How often do you have ultrasounds during pregnancy
Ultrasounds During Pregnancy: How Many and How Often?
Ultrasounds During Pregnancy: How Many and How Often? | BIDMC of Boston Skip to content SearchFind a Doctor
Search for doctors by name, specialty, hospital, or location.
Find a Doctor
For Patients
Call 1-800-667-5356, Monday-Friday, 8:30am-5:00pm or Find a Doctor
For Physicians
For help with specialty consultations, call 617-667-2020, Monday-Friday, 8:30am-5:00pm or refer to our ED
PatientSite
Manage your health care online.
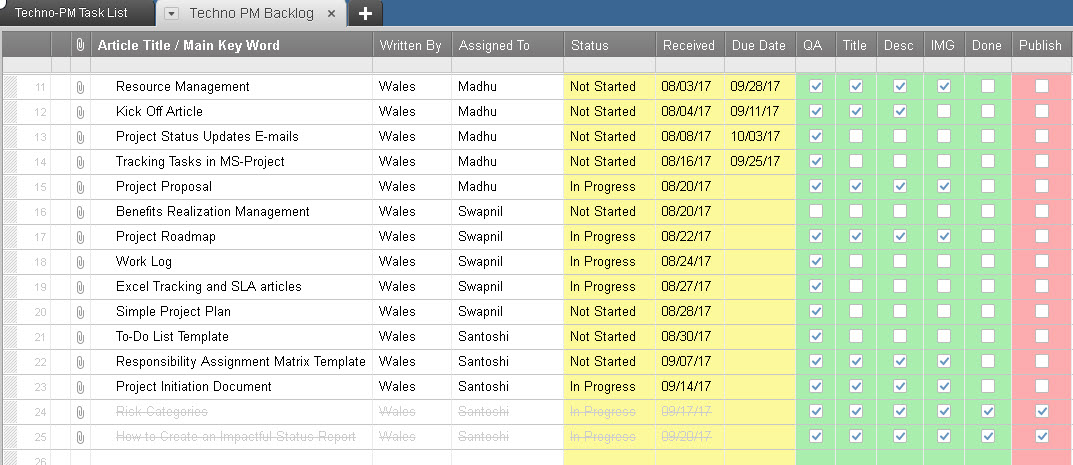
PatientSite Login New User? Sign up now
Medical Records
Pay Hospital Bill
Now available: new PatientSite design and features for a simpler user experience.
Learn more.
Request an Appointment
If you are experiencing a medical emergency, call 911. Please do not use this form.
New Patients
Request
Current Patients
Schedule through PatientSite
Urgent Care
If this is an emergency, call 911 or visit the nearest emergency room.
Chelsea Urgent Care
Chestnut Hill Urgent Care
Dedham Urgent Care
Quincy Urgent Care
Walk-ins are welcome or reserve your spot online.
Close
Close Alert
ALERTS & COVID-19 UPDATES
Learn more: COVID-19 Resources; COVID-19 Testing; Vaccine Info; Visitor Policy; Support Us
BIDMC Contributor
SEPTEMBER 18, 2018
Back to All Articles
Ultrasounds are a regular part of prenatal medical care for most pregnant women, and also provide parents with their first glimpses of their developing baby. Although these photographs make for nice keepsakes, most women need very few scans, and medical guidelines firmly state that ultrasounds during pregnancy should be performed only when there is a valid medical indication.
Although these photographs make for nice keepsakes, most women need very few scans, and medical guidelines firmly state that ultrasounds during pregnancy should be performed only when there is a valid medical indication.
According to the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, there have been no reports of documented negative effects on the fetus from diagnostic ultrasound procedures. But, the ACOG discourages the use of ultrasounds for nonmedical purposes because while there are no confirmed biological effects caused by scans, there's always a possibility that some could be identified in the future.
"2D ultrasounds are the safest radiological modality offered to pregnant women, but as with everything, should be used in moderation," says Monica Mendiola, MD, a practicing physician in Women's Health at Beth Israel Deaconess HealthCare-Chelsea and an instructor in Obstetrics & Gynecology at Harvard Medical School.
Most healthy women receive two ultrasound scans during pregnancy.
