How to gain full custody of child
Getting or Obtaining Full Custody of a Child
Child custody refers to the legal and practical relationship between a child and a parent or guardian. Custody is generally determined in the event of a divorce or legal separation. State laws regarding child custody vary by jurisdiction, although the overall standard for child custody decisions is the child’s best interests standard. The needs of the child, and what would be in their best interests, are placed above the parent’s preferences. Additionally, family courts will only make child custody decisions if those decisions best benefit the child.
Although there are different types of child custody arrangements, the two types that a family court will generally consider are full custody, and joint custody. Simply put, full custody refers to one parent being designated the primary custodial parent; that parent has the majority of the custody time, as well as legal rights regarding the child. Joint custody refers to an arrangement in which both of the child’s parents split physical custody of the child, with one parent possibly retaining legal custody.
Full custody is an arrangement in which only one parent assumes all of the responsibilities associated with caring for and raising their child. Full custody may be granted to the primary custodial parent when the following situations are present:
- One parent has become ill, disabled, or otherwise incapacitated;
- The court has determined that the other parent is unfit to raise a child;
- The other parent has been incarcerated, or has a considerably negative criminal record; and/or
- There is a history of abuse or neglect by the other parent.
When a parent is awarded full custody, it means that they are the only parent entrusted with both legal and physical custody. However, full custody does not necessarily mean that the other parent has no visitation rights at all. In some full custody cases, the non custodial parent could have some short periods of visitation with their child.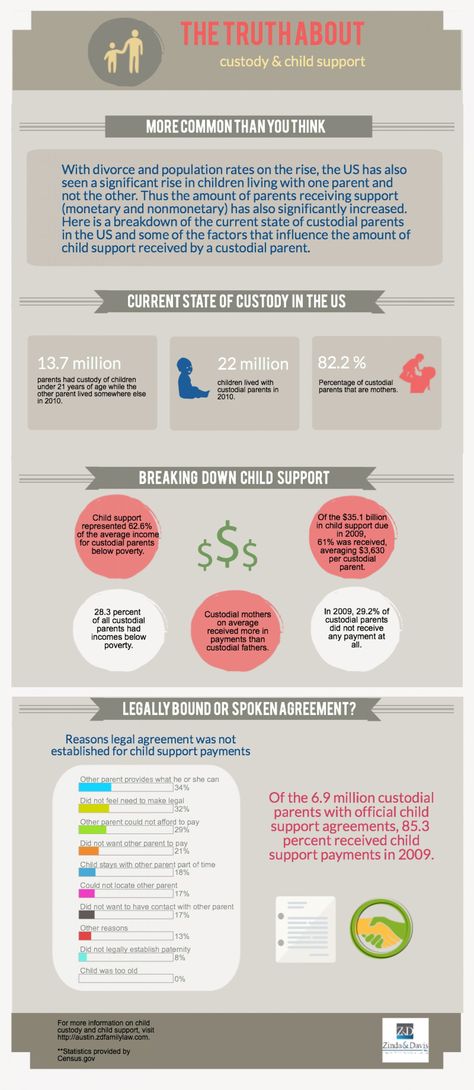 Full custody and sole custody are often used interchangeably, although there are some differences between the two custody arrangements. An example of this would be how sole custody generally means that the non custodial parent was not awarded any visitation or custody rights at all.
Full custody and sole custody are often used interchangeably, although there are some differences between the two custody arrangements. An example of this would be how sole custody generally means that the non custodial parent was not awarded any visitation or custody rights at all.
It is common for the non-custodial parent to be required to assist in the child’s upbringing by providing monthly child support payments. However, this depends on the factors present in each individual case.
What Is the Process of Getting Full Custody of a Child? What Are Some Tips on How to Get Full Custody of My Child?
As previously mentioned, courts will generally only award full custody rights under specific circumstances, such as one parent being unfit or physically unable to care for their child. Generally speaking, it is in the child’s best interest to maintain an equal relationship with both parents.
