How to know breast is full of milk
Signs your breast milk is flowing
Signs your breast milk is flowing
- A change in your baby’s sucking rate from rapid sucks to suckling and swallowing rhythmically, at about one suckle per second.
- Some mothers feel a tingling or pins and needles sensation in the breast.
- Sometimes there is a sudden feeling of fullness in the breast.
- While feeding on one side your other breast may start to leak milk.
- You may become thirsty.
Your milk flow can be affected by emotions like anxiety, embarrassment, tension or extreme tiredness. Being relaxed when breastfeeding helps your milk flow.
Breast compression
Breast compressions can help you to feed effectively if your baby is:
- falling asleep whilst feeding
- slow to gain weight
- feeding frequently
- taking a long time to feed.
By compressing your breast you will encourage your milk to flow which will provide your baby with more milk.
Place your hand around the breast close to your chest wall and compress your breast without causing pain. When your baby is no longer drinking release the pressure.
When your baby starts to suckle again he or she may be drinking but if your baby doesn’t resume suckling well, compress your breast again. Keep doing this until your breast feels soft and drained and baby is no longer drinking whilst compressing. Then offer your baby the other breast and if he or she becomes tired start your compressions again.
How your milk supply increases
As your baby grows their appetite increases and he or she will demand more feeds. Your breast milk will increase to match your baby’s needs if you breastfeed more frequently. Growth spurts occur at anytime but are often around 6 weeks, 3 months and 6 months.
Remember your breasts are never empty. As your baby feeds, your body makes more breast milk.
As your baby feeds, your body makes more breast milk.
You can build up your milk supply by:
- feeding more often
- offering both breasts twice
- putting baby back to the breast 20 to 30 minutes after a feed
- expressing breast milk after feeds
- avoiding giving formula feeds, water or juice
- resting as much as possible – a few quiet days at home are helpful
- eating well and drinking when thirsty
- gently stroking or compressing your breasts during feeds.
Where to get help
Breastfeeding Centre of WA
- Counselling and appointments 8.00am to 4.00pm Monday to Friday
- Phone: (08) 6458 1844
- More information about Breastfeeding Centre of WA
Australian Breastfeeding Association (ABA)
- National Breastfeeding Helpline available 24 hours, 7 days a week
- Phone: 1800 mum 2 mum (1800 686 268)
- Visit the ABA website (external site)
Ngala Parenting Line
- Phone: (08) 9368 9368 – 8.
 00am to 8.00pm 7 days a week
00am to 8.00pm 7 days a week - Outside metro area – Free call 1800 111 546 (free from land line only)
- Visit the Ngala website (external site)
You can also:
- See your doctor
- Visit healthdirect (external site) or call 1800 022 222
Acknowledgements
Breastfeeding Centre of WA
This publication is provided for education and information purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical care. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not imply endorsement and is not intended to replace advice from your healthcare professional. Readers should note that over time currency and completeness of the information may change. All users should seek advice from a qualified healthcare professional for a diagnosis and answers to their medical questions.
See also
- Using expressed breast milk for extra feeds
- Caring for your nipples when breastfeeding
- Common breastfeeding issues
What are Breast Fullness and Breast Engorgement
Learn the difference between normal breast fullness and breast engorgement, so you always know when it's time to empty your breasts to keep your milk supply strong!
Share this content
Difference Between Breast Fullness and Engorgement
Video Transcript
It’s normal for your breasts to feel full on average around the 2nd to 3rd days after birth. When we describe the milk as “coming in”, what is actually meant is that the volume of milk increases. Once your milk comes in, you will definitely know it! For most moms, there is no missing the increase in size of their breasts!
When we describe the milk as “coming in”, what is actually meant is that the volume of milk increases. Once your milk comes in, you will definitely know it! For most moms, there is no missing the increase in size of their breasts!
As your milk comes in, obviously there is a lot of activity happening so you may feel a little warmer around the breast area, and this can even feel uncomfortable for 24 hours or so. As your baby starts to drink more, your breasts will regulate themselves and the sense of over-fullness will settle.
With normal fullness, the breast and areola (which is the darker skin around your nipple) remain soft, your milk flow is normal, and your baby can still latch on easily.
