Frequent urination pregnancy second trimester
Common Second Trimester Symptoms | EvergreenHealth
Braxton Hicks contractions
Braxton Hicks contractions are painless, random contractions of the lower abdomen and groin, often a tightening feeling of the uterus.
These are “warm-ups” to labor contractions and may occur during the 2nd and 3rd trimester.
On the other hand, if you experience timeable, and/or regular contractions, try to lay down and drink fluids, and call us they do not decrease or resolve with these measures.
Leg Cramps
Leg cramps may occur especially at night and usually in the calves.
Flex your toes up towards your leg if this happens and massage the calf until it resolves.
Avoid pointing your toes when stretching.
Heartburn
Heartburn may be an effect of sluggish digestion or the expansion of the uterus.
- eat several small meals a day instead of three large ones
- avoid triggers (fried foods, chocolate, peppermint, garlic, onion)
- drink plenty of fluids
- stay up for 2-3 hours after your evening meal.
Antacids (Tums, Mylanta, Maalox) and medications such as Zantac or Tagamet are fine to take for relief.
Constipation
Constipation affects at least half of all pregnant women and is caused by an increase in progesterone, which slows the digestive process.
- Try to eat on a regular schedule
- drink plenty of fluids
- get some exercise daily
- eat high-fiber fruits, vegetables, and grains
- try fiber supplements (Metamucil, Citrucel) or a mild laxative (such as milk of magnesia
Shortness of breath
Your lungs are processing more air than they did before pregnancy, which may leave you breathing slightly faster and feeling short of breath.
Contact us if you experience chest pain , especially if it is localized to one side or the other.
Round ligament pain
The round ligaments support your uterus in your pelvis. As your uterus grows, the ligaments stretch and thicken to accommodate and support it.
These changes can cause pain on one or both sides of the pelvis.
Pain may start deep within the groin and move upward and outward towards the hips. It may also present as a dull ache after an active day.
To help relieve discomfort, you may try:
- warm baths
- flexing your knees toward your abdomen
- lying on your side with a pillow under your belly
- decrease activity if necessary.
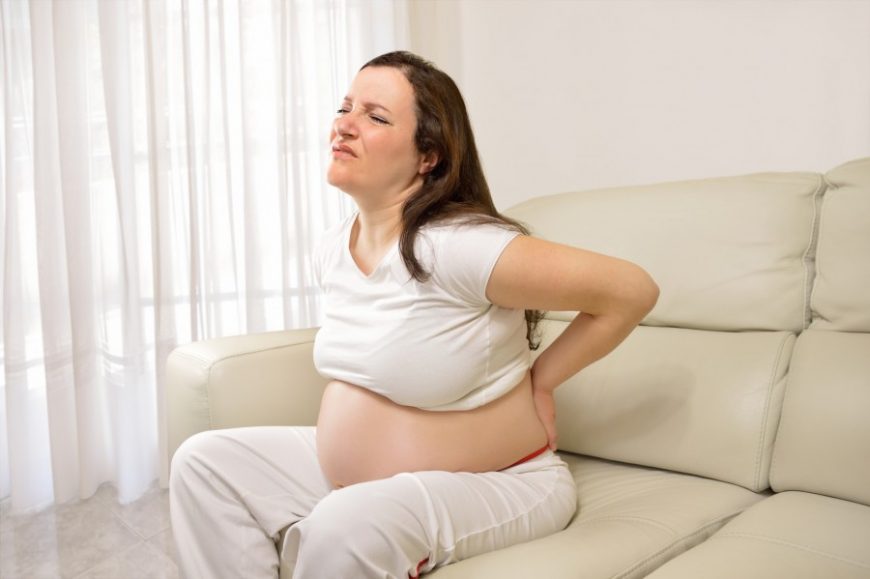
Hip pain and backaches
As pregnancy advances, the baby gains weight and puts more pressure on your back, while hormones relax the joints between your pelvic bones.
