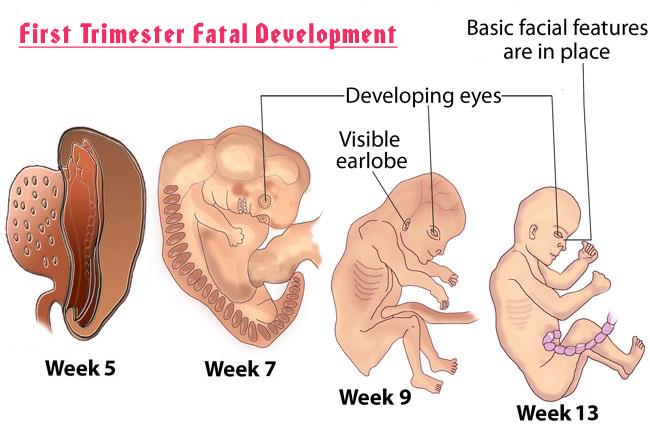
Is bleeding during the first trimester of pregnancy normal
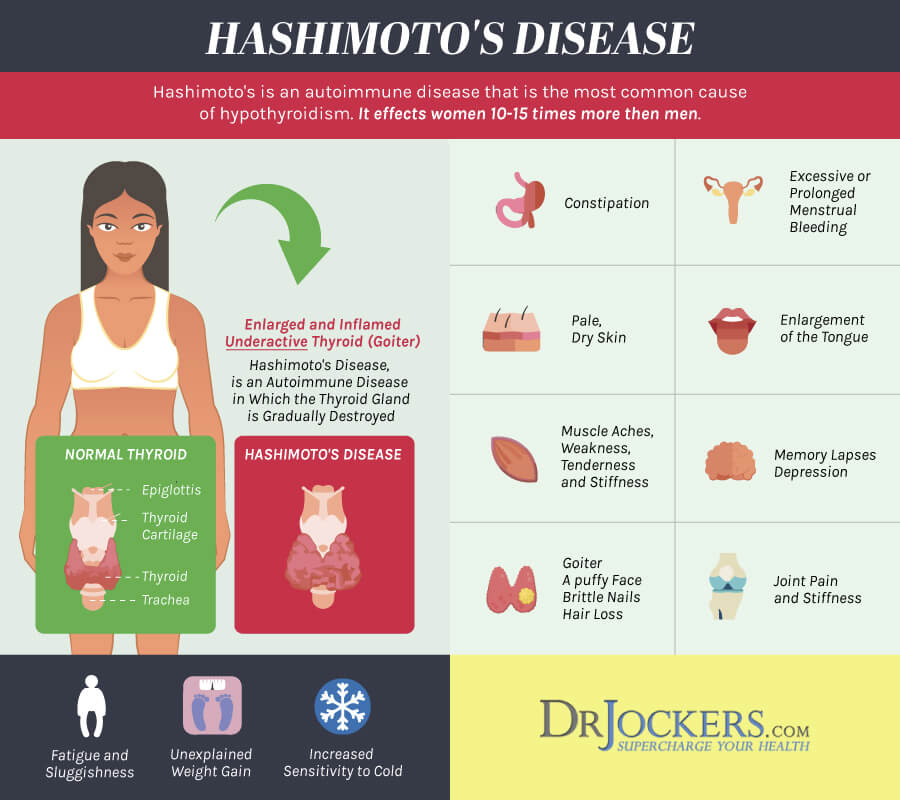
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy
Topics
In This Topic
KEY POINTS
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy are common
If you bleed or spot during pregnancy, it doesn’t always mean there’s a problem but in some cases they may be signs of a problem for you or your baby’s health
If you have heavy bleeding, call your health care provider right away
Tell your provider about any bleeding or spotting you have during pregnancy
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy are common. Up to 1 out of 4 (up to 25%) of all pregnant women have some bleeding or spotting during their pregnancy.