Engorgement is slightly different:
- Engorgement typically begins on the 3rd to 5th day after birth, and subsides within about 12 - 48 hours, if properly treated.
- It might occur in one or both breasts.
- Your breast and areola will likely feel hard, with tightly stretched skin that may appear shiny, and you may experience warmth and tenderness.
 Engorgement may extend up into your armpit as well, as the breast tissue inside is shaped like a teardrop.
Engorgement may extend up into your armpit as well, as the breast tissue inside is shaped like a teardrop. - Your nipple may also increase in size and become flatter or pulled in towards your breast slightly, making latching on more challenging for your baby.
- You may also have a low-grade fever.
So, What are the Best Tips to Prevent Breast Engorgement?
Breastfeed early and often:
- Don’t skip or delay feeds (even at night).
- Breastfeed every time your baby cues for a feed.
- If your baby is very sleepy, then wake them every 2-3 hours and allow one longer stretch of 4-5 hours at night.
- Allow your baby to finish feeding at the first breast before offering the other side.
- Seek help to ensure you are latching your baby onto the breast correctly and comfortably.
- If your baby is not able to breastfeed well or frequently enough, you will need to pump your breasts to make up for the missing feeds. A baby should be feeding a minimum of 8 times in 24 hours (i.
 e. if your baby is sleepy and only breastfeeding 4 or 5 times a day, it is important to pump the extra 4 times to keep your milk supply flowing and to minimize the engorgement).
e. if your baby is sleepy and only breastfeeding 4 or 5 times a day, it is important to pump the extra 4 times to keep your milk supply flowing and to minimize the engorgement).
How Can I Cure Breast Engorgement?
Before breastfeeding:
- Gently massage your breast from the chest wall toward the nipple.
- You may find cool compresses are both soothing and helpful. Use these for up to 20 minutes before feeding.
- A warm, wet cloth held on your breasts or a warm shower (with shower hitting your back, rather than directly onto your breasts) for a few minutes before breastfeeding may help your milk begin to flow (but do not use this if you have any oedema/swelling in your breast as it could make it worse!)
- If your baby is having difficulty latching on to feed, try expressing some milk out first to soften the nipple and areola.
- Something called reverse pressure softening can also be a helpful tip to look up.
- Continue to gently massage your breast during breastfeeding as well, to help the milk flow.

Between feeds:
- If your breast is uncomfortably full at the end of a feed, then express your milk until your breast feels a little more comfortable. But only express to comfort!
- Some moms find that using a cold compress (over a layer of clothing) for 20 minutes can be very soothing.
- Make sure your bra is also comfortable and well-fitting. Tight or poor-fitting bras can dig in on your breast and potentially lead to blocked ducts and mastitis.
Contact your lactation specialist or healthcare provider if the engorgement is not relieved within 24 - 48 hours, or you feel that it is getting worse. And if your baby is unable to breastfeed, not waking regularly for feeds (i.e. feeding less than 8 times in 24 hours), or they’re showing signs that they are not getting enough milk, please seek further support and advice from a healthcare professional.
How do you know if you have enough breast milk?
Nowadays, almost all mothers want to breastfeed their babies. But not one mother during pregnancy does not think that there may be any problems with feeding. These problems overtake already in the hospital. It seems that all the problems, suffering, pain are behind you, your baby is next to you, but now a new stage in your life begins.
But not one mother during pregnancy does not think that there may be any problems with feeding. These problems overtake already in the hospital. It seems that all the problems, suffering, pain are behind you, your baby is next to you, but now a new stage in your life begins.
Breastfeeding. Will I succeed?
Every woman is capable of breastfeeding. The main attribute for this is your chest and a positive attitude. Every woman has colostrum, that is, the first milk appears at different periods: for someone in the middle of pregnancy, for someone on the day of birth, sometimes it comes only on the third day.
If colostrum does not come on the third day, then you should not give up. Continue to apply the baby to the breast and this will stimulate the production of milk. Find a comfortable position for you and your baby and enjoy being with each other.
Preparation for feeding during pregnancy
You don't have to worry about your breasts losing their shape.
The first thing you need to do is to buy good support underwear to lighten your breasts. Owners of large breasts should use such a bra from the middle of pregnancy. When buying this bra, keep in mind that your breasts will increase in volume when the milk arrives.
