How to know if baby is stressed in womb
Fetal distress | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
Fetal distress is a sign your baby isn’t coping with labour. It might mean they need closer monitoring and possibly a caesarean to speed up the birth.
What is fetal distress?
Fetal distress is a sign that your baby is not well. It happens when the baby isn’t receiving enough oxygen through the placenta.
If it’s not treated, fetal distress can lead to the baby breathing in amniotic fluid containing meconium (poo). This can make it difficult for them to breathe after birth, or they may even stop breathing.
Fetal distress can sometimes happen during pregnancy, but it’s more common during labour.
What causes fetal distress?
The most common cause of fetal distress is when the baby doesn’t receive enough oxygen because of problems with the placenta (including placental abruption or placental insufficiency) or problems with the umbilical cord (for example, if the cord gets compressed because it comes out of the cervix first).
Fetal distress can also occur because the mother has a health condition such as diabetes, kidney disease or cholestasis (a condition that affects the liver in pregnancy).
It is more common when pregnancy lasts too long, or when there are other complications during labour. Sometimes it happens because the contractions are too strong or too close together.
You are more at risk of your baby experiencing fetal distress if:
- you are obese
- you smoke
- you have high blood pressure in pregnancy or pre-eclampsia
- you have a chronic disease, such as diabetes or kidney disease
- you have a multiple pregnancy
- your baby has intrauterine growth restriction
- you have had a stillbirth before
How is fetal distress diagnosed?
Fetal distress is diagnosed by reading the baby’s heart rate. A slow heart rate, or unusual patterns in the heart rate, may signal fetal distress.
Sometimes fetal distress is picked up when a doctor or midwife listens to the baby’s heart during pregnancy. The baby’s heart rate is usually monitored throughout the labour to check for signs of fetal distress.
The baby’s heart rate is usually monitored throughout the labour to check for signs of fetal distress.
Another sign is if there is meconium in the amniotic fluid. Let your doctor or midwife know right away if your notice the amniotic fluid is green or brown since this could signal the presence of meconium.
How is fetal distress managed?
The first step is usually to give the mother oxygen and fluids. Sometimes, moving position, such as turning onto one side, can reduce the baby’s distress.
If you had drugs to speed up labour, these may be stopped if there are signs of fetal distress. If it’s a natural labour, then you may be given medication to slow down the contractions.
Sometimes a baby in fetal distress needs to be born quickly. This may be achieved by an assisted (or instrumental) delivery which is when the doctor uses either forceps or ventouse (vacuum extractor) to help you deliver the baby, or you might need to have an emergency caesarean.
Does fetal distress have any lasting effects?
Babies who experience fetal distress, such as having an usual heart rate or passing meconium during labour, are at greater risk of complications after birth. Lack of oxygen during birth can lead to very serious complications for the baby, including a brain injury, cerebral palsy and even stillbirth.
Lack of oxygen during birth can lead to very serious complications for the baby, including a brain injury, cerebral palsy and even stillbirth.
Fetal distress often requires birth by caesarean section. While this is a safe operation, it carries extra risks to both the mother and baby, including blood loss, infections and possible birth injuries.
Babies born with an assisted delivery can also be at greater risk of short-term problems such as jaundice, and may have some difficulty feeding. Having lots of skin-to-skin contact with your baby after the birth and breastfeeding can help reduce these risks.
You won’t necessarily experience fetal distress in your next pregnancy. Every pregnancy is different. If you’re worried about future pregnancies, it can help to talk to your doctor or midwife so they can explain what happened before and during the birth.
Women whose labour didn’t go to plan often feel quite negative about their birth experience.
If you feel sad or disappointed or traumatised about what happened, it is important to talk to someone. You can contact or talk to a range of people and organisations, including:
You can contact or talk to a range of people and organisations, including:
- Your doctor
- PANDA on 1300 726 306
- Australasian Birth Trauma Association
- Beyond Blue on 1300 22 4636
- Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436
Sources:
Australian Family Physician (Decreased fetal movements: a practical approach in primary care setting), Australasian Birth Trauma Association (What is birth trauma?), Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (Labour and birth), Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (Provision of routine intrapartum care in the absence of pregnancy complications), Birth (The effect of medical and operative birth interventions on child health outcomes in the first 28 days and up to 5 years of age), MSD Manual (Fetal distress), Kidspot (All about foetal distress), King Edward Memorial Hospital (Fetal compromise), Journal of Translational Medicine (Reducing the risk of fetal distress with sildenafil study)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: January 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Labour complications
- Interventions during labour
- Induced labour
- Giving birth - stages of labour
- Fetal heart rate monitoring
- Baby movements during pregnancy
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
How Can You Tell If Your Baby Is Stressed In The Womb?
Becoming a parent brings with it a whole new spectrum of emotions.
Although there may be joy at the news you’re expecting, you could experience some unexpected emotions too.
You might worry about how you’ll take care of this precious new baby, or what impact it will have on your relationship.
You could feel stressed about your financial situation. Or perhaps you wonder how you’ll cope with the demands of a newborn, or even how a new baby will fit into the dynamics of your family.
But is worrying and stressing bad for your baby?
Read on to find out more about stress in pregnancy, the effects on your baby, and some practical tips about what you can do to reduce it.
Can babies pick up on stress in the womb?
During pregnancy, we consider the mother and baby as a duo or pair.
A pregnant woman and her unborn baby have a shared experience. The baby experiences everything the mother does.
Maternal emotions cause certain hormones to be produced, and they will have an impact on the baby.
The hormones include:
- Oxytocin. Known as the ‘love’ hormone, it triggers feelings of love, and nurturing behaviors. It’s essential for labor, birth, and breastfeeding
- Endorphins. These are our ‘feel good’ hormones, and a natural form of pain relief, released during stress, exercise, or pain
- Adrenaline.
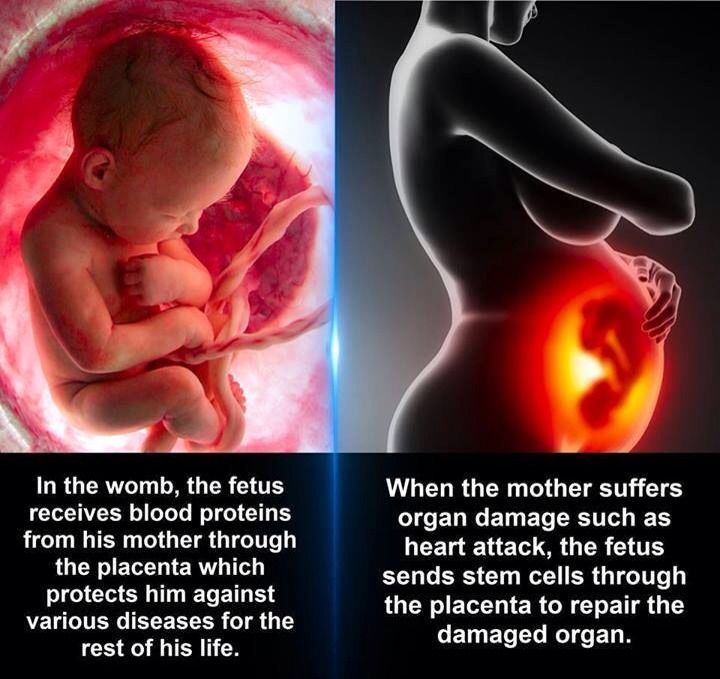 Also known as epinephrine, it is responsible for our ‘fight or flight’ response. High adrenaline levels can work against oxytocin in labor and birth
Also known as epinephrine, it is responsible for our ‘fight or flight’ response. High adrenaline levels can work against oxytocin in labor and birth - Cortisol. This is released in any stressful situation and also plays a role in our ‘fight or flight’ response. Cortisol provides the body with glucose for energy, in case we need to make a quick getaway.