In a full custody arrangement, only one parent is entrusted with responsibilities of both physical and legal custody.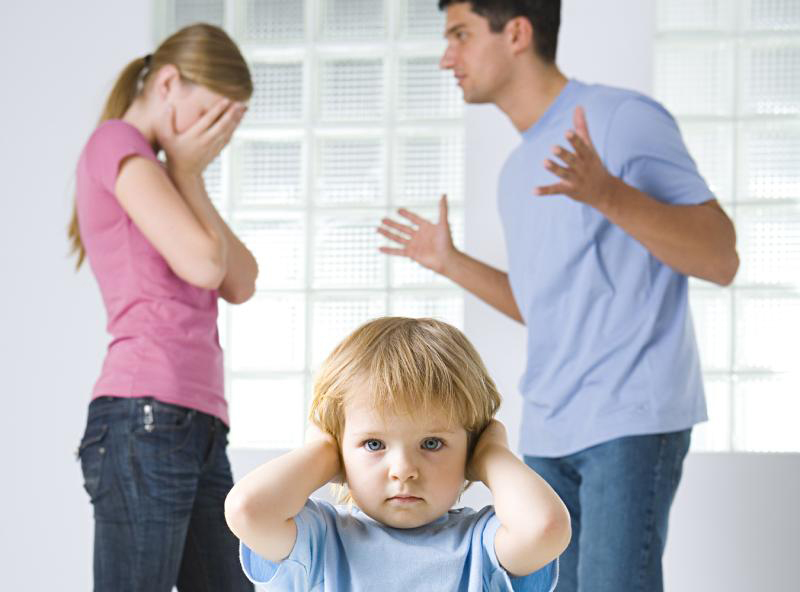 Physical custody refers to the periods of time in which the child is staying or living with the parent. The parent would then be responsible for matters such as:
Physical custody refers to the periods of time in which the child is staying or living with the parent. The parent would then be responsible for matters such as:
- Food;
- Clothing;
- Shelter;
- Educational matters; and
- Other related expenses.
Legal custody refers to the parent’s responsibilities in terms of making various legal decisions on behalf of the child.
A full custody arrangement may also grant some visitation rights. An example of this would be how the noncustodial parent may have some short periods of visitation with the child. They may only be assuming physical custody for a short while, but the custodial parent still retains legal custody of their child. Full custody can be much more demanding when compared to other forms of custody such as shared or split custody. This is largely due to the fact that the custodial parent is essentially assuming all responsibility for their child.
Full custody is not granted simply because one parent requests it. Rather, full custody is only granted if the family court determines that it will truly benefit the child. If you would like to obtain full custody of your child or children, some tips to consider when petitioning the court include:
- Be prepared to provide documentation, as you may need proof that you have the capability of raising the child on your own. This could include bank account statements, as well as other financial statements;
- Do not intentionally falsify or exaggerate any information simply to obtain custody. This would be a violation of court laws, and can lead to being held in contempt of court or other criminal charges; and
- While it is necessary to point out important differences between the two parties, it is never prudent to belittle, make fun of, or insult the opposing parties.
If full custody is not an option, there may be other suitable alternatives, such as:
- Legal guardianship;
- Shared or joint custody; or
- Planned visitation.

How Is Custody Determined?
To reiterate, the determining factor in any child custody case is the child’s best interests. Most consider the following factors in order to determine custody decisions:
- The child’s background, including their sex assigned at birth, age, and personal health characteristics;
- Children with special needs or disabilities may be used to a certain home, and accustomed to a parent who provides daily specialized care;
- If the child is at least 12-14 years old, many jurisdictions will consider the child’s preferences;
- Environmental factors, such as the quality of education in each parent’s school district, the safety of each neighborhood, and proximity to other extracurricular activities;
- The physical and mental health of each parent;
- Each parent’s ability to provide emotional and financial support for the child while the child is in their care;
- The stability of each parent’s lifestyle and background;
- The existence and level of attachment to other siblings, or important family members in the home; and
- Each parent’s commitment to facilitating an ongoing and healthy relationship between the child and the other parent.

Child custody determinations are generally finalized into a formal child custody order, once the family court finalizes the decisions made. To obtain a custody order, you will need to petition the family court in connection with the divorce or legal separation proceeding. If there are any questions associated with paternity, they can be resolved at that time. In some jurisdictions, if the parents are unmarried, the mother is issued primary custody initially until the father petitions the court to be awarded custody and visitation.
If the person seeking custody is not the child’s parent, they may seek a non-parent custodial order. An example of this would be if a grandparent wished to obtain custody of their grandchild.
Is It Necessary to Hire a Lawyer for Help with Custody Matters?
