How to keep my child from coughing at night
9 Cough Remedies to Stop Your Child Coughing at Night
If your child’s constant coughing is keeping them (and you) up at night, try some of these home and pharmacist-approved cough remedies that could help them on the road to recovery.With cold and flu season now in full swing, the chances are, your little one is likely to catch a cold at some point during the winter season. Coughs and colds are common in young children, so don’t be alarmed if illness strikes from one week to the next. In fact, exposure to these germs helps to develop their immune systems, and fight off infections naturally.
Of course, you need peace of mind that your child’s cough is nothing more sinister — if you’re concerned at all, pay a visit to your GP so they can give them a thorough examination. Although, more often than not, it’s purely a virus that they have to fight off.
A regular cough can last up to two weeks, which can be challenging for both them and you! But thankfully, there are some helpful treatments that can speed up the recovery process.
The first, and easiest, is to keep them hydrated, comfortable and relaxed, allowing them as much rest as possible. Making them comfortable will help to relieve any nasty, painful symptoms, and hopefully encourage them to relax. That way they’ll be able to sleep off their virus until they feel well enough to run around again!
So, to stop your child from feeling down in the dumps (and tossing and turning all night), try some of our home and pharmacist-approved cough remedies that are suitable for toddlers and young children.
These treatments are guaranteed to relieve their symptoms and stop your child from coughing all through the night.
How to Stop Your Child Coughing at Night: 9 Cough Remedies That Work
1. Keep their head elevated
If your child is over 1 year, arrange a few pillows under their back, shoulders and head so that they can sleep in a slightly upright position. This helps them to breathe more easily and in turn, helps to ease their coughing.
2. Drink lots of fluids
Keeping little ones hydrated is particularly important when your child is sick. Water helps the body fight illness and keeps airways moist and strong. Water also thins mucus secretions, which helps to drain any excess mucus that could be causing congestion and coughs. Make sure they are fully hydrated throughout the day, and give them a glass of water before bed in case they wake up in the night.
As a general rule of thumb, this is how much water a child should drink per day:
- 5 to 8 years old: 5 glasses (1 litre)
- 9 to 12 years old: 7 glasses (1.5 litres)
- 13 years old and over: 8 to 10 glasses (2 litres)
However, it’s a good idea to encourage them to drink extra fluids when they’re sick — the more water they drink, the quicker the mucus will be expelled from the body, and that means quicker recovery and less coughing!
Replacing lost electrolytes when a child is sick is a great way to enhance fluid that has been lost, especially when they've also been vomiting or have had diarrhoea. Hydralite is great for both dry and chesty coughs.
Hydralite is great for both dry and chesty coughs.
Berocca Performance Effervescent Orange 15 Tablets
Shop Now
Hydralyte Apple Blackcurrant Effervescent Electrolyte 20 Tablets
Shop Now
VOOST Multivitamin C + Minerals Effervescent Tablets 20 Pack
Shop Now
3. Use a nasal spray or saline solution
Using a nasal spray or saline drops help to clear the nose and break up any mucus. Just follow the instructions on the bottle to administer the nasal drops safely. You may want to use saline drops before bed or in the middle of the night if your toddler wakes up coughing, to help relieve their symptoms.
We love Fess Little Noses Nasal Spray for babies 0-2 years, and FESS Children's Nasal Spray for 2yrs+
Mundicare Kids Cold Defence Nasal Spray 20mL
Shop Now
Brauer Baby Saline Nasal Spray 30mL
Shop Now
FESS Children's Nasal Spray 2 Years+ 20mL
Shop Now
4.
 Take lozenges to soothe the throat
Take lozenges to soothe the throatConstant coughing can cause the throat to become sore and painful — coughs and colds are usually accompanied by a sore throat — so taking something to help soothe the pain will make them more relaxed come bed time, and kill off any harmful bacteria that could cause further illness or infection.
Children over 6 can take Strepsils Lozenges, which contain an effective combo of antibacterial agents to help kill the bacteria that can cause sore throats and mouth infections, whilst at the same time providing soothing relief from discomfort and pain.
Sambucol Kids Soothing Throat Pops 8 Pack
Shop Now
Vicks VapoNaturals Lemon Menthol Throat Lozenges
Shop Now
Strepsils Sore Throat Lozenges
Shop Now
When a child has a dry cough this can make their throat more susceptible to becoming dry and tickly. Lozenges are a great way to temporarily lubricate the throat to reduce this dry and tickly feeling.
5. Massage with Vicks
For children over 2, massage Vicks VapoRub Ointment Decongestant Chest Rub on their chest and throat before bedtime to reduce coughs and congestion. Infused with camphor, eucalyptus oil and menthol, this vaporising ointment works to unblock noses, relieve coughs and soothe sore muscles, aches and pains. A nightly dose should help your child sleep more restfully at night.
If your little one is really congested and finding it hard to breathe, you can also put two teaspoons of Vicks into a bowl of steaming water, then cover with a towel. Carefully place your child’s head over the bowl with a towel over their head so they can inhale the steam — this will help unblock any congestion and help them breathe easier before bed.
For babies under 2, use Vicks BabyBalsam made with a relaxing combo of rosemary, lavender and eucalyptus and extract of aloe vera.
6. Try a cough syrup
For children aged 6 and above, cough syrups like DURO-TUSS Expectorant Cough Liquid work to break down and clear excess mucus from the chest, which in turn, helps to relieve the urge to cough. It can also cause slight drowsiness, so it may also help your child to rest through the night. The pomegranate flavour is also very kid-friendly, so it won't be hard getting little ones to swallow.
It can also cause slight drowsiness, so it may also help your child to rest through the night. The pomegranate flavour is also very kid-friendly, so it won't be hard getting little ones to swallow.
