Red bumps on baby tongue
Causes and when to see a doctor
The tongue has lots of small spots on it for taste and sensation. They are not usually very noticeable. If spots are an unusual color, cause irritation, or other symptoms accompany them, they can be the sign of a health problem.
In this article, we look at what healthy spots on the tongue do, and the causes of unusual spots. We also cover diagnosis, treatment, and prevention tips.
Tongue spots that are unusual in color, size, or appearance or are accompanied by other symptoms could signal a health problem.
Causes of unusual tongue spots include:
Lie bumps
Transient lingual papillitis is a condition more commonly referred to as lie bumps. A key symptom is small red or white bumps on the tongue. These bumps are enlarged or inflamed papillae.
Lie bumps can affect one or several papillae. Other symptoms can include:
- pain
- a burning or itching sensation
- greater sensitivity to heat
Lie bumps commonly result from injury to the tongue, for example, when a person accidentally bites their tongue.
Viruses, psychological stress, and poor nutrition can also cause the condition.
Lie bumps usually heal without treatment within a week. If treatment is necessary, a person can try a medicated mouthwash or antihistamines to help them reduce the swelling.
A person with lie bumps can quicken the healing of the tongue by:
- avoiding spicy foods
- avoiding hot liquids or food
- not sucking sweets
- brushing teeth with care
Tongue burn
If a person burns their tongue on hot food or liquid, it can cause blisters. These can appear as small, fluid-filled spots on the tongue.
Blisters will heal more quickly if they remain unbroken. A person can promote healing and prevent blisters from breaking by taking care when brushing the teeth and eating and drinking.
A burn on the tongue does not usually require treatment. Keeping the mouth clean by using mouthwash can help to prevent an infection.
Canker sores
Canker sores are very common. These small ulcers look white or yellow and can appear on the tongue, inside of the mouth, and on the lips. The cause of canker sores is not clear.
These small ulcers look white or yellow and can appear on the tongue, inside of the mouth, and on the lips. The cause of canker sores is not clear.
Canker sores usually go away without treatment. Directly applying an over-the-counter (OTC) medication, such as benzocaine, to the ulcer can relieve discomfort and promote healing.
In some cases, canker sores can be a sign of an underlying health condition. If a person has other symptoms, they may wish to seek medical advice. These symptoms include fever, stomach pain, and a rash elsewhere on the body.
Geographic tongue
Share on PinterestGeographic tongue may appear as a blotch or spot of redness with a white border.Image credit: Dimitrios Malamos, 2015
The medical term for geographic tongue is benign migratory glossitis.
Geographic tongue causes inflammation on the sides or top of the tongue and usually appears as a blotch or spot of redness surrounded by a white border.
Doctors are not sure what causes geographic tongue, but it may be related to stress, allergies, or diabetes. The condition does not usually cause any other symptoms and should heal without treatment.
The condition does not usually cause any other symptoms and should heal without treatment.
Oral yeast infection
A yeast infection known as oral thrush can affect the mouth and tongue. Symptoms include:
- white spots, bumps, or patches on the inside surfaces of the mouth
- a bad taste
- pain or soreness inside the mouth
If a person scrapes off a white patch on the tongue, they will usually see a red, inflamed patch underneath.
Oral thrush results from an overgrowth of yeast that occurs naturally in the mouth. Certain groups of people are more at risk of developing the infection, including:
- newborn babies
- people who wear retainers or dentures
- people with diabetes
- people receiving chemotherapy
- people with a dry mouth due to medication or a medical condition
- people living with HIV
A person can usually treat oral thrush using OTC antifungal medications. A doctor may also recommend:
- changing a person’s dentures
- changing how a person cleans their mouth or teeth
- trying a different medication that does not dry out the mouth
Scarlet fever
Share on PinterestSymptoms of scarlet fever can include “strawberry tongue. ”
”Image credit: SyntGrisha, 2015
Scarlet fever is a bacterial infection in the nose and throat. One of the key symptoms is a red, bumpy tongue that people often refer to as “strawberry tongue.” Other symptoms include:
- a red, sore throat
- fever
- a red, blotchy rash that usually starts on the chest and stomach
- headache
- stomach pains
Doctors treat scarlet fever with antibiotics. Following antibiotic treatment, scarlet fever usually goes away in around one week, but the rash can last for longer.
Scarlet fever most commonly affects children and is contagious. The infection can be passed on through:
- coughing and sneezing
- sharing or using contaminated objects, such as cups, foods, towels, baths, and clothes
Oral allergy syndrome
An allergy to certain raw fruits and vegetables can cause itching and swelling in the mouth or on the tongue. Swollen patches on the tongue may appear red and irritated.
The reaction is often mild, and a person can avoid it by cutting out the foods that cause the allergy. Cooking or peeling the fruit or vegetable can often prevent a reaction.
Tongue cancer
Tongue cancer is a form of head and neck cancer. Drinking alcohol, smoking, and infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV) can increase a person’s risk of developing tongue cancer.
A bump or spot on the side of the tongue, or a red patch on the tongue, is usually harmless. But if it does not go away, it could be a symptom of tongue cancer. Other symptoms include:
- a sore throat that lasts for a long time
- pain when swallowing
- numbness in the mouth
Anyone who has a painless sore, lump, or red or white patch on the tongue that does not go away should see a dentist or doctor.
There are four kinds of healthy spots or bumps that typically appear on the tongue. The medical term for these spots is papillae.
- Fungiform papillae are the small spots that appear all over the tongue.
 A person usually has 200 to 400 of these, mostly at the tip and edges of the tongue. Each of these papillae contains three to five taste buds.
