Clotrimazole in pregnancy
Clotrimazole for thrush: a medicine used to yeast infections including thrush in men and women
1. About clotrimazole for thrush
Clotrimazole is an antifungal medicine.
It's used to treat yeast infections including thrush in women and men, although thrush is more common in women.
Thrush is caused by a fungus (yeast) and can affect the vagina and area around the vagina, breasts and nipples or the end of the penis. It can also affect other areas of skin, such as the armpits, top of the inner thighs (groin) and between the fingers.
Clotrimazole comes as an external cream, an internal cream and a pessary (a tablet you insert into your vagina).
For vaginal thrush you can use pessaries or cream or both at the same time. The pessaries and internal cream are sometimes sold together.
For thrush on the penis, breasts, armpits, groin or between the fingers you would use the external cream.
Clotrimazole is available to buy in pharmacies and shops. Some stronger treatments are only available with a prescription.
2. Key facts
- Clotrimazole works by killing the yeast that causes the fungal infection.
- It usually treats thrush within 7 days but it's best to treat the infection for at least 2 weeks to stop it coming back.
- The most common side effect is an itching or burning feeling in the area being treated.
- Clotrimazole is also known by the brand name Canesten, including Canesten pessaries and cream. However, not all Canesten products contain clotrimazole, and some contain clotrimazole combined with another medicine.
3. Who can and cannot use clotrimazole
Clotrimazole creams can be used by most adults and children.
However, some creams and pessaries are not recommended for children under the age of 16 years or adults aged 60 and above. Thrush affecting the vagina is rare in these age groups so a doctor will need to check what's causing your symptoms before you start any treatment.
Thrush affecting the vagina is rare in these age groups so a doctor will need to check what's causing your symptoms before you start any treatment.
Clotrimazole may not be suitable for some people. To make sure clotrimazole is safe for you, tell a pharmacist or doctor if:
- this is the first time you've had thrush
- you've had thrush more than twice in the past 6 months
- you or your partner have ever had a sexually transmitted infection (STI)
- you're a man with thrush but your sexual partner does not have it
- you have an abnormal discharge from your penis
- you have sores, ulcers or blisters on your penis
- you have abnormal or irregular bleeding from your vagina, or bloody discharge
- you have sores, ulcers or blisters on, or around, your vagina
Do not use clotrimazole pessaries if:
- you're allergic to clotrimazole or any of the ingredients in the medicine
- you have an intolerance to some sugars unless your doctor has said it's OK (the pessary contains lactose)
- you're having your period; wait until it's finished
4.
 How and when to use external cream
How and when to use external cream - Wash your hands before you start.
- Put the cream on in a thin layer and rub it in gently. A strip of cream (0.5cm long) is enough to treat an area the size of the hand.
- Put the cream onto the affected area 2 or 3 times a day for at least 2 weeks. The cream will work better if you can use it 3 times a day.
What if I forget to use it?
If you forget to put your cream on, just do it as soon as you remember. Use the cream as soon as possible and then go back to putting it on 2 to 3 times a day as usual.
What if I use too much?
If you use too much clotrimazole cream or use it more often than you need to, it may make your skin red or irritated. Use less cream the next time if this happens.
5. How and when to use internal cream and pessaries
Pessaries and internal cream are made to go into your vagina only. Do not swallow them.
Do not swallow them.
Pessaries need moisture in the vagina to dissolve completely. If they do not dissolve, pieces of the pessary may crumble and fall out of the vagina. You may notice this if you have vaginal dryness.
To help the pessary dissolve, insert it as far as possible into your vagina at bedtime.
How much to use
Clotrimazole pessaries are available in different strengths: 100mg, 200mg and 500mg.
- 100mg – use 1 pessary every night for 6 nights in a row
- 200mg – use 1 pessary every night for 3 nights in a row
- 500mg – use 1 pessary for 1 night only
If you're using the 100mg clotrimazole pessary, you can use 2 pessaries for 3 nights in a row.
5g of vaginal cream contains 500mg clotrimazole (10%). It's a single application to be used once.
Do not use pessaries during your period. Wait until your period has finished.
How to use a pessary
Each pessary comes in a foil blister pack, together with an applicator to help you insert it. Make sure the foil is not broken before you use it.
- Wash your hands before you start.
- Remove the applicator from the packet.
- Pull the plunger (the thinner end of the applicator) out as far as it will go.
- Take the pessary out of the blister pack.
- Gently squeeze the holder (the wider end of the applicator) to open it.
- Push the pessary into the application following the instructions that come in the medicine packet.
- Lie on your back, bend your knees then let your knees fall to each side.
- Gently put the applicator into your vagina and push it in as far as you can comfortably.
- Holding the applicator in place, slowly press the plunger in until it stops moving.
- Remove the applicator.
- Throw the applicator away safely, out of the reach of children. Do not flush it down the toilet.
- Wash your hands thoroughly when you've finished.
Only insert 1 pessary at a time. Do not use tampons or other vaginal products while you're using the pessary. Do not use pessaries during your period – wait until your period has finished.
How to use internal cream
- Wash your hands before you start.
- Remove the applicator from the packet.
- The "internal" vaginal cream is already in the applicator. You will need to put the plunger into the applicator.
- Carefully twist and pull off the cap following the instructions that come in the medicine packet.
- Lie on your back, bend your knees then let your knees fall to each side.
- Gently put the applicator into your vagina and push it in as far as you can comfortably.
- Holding the applicator in place, slowly press the plunger in until it stops moving.
- Remove the applicator.
- Throw the applicator away safely, out of the reach of children. Do not flush it down the toilet.
- Wash your hands thoroughly when you've finished.
It's quite common to notice a slight discharge after using the cream so it may help to wear a panty liner. This does not mean that the treatment has not worked.
What if I forget to use it?