Sambucol Kids Cough Oral Liquid 120mL
Shop Now
Vicks Chesty Cough Syrup 180mL
Shop Now
Brauer Kids Manuka Honey Dry Cough 100mL
Shop Now
7. Steam up the bathroom
Run a hot shower and turn your bathroom into a steam room 15 mins before bed, and 15 mins in the morning to help loosen chest and nasal congestion. The steam helps to loosen chest and nasal congestion, making it easier for them to cough or blow it out when they have trapped mucus from a chesty cough. As an added measure you can pat their back and chest lightly using open palms (like you are burping them) to help break up congestion. This will hopefully clear away any mucus or phlegm before they go to bed, encouraging them to breathe a little easier, and hopefully sleep more soundly.
8. Use a humidifier
Use a cool-mist humidifier all night to keep your child’s airways clear and moist. Open the windows first thing in the morning to air the room, humidity in the room can cause mould to grow which can make congestion worse.
Try the Able Ultrasonic Vaporiser, it works miracles by adding more humidity to the air. The low humidity in winter can inflame and dry out the mucous membrane lining in your respiratory tract, which increases the risk of a cold, flu, and other infections like coughs. Flu germs and other viruses survive and spread more easily in dry air conditions, so boosting your indoor humidity level makes it less likely for germs to survive and transmit to those around you.
Able Ultrasonic Vaporiser
Shop Now
Vicks WarmSteam Vaporiser
Shop Now
The Able Ultrasonic Vaporiser's ultrasonic frequency creates fine water droplets that evaporate into the air as a cool fog, helping you to breathe easier and stop winter germs dead in their tracks.
Double up with Vicks VapoSteam Double Strength. Add a few drops to your humidifier and allow the soothing vapours of eucalyptus and peppermint to penetrate nasal and throat passages, which help to gently soothe and comfort
Vicks VapoSteam Double Strength Inhalant 200mL
Shop Now
Euky Bear Sniffly Nose Inhalant 200mL
Shop Now
Able VapourMist Essential Oils 125mL
Shop Now
Be sure to keep your humidifier clean with Euky Bear Vaporiser Cleaning Tablets. Just pop one or two tablets in with your steam inhalent and it will clean at the same time.
9. Give them a teaspoon of honey
For children 1-6, a spoonful of honey will work as a natural soothing agent for sore throats. Some studies show that it also works as a natural remedy to relieve dry cough symptoms too, as it has antibacterial properties that can help fight off infections. Give them a teaspoon before bed, or infused into some warm water for added hydration.
Loved our advice on child cough remedies? We've got plenty more health advice on our Health & Wellness Edit, guaranteed to give your body a well-deserved boost. Want to know if it's safe to take someone else's antibiotics? Plus, do you know the difference between over-the-counter and practitioner-only supplements? Here's everything you need to know.
Related Posts
Heat Stroke vs. Heat Exhaustion: How to Recognise the Signs
Spent too much time in the sun? Heat exhaustion and heat stroke are most common during summer, so it’s important to k...
Read More
5 of the Best Vitamins to Take in Summer for an Instant Health Boost
Boost your health over the sunny season with our pick of the best vitamins to take in summer. Keeping your body toppe...
Read More
Is Magnesium Good For you?
Magnesium is a nutrient that is essential for healthy muscles, nerves, bones and blood sugar levels, but how much sho. ..
..
Read More
Coughing (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
What Are Coughs?
Coughs are one of the most common symptoms of childhood illness. A cough can sound awful, but usually isn't a sign of a serious condition. In fact, coughing is a healthy and important reflex that helps protect the airways in the throat and chest.
What Are the Different Types of Coughs?
Sometimes, though, a cough needs a doctor's care. Understanding the different types of cough can help you know when to handle them at home and when to call your doctor.
The most common types of coughs are:
- "barky" cough
- whooping cough
- cough with wheezing
- nighttime cough
- daytime cough
- cough with a fever
- cough with vomiting
- persistent cough
"Barky" Cough
Barky coughs are usually caused by swelling in the upper airway. Most of the time, a barky cough comes from croup, a swelling of the larynx (voice box) and trachea (windpipe). Younger children have smaller airways that, if swollen, can make it hard to breathe. Kids younger than 3 are most at risk for croup because their airways are so narrow.
Younger children have smaller airways that, if swollen, can make it hard to breathe. Kids younger than 3 are most at risk for croup because their airways are so narrow.
A cough from croup can start suddenly, often in the middle of the night. Most kids with croup will also have stridor, which is a noisy, harsh breathing that happens when the child inhales (breathes in).
Whooping Cough
Whooping cough (pertussis) is an infection of the airways caused by the
bacteriaBordetella pertussis. Kids with pertussis will have spells of back-to-back coughs without breathing in between. At the end of the coughing, they'll take a deep breath in that makes a "whooping" sound. Other symptoms are a runny nose, sneezing, mild cough, and a low-grade fever.
Whooping cough can happen at any age, but is most severe in infants under 1 year old who did not get the pertussis vaccine, which is part of the DTaP vaccine (diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis). It's very contagious, so all kids should get the pertussis shot at 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 15 months, and 4–6 years of age.
It's very contagious, so all kids should get the pertussis shot at 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 15 months, and 4–6 years of age.
Cough With Wheezing
If your child makes a wheezing (whistling) sound when breathing out (exhaling), this could mean that the lower airways in the lungs are swollen. This can happen with asthma or with the viral infection bronchiolitis. Wheezing also can happen if the lower airway is blocked by a foreign object. A child who starts to cough after inhaling something such as food or a small toy should see a doctor.
Nighttime Cough
Lots of coughs get worse at night. When your child has a cold, the mucus from the nose and sinuses can drain down the throat and trigger a cough during sleep. This is only a problem if the cough won't let your child sleep.
Asthma also can trigger nighttime coughs because the airways tend to be more sensitive and irritable at night.
Daytime Cough
Cold air or activity can make coughs worse during the daytime. Try to make sure that nothing in your house — like air freshener, pets, or smoke (especially tobacco smoke) — is making your child cough.
Try to make sure that nothing in your house — like air freshener, pets, or smoke (especially tobacco smoke) — is making your child cough.