"The first is, ideally, in the first trimester to confirm the due date, and the second is at 18-22 weeks to confirm normal anatomy and the sex of the baby," explains Mendiola. "As long as these ultrasounds are normal and mom's abdomen measures consistent with her gestation, then that is all most women need."
Mendiola notes that if there are any problems with these initial ultrasounds, or if there is a discrepancy in the fetus size along the way, a repeat ultrasound is warranted.
"Additionally, if moms have medical issues such as diabetes or hypertension, then they will also receive additional scans," she says.
Above content provided by Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. For advice about your medical care, consult your doctor.
View All Articles
How Many Ultrasounds During Pregnancy Are Normal and What They're for
- A healthy pregnancy typically requires two ultrasounds: one around 11 to 14 weeks and the other at about 18 to 20 weeks.
- If any abnormalities or complications are detected during either of the routine ultrasounds, you might need more.
- In high-risk pregnancies — usually due to the weight, age, or medical history — weekly ultrasounds may be recommended during the final month of pregnancy.
- This article was reviewed by Olivia P. Myrick, MD, who is a clinical assistant professor with the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at NYU Langone.
- Visit Insider's Health Reference library for more advice.
Ultrasounds are standard for every pregnancy because they're an effective way for doctors to monitor the health of both the growing fetus and mother-to-be.
In general, a healthy pregnancy should involve two ultrasounds: one in the first trimester and another mid-way through the second trimester.
However, each pregnancy is different and you may require more ultrasounds based on factors including age, weight, and medical history.
Here's what you need to know about when to get an ultrasound, what to expect during your appointment, and why you might need more than the standard two ultrasounds.
True to its name, an ultrasound works by sending and detecting sound waves. An OB-GYN or an ultrasound technician uses a device called a transducer to send sound waves through the skin into the womb. The sound waves bounce off the fetus to create an image of the baby in the womb.
While getting ultrasound pictures is considered an early milestone for many parents, the primary purpose of an ultrasound is not for a keepsake. Doctors use this time to check on the baby's development, detect any genetic abnormalities, and examine the uterus, placenta, and amniotic fluid.
Generally speaking, ultrasounds are safe to perform during pregnancy, but in terms of how many to plan for, it's important to talk to your doctor to establish clear medical reasons as to why an ultrasound is needed.
"An ultrasound does not involve radiation, and, at the frequencies used for diagnostic imaging, poses no known risk to the mother or developing baby," says Dr. Stephen Chasen, director of obstetric imaging at NewYork-Presbyterian and Weill Cornell Medicine.
Stephen Chasen, director of obstetric imaging at NewYork-Presbyterian and Weill Cornell Medicine.
If you have a healthy pregnancy, you'll typically only need two ultrasounds. The first one is usually scheduled for late in the first trimester, around the 11 to 14-week mark. If the pregnancy has no major complications, the second ultrasound comes at about 18 to 20 weeks.
What to expect from the first trimester ultrasoundMany women experience their first ultrasound between 11 to 14 weeks into their pregnancy. With this examination, also known as a "dating ultrasound," the doctor will evaluate gestational age and rule out or identify any major abnormalities in early development.
During this early ultrasound, you can expect the doctor to:
- Confirm the pregnancy: This is done by checking the fetal heartbeat.
- Establish a due date: By measuring the fetus, doctors are able to confirm the gestational age — or how far along the pregnancy is — and establish an estimated due date.

- Detect the number of babies: If there is more than one fetus, the doctor should be able to see it.
- Check for ectopic pregnancy: A doctor can evaluate if the pregnancy is developing where it's supposed to. An ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilized egg attaches outside the uterus.
- Screen for genetic orders: This exam typically includes a nuchal translucency screening, which is used to rule out Down Syndrome and physical defects of the heart like congenital heart disease.
The second ultrasound comes around 18 to 20 weeks. Also known as the "anatomy scan," the second trimester ultrasound is administered to check on the growth of the baby's vital organs and the position of the placenta. And yes, for those of you eager to start planning or choosing names, "fetal genitalia can also be imaged," says Chasen.
During the second ultrasound, you can expect the doctor to:
- Examine the fetal anatomy: At this point, a doctor can detect any abnormalities in structures like the spine, heart, kidneys, brain, face, and limbs.