Also consider comfortable nursing clothes. It will be useful to you already in the hospital.
No need to torture your nipples during pregnancy by rubbing them with a terry towel, wearing rags in your bra and other manipulations with your breasts.
Examine the shape of your nipples: they may be flat or protruding.
A flat nipple will be more difficult for a baby to latch on to and will likely require silicone breast pads to allow the baby to draw on the milk. Don't worry that you will feed your baby all the time through these pads, after a couple of weeks the baby will pull on your nipples.
The most sensible advice for mothers when it comes to breastfeeding is to cook the head, not the chest.
Does the baby need formula?
What to do if the milk does not come? Here, rather, everything depends on the mother and the behavior of the child, if the child cries, perhaps he is hungry. The hospital staff will offer you to feed your baby. In principle, the baby has enough colostrum for the first days of life, but if it is not there, do not torment the child, feed the mixture and continue to apply.
What happens if a child loses weight?
Weight loss of 10% at the time of discharge is considered normal - the baby has edema , a lot of meconium comes out. Usually a baby gains 150-200 grams in the first week of life.
How can you tell if your baby is getting enough milk?
The main indicator that the baby is full is his good behavior. If the baby lets go of the breast after feeding, plays for a while, and then falls asleep, then he has enough milk. If the baby is capricious, sleeps poorly, you should think about the lack of milk.
The first and surest way to check is baby weights. The disadvantage of this method is the purchase of such scales, which are not cheap. You can ask your hospital if they rent weights or look in ads.
So, we weigh the baby before feeding and after, and by the difference we look at how much the baby ate. The norm for children under 4 months is 1/5 of their weight. For example, with a child weighing 3500 grams, his norm will be 700 grams of milk per day. With 7 feedings a day, the baby should gain about 100 grams after feeding.
The second method is the old method called “wet diapers”. There are two ways to carry out this method. The first involves the rejection of modern diapers for a day. You can buy a piece of gauze and make diapers, you can just put the child in sliders, by the way, in the sliders it will be clearly visible when the child has urinated. For example, we start the experiment at 7 am today and end at 7 am tomorrow. These days you need to feed the baby only breast milk and not give any more liquid.
These days you need to feed the baby only breast milk and not give any more liquid.
Record the number of times the child has urinated on the tablet, so it is more convenient to count.
Do not worry that you will not succeed, be patient and dry things.
During the day you can do this:
- normal or disposable absorbent diapers can be used;
- the child may be dressed in a romper suit or gauze diaper;
It is better to cancel a walk in the cold season. In the summer, we cover the stroller with a diaper and take clean clothes with us.
At night it is more difficult, but it can be done really well. We act in the same way as with the stroller - we cover the bed with a diaper. It is better to prepare a supply of diapers for the night. You may have noticed that the child pees, when he comes out of deep sleep, he begins to move.
So the day has passed. Wet diapers will tell us if your baby is getting enough milk and if the kidneys are working well. Urine during the day can be transparent, and in the morning it can be more concentrated, that is, it can be yellow.
Wet diapers will tell us if your baby is getting enough milk and if the kidneys are working well. Urine during the day can be transparent, and in the morning it can be more concentrated, that is, it can be yellow.
The number of urinations depends on the age of the child:
- 1-3 days a day 2-5 urinations;
- 3-6 days a day 4-8 urinations;
- 6-14 days a day approximately 12 urinations;
- after 14 days a day 12 or more urination .
Test result (after 14 days):
- 12 or more diapers - your lactation is normal;
- 8-10 diapers per day - lactation is reduced;
- less than 8 diapers - the baby does not have enough of your milk. Discuss supplementary feeding with your pediatrician.
The second method of counting urination baby is the weighing of wet diapers . Day collect use diapers , each of them is tightly tied in a bag to avoid evaporation of urine, feces are cleaned from diapers . In a day, we weigh the use of diapers and the same number of clean diapers . The difference between used and clean diapers is the amount of urine per day. Next, divide this number by 30 (the approximate weight of one urination) and get the number urination .
Day collect use diapers , each of them is tightly tied in a bag to avoid evaporation of urine, feces are cleaned from diapers . In a day, we weigh the use of diapers and the same number of clean diapers . The difference between used and clean diapers is the amount of urine per day. Next, divide this number by 30 (the approximate weight of one urination) and get the number urination .