Cough With a Fever
A child who has a cough, mild fever, and runny nose probably has a common cold. But coughs with a fever of 102°F (39°C) or higher can sometimes be due to pneumonia, especially if a child is weak and breathing fast. In this case, call your doctor immediately.
Cough With Vomiting
Kids often cough so much that it triggers their gag reflex, making them throw up. Also, a child who has a cough with a cold or an asthma flare-up might vomit if lots of mucus drains into the stomach and causes nausea. Usually, this is not cause for alarm unless the vomiting doesn't stop.
Persistent Cough
Coughs caused by colds due to viruses can last weeks, especially if a child has one cold right after another. Asthma, allergies, or a chronic infection in the sinuses or airways also might cause lasting coughs. If your child still has a cough after 3 weeks, call your doctor.
How Are Types of Coughs Diagnosed?
If you're concerned about your child's cough, call your doctor. Depending on the type of cough, other symptoms, and how long it's lasting, the doctor might want to see your child.
Many health care providers now offer telehealth visits, which can save parents a trip to the office (especially for a nighttime cough). "Video chatting" lets doctors see and hear a child cough, and often this is enough to make a diagnosis or rule out a serious problem. Hearing the cough will help the doctor decide whether (and how) to treat it.
How Are Coughs Treated?
Most coughs are caused by viruses and have to just run their course. Sometimes, this can take up to 2 weeks. Doctors usually don't prescribe antibiotics because these only work against bacteria.
Unless a cough won't let your child sleep, cough medicines are not needed. They might help a child stop coughing, but they don't treat the cause of the cough. If you do use an over-the-counter (OTC) cough medicine, call the doctor to be sure of the correct dose and to make sure it's safe for your child.
Do not use OTC combination medicines (like "Tylenol Cold") — they have more than one medicine in them, and kids can have more side effects than adults and are more likely to get an overdose of the medicine.
Cough medicines are not recommended for any children under 6 years old.
How Can I Help My Child Feel Better?
To help your coughing child feel better:
- For a "barky" or "croupy" cough, turn on the hot water in the shower in your bathroom and close the door so the room will steam up. Then, sit in the bathroom with your child for about 20 minutes. The steam should help your child breathe more easily. Try reading a book together to pass the time.
- A cool-mist humidifier in your child's bedroom might help with sleep.
- Sometimes, brief exposure to cool air outdoors can relieve the cough. Make sure to dress your child appropriately for the outdoor weather and try this for 10–15 minutes.
- Cool beverages like juice can be soothing and it is important to keep your child hydrated.
 But do not give soda or orange juice, as these can hurt a throat that is sore from coughing.
But do not give soda or orange juice, as these can hurt a throat that is sore from coughing. - You should not give your child (especially a baby or toddler) OTC cough medicine without first checking with your doctor.
- If your child has asthma, make sure you have an asthma action plan from your doctor. The plan should help you choose the right asthma medicines to give.
- Cough drops are OK for older kids, but kids younger than 3 years old can choke on them. It's better to avoid cough drops unless your doctor says that they're safe for your child.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Always call your doctor if your child is coughing and:
- has trouble breathing or is working hard to breathe
- is breathing faster than usual
- has a blue or dusky color to the lips, face, or tongue
- has a high fever (especially if your child is coughing but does NOT have a runny or stuffy nose)
- has any fever and is younger than 3 months old
- is younger than 3 months old and has been coughing for more than a few hours
- makes a "whooping" sound when breathing in after coughing
- is coughing up blood
- has stridor (a noisy or musical sound) when breathing in
- has wheezing when breathing out (unless your doctor already gave you an asthma action plan)
- is weak, cranky, or irritable
- is dehydrated; signs include dizziness, drowsiness, a dry or sticky mouth, sunken eyes, crying with little or no tears, or peeing less often (or having fewer wet diapers)
Emergencies
Cough
Cough is probably the most common problem parents face. Very often, a cough, even if it sounds scary, has a harmless cause and goes away on its own. Sometimes coughing is a serious symptom. Let's try to figure out how to behave when a child coughs and when to start sounding the alarm.
Very often, a cough, even if it sounds scary, has a harmless cause and goes away on its own. Sometimes coughing is a serious symptom. Let's try to figure out how to behave when a child coughs and when to start sounding the alarm.
What is a cough?
Cough is a protective reflex designed to clear the airways. During a cough push, the air abruptly leaves the lungs and forces everything that interferes with breathing - sputum and foreign bodies - to come out. If you think about the mechanism of coughing, it becomes clear that it is far from always necessary to “suppress” it. nine0005
What causes and what does a cough look like?
The most common cause of cough is a viral infection. Viruses can cause damage to the respiratory tract at different levels - from the nose (with a common cold) to the bronchi, bronchioles and lungs, and coughing is a common symptom in all these diseases. For example, sore throat and nasal discharge flowing down the back of the throat irritate the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract and stimulate the cough reflex. Due to irritation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx, a dry, hacking cough occurs, which will definitely pass without treatment, but in the acute period it can be quite frequent and painful, and even disrupt night's sleep. A runny nose and discharge along the back of the throat provoke a wet cough, while the child begins to cough when changing position of the body, especially in the morning and at night when he gets up, lies down or rolls over. If the virus infects the mucous membrane of the larynx, a false croup develops, that is, swelling and, as a result, narrowing of the lumen of the larynx, which is accompanied by a "barking" cough, hoarseness, and a characteristic noisy breath (the so-called stridor). With inflammation of the bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli - bronchitis, bronchiolitis and pneumonia, respectively - sputum accumulates in the lumen of the respiratory tract, swelling of the mucous membrane occurs, resulting in cough and shortness of breath.