If you forget to use a pessary or internal cream at bedtime, use it during the night if you remember. If you only remember the next day, wait until bedtime for your next dose. Pessaries and internal cream work best at night.
Pessaries and internal cream work best at night.
If you have forgotten for more than 1 day, your infection may not be treated properly. If you still have symptoms after you finish your course, speak to a doctor.
What if I use too much?
If you insert too many pessaries at once you may feel discomfort or irritation. Stop using the pessaries and see a doctor if the discomfort or irritation does not go away.
Only use 1 pessary a night, unless you're using a 100mg pessary, then you can use 2.
6. Side effects
Like all medicines, clotrimazole can cause side effects in some people, although not everyone gets them.
Common side effects
Side effects from the external cream
Talk to a doctor or pharmacist if these side effects bother you or do not go away:
- red, irritated skin
- pain, burning or stinging sensation
If the side effects do not go away, try using smaller amounts of the cream or stop using it completely.
Side effects from the pessary or internal cream
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if these side effects bother you or do not go away:
- discomfort or swelling in or around your vagina
- pain or burning/stinging after putting the pessary in
- lower stomach pain or pain in the pelvic area
- bleeding from the vagina
Side effects will usually go away when you stop using the pessaries or internal cream.
Serious allergic reaction
In rare cases, clotrimazole can cause a serious allergic reaction (anaphylaxis).
Immediate action required: Go to A&E now or call 999 if:
- you get a skin rash that may include itchy, red, swollen, blistered or peeling skin
- you're wheezing
- you get tightness in the chest or throat
- you have trouble breathing or talking
- your mouth, face, lips, tongue or throat start swelling
These are warning signs of a serious allergic reaction. A serious allergic reaction is an emergency.
A serious allergic reaction is an emergency.
These are not all the side effects of clotrimazole. For a full list, see the leaflet inside your medicine packet.
Information:
You can report any suspected side effect to the UK safety scheme.
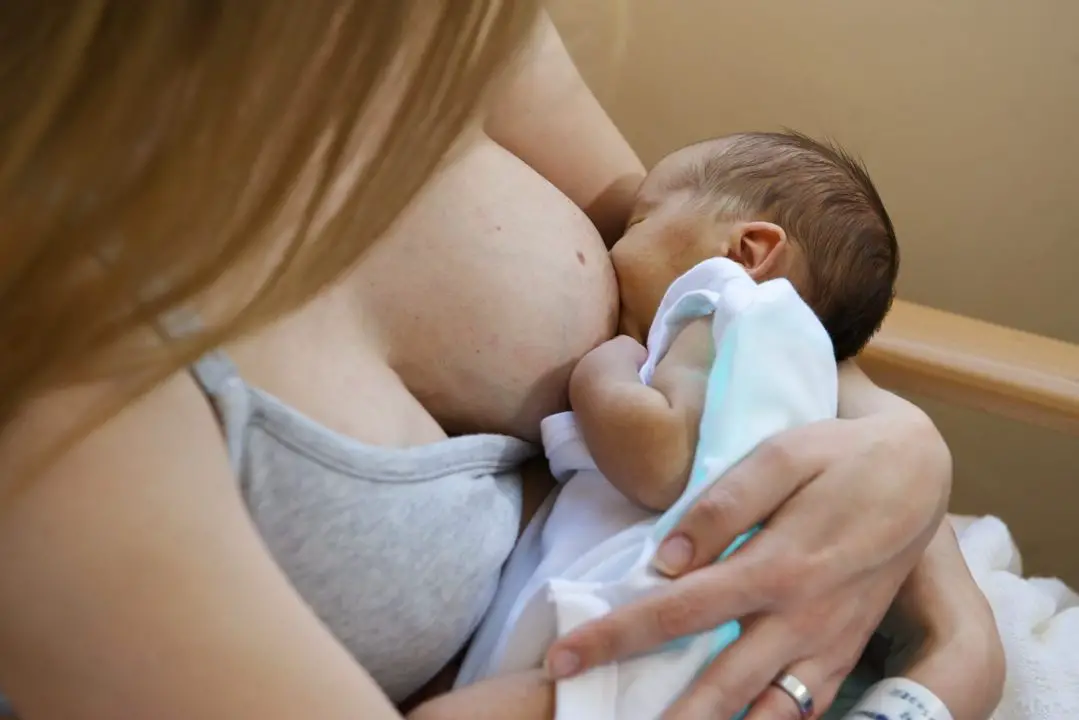
7. Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Clotrimazole pessaries and internal and external cream are generally considered safe to use during pregnancy.
Find out more about how clotrimazole can affect you and your baby during pregnancy by Best Use of Medicines in Pregnancy (BUMPS).
Clotrimazole and breastfeeding
Clotrimazole cream is generally considered safe to use while you're breastfeeding.
If you are using clotrimazole on your breasts, wash off any cream from your breasts before feeding your baby. Then wash your hands before you touch your nipple to your baby's mouth.
Then wash your hands before you touch your nipple to your baby's mouth.
If your baby is being treated for oral thrush, you can carry on breastfeeding, but you'll need to be treated at the same time. Apply clotrimazole cream on and around your nipples after each time you breastfeed.
Important: Important
Tell a pharmacist or doctor if you're trying to get pregnant, are already pregnant or if you're breastfeeding.
8. Cautions with other medicines
There are no known problems with using clotrimazole creams and taking other medicines.
However, tell a doctor before using clotrimazole pessaries if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- amphotericin, or other antifungal medicines like nystatin
- tacrolimus or sirolimus (given after transplant surgery, or to treat psoriasis or rheumatism)
Mixing clotrimazole with herbal remedies and supplements
There's very little information about taking herbal remedies and supplements while using clotrimazole.
Important: Important
For safety, tell a pharmacist or doctor if you're taking any other medicines, including herbal remedies, vitamins or supplements.