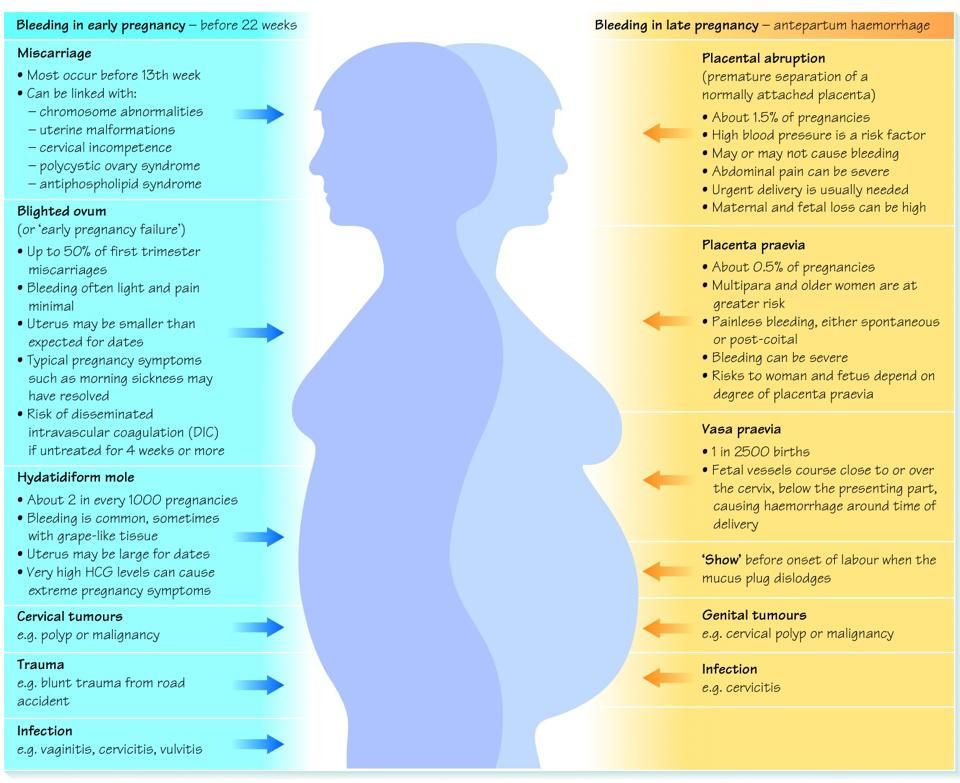
Bleeding and spotting in pregnancy don’t always mean there’s a problem, but they can be a sign of miscarriage or other serious complications. Miscarriage is when a baby dies in the womb before 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Call your health care provider if you have any bleeding or spotting, even if it stops. It may not be caused by anything serious, but your provider needs to find out what’s causing it.
What’s the difference between bleeding and spotting?
Bleeding or spotting can happen anytime, from the time you get pregnant to right before you give birth. Spotting is light bleeding. It happens when you have a few drops of blood on your underwear. Spotting is so light that the blood wouldn’t cover a panty liner. Bleeding is when the blood flow is heavier, enough that you need a panty liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your underwear and clothes.
What should you do if you have bleeding or spotting during pregnancy?
Call your health care provider if you have any kind of bleeding during pregnancy and do these things:
- Keep track of how heavy your bleeding is, if it gets heavier or lighter, and how many pads you are using.

- Check the color of the blood. Your provider may want to know. It can be different colors, like brown, dark or bright red.
- Don’t use a tampon, douche or have sex when you’re bleeding.
Call your health care provider right away at any time during pregnancy or go to the emergency room if you have:
- Heavy bleeding
- Bleeding with pain or cramping
- Dizziness and bleeding
- Pain in your belly or pelvis
What causes bleeding or spotting early in pregnancy?
It’s normal to have some spotting or bleeding early in pregnancy. Bleeding or spotting in the first trimester may not be a problem. It can be caused by:
- Having sex
- An infection
- Implantation. When a fertilized egg (embryo) attaches to the lining of the uterus (womb) and begins to grow.
- Hormone changes. Hormones are chemicals made by the body.
- Changes in your cervix. The cervix is opening to the uterus that sits at the top of the vagina.

- Certain types of testing during pregnancy like an amniocentesis or Chorionic villus sampling (CVS). These are tests that are done to check for genetic abnormalities in your baby. Genetic abnormalities are changes in the genes that are passed down to a baby from mom or dad. These genetic changes can cause health problems for a baby.
- Problems related to smoking. If you smoke, it’s best to stop before pregnancy or as soon as you know you’re pregnant.
Sometimes bleeding or spotting in the first trimester is a sign of a serious problem, like:
- Miscarriage. Almost all women who miscarry have bleeding or spotting before the miscarriage.
- Ectopic pregnancy. This is when a fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus and begins to grow. An ectopic pregnancy cannot result in the birth of a baby. It can cause serious, dangerous problems for the pregnant woman.
- Molar pregnancy. This is when a mass of tissue forms inside the womb, instead of a baby.
 Molar pregnancy is rare.
Molar pregnancy is rare.
What causes bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy?
Bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy may be caused by:
- Labor
- Having sex
- An internal exam by your health care provider
- Problems with the cervix, like an infection, growths, inflammation or cervical insufficiency. This is when a woman’s cervix opens too early. Inflammation of the cervix is when it may be painful, swollen, red or irritated.
Bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy may be a sign of a serious problem, like:
- Preterm labor. This is labor that happens too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Placenta previa. This is when the placenta lies very low in the uterus and covers all or part of the cervix.