Can crying and stress affect unborn baby?
The uterus is a baby’s first home or environment. A baby in the womb becomes attuned to the environment of the mother and can be affected by her emotional state.
Stress acts as a stimulus, causing a specific reaction in the mother’s body. This means the baby will adapt accordingly, creating physical change.
We’re now learning these physiological changes can alter a child’s development and have long lasting consequences.
What happens when we are stressed?
When we enter a stressful state, the brain triggers a response, and goes into ‘fight or flight’ mode. This response causes the release of several hormones that help tackle the perceived danger or threat.
This response causes the release of several hormones that help tackle the perceived danger or threat.
These hormones temporarily divert blood away from ‘non essential’ organs and systems, and supply a greater blood flow and more oxygen to our major muscles and organs. This happens in case we need to make a quick escape.
Glucose is also made available for energy. Our senses become heightened. We become laser-focused and we pick up on potential red flags around us that could mean more danger.
Once this short-term situation resolves, the body returns to normal.
This response is vital and helps protect us and keep us safe. It’s an ancient adaptation, left over from the time when human beings were still part of the food chain and hunted by saber-toothed tigers.
Being constantly stressed, however, leaves us on ‘high alert’ and exposed to these hormones for extensive periods. If we remain in this state for too long, it can lead to chronic health problems and complications.
Stress increases the risk of developing any of the following health conditions:
- Heart disease
- Type 2 diabetes
- Obesity
- Depression and anxiety
- Gastrointestinal problems, such as stomach ulcers or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
What will stress do to an unborn baby?
Hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline have an effect on the placenta. This affects your baby’s growth.
Adrenaline constricts blood vessels, reducing oxygen supply and blood flow. This can lead to problems for your baby in the womb.
Excessive stress in pregnancy increases the chance of:
- Maternal hypertension (raised blood pressure)
- Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR)
- Poor placental function/placenta abnormalities
- Low birth weight
- Premature babies – prematurity significantly increases infant mortality
- Infection within the uterus
- Obstetric intervention – including induced labor and c section birth due to fetal concerns
- Admission to neonatal intensive care unit
- Delayed onset of breastfeeding, skin to skin, and bonding opportunities after birth.

It also increases the risk of a baby developing chronic health conditions in later life, such as:
- Raised blood pressure
- Cardiovascular disease
- Obesity
- Diabetes.
Interestingly, researchers are now examining links between the effects of stress in pregnancy and brain development.
It’s thought babies exposed to chronic high levels of stress, particularly in the first trimester, show increased signs of depression, irritability, and lowered IQ.
Stresses might also leave children less equipped to handle stressful situations, which makes it difficult for them to regulate their own emotions. It can also make them more likely to experience mental illness and behavioral problems.
There’s emerging evidence of a link between maternal stress, autism, and ADHD. Although this is relatively new research, it’s believed these neurodiversities are linked to a specific stress-sensitive gene.
Signs that your baby is stressed in the womb
It’s important to know that normal, small amounts of worrying aren’t going to cause problems for you or your baby.
Extreme or ongoing chronic stress appears to be of most concern for both women and babies.
How do you know if your baby is stressed?
Here are several things both you and your doctor can look out for, which could cause complications.
Fetal heartbeat
Observing and listening to your baby’s heartbeat is one of the ways your doctor can decide whether your baby is stressed in the womb. This is often diagnosed as ‘fetal distress’.
Your doctor will observe the heart rate pattern over a period of time, using a CTG (cardiotocograph) machine, or an electronic fetal monitor. Used along with ultrasound, this can give your doctor an insight into your baby’s overall health.
It isn’t advised for women to use home dopplers, monitoring devices, or apps to listen to their baby. It can lead to false reassurance. Leave this one to your doctor.
Abnormal fetal heart rate patterns
There are a number of characteristics that can be observed during a CTG monitoring, and show whether your baby is in distress:
- Fetal tachycardia – a consistently raised heart rate of >160 beats per minute
- Fetal bradycardia – a consistently lowered heart rate of <110 beats per minute.

- Decelerations – a temporary drop in the fetal heart rate
- Reduced variability – prolonged reduced variation in the fetal heart rate.
Abnormal patterns can indicate fetal distress, which can lead to oxygen deprivation if not acted on accordingly.
Other signs that your baby is experiencing fetal distress in the womb
- Decreased fetal movement or change in fetal movements. An active baby normally signals a happy and healthy baby. Any change or reduction in baby’s movements can be an early indicator your baby is in distress
- Cramping or back pain. This can be an early sign of miscarriage, preterm labor or urine infection
- Preterm contractions (under 37 weeks) is a likely sign your baby is on their way a little early
- Vaginal bleeding. Bleeding in pregnancy is always a cause for concern. It can indicate problems with the placenta, such a placental abruption or vasa previa.
 Seek medical advice from your doctor right away if you experience any bleeding in pregnancy
Seek medical advice from your doctor right away if you experience any bleeding in pregnancy - Abnormal AFI (Amniotic Fluid Index). Whether oligohydramnios (low) or polyhydramnios (high), this is considered a complication of pregnancy. Amniotic fluid levels are an indicator of your baby’s health
- High blood pressure or preeclampsia. Blood pressure problems can affect the way your baby grows and, if very high, increase the chance of your baby needing to be born early
- Sudden weight gain. Pregnancy weight gain outside of the normal range can cause fetal distress
- Meconium. Meconium in amniotic fluid can be an indicator of distress in your baby
- Maternal illness. If you are unwell in pregnancy it may also affect your baby.
How much is ‘too much’ stress?
All women will experience a certain amount of stress in pregnancy and that’s normal. Just because women become pregnant, doesn’t mean life stops happening around them.
Just because women become pregnant, doesn’t mean life stops happening around them.
Fleeting ‘every day’ stresses, such as running late for an appointment, getting stuck in traffic, or forgetting to pack the kids’ lunch boxes isn’t likely to cause a problem.
Ongoing stress that interferes with your ability to cope with other things is the type that is called chronic. This can be considered ‘too much’, and needs to be managed.
What kinds of stress are harmful?
Stress becomes harmful when it becomes chronic. Stresses might caused by major events such as the death of a loved one, poverty, homelessness, domestic violence, acts of discrimination or racism, or by excessive worrying or fears.
Constant fears about pregnancy, loss of life, or losing the baby, as well as trauma or prolonged stress, all increase stress hormones in the amniotic fluid.
This level of stress is likely to have an impact on your baby’s development.
