Bladder pain after birth
Bladder Problems After a Baby
Episiotomies and Tears
An episiotomy is where the muscle is cut to allow an easier birth. Tearing of the perineal tissues can be localised to small lacerations around the vagina to more complex tears involving the perineum and anal canal.
Third and Fourth Degree Tears
A third degree tear may involve damage to one or both of the circular muscles and a fourth degree tear will also include the lining of the anus. When this occurs, it is necessary for the tear to be stitched in theatre and that an epidural or spinal anaesthetic will be required.
At Home
At the time of discharge the following advice will be given to help with the healing process and reduce the risk of problems:
- Shower or bath at least once a day to keep the area clean and dry.
- Drink 2-3 litres of fluid every day and eat a healthy well balanced diet, including breakfast, to achieve a normal consistency stool.
- Do pelvic floor muscle exercises as soon as you can after birth. This will increase the circulation of blood to the area, reduce the swelling and ease discomfort. Establishing a routine of practicing pelvic floor muscle exercises whilst sitting feeding the baby and having a glass of fluid at hand to satisfy thirst, makes the most of the time available.
- Follow the programme of pelvic floor muscle exercises given to you by your midwife or physiotherapist to strengthen the muscles which will have been affected during pregnancy and delivery.
- Many women find that they have to rush to the toilet to have their bowels open or have problems controlling wind from the bowel during the first few weeks after delivery, but this control gradually improves. It can be helped by practicing anal sphincter exercises and bowel habit training will help to resist urgency and gradually increase the time between feeling sensation and the need to empty the bowel.

- Whilst the area is healing it may be necessary to take laxatives to make it easier to empty the bowel and to prevent constipation.
The next clinic appointment is usually 6-12 weeks after delivery. During this appointment the doctor/ midwife will check on the woman’s recovery, but most importantly it allows the woman to discuss any concerns that she has. Most women report no problems at this stage, those that do benefit from seeing a specialist physiotherapist who will help the woman to regain pelvic floor strength. Most women are able to have further vaginal delivery following a 3rd or 4th degree tear, if the tear has healed and there are no bowel control problems.
Haemorrhoids
Haemorrhoids, commonly known as piles, are enlarged and swollen blood vessels in or around the lower rectum and the anus.
Piles are common during or after pregnancy due to the pressure from the developing baby, hormonal changes and the delivery of the baby. There are a range of treatments available if they provide discomfort, although be sure to consult your Midwife or GP before seeking any of these.
There are a range of treatments available if they provide discomfort, although be sure to consult your Midwife or GP before seeking any of these.
Urinary Retention after Childbirth
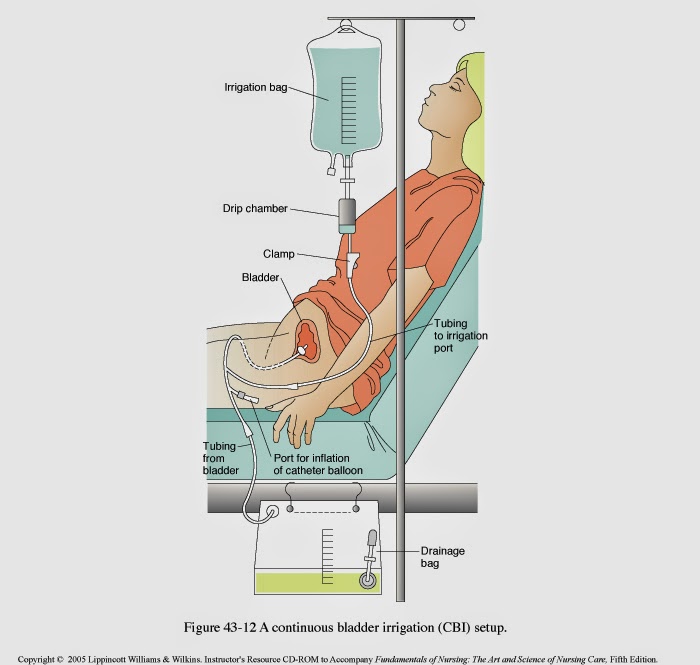
Difficulty passing urine or urinary retention, as it is known, is a common problem in the first day or two following childbirth, but with careful management this should resolve without long term consequences. The small numbers of women, who are unable to pass urine, experience the discomfort of a very full bladder and may need to self catheterise or use a temporary indwelling catheter .