If you are experiencing issues related to your child custody order, or wish to petition the court for a specific type of custody, you should consult with an experienced and local child custody lawyer. As previously mentioned, much of family law including how child custody is determined varies from state to state.
As previously mentioned, much of family law including how child custody is determined varies from state to state.
An attorney will be best suited to helping you understand your parental rights and legal options according to the laws set by your specific state. Your child custody attorney will also be able to represent you in court, as needed.
Travis Peeler
LegalMatch Legal Writer
Updating Author
Travis earned his J.D. in 2017 from the University of Houston Law Center and his B.A. with honors from the University of Texas in 2014. Travis has written about numerous legal topics ranging from articles tracking every Supreme Court decision in Texas to the law of virtual reality. In his spare time off from the legal world and quest for knowledge, this 3rd degree black belt and certified instructor aspires to work with various charities geared towards bringing access to entertainment and gaming to all persons.
Jose Rivera
Managing Editor
Original Author
Jose Rivera
Managing Editor
Editor
Last Updated: Oct 15, 2021
Full Custody in Texas: How to File and Win Custody of Your Children
We don’t have to tell you that raising children isn’t easy. Furthermore, figuring out how to raise a child after separating from the child’s other parent can overwhelm the best of us.
Furthermore, figuring out how to raise a child after separating from the child’s other parent can overwhelm the best of us.
Sometimes, you may feel that getting full custody in Texas is your best option. If you’re asking how to win full custody as a father or how to win full custody as a mother, we want to help you understand the process.
As a preliminary matter, there is no actual term of “full custody” under the Texas Family Code, even though most people use that term. Most often, when people say “full custody” they mean who the children live with during the school week, which is referred to as “primary” in Texas.
Sometimes though people use “full custody” as meaning the other parent relinquishing or terminating their parental rights. Other times people use “full custody” as meaning sole managing conservatorship and supervised custody for the other parent. In this article, “full custody” will be treated as synonymous with “sole managing conservatorship”
Basic Parental Rights in Texas
The first thing to understand when determining how to get full custody of a child in Texas is the scope of the general rights that every Texas parent has. Under Texas law, every parent typically has the right to have “physical possession” of their child.
Under Texas law, every parent typically has the right to have “physical possession” of their child.
Additionally, every parent normally has the right to participate in making legal, health, educational, moral, religious, relationship, and residential decisions for their child. Each parent also has multiple duties to care for and support their child.
When parents separate, Texas law wants both parents to share their parental rights and responsibilities. If you don’t believe this sharing is possible in your situation, there are a handful of ways you can get sole custody in Texas.
How to Get Full Custody in Texas
You can fight for two kinds of custody in the Texas family law system: physical custody and legal custody. Texas law calls physical custody “possessory conservatorship,” and it labels legal custody as “managing conservatorship.” If you have sole physical custody, your child lives with you full time. If you have sole legal custody, you normally have exclusive rights to:
- Decide the location of your child’s residence,
- Consent to healthcare for your child,
- Hold or spend support payments for your child,
- Handle your child’s legal issues,
- Make decisions about your child’s education,
- Consent to your child’s marriage,
- Apply for and keep travel documents for your child,
- Consent to your child’s military service, and
- Utilize your child’s earnings and services.

You can fight for one or both of these kinds of custody. Once you determine what kind of child custody you’re seeking, you need to determine the best way to file for it.
How to File for Full Custody in Texas
There are two ways you can win full custody in a family court:
- You can file for sole custody or
- You can file to terminate the other parent’s rights.
You start your case by filing a custody or termination petition in the court where your child is a resident or in the court that presides over your divorce (if applicable). You then serve the other parent, or anyone else with custody rights, with the citation.
Now that you know how to get your case started, you need to know how to fight for your position.
How to Fight for Full Custody in Texas
Petitioning for termination of the other parent’s rights requires you to meet a different burden of proof than simply petitioning for sole custody.
Fighting for sole custody
To win sole custody, you generally have to prove that it’s in the best interest of your child. When deciding what’s in your child’s best interest, the court might look at many factors, including:
When deciding what’s in your child’s best interest, the court might look at many factors, including:
- Your child’s specific needs,
- Any relevant history of abusive behavior from you or the other parent,
- Any relevant history of neglect by you or the other parent, and
- Any relevant history of violence from you or the other parent.
It’s important to gather and organize as many records and statements as you can regarding your child’s needs and how they haven’t been met by the other parent.