- sit in chairs with good back support
- apply heat and/or ice to painful areas
Contact our office if the pain does not go away or is accompanied by other symptoms.
Swelling
Blood return from your veins is compromised during pregnancy and fluid retention may be evident in your feet, ankles, face and hands.
- drink plenty of fluids
- elevate your feet at night
Frequent urination
Extra pressure on your bladder may cause you to urinate more often or leak urine, especially with laughing, coughing or sneezing.
Watch for signs of a bladder infection, such as burning with urination, fever, or blood in your urine, and call your health care provider if these symptoms are present.
Contact your provider if you experience any of the following during your pregnancy
- moderate to heavy vaginal bleeding or passing of tissue
- any amount of vaginal bleeding accompanied by pain, cramping, fever, or chills
- timeable, regular contractions unrelieved by rest and fluids
- a severe, persistent headache, especially with dizziness, faintness, nausea, vomiting, or visual disturbance
- moderate or severe pelvic pain
- pain with fever or bleeding
- vomiting with pain or fever
- chills or fever (101 degrees or higher)
Prenatal Care: Urinary Frequency and Thirst
Prenatal Care: Urinary Frequency and Thirst - HealthlineMedically reviewed by University of Illinois — By Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA on March 1, 2016
From morning sickness to back pain, there are many new symptoms that come with pregnancy. Another symptom is the seemingly never-ending urge to urinate – even if you’ve just gone a few minutes prior. Pregnancy increases your urge to urinate. This can keep you up at night, especially during your third trimester.
Another symptom is the seemingly never-ending urge to urinate – even if you’ve just gone a few minutes prior. Pregnancy increases your urge to urinate. This can keep you up at night, especially during your third trimester.
Causes
Increased urinary frequency is an early symptom of pregnancy in women. It’s caused by an increase of the hormones progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin. The urges tend to reduce in the second trimester. The uterus is also higher in the second trimester. This results in less pressure on your bladder.
In addition to rising hormones, your body’s fluid levels start to increase during pregnancy. This means your kidneys have to work extra hard to flush the extra fluid. The amount of urine you release will increase as well.
In the third trimester, your baby’s growing size means they’re pressing even more on your bladder. As a result, you may have to wake up several times during the night to urinate. You also may experience increased urgency to urinate due to the added pressure.
Symptoms
If you’re experiencing urinary frequency in pregnancy, you’ll feel the need to urinate more often. Sometimes you may go to the bathroom, but urinate very little, if at all.
Some women may also experience urinary leakage while pregnant. This leakage may occur when you:
- cough
- exercise
- laugh
- sneeze
It’s important to note that sometimes urinary frequency symptoms can indicate an underlying urinary tract infection (UTI). Women are more likely to experience UTIs during pregnancy. In addition to symptoms of urinary frequency or urgency, other UTI symptoms include:
- urine that appears cloudy
- urine that is red, pink, or concentrated
- urine that has a strong or foul smell
- a burning sensation when urinating
- pain when urinating
If you have these symptoms, tell your doctor. An untreated UTI could progress up the urinary tract and cause more serious symptoms.
Diagnosis
Doctors can usually diagnose urinary frequency and urgency by your symptoms. Your doctor will ask how often you’re going to the restroom and how much you urinate with each trip. They may suggest keeping a journal of how often you go and how much you urinate.
Your doctor will ask how often you’re going to the restroom and how much you urinate with each trip. They may suggest keeping a journal of how often you go and how much you urinate.
Your doctor may order diagnostic tests if they’re concerned your symptoms aren’t pregnancy-related. Tests your doctor may use include:
- urinalysis: This tests the urine for infective bacteria.
- ultrasound: This test can identify any abnormalities of your bladder, kidneys, or urethra.
- bladder stress test: This test measures how much urine is leaking when you cough or bear down.