A person usually has 200 to 400 of these, mostly at the tip and edges of the tongue. Each of these papillae contains three to five taste buds. - Circumvallate papillae are bigger spots that appear at the back of the tongue. They are slightly raised and are arranged in a ‘v’ pattern. A person usually has 7 to 12, with each one containing thousands of taste buds.
- Foliate papillae appear on the back of the tongue and at the edges. A person usually has around 20, with each one containing hundreds of taste buds.
- Filiform papillae are found in the center and at the front of the tongue. There are more of this type of papillae than any other. They do not contain taste buds.
Papillae help people to sense and taste with the tongue. Nerves that send messages about flavor to the brain are connected to taste buds. Papillae are also important for giving information about temperature, chewing food, and speaking.
People should consider seeing a dentist or doctor for:
- unusual spots on the tongue last longer than a week
- spots that bleed, become more painful, or spread
A doctor will usually ask about any other symptoms, when the spots appeared, and any pain a person is feeling. This information can help a doctor give a diagnosis and offer further advice or treatment.
This information can help a doctor give a diagnosis and offer further advice or treatment.
Practicing good oral hygiene can help to prevent oral yeast infections and may help the tongue to heal after an injury or illness. To keep the mouth, teeth, and tongue healthy, dentists usually recommend:
- brushing teeth twice per day
- flossing daily
- avoiding too much sugar
It is not possible to prevent all spots on the tongue, particularly those due to infections and canker sores.
Taking medication correctly, keeping the mouth clean, and avoiding irritating the mouth when eating or cleaning teeth can promote healing and prevent spots from reoccurring.
People have many tiny spots on their tongues that are crucial for taste and sensation. But spots that are unusual in color, size, or appearance could be the signs of a health problem.
Unusual spots can have a range of causes, from tongue injuries to an infection. They often go away without treatment but can sometimes be a symptom of a more serious medical condition, such as scarlet fever or tongue cancer.
People may wish to see a dentist or doctor if tongue spots do not go away on their own within a week. If a person has other symptoms, or if the spots bleed or become more painful, they may need treatment.
Causes and when to see a doctor
Bumps under the tongue often appear suddenly and without an identifiable cause. Although they may feel strange, bumps under the tongue are usually harmless.
In this article, we cover possible causes of bumps under the tongue and how doctors diagnose and treat them. We also discuss home remedies and when to seek medical treatment.
Share on PinterestUsing medicated mouthwash and practicing good oral hygiene may help relieve symptoms of bumps under the tongue.There are many possible causes of bumps under the tongue. Some of the more common ones are those below:
Canker sores
Canker sores, also known as aphthous ulcers, are open lesions that can develop anywhere inside the mouth, including under the tongue.
Canker sores appear suddenly. They have no known cause but are not contagious. Some researchers believe that canker sores are a type of immune system response.
They have no known cause but are not contagious. Some researchers believe that canker sores are a type of immune system response.
Other factors can also trigger canker sores, such as:
- an injury or damage to the tissue underneath the tongue
- exposure to spicy, acidic, or dairy foods
- hormonal changes, such as those during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause
- gastrointestinal (GI) disorders, such as celiac disease
- nutritional deficiencies, such as low iron, folate, and vitamin B12
- physical or emotional stress
- genetics
- infections
Most canker sores are minor and resolve on their own within 4–14 days.
Learn more about canker sores on the tongue.
Oral mucous cyst
Mucous cysts are fluid filled sacs that form in the tissues of the fingers, toes, and mouth. An oral mucous cyst will develop near one of the openings of the salivary glands under the tongue or on the lips, cheeks, or floor of the mouth.
Mucous cysts appear as soft, swollen lumps that range in color from flesh-colored to dark blue. Mucous cysts tend to periodically disappear when they rupture and reappear when they become irritated by saliva.
Although a person can develop an oral mucous cyst at any age, they usually occur between the ages of 10 and 30 years.
Learn more about mucous cysts.
Human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus, or HPV, is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Scientists have identified more than 180 HPV subtypes.
HPV infections lead to lesions in the skin and mucous membranes. According to the CDC, about 40 subtypes of HPV can infect the mouth and throat.
People with minor oral HPV infections do not develop symptoms. However, those who do may notice:
- small, hard bumps under the tongue or in the mucous membrane inside the mouth
- bumps that appear white, pink, red, or flesh-colored
- painless, smooth, and slightly raised bumps
- a single bump or cluster of bumps
The body can clear an HPV infection within 2 years without medical treatment. However, HPV is the leading cause of oropharyngeal cancers.
However, HPV is the leading cause of oropharyngeal cancers.
Learn more about HPV in the mouth.
Lymphoepithelial cyst
Lymphoepithelial cysts are slow growing, noncancerous lesions that develop in the salivary glands. They often occur as a symptom of HIV infections.
These small, firm nodules sit just below the mucus membrane that lines the inside of the mouth. Lymphoepithelial cysts usually appear as flesh-colored, white, or yellow bumps under the tongue or on the floor of the mouth.
Sialolithiasis
Sialolithiasis, also known as salivary stones, is a condition in which stones of crystalized minerals form in the ducts of the salivary glands. Sialolithiasis is the most common cause of salivary gland swelling.
A stone that forms in the sublingual gland, located underneath the tongue, can lead to a sore, painful bump.
Other symptoms of sialolithiasis include:
- pain or discomfort in the mouth that worsens when eating
- pain or swelling below the jaw
- infection in or near the affected gland
- dry mouth
Learn more about salivary stones.
Salivary gland tumor
A salivary gland tumor that forms in the sublingual gland can lead to a lump or swelling under the tongue or near the jaw.
