How to remove child domain from forest
How to remove orphaned domains from Active Directory - Windows Server
Edit
Twitter LinkedIn Facebook Email
- Article
- 3 minutes to read
Applies to: Windows 10, Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: 230306
Summary
Typically, when the last domain controller for a domain is demoted, the administrator selects the This server is the last domain controller in the domain option in the DCPromo tool. This procedure removes the domain metadata from Active Directory. This article describes how to remove domain metadata from Active Directory if this procedure isn't used, or if all domain controllers are taken offline but not demoted first.
Caution
The administrator must verify that replication has occurred since the demotion of the last domain controller before manually removing the domain meta-data. Using the NTDSUTIL tool improperly can cause partial or complete loss of Active Directory functionality.
Removing orphaned domains from Active Directory
Determine the domain controller that holds the Domain Naming Master Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO) role. To identify the server holding this role:
- Start the Active Directory Domains and Trusts Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in from the Administrative Tools menu.
- Right-click the root node in the left pane titled Active Directory Domains and Trusts, and then select Operations Master.
- The domain controller that currently holds this role is identified in the Current Operations Master frame.
Note
If it's changed recently, not all computer may have received this change yet due to replication.
For more information about FSMO roles, see Active Directory FSMO roles in Windows.
Verify that all servers for the domain have been demoted.
Open a command prompt window.
At the command prompt, type
ntdsutil, and then press Enter.Type
metadata cleanup, and then press Enter.Type
connections, and then press Enter. This menu is used to connect to the specific server on which the changes will occur. If the currently logged-on user isn't a member of the Enterprise Admins group, alternate credentials can be supplied by specifying the credentials to use before making the connection. To do so, type:set creds <domainname> <username> <password>, and then press Enter. For a null password, type null for the password parameter.
For a null password, type null for the password parameter.Type
connect to server <servername>, where <servername> is the name of the domain controller that holds the Domain Naming Master FSMO Role. Then press Enter. You should receive confirmation that the connection is successfully established. If an error occurs, verify that the domain controller used in the connection is available. And verify that the credentials you supplied have administrative permissions on the server.Type
quit, and then press Enter. The Metadata Cleanup menu is displayed.Type
select operation target, and then press Enter.Type
list domains, and then press Enter. A list of domains in the forest is displayed, each with an associated number.Type
select domain <number>, and then press Enter, where number is the number associated with the domain to be removed.
Type
quit, and then press Enter. The Metadata Cleanup menu is displayed.Type
remove selected domain, and then press Enter. You should receive confirmation that the removal was successful. If an error occurs, see the Microsoft Knowledge Base for articles on specific error messages.Type
quitat each menu to quit the NTDSUTIL tool. You should receive confirmation that the connection disconnected successfully.
References
For more information about the NTDSUTIL tool, see the Support Tools documentation located in the Support\Reskit folder on the Windows 2000 CD-ROM. The Help files included with the Microsoft Windows 2000 Resource Kit contain a Books Online link. You can click the link for information that describes the NTDSUTIL tool in greater detail.
For more information about removing domain controllers from the domain that you're attempting to delete, see the following article:
216498 How to remove data in Active Directory after an unsuccessful domain controller demotion
Problem with removing a child domain in an Active Directory Forest
Active Directory Domain Demotion
- When you try to demote the last domain controller in a child domain, it fails.
- The server is still a domain controller after the demotion reports that it was successful.
- The last domain controller is a Windows 2000 Server in a mixed environment which contained.
- You observe the DCPromo log (c:\windows\debug\DCPromo.log), and find the following:
02/02 06:34:14 [INFO] Error - According to the information stored locally, this dc is the last dc in the domain, and the domain has a child domain. (8398)
02/02 06:34:14 [INFO] NtdsDemote returned 8398
02/02 06:34:14 [INFO] DsRolepDemoteDs returned 8398
02/02 06:34:14 [ERROR] Failed to demote the directory service (8398)
- You then try using the NTDSUTIL tool from the forest root domain controller to delete the child domain and get the following error:
DsRemoveDsDomainW error 0x2015
When you promote a Windows Server 2003 server to a Domain Controller, it creates a naming context (DC=DomainDnsZones) in the application partition.