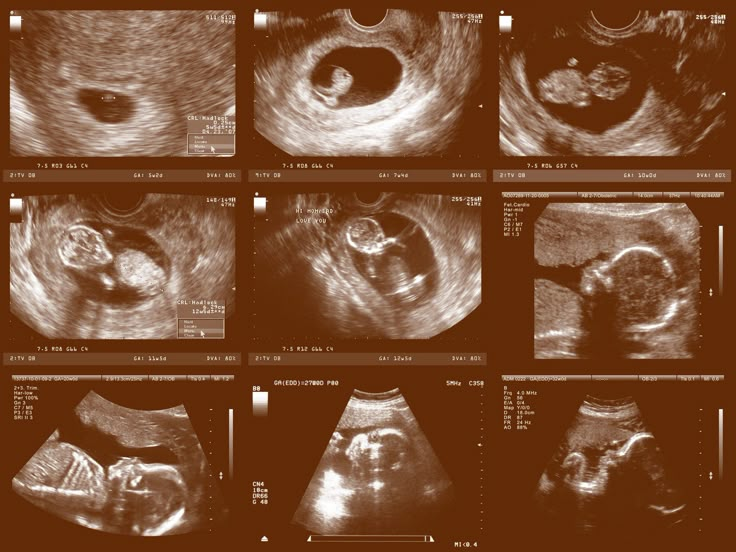
- Check the biological sex: If you don't want to know the biological sex of the baby, be sure to let your health care provider know beforehand.
- The position of the placenta: A low-lying placenta, or placenta previa is when a woman's placenta covers the cervix and can block the fetus's path through the birth canal during labor. In this case, your obstetrician will suggest at least one additional ultrasound to see if the placenta reorients and clears the way. If it doesn't, a cesarean delivery is required.
While two standard ultrasounds are considered routine, there are many reasons why an expecting parent may need more.
Some patients may have their first ultrasound prior to 11 weeks. The start of an intrauterine pregnancy is visible around 6 weeks, so an ultrasound that occurs any time after six weeks is generally reliable for determining how far along a patient may be. If you have an early ultrasound, you still will need an ultrasound at the 11 to 14 week period to properly assess development.
If you have an early ultrasound, you still will need an ultrasound at the 11 to 14 week period to properly assess development.
If any abnormalities or complications are detected during either of the routine ultrasounds, such as the position of the placenta, you might need more, says Chasen.
You may also need additional ultrasounds if your baby's at risk of birth defects or is extremely under or overweight by the time you reach term. The following can increase your baby's risk:
- If you smoke or drink alcohol while pregnant, or have a family history of birth defects, it can increase your baby's risk of birth defects.
- If you have asthma, inadequate weight gain during pregnancy, or high blood pressure, it can increase your baby's risk of being underweight.
- If you're overweight or develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy, it can increase your baby's risk of being overweight come delivery time.
In high-risk populations — usually due to weight, age, or medical problems — weekly ultrasounds may be recommended during the final month of pregnancy. For these patients, these quick ultrasounds are used to assess amniotic fluid and fetal movement to make sure all is well with the pregnancy.
For these patients, these quick ultrasounds are used to assess amniotic fluid and fetal movement to make sure all is well with the pregnancy.
An ultrasound may cost several hundred to over one thousand dollars, but you usually should not have to pay the entire bill.
Normally, your health insurance will cover most, or all of, the cost of an ultrasound if it deems the scan to be medically necessary. However, depending on your insurance plan, you may have to pay for the scan as part of your deductible.
The cost also depends on where you get an ultrasound and in what region. For example, an ultrasound at a hospital could run over $1,000. Whereas you can visit your local Planned Parenthood health center for low-cost ultrasounds whether you have health insurance, or not.
And an ultrasound in central Ohio can be as high as $1,205 while the max cost in NYC is $2,315. That's according to the free online tool HealthcareBluebook, which collects prices from large health plans nationwide. You can look up cost estimates for your specific area on HealthcareBluebook.com.
You can look up cost estimates for your specific area on HealthcareBluebook.com.
