Brown spots pregnancy
Skin Conditions During Pregnancy | ACOG
-
Many women notice changes to their skin, nails, and hair during pregnancy. Some of the most common changes include the following:
-
Dark spots on the breasts, nipples, or inner thighs
-
Melasma—brown patches on the face around the cheeks, nose, and forehead
-
Linea nigra—a dark line that runs from the navel to the pubic hair
-
Stretch marks
-
Acne
-
Spider veins
-
Varicose veins
-
Changes in nail and hair growth
-
-
Some are due to changes in hormone levels that happen during pregnancy. But for most skin changes health care professionals are not sure of the exact cause.
-
Dark spots and patches are caused by an increase in the body's melanin—a natural substance that gives color to the skin and hair. The patches are called melasma or "the mask of pregnancy."
To help prevent melasma from getting worse, wear sunscreen and a wide-brimmed hat every day when you are outside. The sun's UV rays can reach you even on cloudy days.
Dark spots and melasma usually fade on their own after you give birth. But some women may have dark patches that last for years. If melasma does not go away, you can talk with a dermatologist about treatment options. Dermatologists are specialists in skin conditions.
-
As your belly grows during pregnancy, your skin may become marked with reddish lines called stretch marks. These marks occur when the skin stretches quickly as the fetus grows.
 By the third trimester, many pregnant women have stretch marks on the abdomen, buttocks, breasts, or thighs. Sometimes the marks are faint. Sometimes they can be quite dark.
By the third trimester, many pregnant women have stretch marks on the abdomen, buttocks, breasts, or thighs. Sometimes the marks are faint. Sometimes they can be quite dark.There are many products on the market that claim to prevent stretch marks. There is no proof that any of these treatments work. Using a heavy moisturizer may help keep your skin soft, but it will not help get rid of stretch marks. Most stretch marks fade after the baby is born, but they may never disappear completely.
-
Many women have acne during pregnancy. Some already have acne and notice that it gets worse during pregnancy. Other women who may always have had clear skin may develop acne while they are pregnant.
-
If you get acne during pregnancy, take these steps to treat your skin:
-
Wash your face twice a day with a mild cleanser and lukewarm water.

-
If you have oily hair, shampoo every day and try to keep your hair off your face.
-
Avoid picking or squeezing acne sores to lessen possible scarring.
-
Choose oil-free cosmetics.
-
-
Over-the-counter (OTC) products containing the following ingredients can be used during pregnancy:
If you want to use an OTC product that contains an ingredient not on this list, contact your obstetrician–gynecologist (ob-gyn).
-
Some prescription acne medications should not be used while you are pregnant:
-
Hormonal therapy—Several medications that block specific hormones can be used to treat acne. Their use during pregnancy is not recommended due to the risk of birth defects.

-
Isotretinoin—This drug is a form of vitamin A. It may cause severe birth defects in fetuses, including intellectual disabilities, life-threatening heart and brain defects, and other physical deformities.
-
Oral tetracyclines—This antibiotic can cause discoloration of the fetus’s teeth if it is taken after the fourth month of pregnancy and can affect the growth of the fetus's bones as long as the medication is taken.
-
Topical retinoids—These medications are a form of vitamin A and are in the same drug family as isotretinoin. Unlike isotretinoin, topical retinoids are applied to the skin, and the amount of medication absorbed by the body is low. But it is generally recommended that use of these medications be avoided during pregnancy. Some retinoids are available by prescription. Other retinoids can be found in some OTC products. Read labels carefully.
If you are concerned about which products to use to treat your acne, talk with your dermatologist and ob-gyn.
 Together you can decide which option is best for you.
Together you can decide which option is best for you. -
-
Hormonal changes and the higher amounts of blood in your body during pregnancy can cause tiny red veins, known as spider veins, to appear on your face, neck, and arms.
Spider veins are most common during the first half of pregnancy. The redness should fade after the baby is born.
-
The weight and pressure of your uterus can decrease blood flow from your lower body and cause the veins in your legs to become swollen, sore, and blue. These are called varicose veins. Varicose veins can also appear on your vulva and in your vagina and rectum (usually called hemorrhoids). You are more likely to have varicose veins if someone else in your family has had them.
In most cases, varicose veins are a cosmetic problem that will go away after delivery.

-
You cannot prevent them, but there are some things you can do to ease the swelling and soreness and prevent varicose veins from getting worse:
-
Be sure to move around from time to time if you must sit or stand for long periods.
-
Do not sit with your legs crossed for long periods.
-
Prop your legs up on a couch, chair, or footstool as often as you can.
-
Exercise regularly—walk, swim, or ride an exercise bike.
-
Wear support hose.
-
Avoid constipation by eating foods high in fiber and drinking plenty of liquids.
If a tender, red spot appears on your leg, it should be checked by your health care professional.
-
-
The hormone changes in pregnancy may cause the hair on your head and body to grow or become thicker.
 Sometimes women grow hair in areas where they do not normally have hair, such as the face, chest, abdomen, and arms.
