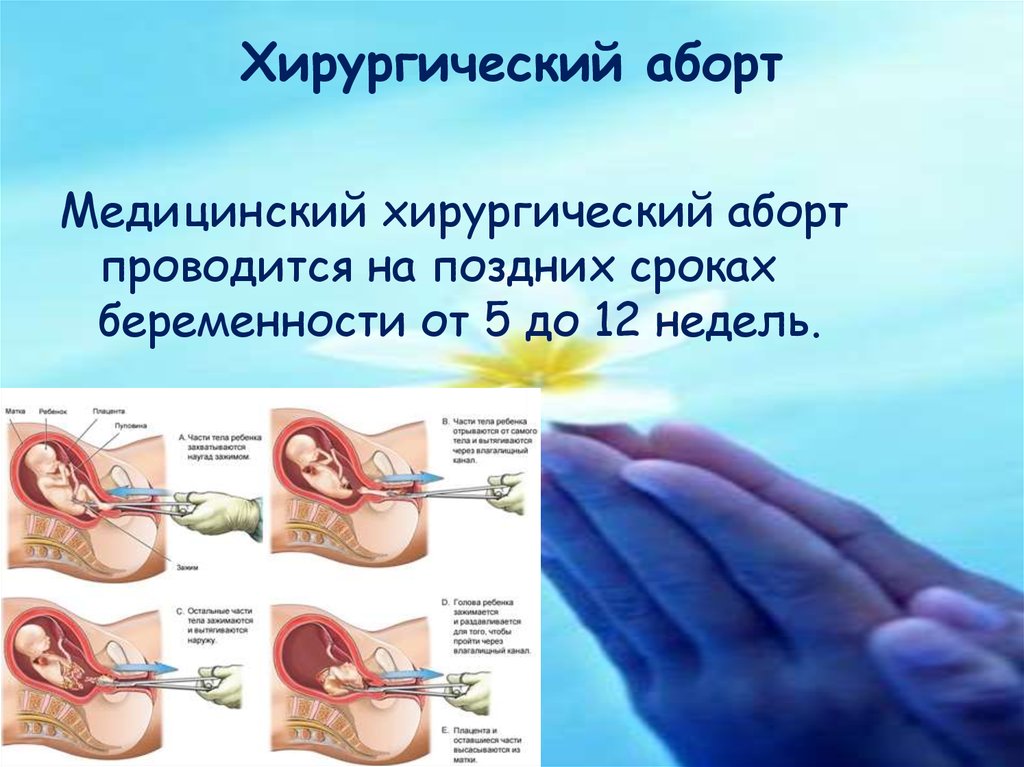
Abortion surgical procedures
Abortion - surgical: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
URL of this page: //medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002912.htm
To use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript.
Surgical abortion is a procedure that ends an undesired pregnancy by removing the fetus and placenta from the mother's womb (uterus).
Surgical abortion is not the same as miscarriage. Miscarriage is when a pregnancy ends on its own before the 20th week of pregnancy.
Surgical abortion involves dilating the opening to the uterus (cervix) and placing a small suction tube into the uterus. Suction is used to remove the fetus and related pregnancy material from the uterus.
Before the procedure, you may have the following tests:
- A urine test checks if you are pregnant.
- A blood test checks your blood type. Based on the test result, you may need a special shot to prevent problems if you get pregnant in the future.
The shot is called Rho(D) immune globulin (RhoGAM and other brands).
- An ultrasound test checks how many weeks pregnant you are.
During the procedure:
- You will lie on an exam table.
- You may receive medicine (sedative) to help you relax and feel sleepy.
- Your feet will rest in supports called stirrups. These allow your legs to be positioned so that your doctor can view your vagina and cervix.
- Your health care provider may numb your cervix so you feel little pain during the procedure.
- Small rods called dilators will be put in your cervix to gently stretch it open. Sometimes laminaria (sticks of seaweed for medical use) are placed in the cervix. This is done the day before the procedure to help the cervix dilate slowly.
- Your provider will insert a tube into your womb, then use a special vacuum to remove the pregnancy tissue through the tube.
- You may be given an antibiotic to reduce the risk of infection.
After the procedure, you may be given medicine to help your uterus contract. This reduces bleeding.
This reduces bleeding.
Reasons a surgical abortion might be considered include:
- You have made a personal decision not to carry the pregnancy.
- Your baby has a birth defect or genetic problem.
- Your pregnancy is harmful to your health (therapeutic abortion).
- The pregnancy resulted after a traumatic event such as rape or incest.
The decision to end a pregnancy is very personal. To help you weigh your choices, discuss your feelings with a counselor or your provider. A family member or friend can also be of help.