While most women can expect at least two ultrasounds during pregnancy — in their first and second trimesters respectively — there are many reasons why your doctor may advise for more.
Ultrasound exams are important when monitoring the development of your baby, and it's normal to feel anxiety with the idea of needing more screenings beyond the routine checkups. Be sure to ask your healthcare provider questions, as well as for resources pertaining to any unforeseen issues that may arise.
- Yes, you can breastfeed while pregnant but there are risks
- How long experts recommend mothers breastfeed to keep their baby healthy
- How to increase your breast milk supply right after giving birth
- When to take a pregnancy test for the most accurate result
- Doctors debunk the 25 biggest pregnancy myths
Jennifer Larson
Jennifer Larson is a freelance writer for Insider.
Read moreRead less
When to do the first ultrasound during pregnancy - "happy days" for screening of the 1st trimester
The world of a modern woman is always full of important events, meetings and an endless series of pre-planned things. When pregnancy occurs, many planned events can be moved from “expected” to “impossible” or simply postponed indefinitely. It is quite difficult to worry in advance and reschedule an important event at the most appropriate time, because planning events against the backdrop of pregnancy is a very difficult science.
Therefore, when pregnancy occurs, it is advisable to draw up at least an approximate “life plan for 9 months”. For example, it is known that maternity leave is most often preceded by unspent regular leave, and registration for pregnancy is preceded by the fact that a pregnancy has occurred and is developing normally.
Many events will now depend on how the new life develops. So, when a multiple pregnancy is diagnosed, not only the estimated due date will change, but maternity leave will come 14 days earlier, and the beginning of unspent leave will move with it. Therefore, one of the first steps in the event of a desired pregnancy is the passage of an ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Scientific and technological progress is rapidly changing the whole world, including the state of the prenatal ultrasound diagnostic service. Opportunities are changing, and with them the timing of the passage of research, which I would like to dwell on in more detail.
So, when a multiple pregnancy is diagnosed, not only the estimated due date will change, but maternity leave will come 14 days earlier, and the beginning of unspent leave will move with it. Therefore, one of the first steps in the event of a desired pregnancy is the passage of an ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Scientific and technological progress is rapidly changing the whole world, including the state of the prenatal ultrasound diagnostic service. Opportunities are changing, and with them the timing of the passage of research, which I would like to dwell on in more detail.
When to do an ultrasound scan during pregnancy
In 2012, the regulation “Decree of the Health Committee of the Government of St. Petersburg No. 39-r”1 came into force in St. Petersburg. Based on the above document, for a full-fledged ultrasound screening, it is desirable to undergo a study in “... the first trimester: 11 + 0-13 + 6 weeks; 18+0-20+6 weeks; and 32+0-34+6 weeks of pregnancy. ” However, these terms apply only to uncomplicated singleton pregnancies. At the same time, early registration is limited to up to 12 weeks of pregnancy with the ensuing consequences (payment of a lump-sum allowance to women registered in medical institutions in the early stages of pregnancy, clause 2-c of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 15, 2001 N 727 (as amended on 04.09.2012).
” However, these terms apply only to uncomplicated singleton pregnancies. At the same time, early registration is limited to up to 12 weeks of pregnancy with the ensuing consequences (payment of a lump-sum allowance to women registered in medical institutions in the early stages of pregnancy, clause 2-c of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 15, 2001 N 727 (as amended on 04.09.2012).
Therefore, at 11 weeks, a pregnant woman can be registered when establishing the fact of a developing pregnancy , for which ultrasound "... in the first trimester" is recommended. Most doctors recommend doing it at terms 7-8 weeks of pregnancy , because it is at this time that the heartbeat of a developing embryo is always determined as a sign of the physiological development of pregnancy.
The next obligatory steps in the ultrasound are screening. The entire pregnancy is divided into three periods (trimesters) and ultrasound plays an important role in each.
What is the diagnostic window for ultrasound during pregnancy
The first screening study is carried out from 11 weeks 0 days of pregnancy to 13 weeks 6 days of pregnancy. These limits are adopted for the timely detection of pathological conditions that determine the prognosis for the health of the fetus. Theoretically, any pregnant woman can apply for an ultrasound both at the beginning of the eleventh and at the end of the thirteenth week - the entire period is screening. However, among doctors who have dedicated their lives to prenatal ultrasound diagnostics, there is an opinion about the most preferable period in each screening period - the so-called " diagnostic window" or "happy days" .