Fighting to terminate the other parent’s rights
Filing to terminate someone else’s parental rights is a drastic measure, but it’s unfortunately necessary in some cases. If you believe it’s necessary to terminate the rights of your child’s other parent, we empathize with how difficult it must have been to come to that conclusion.
The State of Texas does not terminate parental rights easily. To terminate their rights you must prove that the other parent:
- Abandoned your child,
- Endangered your child,
- Neglected your child,
- Caused serious injury or death to a child,
- Committed certain criminal offenses,
- Engaged in certain forms of substance abuse, or
- Had their parental rights to another child terminated because of endangerment.

You might need to compile relevant police reports, court documents, medical reports, protection orders, and testimony to prove by clear and convincing evidence that the other parent committed one of the listed acts. Clear and convincing evidence is a high standard to fulfill. Your best option for success is to hire a skilled child custody attorney who can meet this standard for you.
How Can a Father Get Full Custody in Texas?
If you’re a father trying to figure out how to get full custody of your child in Texas, don’t assume that you don’t have equal custody rights in family court. Gone are the days when courts automatically determined that a mother should have sole custody regardless of the facts of the case. When deciding custody matters, Texas family law doesn’t consider your sex, the sex of your child, or your marital status.
In general, the court considers your characteristics as a parent, your child’s needs, and the characteristics of the other parent when making its decision. That being said, sometimes the best way for a father to get custody in Texas is by being proactive about his paternity and parental involvement from the beginning.
That being said, sometimes the best way for a father to get custody in Texas is by being proactive about his paternity and parental involvement from the beginning.
There are a few custody laws that specifically affect fathers
Fathers who voluntarily and knowingly abandon mothers who are pregnant with their children can be subject to termination of their parental rights. And fathers who weren’t married to the mother, weren’t living with the child for the first two years, or didn’t acknowledge their paternity might not be recognized as parents.
If you’re not married to the pregnant mother of your child, do what you can to support the mother and your child. You might need to prove you were around once you knew about the child to get any custody rights, let alone sole custody.
The Best Way for a Mother to Get Custody in Texas
Remember, the rules and standards for how to get sole custody in Texas are the same for mothers and fathers. But mothers’ parental rights can be terminated if they used alcohol or illegal, nonprescription drugs while pregnant.
If you have a notion that the other parent of your child might try to use this argument to terminate your rights, you should speak to an attorney immediately. And you should collect as many documents as possible to prove that you didn’t engage in that activity. Also, remember to keep any documents that prove that a father claiming custody doesn’t legally qualify as a parent.
Don’t Wait to Speak to an Attorney When Your Child’s Wellbeing Is at Stake
At The Larson Law Office, we know how to win child custody in Texas. The fight for sole custody isn’t always easy or realistic, and it’s often emotional. But if you’re in the greater Houston area, we’re here to help you make the best possible decisions in your custody battle and help you put yourself in a position to obtain the best possible results with the facts of your case.
Our lawyers focus on our clients’ unique needs for protecting their families. We are highly experienced and ready to fight for you. Contact us online or call us at 713-221-9088.
Children in divorce
Divorce also affects children. The child must have an official guardian and a home address. In addition, the child has the right to meet with both parents.
- If you cannot come to an agreement ,
- housing
- Guardianship
- The right to meet
- If difficulties arose with the right to meet ,
- child support
- Surne of the child when divorce
- The kidnapping (LapsikaAppaas)
If the family has children under the age of 18, and the marriage ends, the following issues must be agreed upon divorce:
- place of residence of the child,
- who will be the guardian of the child,
- how the right to meet will be organized,
- alimony.
If the parents have agreed on the place of residence of the child, his custody, the right to meet and alimony, then the local social department can approve this agreement. After the agreement is approved by the social department, it receives the same legal force as a court decision.
After the agreement is approved by the social department, it receives the same legal force as a court decision.
If you cannot agree on the child's place of residence, custody, visitation rights and maintenance, you can ask for help in the form of a family dispute settlement procedure (perheasioiden sovittelu). If this procedure also fails to reach an agreement, you must file an application with the county court. When making a decision, the judicial authority will take into account the interests of the child and his own opinion. The judicial authority may also request an opinion from the social welfare office in your place of residence.
Find out about the procedure for settling family disputes with the social office of your commune.