- Placenta accreta. This is when the placenta grows into the wall of the uterus too deeply.
- Placental abruption. This is when the placenta separates from the wall of the uterus before birth.

- Uterine rupture. This is when the uterus tears during labor. This happens very rarely. It can happen if you have a scar in the uterus from a prior cesarean birth (also called c-section) or another kind of surgery on the uterus. A c-section is surgery in which your baby is born through a cut that your doctor makes in your belly and uterus.
How are bleeding and spotting treated?
Your treatment depends on what caused your bleeding. You may need a medical exam and tests.
Most of the time, treatment for bleeding or spotting is rest. Your provider may also suggest treatments like:
- Take time off from work and stay off your feet for a little while
- You may need medicine to help protect your baby from Rh disease. Rh disease is when your blood and baby’s blood are incompatible (can’t be together). This disease can cause serious problems — even death — for your baby.
- Don’t have sex, douche or use tampons
- If you have heavy bleeding, you may need a hospital stay or surgery
Last reviewed: April 2020
') document. write('
write('
Preterm labor & premature birth
') document.write('') }
') document.write('') }
Bleeding in Early Pregnancy: When Should you Worry?
Tags:
- Pregnancy
- Your health
-
Share this:
Light bleeding or spotting during your first trimester is common.
 Here’s what it could mean (and when to seek help).
Here’s what it could mean (and when to seek help).During pregnancy, your body changes. A lot. And in early pregnancy, you may deal with some pretty substantial hormonal shifts. Between mood swings, exhaustion and morning sickness, you might not feel your best. But there’s another symptom that can happen in early pregnancy that you might not be thinking about — bleeding or spotting.
“Bleeding in early pregnancy happens to 20 to 40% of women,” says Deidre Heber, DO, OB-GYN at Geisinger. “Most of the time, it’s nothing to worry about.”
Potential causes of first trimester bleeding
Bleeding during the first trimester can look different for everyone. The amount can range from light to heavy. For some, it can be intermittent. Others may have more constant bleeding or spotting. And it may or may not be painful.
Here are a few things that might be behind it.
Implantation bleeding
Early in pregnancy (sometimes before you know you’re pregnant), you may have some spotting when your period is due. This common occurrence is called implantation bleeding. “It happens between 6 and 12 days after conception as the fertilized egg implants into your uterus,” Dr. Heber says. This bleeding is typically light and may last for a few days.
This common occurrence is called implantation bleeding. “It happens between 6 and 12 days after conception as the fertilized egg implants into your uterus,” Dr. Heber says. This bleeding is typically light and may last for a few days.
Cervical changes
During pregnancy, there’s increased blood flow to your cervix. Having sex or getting a Pap smear, which cause contact with the cervix, can trigger light bleeding. Other cervical changes that can trigger bleeding include:
- Polyps
- Minor infections
- Cervical ectropion (when cells from the inside of the cervix move to the outside)
Hormones
In the early weeks of pregnancy, your body starts making the hormones you need to sustain a pregnancy. This change can cause your progestin levels to drop. That drop may lead to spotting or light bleeding.
Miscarriage
Since miscarriages are most common during the first trimester, worrying about bleeding is normal. Light bleeding or spotting doesn’t automatically mean you’re miscarrying. But if your bleeding is heavy, bright red or you’re passing clots and in pain, contact your healthcare provider. They can explain next steps.
But if your bleeding is heavy, bright red or you’re passing clots and in pain, contact your healthcare provider. They can explain next steps.
Most women who miscarry go on to have healthy pregnancies. But having a miscarriage is a loss that families may need help handling. Don’t rush the grieving process, and find a support group or counselor if you feel you need it.
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy happens when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, like in your fallopian tube. When that happens, it can lead to heavy bleeding, pain and other serious symptoms. “An ectopic pregnancy is an emergency,” says Dr. Heber. “If you have symptoms, contact your provider immediately.”
When to call the doctor about bleeding
Call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room if you have any of these symptoms:
- Severe pain or cramps low in the abdomen
- Severe bleeding, soaking greater than one heavy pad per hour, with or without pain
- Passage of blood clots or tissue
- Dizziness or fainting
- Chills
- Fever higher than 100.
 4° F
4° F
If you’re pregnant and bleeding heavily, don’t use a tampon. Wear a pad instead. “Doctors need to know how much you’re bleeding to gauge the severity,” says Dr. Heber.
And if you’re passing tissue, consider bringing it in for testing.
Your doctor may use an ultrasound to determine the cause of your bleeding. Once they find the cause, they’ll work with you on a treatment plan.
Healthy parent, healthy baby
Building good habits now can help you have the healthiest pregnancy possible. Dr. Heber makes these suggestions to help you (and your baby) feel your best.
