How do i know if my child has tonsillitis
Tonsillitis (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
What Is Tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis (tahn-suh-LYE-tus) is an infection of the tonsils. Tonsils are lumps of tissue on both sides of the back of the throat that help the immune system protect the body from infections. Inflamed tonsils get red and swollen and can cause a sore throat.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Tonsillitis?
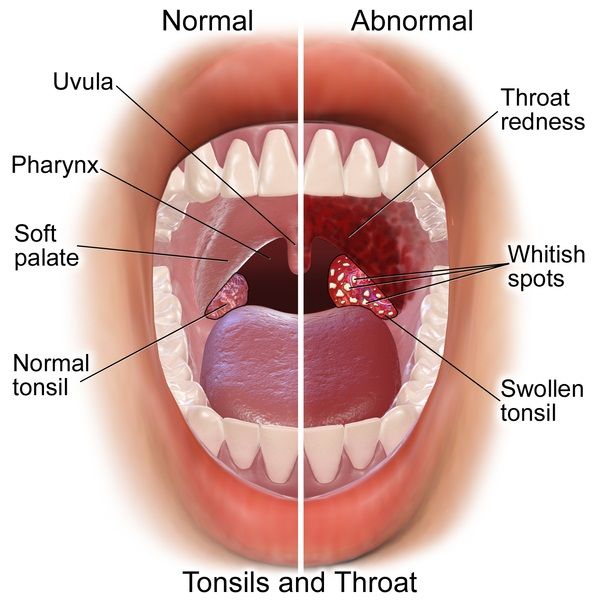
Inflamed tonsils look red and swollen, and may be covered with a yellow or whitish coating or spots. A child with tonsillitis may have:
- a sore throat
- fever
- bad breath
- swollen glands (lymph nodes) in the neck
- trouble swallowing
- stomachache
- headache
What Causes Tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is usually caused by a
virussuch as:
- adenovirus
- the flu
- Epstein-Barr virus (mono)
Bacteria also can cause it, most commonly group A streptococcus (strep throat). Rarely, tonsillitis can be caused by something other than an infection.
Who Gets Tonsillitis?
Anyone at any age can get tonsillitis. Strep throat is most common in kids and teens ages 5 to 15.
How Is Tonsillitis Diagnosed?
Health care providers will ask about symptoms and do an exam. They'll check the inside of the mouth, the back of the throat, and the neck.
A health care provider may use a soft cotton swab to gently collect a sample from the tonsils and back of the throat. This can be:
- tested quickly with a rapid strep test that gives an answer within minutes
- sent to a lab for a throat culture, which takes a few days
If the rapid strep test doesn't show signs of strep, the health care provider will depend on the culture for a final diagnosis.
It's important to call your health care provider if your child has tonsillitis symptoms.
How Is Tonsillitis Treated?
Treatment depends on whether the tonsillitis is caused by:
- a virus, in which case the body will fight the infection on its own
- bacteria, in which case the doctor will prescribe an antibiotic.
 Help your child take the antibiotic exactly as directed. This helps symptoms clear up quickly and prevents spreading the infection to others.
Help your child take the antibiotic exactly as directed. This helps symptoms clear up quickly and prevents spreading the infection to others.It's important to finish the entire prescription — even if your child feels better in a few days — or the infection could come back. This also helps prevent a more serious health problem that streptococcus can cause, called rheumatic fever, which can damage the heart.
Rarely, a health care provider might recommend a tonsillectomy (surgery to remove the tonsils) if a child's tonsils get infected a lot or are so big they make it hard to breathe at night. Tonsillectomy used to be very commonly done. Now, experts use guidelines to decide if tonsil removal is the best treatment. In general, tonsillectomy may be considered if a child has seven sore throat episodes in 1 year, five episodes 2 years in a row, or three episodes 3 years in a row.
How Can I Help My Child Feel Better?
Make sure that your child drinks lots of fluids and gets plenty of rest. If swallowing hurts, serve liquids and soft foods. Some kids prefer warm drinks, like soup or sweetened tea. Other kids like the feel of cold or frozen foods on their throat, such as milkshakes, smoothies, ice pops, or ice cream. Older kids can suck on hard candies or throat lozenges.