Everyone deals with stresses differently, but they commonly lead to some unhealthy habits or behaviors, such as:
- Under or over eating
- A reliance on comfort or junk foods, or ‘treats’
- Poor sleep patterns
- Alcohol use
- Smoking
- Drugs or substance misuse.
So no stress is best, right?
Having said all that, it’s impossible to eliminate all elements of stress from our lives.
Although it would be nice to cocoon ourselves in a layer of bubble wrap and ward off potential worries as they head our way, it’s just not possible.
Added to that, the human brain actually requires a certain amount of stress – not too much, but not too little – for its normal development.
Are You Getting BellyBelly’s Pregnancy Week By Week Emails?
We think they’re the best on the internet!
Click to get the FREE weekly updates our fans are RAVING about.
Is it normal if baby moves a lot in the womb?
Generally, an active little one is a reassuring sign all is well with your baby in the womb.
Throughout your pregnancy, you’ll get to know the normal pattern of your baby’s movements. This pattern of movement should continue throughout pregnancy, even as you approach the onset of labor.
There isn’t really such a thing as ‘too much’ fetal movement.
Very occasionally, a sudden short, violent increase in your baby’s movements, can be a sign of acute fetal distress, related to problems with the cord, or placental abruption.
Rest assured, though; this is extremely rare.
Be sure to read Do All Babies Go Quiet Before Labor for more information on normal fetal movements.
Tips to reduce stress in pregnancy
It’s unrealistic to expect we can banish all stressful scenarios from our lives. Stress often comes, though, from the worry we feel when we are in certain situations, or facing certain problems.
Even if we can’t change those situations, taking positive action to tackle the problems can sometimes make us feel a lot better.
Use this time in your pregnancy to make sure a few plans are in place. Set up a system of support for yourself and your partner.
Be sure to:
- Ask for help
- Speak to someone you trust about your concerns
- Seek professional help if – maybe a doula/midwife, support for your business, a cleaner, or child minder
- Tackle your finances
- Get outdoors and exercise
- Consider mindfulness practices, such as yoga, which have been shown to reduce the chance of pregnant women developing depression and anxiety.

Find more practical tips in how to reduce stress in Stress During Pregnancy | How Does Stress Affect Pregnancy?
Trust your instinct
Some health care professionals discount a mother’s intuition in favor of ‘facts’ or ‘data’. Pregnant women, however, are normally very much in tune with their unborn babies, and have a ‘sixth sense’ telling them when things are wrong.
Trust that instinct and be guided by it. No one knows your baby better than you.
If you’re worried about your baby, make sure you speak to your health care provider for further advice.
Pregnancy stress threatens the health of the unborn child - DW - 11/07/2013
Vladimir FradkinNovember 7, 2013
It is well known that severe stress is harmful. Now scientists have taken up the question of how the stress experienced by the mother during pregnancy affects the health of the child.
https://www.dw.com/en/%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B5%D1%81%D1%81-%D0%B1%D0%B5%D1% 80%D0%B5%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B9-%D1%83%D0%B3%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B6 %D0%B0%D0%B5%D1%82-%D0%B7%D0%B4%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B2%D1%8C%D1%8E-%D0%B1 %D1%83%D0%B4%D1%83%D1%89%D0%B5%D0%B3%D0%BE-%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%B1%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BA%D0%B0/a-17211948
Advertising
Pregnancy, even if it is not the first, in itself, of course, is a fair amount of stress. But even if this were not so, hardly any woman manages to avoid the stress caused by various events of everyday life for all nine months. And therefore, almost any expectant mother asks the question: how will the stress she experiences affect the child? Can the fear, pain, grief, irritation, or arousal of the mother be transmitted to the fetus in the womb?
But even if this were not so, hardly any woman manages to avoid the stress caused by various events of everyday life for all nine months. And therefore, almost any expectant mother asks the question: how will the stress she experiences affect the child? Can the fear, pain, grief, irritation, or arousal of the mother be transmitted to the fetus in the womb?
Maternal stress hormone in fetal blood
Not only can they be transmitted, but they must be transmitted, although, of course, still not fully, doctors say. The placenta contains a number of hormones designed to protect the fetus from the harmful effects of cortisol, the mother's stress hormone. But it still penetrates into the blood of the embryo. True, there its concentration is about 10 times lower than the maternal one, however, it is also enough to have a significant effect on the fetal body.
And not just significant, but long-term, often even permanent. This conclusion was reached by a group of doctors led by Professor Matthias Schwab (Matthias Schwab) from the Hans Berger Neurological Clinic at the University Hospital of Jena. The scientists reported the results of their research at the 21st annual session of the German Somnological Society, which took place in Wiesbaden.
The scientists reported the results of their research at the 21st annual session of the German Somnological Society, which took place in Wiesbaden.
“Antenatal stress leads to a long-term increase in fetal cortisol levels and accelerates brain maturation,” says Prof. Schwab, who heads the Intrauterine Brain Development and Later Life Programming of Disease Working Group. “For this reason, the stress experienced by the mother during pregnancy , is a serious risk factor that increases the likelihood of a child developing later depression and other pathologies.
Dreaming of a lamb in the womb of a sheep
Professor Schwab and his colleagues conducted their experiments on sheep, since in these animals the course of pregnancy and the formation of the embryo have a significant similarity with the same processes in humans. Pregnant - that is, pregnant - sheep, the researchers injected betamethasone, a synthetic glucocorticoid drug related to cortisol, which is often prescribed to women with the threat of preterm birth. This drug speeds up the development of the lungs in the fetus, which increases the chances of a premature baby to survive. Betamethasone was administered to pregnant sheep at a stage corresponding in pregnant women to the period between the 25th and 32nd weeks.
This drug speeds up the development of the lungs in the fetus, which increases the chances of a premature baby to survive. Betamethasone was administered to pregnant sheep at a stage corresponding in pregnant women to the period between the 25th and 32nd weeks.
At the same time, scientists monitored the intrauterine brain activity of embryos using electroencephalography. It turned out that betamethazole accelerates the maturation of not only the lungs, but also the brain, says Professor Schwab: “This is evidenced, first of all, by the early appearance of dreams. Usually, the formation of dreams occurs in the last third of pregnancy, and this development occurs very gradually. And betamethasone literally includes there is some kind of toggle switch in the brain, and dreams are formed in 2-4 days."
Brain development inhibits cell growth and division
Another consequence of the introduction of the hormone was an abnormally frequent alternation of the phases of REM and non-REM sleep. This fragmentation of sleep, if it becomes permanent, indicates a high risk of developing depression later in life and, according to Professor Schwab, is often diagnosed in newborns whose mothers experienced severe stress during pregnancy.
This fragmentation of sleep, if it becomes permanent, indicates a high risk of developing depression later in life and, according to Professor Schwab, is often diagnosed in newborns whose mothers experienced severe stress during pregnancy.
The problem is that the premature maturation of brain structures occurs due to a slowdown in cell division and body growth, the scientist says. This is confirmed by other doctors. "Children given injections to accelerate lung maturation showed a very significant increase in stress axis activity and had a markedly lower birth weight," says Thorsten Braun, a gynecologist at the Charité University Hospital in Berlin.