Urinary retention may also present itself as having to pass small amounts of urine frequently – but only in very small amounts.
Research indicates that approximately 1 in 500 women may have a problem with bladder emptying which lasts longer than 3 days.
What Causes Urinary Retention?
Hormonal changes in pregnancy cause the bladder muscle to lose some of its tone and so bladder capacity increases from the third month of pregnancy.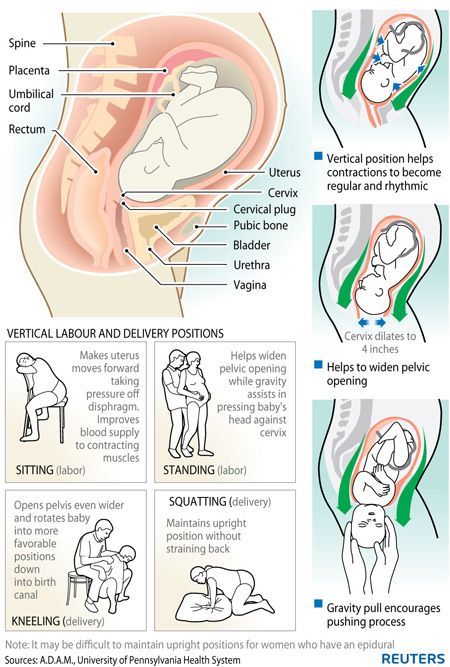 This increase may not be obvious to the pregnant woman apart from experiencing an increased number of visits to the toilet to empty her bladder.
This increase may not be obvious to the pregnant woman apart from experiencing an increased number of visits to the toilet to empty her bladder.
After delivery, the loss of tone of the bladder muscle can cause difficulties in emptying out.
There are procedures that may contribute to the development of difficulties in passing urine, such as: epidural for pain relief, long labour, prolonged second stage of labour, forceps or ventouse delivery and extensive vaginal lacerations. An effect of epidural or spinal anaesthetic is that it blocks normal sensation from the bladder and interferes with the normal bladder filling and emptying function. Bladder function should be closely monitored if an epidural is used.
Further Information
If you are experiencing any of the problems mentioned in this factsheet, you may wish to seek advice from your GP or local continence clinic. The continence clinics are run by the NHS and you don’t always need to be referred to a clinic by your GP, as some clinics will allow you to book an appointment yourself.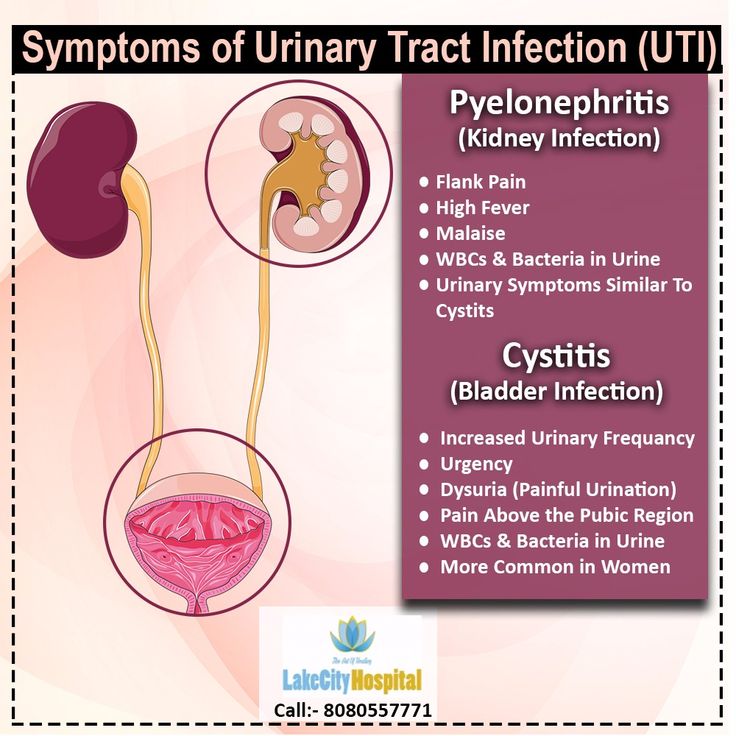 You may wish to use our search tool to find your nearest clinic. Pelvic floor muscle exercises are also very useful for strengthening the muscles that support the bladder and bowel. Performing these exercises can help alleviate symptoms and can often prevent the problem from worsening.