Such weighings are carried out either once to compile a general picture, or over a couple of days to dispel doubts that there is not enough milk. Weigh your child once a week.
What if the baby does not get enough breast milk?
First of all, calm down and don't panic. Next, if possible, find a lactation consultant. Perhaps you have the wrong feeding process. Perhaps the baby is not grasping the breast correctly, is the baby tightly pressed against your body with the tummy. It would seem nonsense, but perhaps the whole problem is precisely in this. Also, the consultant should examine your child, he may have a short bridle, the anatomy of the jaw, you may need to try other positions for comfort and proper grip. Also pay attention to how often you change breasts, perhaps the baby is sucking out your foremilk, which is less fat.
It would seem nonsense, but perhaps the whole problem is precisely in this. Also, the consultant should examine your child, he may have a short bridle, the anatomy of the jaw, you may need to try other positions for comfort and proper grip. Also pay attention to how often you change breasts, perhaps the baby is sucking out your foremilk, which is less fat.
Increased lactation
In order to increase lactation, two breasts can be given in one feeding. In order to prevent the baby from sucking only the foremilk, it is necessary to monitor when the baby stops swallowing milk, but simply sucks at the breast
An equally important aspect is the calmness of the mother. Households should take care during these periods so that the mother does not get tired of household chores, help her in everything and be affectionate with her.
An excellent stimulation of lactation is facilitated by the fact that mother and baby feel each other's skin.
When a baby suckles, the mother's brain receives a signal about how much milk her child needs. If the baby is hungry, then, accordingly, he will suckle the breast more, in response to this, the mother's brain will send more hormones that stimulate milk production, which then send a command to your breast to produce more milk. This is the supply-demand system. That is why it is important not overdo it with hormone signals.
If you still need to stimulate the production of milk, then you can use lactogonal agents: fennel seeds, lactation teas, appilac .
Breast massage with oils also helps.
In bad weather, refuse to walk, lie in an embrace with the baby, this will also be a good stimulation.
If this does not help, then consider supplementing your baby with formula.
Complementary formula.
Formula supplementation is a type of infant feeding that combines breastfeeding and formula feeding. But the percentage of the mixture per day should not be more than 50%, otherwise such feeding will be considered artificial.
But the percentage of the mixture per day should not be more than 50%, otherwise such feeding will be considered artificial.
Supplementation with formula during breastfeeding is required temporarily. The task of the mother in this situation is to maintain lactation, and not transfer the child to the mixture.
In the first six months of a baby's life, he is prescribed supplementary feeding with formula, since it is not allowed to feed cereals and vegetable purees until six months. After six months, the issue of supplementary feeding is decided individually.
Start giving your baby some formula, approximately 15-30 grams per feeding. We monitor urination, if less than 8 times a day, then the same amount of the mixture should be added. If the baby urinates more than 15 times, then the amount of the mixture can be slightly reduced.
Offer the mixture strictly after breastfeeding. If he has not eaten it, then it is poured out and a new one is prepared for the next feeding.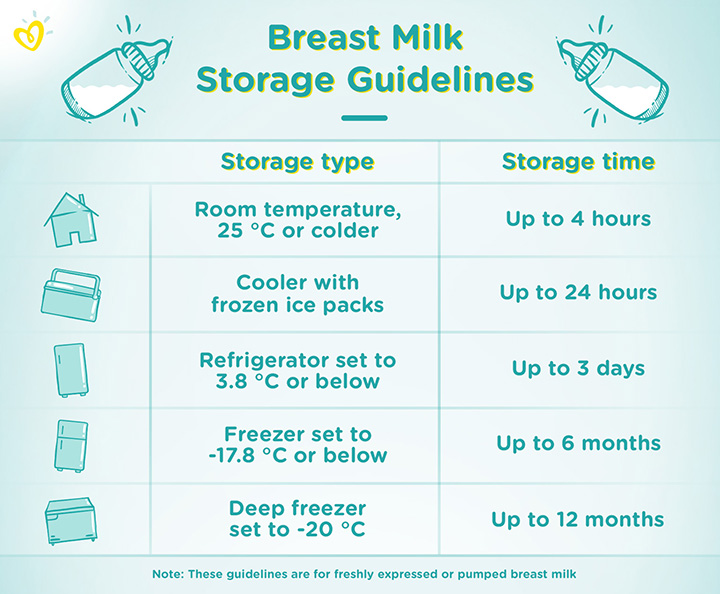 If the baby does not finish eating the formula on subsequent occasions, try removing it and doing the wet diaper test again.