For more information about the services of a lawyer and legal assistance, see the InfoFinland page Do you need a lawyer?.
Housing
Always consider your child's best interests when deciding where to live.
Officially, a child can only live in one place. When a divorce occurs, it is necessary to agree on which parent the child will officially live with.
When a divorce occurs, it is necessary to agree on which parent the child will officially live with.
In practice, a child may live for some time with either parent.
Child allowance is paid to the parent with whom the child officially resides. The child's official address also affects the housing allowance paid by Kela.
Guardianship
Child custody means:
- child care
- his upbringing
- managing and making decisions about the child's affairs.
The child's guardian has the right to receive information about the child's affairs from officials.
At the end of the marriage, the child's parents decide on the organization of guardianship over him. Parents may agree on joint custody or sole custody by one of the parents. Guardianship does not depend on who the child lives with. More information about sole and joint custody is available on the InfoFinland website under Single-parent families.
External link Yhden Vanhemman Perheiden Liitto ry
General care and single care External link
Finnish
Right to meet
The child has the right to maintain contact after the divorce with both parents. He also has the right to meet with the parent with whom he does not live.
He also has the right to meet with the parent with whom he does not live.
The right to visit may mean, for example, that the child lives with one of the parents and meets with the other parent every second weekend, and also during the holidays for a certain period of time. If the child is still small, meetings can take place during the day.
The right to visit may be so extensive that the child will live with both parents for the same amount of time. Officially, a child can have only one address. Always consider the interests of the child when making decisions.
In the event of a divorce, you can agree in advance how often the child can see the parent who will be living separately. If you wish, you can make a written agreement about the order of meetings. You can also decide that the order of the meetings will be agreed each time separately.
External linkYhden Vanhemman Perheiden Liitto ry
How to arrange an appointmentExternal link
Finnish
If you have difficulty exercising the right to an appointment
If you have entered into a meeting agreement with the child, but the parent living with the child does not comply with this agreement, then the parent living apart may contact the child inspector at the place of residence of the child. The children's inspector organizes negotiations between parents.
The children's inspector organizes negotiations between parents.
If you think that there is a risk to the child's health and safety when meeting with the other parent, tell the social worker about it. If you have good reason to be so suspicious, you can request that social workers be present at the meeting.
Child support
Both parents are responsible for the maintenance of a child under the age of 18, even if they live separately from each other. The parent who does not live with the child pays child support to the parent who lives with the child.
For more information on child support, see the InfoFinland page Single-parent families.
Link to an external resource Elatusvelvollisten liitto ry
Information for persons receiving and paying alimony Link to an external resource
Finnish
Child's surname upon divorce
The child's surname does not change when the parents divorce. However, the name can be changed. An application for a change of surname should be sent to the Agency for Digital Information and Population Records. If the child is over 12 years old, the written consent of the child is required to change the surname. If the child is under 12 years old, it is also recommended to have a preliminary conversation with him before changing the surname.
An application for a change of surname should be sent to the Agency for Digital Information and Population Records. If the child is over 12 years old, the written consent of the child is required to change the surname. If the child is under 12 years old, it is also recommended to have a preliminary conversation with him before changing the surname.
Abduction of a child (lapsikaappaus)
We are talking about the abduction of a child when:
- a child under the age of 16 living in Finland is taken abroad without the consent of the guardian
- a child taken abroad was not returned to Finland within the agreed period.
Child abduction is a crime in Finland. Contact the police in your area. For more information and advice, please contact Kaapatut Lapset ry.
External link Oikeus.fi
International child abduction External link
What is guardianship?
In Russia, citizens who need guardianship include minors, that is, children under 14, as well as persons recognized by the court as incompetent. We are talking about people who, due to a mental disorder, cannot understand the meaning of their actions or control them. This is stated by the Federal Law "On guardianship and guardianship". Based on the document, citizens appointed by the guardianship and guardianship authority “are the legal representatives of the wards, and perform all legally significant actions on their behalf and in their interests.”
We are talking about people who, due to a mental disorder, cannot understand the meaning of their actions or control them. This is stated by the Federal Law "On guardianship and guardianship". Based on the document, citizens appointed by the guardianship and guardianship authority “are the legal representatives of the wards, and perform all legally significant actions on their behalf and in their interests.”
