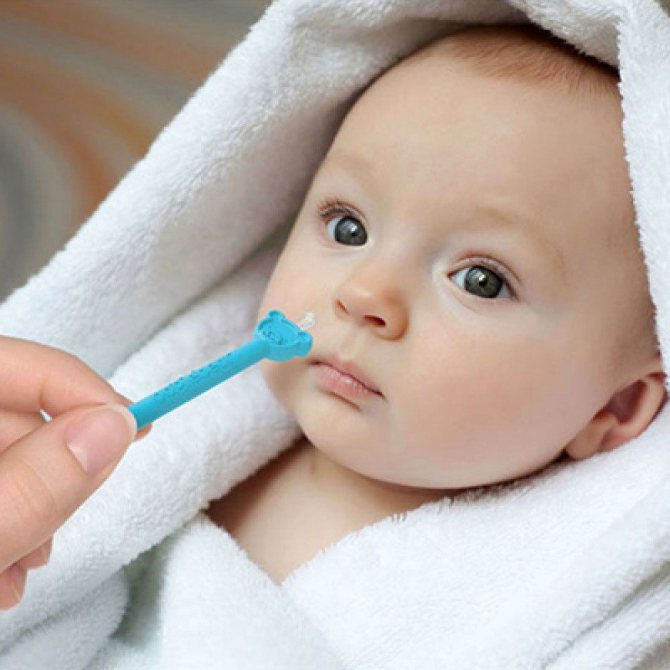
Yellow eye boogers in newborns
Is it normal and how to treat it?
Eye discharge is common in newborns and typically occurs due to a blocked tear duct. However, parents and caregivers can often treat this at home.
Eye discharge is typically harmless and self-resolving. However, discharge that occurs alongside other symptoms in the eye area, such as swelling or tenderness, could indicate an infection or another eye problem. A parent or caregiver of a newborn with these symptoms will need to consult a doctor.
This article discusses how common eye discharge is and explains how to treat it at home. We also cover medical treatment, other causes, complications, and when to contact a doctor.
Eye discharge in newborns is common and rarely a cause for concern. A common cause of eye discharge is a blocked tear duct.
According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, almost 20% of newborns have a blocked tear duct. This condition can occur because the end of the tear duct does not open properly when the baby is born.
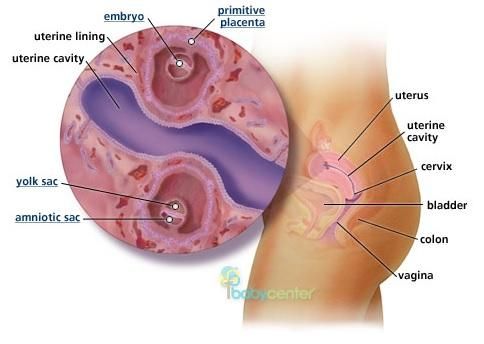
Tears form in the lacrimal gland, which sits just above the eye. Tear fluid helps clean and lubricate the surface of the eye. When a person blinks, the eyelids sweep the tear fluid into these ducts, which drain it into the nose.
If something blocks a tear duct, fluid may no longer be able to drain away from the eye’s surface. Blockages can cause very watery eyes, and sticky discharge may form in the corners.
Learn more about blocked tear ducts.
Blocked tear ducts are a common cause of eye discharge in infants. However, other conditions and factors can also cause discharge.
Conjunctivitis
Eye discharge in newborns can also be a sign of conjunctivitis or pinkeye. Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, a thin membrane that protects the front of the eye. Unlike a blocked tear duct, conjunctivitis often causes the white part of the eye to appear red.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis in newborns can include:
- drainage or discharge that develops between 5 and 12 days after birth
- puffy or tender eyelids, often with skin discoloration
- red, irritated eyes
Conjunctivitis in newborns can sometimes occur alongside a blocked tear duct. However, a pregnant person can also pass on a bacterial or viral infection to their baby when giving birth, leading to conjunctivitis.
However, a pregnant person can also pass on a bacterial or viral infection to their baby when giving birth, leading to conjunctivitis.
Learn more about the symptoms of eye infections.
Chemical irritation
Chemical irritation can also cause conjunctivitis in newborns. Healthcare professionals often give antibacterial eye drops to newborns to prevent infections. These eye drops can sometimes cause irritation that can result in conjunctivitis symptoms.