If swallowing hurts, serve liquids and soft foods. Some kids prefer warm drinks, like soup or sweetened tea. Other kids like the feel of cold or frozen foods on their throat, such as milkshakes, smoothies, ice pops, or ice cream. Older kids can suck on hard candies or throat lozenges.
You can give a pain reliever, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, for throat pain. Don't give aspirin or other products that contain aspirin, though, because these can put kids at risk for Reye syndrome.
Is Tonsillitis Contagious?
Tonsillitis is contagious. Sneezing and coughing can pass the germ causing the illness from one person to the next.
Can Tonsillitis Be Prevented?
Try to keep kids away from anyone who already has tonsillitis or a sore throat, and make sure everyone in your family washes their hands well and often.
If someone in the family has tonsillitis, keep their drinking glasses and eating utensils separate, and wash them in hot, soapy water. They should not share food, drinks, napkins, or towels with other family members. Give them a new toothbrush after they're treated and no longer contagious.
Give them a new toothbrush after they're treated and no longer contagious.
What Else Should I Know?
If the sore throat gets worse, especially on one side, call your doctor. This could be a sign of a peritonsillar abscess. This happens when bacteria spread from the tonsil to the space around it and fill it with pus. Other signss of an abscess include fever, headache, earache, drooling, or a muffled voice. Treating an abscess might be done in a hospital, possibly with surgery to drain the infection. Tonsillectomy may be considered for kids who get multiple peritonsillar abscesses.
Tonsillitis (for Kids) - Nemours KidsHealth
Reviewed by: Steven M. Andreoli, MD
en español Amigdalitis
Way in the back of your throat are your tonsils — one on the right and one on the left. They are part of your body's infection-fighting system to keep you from getting sick.
But what happens if these infection fighters get infected? Then you have tonsillitis (say: tahn-suh-LYE-tus).
What Are Tonsils?
The tonsils' job is to help fight germs that come in through our mouth or nose before they cause infections in the rest of the body. Usually, tonsils do their job well. But sometimes bacteria or viruses get into the tonsils and infect them. When this happens, you have tonsillitis.
How Can I Tell if I Have Tonsillitis?
If you have tonsillitis, your throat usually hurts and it's hard to eat, drink, or even swallow. You also might have a fever.
Here are some other signs that bacteria or a virus are infecting your tonsils:
- red (swollen or irritated) tonsils
- a yellow or white coating on the tonsils
- swollen glands in the neck
- bad breath
- headache
- stomachache
What Will the Doctor Do?
The doctor will ask you how you've been feeling and then look at your tonsils. He or she will probably use a wooden stick called a tongue depressor to help hold your tongue down to get a good look at what's going on in there.
The doctor also might look into your nose and ears, listen to your chest, feel your neck, and look for other signs of infection. Bacteria and viruses both can cause tonsillitis. It's important for your doctor to know if it's caused by strep bacteria. If you have this kind of infection, known as strep throat, you need medicine to kill the strep bacteria.
To check for strep, the doctor will use a long cotton swab to swipe the back of your throat. This test, called a throat culture, doesn't hurt but can feel a little weird. Your doctor may use the swab to do a test called a rapid strep test. Within minutes, this test will tell your doctor if there are any strep bacteria in your throat. If it's positive, you have strep throat. If it's negative, the doctor will send a sample to a lab for testing and get the result in a couple of days.
How Is Tonsillitis Treated?
If the tonsillitis is caused by strep bacteria, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics, a type of medicine that kills bacteria. It's very important to take the antibiotics exactly as directed and to finish the entire prescription — even if you start feeling better in a few days — or the infection could come back.
It's very important to take the antibiotics exactly as directed and to finish the entire prescription — even if you start feeling better in a few days — or the infection could come back.
If the tonsillitis is caused by a virus, antibiotics won't work and your body will fight off the infection on its own.
Sometimes kids get an operation to remove their tonsils, but only if their tonsils get infected a lot or are so big they make it hard for the kid to breathe at night.
If you get tonsillitis, here are some tips that can help you feel better:
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- If it hurts to swallow regular food, try smooth foods, like flavored gelatin, soups, ice pops, and applesauce.
- Take it easy until you feel better.
- Wash your hands well and often.
Soon your tonsils will be back in action and ready to fight germs again!