Generally, if the tumor develops in a smaller salivary gland, there is a higher probability that it is malignant.
For example, although less than 1% of salivary gland tumors develop in the sublingual gland, 70–90% of sublingual gland tumors are malignant. A malignant tumor grows rapidly and can spread to other parts of the body.
Salivary gland tumors can lead to the following symptoms:
- a lump or painful swelling under the tongue or in the jaw, ear, or neck
- numbness or muscle weakness in part of the face
- difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
- fluid draining from the ear
Learn more about salivary gland cancer.
A doctor can diagnose most causes of bumps under the tongue by carrying out a physical examination and asking the person to describe their current symptoms.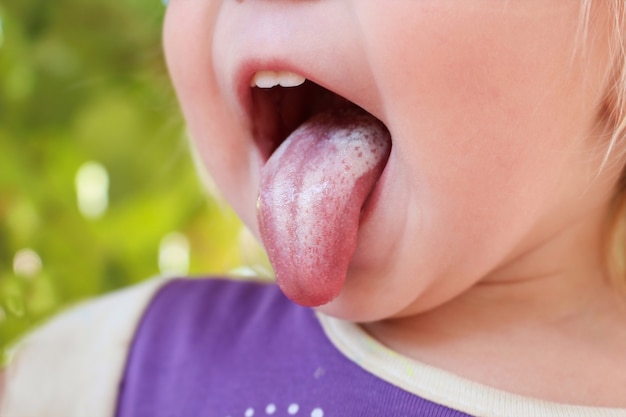 They may also review the medical history of the person and their family for indications of risk factors for certain diseases.
They may also review the medical history of the person and their family for indications of risk factors for certain diseases.
A doctor may use one or more diagnostic tests to confirm a diagnosis or rule out other potential causes. These tests can include:
- blood tests that measure white blood cell counts, to check for an infection
- a swab culture analysis, to identify infectious pathogens, such as bacteria or fungi
- imaging tests, such as a CT scan or MRI scan, to identify structural abnormalities in the mouth
- a biopsy, to analyze tissue samples for cancer cells
Treatment varies depending on the underlying cause. Many types of bumps under the tongue, such as canker sores and mild HPV infections, resolve on their own without medical intervention.
- HPV mouth sore: A doctor can freeze an HPV mouth sore using cryotherapy or inject it with an antiviral drug called interferon alfa-2B.
- Cysts: A doctor may attempt to drain lymphoepithelial cysts and oral mucous cysts.
 They may recommend removing a cyst using laser therapy or freezing it with cryotherapy.
They may recommend removing a cyst using laser therapy or freezing it with cryotherapy. - Sialolithiasis: A doctor may treat salivary stones with anti-inflammatory drugs. They can push the stone out by massaging the salivary gland or gently probing the affected area with a blunt object. A doctor may recommend surgery to remove a large salivary stone.
- Salivary gland tumors: A doctor will likely recommend surgery for salivary gland tumors. During surgery, they will remove the tumor along with some of the surrounding tissue. If they identify cancer cells elsewhere in the body, they may recommend a systemic treatment, such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
The following home remedies may promote healing and help relieve uncomfortable symptoms of tongue bumps:
- practicing good oral hygiene
- using medicated mouthwash
- avoiding acidic, spicy, and sugary foods
- using topical gels and numbing solutions on painful oral sores
- quitting smoking, if a smoker, and avoiding secondhand smoke
Most causes of bumps under the tongue heal on their own.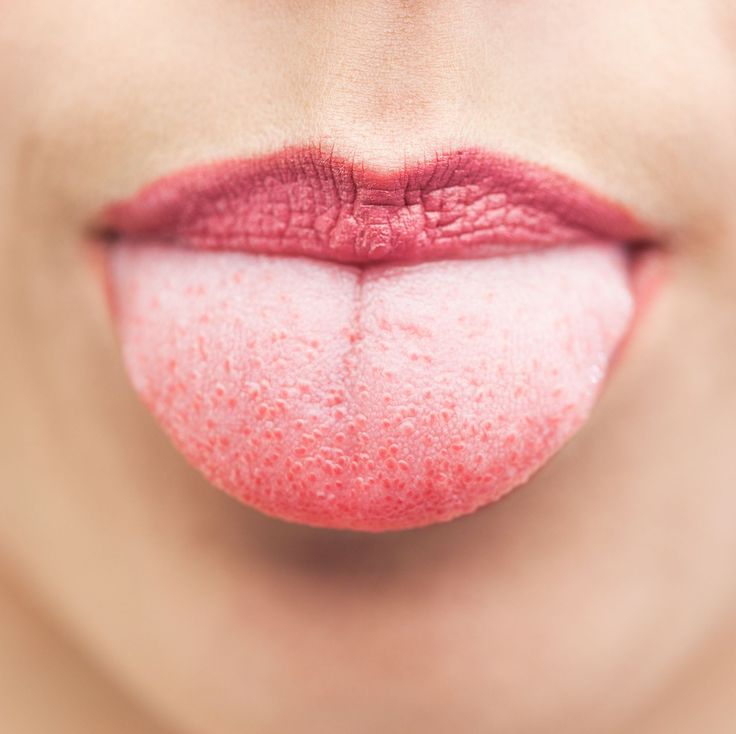 However, people should speak with a doctor if they have a bump under the tongue that does not heal within 10 days.
However, people should speak with a doctor if they have a bump under the tongue that does not heal within 10 days.
People should also seek medical attention if they have a bump under the tongue or swelling in the mouth that interferes with their ability to speak, swallow, or chew.