Learn more about eye irritation.
If the eye discharge is due to a blocked tear duct, it will usually resolve without treatment within 4–6 months.
However, wind, cold weather, and strong sunlight can also worsen symptoms, so a parent or caregiver should aim to protect a newborn’s eyes from these elements.
Clearing discharge
A parent or caregiver can often treat a newborn with a blocked tear duct at home. Before touching the area close to the child’s eyes, it is essential to wash the hands with soap and warm water to prevent infections. A person should also take care to rinse the hands thoroughly after cleaning them to avoid getting soap in the baby’s eye.
A person should also take care to rinse the hands thoroughly after cleaning them to avoid getting soap in the baby’s eye.
To clear away discharge, dip a clean piece of gauze or soft cloth in some lukewarm water, then gently wipe the corner of the eye. If a blocked tear duct affects both eyes, always use a new area of the cloth or gauze to clean the other eye.
Tearduct massage
A doctor may also recommend gently massaging the blocked tear duct to help it open, and they will demonstrate how to do this safely.
To massage the tear duct:
- Lightly press the tip of the index finger against the inside bridge of the newborn’s nose, on the side of the blocked tear duct.
- Make 2 or 3 short downward strokes with the finger along the side of the nose. These should be gentle but firm.
- Perform the massage twice a day — once in the morning and once in the evening.
If the side of the newborn’s nose becomes red or swollen, stop the massage immediately and contact a doctor.
In newborns, blocked tear ducts tend to open up within several months of birth. However, medical intervention may be necessary in some cases.
Surgery
If the blockage has not gone away by the baby is 1 year of age, a doctor may recommend a medical treatment called a nasolacrimal duct probing.
This procedure involves inserting a small probe into the infant’s tear duct. By using probes that gradually increase in size, a doctor will be able to open up the tear duct. They will then use a saline solution to flush out any remaining debris.
Sometimes, the doctor may also insert a small tube, or stent, into the duct to keep it open.
Probing is usually successful in opening the tear duct. For children with a severe blockage, a doctor may recommend a more complicated surgical procedure called a dacryocystorhinostomy to clear out and open the tear duct.
Antibiotics
If an infection is causing eye discharge, the newborn will need prompt medical attention. To treat cases of infectious discharge, a doctor may prescribe topical, oral, or intravenous antibiotics.
To treat cases of infectious discharge, a doctor may prescribe topical, oral, or intravenous antibiotics.
Blocked tear ducts can sometimes lead to an infection called dacryocystitis. Symptoms of this condition may include:
- excessive thick discharge from the eye
- redness in the corner of the eye
- a tender bump or swelling at the side of the nose
- fever
If a newborn has any of these symptoms, a parent or caregiver should consult a doctor.
Newborns with eye discharge or very watery eyes should speak with a pediatrician or an eye doctor specializing in children, called a pediatric ophthalmologist. These healthcare professionals can diagnose the cause of the discharge and check for signs of infection.
Parents or caregivers should seek medical attention if an infant’s eye discharge persists for more than 6 months.
Newborns with signs of an eye infection require immediate medical attention. Signs of an eye infection can include:
- sore or puffy eyes
- swollen eyelids
- yellow or green pus or discharge
- a bump or swelling on the inside corner of the eye
If a parent or caregiver notices any of these symptoms, they should contact a doctor immediately.
Eye discharge in newborns is common and often results from a blocked tear duct. The blockage will usually clear up by itself within 4 to 6 months.
However, newborns with eye redness, eye discharge, or excessive watering of the eyes should speak with a doctor to diagnose the cause and rule out an eye infection.
Parents and caregivers can treat a baby with a blocked tear duct at home by wiping away any discharge and gently massaging the area twice a day. A doctor can demonstrate how to do this.
Discoloration, swelling, or soreness in the eye can indicate an eye infection. Speak with a doctor immediately if an infant has these signs.
Is My Baby’s Eye Discharge Normal?
Written by Nicole Blades
In this Article
- What’s Normal?