Surgical abortion is very safe. It is very rare to have any complications.
Risks of surgical abortion include:
- Damage to the womb or cervix
- Uterine perforation (accidentally putting a hole in the uterus with one of the instruments used)
- Excessive bleeding
- Infection of the uterus or fallopian tubes
- Scarring of the inside of the uterus
- Reaction to the medicines or anesthesia, such as problems breathing
- Not removing all of the tissue, requiring another procedure
You will stay in a recovery area for a few hours. Your providers will tell you when you can go home. Because you may still be drowsy from the medicines, arrange ahead of time to have someone pick you up.
Your providers will tell you when you can go home. Because you may still be drowsy from the medicines, arrange ahead of time to have someone pick you up.
Follow instructions for how to care for yourself at home. Make any follow-up appointments.
Problems rarely occur after this procedure.
Physical recovery usually occurs within a few days, depending on the stage of the pregnancy. Vaginal bleeding can last for a week to 10 days. Cramping most often lasts for a day or two.
You can get pregnant before your next period, which will occur 4 to 6 weeks after the procedure. Be sure to make arrangements to prevent pregnancy, especially during the first month after the procedure. You may want to talk with your provider about emergency contraception.
Suction curettage; Surgical abortion; Elective abortion - surgical; Therapeutic abortion - surgical
- Abortion procedure
Katzir L. Induced abortion. In: Mularz A, Dalati S, Pedigo R, eds. Ob/Gyn Secrets.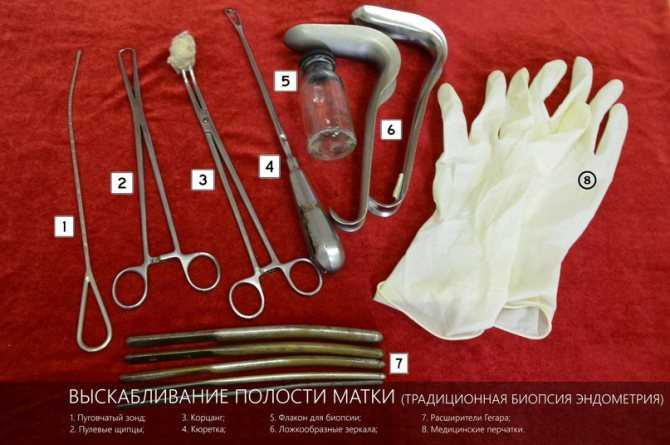 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 13.
4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 13.
Leeman L, Godfrey E. Pregnancy termination: first-trimester suction aspiration. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 113.
Magowan BA, Owen P, Thomson A. Abortion. In: Magowan BA, Owen P, Thomson A, eds. Clinical Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2019:chap 20.
Rivlin K, Westhoff C. Family planning. In: Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 13.
Updated by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Surgical Abortion (First Trimester) | Conditions & Treatments
You will be in a private room during your health education session, exam, procedure and recovery. The entire visit will take around three hours if you are less than 12 weeks pregnant. If you are 12 to 14 weeks pregnant, your visit will last five to six hours. In either case, you will need to arrange for someone to drive you home after the procedure.
The entire visit will take around three hours if you are less than 12 weeks pregnant. If you are 12 to 14 weeks pregnant, your visit will last five to six hours. In either case, you will need to arrange for someone to drive you home after the procedure.
Preparation
When you check in for your appointment, we will verify your insurance information, collect your co-payment if applicable and ask you to complete some forms, including a medical history. The UCSF Center for Pregnancy Options is integrated into the general Women's Health Center practice; women are not identified in the reception area as desiring pregnancy termination and there are no signs advertising our clinic. This ensures the privacy and safety of our patients and staff.
Shortly after you arrive, one of our female health educators will bring you to a private room. You will discuss and learn about pregnancy options, the abortion procedure and various birth control methods. You may remain fully dressed for this part of your appointment. The health educator will take your blood pressure, pulse and weight. If you brought a support person with you, he or she may stay with you during the health education. Since UCSF Medical Center is a teaching hospital, we may ask your permission to have a doctor-in-training listen in on the health education session, which takes around 20 to 40 minutes.
The health educator will take your blood pressure, pulse and weight. If you brought a support person with you, he or she may stay with you during the health education. Since UCSF Medical Center is a teaching hospital, we may ask your permission to have a doctor-in-training listen in on the health education session, which takes around 20 to 40 minutes.