- Eat a nutritious, well-balanced diet
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid alcohol, recreational drugs and cigarettes
- Reduce caffeine intake to 1-2 cups a day
- Attend regular prenatal visits
- Take your prenatal vitamins
Next steps:
Meet Deidre Heber, DO
Learn about pregnancy care at Geisinger
Separating fact from fiction: 6 pregnancy myths
- Sign up for our wellness email
Bleeding in early pregnancy: When should you see your doctor?
How to get more folic acid naturally
Can you drink coffee while pregnant?
Is it too late for a baby?
2022 Geisinger Health
- Developer
- Terms & conditions
- HIPAA (new)
- Privacy policy
- Non-discrimination notice
- Social media guidelines
- Corporate compliance reporting
- Report fraud
- Employee login
- Provider resources
- Geisinger company stores
Geisinger Health Plan may refer collectively to Geisinger Health Plan, Geisinger Quality Options Inc. , and Geisinger Indemnity Insurance Company, unless otherwise noted. Geisinger Gold Medicare Advantage HMO, PPO, and HMO D-SNP plans are offered by Geisinger Health Plan/Geisinger Indemnity Insurance Company, health plans with a Medicare contract. Continued enrollment in Geisinger Gold depends on annual contract renewal. Geisinger Health Plan Kids (Children’s Health Insurance Program) and Geisinger Health Plan Family (Medical Assistance) are offered by Geisinger Health Plan in conjunction with the Pennsylvania Department of Human Services (DHS). Geisinger Health Plan is part of Geisinger, an integrated health care delivery and coverage organization.
, and Geisinger Indemnity Insurance Company, unless otherwise noted. Geisinger Gold Medicare Advantage HMO, PPO, and HMO D-SNP plans are offered by Geisinger Health Plan/Geisinger Indemnity Insurance Company, health plans with a Medicare contract. Continued enrollment in Geisinger Gold depends on annual contract renewal. Geisinger Health Plan Kids (Children’s Health Insurance Program) and Geisinger Health Plan Family (Medical Assistance) are offered by Geisinger Health Plan in conjunction with the Pennsylvania Department of Human Services (DHS). Geisinger Health Plan is part of Geisinger, an integrated health care delivery and coverage organization.
Pathological and physiological causes of bleeding during early pregnancy
The gestation period is a complex process that does not always go well. Every second woman has various complications. Most often, women go to the doctor with complaints of spotting. Why does bleeding occur during early pregnancy, how dangerous is it?
Causes of bleeding in pregnancy
Blood in the first trimester of pregnancy in the vaginal secretion is observed in 30% of expectant mothers.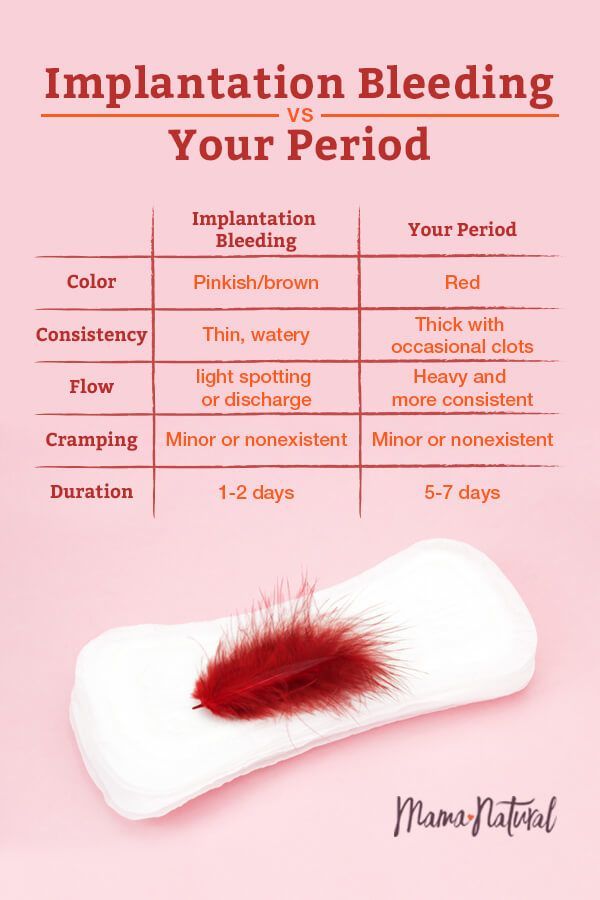 Bleeding can be weak, spotting, plentiful.
Bleeding can be weak, spotting, plentiful.
Most often, blood during early pregnancy is observed during implantation of the fetal egg. When the egg is attached, the vessels are often damaged, which leads to the appearance of blood secretions. They are similar to menstruation, last 1-2 days. This process is considered natural, does not indicate any pathologies.