For example, sore throat and nasal discharge flowing down the back of the throat irritate the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract and stimulate the cough reflex. Due to irritation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx, a dry, hacking cough occurs, which will definitely pass without treatment, but in the acute period it can be quite frequent and painful, and even disrupt night's sleep. A runny nose and discharge along the back of the throat provoke a wet cough, while the child begins to cough when changing position of the body, especially in the morning and at night when he gets up, lies down or rolls over. If the virus infects the mucous membrane of the larynx, a false croup develops, that is, swelling and, as a result, narrowing of the lumen of the larynx, which is accompanied by a "barking" cough, hoarseness, and a characteristic noisy breath (the so-called stridor). With inflammation of the bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli - bronchitis, bronchiolitis and pneumonia, respectively - sputum accumulates in the lumen of the respiratory tract, swelling of the mucous membrane occurs, resulting in cough and shortness of breath. Unlike viral bronchitis and bronchiolitis, pneumonia is more commonly caused by bacteria and is accompanied by fever in addition to coughing and shortness of breath. In bronchial asthma, bronchospasm and accumulation of thick sputum in them occur after contact with an allergen, which also provokes a cough. nine0005
Unlike viral bronchitis and bronchiolitis, pneumonia is more commonly caused by bacteria and is accompanied by fever in addition to coughing and shortness of breath. In bronchial asthma, bronchospasm and accumulation of thick sputum in them occur after contact with an allergen, which also provokes a cough. nine0005
When should an ambulance be called for a child with a cough?

If the child does not have the most severe symptoms, but the child is concerned, see a doctor. An important sign of trouble is the appearance of the child - if he is lethargic, looks sick and if you cannot attract his attention and catch his eye. Shortness of breath, that is, rapid breathing, accompanied by an effort of the respiratory muscles and retraction of the intercostal spaces and the jugular fossa (depression above the sternum), is a sign that indicates damage to the lower respiratory tract. If you notice shortness of breath in a child, be sure to consult a doctor. Increased body temperature, especially fever above 39- 40 ° C, also requires that the child be examined by a doctor, as cough and fever can be symptoms of pneumonia.
Special attention should be given to children in the first months of life, because in young children, serious illnesses can be erased, and the condition may worsen suddenly. If you have a fever (that is, if the child's rectal temperature is > 38 ° C) in children under three months old, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Should yellow or greenish sputum cause concern? nine0008
Yellow or green sputum does not always indicate a bacterial infection. With viral bronchitis and bronchiolitis, the yellow-green color of sputum is associated with the fact that cells of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, which the virus has damaged, enter the sputum. As a new mucous membrane is formed, the desquamated cells come out with sputum, so there is no need to be scared if the child coughs up yellow or even greenish sputum, since in most cases this is a normal manifestation of a viral infection that does not require antibiotics. nine0005
What should I do if my child coughs at night?
Most often, nocturnal cough is associated with the fact that when the child lies in bed, discharge from the nose and paranasal sinuses drain into the throat and cause a cough reflex. When a child rolls over in bed or gets up from a horizontal to an upright position, a coughing fit occurs. In such cases, the doctor will prescribe a topical treatment for the child to reduce the runny nose and, as a result, reduce the cough.
In such cases, the doctor will prescribe a topical treatment for the child to reduce the runny nose and, as a result, reduce the cough.
Night cough also occurs with pathology of the lower respiratory tract. Therefore, if your child is concerned about a nighttime cough, consult a doctor.
What if the child coughs to vomit?
If your child has a paroxysmal cough before vomiting, contact your pediatrician as this may be a symptom of whooping cough. Whooping cough is especially dangerous for children in the first months of life. Sometimes whooping cough develops even in children who were vaccinated against it, but a lot of time has passed since the last revaccination. nine0005
Some children have a very easy gag reflex and may vomit when they cough, even if the cough is simply due to a runny nose. If vomiting occurs against the background of coughing, feed the child more often, but in small portions.
Prolonged cough
It is not uncommon for a prolonged cough to be caused by several successive viral infections. The child does not have time to recover from one infection and picks up another. In this case, the cough can last for several weeks and greatly frighten parents, although its cause is trivial. nine0005
However, a prolonged cough may be associated with allergies, including bronchial asthma, as well as whooping cough and other diseases of the respiratory tract and ENT organs (a chronic cough may even be due to earwax plugs in the ears!), so in case of persistent cough, consult your doctor.
How to treat a cough?
Cough can have many causes, and each case is treated differently. Show the child to the doctor to understand what the cough is connected with and how to help the child. nine0005
If the cough is accompanied by sputum production (wet, productive cough), sputum production should be stimulated to facilitate expectoration. Give your child more fluids (for example, apple juice or warm chicken broth can be given if age-appropriate and not allergic to these foods). If the air in the children's bedroom is dry, install a humidifier.
Give your child more fluids (for example, apple juice or warm chicken broth can be given if age-appropriate and not allergic to these foods). If the air in the children's bedroom is dry, install a humidifier.
Fight nonproductive (dry) cough by reducing upper airway irritation. To soften the cough and soothe the airways, give the child a drink of water or apple juice, this also helps with a coughing fit. Avoid giving carbonated drinks or citrus drinks as they can irritate inflamed mucous membranes. If the child is intolerant of honey, try giving it. Children over 6 years old can suck on cough drops. If a cough interferes with sleep, going to kindergarten and school, consult a doctor, he will prescribe an antitussive. nine0005
Steam in the bathroom can help with a fit of coughing. Go into the bathroom, close the door, turn on the hot shower and wait a few minutes. After the bath is filled with steam, go there with the child, sit for about 20 minutes. Try reading a book or playing with the child so that he is distracted.
Try reading a book or playing with the child so that he is distracted.
Smoking is strictly prohibited at home! This contributes to frequent respiratory infections in the child and aggravates their course.
Medicines such as antibiotics and inhaled bronchodilators, anti-inflammatory and mucolytic drugs are prescribed only by a doctor and are not required in every case. nine0005
Up
Fever
Fever is an increase in body temperature of more than 38 ºС. Some symptoms and laboratory and instrumental studies help to understand the cause of the fever and prescribe the necessary treatment.