Terms of fetal ultrasound examination
| Legally regulated period (order KZ SPb No.  39-r dated 02/01/12) 39-r dated 02/01/12) | Optimal timing/happy days |
| - | 7-8 |
| 11 weeks 0 days – 13 weeks 6 days | 12 weeks 2 days - 12 weeks 4 days |
| 18 weeks 0 days – 20 weeks 6 days | 20 weeks 0 days - 20 weeks 6 days |
| 32 weeks 0 days – 34 weeks 6 days | 32 weeks 0 days - 33 weeks 3 days |
Diagnostic window in the 1st trimester of pregnancy
For the first screening study, these days include the interval from 12 weeks to 12 weeks. 2 days to 12 weeks 4 days . It is in this interval that the fetus has already grown enough to evaluate the smallest organs (eye lenses, heart), and the probability of ascertaining the most important morphological changes is significantly higher than at 11 weeks 0 days. On the other hand, each day lived by the baby increases not only the height and weight of the body, but the quality of the picture on the ultrasound machine.
On the other hand, each day lived by the baby increases not only the height and weight of the body, but the quality of the picture on the ultrasound machine.
According to various authors, the frequency of congenital pathology reaches 5%, and for patients in this group it is especially important to identify the problem at an early stage. In such special cases, it may be necessary to expand the range of diagnostic procedures, including prenatal karyotyping (obtaining samples of fetal tissue or amniotic structures in order to determine its karyotype). It takes time to carry out these procedures, from preparing the necessary tests for a pregnant woman, ending with directly invasive diagnostics and obtaining results about the health of the fetus.
In some cases, the established disease of the fetus raises the question of the impossibility of prolonging the pregnancy. According to the current legislation of the Russian Federation, the procedure of medical termination of pregnancy by the decision of the woman can be performed ". .. no later than the end of the twelfth week of pregnancy", but "... not earlier than 48 hours from the moment the woman applied to the medical organization for artificial termination of pregnancy" (clause 3.1, clause 3-b of article 56. Federal Law No. 323 of November 21, 2012)2. In other words, if a patient goes for an ultrasound scan at 12 weeks 5 days, if a serious pathology is detected, she is no longer sent for an artificial medical abortion, but for an abortion, which is a more complex and traumatic procedure. Therefore, when asked about the best rock for the first screening, almost any practitioner will answer: "up to 12 weeks 4 days" .
.. no later than the end of the twelfth week of pregnancy", but "... not earlier than 48 hours from the moment the woman applied to the medical organization for artificial termination of pregnancy" (clause 3.1, clause 3-b of article 56. Federal Law No. 323 of November 21, 2012)2. In other words, if a patient goes for an ultrasound scan at 12 weeks 5 days, if a serious pathology is detected, she is no longer sent for an artificial medical abortion, but for an abortion, which is a more complex and traumatic procedure. Therefore, when asked about the best rock for the first screening, almost any practitioner will answer: "up to 12 weeks 4 days" .
Diagnostic window in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy
The second screening period occurs at 18 weeks. 0 days and ends at 20 weeks 6 days pregnant . "Lucky days" is considered the entire twentieth week: 20 weeks. 0 days - 20 weeks 6 days . Not all the subtleties of the architectonics of the main organs can be considered so successfully, especially in pregnant women with increased body weight at 18 weeks of pregnancy. If so-called "markers of chromosomal problems" are detected, it may be necessary to perform prenatal karyotyping (obtaining fetal blood or amniotic fluid), which may take some time.
Not all the subtleties of the architectonics of the main organs can be considered so successfully, especially in pregnant women with increased body weight at 18 weeks of pregnancy. If so-called "markers of chromosomal problems" are detected, it may be necessary to perform prenatal karyotyping (obtaining fetal blood or amniotic fluid), which may take some time.