Sometimes women grow hair in areas where they do not normally have hair, such as the face, chest, abdomen, and arms.Your hair should return to normal within 6 months after giving birth. In the meantime, it is safe to use tweezing, waxing, and shaving to remove unwanted hair during pregnancy.
-
About 3 months after childbirth, most women begin to notice hair loss from the scalp. This happens because hormones are returning to normal levels, which allows the hair to return to its normal cycle of growing and falling out. In most cases, your hair should grow back completely within 3 to 6 months.
-
Some women find that their nails grow faster during pregnancy. Others notice that their nails split and break more easily. Like the changes to your hair, changes that affect your nails will ease after birth.

-
Some uncommon health conditions can arise during pregnancy and cause skin changes. These include the following:
-
Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP)
-
Prurigo of pregnancy
-
Pemphigoid gestationis
-
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP)
-
-
In PUPPP, small, red bumps and hives appear on the skin later in pregnancy. The bumps can form large patches that can be very itchy. These bumps usually first appear on the abdomen and can spread to the thighs, buttocks, and breasts.
It is not clear what causes PUPPP. It usually goes away after you give birth. In the meantime, your health care professional may prescribe anti-itch medication to help with the itching.

-
With prurigo of pregnancy, tiny, itchy bumps that look like insect bites can appear almost anywhere on the skin. This condition can happen anytime during pregnancy. It usually starts with a few bumps that increase in number each day. It is thought to be caused by changes in the immune system that occur during pregnancy.
Prurigo can last for several months and may even continue for some time after the baby is born. It is usually treated with anti-itch medication applied to the skin and other medications, such as antihistamines and corticosteroids.
-
Pemphigoid gestationis is a rare skin condition that usually starts during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy or sometimes right after childbirth. With this condition, blisters appear on the abdomen, and in severe cases, the blisters can cover a wide area of the body.
 It is thought to be an autoimmune disorder. Sometimes the condition returns during future pregnancies.
It is thought to be an autoimmune disorder. Sometimes the condition returns during future pregnancies.There is a slightly increased risk of pregnancy problems with this condition, including preterm birth and a smaller-than-average baby. There is also a small chance that your baby will have similar blisters at the time of birth. These blisters are usually mild and go away within a few weeks.
If your health care professional diagnoses pemphigoid gestationis after checking your blisters, you and your fetus should be monitored closely during the last part of pregnancy. Your health care professional may also give you medications to control the outbreak of blisters and help relieve your discomfort.
-
ICP is the most common liver condition that happens during pregnancy. Bile is a substance that is made in the liver. Bile travels from the liver to the small intestine, where it is used to break down fats in food.
 In ICP, this flow of bile is blocked and the components of bile are deposited in the skin.
In ICP, this flow of bile is blocked and the components of bile are deposited in the skin.The main symptom of ICP is severe itching in the absence of a rash. Itching commonly occurs on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, but it can also spread to the trunk of the body. It is typically worse at night.
Symptoms usually start during the third trimester of pregnancy and often go away a few days after childbirth. But ICP can happen again in future pregnancies.
If your health care professional diagnoses ICP after doing blood tests, you and your fetus should be monitored closely during the third trimester. Close monitoring is needed because ICP may increase the risk of preterm birth and other problems, including, in rare cases, stillbirth. In some cases, your ob-gyn may recommend an early delivery to help reduce the risk of stillbirth. You may also be given medication to help control severe itching.
-
Women who already have certain skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, may see their conditions worsen or improve while they are pregnant.
 The changes are different for every woman and every pregnancy.
The changes are different for every woman and every pregnancy.If you have any type of skin disease, let your ob-gyn know of any changes in signs or symptoms during your pregnancy. You should also review any medications that you take to treat your condition with your ob-gyn to make sure they are safe to use during pregnancy.
-
For conditions that cause itchy skin, using an over-the-counter anti-itch cream may help provide relief. You also can try the following tips:
-
Wash with mild, fragrance-free soaps.
-
Add uncooked oatmeal or baking soda to your bath.
-
Place a cool, wet cloth on the area to ease the burn.
-
Use a heavy moisturizer on your skin twice a day.
-
-
Antibiotic: A drug that treats certain types of infections.
Autoimmune Disorder: A condition in which the body attacks its own tissues.
Bile: A substance made by the liver that helps digest fats.
Hormone: A substance made in the body that controls the function of cells or organs.
Immune System: The body’s natural defense system against viruses and bacteria that cause disease.
Linea Nigra: A line running from the belly button to pubic hair that darkens during pregnancy.
Melasma: A common skin problem that causes brown to gray-brown patches on the face. Also known as the “mask of pregnancy.”
Obstetrician–Gynecologist (Ob-Gyn): A doctor with special training and education in women's health.
Preterm: Less than 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Rectum: The last part of the digestive tract.
Stillbirth: Birth of a dead fetus.
Trimester: A 3-month time in pregnancy.
 It can be first, second, or third.
It can be first, second, or third.Uterus: A muscular organ in the female pelvis. During pregnancy this organ holds and nourishes the fetus.