- If the last Domain Controller in the child domain is a Windows 2000 Server, it checks Active Directory and finds this naming context and thinks it's a child domain.
- The child domain thinks it has another child domain, which causes DCPromo to fail.
Active Directory
Check: System Event Logs, Directory Services Event Logs, and DCPromo Log
Solution :
1. You have to remove the DomainDNSZones naming context in Active Directory by using the following steps (Make sure you are running these steps on the forest root domain controller):
"DsRemoveDsDomainW error 0x2015" error message when you use Ntdsutil to try to remove metadata for a domain controller that was removed from your network in Windows Server 2003
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/887424/
- Click Start, click Run, type ntdsutil, and then press ENTER.
- At the Ntdsutil command prompt, type domain management, and then press ENTER.
- Type connections, and then press ENTER.
- Type connect to server Domain_Controller_Name, and then press ENTER.
- After the following message appears, type quit, and then press ENTER:
- Connected to Domain_Controller_Name using credentials of locally logged on user
- At the domain management prompt, type list, and then press ENTER.
- Note the following entry:
- DC=DomainDnsZones,DC=Child_Domain, DC=extension
- For example, if the child domain is Contoso.com, note the following entry:
- DC=DomainDnsZones,DC=contoso,DC=com
- Type the following command, and then press ENTER.
- delete nc dc=domaindnszones,dc=Child_Domain,dc=extension
- Note: In this command, Child_Domain represents the name of the child domain that you want to remove. For example, if the child domain is Contoso.com, type the following command, and then press ENTER:
- delete nc dc=domaindnszones,dc=contoso,dc=com
- Quit Ntdsutil.
2. Use NTDSUTIL to delete the domain controller from the child domain.
How to remove data in Active Directory after an unsuccessful domain controller demotion
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/216498
3. Then use NTDSUTIL on the Forest Root DC to delete the child domain.
- C:\>ntdsutil
- ntdsutil: metadata cleanup
- metadata cleanup: connections
- server connections: connect to server DC01
Binding to DC01 ...
Connected to titanic using credentials of locally logged on user
- server connections: quit
- metadata cleanup: select operation target
- select operation target: list domains
Found 3 domain(s)
0 - DC=Microsoft,DC=com
1 - DC=Child1,DC=Microsoft,DC=com
2 - DC=Child2,DC=Microsoft,DC=com
- select operation target: select domain 2
Site - CN=London,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=Microsoft,DC=com
Domain - DC=Child2,DC=Microsoft,DC=com
No current server
No current Naming Context
- select operation target: quit
- metadata cleanup: remove selected domain
4. On the last domain controller (Windows 2000 Server), you can run DCPROMO /Forceremoval (Start >> Run) to remove any Active Directory information from that server.
On the last domain controller (Windows 2000 Server), you can run DCPROMO /Forceremoval (Start >> Run) to remove any Active Directory information from that server.
How to prevent this from happening:
- If you have a child domain which contains mixed domain controllers (Windows 2000 Server, and Windows Server 2003), you have to demote the Windows Server 2003 domain controllers last. With new operating systems come new changes to the schema and Active Directory Partitions. Older operating systems may not understand these changes.