If the baby does not finish eating the formula on subsequent occasions, try removing it and doing the wet diaper test again.
Can full breastfeeding be brought back?
Moreover, this is what needs to be achieved. Lactation consultants have a lot of experience in transitioning from mixed to natural feeding. Of course, this is not a one-day job, mom needs to be patient, be confident in her abilities.
It is necessary to breastfeed before each feeding with the formula, gradually reducing its amount, but we also do a wet diaper test to understand if the baby is full. Applications during breaks should be very frequent.
So, to return to breastfeeding you need:
- to restore bodily contact;
- accustom the baby to the breast;
- gradually reduce the amount of supplementary feeding;
- disperse lactation.
How many months to breastfeed?
There is no consensus on the duration of breastfeeding.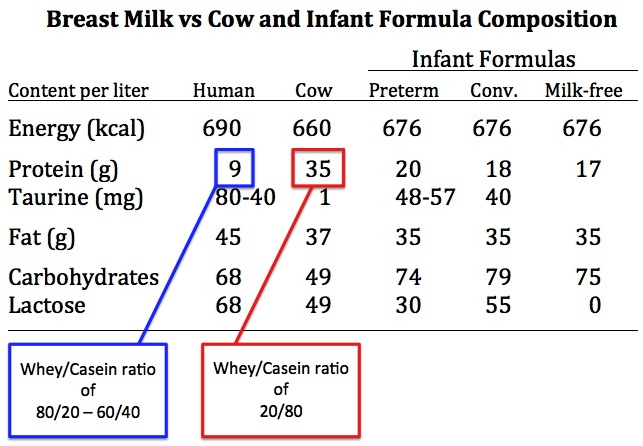 There are opinions that a child needs to be fed up to a year, others say that up to three years, others say until the moment the child refuses to breastfeed.
There are opinions that a child needs to be fed up to a year, others say that up to three years, others say until the moment the child refuses to breastfeed.
The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding your baby until two years of age. But from 6 months of age, your milk can't provide all of your baby's nutritional needs, and it's time to introduce complementary foods.
Most often, a one-year-old child has only nighttime breastfeeding, as it is convenient for both mother and baby.
Benefits of long-term breastfeeding:
- nutritional value;
- protection against diseases;
- reducing the risk of allergies;
- the formation of the correct bite.
You should not stop breastfeeding if your baby is sick, it is during this period that your milk adjusts to his needs and can be the best medicine.
How to set up a milk bank?
Your lactation has picked up and now you have more than enough milk. In such a situation, we create a milk bank. To do this, you need a breast pump and airtight milk storage bags. You can even without a breast pump if you have learned how to pump with your hands. We express milk, seal it in an airtight bag and the supply is ready.
In such a situation, we create a milk bank. To do this, you need a breast pump and airtight milk storage bags. You can even without a breast pump if you have learned how to pump with your hands. We express milk, seal it in an airtight bag and the supply is ready.
Breast milk can be stored this way for up to 3 months.
To feed your baby with such milk, you just need to take it out of the freezer and defrost it, warm it up a little and you can feed the baby.
Can I breastfeed my second child?
It's real. The main thing is to believe in yourself. It is best to find a lactation consultant who would help from the first days.
Is it necessary to follow the diet of a breastfeeding mother?
You need to eat more consistently during the first 2 weeks of your baby's life. Your diet should include cereals, not fatty meat, fish. Vegetables should not be bright colors.
Then gradually introduce one product into the diet and monitor the baby's reaction. If you are not prone to allergic reactions, then most likely your child is too.
Eating for two, as our grandmothers said, is not necessary. It is enough to increase your diet by 500 kilocalories.
The best diet during breastfeeding is proper nutrition with a varied diet.
Breast care while breastfeeding
No need to wash your breasts with soap before every feeding.
It is necessary to do air baths for the chest before feeding, so that the chest would rest from clothes.