- cystoscopy: This procedure involves inserting a thin, lighted scope with a camera into the urethra to examine the bladder and urethra.
Treatment
Pregnancy-related urinary frequency and urgency usually resolve after you give birth. These symptoms will often subside about six weeks after giving birth.
Your doctor may recommend strengthening your bladder muscles through exercises known as Kegels.:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/2785562/original/028627600_1556001360-shutterstock_1019963743.jpg) These exercises strengthen your pelvic floor. This helps you gain better control over your urine flow, especially after giving birth.
These exercises strengthen your pelvic floor. This helps you gain better control over your urine flow, especially after giving birth.
You can perform Kegel exercises daily, ideally about three times a day. Follow these steps:
- Tighten the muscles of your pelvic floor by imagining you’re stopping the flow of urine.
- Hold the muscles for 10 seconds, or as long as you can.
- Release the contracted muscles.
- Repeat 15 times to complete a single set.
You will know you’re performing Kegel exercises correctly if no one can tell you’re doing them.
You may have underlying medical causes besides pregnancy that are leading to urinary frequency and urgency. If so, your doctor will treat those as they are diagnosed.
At-Home Treatment
Drinking enough fluids is vital to maintaining your health and your baby’s health while pregnant. You shouldn’t cut back on what you’re drinking just to reduce your trips to the bathroom.
However, you can cut back on caffeinated beverages, which act as natural diuretics. Doctors often recommend reducing caffeine intake to avoid potential pregnancy complications.
Doctors often recommend reducing caffeine intake to avoid potential pregnancy complications.
You could also keep a journal of the times of day you use the restroom. You can then plan on going to the restroom on or before these times to reduce the likelihood of urinary leakage. Leaning forward while urinating can help you to better empty your bladder.
Performing Kegel exercises at home can also help you to continue strengthening the pelvic floor muscles. Strengthening these muscles during pregnancy can also help you prepare for labor.
Prevention
Practicing regular Kegel exercises can help you to gain some control over your pelvic floor and increase urinary control. However, there aren’t many other ways to prevent urinary frequency and urgency in pregnancy. As your baby grows inside your body, you may experience these symptoms.
Outlook
Pregnancy can lead to more frequent urination and sometimes a lack of control over urination. Urinary frequency goes away after childbirth for most women. You should let your doctor know if you’re still having bladder problems six weeks after having your baby.
You should let your doctor know if you’re still having bladder problems six weeks after having your baby.
Last medically reviewed on March 2, 2016
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Health
How we vetted this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Adaji, S. E., Shittu, O. S., Bature, S. B., Nasir, S., Olatunji, O. (2011, August 11). Bothersome lower urinary symptoms during pregnancy: A preliminary study using the international consultation on incontinence questionnaire. African Health Sciences, 11(1), S46-S52
- Early signs of pregnancy. (2016, February 8)
cyh.com/HealthTopics/HealthTopicDetails. aspx?p=438&np=456&id=2742
aspx?p=438&np=456&id=2742 - Frequent urination. (2013, December)
marchofdimes.org/pregnancy/frequent-urination.aspx# - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2015, July 23). Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Pregnancy childbirth and bladder control. (2012, July 23)
- Urinary frequency during pregnancy. (2010)
- Urinary incontinence fact sheet. (2012, July 16)
womenshealth.gov/publications/our-publications/fact-sheet/urinary-incontinence.html
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Mar 2, 2016
By
Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA
Edited By
Nizam Khan (TechSpace)
Medically Reviewed By
University of Illinois-Chicago
Share this article
Medically reviewed by University of Illinois — By Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA on March 1, 2016
related stories
First Trimester Pregnancy Back Pain: Causes and Treatments
The Pregnancy Quiz: Am I Pregnant?