Reviewed by: Steven M. Andreoli, MD
Date reviewed: October 2019
Tonsillitis (angina) in children: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
November 5, 2020
Tonsillitis is an infectious disease that affects one or more tonsils. 1
1
There are 6 tonsils in total: two palatine, two tubal, one lingual and one pharyngeal (aka adenoid). All these tonsils form the lymphoid-pharyngeal ring, which is responsible for local immunity. Also included in this ring are lymphoid granules located on the back of the pharynx. 2
Due to the immaturity of immunity, children are more susceptible to various infections, as well as the development of tonsillitis as an independent disease. Children of preschool and school age are especially often sick. And this is quite logical, the frequency of tonsillitis is higher in those children who attend kindergartens, schools, clubs, playrooms. You can also get tonsillitis by airborne droplets and contact during close contact with a patient with acute tonsillitis or when playing with toys that a sick child has played before. In infants, tonsillitis is less common. 3
The incidence of tonsillitis in children and adults may differ not only because of the difference in immunity, but also because of the anatomy. Children have tonsil-adenoid. Since the tonsil is not a steam room, it is more correct to call it in the singular - adenoid. Inflammation of this tonsil is called adenoiditis. 4 With age, the adenoid ceases to function and, one might say, disappears, so adults do not get sick with adenoiditis.
Children have tonsil-adenoid. Since the tonsil is not a steam room, it is more correct to call it in the singular - adenoid. Inflammation of this tonsil is called adenoiditis. 4 With age, the adenoid ceases to function and, one might say, disappears, so adults do not get sick with adenoiditis.
Forms and classification of tonsillitis in children
5It should be noted that there is no fundamental difference between adult and child forms.
Disease share:
- in the form
- according to the pathogen
- in the form of defeat
| Classification | Comment | Classification: | comment: | |
| Classification: | Tonsillitis can be: | Comment: | 9000 bacterial: - bacterial BotTereal: - Bacterial Bacterial Bacterial: Bacterial A and other groups Viral: - influenza and parainfluenza virus - Corey |
| Classification: | In the form of defeat: 9004 9,9004 | 9004 9004 9004 comments: | - catarrhal |
6
Symptoms of acute tonsillitis in children
- the disease is characterized by a sharp rise in temperature up to 40 °C
- the child may complain of a sore throat, refuse to eat and drink because of this
- the child becomes lethargic and capricious, contact with him can be difficult
Throat with sore throat
When examining the throat, the picture may differ due to the pathogen, the form of the lesion and the localization of the process.
Lymph nodes may be enlarged and painful.
In the child's throat, one can mainly see red mucous, enlarged and edematous tonsils. The appearance of raids of a different nature is possible.
When the adenoid is inflamed, there is difficulty in breathing through the nose, the child breathes mainly through the mouth. This is due to the enlargement of the pharyngeal tonsil due to edema and occlusion of the nasopharynx.
In children, the adenoid becomes inflamed regularly, which is why the disease quickly becomes chronic.
How to treat a sore throat in a child
It is necessary to provide the child with bed rest, the room must be well ventilated. Drinking plenty of water will help reduce signs of intoxication.
In drug therapy, drugs are used to eliminate the causative agent. In some cases, an antibiotic is needed. Only a doctor can prescribe an antibiotic!
Antipyretic drugs can be given strictly according to the instructions and according to the recommended dosage.
In children, many antiviral drugs are allowed to be taken only from the age of 3 years. Consultation with a pediatrician before using any medication is required.
Consultation with a pediatrician before using any medication is required.
The age of the child should be taken into account when choosing the form of the preparation for topical therapy.
- Children from 3 years old can be recommended Spray Tantum ® Verde 7
- from 6 years old can be used Tantum ® tablets
- from 12 years old - Solution for rinsing tantum ® Verde 8
Benzidamin, which is part of Tantum ® Verde, is absorbed in the necessary concentration and is influenced for edema 10 . The drug has anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and analgesic effects and is effective from the 1st minute after application. 9
Tantum Spray ® Verde
Read more
Solution Tantum ® Verde
Read more
Tantum tablets ® Verde
Read Tonsillitis Prevention in children
In the basis of the prevention of tonsillitis in children, regular pedestrian walks are lying, classes, classes. sports and hardening.
sports and hardening.