After your conversation with the health educator, you will meet the doctor. Our doctors are obstetrician-gynecologists with specialized training and interest in abortion provision and family planning. The doctor will review your medical history, perform an ultrasound exam to determine your pregnancy's gestation, and give you medications. If you are less than 12 weeks pregnant, you will receive oral pain medications, including Vicodin, Valium and ibuprofen, at this time. If you are 12 to 14 weeks pregnant, you also will receive a medication called misoprostol, which softens your cervix to make dilation easier. This portion of the visit takes about 20 minutes.
If you are less than 12 weeks pregnant, the oral medications need 45 to 60 minutes to be most effective. You will be awake, but well relaxed. You may stay in your room or wait in the reception area. We have magazines and portable stereos; you may want to bring something to read or a CD to occupy your wait time, which will be 45 to 60 minutes.
If you are 12 to 14 weeks pregnant, the misoprostol needs two to three hours to work. We will loan you a beeper so you can walk around the neighborhood or go downstairs to our café and garden area. We will page you when it is time for you to return to the clinic. When you return, we will give you oral medications, including Vicodin, Valium and ibuprofen, and ask you to wait an additional 30 to 60 minutes for those to fully relax you.
Continue reading
Procedure
When you are fully relaxed, the doctor, health educator and/or doctor-in-training, will ask you to undress from the waist down and put on a patient gown. Your support person can be right next to you for the whole procedure.
Your support person can be right next to you for the whole procedure.
During the procedure, the doctor will:
1. Use a speculum to view inside your vagina
2. Clean your vagina and cervix with gauze soaked in soap
3. Apply numbing medication to your cervix
4. Dilate your cervix, the tight opening to your uterus, with thin metal rods
5. Insert a narrow flexible tube into your uterus
6. Apply gentle suction to the other end of the tube to remove all of the pregnancy tissue
Toward the end of the procedure, you may feel a cramp that feels similar to a menstrual cramp in your uterus, as it is shrinking down to its usual size.
Most of the procedure time is spent preparing your body for the procedure. The suction portion only takes about a minute and the entire procedure takes around 15 to 20 minutes.
Recovery
After the procedure, you should remain resting for a few minutes. You will probably have some cramping and spotting. We will provide you with a heat pack and a menstrual pad as well as juice and crackers.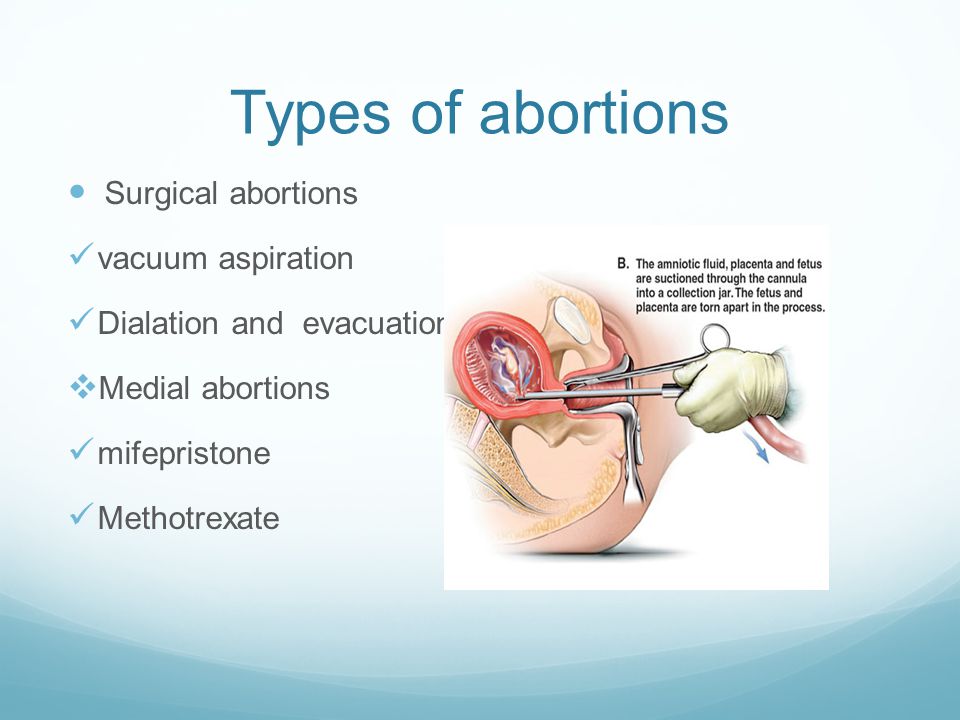 When you feel able, you may get dressed.
When you feel able, you may get dressed.
Your health educator will then give you instructions on how to take care of your body. The doctor will give you antibiotics and a prescription for birth control if you desire it. You will have arranged ahead of time to have someone drive you home. You should go immediately home to rest and let the medications wear off. You should be able to return to normal activities, such as work and school, the next day.