Bumps under the tongue can appear suddenly and without an apparent cause. These bumps often resolve on their own without treatment.
Some bumps heal and reappear months or years later. Other types of tongue bumps resolve and never occur again.
People with more serious underlying conditions, such as HPV infections and salivary gland cancer, can have very positive outlooks if doctors catch the condition at an early stage.
Most HPV infections resolve within 2 years. Localized salivary gland cancer has a 94% 5-year relative survival rate if it has not had time to spread.
Bumps can develop under the tongue due to a mouth injury, exposure to viruses, eating certain foods, or salivary stones, among other causes.
Regardless of the underlying cause, most bumps under the tongue resolve relatively quickly and do not require medical treatment. More serious tongue bumps, such as tumors, salivary stones, and infections, are easily treatable with medication or surgery.
Acne on the tongue: causes and what to do
Pimples on the tongue are familiar to many. They are painful, uncomfortable and cause suffering. In fact, they are easily treated and do not cause complications. A pimple on the tongue can appear for many reasons, most often due to a microtrauma of the tongue, stomatitis or herpes. We will tell you why white, red and pink pimples appear on the tongue, as well as how to cure them.
Content:
- What does a pimple mean on the tongue
- Causes
- What to do
- Based on
- He's on the tip
What is it
If a pimple appears on the tongue, the main thing to understand is the following - in principle, there can be no pimples on the tongue, since the sebaceous glands are completely absent on it.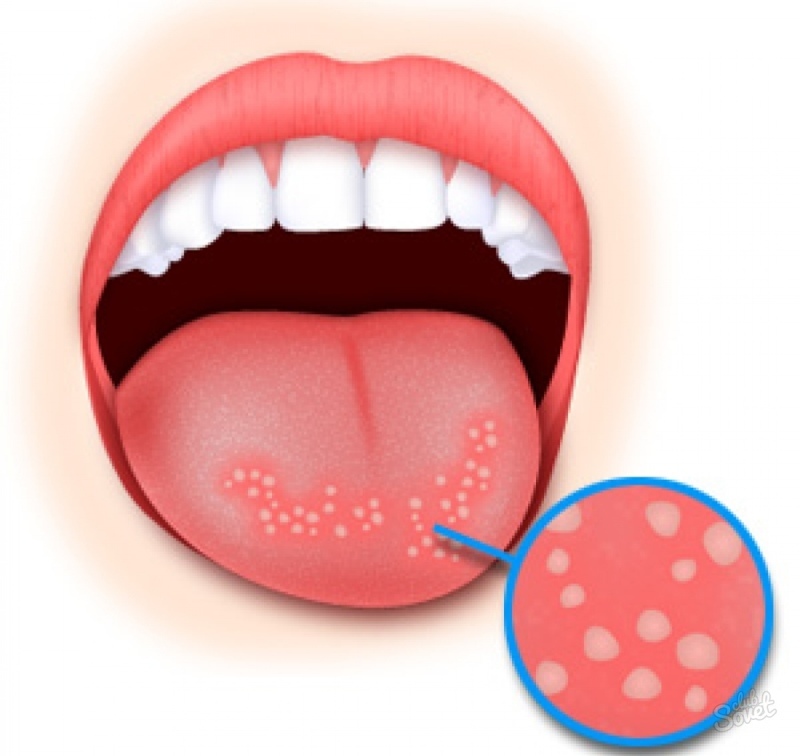 Those formations that are mistaken for acne are not actually acne - they are not filled with purulent exudate. In fact, these are small swellings and sores on the surface of the tongue. They are called "pimples" because they are very similar. They are white, pink, red, yellow, depending on the complexity of the disease and the cause of the formation.
Those formations that are mistaken for acne are not actually acne - they are not filled with purulent exudate. In fact, these are small swellings and sores on the surface of the tongue. They are called "pimples" because they are very similar. They are white, pink, red, yellow, depending on the complexity of the disease and the cause of the formation.
Dental consultation: Pimple on tongue after injury
Small pimples are very painful, they interfere with eating, talking, and even at rest annoy the patient. Let's try to figure out what to do, how to cure, as well as what they are and why they appear.
White pimple
White pimples most often appear as a result of stomatitis or candidiasis. Since these two diseases are treated completely differently, you should consult a doctor at the first symptoms in order to correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Candidiasis is characterized by white pimples and a coating on the tongue that looks like cottage cheese and covers the entire surface of the oral cavity. There are also white pimples on the base, tip and under the tongue. Sometimes the entire surface can be covered with small pimples and curdled plaque.
There are also white pimples on the base, tip and under the tongue. Sometimes the entire surface can be covered with small pimples and curdled plaque.
Diagnosis of candidiasis is not difficult - if you wake up in the morning and find plaque and pimples on your tongue, you have every reason to assume the presence of candidiasis or thrush. You should consult a doctor for confirmation of the diagnosis and treatment.
With stomatitis, small pimples appear on the tongue. There are usually many of them, they can merge with each other. Such small white pimples on the tip or root, at the base or under it are very painful and itchy. The pain is worse after eating.
Without proper treatment, stomatitis will not go away on its own - you need to see a doctor to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. As a rule, it consists in antiseptic treatment of the surface of the oral cavity and in the correction of lifestyle, since the main cause of stomatitis is insufficient oral hygiene.
Red
Red pimples on the tongue are the main symptom of glossitis - an inflammatory disease. Outwardly, they look like inflamed red dots that hurt and hurt.
Glossitis can appear for many reasons:
- allergic reaction;
- eating too hot and spicy food;
- alcohol abuse;
- presence of herpes virus.