Vagina: A tube-like structure surrounded by muscles. The vagina leads from the uterus to the outside of the body.
Vulva: The external female genital area.
Don't have an ob-gyn? Search for doctors near you.
FAQ169
Last updated: July 2022
Last reviewed: December 2021
Copyright 2022 by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. All rights reserved. Read copyright and permissions information.
This information is designed as an educational aid for the public. It offers current information and opinions related to women's health. It is not intended as a statement of the standard of care. It does not explain all of the proper treatments or methods of care. It is not a substitute for the advice of a physician. Read ACOG’s complete disclaimer.
Read ACOG’s complete disclaimer.
Melasma in Pregnancy: Treatment and Causes
Your body goes through tremendous changes during pregnancy.
Your belly gets larger and your blood volume increases as your baby grows. You may experience cramping, morning sickness, and all sorts of unfamiliar aches and pains. Your hair and skin may also go through a transformation for the better — or worse. (You’re beautiful all the same.)
If you’ve noticed dark patches of skin on your face, you may have melasma. Here’s more about this condition, why it crops up in pregnancy, and how you can treat it safely.
Melasma is a skin disorder where the melanocytes (color-producing cells) in your skin produce extra pigment for some reason. In pregnancy, it’s often referred to as chloasma, or the “mask of pregnancy.”
Chloasma is a cosmetic concern. It doesn’t affect your baby in any way or indicate any other pregnancy complications.
People with more pigment in their skin — for example, those of African, North African, Middle Eastern, Latin or Hispanic, Asian, Indian, or Mediterranean descent — are more likely to develop chloasma, as they naturally have more active melanin production.
Overall, between 50 and 70 percent of people will develop some form of melasma during pregnancy.
Related: Skin color needs to be factored in when discussing skin diseases
The primary symptom of chloasma is darkening of the skin on the face. You may notice dark patches or splotches on your forehead, cheeks, chin, or around your mouth. These areas may get darker the more you’re exposed to the sun or the further along you are in your pregnancy.
Pain, itchiness, or soreness are not symptoms of melasma. If you experience these signs or develop severe irritation, you may be dealing with another condition. Bring up any additional symptoms you have with your doctor.
A dermatologist can accurately diagnose your condition using a Wood’s lamp, which helps show whether a skin condition is bacterial, fungal, or otherwise concerning.
Skin hyperpigmentation during pregnancy is very common. You may notice your nipples/areolas, armpits, or genitals become darker. You may see a line (linea nigra) extending from the pubic area over the belly, or darkening of the skin all over the body.
You may see a line (linea nigra) extending from the pubic area over the belly, or darkening of the skin all over the body.
Changing hormones, particularly the excess of estrogen and progesterone, is the main cause of melasma during pregnancy. Beyond that, the dark patches on the face can be exacerbated by sun exposure, the use of certain skin care products or treatments, and even genetics.
Chloasma may also be worsened by hormonal imbalances that may have been present even before pregnancy.
Whatever the case, your melanocyte-stimulating hormones react to these triggers by making an excess of protective pigments (dark patches) on the skin called melanin.
Melasma may start at any point in your pregnancy, though it most commonly begins in the second or third trimester.
Again, there are a variety of factors at play when it comes to darkening pigment. Your skin color and type may make this condition more or less noticeable. How much you’re out in the sun or even the time of year when you’re pregnant may also affect when you first notice it.
The good news is that this hyperpigmentation likely won’t get worse after you deliver your child. That said, it may take time — possibly months — for it to completely fade without any targeted treatment.
Speak with your doctor about ways to treat your melasma during pregnancy. Your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist for more information.
Some experts don’t recommend treating melasma during pregnancy. One reason is that it may resolve on its own. And some treatment methods may not be safe or effective to use when pregnant.
The best course of treatment may actually be prevention, with the help of a few lifestyle changes.
Seek shade
Since the sun may trigger the development of more pigment, it’s a good idea to stay out of its rays, especially for long periods of time.
Yes, this also applies to tanning beds or any other environment where you would be exposed to UVA and UVB rays. Limit sunbathing and try relaxing under a tree or umbrella instead.
If you’re exercising, try avoiding peak sun hours in your area, generally the middle of the day. Head out early in the morning or later in the evening when the sun is low.
Wear sunscreen
This doesn’t mean you have to stay indoors when the sun is out, though. Wearing a good pregnancy-safe sunscreen with SPF 30+ is key.
Look for products that contain zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, or other physical blockers (mineral sunscreens) versus those that rely on chemical blockers. Physical blocking sunscreens tend to offer broader protection and may be less irritating to the skin.
Dress for success
Another option for sun cover is clothing with or without UV protection, such as SPF rash guards or sun protective clothing. Even if it’s hot outside, loose-fitting clothing can be comfortable and protect your skin.
What about the face? Wide brimmed hats are your best friend. And don’t forget a stylish pair of sunglasses — the bigger the better.