Any bloody discharge during early pregnancy is a reason for an urgent appeal to a gynecologist. Even if there is no additional discomfort. At a remote consultation, our doctor will collect an anamnesis, draw up a clinical picture in order to identify the cause of bleeding. And he will select effective methods to eliminate the problem.
Blood during pregnancy - other common causes
In addition to the main ones, there are some other reasons why pathology can develop.
| No. | Cause |
| one | Excessive exercise, deep penetration during intercourse. If the cervix is damaged, slight red discharge occurs, which disappears within two hours. |
| 2 | Progesterone deficiency. With a low level of the hormone, the body starts the process of menstruation. Bloody discharge during pregnancy appears when the uterine mucosa is exfoliated. The situation may adversely affect the implantation of the fetal egg. |
| 3 | Miscarriage - occurs in 2-8% of pregnant women. It is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen, which is rapidly increasing, bloody discharge at the beginning of pregnancy. The causes of the pathological condition can be different - infectious diseases, fetal malformations that are incompatible with life, dehydration, abdominal trauma, taking certain drugs. |
| four | Ectopic pregnancy. |
| 5 | A failed miscarriage. Blood discharge during pregnancy, abdominal pain are the main manifestations of intrauterine development of the fetus. |
| 6 | Infections. To avoid dangerous complications, it is necessary to treat diseases. Parents of both sexes should be tested. |
| 7 | Full or partial hydatidiform mole. Pathology of the chorion, in which the size of the villi increases, bubble expansions form. The risk group includes women with ovarian dysfunction, inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, and a history of cystic mole. Bleeding is profuse and constant, characteristic blisters are present. The symptoms of early toxicosis are very pronounced, the size of the uterus, the hCG indicators do not correspond to the gestational age. |
| eight | Cervical cancer. |
| 9 | Subchorionic hematoma. Hemorrhage around the placenta most often resolves on its own. But it increases the risk of preterm birth and other complications. |
| ten | Cervical erosion. Detected in 50% of women. For pregnant women, the disease is not dangerous, but constant medical supervision is needed. |
Bleeding in the first trimester can be caused by causes that appear at any gestational age. These are fibroids, polyps in the uterus and cervical canal, cardiovascular pathologies that are associated with a weakening of the endothelium.
Physiological or pathological bleeding during gestation - differences
Clinical manifestations of bleeding in pregnant women depend on the causes. Physiological discharge of blood from the genital tract in the early stages of gestation proceeds without deterioration in well-being. With bleeding caused by erosion, fibroids and polyps, there are also no additional discomfort. In this case, only a few drops of blood are released, it bleeds for a short time.
Physiological discharge of blood from the genital tract in the early stages of gestation proceeds without deterioration in well-being. With bleeding caused by erosion, fibroids and polyps, there are also no additional discomfort. In this case, only a few drops of blood are released, it bleeds for a short time.
Abundant bleeding, similar to menstruation, against the background of a general satisfactory condition, occurs with a deficiency of progesterone.
Bleeding with spontaneous interruption is accompanied by constant or periodic pain in the lumbar region, abdomen. Disturbed by nausea, bouts of dizziness, slightly increased body temperature. Bleeding can be weak or intense, and clots are often observed in the discharge.
When a fertilized egg is fixed outside the uterus, internal bleeding often occurs, and discharge from the genital tract may appear much later. Characteristic manifestations - acute pain in the abdomen radiates to the anal region, right or left side, blood pressure decreases, cold sweat appears, fainting is possible. Significant blood loss leads to the development of a state of shock with a high probability of death.
Significant blood loss leads to the development of a state of shock with a high probability of death.
Learn more about implantation bleeding
Why does it bleed at the initial stages of gestation? Most often, the appearance of spotting during pregnancy is associated with the implantation of the embryo. They occur 6-12 days after conception and are often one of the first signs of conception.
Usually, the appearance of spotting at the beginning of pregnancy coincides with the time of the onset of menstruation, if the cycle is regular. But discharge in pregnant women is not as abundant as menstrual bleeding. Duration - from several hours to three, with the first pregnancy up to 5 days.
How does implantation bleeding manifest?
- weak, pulling pain in the lower abdomen;
- headache, dizziness;
- sudden change of mood;
- bouts of nausea;
- increased sensitivity, swelling of the mammary glands;
- fatigue, drowsiness.
Important! When the embryo is implanted, little blood is released, usually these are small spots. The discharge may be pink, brown, orange, and there should be no clots.
Possible causes of early bleeding by week
The first months of pregnancy are the most difficult and dangerous. It is in the early stages that various pathologies and complications often appear.