Therapy with betamethasone is fraught with behavioral disorders
In Germany, 8 to 10 percent of pregnant women receive betamethasone. The fact that this drug reduces mortality among premature babies by 31 percent has long been scientifically proven. However, animal experiments have shown that taking the drug also causes long-term side effects - in particular, hypertension - and also contributes to the development of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes in later life.
As for a person, here scientists have identified, first of all, an increased risk of developing depression and behavioral abnormalities. Recently, Professor Schwab and his colleagues examined 40 eight-year-old children who had previously undergone intrauterine therapy with betamethasone. Comparing the test results of these children with the test results of children in the control group revealed significant differences, the scientist emphasizes: ". Electroencephalography also showed that these children could not relax before testing, and could not concentrate during testing.
No reason to panic
Apparently, the increased content of the stress hormone in the blood at the stage of intrauterine development leads to the fact that the body of the embryo gets used to this situation and begins to perceive it as the norm. "These babies are already programmed in the womb to produce too much of the stress hormone later in life," says Professor Schwab.
The Dutch colleagues of the German scientist - doctors at the University of Tilburg - found that maternal stress affects the fetus most negatively between the 12th and 22nd weeks of pregnancy: its consequences make themselves felt even 20 years later.
But still, one should not panic, says Professor Schwab: “Stress during pregnancy is a completely normal thing. And injections of betamethasone, this hormonal accelerator of lung development, are an important and necessary therapy if there are indications for it. You just need to keep in mind that An elevated level of stress hormone in the blood of the embryo seems to play a more important role in the development of later diseases than has been previously believed.
Write to the editor
Advertising
Skip this section Top topic1 page of 3
Skip this section Other publications DWHome
The nature of a child depends on the mother's stress during pregnancy
The period of childbearing is an exciting stage in a woman's life. She finds herself in the center of care and attention, but at the same time she bears a huge responsibility for the little man.
Preparing for the birth of a baby, solving work issues, household chores occurring against the backdrop of hormonal storms can provoke a full-fledged stress reaction.
The magazine "Together with You" figured out how stress affects pregnancy, whether it is worth worrying about the health of the child, and how to minimize this effect.
photo from the site http://queen-time.ru/
Stress during pregnancy: causes
The very fact of pregnancy is already a stress for the body. In the next 9 months, he will have to go through serious changes associated with an increased load on all organs and systems. Therefore, a woman should avoid any additional stressful situations, and the truism that pregnant women should not be nervous is fully justified.
In reality, almost no expectant mother can do without worries, but how strong the effect of stress on pregnancy depends on the intensity of the worries. The following reasons can become provoking factors:
- Fear for the child.
 While the baby is inside the abdomen, the mother cannot control his condition, know if he is healthy. This is especially annoying for women who have experienced unsuccessful pregnancies. Fear recedes a little with the onset of movements and the passage of all planned analyzes.
While the baby is inside the abdomen, the mother cannot control his condition, know if he is healthy. This is especially annoying for women who have experienced unsuccessful pregnancies. Fear recedes a little with the onset of movements and the passage of all planned analyzes. - Contacts with others. Registering with a antenatal clinic is not a task for the faint of heart. Queues, tests, unfriendly staff shock women who are not accustomed to the realities of our medicine. However, a vulnerable pregnant woman can be hurt anywhere, and a trip in transport or a trip to the store turns into a mini-stress.
- Working moments. It becomes difficult to work in the previous mode, and if colleagues and superiors do not treat with understanding, then it is almost impossible. If your manager is comfortable with late due to testing and delayed due to morning sickness, you can consider yourself lucky.
- Shock situations. The special position of a woman cannot insure her against life's upheavals.
 An accident, natural disaster, death of loved ones, betrayal or divorce can overtake her during this especially vulnerable period.
An accident, natural disaster, death of loved ones, betrayal or divorce can overtake her during this especially vulnerable period.
photo from the site https://mamapedia.com.ua
- Fear of childbirth. He usually overcomes women in the third trimester, closer to the hour "H". In this stress factor, the fear of pain, complications, mistakes of medical personnel and many other, often vague and irrational fears are intertwined.
- Preparatory chores. There are so many things to choose - a stroller, a crib, a mattress, decide whether a pillow is needed, and what to take with you to the hospital. Despite the fact that these chores are rather pleasant, for the nervous system it is a complete stress.
Bad and good stress
Both positive and negative emotions have a stressful effect. In psychology, the concepts of eustress (caused by positive experiences) and distress (provoked by negative events) are distinguished. Both varieties load the nervous system, although with different emotional overtones.
Do not think that a scolding from your boss is a meaningless trifle that does not lead to a stressful situation. In practical psychology, such an assessment method as a stress scale is used.
At the same time, real catastrophes, such as the death of relatives, are estimated at 100%, and small episodes, like not given a seat in transport, are only 5%. All the negative emotions received are summed up, and in a couple of days the overall degree of stress can exceed 100%.
So multiple small experiences are no better than single strong ones.
Stress during early pregnancy: is it worth it to be afraid
The beginning of pregnancy is a rather ambiguous period. On the one hand, the expectant mother feels completely pregnant, and often experiences unpleasant sensations of toxicosis. On the other hand, outwardly nothing is visible yet, and even close people do not always consider it necessary to treat a woman with reverence, not to mention outsiders.
photo from the site http://qulady. ru
ru
Any damaging factors, as well as stress, in the early stages of pregnancy affect the child according to the “all or nothing” principle:0005
- On the one hand, the fetus is completely protected from physical influences by the fact that, due to its small size, the uterus is located in the pelvic cavity. The effects of high levels of stress hormones are also not to be feared, because the uteroplacental blood flow begins to function only after 10 weeks, and everything that circulates in the mother's blood cannot get to the fetus.
- On the other hand, the organs and systems of the fetus are not yet differentiated, which means that even the slightest damage causes severe pathology, most often incompatible with life.
photo from the site http://pervenets.com
By themselves, stress during pregnancy does not have consequences for the child in the first trimester, but they can provoke changes in the mother's body:
- Increased toxicosis.
 Against the backdrop of experiences, mild morning sickness can develop into round-the-clock, reaching vomiting. Women note drowsiness, a desire to sleep almost around the clock and other manifestations.
Against the backdrop of experiences, mild morning sickness can develop into round-the-clock, reaching vomiting. Women note drowsiness, a desire to sleep almost around the clock and other manifestations. - Stress in the early stages can provoke hormonal changes, due to which the implantation of the embryo is disrupted, but in this case, the woman will not even know that the pregnancy was.
- Anxiety and excitement of the mother lead to an increase in the tone of smooth muscles, which carries the threat of miscarriage.
- Severe stress during pregnancy is one of the likely factors for fetal freezing.
A fairly common pathology in which an absolutely healthy fetus stops developing and dies in utero without any physical cause. This can happen at any time, up to 42 weeks.
If you notice bloody or spotting discharge, feel a pulling pain in the lower abdomen, contact your doctor immediately. A delay of even a few hours can become critical, so do not hesitate to call an ambulance or call the doctor after hours.
Second trimester: keep your nerves under control
A woman feels relieved as the second trimester begins. Toxicosis, hormonal changes and the first tests are already behind us, and the time for sluggishness and swelling has not yet come.