Use gentle skin care products
Face washes, lotions, and serums that irritate your skin may make melasma worse. Slather up with gentle products instead. Look on the label for words like “noncomedogenic,” “sensitive,” “fragrance-free,” or “dermatologist approved” if you get overwhelmed in the beauty aisle.
Slather up with gentle products instead. Look on the label for words like “noncomedogenic,” “sensitive,” “fragrance-free,” or “dermatologist approved” if you get overwhelmed in the beauty aisle.
The same goes for makeup you may use to conceal the dark areas. Look for noncomedogenic or hypoallergenic foundations, concealers, powders, and other products.
Related: Your guide to pregnancy-safe skin care
Try at-home masks and methods
You may be able to lighten your melasma using ingredients from your pantry. While there are no specific studies on these methods for chloasma, the following topical treatments may help:
- Lemon juice. Mix together a solution of half fresh lemon juice and half cucumber juice or water. The acid in the juice may help remove pigmentation in the top layer of the skin.
- Apple cider vinegar (ACV). Similar idea here. Mix a solution of half ACV and half water to use as a toner on dark areas.
- Milk of magnesia.
 After washing your face, apply milk of magnesia to dark areas using a cotton ball. Leave on the skin overnight and wash off in the morning.
After washing your face, apply milk of magnesia to dark areas using a cotton ball. Leave on the skin overnight and wash off in the morning. - Oatmeal and honey. Whip up a mask made with cooked oatmeal (let it cool down so it isn’t hot) and raw honey. Leave on the skin for 10 minutes before washing away. The mask helps to exfoliate your skin and the enzymes in the honey may lighten it a bit.
Eat well, rest, and try a few supplements
Since melasma may also be the result of hormonal imbalances, you may improve matters by giving yourself some much-needed TLC. Make sure you’re staying hydrated, eating a diet with plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, and getting enough sleep each night.
Be sure that you’re rounding out your diet by consuming supplemental omega-3 fatty acids. And ask your doctor about any potential vitamin deficiencies. Some studies link melasma to deficiency in iron and possibly vitamin B12.
Be patient
After pregnancy, you may ask your dermatologist about other treatments if your melasma doesn’t fade on its own.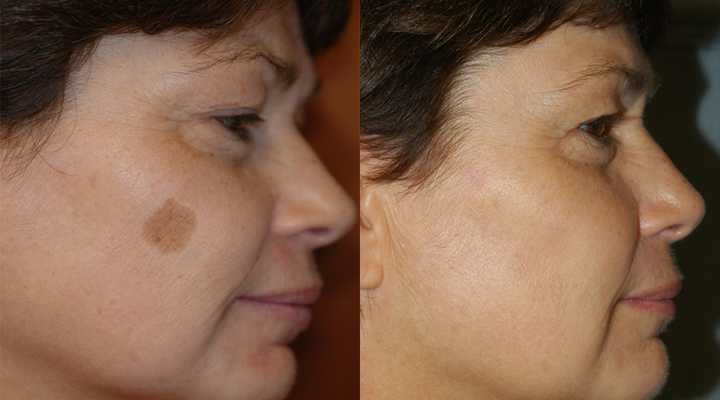 Treatments include topical medications like:
Treatments include topical medications like:
- hydroquinone
- tretinoin
- corticosteroids
Your doctor may also recommend certain acids that lighten the skin, alone or in combination. There are also some procedures — including chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser treatments, and other light therapies — that may work.
It can be frustrating to deal with changes to your skin during pregnancy. Fortunately, chloasma generally fades within a few months after giving birth.
There are various lifestyle changes you can try to prevent the condition from progressing during pregnancy. Otherwise, speak with your doctor about the options for treatment and the benefits and risks of each. You’ll be glowing again before you know it!
What is it? Normal and abnormal discharge during pregnancy
Today we will talk with Elena Yurievna Romanova, an obstetrician-gynecologist at the Expert Center for Pregnancy Management at the Mother and Child Clinic, about what discharges during pregnancy should be feared and what discharges from the genital tract are regarded as normal.
Increased vaginal discharge during pregnancy is natural
Normal pregnancy discharge is milky white or clear mucus without a strong odor (although the smell may change from before pregnancy), this discharge does not irritate the skin and does not cause discomfort to the pregnant woman. The discharge can have a different color - from completely colorless (most often) to whitish and yellowish. The consistency of discharge at the beginning of pregnancy resembles raw chicken yolk - they are thick, jelly-like, often released in the form of clots. nine0003
With normal discharge, it is enough to use panty liners or change underwear twice a day.
Due to the activity of progesterone in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, the discharge will be scarce and viscous.
Due to the increase in estrogen activity from 13 weeks, the discharge becomes less viscous and more abundant.
By the end of the pregnancy, vaginal discharge becomes more and more abundant. Each time you need to evaluate the nature of the discharge, change the gasket. If the fluid continues to ooze, this may mean leakage of amniotic fluid and the need to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist in the emergency department of a hospital with a maternity ward. There are auxiliary tests, thanks to which, as well as obstetric ultrasound, leakage of water can be excluded. nine0003
Each time you need to evaluate the nature of the discharge, change the gasket. If the fluid continues to ooze, this may mean leakage of amniotic fluid and the need to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist in the emergency department of a hospital with a maternity ward. There are auxiliary tests, thanks to which, as well as obstetric ultrasound, leakage of water can be excluded. nine0003
Not all discharge in pregnant women is the norm.