You don't need to put nipple ointments on your breasts if your breasts are okay. We use ointment if there really are cracks. The best cream will be your milk. Just after each feeding, you need to squeeze out a little milk and lubricate the nipples with it.
Warm your breasts before feeding to help you relax and increase your milk supply.
If breastfeeding failed
The main thing is not to self-flagellate. You have done a great job in order to establish feeding and feed the baby with your milk.
The next step is to choose an adapted formula. Sometimes it takes a while to get the mix right.
The main thing to remember is that your baby will love you whether you breastfeed or formula feed him!
Breast milk production | Child's needs
Did you know that the amount of breast milk adapts to your baby's needs? In this article, you will learn amazing facts about breast milk production in the first days, weeks and months.
Share this information
Your body is capable of producing breast milk for your baby at every stage of development. Understanding how milk production “turns on”, what happens to milk when you feed your baby, and why production adjusts to his needs as he grows, will help you start this amazing process in the right way.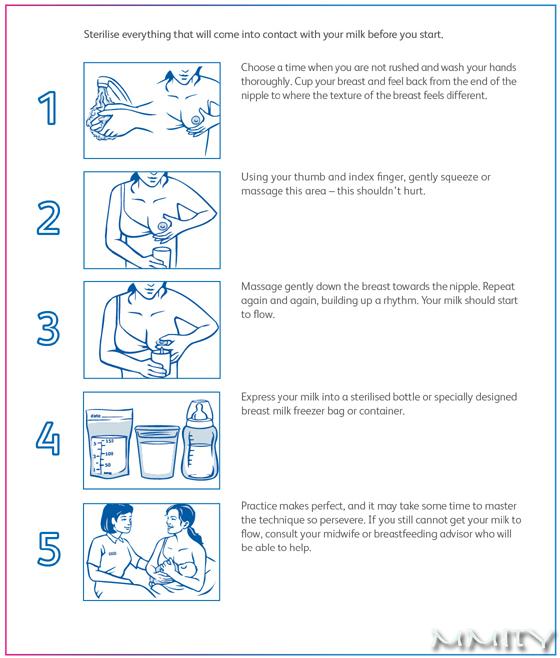
Day one: milk production at birth
The baby is usually ready to breastfeed from birth. When he grabs the breast and begins to suck rhythmically, the milk-producing cells “turn on” and the formation of the first breast milk, colostrum, starts. 1 Try to feed your baby in the first hour of his life if possible, and then as soon as he shows interest in feeding. This will help lay the foundation for good milk production later on. 2
The first days: the arrival of milk
At this stage, your body's level of progesterone,
the pregnancy hormone, which begins to fall after the placenta is delivered, is reduced, and the hormones responsible for milk production - prolactin, insulin and hydrocortisone - are included in the work. These hormones will help start milk production. 3 Approximately on the third day of the baby's life, milk will begin to come in, and you will feel that your breasts are full and noticeably firmer.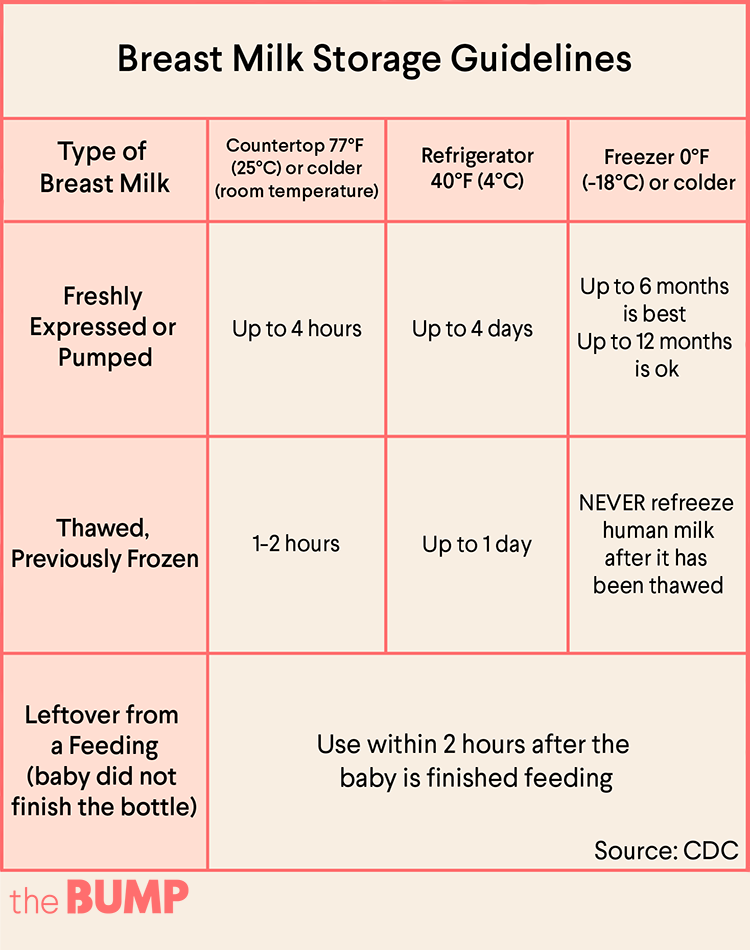 1
1
First month: shaping milk production
During the first weeks, your body will be especially sensitive to the amount of milk produced as it learns to produce the right amount. Prolactin levels increase dramatically each time you empty your breasts, thereby helping shape the lactation process. It also contributes to the maturation of your milk in terms of composition. At this stage, transitional milk is produced and the amount continues to grow. 3.4
For good long-term milk production, it is very important that you are close to your baby during the first few weeks. The more often you breastfeed, the more milk will be produced. This process resembles the law of supply and demand. Each time after emptying the breast, whether it is feeding the baby or pumping, even more milk will be produced.