Follow-Up Visits
Unless you are experiencing complications related to the procedure, you do not need to visit our office again. We recommend that you make an appointment to see your regular doctor for an annual pap smear, physical or gynecologic exam and birth control refill requests.
Preparation for medical and surgical abortion. Indications and pre-indications
Before the abortion procedure, the patient is required to undergo an examination by a gynecologist and pass the prescribed tests. This is necessary to identify possible pathologies that will affect the patient's condition during surgery. At the appointment, the doctor determines the gestational age and determines the appropriate method for terminating the pregnancy.
At the appointment, the doctor determines the gestational age and determines the appropriate method for terminating the pregnancy.
Artificial interruption is done at the request of the patient at a gestational age of up to 12 weeks. As an exception, the legislation takes into account abortions for medical or social reasons.
- For medical reasons, pregnancy is terminated regardless of the term.
- According to social indications, abortion is done at a period of up to 22 weeks. The list of social indications is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Indications for medical abortion:
- the patient's desire to terminate an unplanned pregnancy up to 9 weeks: up to 63 days from the first day of the last menstruation;
- the presence of medical indications for termination of pregnancy, including frozen pregnancy up to 63 days from the first day of the last menstruation.
Contraindications for medical abortion:
- infection of the genital and digestive organs;
- tumors of the reproductive organs;
- the presence of an intrauterine device;
- abnormal position of the ovum;
- scars on the uterus;
- pregnancy disorders while taking hormonal contraceptives;
- tuberculosis;
- diabetes mellitus in a dangerous stage;
- severe mental disorders;
- heart defects;
- acute autoimmune diseases;
- blood diseases.

Surgical abortion
The procedure is done under general anesthesia so that the girl does not feel pain. The doctor removes the fetal egg from the uterus and scrapes the walls with surgical instruments. To avoid complications, the girl remains under medical supervision until her condition stabilizes. If the patient's health is not in danger, then the discharge takes place on the same day.
The World Health Organization has recognized surgical termination of pregnancy as an outdated method, but the method remains popular in Russia. It is used when the deadline for medical abortion is missed.
Preparation for surgical abortion
Surgical abortion is equated to an operation, so a consultation and examination by a gynecologist is required before the procedure. It is advisable to contact the doctor in the clinic where you plan to have an abortion. At the appointment, the doctor collects an anamnesis, learns about chronic diseases, what medications the girl takes, and asks about previous pregnancies. Next, the patient is prescribed tests and sent for an ultrasound. This is necessary to determine the pathologies of the reproductive system, in which abortion is contraindicated.
Next, the patient is prescribed tests and sent for an ultrasound. This is necessary to determine the pathologies of the reproductive system, in which abortion is contraindicated.
Curettage of the fetus remains the fastest and most reliable method, because the mucous layer of the uterus is completely removed. In addition, the gestation period for surgical abortion is longer than for other methods - up to 12 weeks.
Medical abortion
The method consists in taking pharmacological drugs that stop the development of the fetus. Pill abortion is a modern alternative to surgical intervention. The gestational age for medical abortion is no longer than 7 weeks from the last menstrual cycle. Pharmacological abortion at a later date leads to the development of pathologies.
The drugs artificially stimulate a miscarriage in the body: the uterus contracts, accelerates the hatching of the egg and does not allow to gain a foothold. Within 10 days, the patient has bleeding similar to menstruation.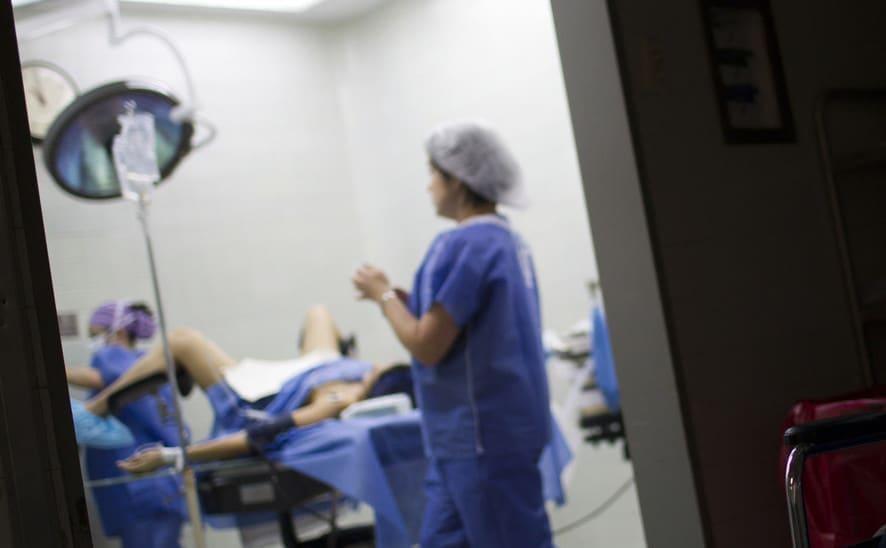 After that, it is necessary to do an ultrasound to monitor the state of the reproductive system.