- When It’s Conjunctivitis
- When Treatment Is Needed
As the parent of a newborn, nothing beats staring lovingly into your sweet little bundle’s eyes. (Well, watching your baby sleeping soundly comes pretty close!) But what if when you look into your child’s eyes, you see that they have goopy, sticky discharge? Is it something to be concerned about?
What’s Normal?
First of all, take a breath, because sticky eye discharge in newborns is very common. If the white part of your baby’s eye -- the sclera -- is clear and there is no redness, but there is discharge, it’s most likely a blocked tear duct.
If the white part of your baby’s eye -- the sclera -- is clear and there is no redness, but there is discharge, it’s most likely a blocked tear duct.
About 1 in 5 babies are born with tear ducts that haven’t fully developed. The blockage is usually in one eye but can be in both. It often clears up on its own. A warm compress can help, but if it lasts a long time, it might need surgery.
When It’s Conjunctivitis
Since a newborn hasn’t been around that long -- under 2 months -- it’s not common for them to get a lot of viral infections. But sometimes their clogged tear duct can lead to an infection such as conjunctivitis.
This happens when there is inflammation of the thin layer of tissue (conjunctiva) that covers the sclera. Symptoms are similar to the sticky, watery eyes that come with a blocked tear duct. But with conjunctivitis, there is more swelling, tenderness, and redness of the eye area, and the whites of the eye will be pink or red. Your baby’s eyelid might be red, sticky, and itchy, and the discharge takes on a yellowish color. Also, their eyes might be more watery than usual. The infection often starts in one eye and spreads to the other.
Also, their eyes might be more watery than usual. The infection often starts in one eye and spreads to the other.
Chemical conjunctivitis can happen when eye drops and ointments, typically used on newborns at birth to help prevent infection, actually cause the irritation. It can show up as mildly red eyes and some puffiness in the eyelids.
It’s rare, but red, angry, itchy eyes with swollen eyelids and discharging pus could mean ophthalmia neonatorum (ON).This is a bacterial infection that can happen during childbirth if the baby passes through a birth canal infected with chlamydia. The symptoms usually show up 5-12 days after birth. Among newborns with ON, half also have the infection other areas of their bodies.
Call the doctor if the baby has a fever and:
- Your baby cannot open their eyes or you cannot see the eye
- The area is tender to touch and the skin around the eye is red
- There is a lot of eye discharge
These may be signs of a bacterial infection of the sclera.
When Treatment Is Needed
Doctors usually recommend a wait-and-see approach, as this issue often clears up on its own. You can also apply a warm compress to the bothered eye.
If the tear duct is still blocked and the eye discharge continues up to the baby’s first birthday, you should see your child’s doctor. They may refer you to a pediatric eye specialist, as it may need surgery.
To treat conjunctivitis caused by the blocked tear duct, try a gentle warm massage with your clean hand between your baby’s eye and nasal area. For chemical conjunctivitis, the symptoms usually only last for 1-3 days after birth, so no treatment is needed. And if it’s ON, doctors usually treat that with oral antibiotics.
Snot in a child is green and yellow, what are the symptoms?
Snot (runny nose, discharge) in a child is a problem that all parents periodically face. Nasal congestion prevents a small person from developing normally, playing, learning about the world around him. Even to fully feel the taste of any delicacy becomes inaccessible to him.
Even to fully feel the taste of any delicacy becomes inaccessible to him.
Snot (discharge) is a secretion produced by the nasal glands of the mucous membrane that covers the inside of the nasal cavities. They perform a protective function.
Sticky mucus serves as an obstacle to bacteria, viruses, dust, other foreign substances penetrating into the nasal cavity, which settle on it and then, with the help of the ciliated epithelium covering the mucosa from the inside, are brought out. This is "snot".
When a child gets sick, catches a cold, catches the flu, he develops an allergy, the secretion production increases many times over. Runny nose develops.
What color can a child's snot (discharge) be?
The nasal secretion itself is liquid and transparent, colorless. Gradually, it acquires a thick consistency and dissolves on its own. If the problem is caused by microorganisms that fill the substance, then the compartments become profuse and may change color.
If the problem is caused by microorganisms that fill the substance, then the compartments become profuse and may change color.
Abundant secretion of a clear liquid without color may indicate an allergic reaction or the initial stage of a cold, but yellow or green snot (discharge) in a child should attract special attention of parents. This is reliable evidence of the presence of a bacterial agent that can provoke the development of sinusitis, otitis media.