A red pimple on the tip of the tongue may also be the result of a burn from too hot food. The papillae on the surface of the burn greatly increase and swell, outwardly it looks like a pimple. After a few days everything is back to normal.
In case of allergy, many red pimples form on the surface of the tongue, which itch and cause anxiety.
With the herpes virus, a red pimple may not be the only manifestation of the disease; the entire surface of the oral cavity is usually affected.
Yellow
The appearance of yellow spots on the tongue is usually not an independent disease.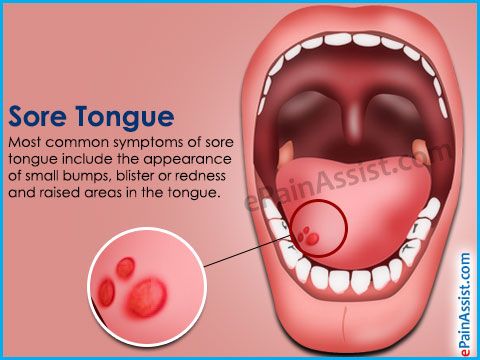 Often with stomatitis or candidiasis, the plaque on the surface of the tongue does not take on a white, but a yellowish tint. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. In addition, the definition of shade is an individual matter. Therefore, yellow acne most often also means either candidiasis or stomatitis. To eliminate doubts, consult a doctor, he will be able to determine for sure what disease you have encountered.
Often with stomatitis or candidiasis, the plaque on the surface of the tongue does not take on a white, but a yellowish tint. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. In addition, the definition of shade is an individual matter. Therefore, yellow acne most often also means either candidiasis or stomatitis. To eliminate doubts, consult a doctor, he will be able to determine for sure what disease you have encountered.
Pink
Pink pimples on the tongue, like yellow ones, are not an independent disease. Usually they are an early stage of glossitis, when the inflammatory process has not yet reached its peak. At the initial stage of the disease, they have a light pink tint, which after a few hours will become intense red. Given the fact that the disease is easier to treat at an early stage, when pink acne appears, you should immediately consult a doctor for advice.
Why appear
As already mentioned, there are no sebaceous glands in the tongue, so "pimples" cannot appear on it in principle.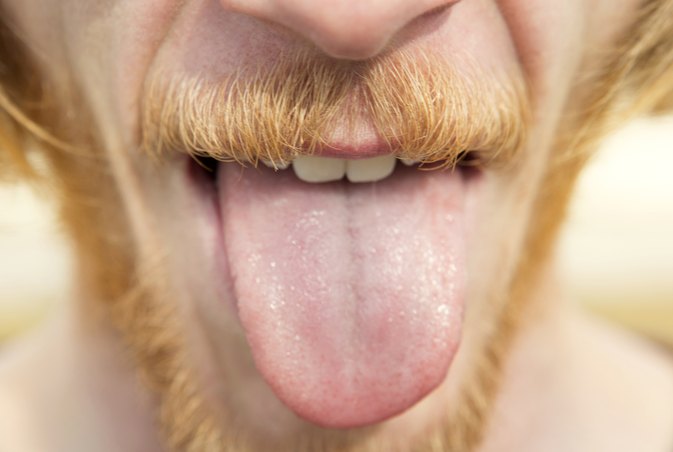 After all, a pimple is an inflammation of the sebaceous gland. But the bumps and nodules that sometimes appear on the surface are very similar in appearance to acne, which is why they got their name. Pimples under the tongue or on the tip cause a lot of trouble and are extremely painful. Consider the reasons for their appearance.
After all, a pimple is an inflammation of the sebaceous gland. But the bumps and nodules that sometimes appear on the surface are very similar in appearance to acne, which is why they got their name. Pimples under the tongue or on the tip cause a lot of trouble and are extremely painful. Consider the reasons for their appearance.
Mechanical damage
Often in the process of chewing or biting food, we bite the tongue, resulting in a small mechanical injury. The risk of surface damage increases with the consumption of hard foods with sharp edges (crackers, chips, seeds). At the site of damage, a small painful swelling or bump is formed, which after a while turns into a white pimple. During eating, the pain intensifies. With severe mechanical damage, a slight edema may occur.
You should exclude spicy and hot foods from your diet, carefully monitor oral hygiene, and after a few days the pimple will disappear on its own.
Allergic reaction
The appearance of pimples on the tongue may indicate an allergic reaction to food, medicine or toothpaste. In this case, small white pimples and sores form, which hurt and hurt when eating or drinking liquids.
In this case, small white pimples and sores form, which hurt and hurt when eating or drinking liquids.
If your doctor suspects an allergy, it is very important to identify the allergen and eliminate it from your diet. First of all, you should stop chewing gum, change your toothpaste and tooth elixir - you may be allergic to oral hygiene products. If these measures have not brought the desired result, it is necessary to analyze whether you have recently taken medication. Acne on the tongue after antibiotics and other medications is a common occurrence. In this case, it is necessary to consult a doctor and stop taking the drug or try to replace it with another one.
If the cause of acne is a food allergy, you need to track what foods they appear after and eliminate these foods from your diet.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is a common cause of white or red pimples on the surface of the tongue. The main cause of stomatitis is insufficient oral hygiene, contact with mucous membranes of pathogenic bacteria due to dirty hands, unwashed fruits and vegetables. Most often, children suffer from stomatitis, because they tend to pull everything into their mouths.
Most often, children suffer from stomatitis, because they tend to pull everything into their mouths.
With stomatitis, small white, pink or red pimples appear on the surface of the tongue and other oral mucosa, which bake, sore and hurt not only during meals, but also at rest. It is sometimes difficult not only to eat, but also to talk or just swallow saliva. Small pimples under the tongue or at the root cause severe discomfort.