Why blood may appear in the early stages during pregnancy:
- At the 4th week of pregnancy, discharge with an admixture of blood may appear - this is implantation bleeding. Heavy bleeding is a dangerous sign, most often indicates a miscarriage. Spontaneous abortion can be caused by exercise, fever, infections, drugs or alcohol. Such bleeding is profuse, painful, blood clots are present.
- The appearance of sanious discharge at the 5th week of pregnancy may be a sign of a missed pregnancy. The reasons are overwork, Rh conflict, bad habits, bacterial and viral diseases of the reproductive system, genetic disorders in the embryo.
 Symptoms - causeless fever, severe pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, the disappearance of signs of toxicosis.
Symptoms - causeless fever, severe pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, the disappearance of signs of toxicosis. - Blood in the discharge at the 6th week of pregnancy appears with an ectopic attachment of the fetal egg, fetal fading, Rhesus conflict. Discharge with blood at 6 weeks of pregnancy is a reason for an urgent visit to the gynecologist.
- At the 7th week of pregnancy, discharge with blood is not the norm. May indicate a miscarriage, missed or ectopic pregnancy.
- From the 8th week of pregnancy, one of the most dangerous periods of pregnancy begins. The formation of the placenta begins, the hormonal background changes. Bloody discharge appears with the threat of miscarriage or spontaneous abortion. Pregnancy is often not saved.
Pay attention! In the second trimester, bleeding occurs only in 5-10% of women. Most often this is due to late spontaneous abortion, isthmic-cervical insufficiency. The appearance of blood in the third trimester mainly occurs with presentation, placental abruption.
Early bleeding after IVF
The appearance of blood discharge during pregnancy on the 8-10th day after IVF is not considered a pathology, provided that the woman feels normal. After the introduction of the embryo into the uterine cavity, minor damage to the small uterine vessels often occurs. Brown, dark cream, pale pink, odorless discharge most often indicates a successful transplant, pregnancy.
If spotting after IVF is observed for 1-2 days, slight pulling pains in the lower abdomen are disturbing, this may be due to a progesterone deficiency. After the examination, the doctor will adjust the hormonal maintenance therapy.
Pink discharge on the 16th day after the transfer is a dangerous symptom. It may be a sign of detachment of the fetal egg, the threat of termination of pregnancy.
According to studies, uterine bleeding in the first trimester is a common occurrence in pregnancy after IVF. Discharge does not affect the incidence of adverse reproductive outcomes. The number of embryo rejections in women with and without uterine bleeding is approximately the same. Consult with our doctors by phone for more details.
The number of embryo rejections in women with and without uterine bleeding is approximately the same. Consult with our doctors by phone for more details.
Diagnostics
If blood has gone from the genitals of a pregnant woman, the doctor conducts an external and gynecological examination.
Analyzes and examinations:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- tests for hCG, other hormones;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- CTG is performed to assess the vital activity of the fetus.
Treatment
Methods of treatment depend on the results of the examination.
Bloody discharge in the first trimester - causes and therapeutic measures:
| The reasons | Treatment |
| Miscarriage | Cleansing the uterus. |
| Ectopic pregnancy | Diagnostic laparoscopy, removal of residual fetal tissues, antibiotic therapy. |
| Risk of miscarriage | Hospitalization, bed rest, prescribing drugs to maintain pregnancy, sedatives and tocolytics to reduce uterine tone. |
| bubble skid | Curettage of the uterine cavity. |
| Cervical cancer | Operational intervention. |
| Polyp injury, cervical erosion | Expectant management, if the condition does not worsen, removal and cauterization is carried out after childbirth. |
| progesterone deficiency | hormone therapy. |
| Damage to the uterus | Complete bed rest. |
| Infectious pathologies | Depending on the type of pathogen - antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs. |
Complications and consequences
It is impossible to ignore bloody impurities in vaginal discharge during pregnancy. Without proper and timely assistance, the following complications may occur:
- miscarriage;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- the development of an infectious process, sepsis due to the remainder of dead tissues in the uterine cavity;
- profuse blood loss can lead to death.
Important! Urgent medical attention is needed in case of heavy bleeding, discharge of bright scarlet blood, presence of blood clots in the discharge. In life-threatening and fetal conditions, severe pain in the abdomen, lower back, convulsions, profuse cold sweat, and loss of consciousness are disturbing.
Methods of prevention
If there is blood in the first trimester, it is important to remain calm. Stress and anxiety will only exacerbate the situation. But any health problem is easier to prevent than to treat.
But any health problem is easier to prevent than to treat.