Remember that it is normal for newborns to eat frequently, perhaps even every 45 minutes, and this does not mean that they are not getting enough milk. Frequent feedings help shape milk production, so feed your baby on demand, not on a schedule.
Frequent feedings help shape milk production, so feed your baby on demand, not on a schedule.
“During the first few weeks, you may not feel like you are getting enough milk because your baby will be feeding all the time, but that’s okay,” says UK mom-of-two Jo, “We tend to think that a baby wants to eat every few hours, but that is not necessarily the case."
Don't forget that babies also breastfeed for comfort. Breastfeeding helps them calm down and adjust to their new life outside the womb. In addition, feeding helps to establish a connection between you.
Stable milk production in the first month
If you follow your baby's needs and feed him as often and for as long as he wants, milk production should adjust. 5
Some mothers try to increase the period between feedings so that the breasts can produce more milk during this time, but this should not be done, as this may have the opposite effect. 2
If you are unable to breastfeed directly for the first two weeks, express your milk to build and maintain your milk supply during this critical period and beyond.
Did you know that feeding your baby extra formula unnecessarily can reduce your milk production? The chest will not receive a signal to increase production, because it will not be emptied. In addition, if the baby sleeps longer after formula, he may miss his usual next feeding time.
This is a kind of "supplementary trap". After three to four days of formula supplementation, during which the breasts have emptied less, the body will receive a signal that breastfeeding has stopped, and the amount of milk produced will begin to decrease. As a result, the baby will remain hungry and will need additional formula supplementation. And so on in a circle ... As a result, this will lead to really low milk production, and the baby will eat mainly the mixture.
Breast milk production after six weeks
After a month of breastfeeding, post-feeding spikes in prolactin secretion begin to decrease, milk matures, and the body gets used to producing as much milk as your baby needs. In fact, the chest begins to work "on autopilot." 4 You may also notice at this time that your breasts are softer and your milk flow has stopped.
In fact, the chest begins to work "on autopilot." 4 You may also notice at this time that your breasts are softer and your milk flow has stopped.
At this stage, women often have fears of "losing milk".
However, this only means that milk production has been established and now fully meets the needs of the child. It is noteworthy that although the baby continues to grow, he will consume approximately the same amount of milk both at six weeks and at six months. You may notice that the baby began to suckle the breast longer, but less often. On some days he may eat a little less than usual - his appetite changes in the same way as an adult.
Now your body will produce exactly the amount of milk,
as much as your baby needs. Therefore, the more milk the baby drinks (or you express), the more milk will be produced.