The tummy is just emerging and looks nice and neat, you rarely need to go to the consultation, so if there are no deviations, it's time to enjoy your special status.
Stress during pregnancy in the second trimester is usually associated with factors beyond the woman's control, more often these are strong shocks than minor experiences.
photo from the site http://womee.ru
Despite the fact that the second trimester is relatively easy for the mother, it is a hot time for the baby. Now there is a formation and development of all organs and systems, and damage at this time is of the most severe nature. Do not be alarmed, stress during pregnancy will not cause consequences in the form of congenital anomalies, but still it cannot be called absolutely safe: Among newborns whose mothers experienced stress, low birth weight and intrauterine growth retardation are more common.
photo from the site http://zsz.pp.ua
If you could not avoid shocks during this period, be sure to ask the doctor to prescribe herbal sedatives for you. Also ask about the possibility of a trip to a sanatorium for pregnant women, if there is one in your city. With timely measures taken, stress during pregnancy does not have consequences for the child.
Also ask about the possibility of a trip to a sanatorium for pregnant women, if there is one in your city. With timely measures taken, stress during pregnancy does not have consequences for the child.
The last trimester is not a time for stress
If you have crossed the threshold of 28 weeks, you can breathe out. The child is practically no longer in danger, all organs and systems have developed, and are only in the final stages of formation.
The main task of the peanut now is to build up mass, and only this can be prevented by stress. If a baby is born now, even in run-down hospitals without modern equipment, it is likely to be saved.
But still, it is better not to take risks and be careful, because mild or severe stress during pregnancy can have the following consequences:
- Premature birth. Your body takes care of the health of the baby, and if he judges that hormone surges and uterine hypertonicity are more dangerous for him than premature birth, childbirth may well begin unplanned.
- Weakness of labor activity. The process of giving birth to a child is a complex mechanism that is triggered and regulated by changes in the hormonal background. If your hormone levels are not up to par throughout your pregnancy, labor will not be effective, and doctors will need labor induction or delivery by caesarean section.
- Light weight. No one has canceled hypoxia and impaired uteroplacental circulation, and since the main process of the third trimester is weight gain, it is he who suffers from stress.
- Malposition of the fetus. Periodic hypertonicity in various segments of the uterus leads to the fact that the baby cannot take the correct position for childbirth with the head down. Breech and oblique presentation makes it impossible or significantly complicates the course of childbirth through the natural birth canal.
photo from the site http://www.likar.info
In addition to the risks listed above, stress during pregnancy has non-specific consequences. Children in the first year of life often do not sleep well and behave restlessly, and if the stress factor is not eliminated, problems with lactation may occur.
Children in the first year of life often do not sleep well and behave restlessly, and if the stress factor is not eliminated, problems with lactation may occur.
How to deal with stress during pregnancy: useful tips
First of all, calm down. This is not a joke, nothing matters now, except for the crumbs that live under the heart. Your experiences now can result in serious problems for a defenseless creature. Therefore, pull yourself together and implement the recommendations of psychologists into your life:
- Stop being afraid. The fear that something is wrong with the child is unconstructive. Follow the doctor's recommendations, go through all the examinations, and do not think about the bad.
- Find yourself a hobby. It is best if it is something creative - drawing, knitting or hand-made.
- Treat yourself. Don't deny yourself small pleasures. One cookie will harm the body less than an evil mother. Eat what you want, just control the amount.

photo from the site http://bagiraclub.ru
- Fear of pain in childbirth should recede. Accept that you will have to work hard and endure in childbirth, but a few hours of pain are nothing compared to the years of joy of motherhood.
- Announce your position to everyone. Often a pregnant woman wants to keep her secret longer, but if you do not have enough attentive attitude, do not hesitate to say that you are pregnant. Let the boss not start to tremble in front of you, but at least he will not raise his voice.
- Talk about your desires. Not a single man will refuse to give up his seat if you ask him directly and explain that you are expecting a baby. Do not wait for your husband to pamper you with a bouquet of flowers, directly tell him about it.
Don't let stress ruin your pregnancy. After all, this wonderful period happens so rarely that you should definitely get the most out of it. Moreover, the course of pregnancy, the ease of childbirth, and the health of the child now depend on your peace of mind.
data-block2= data-block3= data-block4=>
Mother's influence on the child during pregnancy
Mother's influence on the child begins during pregnancy and manifests itself especially intensively during this period.
The very fact that the child's body is completely formed from the materials that the mother's body supplies, determines his strongest physical dependence on everything that his mother does: on her health (or ill health), her nutrition system, the presence or absence of bad habits.
The mother's influence on the child also manifests itself emotionally.
The mother's emotions are transmitted to the fetus through hormones and energy channels, having either a positive or negative effect on his psyche.
The works of specialists in the field of theoretical medicine, explaining the ways of recording information at the cellular level, also indicate that the mother's psychological environment affects the internal properties of the child's cells.
Elementary particles that make up atoms, molecules and living cells obey both the laws of physics and the basic laws of physiology. They are able to store information about the environment in their memory, as well as reproduce it at will and transmit some information to other particles. Recording information, memorization and transmission are properties of the psyche. The mother's influence on the child is due to the fact that information about the psyche, thoughts and feelings of the mother, received by the emerging being, determines the vibrational properties of its cells. Thus, everything that we go through is recorded in the chromosomes of the cells. In particular, this applies to germ cells that make up the genetic capital of the child.
A pregnant woman, like no other, is the focus of various energies that structure matter, since she carries within herself the project of a new being. The actions, thoughts and feelings of a woman are the cause of the formation or attraction of quite certain types of energy.
She can either brush this fact aside or decide to use her best efforts to direct her mental or physical energy in the direction most convenient for the child.
This decision also applies to people around you, both family members and society as a whole.
The intrauterine period of development directly depends on the mother and on the psychological, physical and information space surrounding her. If the expectant mother knows about this and tries to exclude all negative aspects from her life, then she, as it were, forms a positive, favorable background for the development of the baby.
In other words, the mother's influence on the child in this case is characterized by the fact that she provides the developing child with the best physical material and the highest quality information that exists on the sensory, emotional and mental levels.
In close cooperation with nature, a woman becomes another conscious creator of a child, to whom she provides the best chance of all existing
The mother's influence on the child on the physical level is manifested in her attitude to food. Choosing a balanced menu, focusing on foods that are necessary for the development of the child, eating organic, healthy foods, of course, will have a positive effect on the child.
Choosing a balanced menu, focusing on foods that are necessary for the development of the child, eating organic, healthy foods, of course, will have a positive effect on the child.
The mother's influence on the child on the emotional level should be manifested in her positive emotional mood. Emotions and space are characterized by a very close relationship. Misfortune, mental pain cause a feeling of constriction of the heart, lack of air.
Such negative emotions as fear, jealousy, anger lead to feelings of heaviness, feeling unwell and enslavement. Joy makes our heart sing. For example, when we are in love, it is easy and good for us. It seems that wings have grown behind our backs, we are overwhelmed with energy, we are ready to embrace the whole world.
It is very useful to cultivate such a state of happiness and inner freedom in oneself, passing it on to a child who will fix this feeling of inescapable joy in his cells.