At the first suspicion of stomatitis, you should consult a doctor, he will prescribe drugs that relieve itching and soreness of the tongue, as well as promote the speedy healing of sores and pimples.
Herpes
The herpes virus most often affects the area around the lips. However, this is not the only place of its localization, herpes can affect all the mucous surfaces of the human body, including the oral cavity. In this case, watery pimples may appear on the tongue and the inner surface of the cheeks in the amount of one or more.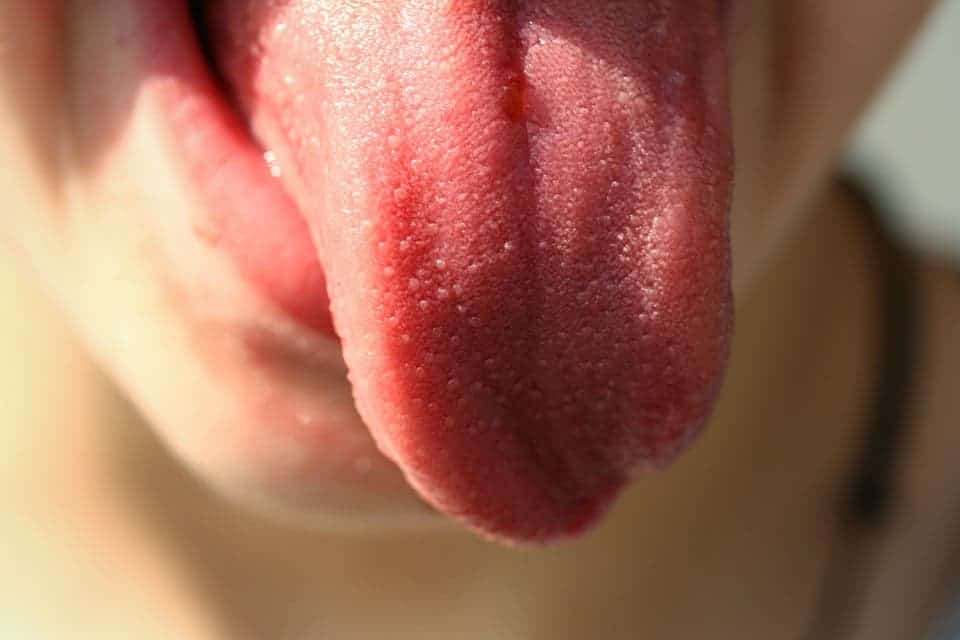 Many do not pay due attention to the herpes virus, believing that it will go away on its own. In fact, this is not such a harmless disease.
Many do not pay due attention to the herpes virus, believing that it will go away on its own. In fact, this is not such a harmless disease.
Without proper treatment, herpes can eventually affect the entire body, including the brain. Therefore, in the presence of the herpes virus, you should consult a doctor and undergo a course of antiherpetic therapy.
Malnutrition
If you eat too much spicy and hot food, inflammation of the tongue, or glossitis, may occur. The papillae on the surface of the tongue are constantly irritated by hot or spicy food, which leads to their inflammation. If you constantly include spicy foods in your diet, inflammation can become chronic.
Inflammation of the tongue can be caused by drinking in large quantities, as well as smoking. Therefore, when the first problems appear, you should immediately try to get rid of addictions.
Pathologies of the internal organs of the patient
Pimples on the surface of the tongue can be a manifestation of various diseases, including candidiasis or tuberculosis.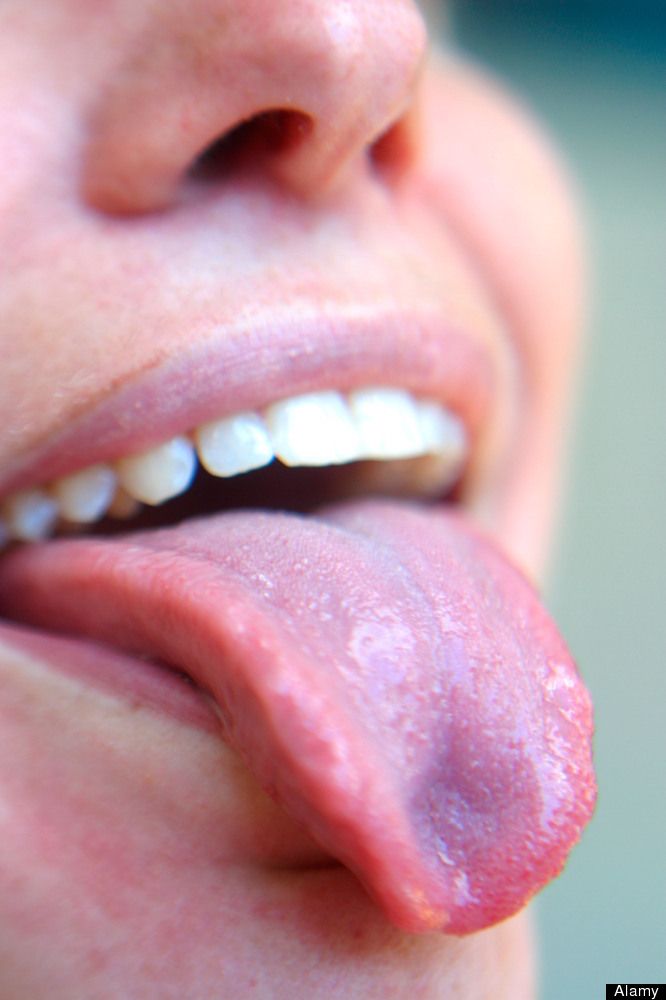 Therefore, the appearance of small pimples should not be taken lightly. Be sure to watch their behavior. If the pimple does not go away for a long time, be sure to consult a doctor.