The collection of the material itself takes several minutes, but the preparation of the pregnant woman (examination, obtaining the results of blood and urine tests, etc.), transporting the material to the laboratory, examination and obtaining the results can take several days. If serious deviations in the state of health of the fetus are detected, in order to resolve the issue of further management tactics, the pregnant woman is sent to undergo a prenatal consultation consisting of an ultrasound doctor, a specialist in the field to which the identified disease belongs (for example, a surgeon, neurosurgeon, cardiologist, etc. ) .
) .
Prior to the new regulation, the second screening period ranged from 18-22 weeks, even earlier than 18-24 weeks of pregnancy. According to WHO recommendations, the fetus becomes viable from the 22nd week of pregnancy, therefore, before this period it is very important to obtain all possible information about its condition and form a prognosis for health and later life. That is why now there is a restriction regulated by law, so that if serious problems with the health of the fetus are detected, all additional diagnostic procedures should be carried out in a timely manner and, if necessary, terminate the pregnancy without violating the Legislation of the Russian Federation2.
Diagnostic window in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy
The third screening period (32 weeks 0 days - 34 weeks 6 days of pregnancy) has two main objectives: the exclusion of congenital malformations with late manifestation and assessment of the fetal condition. Issuance of a referral for the passage of the third ultrasound along with maternity leave of 30 weeks. 0 days of pregnancy potentiates untimely early appeal of pregnant women for the third screening ultrasound before the period of 32 weeks 0 days, which in turn may require a second planned ultrasound in the "scheduled time". A later turnout (after 34 weeks) reduces the quality of the ultrasound picture obtained by changing the relationship between the amount of amniotic fluid and the volume of the fetal body towards the latter. Therefore " happy days" the third trimester can be considered the period 32 weeks 0 days - 33 weeks 3 days of pregnancy .
Issuance of a referral for the passage of the third ultrasound along with maternity leave of 30 weeks. 0 days of pregnancy potentiates untimely early appeal of pregnant women for the third screening ultrasound before the period of 32 weeks 0 days, which in turn may require a second planned ultrasound in the "scheduled time". A later turnout (after 34 weeks) reduces the quality of the ultrasound picture obtained by changing the relationship between the amount of amniotic fluid and the volume of the fetal body towards the latter. Therefore " happy days" the third trimester can be considered the period 32 weeks 0 days - 33 weeks 3 days of pregnancy .
Unscheduled ultrasound at any stage is required, as a rule, only in case of complicated pregnancy, therefore, it is prescribed only according to indications and is performed regardless of the gestational age.
Notes: 1 - Order of the Health Committee of the Government of St.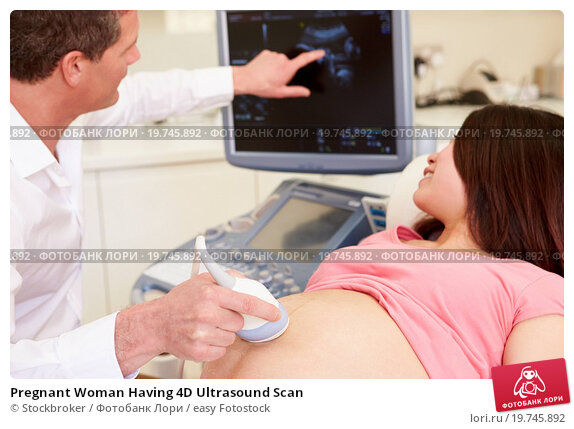 Petersburg dated February 1, 2012 N 39-r "On measures to reduce hereditary and congenital diseases in children in St. Petersburg".
Petersburg dated February 1, 2012 N 39-r "On measures to reduce hereditary and congenital diseases in children in St. Petersburg".
2- Article 56 "Artificial termination of pregnancy". Federal Law of the Russian Federation of November 21, 2011 N 323-FZ "On the basics of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation", entered into force: November 22, 2011, published on November 23, 2011 in "RG" - Federal issue No. 5639
Ultrasound in early pregnancy: 3D and 4D, when to do, is it harmful, what shows
Ultrasound in early pregnancy: 3D and 4D, when to do, is it harmful, what shows - Juno -->home
Articles
ultrasound during pregnancy
An ultrasound is scheduled for every woman in an "interesting position". The expectant mother must undergo this procedure at least twice in 40 weeks. The study allows you to specify the gestational age, make measurements of the height and weight of the fetus. You will learn about the benefits and harms of ultrasound in our article.