9. Common questions
How does clotrimazole work?Clotrimazole works by killing the fungus (yeast) that is causing the infection.
Clotrimazole kills fungus by causing holes to appear in its cell membrane and the contents leak out. This kills the fungus and treats the infection.
How long does it take to work?External symptoms such as itching and discharge should get better within 3 days. Talk to a doctor if your symptoms do not get better or get worse.
If internal symptoms such as pain or soreness do not go away within 7 days, talk to a doctor.
What if it does not work?Talk to a doctor if your symptoms do not get better within 7 days. You may need a longer course of treatment or a stronger medicine.
You may need a longer course of treatment or a stronger medicine.
If your vaginal thrush improves within 7 days but then comes back after 7 days, you can use another pessary or internal cream.
Is it safe to use for a long time?Do not use clotrimazole for more than 7 days, unless a doctor tells you to. The fungal infection may become resistant to clotrimazole which means it will no longer work properly.
Talk to a doctor if you have thrush more than twice in 6 months.
You may need a longer course of treatment or a stronger medicine.
Are there other similar treatments?There are other antifungal medicines available that are similar to clotrimazole, including:
- econazole
- miconazole
- ketoconazole
- fenticonazole
These are available as creams and pessaries for the treatment of thrush. You will need a prescription from a doctor for these medicines.
You will need a prescription from a doctor for these medicines.
There is an antifungal medicine called fluconazole which is available as a capsule to be taken by mouth. It can be bought from a pharmacy for treating thrush of the vagina or penis.
Will it affect my contraception?It's best to avoid sex until thrush has cleared up.
Clotrimazole cream can damage the latex used in condoms and diaphragms. This can mean your contraception will not work as well as it should.
Will it affect my fertility?There is no firm evidence that clotrimazole will affect fertility in men or women.
Can I drink alcohol?Yes, you can drink alcohol while using clotrimazole.
Is there any food or drink I need to avoid?No, you can eat and drink normally while using clotrimazole.
No, thrush is not an STI, but it can sometimes be passed on by having sex.
It's best to avoid having sex until thrush has cleared up.
Clotrimazole cream can damage the latex used in contraceptives such as condoms and diaphragms.
Can lifestyle changes help thrush?These steps can help stop thrush from coming back after you've treated it:
- wash daily and dry the affected area properly after washing
- avoid using perfumed soaps or deodorants
- avoid hot baths and perfumed bath oils
- wear cotton underwear
- avoid wearing tights or tight underwear
- avoid sex until thrush has cleared up
Clotrimazole 500mg Vaginal Tablet - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)
This information is intended for use by health professionals
Clotrimazole 500mg Vaginal Tablet
Each tablet contains clotrimazole 500mg.
Excipient with known effect: Each tablet contains 657mg of lactose.
For the full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Vaginal tablet
White, oblong, uncoated tablets with “500” debossed on one side & plain on the other.
Clotrimazole vaginal tablets are indicated for the treatment of candidal vaginitis.
Posology
The treatment consists of one vaginal tablet to be inserted in the evening.
Method of administration
The tablet is placed into the holder of the applicator provided. The applicator is inserted into the vagina as deeply as is comfortable. This is best achieved when lying on the back with the legs slightly bent. The plunger is slowly pushed in as far as it will go depositing the tablet in the vagina. The applicator should then be removed from the vagina and disposed of carefully, out of the reach of children.
As a matter of practicality the treatment should not be undertaken during menstruation.
If the external symptoms of the disease (e.g. discharge, itching) have not subsided completely within three days after termination of therapy, treatment should be continued only after consulting the attending doctor.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1
Medical advice should be sought if this is the first time the patient has experienced symptoms of candidal vaginitis.
Before using Clotrimazole vaginal tablet, medical advice must be sought if any of the following are applicable:
- more than two infections of candidal vaginitis in the last 6 months.
- previous history of sexually transmitted disease or exposure to partner with sexually transmitted disease.
- pregnancy or suspected pregnancy.
- aged under 16 or over 60 years.
- known hypersensitivity to imidazoles or other vaginal antifungal products.
Clotrimazole vaginal tablet should not be used if the patient has any of the following symptoms where upon medical advice should be sought:
- irregular vaginal bleeding.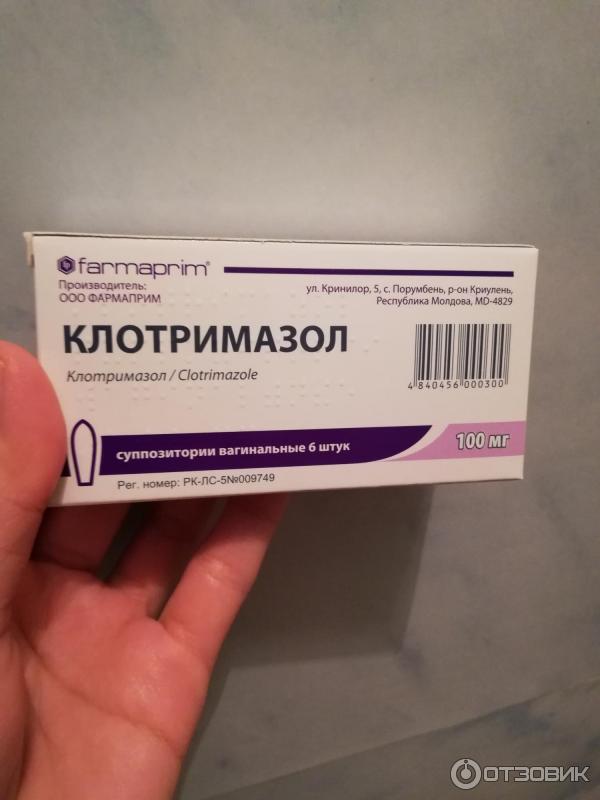
- abnormal vaginal bleeding or a blood-stained discharge.