If the fever is accompanied by a runny nose, cough, and "red throat", the most likely cause is a viral infection. Since antibiotics have no effect on viruses, antibiotic therapy in case of a viral infection is not prescribed. nine0005
High fever (greater than 39°C) with chills should alert. Other symptoms that require immediate medical attention are the refusal of the child to eat and drink, severe lethargy, lack of "eye" contact with the child.
Other symptoms that require immediate medical attention are the refusal of the child to eat and drink, severe lethargy, lack of "eye" contact with the child.
Parents should know how to help a child with a fever .
Only ibuprofen (10 mg/kg per dose) and paracetamol (15 mg/kg per dose) are allowed for use in children. From drugs based on ibuprofen in a pharmacy, you can buy nurofen, and from drugs based on paracetamol - panadol, cefecon, efferalgan. Metamizole sodium (or analgin), including as part of a "lytic mixture", can cause severe blood complications, and nimesulide (nimulide, nise) can cause life-threatening liver damage. If the child does not have a severe background pathology, such as heart disease or epilepsy, and if he satisfactorily tolerates fever (is interested in others, does not refuse to drink, does not complain of pain), antipyretic drugs are given at a temperature of 38.5 - 39ºС and above.
And there is no need to achieve a decrease in body temperature immediately to 36. 6 ºС! A good effect is considered to be a decrease in fever to 38 ºС. Safe and effective methods of physical cooling are rubbing with water at room temperature (not alcohol or vinegar!), which allows you to reduce body temperature by 0.5 - 1.0 ºС in a few minutes. However, if the child has chills, if he has cold hands and feet, rubbing will not be effective. In such cases, massage of the hands and feet helps, which reduces vasospasm and improves peripheral circulation, and antispasmodic drugs, such as no-shpa, are also used. nine0005
6 ºС! A good effect is considered to be a decrease in fever to 38 ºС. Safe and effective methods of physical cooling are rubbing with water at room temperature (not alcohol or vinegar!), which allows you to reduce body temperature by 0.5 - 1.0 ºС in a few minutes. However, if the child has chills, if he has cold hands and feet, rubbing will not be effective. In such cases, massage of the hands and feet helps, which reduces vasospasm and improves peripheral circulation, and antispasmodic drugs, such as no-shpa, are also used. nine0005
Up
False croup
In babies, false croup occurs quite often, so mothers need to know about it. Only parents can notice the first signs of narrowing of the larynx in time and help the child in time. The reason is viral infections. In children under 5 - 6 years of age, the airways are narrower than in adults, and therefore croup develops much more often. nine0026
 If this does not help, and the breath becomes noisy and difficult, call an ambulance without stopping the inhalation of steam.
If this does not help, and the breath becomes noisy and difficult, call an ambulance without stopping the inhalation of steam. What is false croup?
Croup is difficulty in breathing due to constriction of the larynx. To feel where the larynx is, you can put your hand on the front of the neck and make any sound - the larynx will vibrate. nine0005
This part of the airway is quite narrow, and if the mucous membrane swells, it can completely block the lumen of the larynx, and air will not enter the lungs. In children under 5 - 6 years of age, the airways are narrower than in adults, and therefore croup develops much more often.
Unlike false, true croup begins with diphtheria, when the lumen of the larynx is blocked by dense films. Thanks to vaccinations (DPT, ADS-M), this disease, fortunately, has become rare.
Pseudocroup is caused by acute viral infections (eg parainfluenza virus or respiratory syncytial virus). The mucous membrane becomes inflamed, swells, and although films do not form, as in diphtheria, the result is the same - it is difficult for the child to breathe. nine0005
The mucous membrane becomes inflamed, swells, and although films do not form, as in diphtheria, the result is the same - it is difficult for the child to breathe. nine0005
How does it all start?
Usually, the usual symptoms of acute respiratory infections appear first, i.e. runny nose, cough, fever. The first signs of the proximity of a false croup appear or intensify in the evening - this is a growing dry "barking" cough and a hoarse voice.
Then the breath becomes "noisy" - at first only during crying or anxiety, that is, when the baby breathes deeper and faster. After a while, these symptoms persist even in a calm state. nine0005
With croup, it is difficult for the baby to inhale exactly, that is, the inhalation turns out to be noisy, with effort, and the exhalation remains normal. During inhalation, you can notice how the jugular fossa (depression in the lower part of the neck between the collarbones) is drawn inward.
Is it possible to prevent false croup?
There are pathogens that most often cause croup: parainfluenza virus, influenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus. If a child has contracted this particular infection, the risk of developing croup is high, and, unfortunately, there are no remedies that protect against it. nine0005
There are children who get colds without this complication, but in some the mucous membrane is more prone to swelling, and if one episode of difficulty breathing with acute respiratory infections has already been, it is likely that such conditions will recur. Parents need to be ready for them - until the child grows up, and the croup ceases to threaten him.
What to do with false croup?
If you notice its signs, first of all, you need to calm yourself and the child, because when you are excited, the muscles of the larynx contract, and it becomes even harder to breathe. nine0005
nine0005
For a "barking" cough, as long as breathing is silent and not labored, steam inhalation may help. Turn on hot water in the bathroom, let the child breathe in moist air for a few minutes.
If this does not help and breathing becomes difficult (noisy breathing, indrawing of the jugular fossa), call an ambulance and continue to do steam inhalation until it arrives. The doctor will prescribe special inhalations with a local hormonal preparation for croup. Don't let the word "hormonal" scare you, because this drug works only in the respiratory tract, eliminating inflammation, and no other medicine for false croup will not be so effective. In severe cases, the doctor will inject a hormone (prednisolone or dexamethasone) intramuscularly. Don't worry about side effects because short cycles of hormones are safe and life-saving in these situations. nine0005
If you are offered to hospitalize your child, do not refuse, because after temporary relief, breathing problems may recur.