You will learn about the benefits and harms of ultrasound in our article.
Planned ultrasound during pregnancy
From 2021, the expectant mother will have to undergo at least two ultrasound examinations during pregnancy. The timing of the planned examination is determined by the Ministry of Health. These studies are called screening. Their task is to identify possible violations in the development of the fetus and the course of pregnancy and provide the woman with qualified medical care in time.
Until 2021, a pregnant woman underwent an ultrasound in trimesters - one in each specified period. But according to order N 1130n, now the expectant mother will be screened only twice - in the first and second trimester.
First trimester
The first screening ultrasound is performed at 11-14 weeks. At the same time, biochemical screening is done. The expectant mother donates blood for the determination of β-hCG and PAPP-A. The data obtained are evaluated together with the results of the first ultrasound screening. Together, these methods make it possible to identify disorders in the development of the fetus, such as Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities.
Together, these methods make it possible to identify disorders in the development of the fetus, such as Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities.
In the first trimester, ultrasound can determine:
- Gestational age. If the expectant mother does not remember when her last menstruation was or she has an irregular menstrual cycle, an ultrasound examination will help. The doctor will specify the gestational age by ultrasound. But you need to remember: these calculations will not be too accurate, and therefore, if possible, gynecologists are guided by the date of the last menstruation and calculate the due date from it.
- Number of fruits. In a multiple pregnancy, the doctor examines the placenta (or chorion) and membranes in detail. The tactics of managing pregnancy and childbirth depend on their location and quantity.
- Fetal malformations. For example, to diagnose Down syndrome, the doctor evaluates the thickness of the collar space and visualization and the length of the nasal bone, the length of the thigh.
 Ultrasound in early pregnancy can also reveal malformations of the internal organs and nervous system.
Ultrasound in early pregnancy can also reveal malformations of the internal organs and nervous system. - The condition of the cervix (cervicometry), uterine appendages and uterine wall are assessed.
Despite a thorough examination, it is impossible to completely exclude fetal malformations only by the results of ultrasound. If in doubt, your doctor may recommend an invasive test such as amniocentesis or cordocentesis. The second ultrasound screening also helps to clarify the diagnosis, in which it is possible to examine the organs and tissues of the fetus in more detail.
Second trimester
The second screening ultrasound is done at a period of 19-21 weeks. Here is what the doctor evaluates:
- Correspondence of the size of the fetus to the gestational age. If they are less than normal, they talk about fetal growth retardation.
- Structure of internal organs and nervous system. At this time, malformations of the heart, brain, digestive tract and other organs and systems can be detected.
- The state of the placenta and umbilical cord, features of blood flow in them. If the blood flow is disturbed, the fetus will suffer from a lack of oxygen.
- Volume of amniotic fluid. If there is too much amniotic fluid, they talk about polyhydramnios, a little - about oligohydramnios.
At the second ultrasound screening, the sex of the fetus can be determined. This is not necessary, and if the expectant mother wants a surprise, she can ask the doctor not to report the results.
The timing of the ultrasound and the interpretation of the results is done by a gynecologist observing a pregnant woman. The doctor will tell you when to do an ultrasound scan during pregnancy, and if necessary, he will prescribe an unscheduled examination.
Unscheduled ultrasound during pregnancy
Outside of screenings, ultrasound is prescribed in such situations:
- Confirm pregnancy. This is necessary in order to make a correct diagnosis - after all, tests are sometimes wrong, and a delay in menstruation is not always associated with an interesting situation.
 Such an ultrasound is done in the early stages - at 4-6 weeks.
Such an ultrasound is done in the early stages - at 4-6 weeks. - Determine the location of the gestational sac. This is necessary in order to exclude an ectopic pregnancy.
- When bloody discharge from the genital tract appears, ultrasound is done on an emergency basis at any stage of pregnancy - it is necessary to exclude the development of complications.
- In the later stages - if the fetus has stopped moving or, on the contrary, has become overly active. In addition to ultrasound, CTG (cardiotocography) is done from the 33rd week to assess the fetal heartbeat.