- vulval or vaginal ulcers, blisters or sores.
- lower abdominal pain or dysuria.
- any adverse events such as redness, irritation or swelling associated with the treatment.
- fever or chills.
- nausea or vomiting.
- diarrhoea.
- foul smelling vaginal discharge.
Patients should be advised to consult their physician if the symptoms have not been relieved within one week of using Clotrimazole vaginal tablet. Clotrimazole vaginal tablet can be used again if the candidal infection returns after 7 days. However, if the candidal infection recurs more than twice within six months, patients should be advised to consult their physician.
Clotrimazole reduces the efficacy of other drugs which are used for the treatment of fungal diseases (amphotericin and other polyene antibiotics, e.g. nystatin).
Laboratory tests have suggested that, when used together, this product may cause damage to latex contraceptives. Consequently the effectiveness of such contraceptives may be reduced. Patients should be advised to use alternative precautions for at least five days after using this product.
Consequently the effectiveness of such contraceptives may be reduced. Patients should be advised to use alternative precautions for at least five days after using this product.
Concomitant medication with Clotrimazole vaginal tablet and oral tacrolimus (FK-506; immunosuppressant) might lead to increased tacrolimus plasma levels. Patients should thus be closely monitored for signs and symptoms of tacrolimus or sirolimus overdosage, if necessary by determination of the respective plasma levels.
Fertility:
No human studies of the effects of clotrimazole on fertility have been performed; however, animal studies have not demonstrated any effects of the drug on fertility.
Pregnancy:
In animal studies, clotrimazole have shown reproductive toxicity at high oral doses (see section 5.3). At the low systemic exposures of clotrimazole following vaginal treatment, harmful effects with respect to reproductive toxicity are not predicted.
There are limited amount of data from the use of clotrimazole in pregnant women.
Clotrimazole can be used during pregnancy, but only under the supervision of a physician or midwife.
During pregnancy, the vaginal tablet can be inserted without using an applicator.
Breast-feeding:
Available pharmacodynamic/toxicological data in animals have shown excretion of clotrimazole/metabolites in milk after intravenous administration (see section 5.3). A risk to the suckling child cannot be excluded. A decision must be made whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue/abstain from clotrimazole therapy taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of therapy for the woman.
This medication has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive or use machinery.
As the listed undesirable effects are based on spontaneous reports, assigning accurate frequency of occurrence for each is not possible.
Immune system disorders:
allergic reaction (syncope, hypotension, dyspnea, urticaria, pruritus)
Rarely patients may experience local mild burning or irritation immediately after applying the vaginal tablet. Very rarely, the patient may find this irritation intolerable and stop treatment. Hypersensitivity reactions may occur.
Very rarely, the patient may find this irritation intolerable and stop treatment. Hypersensitivity reactions may occur.
Reproductive system and breast disorders:
genital peeling, pruritus, rash, oedema, erythema, discomfort, burning, irritation, pelvic pain, vaginal haemorrhage.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
abdominal pain
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via the Yellow Card Scheme at www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard
No risk of acute intoxication is seen as it is unlikely to occur following a single vaginal or dermal application of an overdose (application over a large area under conditions favourable to absorption) or inadvertent oral ingestion. There is no specific antidote.
There is no specific antidote.
In the event of accidental oral ingestion, routine measures such as gastric lavage should be performed only if clinical symptoms of overdose become apparent (e.g. dizziness, nausea or vomiting). It should be carried out only if the airway can be protected adequately.
ATC Code: G01A F02
Clotrimazole is an imidazole derivative with a broad spectrum of antimycotic activity.
The antimycotic effect of clotrimazole is primarily fungistatic, and at high concentrations also fungicidal. Clotrimazole is only effective against proliferating fungi; fungal spores are only slightly sensitive, in-vitro.Current knowledge indicates that the antimycotic effect of clotrimazole is due to inhibition of ergosterol synthesis. Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis leads to structural and functional impairment of the cytoplasmic membrane.
Clotrimazole has a broad antimycotic spectrum of action in vitro and in vivo, which includes dermatophytes, yeasts, moulds, etc.
Primarily resistant variants of sensitive fungal species are very rare; the development of secondary resistance by sensitive fungi has so far only been observed in very isolated cases under therapeutic conditions.
Absorption of Clotrimazole from the vagina following administration as a vaginal tablet is 3-10%. Fungicidal concentrations of clotrimazole are found in the vaginal fluid up to 3 days after the application of one 500 mg vaginal tablet. In contrast plasma levels of clotrimazole up to 72 hours after application are lower than 0.01 μg/ml, demonstrating that clotrimazole is rapidly metabolised and does not lead to measurable systemic effects or side effects..
Binding of clotrimazole to blood serum proteins is about 98% in the undiluted serum, due to its highly hydrophobic properties.
Clotrimazole is metabolised in the liver via oxidation and degradation of the imidazole cycle (desamination, O-desalkylation). Thus inactive hydroxy derivatives occur. These agents are mainly excreted via the gallbladder with the faeces.
The elimination half-life of clotrimazole is 3.5-5 hours.
Toxicity studies in rats, dogs and monkeys showed changes in the liver and adrenal glands after long term administration. However, these changes were reversible after administration ended.
There is no evidence of mutagenicity or teratogenicity in animals, and experience of topical application in pregnant women gives no evidence of embryotoxic or foetotoxic effects.
Adipic acid
Microcrystalline cellulose
Pregelatinised maize starch
Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Stearic acid
Lactose
Polysorbate
Magnesium stearate
Maize starch
Colloidal silicon dioxide
None known.
5 years.
Store at room temperature below 25°C. Store in the original package.in order to protect from moisture.