A child's diet must contain a large amount of fresh vegetables and fruits, greens, low-fat protein foods. Children are not recommended to eat fatty, fried foods, fast food, fast carbohydrates.
Parents need to carefully monitor the personal hygiene of the child: the child should regularly wash his hands and brush his teeth.
At home, it is recommended to maintain optimal humidity (50-60%) and air temperature (no more than 21 °C) and carry out regular wet cleaning with room ventilation.
Tonsillitis: symptoms and treatment | Throat Encyclopedia GEXORAL®
11/23/2022
255 605
9 minutes
Author, editor and medical expert - Klimovich Elina Valerievna. 1 entering the body through the mouth and nose. Sometimes this leads to the development of an inflammatory process. Let's see what signs can be used to suspect tonsillitis, and how to treat it in adults.
Up to contents
A bit of anatomy and physiology
The palatine tonsils are located on the side walls of the pharynx and are shaped like large almond kernels. The second name - "tonsils" - tonsils received because of their resemblance to acorns, which in Latin are called "glandulae". Since the Latin word for tonsils is "tonsilla", their inflammation is called tonsillitis.
The second name - "tonsils" - tonsils received because of their resemblance to acorns, which in Latin are called "glandulae". Since the Latin word for tonsils is "tonsilla", their inflammation is called tonsillitis.
The palatine tonsils belong to the organs of the immune system and are small accumulations of lymphoid tissue 2 . The part of the tonsils protruding into the pharynx has depressions (lacunae), in the walls of which there are numerous slit-like pockets (crypts) 1 . The surface of the crypts is the "working area" of the tonsils. The main physiological processes take place here: immune cells, phagocytes, absorb microbes that have entered the tonsils, “study” them, send the information received to higher sections of the immune system, and then kill the infection 1 . If the microbes are very aggressive and there are a lot of them, and even the immune system is weakened, an infectious inflammation of the tonsils develops - tonsillitis.
Up to contents
Causes of tonsillitis
Depending on the nature of the course, tonsillitis can be:
Acute inflammation of the tonsils is caused by infection 1 . It can be viral, bacterial or mixed 1.2 .
The viral nature of angina prevails in adults and children over 15 years of age 1.2 . It usually develops with acute respiratory viral infections, which are caused by rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, parainfluenza viruses 1 . At the same time, tonsillitis is accompanied by rhinitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis and other diseases of the respiratory tract 1 .
Children 5-15 years old often have bacterial tonsillitis, and in the first place (up to 30% of cases) among them is the most dangerous type of tonsillitis caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus 1 . In adults, this type of tonsillitis is much less common 1 , and among the bacteria that cause the disease, streptococci of other groups, corynebacteria, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria, staphylococci 1 prevail.
The cause of chronic tonsillitis is also an infection, but, unlike acute processes, caused by less aggressive pathogens 2 . In this case, there may not be acute inflammation of the tonsils, the process is initially chronic and is hidden behind frequent acute respiratory viral infections and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx (nonanginal form of chronic tonsillitis) 2 .
Chronic inflammation leads to the death of functional, ie lymphoid, tonsil tissue and its replacement by connective tissue 1 . Tonsils gradually lose their protective functions, often become easy prey for microbes and viruses, become inflamed and turn into a breeding ground for infection 1 and an irritant for the immune system. As a result of chronic tonsillitis, immune disorders often occur, leading to the development of infectious-allergic and autoimmune diseases 1.2 .
Back to Contents
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
The main symptom of both viral and bacterial tonsillitis is a sore throat that worsens when swallowing and talking 1 . Sometimes it reaches such a degree of severity that it is difficult to take even a small sip of water, not to mention the meal.
Sometimes it reaches such a degree of severity that it is difficult to take even a small sip of water, not to mention the meal.
Sore throat may be accompanied by:
- increased body temperature, up to high fever;
- redness of the tonsils and the appearance of plaque or vesicles on them;
- soreness of anterior cervical lymph nodes 1 .
If you also have a runny nose and cough, it is most likely that inflammation of the tonsils is of a viral nature 1 .
General intoxication caused by infection is expressed in the appearance of weakness, daytime sleepiness, lethargy, headache, aching muscles and joints 1 .