Music, singing, poetry, art, nature help to achieve this inner state and bring up a sense of beauty in a child. This is where the father plays an important role. The attitude towards his wife, pregnancy and the expected child is the main factor that forms his feeling of happiness and strength, which is transmitted to him through a self-confident and calm mother.
This is where the father plays an important role. The attitude towards his wife, pregnancy and the expected child is the main factor that forms his feeling of happiness and strength, which is transmitted to him through a self-confident and calm mother.
However, life sometimes disturbs this idyllic picture, as it can be stressful (for example, a car accident), serious situations (father's dismissal from work) or bereavement. What should be done in these difficult circumstances? The smartest thing to do is try to deal with them. Mothers have a kind of protective shield for the child: love for him.
Many women say that during pregnancy they had a reflex to protect their child, as a being already born. For this reason, they consciously suppressed all unwanted emotions in themselves.
These expectant mothers were talking to the child, explaining to him what was happening, calming him down. At this time, the child “recorded” at the cellular level information that there are ups and downs in life that can always be overcome.
Thus, the foundation of a strong, hardy person was laid.
A good mother is one who understands that she will give birth to a person who may be different from her: with her own opinion (even in infancy), with her own convictions, desires and views.
Children should not be a means to compensate for the failures of parents or to achieve their ambitious aspirations. They are free beings with the right to their own lives.
The main task is to lay in them the basis of high qualities of a general nature, which children can develop in the future.
Nature will thank the mother for her conscious efforts. The form of gratitude can be very different and manifest itself in completely different life situations related to the child. For example, in a significant reduction in the negative aspects inherent in pregnancy: feelings of fatigue, anxiety, fear.
With the natural completion of a conscious and full of light sensations of pregnancy, childbirth will also take place, passing also consciously, under control and with a sense of joy and complete unity with the child.
A child born in this way will be easy to nurture and will in all probability have all the qualities that parents can satisfy.
How a child's prenatal memory affects his health in the future
A child's mental state begins to form not in the first days after birth, but from the first days of his existence in the womb. Whether the baby is cheerful or prone to depression and stress depends on the nine months of his life in his mother's stomach.
Professor Grigory Brekhman states that the fetus has emotional perception and memory.
The experiences a child receives during the fetal (before 8 weeks of gestation) and fetal (from 9 weeks to birth) periods affect his thinking, lifestyle and behavior.
Emotional perception and memory of the fetus and their impact on later life is studied by prenatal and perinatal psychology.
WHAT CHILDREN REMEMBER
The nervous system of the embryo begins to emerge even before the heart beats. The formation of neural plates begins from the 18th day of conception.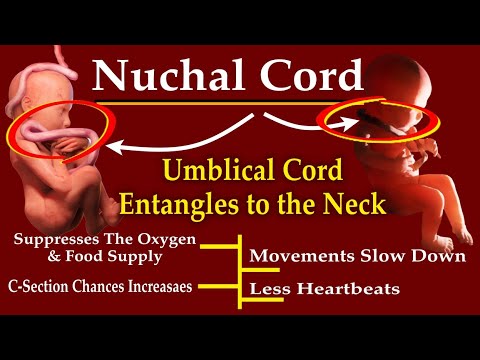
And from the 4th week of pregnancy, the nervous system takes part in the development of internal organs and sense organs. The first emotional facial reactions the fetus can show at 8-14 weeks.
And at the beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy, the fetus perceives information by all organs and can react to it.
Read also: Do you believe the myths about pregnancy?
Being in the womb, the baby remembers the most emotional experiences of his mother. If he receives positive information, it helps to develop the inclinations and talents laid down by his parents.
And negative impressions can later manifest themselves in the form of mental problems.
Therefore, knowledge of prenatal memory will help the mother take care of the psychological and physiological health of the baby even before it is born.
After analyzing the work of scientists, Professor Brekhman claims that prenatal memory does exist and in later life it remains at the level of the unconscious. And it affects the thoughts, behavior, reactions and emotions of a person.
And it affects the thoughts, behavior, reactions and emotions of a person.
- Stanislav Grof believed that the child remembers the birth process itself. Child psychology also says that naturally born babies have stronger personalities.
- Athanassios Kafkalides studied the effect of mother's stress on the child. He argued that the fetus responds to the emotional state of the mother and remembers the most vivid impressions throughout pregnancy. Both negative and positive emotions are taken into account.
- Frakne Lake considered the first trimester of pregnancy to be the most important. Of particular importance is how the expectant mother reacts to the news of pregnancy - whether she wants a child or not.
Read also: Forgetfulness of pregnant women
HOW PRENATAL MEMORIES AFFECT CHILDREN'S HEALTH
Pregnant women sometimes complain that the fetus kicks a lot with legs and arms. Studies at the University of Leuven have shown that excessive motor activity of the baby is often the result of increased anxiety of the mother.
There have been many studies that confirm that the fetus responds to the emotional state of the mother. For example, pregnant women were allowed to listen to recordings of children's songs and at the same time they made a fetal cardiogram. When the melody changed, the baby's heart rate also changed.
This reaction was also to other emotional stimuli.
Read also: Ultrasound during pregnancy: 10 most important rules
The emotional state of a woman affects the position of the fetus. If the expectant mother is often nervous, there may be a breech presentation. And if in her life there was a place for a socio-psychological conflict - the extensor presentation of the head and the transverse position of the fetus. The information that the fetus remembers can result in other deviations.
- A tendency to depression develops in a child if the mother herself was prone to depression during pregnancy. In such women, children often cry, are restless and irritable.
 In the future, children are prone to bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs.
In the future, children are prone to bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs. - Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) develops in children if the mother is prone to anxiety at 12-22 weeks of pregnancy.
- Autism in children can develop if the mother experienced severe stress at 21-32 weeks of pregnancy. Moreover, experiences at 25-28 weeks of pregnancy are especially dangerous.
- The stress of a pregnant woman can also cause phobias and fears in a baby.
- Psychosomatic disorders in the form of asthma, migraine, stuttering, speech disorders can also be consequences of prenatal stress.
- Sexual deviations in a child are born in the womb. Often such consequences can occur when a mother wanted a girl, but a boy was born, and vice versa. On an unconscious level, the child may remember this and feel uncomfortable in their body. The sexual development of a child also depends on the attitude of his mother to sex. Negative experience may affect the sexual function of the baby in the future.
- A child may be unjoyful, touchy and have low self-esteem if the pregnancy was undesirable for his mother. Such children are in dire need of recognition and they seek it by any means.
- Also, some psychologists believe that children whose mothers mentally rejected them or even tried to have an abortion develop aggression and a tendency to violence.
It is believed that complexes and fears arise in childhood. But the prenatal period of the existence of the baby also affects his future life. Injuries received during the development of the fetus are very deep in our unconscious. They can be restored and "cured" with the help of a psychologist. This will help to solve the pressing mental problems of the "patient".
- Read also: Complications during pregnancy: what expectant mothers need to know
- Read also: Pregnancy trimesters: how the baby develops
- Read also: What happens in mom's tummy?
Effect of stress during pregnancy
The stress of a pregnant mother is a very serious threat to the health of the unborn baby.