Original packages with 1 vaginal tablet including an applicator. Each vaginal tablet is packed in an aluminium foil blister.
The vaginal tablet is to be taken out of the aluminium package and inserted into the form of the disposable applicator.
The disposable applicator is to be inserted into the vagina as deep as possible. By carefully pushing the inner plunger as far as it will go, the vaginal tablet is placed in the vagina.
After usage the disposable applicator is to be removed from the vagina and safely disposed of out of the reach of children.
The vaginal tablet is to be taken out of the aluminium package and inserted into the form of the disposable applicator.
The disposable applicator is to be inserted into the vagina as deep as possible.
By carefully pushing the inner plunger as far as it will go, the vaginal tablet is placed in the vagina.
After usage the disposable applicator is to be removed from the vagina and safely disposed of out of the reach of children.
Use of the vaginal tablet in combination with the disposable applicator.
Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Tillomed Laboratories Ltd
220 Butterfield
Great Marlings
Luton
LU2 8DL
United Kingdom
PL 11311/0042
Date of first authorisation: 29/10/1997
Date of latest renewal: 28/02/2009
06/01/2021
| 📜 Instructions for use Clotrimazole 💊 Composition of the drug Clotrimazole ✅ Use of the drug Clotrimazole 📅 Storage conditions Clotrimazole ⏳ Expiration date Clotrimazole Keep Search for analogues Description of the medicinal product clotrimazole (Clotrimazole) Based on the official instructions for use of the drug, approved by the manufacturer and prepared for the electronic edition of the Vidal Handbook 2014 year, update date: 2018.12.24 Marketing authorization holder:GlaxoSmithKline Trading JSC (Russia)
Manufactured:GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals, S.  A. (Poland) A. (Poland)
Contacts for inquiries:GlaxoSmithKline Trading JSC (Russia) ATX code: G01AF02 (Clotrimazole) Active substance: clotrimazole (clotrimazole) Rec.INN WHO registered Dosage form
Release form, packaging and composition drug ClotrimazoleVaginal tablets white, oblong, biconvex, smooth surface, rounded at one end and flat at the other.
Excipients : Monohydride lactose - 1122.2 mg, Potato starch - 180 mg, adipic acid - 140 mg, sodium hydrocernature - 110 mg, magnesium of stearate - 31.3 mg, Kremlin colloidal dioxide - 12.3 mg, sodium lauryl sulfate - 4.2 mg. 6 pcs. - blisters (1) - packs of cardboard. Clinical and pharmacological group: Drug with antifungal action for local use in gynecology Pharmacotherapeutic group: Antifungal agent Pharmacological action Clotrimazole inhibits the growth and division of microorganisms and, depending on the concentration, may have a fungistatic or fungicidal effect. Clotrimazole has a broad spectrum of antifungal and antibacterial activity . It is active against: dermatophytes (Epidermophyton floccosum, Microsporum canis, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton rubrum), yeasts (Candida spp. Clotrimazole is also active against some Gram-positive bacteria. In vitro, clotrimazole has a broad spectrum of fungistatic and fungicidal activity. It affects the mycelium of dermatophytes (Trichophyton, Microsporum, Epidermophyton) similarly to griseofulvin, its effect on budding yeast-like fungi (Candida) is similar to that of polyenes (amphotericin B and nystatin). At concentrations less than 1 μg / ml, clotrimazole inhibits the development of most strains of pathogenic fungi related to Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton floccosum, Microsporum canis. At a concentration of 3 μg / ml, clotrimazole inhibits the development of most other bacteria: Pityrosporum orbiculare, Aspergillus fumigatus, Candida genus, incl. Candida albicans, some strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and some strains of Proteus vulgaris and Salmonella. At concentrations greater than 100 µg/ml it is effective against Trichomonas vaginalis. Clotrimazole-resistant fungi are extremely rare; there are data only for individual strains of Candida guilliermondii. No development of resistance has been reported in clotrimazole-sensitive fungi after passage of Candida albicans and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. No cases of development of resistance to clotrimazole in strains of Candida albicans resistant to polyene antibiotics due to a chemical mutation have been described. PharmacokineticsAbsorption and distribution Pharmacokinetic studies of clotrimazole with intravaginal use have shown that absorption is 3-10% of the administered dose. In the liver, clotrimazole is metabolized to pharmacologically inactive metabolites; therefore, its plasma concentration when intravaginally administered at a dosage of 500 mg is less than 10 ng / ml, confirming the fact that clotrimazole when administered intravaginally does not lead to significant systemic effects or side effects. Metabolism Clotrimazole is primarily metabolized in the liver to metabolites excreted via the kidneys and intestines. Indications of the drug clotrimazole
Open list of ICD-10 codes
Dosing regimen For intravaginal use. If there is no effect within 3 days, confirm the diagnosis. If symptoms persist for more than 7 days, follow up with a physician. Treatment may be repeated if necessary, but recurrent infections may be indicative of an underlying pathology, including diabetes mellitus or HIV infection. If symptoms recur within 2 months, the patient should consult a physician. In case of simultaneous infection of the vulva and adjacent areas, external treatment with a cream is necessary. For complete dissolution of vaginal tablets, normal moisture of the vaginal mucosa is required. In women with dryness of the vaginal mucosa, undissolved parts of the tablet may be excreted. To prevent this, it is necessary to inject the tablet as deep as possible into the vagina before going to bed. Treatment during menstruation is not recommended due to the risk of pill washout and must be completed before menstruation. For sanitation of the birth canal once 1 tablet immediately before childbirth. For children over 12 years of age the same way as for adults. Clotrimazole vaginal tablets are not recommended for use in children under 12 years of age . Repeat therapy is possible according to medical indications. Side effectsThe adverse events listed below are listed according to the damage to organs and organ systems and the frequency of occurrence. The frequency of occurrence