Green snot (discharge)
Prolonged snot (runny nose), accompanied by a rise in temperature to 38 ° C and above, indicates the development of inflammation in the paranasal sinuses, sinusitis
Yellow snot (discharge) ) have yet to say anything. Any process begins with transparent, colorless compartments. If the case is delayed, then the snot (discharge) that continues for a month begins to thicken and acquire a characteristic yellowish tint.
 This is due to the fact that white blood cells, which are responsible for protection, destroy microorganisms that have entered the nasal passages, which accumulate in the nasal secretion, giving it a characteristic yellow tint. It is impossible to launch snot, otherwise it may result in consequences that are difficult to correct
This is due to the fact that white blood cells, which are responsible for protection, destroy microorganisms that have entered the nasal passages, which accumulate in the nasal secretion, giving it a characteristic yellow tint. It is impossible to launch snot, otherwise it may result in consequences that are difficult to correct This is a specific reason to contact the doctors to clarify the cause of severe nasal discharge and to take timely measures.
Transparent snot
Abundant colorless snot indicates that the baby's body is intensively fighting some aggressive agent, but the colorlessness of the discharge indicates that so far the struggle has been quite successful. It is urgent to contact the doctors of our clinic to find out the causes of abundant snot so that the process does not become protracted and the disease does not cause complications. Often, colorless lingering snot (discharge) is the first sign of an allergic reaction, but only a competent ENT doctor can clarify the diagnosis.
c19fd3dbc34b48468774a3cb49ce3.jpg" />
Thick snot (discharge)
The thick consistency of the discharge clearly indicates the development of pathology, but what exactly can only be said by an otolaryngologist. If the snot (discharge) in a child does not go away for a long time, it is necessary to consult an ear-nose-throat doctor to identify the source of the disease and receive his recommendations on how to treat a runny nose.
Treatment
There are many recipes for dealing with the common cold in children, but without finding out the cause, without identifying the pathology itself, it is impossible to prescribe an adequate and targeted method of therapy. Only an otolaryngologist, after examination and examination, will be able to say exactly how to treat snot (discharge) in a child. In most cases, therapy will take place on an outpatient basis, but a doctor should prescribe medications and make recommendations.
When should I see a doctor?
See also
Treatment of ENT diseases
Runny nose in infants
Chronic runny nose
Treatment of rhinitis
Most parents try to cope with the problem of their baby on their own and in most cases it succeeds, but not always.
Reasons for visiting an otolaryngologist in our clinic are:
- Snot (discharge) for a month, which does not stop despite home treatment;
- Change in color and texture - thick, yellow or green snot (discharge) in a child;
- Deterioration - fever, chills, weakness, cough, headaches, sore throat, frontal pain, etc.
- No effect from measures already taken.
Therapy prescribed by a specialist in our clinic consists of drops, tablets, inhalations and other methods of treatment for the child. The etiology of the process is always different, the struggle is aimed at combating the root cause, and not with the external manifestations of the pathological process. Drugs that help with one disease, according to statistics, are absolutely useless for another. Only an ENT doctor can identify the cause, establish a reliable diagnosis and give recommendations on how to treat snot (discharge) in a child.
The etiology of the process is always different, the struggle is aimed at combating the root cause, and not with the external manifestations of the pathological process. Drugs that help with one disease, according to statistics, are absolutely useless for another. Only an ENT doctor can identify the cause, establish a reliable diagnosis and give recommendations on how to treat snot (discharge) in a child.
Parents should not prescribe drugs on their own, being tempted and led by advertising. There is a high risk of only harming the baby, aggravating his serious condition, translating the problem into a protracted or more dangerous form.
Yellow snot in a child - Allergy
Runny nose in childhood is quite common. If a runny nose in a child lasts no more than a week, and the color of the mucous secretions is transparent or slightly whitish, then the parents should not worry. Thus, the child's body adapts to the environment.
Contents:
- What do yellow snot mean
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Medical
- Physiotherapy.