Stress is harmful to absolutely everyone. At this point in time, scientists are studying the impact of stress experienced by the mother during pregnancy on the health of the baby.
Pregnancy itself is stressful for the expectant mother's body. We will try to find out how dangerous the stress endured by the mother is for the baby, and also consider ways to deal with unnecessary excitement and anxiety.
What is stress?
The very concept of "stress" means the body's reaction to certain situations: hormonal changes, changes in external conditions, strong feelings, and so on. And pregnancy entails a lot of changes in a woman's body. Perestroika also concerns the psycho-emotional background, so expectant mothers always react brighter and more painfully to the influence of their environment.
This is a completely natural process necessary for adaptation to a new position and proper bearing of a child.
But such a reaction can also become pathological. If the first two stages of stress are a manifestation of a normal defensive reaction, then the third, last, can cause prolonged depression and other mental disorders.
If the first two stages of stress are a manifestation of a normal defensive reaction, then the third, last, can cause prolonged depression and other mental disorders.
Reasons for stress during pregnancy
1 Fear for the baby's health. Even under ideal conditions of conception and constant examinations, there remains a small percentage of the likelihood of pathologies in the fetus.
But modern medicine is not limited to diagnosing the state of health of the baby in the womb.
If any developmental abnormalities are found, doctors will always be ready to provide the necessary assistance to eliminate them. Your worries about the health of the child can only give the opposite result.
Therefore, it is best to just calm down and not miss scheduled examinations, tests and ultrasounds.
2 Fear of negative changes in appearance. The fear of losing its former shape after childbirth is perhaps the most groundless of the "pregnant" fears.
The appearance of many women who gave birth not only did not deteriorate after gestation, but also became more spectacular, bright and attractive.
And little things like a tummy that has appeared and rounded hips can be easily eliminated with the help of training in the gym.
3 Fear of forthcoming childbirth. How the birth will take place sometimes remains a mystery even for a specialist who observes pregnancy throughout the entire period. Possible pain sensations, insufficient competence of medical personnel - any pregnant woman repeatedly thinks about all this.
The solution to this problem is quite simple. You need to communicate as much as possible with women who have already experienced childbirth, to express your concerns to them.
An experienced mother will definitely give you good advice and help dispel all fears. It will not be superfluous to attend courses in preparation for childbirth. Here you will be taught proper breathing techniques, special gymnastics and other useful things.
Thanks to the knowledge gained, you will never get lost at the most crucial moment, and your baby will be born healthy and strong.
Consequences of stress during pregnancy
No woman has been able to save herself from stress during her entire pregnancy, and therefore the question lurks in the mind of every expectant mother - “How can the stress I experienced affect my child? Does he feel all my feelings?
Interesting! Is polyhydramnios dangerous during pregnancy?
Severe stress in a pregnant woman can cause the following pathologies that are dangerous for both mother and child:
- Intrauterine hypoxia. Oxygen starvation caused by stress in the mother causes abnormalities in the development of the fetus and even complete respiratory arrest.
- Deterioration of placental blood supply. The lack of nutrients coming to the child from the mother provokes developmental delays and prematurity.
- Weak labor activity. With this pathology, contractions do not intensify, which significantly increases the duration of the birth process. In these cases, medical stimulation or surgery is necessary to save the life of the baby.

- Development of neuroses. Increased fatigue, irritability and other features common to pregnant women become critical. To solve this problem, the obligatory help of a psychologist is needed.
- Miscarriages. Premature births often occur after a woman has experienced stressful situations.
- Problems with the appearance of postpartum crying. The first cry of a newborn is an indicator of the viability of the baby. The absence of a cry also means the absence of respiratory activity.
The blood of the embryo contains the mother's stress hormone. A number of hormones contained in the placenta protect the fetus from exposure. And yet, cortisone enters the blood of the fetus, although 10 times less than that of the mother, but this is enough to affect the fetus of the baby.
A bit of theory
At the 21st annual session of the German Society in Wiesbaden, the results of the research were made public. A group of medical scientists led by Matthias Schwad stated that the stress hormone in many cases does not just affect the fetal body, but acts for a long time, in some cases permanently.
Late pathologies and depression developed in a child are the result of prenatal stress by the mother, says Professor Schwad, who led a group of scientists studying the intrauterine formation of the brain.
Experiments carried out on sheep
Significant similarity between the course of pregnancy and the creation of the human embryo was found in sheep. That is why Professor Schwad decided to conduct experiments on sheep. Scientists injected pregnant sheep with a synthetic stress hormone-like drug, betamethasone, designed to prevent preterm labor.
What was the surprise of the scientists when it turned out that under the influence of this drug the dreams of the embryo were formed within 2-4 days.
Inhibition of cell growth and division
Children whose mothers experienced severe stress during pregnancy are diagnosed with later life risks of developing depression, which are the consequences of alternating slow and fast sleep.
The gynecologist at the Charite Clinic Berlin - Thorsten Braun claims that children who were given a drug to improve the maturation of the lungs had an increased activity of the stress axis, while they were significantly behind in weight. All this is directly related to the fact that by slowing down the growth of the body and cell division, there is a more rapid maturation of the cerebral cortex.
All this is directly related to the fact that by slowing down the growth of the body and cell division, there is a more rapid maturation of the cerebral cortex.
What to do when stressed?
1 Treat yourself to something delicious. For most people, food is the main method of dealing with stress. But this does not mean at all that any troubles in life need to be “jammed” with cakes and other sweets. Especially against the background of the fact that a woman needs to carefully monitor her diet during pregnancy.
Contrary to popular belief, the group of food antidepressants does not include chocolates, ice cream or jam. The ability to improve mood is inherent in products that contain B vitamins, manganese and vitamin C.
Interesting! Breech presentation - causes, signs and exercises
Such foods are fish, nuts, lean meat (chicken, turkey, rabbit), cottage cheese, natural yogurt, red fruits (apples, pomegranates), berries and dried fruits. These products will help not only improve the mental state of the mother, but will also be very useful for the baby.
2 Love and be loved. Scientific experiments have shown that it is single women who are most often exposed to stress. Moreover, a woman can feel lonely even when she is married.
It is important to understand that it is not so much sex that can help get rid of stress, but the feeling of complete understanding in the family. Do not withdraw into yourself: it is necessary to share experiences and thoughts with your half.
A joint trip to a film screening, theater or exhibition is a good way to forget about everyday problems and anxieties. New experiences experienced together will surely give you and your life partner a good mood.
3 An interesting hobby is the best cure for stress. Many women begin to discover new talents in themselves during maternity leave or pregnancy. If in the usual pace of life we do not always have time for creativity, then right now you can do something exciting and enjoyable.
A future mother can attend master classes, during which the teacher will give you basic knowledge about a particular art form in an accessible form. In addition, on such courses you can find new acquaintances: communication with interesting creative people always leaves positive impressions.
In addition, on such courses you can find new acquaintances: communication with interesting creative people always leaves positive impressions.
By creating something with your own hands, you will be distracted from negative thoughts. The fruits of your creativity will also be an excellent decoration for the interior of your home.