is defined as follows: very often (≥1/10), often (≥1/100 and <1/10), infrequently (≥1/1000 and <1/100), rare (≥1/10,000 and < 1/1000), very rare (<1/10000, including isolated cases), not known (frequency cannot be estimated from currently available data). Frequency categories were formed on the basis of post-registration observation. From the immune system: unknown - allergic reactions (urticaria, fainting, arterial hypotension, shortness of breath). From the gastrointestinal tract: unknown - abdominal pain. From the genital organs and breast: unknown - discomfort in the vulva and vagina, hyperemia and swelling of the vaginal mucosa, vaginal discharge, burning, peeling, irritation, itching, pain in the pelvic area, burning sensation in the genitals member of a sexual partner, pain during intercourse, rash. If these symptoms appear, clotrimazole therapy should be discontinued. From the side of the nervous system: unknown - headache. From the side of the kidneys and urinary tract: unknown - frequent urination, intercurrent cystitis. Contraindications for use
Caution For the first case of candidal vaginitis, a doctor should be consulted. If any of the following are identified, a doctor should be consulted before prescribing Clotrimazole vaginal tablets:
Use in pregnancy and lactationUse of clotrimazole during pregnancy is allowed only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. In the conducted epidemiological studies, including a retrospective analysis, the use of clotrimazole during pregnancy (even in the first trimester) did not reveal any undesirable effects on the body of the pregnant woman, as well as congenital defects and undesirable effects in the fetus. The use of clotrimazole in women during breastfeeding is allowed only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the child. Fertility No data available. Special instructionsAvoid contact with eyes and ingestion. It is recommended that all affected areas of the body be treated simultaneously. Clotrimazole vaginal tablets should not be used if any of the following symptoms are present, unless otherwise directed by a physician:
Simultaneous treatment of sexual partners is necessary to prevent reinfection. Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and mechanisms Not studied. OverdoseSymptoms: dizziness, nausea, vomiting. Treatment: in case of accidental ingestion, symptomatic treatment should be carried out. Drug interactionsLaboratory data suggest that the use of contraceptives containing latex may cause damage when used together with Clotrimazole. Therefore, the effectiveness of such contraceptives may decrease. Patients should be advised to use alternative methods of contraception for at least five days after using Clotrimazole. Concomitant use of vaginal clotrimazole and oral tacrolimus (FK-506; immunosuppressant) may result in increased plasma concentrations of tacrolimus. Patients should be closely monitored for symptoms of tacrolimus overdose, with drug levels measured if necessary. Amphotericin B, nystatin, natamycin reduce the effectiveness of clotrimazole when used simultaneously. Storage conditions of the drug ClotrimazoleThe drug should be kept out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Shelf life of ClotrimazoleShelf life - 3 years. Terms of saleThe drug is approved for use as an over-the-counter drug.
Contacts for inquiries
Keep |
Clotrimazole - description of the substance, pharmacology, use, contraindications, formula
Contents
- Russian name
- English name
- Latin name of the substance Clotrimazole
- Chemical name
- Gross formula
- Pharmacological group of the substance Clotrimazole
- Nosological classification
- CAS Code
- Pharmacological action
- Feature
- Pharmacology
- Use of the substance Clotrimazole
- Contraindications
- Use in pregnancy and lactation
- Side effects of the substance Clotrimazole
- Interaction
- Overdose
- Dosage and Administration
- Precautions
- Trade names with the active substance Clotrimazole
Structural formula
Russian name
Clotrimazole
English name
Clotrimazole
Latin name of the substance Clotrimazole
Clotrimazolum ( born Clotrimazoli)
Chemical name
1-[(2-chlorfenil) diphenylmetazol
Brutto formula
8 22 h 1728 17 Pharmacological group of the substance Clotrimazole Antifungals Other synthetic antibacterial agents ICD-10 code list 23593-75-1 Pharmacological action - antibacterial , broad spectrum antifungal , antiprotozoal , trichomonacid . Antifungal agent for local use from the group of imidazole derivatives. Odorless white crystalline substance. Practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in ether, very soluble in polyethylene glycol 400, ethanol and chloroform. Molecular weight 344.84. It disrupts the synthesis of ergosterol (the main structural component of the cell membrane of fungi), changes the permeability of the fungal membrane, promotes the release of potassium, intracellular phosphorus compounds from the cell and the breakdown of cellular nucleic acids. Inhibits the synthesis of triglycerides and phospholipids. It reduces the activity of oxidative and peroxidase enzymes, as a result of which the intracellular concentration of hydrogen peroxide rises to a toxic level, which contributes to the destruction of cell organelles and leads to cell necrosis. Clotrimazole acts mainly on growing and dividing microorganisms. In vitro exhibits fungicidal and fungistatic activity against dermatomycetes (Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton floccosum, Microsporum canis), yeast-like fungi Candida spp. (including Candida albicans ). Active against the causative agent of multi-colored lichen - Pityrosporum orbiculare (Malassezia furfur). Fungal strains naturally resistant to clotrimazole are rare. Primary resistance to clotrimazole has only been described for Candida guillermondii. Effective against gram-positive bacteria - the causative agent of erythrasma Corynebacterium minutissimum, and Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., gram-negative bacteria - Bacteroides, Gardnerella vaginalis. Poorly absorbed through the skin and mucous membranes. Accumulates in the stratum corneum of the epidermis, the concentration in the deep layers of the epidermis is higher than the MIC for dermatomycetes. When applied to the nails, it is found in keratin. When administered intravaginally, 3-10% of the dose is absorbed. Rapidly biotransformed in the liver to inactive metabolites and excreted in faeces. Absorbed clotrimazole induces the activity of microsomal liver enzymes, which