You may wish to use our search tool to find your nearest clinic. Pelvic floor muscle exercises are also very useful for strengthening the muscles that support the bladder and bowel. Performing these exercises can help alleviate symptoms and can often prevent the problem from worsening.
For more information about Pelvic floor muscle exercises, please use our guide below:
Quick Facts: Postpartum Bladder and Kidney Infections
Quick Facts
By
The Manual's Editorial Staff
Full review/revision Aug 2022 | Modified Sep 2022
VIEW PROFESSIONAL VERSION
Get the full details
Topic Resources
Postpartum refers to the time period after you have a baby. It's usually considered the first 6 weeks after delivery.
It's usually considered the first 6 weeks after delivery.
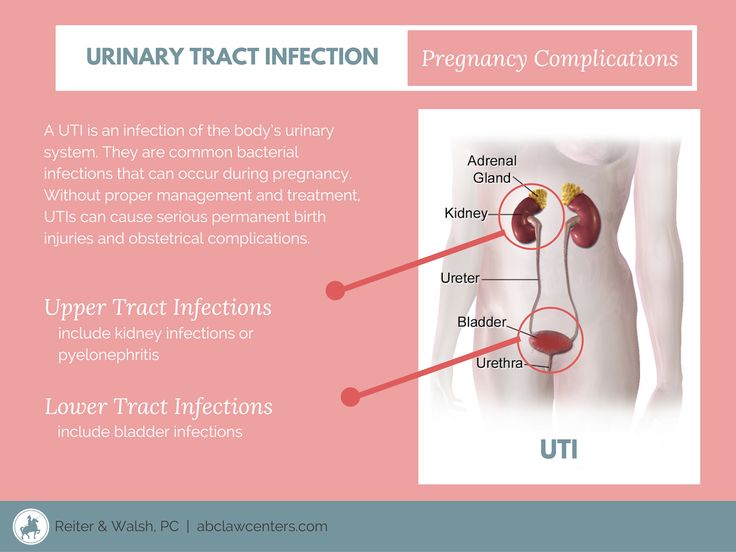
Your kidneys are 2 bean-shaped organs that make urine. Your bladder is a hollow organ that holds urine until you pee. You can get a bladder infection (cystitis Bladder Infection Your bladder is the hollow organ that holds urine until you're ready to urinate (pee). A bladder infection is usually caused by bacteria. Bladder infections are also called cystitis. Bladder... read more ) or kidney infection Kidney Infection Your kidneys are the 2 bean-shaped organs that filter waste products out of your blood and make urine. Sometimes a kidney gets infected by bacteria. Kidney infections are usually caused by the... read more if bacteria get into these organs after delivery Delivery Delivery is the passage of the fetus and placenta (afterbirth) from the uterus to the outside world. (See also Overview of Labor and Delivery.) For delivery in a hospital, a woman may be moved... read more .
The Urinary Tract
Symptoms of a bladder or kidney infection include pain when you pee or needing to pee often
Doctors treat the infection with antibiotics
You’re more likely to get a postpartum bladder infection if you had a catheter (thin, flexible tube) put in your bladder to drain urine before or after you give birth
Symptoms include:
Pain when you pee
Needing to pee often
Fever
Pain in your lower back or side
Feeling sick all over
Doctors do a urine test to check for bladder and kidney infections.
Doctors treat postpartum bladder and kidney infections with antibiotics. Your doctor may also have you drink plenty of fluids to help your kidneys work well and flush the bacteria out of your body.
Doctors will do another urine test 6 to 8 weeks after your baby is born to make sure the infection is cured.