Depending on the picture that can be seen when examining the throat, angina can be catarrhal, follicular, lacunar 1 .
In case of catarrhal angina, the tonsils become red and swollen 1 . With follicular follicles, they increase sharply in volume, whitish dots appear on their surface - follicles filled with pus, which shine through the inflamed mucous membrane 1 . With lacunar angina, the surface of the tonsils is covered with pus, which protrudes from the lacunae 1 .
With lacunar angina, the surface of the tonsils is covered with pus, which protrudes from the lacunae 1 .
Angina caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus is characterized by the appearance of purulent films on the tonsils, which are firmly associated with the underlying tissues 1 . When the films are rejected on the tonsils, bleeding erosions and ulcers are formed 1 .
Tonsillitis associated with the Coxsackie virus proceeds like herpetic sore throat, in which many small bubbles filled with cloudy mucus appear on the tonsils 1 .
Up to content
Features of chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis occurs with exacerbations, during which the same symptoms appear as in angina 2.3 .
During the calm period 3 :
- almost 98% of patients are disturbed by discomfort in the throat;
- putrid breath is noted in up to 88% of patients;
- plugs and purulent deposits on the tonsils are found by doctors in almost 84% of cases;
- adhesions between the tonsils and the arches are detected in approximately 60% of patients;
- enlargement and pain when feeling the cervical lymph nodes are diagnosed in 62% of cases;
- joint pain disturbs every third patient;
- subfebrile temperature (up to 38 0 C) is noted by 18% of patients;
- pain in the heart - about 8% of patients with chronic tonsillitis 3 .

Depending on the stage of development, the disease can proceed in the following forms0006 2.3 .
- Stage I: signs of general intoxication appear, such as subfebrile temperature, weakness, fatigue, as well as joint aches and pain in the heart associated with functional disorders.
- Stage II: complications of tonsillitis, such as paratonsillar abscess, sepsis, rheumatism, heart defects, etc. 2.3 join the general intoxication. In this case, the picture of tonsillitis is complemented by the symptoms of these diseases.
Up to content
Treatment of tonsillitis
The appearance of symptoms of tonsillitis is a reason to visit a doctor. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable. Only a doctor can determine the form of the disease, determine its causes and choose the right treatment.
For tonsillitis caused by bacterial microflora, and especially group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, antibiotics are prescribed 1 ,2 . In addition to these, doctors recommend local treatment - irrigation and gargling with preparations based on antiseptics and analgesics that destroy infection, which relieve pain 1.2 . In mild cases and those who test negative for streptococcus, treatment is generally limited to topical therapy 1.2 .
In addition to these, doctors recommend local treatment - irrigation and gargling with preparations based on antiseptics and analgesics that destroy infection, which relieve pain 1.2 . In mild cases and those who test negative for streptococcus, treatment is generally limited to topical therapy 1.2 .
HEXORAL ® 4,5,6,7,8 can be used as a combination preparation for local therapy of tonsillitis. The GEXORAL ® line includes solutions for rinsing and irrigating the throat, as well as lozenges with various active ingredients and flavors.
hexoral ® Solution
for rinsing the throat
hexoral ® Aerosol
from sore throat
Search for resorption Basil ® - Antiseptic Huxesetid. It is active against most bacteria and some viruses and is capable of providing a mild analgesic effect 4 . HEXORAL ® aerosol has a special nozzle, thanks to which the solution can be evenly distributed over the entire mucous membrane of the pharynx 5 . Traditional treatment of tonsillitis can also be supplemented with lozenges GEXORAL ® TABS 6 , GEXORAL ® CLASSIC 7 and GEXORAL ® 9 0 TAB The last of these drugs contains the powerful anesthetic lidocaine and may be useful in dealing with severe sore throats 8 . Conservative treatment is also indicated for patients with a simple form of chronic tonsillitis 2.3 . It includes not only drug therapy, but also such medical procedures as washing the lacunae of the palatine tonsils, introducing antibacterial and antiseptic drugs into them, as well as various physiotherapeutic procedures that help cleanse the tonsils and stimulate their protective functions 3 .
hexoral ®  It can also help clear the tonsils and relieve a sore throat.
It can also help clear the tonsils and relieve a sore throat.