- Folk remedies
- Complications
- Prophylaxis
What yellow snot means
In babies under one year old, a runny nose with yellow discharge is a serious cause for concern, and may not proceed in the same way as in older children or adults. This is due to the lack of the baby's ability to independently remove the mucus accumulated in the nose. Since infants have an unusual structure of the nasal cavity - the nasal passages are much narrower and thinner, therefore, the blockage of the respiratory passages with mucous secretions is much faster. The appearance of thick yellow mucus in the baby is a serious cause for concern and immediate contact with the pediatrician, because it can provoke swelling of the nasal mucosa and lead to complete loss of breath. It is impossible to postpone a visit to a pediatrician or pediatric ENT doctor. After all, a runny nose in a crumb with a yellow snot is accompanied by nasal congestion and it is difficult for the baby to fully eat, because of this, he begins to lose weight, and an overly prolonged illness can provoke serious complications.
It is impossible to postpone a visit to a pediatrician or pediatric ENT doctor. After all, a runny nose in a crumb with a yellow snot is accompanied by nasal congestion and it is difficult for the baby to fully eat, because of this, he begins to lose weight, and an overly prolonged illness can provoke serious complications.
The main causes of yellow snot
An increase in the accumulation of yellow mucus in the baby's nose or paranasal sinuses indicates that the onset of the disease has been missed, and it has developed quite deeply with a protracted inflammatory process in the nasopharyngeal mucosa. The color of these secretions indicates the cause of inflammation or signals the stage of development of the disease. Thick yellow mucus may appear for a number of reasons:
- In most cases, the final stage of the common cold (sixth to eighth day after a respiratory infection). The appearance of yellow secretions is the result of the "work" of microscopic bacteria that change the color of the mucous secretions.
 The more pathogenic microorganisms, the more saturated color the discharge acquires. The body removes dead pathogens, epithelial cells, cells of the immune system.
The more pathogenic microorganisms, the more saturated color the discharge acquires. The body removes dead pathogens, epithelial cells, cells of the immune system. - There was an exacerbation in the form of a purulent process. Probably, the baby can manifest sinusitis (acute or chronic), otitis media, chronic sinusitis in this way.
- Allergic rhinitis. If this symptom appears at a certain time of the year, then the causative agent of the discharge is a plant that blooms during this period.
- Yellow, thick discharge may occur due to dry indoor air. Often this manifestation of allergy is caused by dust or feathers in the pillow.
- Recovery from a viral infection (yellow mucus without fever).
- Adenoid vegetation (pathologically enlarged and inflamed nasopharyngeal tonsils make it difficult to breathe through the nose, which in turn contributes to the favorable development of infection.
- Anatomical disorders of the structure of the nasal septum.
- Chronic allergic rhinitis.
- Prolonged stay in the nose and foreign body.
All the reasons discussed above are manifested against the background of weakened immunity. Usually, without treatment, a healthy body is able to cope with viruses and bacteria on its own within three to five days.
Symptoms of yellow snot
Parents should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- In case of bacterial infection, one of the first signs of the disease is the appearance of yellow snot.
- Body temperature cannot normalize in any way (above 37 0 С).
- Yellow mucous discharge (often more yellow in the morning).
- Nasal congestion.
- Rhinitis continues for two weeks.
- There is swelling on the face.
- Blood impurities appeared in the mucus.
- Unpleasant odor comes from discharge.
- Mucous discharge from the nose changed color, became green.
- Pain in the nose and cheeks.
- Bronchitis, otitis, pharyngitis joins.
- Restless sleep.
- Loss of appetite.
- Increased moodiness.
Diagnostic methods
The doctor specifies how long the baby has been worried about this phenomenon and what may be the reason for its manifestation. During the examination, the doctor draws attention to the anatomical structure of the nasopharynx and the presence of pathological formations.
An experienced pediatrician can make a correct diagnosis using a detailed medical history when examining a small patient and laboratory and instrumental methods of examination.
- Examination of the patient with endoscopic instruments .
- Nasopharyngeal x-ray helps to examine the sinuses of the nasopharynx.
- Computed tomography - more informative study of the nasopharynx.
- Clinical blood and urine tests allows you to identify the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
- Allergy tests - diagnostics are carried out in order to determine hypersensitivity to allergens.