NOTE: This is the Consumer Version. DOCTORS: VIEW PROFESSIONAL VERSIONVIEW PROFESSIONAL VERSION
Copyright © 2023 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Test your knowledge
Take a Quiz!Urination disorders after childbirth
24.04.2020
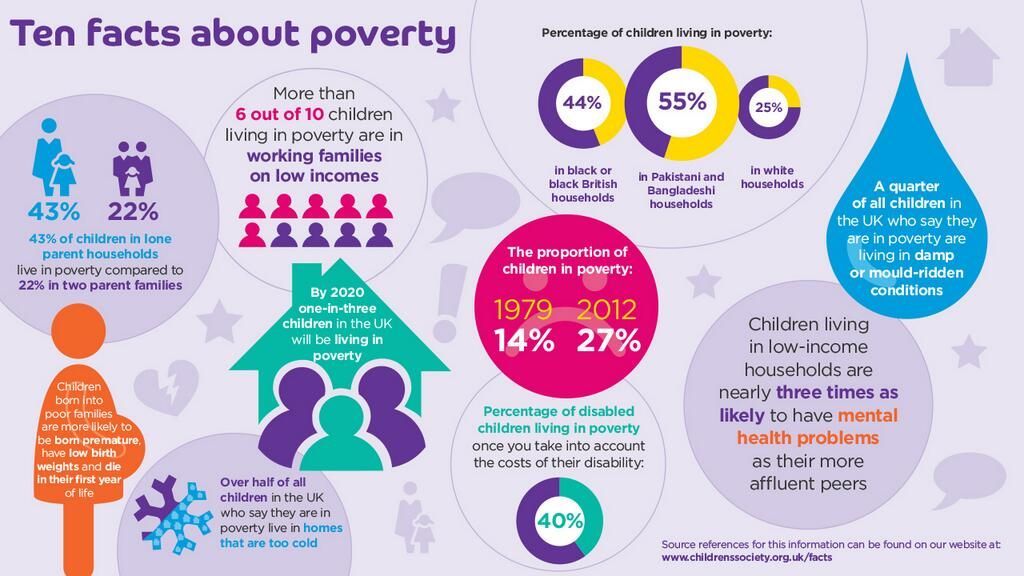
Problems with urination after childbirth are not uncommon. About 80% of new mothers suffer from this problem.
About 80% of new mothers suffer from this problem.
Types of urinary disorders after childbirth
The bladder sometimes suffers from the following disorders:
- urinary incontinence . Characteristic mainly for natural births . The cause may be a large fruit; nine0022
- no signal to urinate . After the birth of a child, the tone of the bladder decreases, the uterus does not press on it, swelling of the walls appears, it becomes larger due to the fullness of urine . In most cases, after a couple of days, the urinary organ returns to normal, and the process of isolating urine does not cause inconvenience;
- pain during urination. Perineal lacerations, stitches and minor injuries cause discomfort during urination . Urine irritates mucous membranes, so pain occurs.
 After the stitches are removed and the perineum is completely healed, the painful condition goes away;
After the stitches are removed and the perineum is completely healed, the painful condition goes away; - urination more often than usual. Fluid is excreted from the body after births , which leads to frequent trips to the toilet. Note: The bladder is inflamed if a small amount of urine is excreted .
Elimination of the causes of urination disorders
Having noticed problems with urination after childbirth , it is important to contact a doctor in time to prescribe a comprehensive treatment. The gynecologist will examine the patient, prescribe a urine test , in some cases ultrasound of the small pelvis, computed tomography, send a consultation to the urologist . Drugs are prescribed that are allowed during feeding breastfeeding .
If the problem is lack of urge to urinate , urine is removed with a catheter. The procedure is painless, but not without it. However, this method should not be abused so as not to injure or infect the ureter .
14 days after births physical activity is allowed. They have a beneficial effect on the body, as they normalize metabolism, increase blood flow, improve urination , the abdominal muscles become elastic, the respiratory system returns to normal.
It is recommended to ride a bicycle, do breathing exercises, train all muscles, especially the pelvic muscles, swim in a pool of warm water, leisurely walks.
An effective remedy is the knee-elbow position, in which it is desirable to stay for 20 minutes, which contributes to a better excretion of urine .
You can do Kegel exercises (squeeze and unclench muscles in your free time vagina ). It is convenient to perform these exercises even outside the home, for example, at the workplace, in transport, in a supermarket.
It is convenient to perform these exercises even outside the home, for example, at the workplace, in transport, in a supermarket.
Proper nutrition and fluid intake will restore normal bladder function . It is necessary to give up spicy, salty foods, exclude seasonings, alcohol, cocoa, coffee, tea.
The ultimate solution to the problem is surgical intervention . It is carried out in case of progression of the disease, the absence of visible results after drug treatment. nine0003
The sooner a woman turns to doctor for qualified help, the sooner she will return to a full life. The baby needs a happy mother, and this largely depends on her health.