Tests Used to Confirm Pregnancy
Symptoms of Severe Dehydration During Pregnancy
Infections in Pregnancy: Asymptomatic Bacteriuria
Read this next
First Trimester Pregnancy Back Pain: Causes and Treatments
Medically reviewed by Kimberly Dishman, MSN, WHNP-BC, RNC-OB
Back pain during the first trimester might be one of the first pregnancy symptoms you experience.
 Here’s what’s causing it and how to treat it safely.
Here’s what’s causing it and how to treat it safely.READ MORE
The Pregnancy Quiz: Am I Pregnant?
Medically reviewed by George Krucik, MD, MBA
There are certain signs and symptoms that indicate pregnancy. Are you experiencing any of them?
READ MORE
Tests Used to Confirm Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of pregnancy, the first step should be a home pregnancy test or a visit to your doctor to confirm the…
READ MORE
Symptoms of Severe Dehydration During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, MD
During pregnancy, it’s important to stay hydrated. We’ll discuss the symptoms of severe dehydration and when you should seek medical help.

READ MORE
Infections in Pregnancy: Asymptomatic Bacteriuria
Medically reviewed by Holly Ernst, PA-C
Asymptomatic bacteriuria occurs when bacteria is present in a voided urine sample. It’s caused by bacterial colonization of the urinary tract. Learn…
READ MORE
Does Swaddling Increase the Risk of SIDS?
Medically reviewed by Mia Armstrong, MD
Is swaddling safe, or is it a risk factor for SIDS? Here's what the most recent research says.
READ MORE
How to Relieve and Prevent Hip Pain During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Holly Ernst, PA-C
Hip pain is a common complication of pregnancy. Here are stretches, other home remedies, causes, and what you can do to prevent it.
READ MORE
Antidepressants in Pregnancy Aren't Linked to Increased Neurological Issues in Children
A cohort study of antidepressant use in pregnancy found that the rate of neurological disorders in children born to those who took antidepressant…
READ MORE
These Guided Pregnancy Journals Will Help You Document All the Feels
Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
The pregnancy and postpartum periods are full of emotions (rightfully so!), and these pregnancy journals are a great place to document it all.

READ MORE
What You Need to Know If You’re Having a High Risk Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
A high risk pregnancy is any pregnancy that comes with increased health risks for either the pregnant parent, the fetus, or both.
READ MORE
Frequent urination during pregnancy - Juno
Article content
When is considered frequent
Urges are frequent if they occur more than 9 times a day. Usually only a small amount of urine is passed at a time. Pregnant women may have about 20 visits to the toilet per day, while the daily amount of urine can also increase to 2 liters.
Is it an early sign of pregnancy?
HCG slightly increases the volume of urine excreted, so frequent urination begins already in the first weeks of pregnancy. The symptom does not 100% indicate the onset of fertilization - it should be considered in conjunction with other manifestations - primarily with a positive test.
However, keep in mind that with an increase in the daily volume of urine at a very early date, a false negative result is possible. Also, the symptom is less pronounced in ectopic pregnancy due to lower hCG levels, so an examination is required in any case.
If you began to frequent the toilet and there is a delay, then pregnancy is very likely.
Physiological causes of frequent urination in pregnant women
In healthy women, this phenomenon is associated with the body getting used to carrying a baby, as well as with other physiological reasons.
In the first half of pregnancy
The main causes of frequent urination during early pregnancy:
- Increased progesterone production. This hormone relaxes muscle tissue, helping to maintain pregnancy. As a result, urine is retained worse, the urge to void becomes more frequent due to the reduced tone of the bladder.
- Increased blood supply in the pelvis. Due to the proximity of the bladder to the uterus, its increased sensitivity occurs - filling receptors react more strongly.
- Active work of the kidneys. During the bearing of a child, the renal blood flow increases 1.5 times for the constant renewal of amniotic fluid and the timely removal of metabolic products. Accordingly, more urine begins to be produced.
Physiological increase in urination does not cause pain and discomfort, itching and burning. In the presence of negative symptoms, you need to consult a doctor to rule out pathologies.