For example, a white, thick, crumbly, odorless discharge that itchs and burns the skin and causes discomfort during intercourse is likely a sign of a yeast infection (candidiasis).
White or grayish discharge, the smell of which after sex begins to resemble the smell of fish, is the main symptom of bacterial vaginosis, vaginal dysbacteriosis.
A yellowish or greenish discharge that has a strong unpleasant odor usually occurs with nonspecific vaginitis, and a foamy discharge is a sign of trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted disease.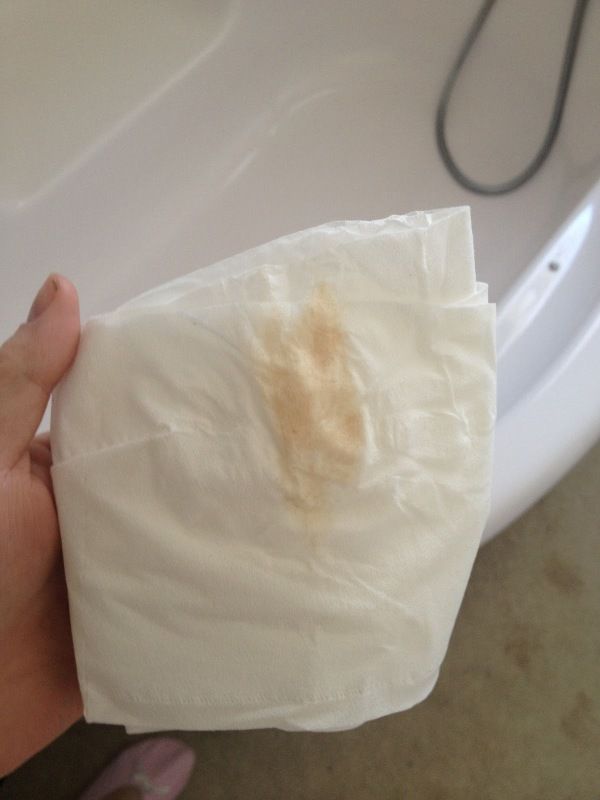 nine0003
nine0003
In all these cases, contact your doctor immediately. It should not be treated with over-the-counter drugs and folk remedies. According to some external signs, a diagnosis cannot even be made by a doctor, in addition, infections in pregnant women should be treated especially carefully and only by a professional. After proper treatment, the discharge returns to normal. There is no need to get rid of the usual discharge for pregnant women. After childbirth, they will stop naturally, and before that they are a sign of the normal course of pregnancy. nine0003
Allocations can change their nature and amount under the influence of irritants or intolerance to a particular substance, for example, when using panty liners. Such secretions are transparent and abundant, they stop when the irritant is removed.
"Thrush" is a disease caused by fungi of the genus Candida, present in small quantities in all women. During pregnancy, immunity decreases and fungi begin to actively multiply, causing inflammation, abundant white flocculent discharge with a sour smell, burning and itching in the vulva. The disease can manifest itself throughout pregnancy. nine0003
The disease can manifest itself throughout pregnancy. nine0003
Bloody discharge in the first half of pregnancy usually indicates a lack of the hormone progesterone, which can lead to spontaneous miscarriage. Discharge may be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. In the treatment of the threat of abortion, the appointment of progesterone drugs, such phenomena disappear.
If bleeding from the vagina appeared during pregnancy during the second or third trimester, then this is a sign of a formidable complication, namely, placenta previa or its premature detachment. With improper attachment of the placenta in the uterine cavity and overlapping of the placental tissue with the area of the internal pharynx, they speak of placenta previa. In this case, spotting occurs in a third of pregnant women. This most often occurs between 28 and 30 weeks, when the lower segment of the uterus is most prone to stretching and thinning. The discharge is repeated, the woman does not experience any pain, so it may be too late to see a doctor for an examination. This threatens the child with a lack of nutrients and oxygen, because it is through the placenta that the fetus is nourished. For a pregnant woman, this is fraught with acute placental abruption and severe bleeding, which is always problematic to stop, especially at home. nine0003
This threatens the child with a lack of nutrients and oxygen, because it is through the placenta that the fetus is nourished. For a pregnant woman, this is fraught with acute placental abruption and severe bleeding, which is always problematic to stop, especially at home. nine0003
Bloody discharge during pregnancy should force a woman to immediately contact her obstetrician-gynecologist.
Brown discharge during pregnancy also indicates the threat of termination of pregnancy, or bleeding "erosion" (decidual polyp) of the cervix. Therefore, you should not understand these issues on your own; when brown discharge appears, it is better to consult your doctor.