There are conditions that can be confused with false croup, such as inflammation of the epiglottis (cartilage that closes the larynx when swallowing). This disease is called epiglottitis: the child's temperature rises above 39 degrees, there is a severe sore throat, the mouth is difficult to open, and hormonal preparations do not help the child. nine0005
If the epiglottis is inflamed, the child is admitted to the hospital and treated with antibiotics. But this disease is rare, and false croup is caused by viruses, so it makes no sense to take antibiotics.
Is it possible to stop an attack of croup on your own?
If it is not the first time that a child has false croup, you can take home a special device for inhalation - a nebulizer (choose a compressor model, since ultrasound can destroy drugs used for croup). Your doctor will tell you what medication to have at home and how much to use if needed. nine0005
nine0005
The child can return to kindergarten as soon as the body temperature returns to normal and the child feels well.
Up
Vomiting and diarrhea
Acute gastroenteritis is characterized by an increase in body temperature (from subfebrile condition to high fever), vomiting, stool thinning. Rotavirus is the most common cause of gastroenteritis. The most severe is the first episode of rotavirus gastroenteritis in children from 6 months to 2-3 years. The peak incidence of this infection occurs in the winter - spring. nine0005
The danger of viral gastroenteritis is associated with rapid dehydration and electrolyte disturbances due to loss of water and salts in loose stools and vomiting. Therefore, feeding the child is of fundamental importance. In order not to provoke vomiting, you need to drink fractionally (1 - 2 teaspoons), but often, if necessary, every few minutes. For convenience, you can use a syringe without a needle or a pipette. In no case should you drink the child with just water, this only exacerbates electrolyte disturbances! There are special saline solutions for drinking - rehydron (optimally ½ sachet per 1 liter of water), Humana electrolyte, etc.
In no case should you drink the child with just water, this only exacerbates electrolyte disturbances! There are special saline solutions for drinking - rehydron (optimally ½ sachet per 1 liter of water), Humana electrolyte, etc.
The daily need for fluid is presented in the table:
Weight of the child Daily need for liquid
2 - 10 kg 100 ml/kg
10 - 20 kg + 50 ml/kg per kg over 10 kg
> 20 kg 1500 ml + 20 ml/kg for each kg over 20 kg
In addition, current fluid losses with loose stools and vomiting are taken into account - for each episode of diarrhea / vomiting, an additional 100 - 200 ml of fluid is given. nine0005
Intravenous rehydration (fluid replenishment with drips) is done only for severe dehydration and persistent vomiting. In all other cases, you need to drink the child - it is safe, effective and painless.
Smecta (but do not give smecta if it induces vomiting), espumizan or Sab simplex are used as adjuvants. Enterofuril is not recommended for use, as it is not effective either in viral infections or in invasive bacterial intestinal infections. In the diet during the acute period, fresh vegetables and fruits (except bananas), sweet drinks are excluded, and whole milk is limited only in older children. nine0005
Enterofuril is not recommended for use, as it is not effective either in viral infections or in invasive bacterial intestinal infections. In the diet during the acute period, fresh vegetables and fruits (except bananas), sweet drinks are excluded, and whole milk is limited only in older children. nine0005
Parents need to be aware of the first signs of dehydration - a decrease in the frequency and volume of urination, thirst, dry skin and mucous membranes. With increasing dehydration, the child becomes lethargic, stops urinating, thirst disappears, the skin loses turgor, and the eyes “sink”. In this case, there is no time to waste, it is necessary to call a doctor and hospitalize the child.
The appearance of blood and mucus in the stool in a child should be alerted, because this is typical for bacterial enterocolitis. Stool with such infections is not large (in contrast to copious watery stools with rotavirus infection), false urge to defecate and abdominal pain may be noted. Drinking water in such cases may not be enough, and, as a rule, antibiotics are required. nine0005
Drinking water in such cases may not be enough, and, as a rule, antibiotics are required. nine0005
Up
Pneumonia
One of the serious diseases in children is pneumonia, or pneumonia. Pneumonia can pose a threat to a child's life. Fortunately, modern medicine has learned to cope well with pneumonia, and this disease can be completely cured in most cases. Therefore, if your baby gets sick with fever and cough, contact your pediatrician. If pneumonia is suspected, a doctor may order an x-ray of the lungs to confirm the diagnosis. nine0005
What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung tissue, that is, the deepest part of the respiratory system. Normally, gas exchange occurs in the lungs, that is, oxygen from the air enters the blood, and carbon dioxide is released from the blood into the environment. When part of the lung is inflamed, the breathing function in the affected lung is affected and the child develops shortness of breath, that is, rapid and labored breathing. Substances produced during the immune system's fight against bacteria cause fever (if the body temperature rises above 38 ° C, this is called a fever). The accumulation of sputum in the alveoli and bronchi and swelling of the mucous membrane stimulate the cough reflex, and a cough occurs. If the focus of pneumonia is near the lining of the lung, called the pleura, chest pains may occur when breathing and coughing. nine0005
Substances produced during the immune system's fight against bacteria cause fever (if the body temperature rises above 38 ° C, this is called a fever). The accumulation of sputum in the alveoli and bronchi and swelling of the mucous membrane stimulate the cough reflex, and a cough occurs. If the focus of pneumonia is near the lining of the lung, called the pleura, chest pains may occur when breathing and coughing. nine0005
What causes pneumonia?
There are many infections that can cause pneumonia. Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common cause of so-called "typical" pneumonia. Pneumococcal pneumonia is accompanied by fever, cough, shortness of breath, lethargy, and decreased appetite. Less commonly, pneumonia is caused by other pathogens - hemophilus influenzae (Haemophilus influenzae) type b, pyogenic streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes) and Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus). "Atypical" pneumonia, which is usually milder and quite contagious, is caused by mycoplasmas and chlamydia. Less commonly, pneumonia is caused by viruses (adenovirus, RS virus) - such pneumonias are rare and can be very difficult. Pneumonia can develop suddenly or be a complication of the flu. nine0005
Less commonly, pneumonia is caused by viruses (adenovirus, RS virus) - such pneumonias are rare and can be very difficult. Pneumonia can develop suddenly or be a complication of the flu. nine0005
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
The most important symptom of pneumonia is fever. In a young child, fever may be the only manifestation. Fever above 39.5°C with chills and fever that is poorly reduced after taking antipyretic drugs should be especially alert. Although not always a high fever that does not respond well to antipyretics is a symptom of pneumonia. This may be a manifestation of a respiratory viral infection.