Second half of pregnancy
The main reason for frequent urge to urinate in the second and third trimester is the increased pressure of the uterus on the bladder. However, diseases can also be the cause:
- Infections. Changes in the pelvis in pregnant women and a decrease in protective forces increase the risk of developing urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis. Such pathologies are accompanied not only by frequent urination, but also by pain, discomfort in the area of inflammation, and a burning sensation.
 The woman's health is deteriorating;
The woman's health is deteriorating; - Gestational diabetes. An increase in blood glucose in violation of carbohydrate metabolism. The amount of urine separated increases significantly.
Other pathologies include neoplasms in the small pelvis, endocrine and neurological disorders.
Soreness with frequent urination in pregnant women - is it normal or not?
Painful urination is not normal. Unpleasant sensations indicate the development of a pathological process. Pain and discomfort are a sign of urinary tract irritation. Cystitis is very likely if a woman has severely reduced immunity or has chronic diseases of the pelvic organs. Sometimes it can be accompanied by a temperature and requires a mandatory visit to the doctor.
Calls at night
Pregnant women often complain about how tired they are at night "hiking". The situation is explained by the fact that the work of the kidneys depends on the position of the body. In the later stages, the female body is prone to fluid retention and edema, especially when in an upright position. When the expectant mother lies down, the renal blood flow and the outflow of fluid from the tissues increase. As a result, the kidneys excrete more urine.
When the expectant mother lies down, the renal blood flow and the outflow of fluid from the tissues increase. As a result, the kidneys excrete more urine.
What is the duration of frequent urination during pregnancy?
The phenomenon begins already from the first days of pregnancy and is especially pronounced up to about 12 weeks. Later, the number of emptyings gradually decreases, because by 4-5 months the body adapts to new conditions. The diaphragm rises, creating more space for the growing uterus and "unloading" the pelvic organs.
Frequent urination during pregnancy in the second trimester may indicate the addition of an infection or the development of inflammation, but it is also possible as a manifestation of the individual characteristics of the body.
In the third trimester, the opposite phenomenon is possible - fluid retention. However, the closer the birth, the more often the urge to urinate becomes. In the last month of gestation, the uterus descends and puts pressure on the organs of the urinary system.
How likely is miscarriage in the absence of frequent urination?
A woman does not always immediately find out about a missed pregnancy. Fetal movements are not felt in the early stages, so pregnant women "listen" to other signs. In the first weeks, the abrupt cessation of toxicosis and frequent urge to urinate are alarming. These symptoms can indeed indicate the death or developmental delay of the fetus, as well as an ectopic pregnancy, but not always. Toward the end of the first trimester, the kidneys excrete less urine, in some this has been observed since 9‒10 weeks.
How to deal with frequent urination during pregnancy: tips
In the absence of pathologies, the discomfort caused by physiological frequent urination can be reduced as follows:
- Stay hydrated. Drink enough, but don't overdo it. Give preference to water over sugary drinks like coffee.
- Eat rationally. Eliminate diuretic foods (citrus fruits, spicy foods), as well as things that cause constipation.
- Exercise. Strengthen your pelvic muscles by training your vaginal and anus sphincters.
- Get more rest. Sleep during the day is very useful, especially in the later stages - after being in a horizontal position, the bladder empties faster, as a result, the load on the kidneys during night rest is reduced.
- Maintain immunity. Avoid hypothermia, take vitamin complexes as prescribed by the doctor.
- Empty your bladder as much as possible. Do not hold back the urge and try to make sure that all the urine comes out completely. In this regard, it is easier to urinate in the shower.
Control your condition. If other symptoms (pain, fever, burning sensation) appear in addition to frequent urination, tell your doctor immediately.
Causes of frequent urination in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy
Frequent urination during pregnancy in the second trimester indicates changes in the female body: changes in the hormonal background and emotional state, fetal growth. The urge should not be a cause for concern unless it is accompanied by pain or changes in the color and volume of the urine.