Brown discharge during a delay in menstruation as a sign of an ectopic pregnancy is very dangerous. This condition requires immediate surgical care, as the growing embryo can rupture the wall of the fallopian tube at any time and cause internal bleeding. Therefore, with pain in the lower abdomen, which is accompanied by brown discharge from the genital tract and delayed menstruation, you should immediately call an ambulance. nine0003
nine0003
When the vagina becomes inflamed, the mucous discharge acquires a mucopurulent character, a greenish-yellow color, an unpleasant odor, burning and itching appear in the genital area. This is how chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis manifest themselves. Is it necessary to treat the infection during pregnancy, or is it better to do it after childbirth?
All sexually transmitted infections in pregnant women require treatment, as they can pass to the fetus and cause intrauterine infection (IUI). IUI is very dangerous for a child - it leads to his death or serious illness. Infection of a child during childbirth can lead to such serious complications as pneumonia, severe damage to the brain, kidneys, liver, and blood poisoning (sepsis). nine0003
Today, obstetricians and gynecologists have learned to treat any infection in pregnant women in accordance with special guidelines for the timing of pregnancy, so that it is effective and safe for mother and fetus.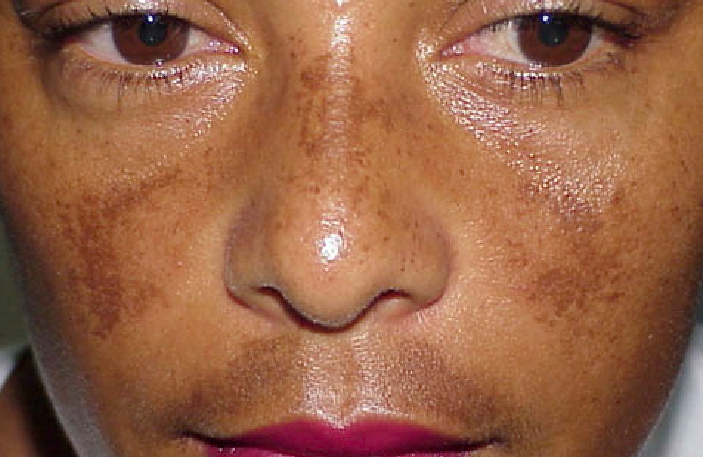 It is not the treatment that should be feared, but the infection itself and its consequences.
It is not the treatment that should be feared, but the infection itself and its consequences.
Medicines that are used to treat pregnant women have passed the necessary clinical trials, during which it was proved that they do not have a negative effect on the pregnant woman and the fetus, including that they do not have a teratogenic effect (do not cause deformities in the fetus). nine0003
Sometimes the discharge is mucous in nature, occurs upon contact with an irritant or allergen. It can be synthetic tight underwear, allergies to fabrics, toiletries, personal care products. If irritation and allergens are not eliminated in time, then an infection that lives on the mucous membranes of the genital organs will definitely join.
Hygiene measures are mandatory for pregnant women. Twice a day you need to take a warm shower, using special gels for pregnant women to wash the genitals. Be sure to monitor the cleanliness of the whole body and underwear - it must be changed daily. Pads (but not tampons!) can be used for discharge. The oral cavity can become the source of infection, so you need to monitor your teeth, brush them twice a day and get an examination by a dentist. Good nutrition strengthens the immunity of a pregnant woman. The diet should contain fresh vegetables and fruits, lean meats and fish, daily dairy products, vegetable oil, a variety of cereals. nine0003
Pads (but not tampons!) can be used for discharge. The oral cavity can become the source of infection, so you need to monitor your teeth, brush them twice a day and get an examination by a dentist. Good nutrition strengthens the immunity of a pregnant woman. The diet should contain fresh vegetables and fruits, lean meats and fish, daily dairy products, vegetable oil, a variety of cereals. nine0003
A mobile lifestyle, therapeutic exercises and maximum exposure to fresh air are very important. Hiking is useful even at the very end of pregnancy - they will help not only maintain immunity, but also strengthen the muscles that will be required during childbirth. Be healthy!