[{"Product":{"code":"SSYYZB","label":"IBM Support for Microsoft Applications"},"Business Unit":{"code":"BU058","label":"IBM Infrastructure w\/TPS"},"Component":"Not Applicable","Platform":[{"code":"PF033","label":"Windows"}],"Version":"1.0","Edition":"Enterprise","Line of Business":{"code":"LOB28","label":"Technology Support Services"}}]
Remove orphaned domains from Active Directory - Windows Server
Twitter LinkedIn Facebook E-mail address
- Article
- Reading takes 2 minutes
Applies to: Windows 10 , Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB Number: 230306
Annotation
Typically, when the last domain controller for a domain is demoted, the administrator selects that server as the last domain controller in the domain setting in the DCPromo tool. This procedure removes domain metadata from Active Directory. This article describes how to remove domain metadata from Active Directory if this procedure is not used, or if all domain controllers are offline but not demoted first.
This procedure removes domain metadata from Active Directory. This article describes how to remove domain metadata from Active Directory if this procedure is not used, or if all domain controllers are offline but not demoted first.
Caution
Before manually deleting domain metadata, the administrator must verify that replication has occurred since the last domain controller was demoted. Incorrect use of the NTDSUTIL tool can result in partial or complete loss of Active Directory functionality.
Remove orphaned domains from Active Directory
-
Identify the domain controller that holds the Domain Naming Master Flexible Operations (FSMO) role. To define a server with this role:
- Launch the Active Directory Domains and Trusts Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in from the Administrative Tools menu.
- Right-click the root node in the pane on the left called " Active Directory Domains and Trusts ", and then select "Master Operations Node" .

- The domain controller that currently holds this role is identified in the current Operations Master frame.
Note.
If it was changed recently, not all computers may have received the change due to replication.
For more information about FSMO roles, see Active Directory FSMO Roles on Windows.
-
Verify that all servers for the domain are downgraded.
-
Open a command prompt window.
-
At the command prompt, type
ntdsutil, and then press Enter. -
Enter
metadata cleanup, and then press Enter. -
Type
connections, and then press Enter. This menu is used to connect to a specific server where changes will be made. If the currently logged on user is not a member of the Enterprise Admins group, you can specify alternative credentials by specifying the credentials to use before connecting. To do this, enter andset credspress the ENTER key. For a null password, enter the null value for the password parameter.
For a null password, enter the null value for the password parameter. -
Type
connect to server, where -
Type
quitand then press Enter. Menu clear metadata is displayed. -
Type
select operation targetand then press Enter. -
Type
list domainsand then press Enter. A list of domains in the forest is displayed, each with a corresponding number. -
Type
select domainand press ENTER, where is the number associated with the area to be deleted.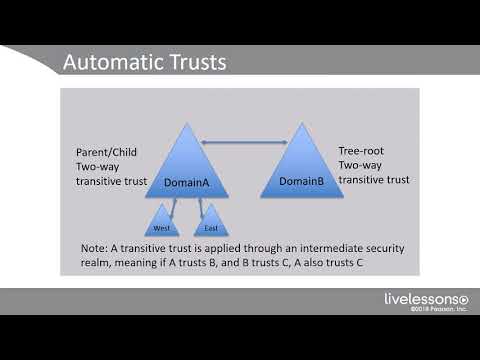
-
Type
quitand then press Enter. Menu clear metadata is displayed. -
Type
remove selected domainand then press Enter. A confirmation that the deletion was successful should appear. If an error occurs, see the Microsoft Knowledge Base article for specific error messages. -
Type
quitat each menu to exit the NTDSUTIL tool. You should see confirmation that the connection was successfully disconnected.
References
For more information about the NTDSUTIL tool, see the Support Tools documentation located in the Support\Reskit folder on the Windows 2000 CD. . You can click the link for more information about the NTDSUTIL tool.