The second important symptom of pneumonia is a cough. The nature of the cough matters. Particularly alarming are the "deep" cough, cough at night and cough before vomiting.
Severe pneumonia is usually accompanied by shortness of breath, that is, rapid and labored breathing. Sometimes a symptom of pneumonia is pain in the abdomen, which occurs due to irritation of the pleura (lung membrane) during inflammation of the lung area adjacent to the pleura and due to frequent coughing and, accordingly, tension in the abdominal muscles. nine0005
nine0005
Very important signs that speak in favor of pneumonia are symptoms of intoxication, such as fatigue, weakness, refusal to eat and even drink. At the same time, unlike pneumococcal pneumonia, with mycoplasmal pneumonia, the child may feel well.
Coughing and wheezing in the lungs are symptoms not only of pneumonia, but also of bronchitis. It is very important that the doctor distinguishes pneumonia from bronchitis, since antibiotics are not always required for bronchitis and only if its mycoplasmal etiology is suspected. nine0005
What can happen if pneumonia is not treated?
This is fraught with complications that are more likely to occur if pneumonia is left untreated. Complications of pneumonia are inflammation of the pleura (pleurisy) and the formation of a cavity in the lung filled with pus (lung abscess). In such cases, a longer course of antibiotics will be required, and sometimes the help of a surgeon.
How to treat pneumonia?
If you have bacterial pneumonia, your doctor will prescribe an antibiotic. The doctor will decide which antibiotic to choose depending on the suspected cause of the pneumonia. In most cases, the child can be given the antibiotic by mouth (as a suspension or tablets) rather than by injection. The effect of the antibiotic occurs within 24-48 hours. If after 1 - 2 days the child does not feel better and the temperature rises, consult a doctor again. nine0005
Usually a child with pneumonia can be treated at home. Hospitalization is required for severe and complicated pneumonia, when the child needs intravenous antibiotics, supplemental oxygen, pleural punctures, and other serious medical interventions.
Give the child an antipyretic (ibuprofen or paracetamol) if the body temperature rises above 38.5 to 39°C. Antitussives, such as butamirate (Sinekod drug), are contraindicated in pneumonia.
Can pneumonia be prevented?
There are vaccines designed to protect against pneumococcus and Haemophilus influenzae, which cause the most severe forms of pneumonia (against pneumococcus - vaccines "Prevenar", "Pneumo 23", against Haemophilus influenzae - "Act-HIB", "Hiberix", a component against Haemophilus influenzae sticks are part of the Pentaxim vaccine, components against pneumococcus and Haemophilus influenzae are simultaneously part of Synflorix). Since pneumococcal pneumonia often develops as a complication of influenza, influenza vaccination is useful. It is very important that parents do not smoke in the presence of a child, as secondhand smoke makes the lungs weak and vulnerable. nine0005
Up
the pediatrician told how to help him - article on TSK
Night cough attacks deprive the child of sleep and prevent the body from restoring the strength needed to fight the disease. Of course, mothers are trying in every way to alleviate this unpleasant symptom.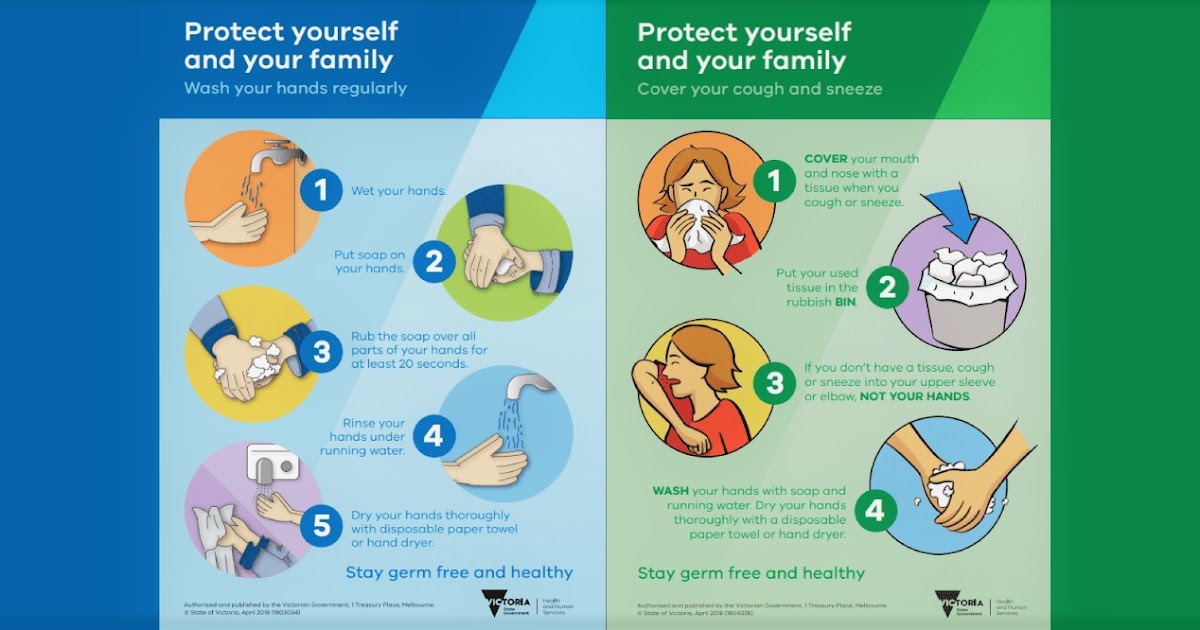 The problem is that this does not always work out, and the wrong actions can provoke an even more severe attack.