Treatment of yellow snot
When yellow mucous discharge appears, you need to contact a pediatrician who will assess the condition of the baby and young child, and after the examination, determine the disease and prescribe drugs and procedures for the treatment of a runny nose. Only a pediatrician or pediatric otolaryngologist decides whether to prescribe drug therapy or use traditional medicine methods of treatment.
- If the cause of the discharge is an allergic reaction, then treatment is prescribed only after the identification of the allergen.
- In the treatment of chronic sinusitis, sinusitis and otitis media, complex therapy is required.
Yellow snot - not a fatal disease, although their appearance should still be paid attention. In the first stage, they are easily eliminated, and much more difficult when time is lost.
Medical treatment
- Antibiotics. In special cases (bacterial rhinitis) - treatment of yellow snot, blocking the development of the disease, protection from complications, the doctor may prescribe systemic antibiotic therapy (tablets or syrups). For uncomplicated bacterial infections, topical preparations are prescribed.
- Antiseptics. Furacilin is a harmless antiseptic (0.5 tablets per 100 ml of water). In otolaryngology, it is often used for sanitation and treatment. With the help of a solution of furacilin, for the purpose of prevention, newborns wipe their eyes. A solution of furacilin is instilled into the nose in two to three drops. three r / day. If the color of the snot brightens, then the number of instillations is reduced.
- Vasoconstrictor drops. They are prescribed (strictly according to the instructions for using the drug) in case of severe nasal congestion, which leads to disruption of the child's sleep and prevents normal food intake.
 Children's vasoconstrictor drops "free" the nose from congestion, help to breathe freely, improve the general condition of the baby. It should be remembered that the use of vasoconstrictor drops for a small child is unsafe, these funds cannot be used for more than a week, otherwise the opposite effect may occur and the drops will become an irritant for the nose. Before using the product, the nose is pre-cleaned of secretions.
Children's vasoconstrictor drops "free" the nose from congestion, help to breathe freely, improve the general condition of the baby. It should be remembered that the use of vasoconstrictor drops for a small child is unsafe, these funds cannot be used for more than a week, otherwise the opposite effect may occur and the drops will become an irritant for the nose. Before using the product, the nose is pre-cleaned of secretions. - Decongestants. Relieve swelling of the mucosal nasopharynx.
- Wound healing. Heal wounds in the nose and increase local immunity.
- Preparations based on silver ions. The product has a pronounced antiseptic and astringent effect.
- Vitamin therapy. Vitamin C intake.
- Antipyretic drugs .
The therapeutic effect is more effective the earlier the treatment is started.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy treatments will help to cope with yellow discharge:
- UHF.

- UFO.
- Laser therapy.
Treatment with folk remedies
The use of traditional medicine recipes at home is recommended after reaching three years. The child's body grew up, twenty teeth erupted in the mouth, the crisis of the infant period and early childhood passed.
Inhalation
Thick yellow snot can be removed by inhalation. In the treatment procedure, a decoction of potatoes, herbal infusions (chamomile, calendula, sage herb), mineral water are used. For older children, and in the absence of an allergic reaction, you can use the essential oil of eucalyptus, pine needles.
For the convenience of the procedure, it is better to use a special device - a nebulizer or inhaler.
Instillation
- Beet juice. The use of beets really shows great results. For children, juice must be diluted in half with water. A couple of drops of juice are instilled into each nostril three times a day. After instillation, thick mucus liquefies and abundantly comes out.

- Kalanchoe juice. Plant juice is a reliable helper in the treatment of rhinitis, especially in cases where the mucus discharge is thick and yellow. Fresh juice is prepared before each instillation. In the nasal passages, 2-4 caps are instilled. juice from one to three r / day.
- Peach oil. To soften and regenerate the mucous membrane of the baby's nose, it is useful to instill a few drops of sterile peach oil. Such instillations help not only the nose, but also the throat, because the oil drains through the nasal passages into the throat.
Oil solutions should not be used in infants under one year of age. In case of accidental ingestion of oil into the lungs, lipid pneumonia can begin to develop.
Warming up
Warming up can be done only in the absence of an inflammatory and purulent process in the body.
- Table salt. The procedure is carried out with salt warmed up in a frying pan and placed in a canvas bag or handkerchief made of natural material.
 The touch of the bag to the body should be pleasant, it is applied to the bridge of the nose for a maximum of seven minutes. The procedure is carried out before going to bed.