leads to an acceleration of its catabolism. High concentrations in vaginal secretion and low concentrations in the blood persist for 48-72 hours Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, effects on fertility . Long-term studies in animals to evaluate the potential carcinogenicity of clotrimazole when administered intravaginally have not been conducted. A mutagenicity study in Chinese hamsters that received orally 5 doses of clotrimazole 100 mg/kg did not reveal a mutagenic effect - structural changes during metaphase in spermatophore chromosomes. Pregnancy. In studies in pregnant rats, intravaginal doses of clotrimazole up to 100 mg/kg showed no adverse effect on the fetus. However, daily oral doses of clotrimazole at doses of 50 to 120 mg/kg resulted in embryotoxicity in rats and mice (possibly secondary to maternal toxicity). So, in mice, when taking clotrimazole in doses 120 times higher than the usual dose in humans, in the period from 9 weeks to mating and until the end of feeding, mating disorders, a decrease in the number of viable cubs, and a decrease in the survival rate of offspring from birth to the end of feeding were recorded. At doses up to 60 times the usual human dose, no adverse effects were observed. In rats at doses 50 times the usual dose in humans, clotrimazole, with a similar observation period, caused a slight decrease in the number of pups in the offspring and a decrease in their survival. There was no teratogenic effect in mice, rabbits and rats when taking clotrimazole orally at doses up to 200, 180 and 100 mg/kg, respectively. Fungal infections of the skin and mucous membranes: ringworm, dermatophytosis, trichophytosis, epidermophytosis, microsporia, candidiasis, interdigital fungal erosion, fungal paronychia; mycoses complicated by secondary pyoderma; versicolor versicolor, erythrasma; candidiasis stomatitis; candidal vulvitis, vulvovaginitis, balanitis, trichomoniasis; for sanitation of the birth canal before childbirth. Hypersensitivity. Should not be used in the first trimester of pregnancy (no adequate and well-controlled studies have been conducted). With intravaginal use in women in the II and III trimesters of pregnancy, no adverse effects on the fetus have been identified, however, the use of a vaginal applicator is undesirable. With caution - during breastfeeding (it is not known whether clotrimazole passes into breast milk). Allergic reactions (itching, urticaria). When applied topically to the skin: erythema, blistering, swelling, burning and stinging, skin irritation and flaking. When applied topically for the treatment of urogenital infections: itching, burning, redness and swelling of the mucous membrane, vaginal discharge, frequent urination, intercurrent cystitis, burning sensation in the partner's penis, pain during intercourse. Topically applied in the mouth: redness of the oral mucosa, burning and tingling sensation at the site of application, irritation. Reduces the activity (mutually) of polyene antibiotics (amphotericin B, nystatin, natamycin). In case of accidental ingestion of drugs, the following symptoms are possible: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, gastralgia, impaired liver function; rarely - drowsiness, hallucinations, pollakiuria, allergic skin reactions. Treatment: activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy. Topically, is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin and mucous membranes 2-4 times a day. The course of treatment is selected individually, usually at least 4 weeks; upon its completion (disappearance of clinical manifestations), it is advisable to continue using the drug for another 14 days. The duration of therapy for erythrasma is 2-4 weeks, for lichen multi-colored - 1-3 weeks. Before greasing, wash the feet with warm water and soap, dry thoroughly, especially between the toes. In fungal diseases of the skin of the legs, it is recommended to continue treatment after achieving a therapeutic effect for 2-3 weeks. Topical in the oral cavity: 10-20 drops (0.5-1 ml) of topical solution are applied to the affected areas of the oral mucosa with a cotton swab/stick 3-4 times a day. Improvement usually occurs on the 3rd-5th day of treatment; treatment should be continued until the complete elimination of the clinical manifestations of the disease. Locally for urogenital infections. For candidal vulvitis or balanitis, use 2-3 times a day for 1-2 weeks. For the treatment of trichomoniasis, vaginitis in adults and adolescents: vaginal tablets (500 mg once or 200 mg for 3 days or 100 mg for 6-7 days, once a day, in the evening), or cream (full applicator) is administered as soon as possible deeper into the vagina 1 time per day (before going to bed). For sanitation of the birth canal, a single administration of the tablet is recommended. For urethritis, instillation of 1% clotrimazole solution into the urethra is also carried out for 6 days. Avoid contact with the mucous membrane of the eyes. Avoid application on areas with violation of the integrity of the skin. Do not use airtight dressings after applying the cream. Simultaneous treatment of the sexual partner is recommended to prevent reinfection. Do not prescribe intravaginally during menstruation. With trichomoniasis, a combined intake with systemic chemotherapeutic agents (metronidazole orally) is recommended. In patients with impaired liver function, its functional state should be monitored periodically. The appearance of irritation or signs of hypersensitivity requires discontinuation of treatment. If there is no clinical improvement within 4 weeks, a microbiological study should be performed to confirm the diagnosis and exclude another cause of the disease. Reset filters Lek. the form All lek. gel vaginal gel for external use cream cream vaginal cream for external use ointment for external use powder for external use topical solution solution for external use topical spray substance-powder suppositories vaginal tablets vaginal Dosage All dosages 0.1 g 1% 10 mg/g 10 mg/ml 100 mg 2% 200 mg 500 mg No dosage Manufacturer All manufacturers AKRIKHIN AO Agio Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Nosological classification
 4 Candidiasis of other urogenital sites
4 Candidiasis of other urogenital sites  1 Erythrasma
1 Erythrasma CAS code
Pharmacological action
Characteristics
Pharmacology
 Depending on the concentration, it exhibits a fungicidal or fungistatic effect. Inhibits blastospore transformation Candida albicans into an invasive mycelial form.