How to avoid bleeding during childbearing - recommendations from a gynecologist:
- eat right and balanced, give up junk and junk food, eat more fresh vegetables and fruits;
- observe the drinking regime;
- in the absence of contraindications, moderate physical activity is indicated - yoga, swimming, special gymnastics for pregnant women;
- more time to walk in the fresh air;
- avoid stress, overwork, observe the daily routine, get enough sleep;
- give up bad habits, do not be in smoky rooms;
- timely visit a gynecologist;
- according to the doctor's prescription, take vitamin complexes for pregnant women;
- do not self-medicate.
The prognosis for bleeding during gestation depends on the causes and timely visit to the doctor. Properly provided medical care can save the life of the fetus and the woman.
FAQ
Why is there blood from the genital tract during gestation?
+
The causes of bleeding in early pregnancy are different. Most often, spotting appears when the fetal egg is fixed, progesterone deficiency, with erosion of the cervix and polyps. Dangerous causes - ectopic, molar, miscarriage, miscarriage.
What to do if there is bleeding during pregnancy?
+
Much depends on the amount of blood released, general well-being. If the bleeding is not strong, not for long, the general condition is normal, it is enough to lie down and rest. Write down the date of the attack, inform the doctor at the next visit. But if even slight spotting during early pregnancy lasts more than 72 hours, is accompanied by cramping or acute pain, fever, you should immediately visit a gynecologist or call an ambulance.
How can you recognize a miscarriage?
+
With the threat of interruption, spotting is scanty, pain in the lower abdomen is absent or may be dull, aching.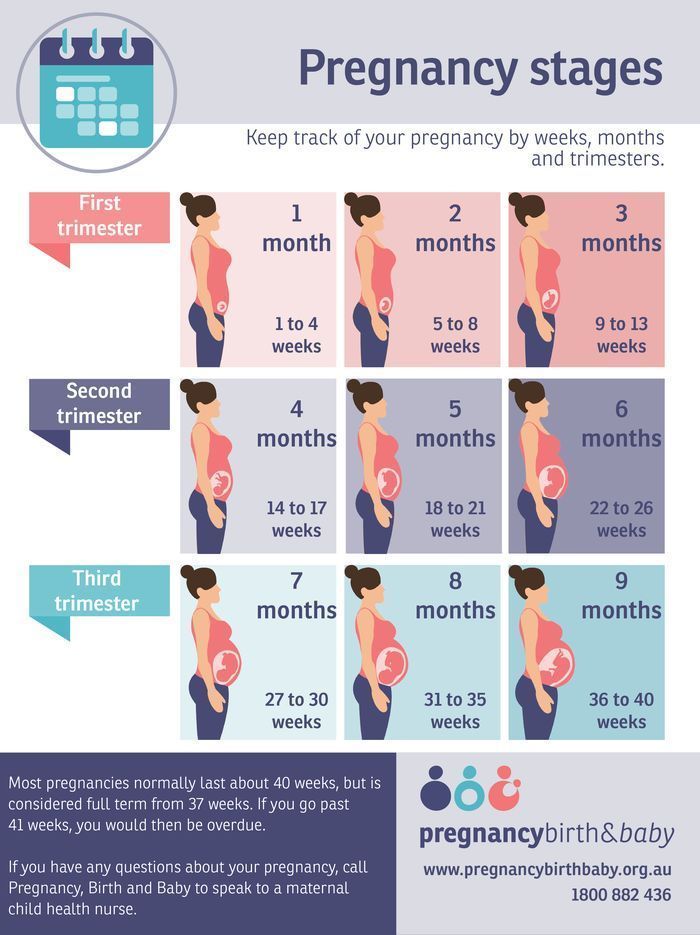 The condition is considered reversible, with timely treatment, pregnancy can be saved. If a miscarriage has begun, bleeding intensifies, cramping pain appears. The general condition is satisfactory. Urgent hospitalization is required, the probability of maintaining pregnancy is decided on an individual basis.
The condition is considered reversible, with timely treatment, pregnancy can be saved. If a miscarriage has begun, bleeding intensifies, cramping pain appears. The general condition is satisfactory. Urgent hospitalization is required, the probability of maintaining pregnancy is decided on an individual basis.
Expert opinion:
Bleeding during pregnancy is a dangerous symptom. Sometimes spotting can be caused by physiological reasons. But often such a symptom appears in life-threatening conditions for the woman and the fetus.
We publish only verified information
Article author
Menshikova Maria Viktorovna obstetrician-gynecologist
Experience 38 years
Consultations 1816
Articles 46
Specialist with extensive practical experience. He has a certificate of a mammologist, a certificate of professional certification. Participates in foreign business trips and individual training programs (Los Angeles).
He has a certificate of a mammologist, a certificate of professional certification. Participates in foreign business trips and individual training programs (Los Angeles).