Therefore, the appearance of small pimples should not be taken lightly. Be sure to watch their behavior. If the pimple does not go away for a long time, be sure to consult a doctor.
Weakened immunity
When the immune system is weakened as a result of a past illness or due to a lack of vitamins and microelements, small painful pimples may appear on the surface of the tongue. If there are no other reasons for their appearance, you should contact an immunologist to check the state of the immune system. In case of detection of malfunctions in its work, it is necessary to take immunomodulators, as well as preparations with lactobacilli to normalize bowel function and correct the activity of the immune system.
What to do
The human oral cavity is inhabited by many bacteria, both beneficial and pathogenic. They have both negative and positive effects on the human body. Pathogenic bacteria cause inflammatory processes, including glossitis, or inflammation of the tongue. Often patients notice a white pimple in themselves, which reacts with pain to every touch. In fact, this is not a pimple, but an inflamed nodule. In medicine, such inflamed nodules are called glossitis.
Often patients notice a white pimple in themselves, which reacts with pain to every touch. In fact, this is not a pimple, but an inflamed nodule. In medicine, such inflamed nodules are called glossitis.
A transparent pimple under the tongue may result from mechanical damage or as an allergic reaction to chemical and food irritants.
It is possible to get rid of glossitis only by complex measures. The first step is to consult a doctor to establish the true cause of its occurrence. The oral cavity should be kept clean, it is advisable to rinse with a soda solution or a decoction of St. John's wort. It is also necessary to strengthen the immune system and limit the consumption of spicy and too hot food so as not to irritate the inflamed nodule.
Location: based on
Pimples at the base of the tongue interfere with swallowing and even talking, hurt and cause a lot of trouble. The reasons for their appearance can be very diverse. It can be stomatitis, and a fungal infection, and tonsillitis or pharyngitis. Only an experienced doctor can make a correct diagnosis. We can only suggest what you should pay attention to.
Only an experienced doctor can make a correct diagnosis. We can only suggest what you should pay attention to.
If a pimple has jumped on the basis of the tongue, other symptoms should be carefully analyzed - fever, enlarged lymph nodes, the presence of allergic reactions. For example, with angina, pimples near the throat form quite often. They are painful, make it difficult to swallow and respond with pain when talking. In this case, the patient also has enlarged tonsils and submandibular lymph nodes, fever. As a matter of fact, acne and temperature almost always occur either with tonsillitis, or with tonsillitis or pharyngitis.
It is undesirable to ignore pimples on the tongue near the throat, since in especially advanced cases they can interfere with breathing, which is fraught with suffocation. Therefore, having discovered them in yourself, you need to contact the ENT for a diagnosis.
Location: at the tip of
A white pimple on the tip of the tongue can jump up at the site of a microtrauma, as a result of infection entering the wound.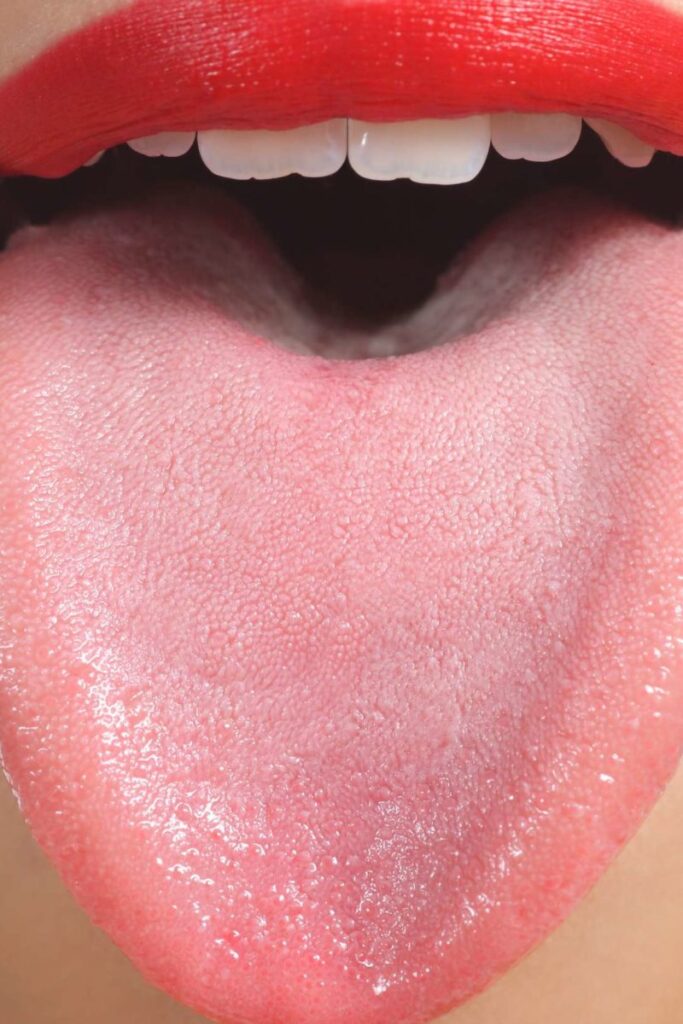 Fans of chips, seeds, pistachios and other nuts are especially susceptible to the appearance of pimples on the tip of the tongue. Solid foods scratch the delicate tip of the tongue, pathogenic bacteria enter the wound, it becomes inflamed and hurts.