why they appear in the early and late periods, in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimester, what to do at home
Brown discharge is not always dangerous for the expectant mother and child. However, in some cases, their appearance is an alarming signal. Together with the highest category obstetrician-gynecologist Elvira Semenova, we will find out which discharge during pregnancy is considered normal, and which is an urgent reason to see a doctor.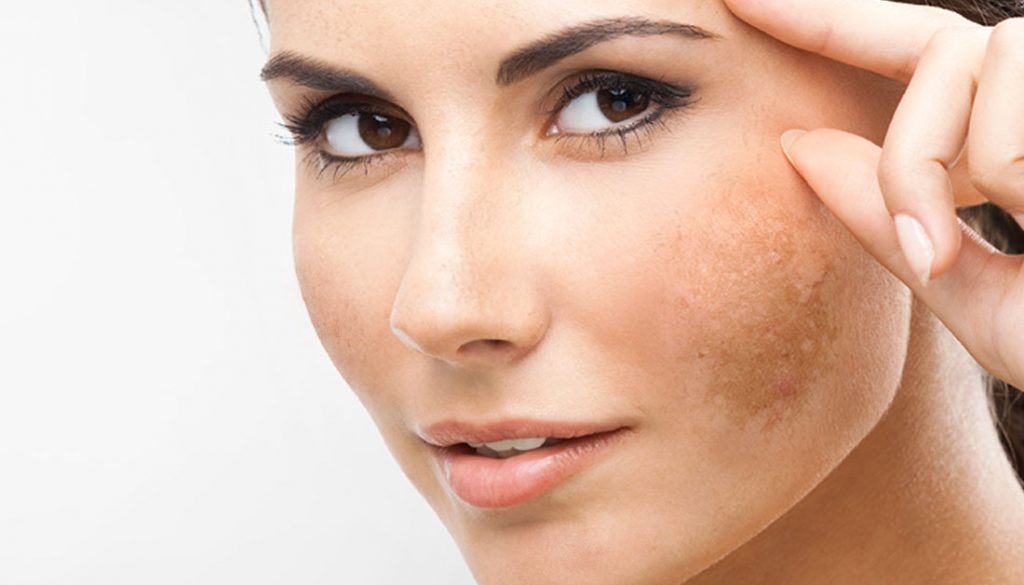 nine0003
nine0003
Why brown discharge occurs during early pregnancy
Brown discharge during early pregnancy is quite common. When they appear, it is recommended to see a doctor to make sure there is no danger. (1)
- Any vaginal discharge that is red and brown in color indicates the presence of blood. Brown discharge is a very small amount of blood, explains obstetrician-gynecologist Elvira Semenova .
The number of possible dangerous states when the brown discharge occurred at the early stages includes:
| The threat of spontaneous termination of pregnancy (miscarriage) | Purpose of the placenta | |||||||
| reflete Exception Excavation Referee | the threat of premature birth |
Obstetrician-gynecologist Elvira Semenova talks about the most common causes of brown discharge. nine0003
nine0003
- Ectopic cervical . More often, blood impurities in the secretions may appear as a result of sexual intercourse or other mechanical effects on the cervix. However, spontaneous occurrence is also possible. In any case, cervical ectopia is a rare cause of brown discharge.
- Cervical polyp is a common cause of blood in vaginal discharge. It is formed during pregnancy, as a rule, from placental tissue and is not dangerous. However, a polyp can cause intermittent spotting that bothers a pregnant woman. nine0100
- Chorion . This is what the future placenta is called. The chorion is located inside the uterus, very close to its neck. Between the chorion and the wall of the uterus, there is an intensive movement of blood, a small part of which can go into the vagina, staining the discharge brown. This is not a dangerous condition. When the placenta migrates higher relative to the cervix, brown discharge will no longer embarrass the expectant mother.

- Premature detachment of the ovum and/or chorion . This can happen with any pregnancy. Usually accompanied by bright bloody discharge, but may be insignificant in volume and then the discharge becomes brown. In this situation, it is urgent to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist and an ultrasound specialist.
1st trimester
The first trimester is considered the most dangerous and problematic. (2) At different stages, brown discharge can be caused by different factors. nine0003
- At 5 weeks. Brown discharge (especially accompanied by pain) may indicate a threat of abortion.
- At 6 weeks. They can be both safe and alarming. The danger is borne by diseases that a woman suffered before conception. Infectious diseases, inflammatory processes, hormonal disorders, miscarriages, abortions, missed pregnancies, stress. The appearance of brown discharge in the presence of a history of such diseases threatens with a miscarriage or missed pregnancy.
 nine0100
nine0100 - At 7 weeks. Danger sign. By this time, the embryo has already implanted in the wall of the endometrium, the body is set to maintain pregnancy. The appearance of brown discharge can be a sign of the development of an ectopic pregnancy or the threat of loss of the fetus.
- At 8 weeks. Dangerous causes include infectious diseases (discharge is accompanied by pain and turns into bleeding), the threat of miscarriage or missed abortion (the symptoms of pregnancy disappear, and the discharge is accompanied by an unpleasant odor). nine0100
- At 9 weeks. The most harmless cause is cervical erosion. Risk factors include spontaneous miscarriage or cessation of fetal development.
- At 10 weeks. Brown and bloody discharge is very dangerous. They most likely indicate a miscarriage or early placental abruption.