Published in Pregnancy & Pregnancy Premium Clinic
Postpartum Cystitis ⛑ Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Postpartum Cystitis
Inflammation of the bladder shortly after childbirth—postpartum cystitis—is relatively rare in the era of antibiotics.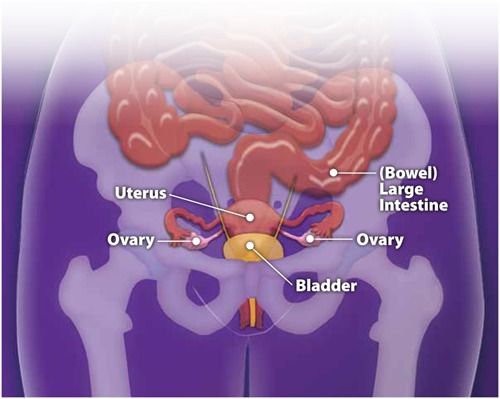 Statistics say that only 1 to 4% of puerperas are at risk of experiencing it 1 . And, as a rule, all such patients had manifestations of the disease even before pregnancy.
Statistics say that only 1 to 4% of puerperas are at risk of experiencing it 1 . And, as a rule, all such patients had manifestations of the disease even before pregnancy.
That is, childbirth exacerbates an existing bladder infection. Therefore, it makes sense for women to take care of their health in advance, before conception.
The complex phytopreparation Canephron ® N will help with this. The product produced using the phytoneering technology has a strictly dosed composition of each tablet or drop, and has proven effectiveness against acute and chronic cystitis 2, 3 .
Prophylactic treatment during pregnancy planning will help maintain urinary health during pregnancy. And it can save you from having to take anti-cystitis medications in the postpartum period when you need to breastfeed your baby.
Symptoms and signs of cystitis after childbirth
Symptoms of cystitis after childbirth are not much different from the classical clinical picture.
During the first 2 weeks after childbirth, puerperas begin to be disturbed:
- discomfort and pain in the area of the bladder, lower abdomen;
- irresistible urge to jog a little every 30-60 minutes;
- portions of urine are meager, the feeling of emptying the bladder does not come for long;
- in the process of urination, pain, burning are noted.
Temperature may remain unchanged, but fever is also possible.
In general, the severity of manifestations is determined by the type of disease. Subacute is milder, gangrenous - acute, with fever and a critical deterioration in general condition 4 .
Approximately 40% of patients will have mild disease and will not require antibiotic therapy 5 . If cystitis causes serious inconvenience and spoils the quality of life, you can turn to herbal medicine.
Canephron ® N drops or tablets contain a complex of active ingredients of plant origin that have anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic and antibacterial effects in urinary bladder infections 6 . And, if necessary, can be used during lactation 7 .
And, if necessary, can be used during lactation 7 .
Causes of puerperal cystitis
The main cause of puerperal cystitis is an inadequately treated bladder infection before pregnancy. The peculiarity is that infection can take place long before conception:
- neglect of hygiene procedures;
- frequent unprotected intimacy with a risk of contracting sexually transmitted infections;
- life in asocial conditions, when a woman simply neglects hygiene and prevention of urinary infections. nine0022
Secondary cause: during birth through the birth canal, the baby changes the anatomical parameters of the pelvic organs, including the bladder. Such changes weaken the immune system of the body and contribute to the activation of the infection.
Often the causative agent is Escherichia coli - a bacterium that enters the bladder from the vagina with vaginosis and as a result of neglect of sexual hygiene.