4 Healthy sleep and proper daily routine. Physical fatigue also has a negative effect on the nervous system. Therefore, it is so important for pregnant women to observe a normal daily routine. Go to bed no later than 22-23 hours. It is during these hours that the body restores its strength to the maximum. Sleep started at a later time is less effective.
And the ideal time to wake up is 6-7 am. Too much sleep is no less harmful to health.
5 Work on yourself. There is a certain category of people who can literally invent problems for themselves.
If you also have this property, try right now to forbid yourself to think about the bad.
Give yourself a session of positive auto-training. Relax, be positive. And you will understand that all fears and worries are just the fruit of your wild imagination. And your favorite aromas and calm, pleasant music, sounds of nature or even mantras will be excellent helpers for relaxation.
Is stress dangerous during pregnancy?
- A high content of the stress hormone in the blood of the embryo often leads to the fact that the baby at the fetal stage takes the stressful situation for granted.
- Scientists at the University of Tilburg have concluded that stress experienced between the 12th and 22nd weeks of pregnancy has the most negative effect on the child, even after 20 years.
- And yet, there is no reason to panic, since stress during pregnancy is a pretty common thing, and injections are made exclusively for the appointment of specialists and under strict control.
Stress during pregnancy: how does the nervous state affect the mother and what are the consequences for the child?
Many consider pregnancy to be the happiest period of life, but not everything is always so carefree. Health problems and worries about the unborn child contribute to stressful conditions in pregnant women.
Health problems and worries about the unborn child contribute to stressful conditions in pregnant women.
Do depression and stressful situations affect the course of pregnancy? It's hard to get a definitive answer. A short-term emotional outburst is to some extent beneficial for the body, which cannot be said about long-term stress, which negatively affects the well-being of the expectant mother and her health, and also prevents the normal development of the fetus.
Symptoms of nervous stress
A woman expecting a baby may not even feel that she is under constant stress. At the initial stage of such a state, only psychological symptoms are present:
- poor sleep;
- apathy;
- tearfulness;
- reduced performance;
- irritability;
- feeling tired;
- panic attacks.
With prolonged depression, the expectant mother develops physical symptoms of stress. These include:
- palpitations;
- high blood pressure;
- migraine;
- nausea;
- frequent SARS and colds;
- weight loss;
- increased muscle tone.

Causes of pregnancy
The most common causes of stress are:
- Fear of childbirth. After listening to the frightening stories of her grandmother or friends, the pregnant woman begins to panic and get nervous in anticipation of the upcoming birth. During this period, in order to reduce emotional stress, you can attend special trainings for pregnant women and read literature on modern methods of childbirth.
- Problems at work. Many pregnant women continue to go to work until they go on maternity leave, and if work is not easy, there are many stressful situations. Some are worried about informal work, as they may lose their job and career growth will be in question.
- Fear of losing beauty and former figure. Often women in a position are worried about their appearance, because mass gain occurs very quickly. In addition, stretch marks appear that do not look aesthetically pleasing. You need to understand that after the birth of a baby, you can restore your previous forms.
 You can start exercising within a couple of months after delivery. It is important to control your diet and follow the correct daily routine even while carrying a child.
You can start exercising within a couple of months after delivery. It is important to control your diet and follow the correct daily routine even while carrying a child. - Experiences regarding the development and intrauterine formation of the fetus, as well as the normal course of pregnancy. Severe stresses on this basis occur quite often. The expectant mother is worried about whether the fetus is developing correctly, whether any pathologies will arise.
- Fear of not being able to cope with the new role of a good mother and wife. After the birth of a baby, a young mother sometimes has a very difficult time. The baby often wakes up at night and requires constant attention. During this period, relatives need to support the young mother and overcome difficulties together.
Danger and consequences for the expectant mother and baby
Experts believe that severe stress experienced during pregnancy can trigger serious complications.
The consequences of mental overstrain may not appear immediately, but have their negative impact only a few years after the birth of the baby.
Problems in such a child may appear not only in primary school age, but also in adolescence.
In the early stages
Stress is dangerous at any stage of pregnancy, because it not only harms the female body, but can also cause abnormalities in the development of the fetus. In the first months of gestation, stressful conditions threaten miscarriage, as the tone of the uterus increases due to the release of hormones.
In addition, there is a tendency to reduce immunity, which contributes to the unhindered penetration of viruses and bacteria into the body of a future woman in labor, causing various diseases.
Between weeks 5 and 9, stress can cause abnormal formation of the maxillofacial bone in the fetus.
This results in a cleft palate or cleft lip (we recommend reading: what is a cleft palate in children: pathology photo).
If a woman experiences super-emotional shock in the second trimester of pregnancy, the child may develop autism in the future. Subsequently, it will be difficult for him to communicate with peers and be in a team. Stress in the early stages provokes the appearance of diabetes in both the mother and her baby.
Subsequently, it will be difficult for him to communicate with peers and be in a team. Stress in the early stages provokes the appearance of diabetes in both the mother and her baby.
In the later stages
Serious emotional overexcitation in the third trimester threatens with early birth or, conversely, the baby will be born post-term. In addition, this condition can affect the course of delivery. Sometimes childbirth is too difficult or doctors decide in favor of a caesarean section.
How to avoid stress during pregnancy?
Every woman who is preparing to become a mother should be aware of the danger of stress for her and the baby, and try to avoid such situations so that unforeseen consequences do not arise. If you can’t overcome nervous tension on your own, you can use useful tips:
- Try to overcome fear. If a woman is afraid for her child, you need to consult a doctor and, if desired, undergo an additional ultrasound. Special trainings for pregnant women or a psychologist will help to cope with fears.

- Hobbies will help to distract from negative thoughts and relax.
- Walk in the fresh air. Walking saturates the body with oxygen and improves blood circulation. Do not forget about the ventilation of living rooms.
- Communicate with people who do not cause negative emotions, irritation and hostility.
- Proper nutrition and good sleep will relieve overwork and provide the body with important substances, as well as energy reserves.
- Perform special physical exercises for pregnant women. Swimming or yoga classes will help keep the body in the right shape and give a charge of vivacity and good mood.
How to relieve stress during pregnancy?
Panic attacks, anxiety and other negativity should not consume a woman during gestation. You need to be able to overcome this condition, because stress affects not only the well-being of the mother, but also the health of the crumbs.
If negative emotions and bad mood often overtake the expectant mother, she should not give in to them, but, on the contrary, eradicate them at the initial stage. A woman should have several useful and effective techniques in her arsenal to help her effectively overcome this or that stressful situation.
A woman should have several useful and effective techniques in her arsenal to help her effectively overcome this or that stressful situation.
Helpful Practices
When a woman feels like she's about to snap, or the situation is almost on the verge of it, it is necessary to resort to useful techniques to relieve stress. In this case, it is recommended:
- take a warm shower or bath with a few drops of your favorite essential oil;
- listen to slow relaxing music;
- perform breathing exercises;
- do yoga or meditation;
- light the aroma lamp;
- go for a light massage session.
These techniques will help you cope with stressful situations. For example, having mastered the practice of relaxation breathing, you can achieve a visible effect in a few minutes. The body relaxes, blood pressure normalizes, heart contractions return to normal.
Medications
Sometimes a doctor may advise a woman to take sedatives to help her sleep.