In the first trimester, brown discharge should be seen as soon as possible. Even if they are not accompanied by pain or an unpleasant odor. nine0003
Why brown discharge appears during late pregnancy
– In the later stages, the causes of brown discharge are the same as at the beginning of pregnancy, explains gynecologist Elvira Semenova.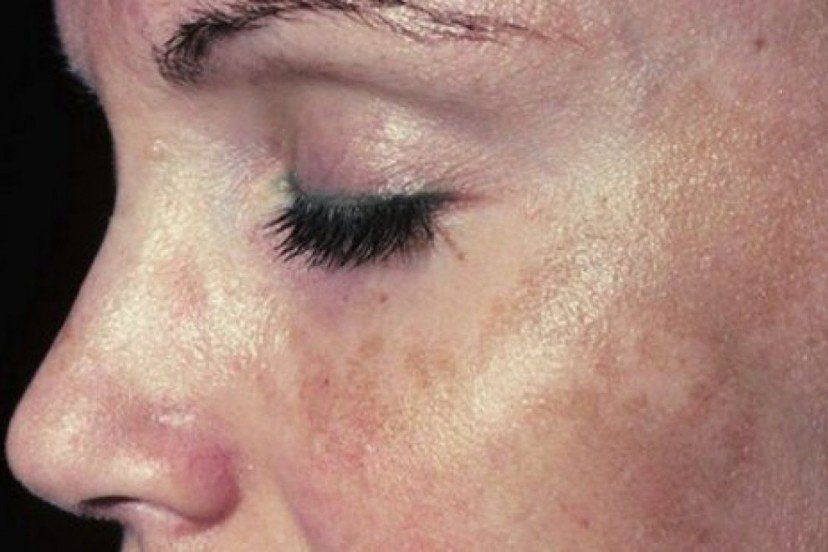 - One new pathology joins, placenta previa. In this complication, the placenta is located directly above the canal in the cervix (cervical canal). Part of the blood exchanged between mother and baby can enter the cervix and flow into the vagina, staining the discharge brown, and with an increase in blood, red. This condition is dangerous with intense and bright discharge. In any case, it is recommended to see a doctor to eliminate risks for the mother and the developing baby. nine0003
- One new pathology joins, placenta previa. In this complication, the placenta is located directly above the canal in the cervix (cervical canal). Part of the blood exchanged between mother and baby can enter the cervix and flow into the vagina, staining the discharge brown, and with an increase in blood, red. This condition is dangerous with intense and bright discharge. In any case, it is recommended to see a doctor to eliminate risks for the mother and the developing baby. nine0003
2nd trimester
The second trimester starts at the 14th week of pregnancy and ends at the 28th. During this period, the fetus is already formed and continues to grow. In most cases, the appearance of brown discharge at this time is the result of the formation of pathologies in the development of the fetus, placenta or internal organs of the mother. Main causes of discharge:
- trauma of the cervix;
- threatened miscarriage;
- placental abruption.
Pay attention to the color and amount of discharge. nine0003
nine0003
Light brown light discharge usually indicates the presence of infections in the birth canal or injuries that could occur due to pressure of the fetus on the cervix, as well as as a result of sexual contact.
Dark brown discharge, accompanied by pain or aching sensations in the lumbar region, kidneys, lower abdomen, require an immediate examination by a doctor. The specialist will diagnose and prescribe treatment.
The main danger of brown discharge in the second trimester is the loss of a child. The fetus may die in a few days. Therefore, the main task of the expectant mother 一 is to timely contact a specialist and diagnose possible problems. nine0003 Photo: @karolina-grabowska, pexels.com
3rd trimester
In the prenatal period, a change in discharge is considered a variant of the norm. The cervix prepares for the birth of the child, becomes soft and pliable. (3) The appearance of brown mucus usually indicates that the mucus plug has come off. The volume of discharge in this case is small, in addition, the passage of the plug may not be noticed (for example, it may move away when a woman takes a shower). The discharge of the mucous plug signals that the body is finally ready for the birth of a child and childbirth can begin at any time. Therefore, noticing her, it is recommended to go to the hospital. nine0003
The discharge of the mucous plug signals that the body is finally ready for the birth of a child and childbirth can begin at any time. Therefore, noticing her, it is recommended to go to the hospital. nine0003
Another reason is a gynecological examination. After it, abundant brown discharge may be observed, which appear due to the fact that the uterus is disturbed.
What to do when brown discharge appears during pregnancy at home
- At home, when brown discharge appears, you must remain calm and be sure to see an outpatient or hospital doctor, advises gynecologist Elvira Semenova. – To do this, you can call an ambulance or come to the antenatal clinic, a private medical clinic or the emergency room of a multidisciplinary hospital (up to 22 weeks of pregnancy) or a maternity hospital (after 22 weeks of pregnancy) on your own. nine0003
Frequently Asked Questions
Expectant mothers are worried about brown discharge. Some important questions regarding the causes and consequences of their occurrence are answered by our expert, obstetrician-gynecologist Elvira Semenova.
Can I play sports if I have brown discharge?
Brown discharge is not always dangerous for the woman and the child. For example, with implantation bleeding, sports are quite acceptable. But with the threat of a miscarriage, it is better to reduce activity as much as possible. Do not forget that in any case, heavy loads during pregnancy are not recommended. Specifically, about what is permissible or prohibited, you should find out from the gynecologist leading the pregnancy. nine0003
Is brown discharge instead of menstruation always a sign of pregnancy?
No, not always. Pregnancy is only one of the reasons. In addition, the following are possible:
● stabilization of the menstrual cycle;
● Climax;
● Antibiotic treatment;
● lack of vitamins and microelements;
● dramatic weight loss;
● Hormone treatment;
● stress;
● abrupt climate change;
● Excessive exercise.
If the discharge is accompanied by pain, bleeding, deterioration of health, you should immediately consult a doctor.