Depending on the concentration, it exhibits a fungicidal or fungistatic effect. Inhibits blastospore transformation Candida albicans into an invasive mycelial form. 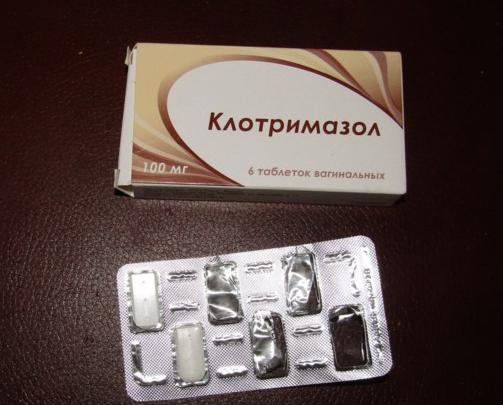 In high concentrations, it is active against Trichomonas vaginalis.
In high concentrations, it is active against Trichomonas vaginalis. 
Application of the substance Clotrimazole
Contraindications
Use in pregnancy and lactation
Side effects of the substance Clotrimazole

Interaction
Overdose
Method of administration and doses

Precautions

Trade names with active substance Clotrimazole
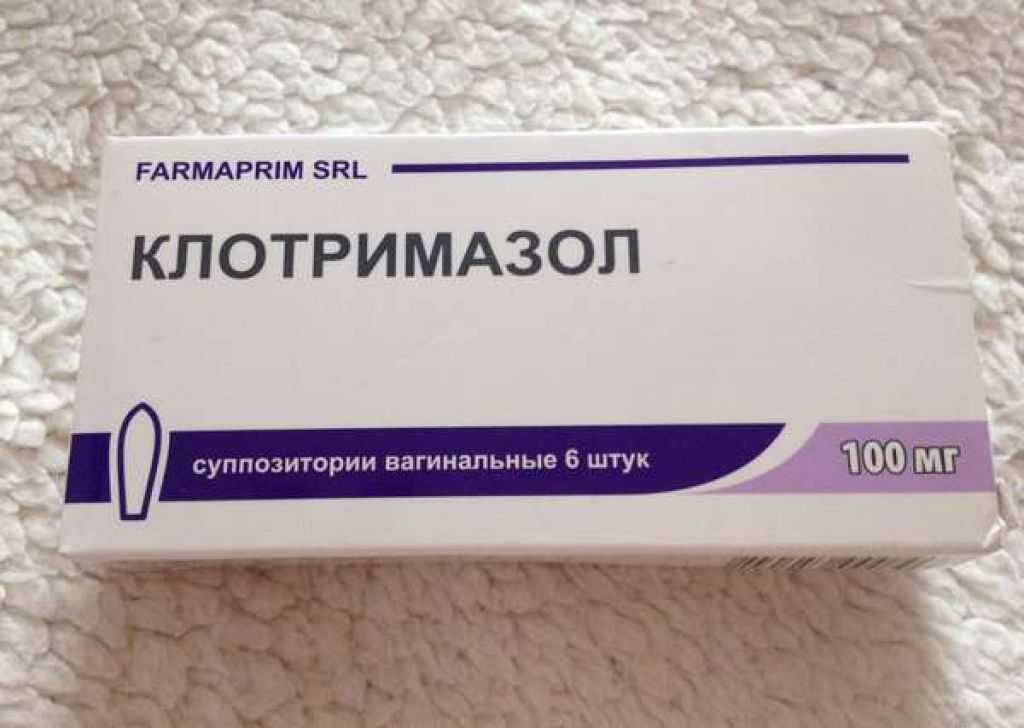
 vaginal 100 mg: 6 pcs. (7003)
vaginal 100 mg: 6 pcs. (7003)  02.17
02.17  The mechanism of action of clotrimazole is associated with a change in the permeability of cell membranes due to the effect on the synthesis of ergosterol and binding to fungal cell wall phospholipids. Clotrimazole inhibits the synthesis of proteins, fats, DNA, polysaccharides, damages nucleic acids in fungal cells and accelerates the excretion of potassium. It can also inhibit the activity of oxidant and peroxidant enzymes and the biosynthesis of triglycerides and phospholipids in fungal cells. At higher concentrations, clotrimazole causes damage to cell membranes by mechanisms independent of sterol synthesis. Clotrimazole prevents the transformation of Candida albicans blastospores into invasive forms of mycelium. A change in the activity of the cell membrane leads to cell death, and this process depends on the contact of the drug with microbes.
The mechanism of action of clotrimazole is associated with a change in the permeability of cell membranes due to the effect on the synthesis of ergosterol and binding to fungal cell wall phospholipids. Clotrimazole inhibits the synthesis of proteins, fats, DNA, polysaccharides, damages nucleic acids in fungal cells and accelerates the excretion of potassium. It can also inhibit the activity of oxidant and peroxidant enzymes and the biosynthesis of triglycerides and phospholipids in fungal cells. At higher concentrations, clotrimazole causes damage to cell membranes by mechanisms independent of sterol synthesis. Clotrimazole prevents the transformation of Candida albicans blastospores into invasive forms of mycelium. A change in the activity of the cell membrane leads to cell death, and this process depends on the contact of the drug with microbes.  , Cryptococcus neoformans), dimorphic fungi (Coccidioides immitis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Paracoccidioides brasiliensis), protozoa (Trichomonas vaginalis).
, Cryptococcus neoformans), dimorphic fungi (Coccidioides immitis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Paracoccidioides brasiliensis), protozoa (Trichomonas vaginalis).  Clotrimazole is active against Sporothrix, Cryptococcus, Cephalosporium, Fusarium.
Clotrimazole is active against Sporothrix, Cryptococcus, Cephalosporium, Fusarium.  .
.  Assign 1 tab. 2 times / day for 3 days or 1 tab. 1 time / day for 6-7 days, preferably at bedtime.
Assign 1 tab. 2 times / day for 3 days or 1 tab. 1 time / day for 6-7 days, preferably at bedtime.