The touch of the bag to the body should be pleasant, it is applied to the bridge of the nose for a maximum of seven minutes. The procedure is carried out before going to bed. - Boiled eggs. Hard-boiled eggs are applied to both sides of the bridge of the nose. The duration of the procedure is five minutes.
Flushing
- Sea salt. Every day, the nose is cleaned of mucous secretions with a solution of sea salt (it is forbidden to use a spray to wash the nose for children under two years old). For washing, prepare a solution - dissolve five grams in 1000 ml of warm boiled water. salt. The solution is injected into each nostril with a pipette. If after blowing out the snot remains, the procedure is repeated after five minutes. For small patients (children under six months), only sterile saline solutions should be used to rinse the nose.
- May be alternated with herbal infusions. For children, it is better to use an infusion of chamomile flowers (one teaspoon of dried flowers of the plant pour 100 ml of boiling water).
 Cool the healing potion and strain. The finished infusion is dripped into each nostril using a disposable syringe or pharmacy pipette. To rinse the nose well, take at least one ml of solution.
Cool the healing potion and strain. The finished infusion is dripped into each nostril using a disposable syringe or pharmacy pipette. To rinse the nose well, take at least one ml of solution.
For the use of medicinal herbs, consult a pediatrician.
- Give your child more decoctions and teas from wild rose, chamomile, St. John's wort - they increase immunity and thin thick snot.
- You can also get rid of a runny nose by humidifying the air in the room.
- Wet cleaning and dust removal shows good results.
- In winter, when the heating is on, it is important to use humidifiers.
Complications
When yellow snot appears as a complication of a cold, urgent measures should be taken immediately and the child should be treated. Complications may be accompanied by nasal congestion, general malaise, fever, headaches.
In children of different ages, against the background of yellow mucous discharge, the following complications may occur:
- Bronchitis.

- Bronchopneumonia.
- Sinusitis and other sinusitis.
- Laryngitis.
- Otitis.
- Pharyngitis.
- Chronic runny nose.
- The spread of infection through the bloodstream can sometimes cause systemic pathologies. The child complains of pain in the heart and joints.
- In rare cases, bacterial snot can be complicated by dacryocystitis (inflammation that affects the nasolacrimal ducts). Tears accumulate in the inner corners of the eye. Also, with dacryocystitis, the eyes swell and turn red, a course of pus appears.
- Chronic coryza with yellow discharge favors the development of polyps.
- May add hyposomia (reduced sense of smell).
It is categorically impossible to treat complications on your own, and even more so with the help of traditional medicine methods. With the spread of the inflammatory process to the paranasal sinuses, in this case, urgent antibiotic therapy will be required, otherwise the disease can take even more serious consequences.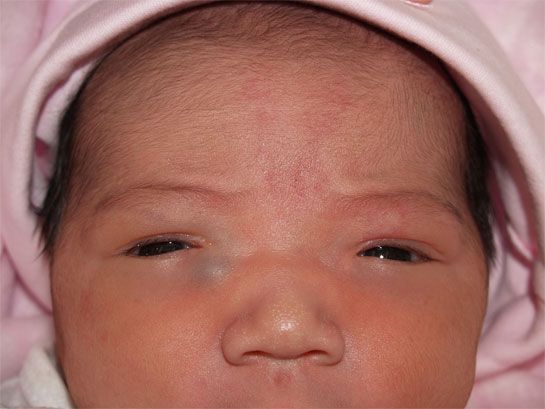
Prevention
Treatment helps to cope with the disease, but it is necessary to constantly strengthen the body's defenses and its ability to resist various infections.
To strengthen the child's body it is necessary:
- Stay outdoors with the child more, active movements must exceed passive actions.
- An excellent way to strengthen the immune system is hardening, which can be performed at home. For this, a contrast shower is suitable. You can visit a group in the pool with a child.
- Dress the child according to the season, so that 15 minutes after going outside, he will not sweat. If this happens, you need to return home and change clothes fidget. In case of hypothermia, you need to rub the baby's hands, offer a warm drink (if the stay on the street continues).
- In the presence of pathological hypertrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsil (adenoid vegetations), all prescriptions of a pediatrician must be observed.