After that, it is necessary to do an ultrasound to monitor the state of the reproductive system.
Preparation for medical abortion
The procedure does not require serious preparation. It is necessary to consult with your doctor, undergo a pelvic ultrasound, pass the prescribed smears and tests. 5 days before the procedure, it is recommended to give up alcohol and intimacy, avoid stress and physical activity. When the pregnancy is terminated, it is necessary to refrain from sexual intercourse for 3 weeks.
Psychological preparation for abortion
When contacting a antenatal clinic to terminate a pregnancy, a girl will have an open conversation with a doctor or psychologist. The patient will have to weigh the arguments again and make a final decision. If the slightest doubt remains, then time is given to rethink the intention. Before an abortion, it is important to overcome internal doubts in order to avoid depression later. However, you should not delay making a decision, as an increase in terms increases the risk of complications.
Social stigma is often present and a girl may attempt to terminate a pregnancy on her own without consulting a doctor. Such attempts cause damage to the reproductive system and pose a danger to life. Therefore, it is necessary to cope with fear and remember that the doctor will help you make the right decision.
The information presented in the material is of a general nature. Check with your doctor for personal recommendations for terminating a pregnancy.
Surgical abortion in Novosibirsk at a bargain price from the Euromed clinic
Surgical abortion is performed using special instruments that must be inserted into the uterus in order to destroy and then remove the fetus. Basically, the manipulation is carried out under anesthesia. At the request of a woman, an abortion can be done no later than the twelfth week.
Benefits
All types of surgical treatment of gynecological diseases
Gynecological surgeons with extensive experience
Individual choice of surgical access method
Preparation for surgery in 2-3 days
Minimally invasive methods of treatment
Equipment from leading world manufacturers
Features of the procedure
Surgical termination of pregnancy is performed under anesthesia (drugs are administered intravenously). The doctor expands the cervical canal to 12 millimeters, using a vacuum tip, the fetal egg is removed. If necessary, special preparations are introduced to reduce the uterus. This will help to significantly reduce bleeding. The duration of the abortion is about fifteen minutes. It is important to know that spotting after a surgical abortion may be present for up to 14 days.
The doctor expands the cervical canal to 12 millimeters, using a vacuum tip, the fetal egg is removed. If necessary, special preparations are introduced to reduce the uterus. This will help to significantly reduce bleeding. The duration of the abortion is about fifteen minutes. It is important to know that spotting after a surgical abortion may be present for up to 14 days.
Indications for abortion
- Vesical skid suspicion;
- The presence of a scar on the uterus, formed due to a caesarean section;
- Frozen pregnancy and concomitant diseases;
- Malformations of the uterus, vagina;
- Incomplete spontaneous / medical abortion and gynecological comorbidities.
Key benefits of surgical abortion:
- Safe method;
- High percentage of efficiency;
- The interrupt occurs directly during the manipulation.
Main cons
- The procedure is invasive;
- The risk of developing side symptoms - prolonged and very heavy bleeding, nausea and vomiting, pain in the lower abdomen, high body temperature;
- The use of anesthesia can provoke various complications;
- Danger of bleeding and damage to the uterus, bladder, intestines;
- In case of complications, a hysterectomy procedure may be required.

Specifics of preparation for surgical abortion
Before the procedure, it is advisable to consult a gynecologist , this will allow you to collect an anamnesis, determine the nature of the menstrual cycle, the outcome and number of previous pregnancies. Then, without fail, an examination is performed on the chair, laboratory tests are carried out. Urine analysis is of great importance - this is an incredibly high-quality test that allows you to confirm pregnancy. HCG blood is a more accurate analysis Regarding the blood test, this test determines the quantitative content of a special hormone, namely chorionic gonadotropin. Ultrasound of the small pelvis Abortion of the surgical type is carried out no later than 12 weeks. At later dates, strong medical and social indications are needed. In addition, the following tests are carried out: analysis for the Rh factor and blood group, tests for AIDS, syphilis, hepatitis B.
After performing an abortion, it is worth focusing on the rehabilitation of a woman, which includes a set of measures aimed at avoiding unpleasant consequences and complications.