The problem is that E.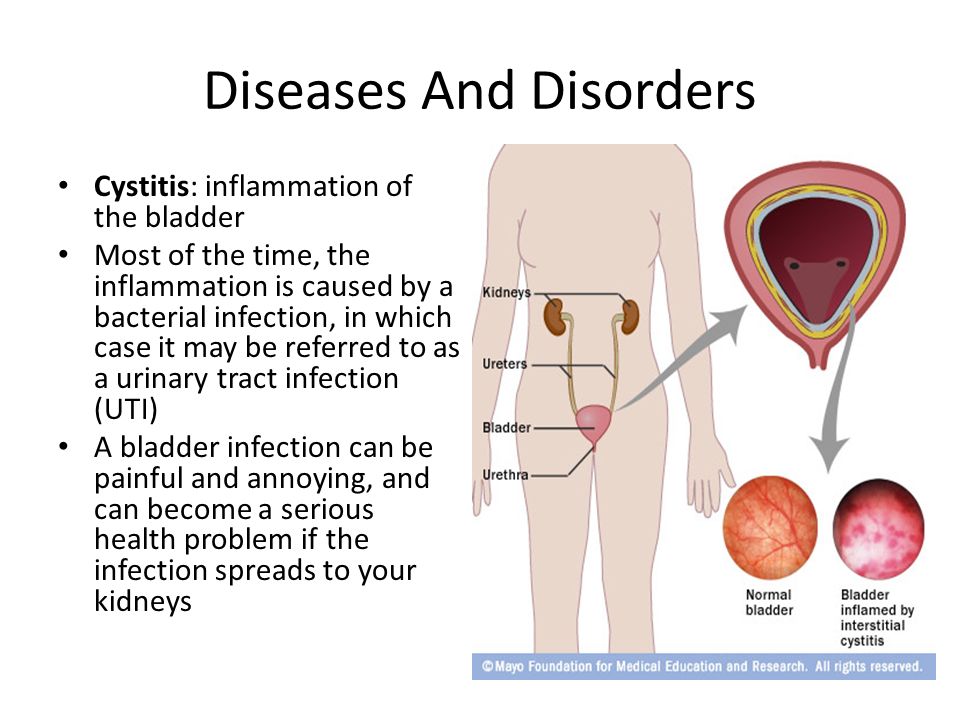 coli is often resistant to antibiotics, deeply embedded in the lining of the bladder. And therefore, even before pregnancy, such cystitis is difficult to treat with chemotherapy drugs. In addition, viruses can be the causative agent. nine0003
coli is often resistant to antibiotics, deeply embedded in the lining of the bladder. And therefore, even before pregnancy, such cystitis is difficult to treat with chemotherapy drugs. In addition, viruses can be the causative agent. nine0003
Against this background, bioflavonoids, alkaloids and phenolcarboxylic acids of the components of Canephron ® H 6 give the best effect.
Treatment of cystitis after childbirth
Treatment of any infection in a woman who has just given birth is a complex medical problem. For each sick woman in childbirth, a decision is made individually, so you need to consult a doctor.
The traditional approach to treating cystitis after childbirth involves the use of antibiotics. In order to kill pathogenic bacteria and not harm the baby, women stop breastfeeding for the duration of treatment. nine0003
It is rational to do a urine culture before prescribing drugs and check to which drugs the bacteria-causative agents of the process have retained sensitivity 8 .
With extended resistance of microbes, it is advisable to add Canephron ® N to the treatment regimen, because it actively works even with antibiotic resistance. Drops and tablets Canephron ® N are produced using phytoneering technology - strict quality control from the stage of seed selection to the preparation of dosage forms. nine0003
The active components of the three medicinal plants themselves have a marked antibacterial effect. Plus, make bacteria more susceptible to antibiotics 9 . It is important to note that the antibacterial effect of Kanefron ® N is primarily associated not with the aggressive action of the drug against microorganisms, but with the suppression of the ability of Escherichia coli to attach to the bladder epithelium. For this reason Canephron ® N, unlike antibiotics, is safe for beneficial intestinal microflora. nine0003
At the end of treatment for cystitis, the woman can resume breastfeeding.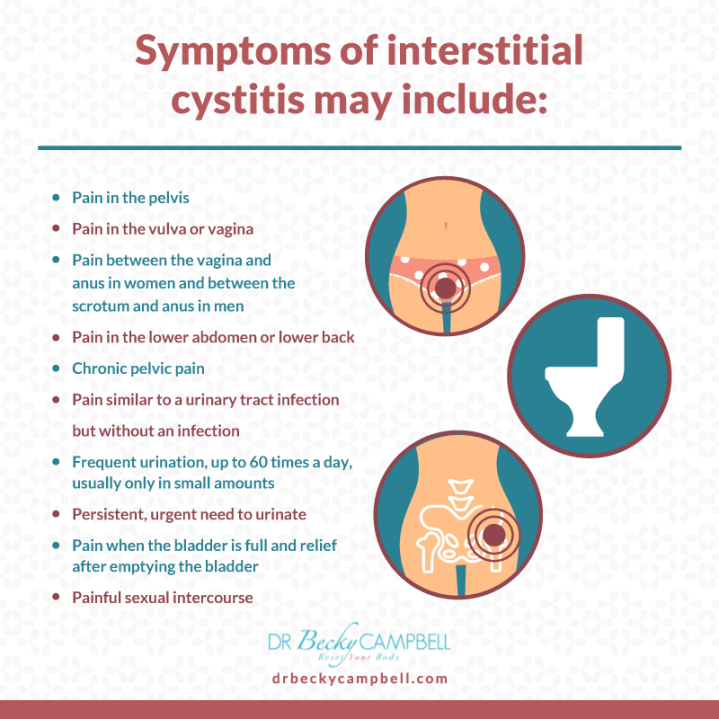
Prevention of cystitis after childbirth
Preventing the development of postpartum cystitis is easy and difficult at the same time.