Guardianship is aimed at protecting the interests of the listed categories of citizens, as well as the very possibility of declaring a citizen legally incompetent in a court of law. This was also emphasized by the Constitutional Court in the framework of Resolution No. 15-P dated June 27, 2012 “On the case of checking the constitutionality of paragraphs 1 and 2 of Article 29, paragraph 2 of Article 31 and Article 32 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in connection with the complaint of citizen I.B. Business".
How is guardianship different from guardianship?
In addition to guardianship, there is also guardianship, under which adolescents aged 14 to 18 years old, as well as persons with limited legal capacity, can fall. Such people cannot be fully responsible for their actions. This category has more rights than minors and the incapacitated. For example, they can independently perform small household transactions and actions provided for by law (dispose of their own income, etc.). However, in other cases, they are obliged to assist the trustee.
Such people cannot be fully responsible for their actions. This category has more rights than minors and the incapacitated. For example, they can independently perform small household transactions and actions provided for by law (dispose of their own income, etc.). However, in other cases, they are obliged to assist the trustee.
It turns out that the guardian has more rights and obligations than the trustee, in connection with which he bears a great responsibility.
Who can become a guardian or custodian?
The main requirement for a candidate is full legal capacity. And since it comes from the age of 18, the guardian must be of age. The law also establishes a list of restrictions. Guardianship cannot be issued by persons:
- deprived of parental rights;
- having an unexpunged or outstanding conviction for an intentional crime against life or health;
- who did not agree to become a guardian.
When it comes to guardianship of young children (under 14), additional restrictions are set. Future guardians must undergo special psychological, pedagogical and legal training, as well as prove that they are in a bisexual marriage. Those who have registered a same-sex marriage in the territory of another state will not be able to arrange guardianship.
Future guardians must undergo special psychological, pedagogical and legal training, as well as prove that they are in a bisexual marriage. Those who have registered a same-sex marriage in the territory of another state will not be able to arrange guardianship.
Registration of guardianship over the child
This process is supervised by the guardianship and guardianship authorities. To find out all the details of the procedure, you must contact the district office. The state is interested in ensuring that children are not left unattended, are not placed in orphanages and boarding schools, and therefore, most likely, those who wish to arrange guardianship will be met halfway and will be helped in every possible way.
The candidate needs to write an application, collect documents confirming, among other things, the passage of special training, and in case of a positive answer, sign an agreement.
How can I get guardianship of an elderly incapacitated person?
The algorithm is the same as for children - the guardianship and guardianship authority will also deal with the issue of guardianship. However, there are also differences. Thus, custody of an elderly or adult person does not always involve the joint residence of the guardian and his ward. This issue is decided individually, but cohabitation, of course, is welcome. It is much easier for a guardian to fulfill his duties and provide supervision, especially when it comes to a pensioner who, most likely, has a sufficient number of health problems.
However, there are also differences. Thus, custody of an elderly or adult person does not always involve the joint residence of the guardian and his ward. This issue is decided individually, but cohabitation, of course, is welcome. It is much easier for a guardian to fulfill his duties and provide supervision, especially when it comes to a pensioner who, most likely, has a sufficient number of health problems.
If cohabitation is intended, consent must be obtained from all family members of the guardian living in the same dwelling, including children aged 10 and over.
How to get paid guardianship?
There are two types of guardianship:
- gratuitous;
- paid.
In the first case, nothing is paid to the guardian. Paid guardianship can have quite flexible conditions, which are fixed by the contract. In accordance with Article 16 of the Federal Law “On Custody and Custody”, remuneration can also be paid at the expense of third parties, from the income from the property of the ward (no more than 5% and only if he is already an adult), as well as from the budget .
Features of the legal status
The guardian has an unlimited range of powers - he represents the interests of the ward in any relationship, no matter what is discussed. Moreover, this rule applies even when registering custody of a minor with living parents. If the ward is a child, then the guardian acts as a father or mother. However, in some cases notification of guardianship authorities is required. They can also establish restrictions on the actions of the guardian or, conversely, oblige him to perform any actions. All this is recorded in the act on the appointment of a guardian or custodian, or in an agreement on the implementation of guardianship or guardianship.
What documents are required for registration of guardianship?
- Written declaration of consent to the establishment of guardianship.
- Guardian's documents: identity proof, proof of income, no criminal record, state of health (medical certificate in the form established for persons wishing to obtain guardianship), marital status and the right to use the living quarters.