How does this happen? The reason for this is thought to be the so-called "feedback lactation inhibitor", which controls milk production.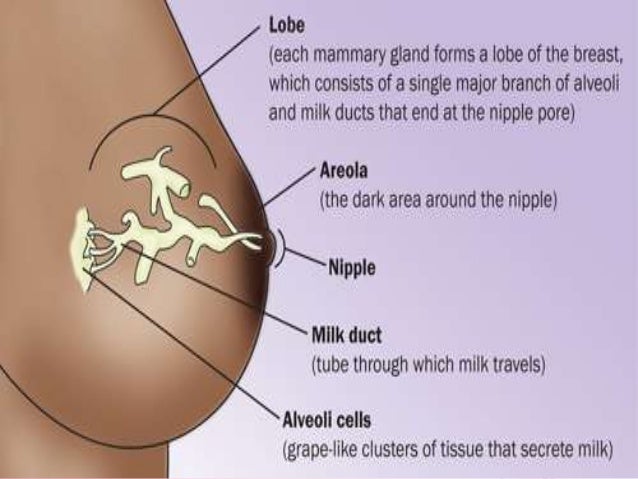 The more milk in the breast, 2 the higher the inhibitor level, so a full breast produces less milk than one that has been emptied.
The more milk in the breast, 2 the higher the inhibitor level, so a full breast produces less milk than one that has been emptied.
What is the rate of milk production?
Mothers often worry about their milk supply and think about how to increase it. However, if the baby is healthy and growing well, problems usually do not arise.
“I was worried that my newborn daughter was not getting enough milk as she was feeding very quickly and always from only one breast, although I offered both,” says Marjorie, mother of two from the UK, “But when I expressed milk from using a breast pump, I was surprised at how much milk I produced, and calmed down. I just had to keep feeding her little and often.”
Keep in mind, however, that not all mothers are able to express a lot of milk right away. You can also try hand expressing milk and see if there is a change in breast fullness.
If you're worried about your milk supply, read our tips for symptoms of too little or too much milk.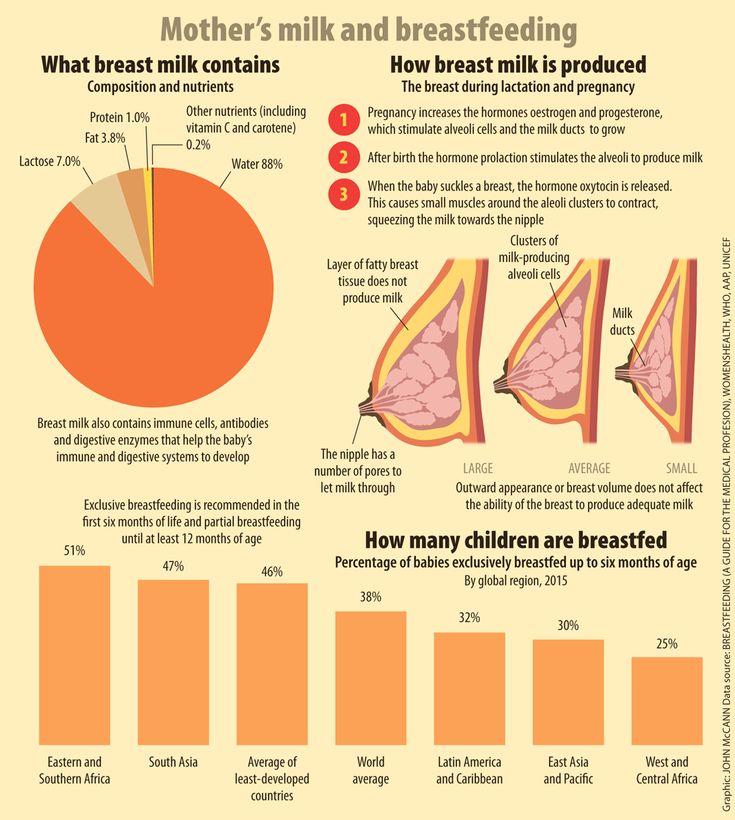
Literature
1 Pang WW, Hartmann PE. Initiation of human lactation: secretory differentiation and secretory activation. J9 Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2007;12(4):211-221. - Pang, W.W., Hartmann, P.I., "Lactation initiation in the lactating mother: secretory differentiation and secretory activation." G Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12(4):211-221.
2 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs . 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". G Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
3 Ostrom KM. A review of the hormone prolactin during lactation. Prog Food Nutr Sci .