On the one hand, it is enough to protect yourself from genitourinary infections, not to infect the membrane of the bladder before pregnancy and childbirth. Use condoms, lube. But it is very rare to maintain the sterility of the urinary tract.
On the other hand, if the infection did take place, then it is not always possible to completely get rid of pathogens. Even in the absence of symptoms of cystitis, many women have asymptomatic bacteriuria - the excretion of microbes in the urine. Therefore, at the stage of observation in the antenatal clinic, pregnant women are examined for the sterility of the urogenital area. nine0003
Shortly before delivery, the bacterial purity of the vaginal mucosa is assessed. If pathogenic microbes are found, local treatment is prescribed. The vagina is treated with antibacterial gels, ointments, candles are placed, hygiene procedures are carried out.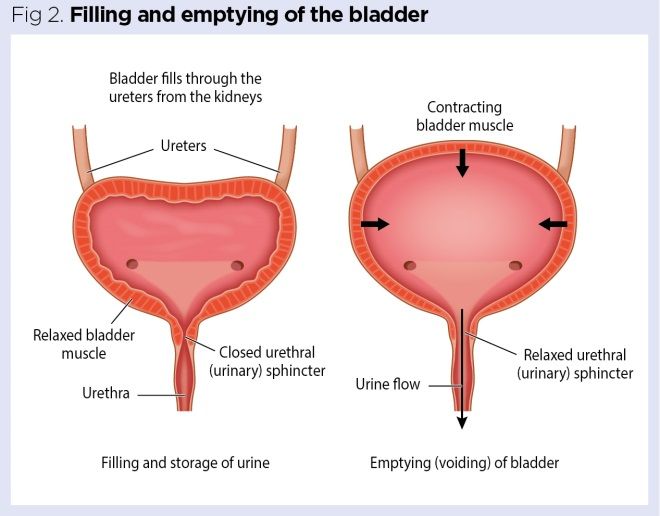 By such measures, the safety of the vagina is achieved and the risk of infection of the bladder during childbirth is removed.
By such measures, the safety of the vagina is achieved and the risk of infection of the bladder during childbirth is removed.
But the best prevention of cystitis after childbirth is the adequate treatment of inflammation at the stage of preparation for pregnancy. Here you can apply the whole range of available methods, one of the safest and most effective is taking Kanefron 9 drops or tablets.0121 ® N for 2-4 weeks. It can be combined with antimicrobial drugs.
1 Le J., Briggs F. F., McKeown A., Bustillo G. Urinary tract infections during pregnancy. Ann. Pharmacother. 2004; 38(10): 1692-701.
2 Amdiy Refat Eldarovich, Al-Shukri Salman Khasunovich, and co-authors. "Experience in the use of Kanefron in the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis in women" Urological Gazette, vol. 6, No. 2, 2016, pp. 16-22.
3 Yu.G. Alyaev, A.V. Amosov, E.A. Sultanova // "Possibilities of using Kanefron N in the treatment of chronic cystitis", ММА them. THEM. Sechenov. "EFFICIENT PHARMACOTHERAPY. Urology and Nephrology" №2.
THEM. Sechenov. "EFFICIENT PHARMACOTHERAPY. Urology and Nephrology" №2.
4 Rai, Rakhi et al. “Gangrenous Cystitis in A Woman Following Vaginal Delivery: An Uncommon Occurrence - A Case Report.” Journal of clinical and diagnostic research : JCDR 9.11 (2015): QD13-4.
5 Ferry S. A., Holm S. E., Stenlund H., Lundholm R., Monsen T. J. The natural course of uncomplicated lower urinary tract infection in women illustrated by a randomized placebo controlled study. J. Infect. Dis. 2004; 36(4):296-301.
6 R. E. Amdiy. "Possibilities for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis in women without the use of antibiotics" Urological Gazette, no. Special issue, 2019, pp. 16-17.
7 Instructions for use "Canephron ®".
8 Grabe M., Bartoletti R., Bjerklund-Johansen T. E., Botto H., Cai T., Qek M., Koves B., Naber K. G., Pickard R. S., Tenke P., Wagenlehner F., Wullt B Guidelines on urological infections.