The problem is that this does not always work out, and the wrong actions can provoke an even more severe attack.
Pediatrician Ekaterina Volkova told how to understand the cause of a nighttime cough and provide a child of any age with the right help. nine0005
What the body defends against by coughing
Cough is not a disease. This is a symptom that indicates a problem, a natural reflex reaction that protects the body, helps the lungs get rid of the irritant and restore normal breathing. This means that we must fight with what irritates: a foreign body, mucus, dust, a pungent odor, and so on.
Main causes of coughing fits in children:
- acute respiratory diseases (viral and bacterial),
- Allergic reactions,
- Dry Air,
- teeth teething,
- Bronchial asthma,
- A foreign body in the respiratory tract,
- Diseases and anomalies of the development of the gastrointestinal tract,
- heart disease,
- submarine in the air of harmful air.
 substances.
substances.
Increasing cough at night occurs because at this time the blood circulation of organs and tissues slows down, sputum dissolves slowly and accumulates in the respiratory tract. Also, attacks often occur in the morning, when the child takes an upright position and coughs up what has accumulated during the night. nine0005
How to relieve nighttime coughing
The first thing parents should do if a child starts coughing at night is to try to understand what is the reason. Your task is to relieve the symptom and go to the doctor in the morning for advice or an appointment.
If the baby is teething
The cough in this case is often caused by increased salivation. You can alleviate the symptom by changing the position of the child. Try elevating the mattress or crib on the side of your head (for example, by placing a couple of books under the legs). So the head will be higher, and the child will not choke on saliva. nine0005
Don't put babies on pillows: babies who haven't learned to roll over with confidence risk suffocating when they bury their nose in it. In principle, a child up to a year in a crib should not have anything other than a mattress and a sheet with an elastic band.
In principle, a child up to a year in a crib should not have anything other than a mattress and a sheet with an elastic band.
If the child is sick
The golden rule, relevant for almost all illnesses, is to drink plenty of warm liquids throughout the day. This will help soothe an irritated throat, reduce the thickness of blood and the viscosity of sputum. It will be easier for the child to cough. nine0005
Breastfed babies should be offered the breast more often if they are sick. This will also avoid overdrying of the throat mucosa.
Severe runny nose often provokes nocturnal coughs. Make sure that the child can breathe freely through the nose. Before going to bed, the sinuses must be washed out: for example, with a light saline solution or special means. Try offering your child a higher pillow: this measure also helps to reduce the frequency of coughing.
Circular stroking movements on the back in the area of the bronchi reduce discomfort and soothe the child, and at the same time improve blood circulation and relieve spasm. Warming ointments also have a similar property. The method should be used for children older than three years with the so-called residual cough. nine0005
Warming ointments also have a similar property. The method should be used for children older than three years with the so-called residual cough. nine0005
Keep your child's feet warm. The warmer the feet, the more blood will flow to them, which means that the swelling in the lungs will decrease. However, be careful: woolen socks and heating pads are acceptable only if the child does not have a high fever.
All the methods described can only relieve the symptom for a short time. Adequate treatment, suitable drugs and dosage should be prescribed by a doctor.
If the cause of the nighttime cough is not obvious
Try changing the climate in the room. For comfortable breathing and cough relief, a temperature of +21 ° C and air humidity up to 50–60% are recommended. Turn on the ionizer or air humidifier, spread wet towels on the radiator, do wet cleaning - all this makes breathing easier. Do not be afraid to open a window or turn on the air conditioner: dry air is more dangerous for a coughing baby.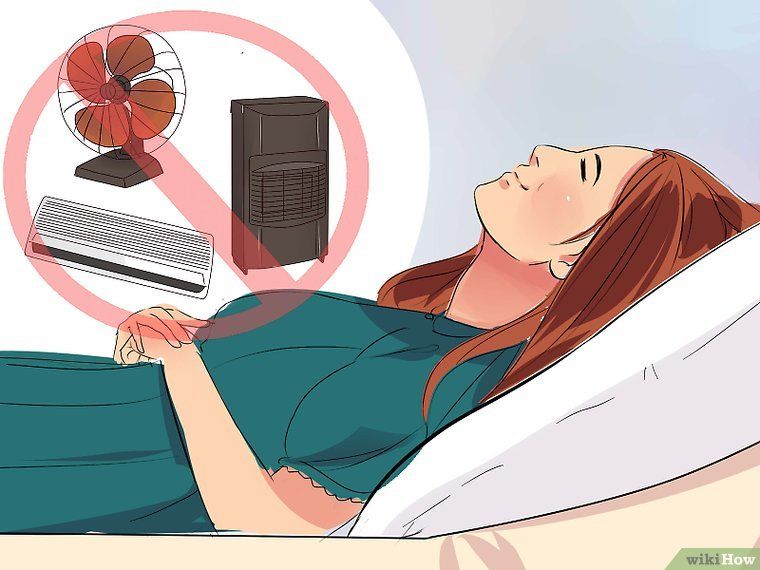 If you're worried, put your child in pajamas and warm socks. However, do not overdo it: too cold air can backfire, and the baby will begin to cough due to spasm when inhaling. nine0005
If you're worried, put your child in pajamas and warm socks. However, do not overdo it: too cold air can backfire, and the baby will begin to cough due to spasm when inhaling. nine0005
Another non-obvious reason for coughing can be allergies. Perhaps you recently changed your laundry detergent or installed a room air freshener, put in a new pillow or toy with an untested filler. The smell does not have to be strong for the baby to react to it with a cough. Watery eyes and puffiness will tell you that the cough is due to an allergic reaction.
What not to do during a nocturnal cough
- If the cough is accompanied by severe rhinitis (runny nose), do not immediately before going to bed, and even more so at night, instill vasoconstrictor drops into the child's nose. They dry out the mucous membrane and can additionally provoke a cough. The procedure is best done an hour before bedtime. nine0026
- Expectorants should not be given to the child during attacks of dry cough.