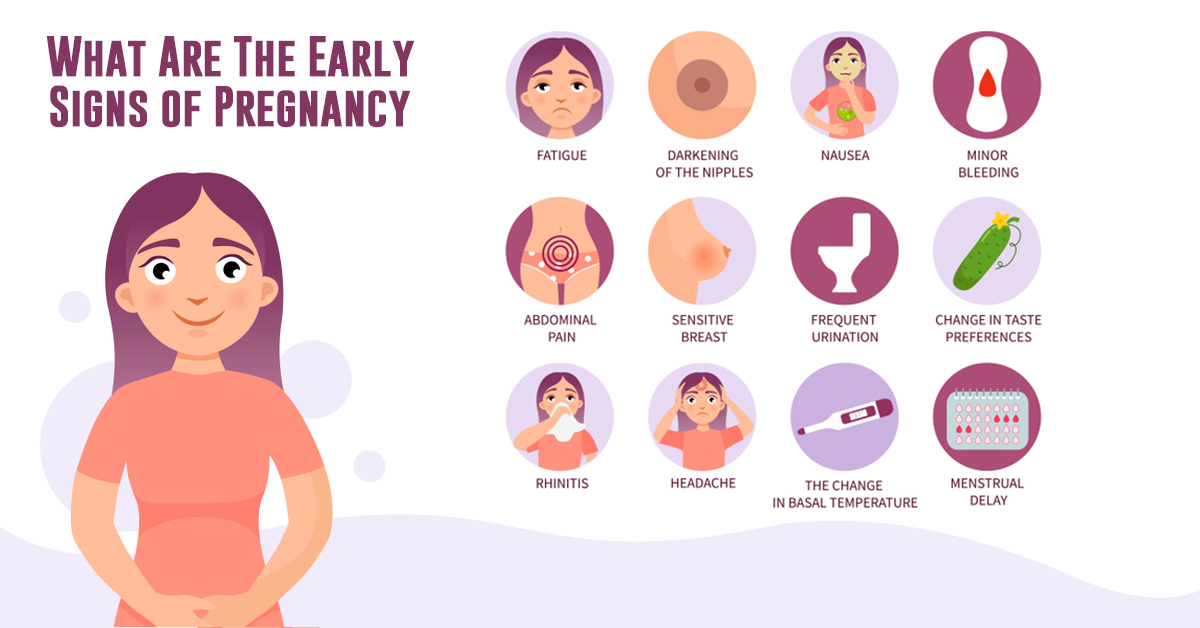 Natural fabrics allow the skin to breathe freely. It is useful for future mothers to take a cool shower without the use of soaps or bathing gels. The skin needs to be effectively protected from external aggressive factors: sun, frost and wind. nine0003
Natural fabrics allow the skin to breathe freely. It is useful for future mothers to take a cool shower without the use of soaps or bathing gels. The skin needs to be effectively protected from external aggressive factors: sun, frost and wind. nine0003
When itching of the skin appears, it is better to refuse the use of perfumes, take the choice of cosmetics very responsibly.
Prophylaxis
Itching during pregnancy can be prevented if you follow the doctor's recommendations and preventive measures. Tips for expectant mothers:
- carefully observe body hygiene, take regular showers or baths without the use of fragrances;
- refuse underwear and clothes made of synthetic fabrics; nine0057
- after taking a shower or bath, moisturize the skin of the body with special products, with a neutral pH level, creams, lotions, emulsions are suitable for this;
- use phosphate-free laundry detergents;
- wear loose clothing that does not restrict movement;
- avoid stuffy rooms or open places under the scorching summer sun;
- exclude intense physical activity that provokes increased sweating; nine0057
- provide the expectant mother with a plentiful drinking regimen that prevents dehydration of the body;
- avoid stressful situations, get positive impressions.

Proper nutrition plays an important role in the prevention of itching of the skin. This is especially important if itching is provoked by various foods. The woman is recommended a hypoallergenic diet, with the exception of fast food, smoked, salty and pickled foods, as well as foods with preservatives, emulsifiers and artificial flavors. The diet of the future mother should be rich in vitamins, minerals, fatty acids, antioxidants. To do this, the menu includes sour-milk products, meat and fish of low-fat varieties, vegetable dishes, fruits. nine0003
Itching during pregnancy when following medical recommendations has a favorable prognosis and is not an obstacle to natural childbirth.
If a woman had signs of atopic dermatitis during her first pregnancy, the likelihood of a recurrence of the disease during subsequent pregnancies is high. At the stage of planning a child, it is necessary to visit a dermatologist.
Itching
A series of products "Emolium" effectively eliminates the symptoms of skin diseases, including itching, peeling, irritability. They are prescribed to moisturize the skin, eliminate dryness and tightness in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, and allergies. Means of the Emolium series are used in the complex treatment of these and other diseases that provoke itching. nine0003
They are prescribed to moisturize the skin, eliminate dryness and tightness in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, and allergies. Means of the Emolium series are used in the complex treatment of these and other diseases that provoke itching. nine0003
The main advantages of the series:
- have a mild anti-inflammatory effect;
- ensure the normal functioning of the skin;
- restore skin structure;
- retain moisture in cells and intercellular space;
- restore the water-lipid layer;
- relieve irritation and itching.
The delicate and delicate consistency of the products makes it easy to apply and distribute them over the entire surface of the affected areas. nine0003
With severe itching of pregnant women, a triactive series is recommended, taking care of atopic and damaged skin. Triactive cream enriched with rapeseed oil and sodium hyaluronate has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antipruritic effects.