- 1982 - 1986 NPO MONIIAG - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 1987 - 1989 VNITs OZMIR - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 1989 - 1992 departmental polyclinic st. Moscow - Kurskaya - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 1992 - 2001 NPO MONIIAG - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 2007 - 2008 NP KMIKM - doctor administrator
- 2009 - 2013 Pereslavl Central District Hospital, women's consultation - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 2020 to present Teledoctor24 LLC - doctor - consultant (gynecologist)
Pregnancy and menstruation | Kotex®
The question “Am I pregnant?” probably occurred at least once to the vast majority of heterosexual women who are sexually active.
Although the absence of periods is the most noticeable early symptom of pregnancy, many women have many questions when it comes to whether menstruation is possible during pregnancy.
Is it possible to have periods during pregnancy?
No, they can't. If you have your period, it means you are not pregnant.
Menstruation occurs only if the monthly egg that comes out of the ovaries has not been fertilized.
If the egg is not fertilized, it leaves the uterus and is excreted along with the menstrual blood through the vagina.
The difference from pregnancy seems obvious at first glance, because during pregnancy there are no periods, and if you are not pregnant and in reproductive age, then you have periods.
But some women have doubts about this, which are related to the fact that about 20-30% of pregnant women have irregular spotting, which in essence is not menstruation and differs from it: most often they have light pink or brown shade and not so abundant. Sometimes women confuse them with menstruation if they occur around the same time that menstruation is expected.
-
normal menstrual bleeding is light at first and then increases, and the blood becomes more saturated red
-
normal menstrual bleeding becomes less intense towards the end of menstruation, the color also becomes less intense
What can cause bleeding during early pregnancy?
Bloody discharge during pregnancy can be associated with many factors, each of which is a reason to urgently visit a doctor to rule out pathology.
Main causes of bleeding in the first trimester of pregnancy:
-
bleeding after attachment of the egg to the wall of the uterus
-
signs of threatened miscarriage
-
infections
-
ectopic pregnancy
Many women who experience this light bleeding go on to have normal pregnancies and give birth to healthy children, but in about a third such bleeding becomes more intense over time and eventually leads to a miscarriage.
Unfortunately, there is no way to determine at home what caused such bleeding, so whenever such light bleeding occurs during pregnancy, you should consult your gynecologist for advice to rule out the possibility of pathology.
Important: If you are pregnant and have bleeding that becomes more intense and does not stop, accompanied by pain in the abdomen and lower back, you should immediately consult a doctor.
When do periods start after pregnancy?
Both after caesarean section and after vaginal delivery, women experience vaginal bleeding.
In the first weeks after childbirth, the blood may clot and be more intense than normal periods, but then they become brown, light red and finally whitish.
This discharge is called lochia and usually lasts no more than 45 days after vaginal delivery and up to 60 days in women after caesarean section. Lochia begins immediately after childbirth, and menstruation occurs only when the level of the hormone prolactin in the woman's body drops, which causes the appearance of breast milk.
If you are not breastfeeding, your periods usually return 6-8 weeks after delivery.
If you are breastfeeding, you may not have your period for as long as you are breastfeeding your baby.
During lochia, it is recommended to use pads rather than tampons.
Abortion and menses
Many questions about menstruation also arise in women who have experienced an unplanned pregnancy and have decided to have an abortion.
How this procedure will affect the body depends on many factors, primarily on whether the abortion was medical or surgical. Bleeding after an abortion is normal, but in the truest sense of the word, menstruation is not.
Medical abortion
During a medical abortion, the doctor gives you two pills.
Usually, the first tablet is taken under the supervision of a doctor, in the clinic. After taking this pill, the endometrium of the uterus, to which the fertilized egg is attached, ceases to thicken, and pregnancy can no longer develop. Some women begin to bleed at this point.
Some women begin to bleed at this point.
The woman then leaves the clinic and takes the second pill at home. After taking it, the endometrium begins to separate from the walls of the uterus and exit through the vagina. Such bleeding usually begins 0.5-4 hours after taking the pill. Usually, at 4-5 hours of bleeding, it becomes more intense, then its intensity decreases, and it becomes similar to normal menstruation.
Surgical abortion
In the case of a surgical abortion, bleeding may begin immediately after the procedure, but in some women it begins after 3-5 days. Usually such bleeding is weaker than normal menstruation. Bleeding may stop or last until the next menstruation.
How long does bleeding last after an abortion?
Bleeding after any type of abortion often lasts 1-2 weeks. Most often, after this period, it becomes quite insignificant, and in some women it completely disappears until the next menstruation.

 Dangerous condition, urgent hospitalization is required.
Dangerous condition, urgent hospitalization is required.  Pregnant women are rarely diagnosed. The risk group includes women with a large number of abortions and childbirth, often changing sexual partners.
Pregnant women are rarely diagnosed. The risk group includes women with a large number of abortions and childbirth, often changing sexual partners.