- Before childbirth - if there is a risk of complications. With ultrasound, you can clarify the weight and position and presentation of the fetus, the condition of the placenta, umbilical cord and amniotic fluid.
With multiple and complicated pregnancies, ultrasound can be done more often. The terms are set by the attending physician individually for each woman.
Ultrasound features in early pregnancy
Many expectant mothers are wondering what week the ultrasound will show pregnancy. Modern devices allow this to be done at about 3-4 weeks if a vaginal sensor is used (transvaginal method). If a specialist conducts a study through the abdominal wall (transabdominal method), then he will be able to detect a fetal egg later, at 5-6 weeks.
Modern devices allow this to be done at about 3-4 weeks if a vaginal sensor is used (transvaginal method). If a specialist conducts a study through the abdominal wall (transabdominal method), then he will be able to detect a fetal egg later, at 5-6 weeks.
Note
Knowing how long the ultrasound shows pregnancy, you can not run for an examination immediately after a missed period. For a very short time, the doctor may not see the fetal egg - and not because it is not there, but because the equipment is not perfect. There is no need to create a cause for alarm for yourself - it is better to wait until 5-6 weeks, when the fetal egg will be clearly visible.
In the early stages, ultrasound can detect serious problems such as ectopic or regressive (non-developing) pregnancy. The sooner the pathology is detected, the easier it will be to avoid complications.
Types of ultrasound during pregnancy
Modern equipment of ultrasound rooms allows for high-precision ultrasound examinations. In addition to the standard 2D ultrasound, three- and four-dimensional studies - 3D and 4D - have now become very popular. Let's consider them in detail.
In addition to the standard 2D ultrasound, three- and four-dimensional studies - 3D and 4D - have now become very popular. Let's consider them in detail.
- 2D is a study in which a black and white image is obtained in two dimensions - in height and length. This option is quite informative. The doctor can measure the growth and proportions of the fetus, as well as assess the condition of the placenta and amniotic fluid. 2d is the most common and "old" procedure among all ultrasound diagnostic formats.
- 3D is a more modern examination method. It gives a detailed and three-dimensional image of the object. 3D ultrasound during pregnancy allows not only to assess the condition of the fetus in detail, but also to take a photo of it. 3D ultrasound is not a mandatory procedure, it is carried out at the request of the baby's parents.
- 4D Pregnancy Ultrasound provides a video image of the fetus. Parents are given the opportunity to watch the child in real time: how he sleeps, eats or sucks his thumb.
 The video material, like the photo, is recorded on a disk and remains as a keepsake for mom and dad.
The video material, like the photo, is recorded on a disk and remains as a keepsake for mom and dad.
Experts say that all existing methods of ultrasound diagnostics are the same in terms of the impact on the fetus: the power of the ultrasound wave and its intensity are identical in all cases.
Many women are interested in seeing a pregnancy ultrasound photo by week. It is not necessary to do an ultrasound without indications so often, but you can find such photographs in scientific papers and see how a child develops in the mother's womb.
Is it harmful to do ultrasound for pregnant women
There is no consensus among experts: some believe that the study should be carried out without fail, others - that it is best to refuse the effect of ultrasound on the fetus. Russian and foreign specialists in the field of gynecology also do not find a compromise on this issue.
Meanwhile, according to statistics, not a single expectant mother or child in the womb suffered as a result of ultrasound diagnostics. So there are no scientific facts proving the harm of ultrasound to humans. In this regard, most experts who observe the pregnancy of their patients adhere to the principle of the "golden mean". They insist on carrying out two planned procedures, more - only according to indications.
So there are no scientific facts proving the harm of ultrasound to humans. In this regard, most experts who observe the pregnancy of their patients adhere to the principle of the "golden mean". They insist on carrying out two planned procedures, more - only according to indications.
Experts rightly believe that it is impossible to do without ultrasound. It allows you to control the development of the fetus and, if necessary, take timely measures to preserve the health of the baby.
Other articles
08/17/2022
Perinatal screening of the 1st trimester of pregnancy
Perinatal screening of the 1st trimester of pregnancy - what are the features? What is important for a future mother to know? We tell you all the important details in our article!
08/05/2022
Insomnia during pregnancy
The need for proper sleep is a natural desire of the body.