For more information about removing domain controllers from the domain you are trying to remove, see the following article: 9
0003216498 How to delete data in Active Directory after an unsuccessful domain controller demotion
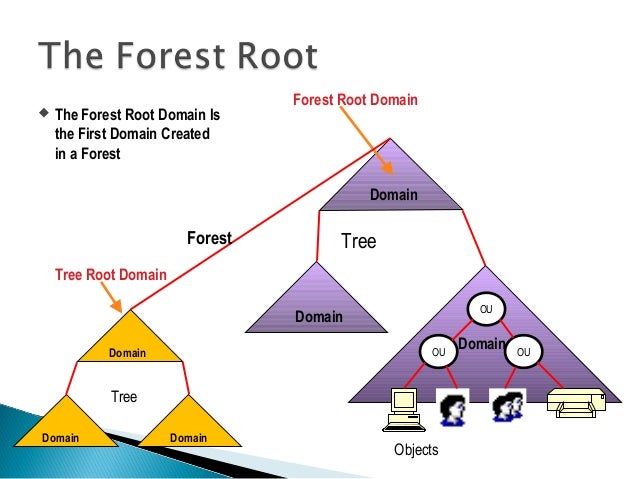
Manual removal of a domain controller and a lost domain
If a situation occurs that the domain controller is dead and there is no way to remove it correctly using DCPROMO, then the NTDSUTIL utility comes to the rescue.
1. First, delete the domain controller
2. If the domain controller was the last in the child domain, then delete the child "lost" domain itself.
Stage #1. Remove controller
- At the command prompt, type ntdsutil , and then press ENTER.
- Type metadata cleanup and press ENTER. By the way, you can abbreviate commands, for example, meta cl
- Type the command connections and press the ENTER key. This menu is for connecting to the server where changes are taking place. If the current user does not have administrator rights, you must specify a different account before connecting. To do this, enter the command set creds domainname username Password and press ENTER. If using a blank password, enter null.
- Type connect to server servername and press ENTER. A message about connecting to the server will appear.
 If an error occurs, make sure that the domain controller that is used to connect is available and that the current account has administrative rights on the server. The server you are connecting to must be a working domain controller, not the one you are removing. This could be the domain controller of the parent domain, for example if you are deleting a child.
If an error occurs, make sure that the domain controller that is used to connect is available and that the current account has administrative rights on the server. The server you are connecting to must be a working domain controller, not the one you are removing. This could be the domain controller of the parent domain, for example if you are deleting a child. Note . If you are connecting to the server you are deleting, you may receive the following error message when you try to delete it (step 15):
Error 2094. Unable to delete object DSA0x2094
- Type quit and press ENTER. Menu Metadata Cleanup appears.
- Enter the command select operation target and press ENTER.
- Enter command list domains and press Enter. A list of forest domains with numbers appears.
- Enter the command select domain number and press ENTER, where number is the number of the domain to which the server to be removed belongs.
 The selected domain is used to check if the server being removed is the last controller in that domain.
The selected domain is used to check if the server being removed is the last controller in that domain. - Type list sites and press ENTER. A list of nodes with numbers will appear.
- Enter the command select site number and press ENTER, where number is the number of the node to which the server to be removed belongs. A confirmation of the selected domain and host appears.
- Type list servers in site and then press ENTER. A list of site servers with numbers appears.
- Enter the command select server number , where number is the number of the server to be deleted. A confirmation will appear that contains the name of the selected server, its DNS name, and the location of the account.
- Type quit and press ENTER. Menu Metadata Cleanup appears.
- Type remove selected server and press ENTER.
 You should see a message that the server was successfully removed. The following error message indicates that the NTDS Settings object was previously deleted from Active Directory by another administrator, or as a result of replicating a successful deletion of the object after running DCPROMO.
You should see a message that the server was successfully removed. The following error message indicates that the NTDS Settings object was previously deleted from Active Directory by another administrator, or as a result of replicating a successful deletion of the object after running DCPROMO. - Type quit on each menu and press ENTER to exit Ntdsutil.
Now we need to clean DNS. To do this, remove the entries referring to the remote domain controller:
_ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.domain-name.com _kerberos._tcp.dc._msdcs.domain-name.com _ldap._tcp.._sites.dc._msdcs.domain-name.com _kerberos._tcp.._sites.dc._msdcs.domain-name.com
where domain-name.com is the domain that contains the controller to be removed.