The urge should not be a cause for concern unless it is accompanied by pain or changes in the color and volume of the urine.
Contents of the article
The very concept of frequent urination is not limited by any framework. The number of trips to the toilet depends on the characteristics of the body, diet, drinking regimen. On average, the process occurs 3-5 times a day. But if it goes beyond comfort and spreads at night, repeats for several days, you should consult a doctor.
Physiological causes of deurination
At this time, the uterus begins to grow actively. Before conception, the dimensions of the organ are 4 x 8 cm, and for a period of 18–21 weeks they reach a length of 19-24 cm. In this state, the uterus puts pressure on the regional organs, one of which is the bladder, and their contact leads to irritation of the latter, which provokes urges. Moreover, the bladder is slightly compressed, from which its volume decreases.
Hormonal changes also provoke frequent urination during pregnancy in the second trimester. This is explained by the high concentration of progesterone - the hormone of pregnancy. Before conception, its content in the blood does not exceed 10 units during ovulation and 57 units during the luteal phase. During the gestation period, its concentration varies between 71.5–303.1 units. Under the influence of progesterone, muscles and ligaments become more elastic. This allows the uterus to stretch and grow with the fetus. The muscle fibers of other organs undergo the same changes. The higher the progesterone content, the more elastic the fibers. Weakening of the smooth muscles of the bladder leads to compensatory urination.
This is explained by the high concentration of progesterone - the hormone of pregnancy. Before conception, its content in the blood does not exceed 10 units during ovulation and 57 units during the luteal phase. During the gestation period, its concentration varies between 71.5–303.1 units. Under the influence of progesterone, muscles and ligaments become more elastic. This allows the uterus to stretch and grow with the fetus. The muscle fibers of other organs undergo the same changes. The higher the progesterone content, the more elastic the fibers. Weakening of the smooth muscles of the bladder leads to compensatory urination.
The volume of circulating blood in the body of a pregnant woman increases by 20-30%. This is due to the need to transport oxygen, vitamins and minerals to the cells of the placenta and fetus. Based on this, urges become more frequent.
Accelerated kidney function may also be the cause. The load on them increases, the production and excretion of urine also increases. It should be noted that the kidneys of the fetus also function. The level of deurination is affected by the tendency of the expectant mother to edema, the formation and frequency of amniotic fluid renewal.
It is easy to provoke frequent trips to the toilet with spicy spices, protein products (meat, cottage cheese, fish), vegetables and fruits that have diuretic properties.
Psychological factors
Oddly enough, but repeated deurination is observed in women on the basis of psycho-emotional disorders. Experiences, stress, unrest caused by various factors may well provoke increased paruria.
Deurination as a result of pathologies in the body
In the middle of the term, expectant mothers are often diagnosed with iron deficiency anemia. It arises on the basis of an unbalanced diet with a predominance of fast carbohydrates.
Iron deficiency anemia is accompanied by lethargy, insomnia, chronic fatigue and fatigue, dizziness and "flies" before the eyes.
The cause of frequent urination during pregnancy in the second trimester is chronic or acquired during the period of gestation diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Cystitis - inflammation of the bladder caused by an infection. In addition to repeated urges, there are complaints about the feeling of residual urine, pain in the abdomen and during emptying, blood in the biological fluid. Turbidity of urine is visually noted, and in the results of the analyzes there is a conclusion about a change in the composition of its sediment. Rarely diagnosed fever and general malaise.
- Pyelonephritis - inflammation of pyelitis, parenchyma and calyces of the kidneys. In pregnant women, this pathology is common: it occurs against the background of a weakened immune system, has a bacterial etiology. Accompanied by pyuria, back pain of varying intensity, fever, chills.
- Urethritis - inflammation of the urethra (urethra), provoked by viruses and bacteria. Deurination is accompanied by burning or itching.