Now delete the object in the FRS.
-
Open the Active Directory Users and Computers (DSA.MSC) snap-in and select Advanced Features from the View menu.

-
Expand the root domain, go to section System , then File Replication Service and Domain System Volume (SYSVOL share)0040 Delete .
Let's check the object in Active Directory Users and Computers in the Domain Controllers section.
If the remote controller is present, delete it with a right click.
If an error occurs, use the command
dsrm "cn=dc-01,ou=domain controllers,dc=domain-name,dc=com"
where instead of dc-01, substitute your controller to be deleted, and instead of dc =domain-name,dc=com your domain.
If you have not deleted the last controller in the domain, then do not forget to transfer the roles of this remote controller to FSMO to other remaining controllers. http://support.microsoft.com/kb/255504
If you removed the last controller in a child domain, then you probably need to remove the child domain itself. Proceed to the second stage.
Proceed to the second stage.
Stage #2. Removing an orphaned domain, i.e. a domain that does not contain controllers.
- At the command prompt, type ntdsutil , and then press ENTER.
- Type metadata cleanup and press ENTER. By the way, you can abbreviate commands, for example, meta cl
- Type connections and press ENTER. This menu is for connecting to the server where changes are taking place. If the current user does not have administrator rights, you must specify a different account before connecting. To do this, type set creds domainname username Password , and then press ENTER. If using a blank password, enter null.
- Type connect to server servername with domain name master role , and then press ENTER. A message about connecting to the server will appear. If an error occurs, make sure that the domain controller that is used to connect is available and that the current account has administrative rights on the server.
 The server you are connecting to must be a working domain controller, not the one you are removing. This could be the domain controller of the parent domain, for example if you are deleting a child.
The server you are connecting to must be a working domain controller, not the one you are removing. This could be the domain controller of the parent domain, for example if you are deleting a child. Note . If you are connecting to the server you are deleting, you may receive the following error message when you try to delete it (step 15):
Error 2094. Unable to delete object DSA0x2094
- Type quit and press ENTER. Menu Metadata Cleanup appears.
- Enter the command select operation target and press ENTER.
- Enter command list domains and press Enter. A list of forest domains with numbers appears.
- Enter the command select domain number and press Enter, where number is the number of the domain you want to delete.
- Type quit and press ENTER. Menu Metadata Cleanup appears.
- Type remove selected domain and press ENTER.
- Type quit on each menu and press ENTER to exit Ntdsutil.
If you get an error
DsRemoveDsDomainW error 0x2015 The directory service can perform the requested operation only on a leaf object To do this, do the following:
- At the command prompt, type ntdsutil , and then press ENTER.
- Type domain management or partition management (depending on OS version) and press ENTER. You can abbreviate, for example, part man
- Type connections and press ENTER.
- Type connect to server servername with the domain name master role, and then press ENTER.
- Type quit and press ENTER. Menu 9 appears0211 domain management or partition management .
- Type list and then press ENTER. A list of naming contexts (NCs) will appear.
e.g. ,DC=savilltech,D
3 - DC=DomainDnsZones,DC=savilltech,DC=com
4 - DC=ForestDnsZones,DC=savilltech,DC=com
5 - DC=child1,DC=savilltech,DC=com
6 - DC=DomainDnsZones,DC=child1,DC=savilltec
If we tried to delete domain 5 - DC=child1,DC =savilltech,DC=com, then we did not succeed, since it contains a child record 6 - DC=DomainDnsZones,DC=child1,DC=savilltec
Therefore, now we need to delete all child objects
7. domain management: delete NC DC=DomainDnsZones,DC=child1,DC=savilltec
Something like this will appear
"The operation was successful. The partition has been marked for removal from the enterprise. It will be removed over time in the background".
8. Type quit at each menu and press ENTER to exit Ntdsutil.