Fans of chips, seeds, pistachios and other nuts are especially susceptible to the appearance of pimples on the tip of the tongue. Solid foods scratch the delicate tip of the tongue, pathogenic bacteria enter the wound, it becomes inflamed and hurts.
Often a pimple occurs due to an exacerbation of the herpes simplex virus against the background of a decrease in immunity. In this case, take care of strengthening the immune system, take vitamin complexes. But in any case, consult a doctor and take tests to make an accurate diagnosis.
Also, a pimple can pop up due to chronic stomatitis. If the patient has a weakened immune system and carious teeth, a persistent infection in the oral cavity sooner or later leads to stomatitis. Without timely treatment, it can turn into a chronic form, periodically aggravating.
Pimples on the child's tongue: causes and treatment of pimples
Contents:
- What is it
- Causes
- Treatment
Pimples on the tongue - what is it?
The mucosa in the oral cavity and on the tongue does not have sebaceous glands, so typical pimples cannot form on it.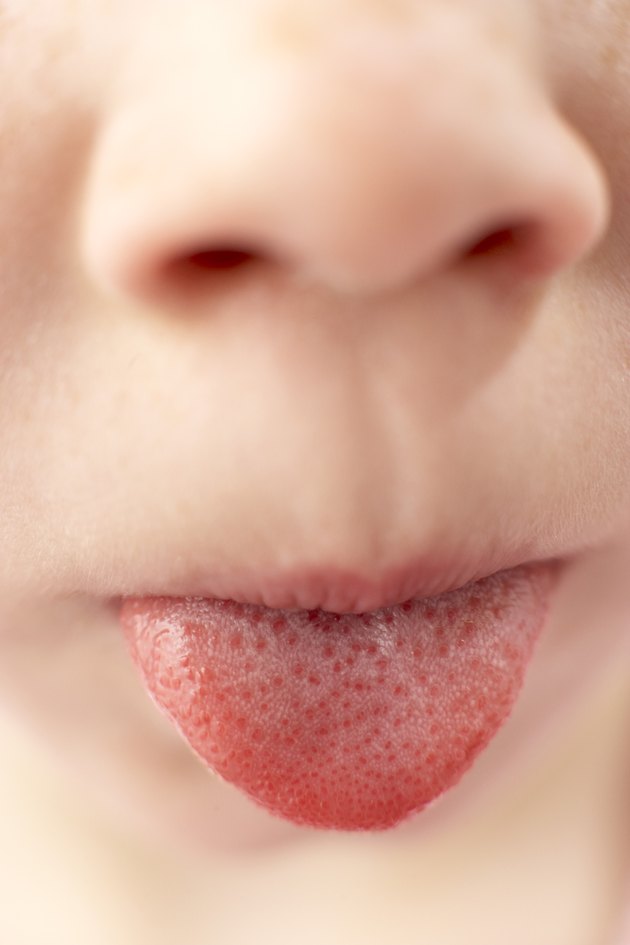 Such formations have two mechanisms of formation:
Such formations have two mechanisms of formation:
- Under the influence of damaging factors, viruses or bacteria, the mucosal stratification occurs, under the upper layer of which liquid accumulates - small bubbles form. If such a formation is not infected, then its contents will be transparent, but if an infection has entered its cavity, then suppuration is possible - the bubble turns white. If blood enters the liquid, then such a formation acquires a red or dark hue. Bubbles can open and painful sores form in their place.
- Sometimes, in response to inflammation, cells on the surface of the tongue begin to actively divide and exfoliate. Whitish or red formations are formed that resemble ordinary pimples, but at the same time they are only enlarged papillae.
Causes of pimples
There are many reasons for the appearance of such formations on the child's tongue. Let's try to understand each of them in more detail.
Tongue injuries
Babies after three months of age begin to actively explore the world around them, including trying to taste everything. But not always those objects that fall into the child's mouth are sterile. Older children often have a habit of chewing on sharp objects, which can also scratch or injure the tongue. Even a slight injury to the mucous membranes, combined with the ingress of microbes, can provoke an inflammatory reaction and the appearance of painful pimples, which are often localized on the tip of the tongue.
But not always those objects that fall into the child's mouth are sterile. Older children often have a habit of chewing on sharp objects, which can also scratch or injure the tongue. Even a slight injury to the mucous membranes, combined with the ingress of microbes, can provoke an inflammatory reaction and the appearance of painful pimples, which are often localized on the tip of the tongue.
Candidiasis or thrush
In children under one year old, the immune system is not fully formed, so any disease leads to a decrease in the protective properties of the body. The consequence of this is candidiasis in the oral cavity - active growth on the mucous membranes of fungi of the genus Candida, which can also be provoked by taking antibiotics. One of the typical manifestations of thrush is the appearance of pimples and curdled white plaque on the entire tongue surface with their spread to the entire oral cavity. If you remove such a plaque, you can find redness, swelling and even the appearance of small ulcers under it.
Stomatitis
When stomatitis occurs on the root of the tongue at its base, on its lateral surfaces or at the tip, a large number of small white pimples appear, which are very painful and cause discomfort when eating or talking. Such pimples can merge to form extensive ulcers. In severe cases, the general poor health of the child and high body temperature are characteristic.
Allergies
Children under two years of age are more likely than adults to experience allergic reactions. One of the manifestations of allergies is the appearance of small whitish or red pimples on the tongue. They can be located both at the tip and in the region of the root of the tongue and move to other parts of the oral mucosa: lips, gums, palate. Most often, such formations disturb the child, itch and cause pain when eating and swallowing. But at the same time, an increase in body temperature is not characteristic.
An increase in allergy symptoms and the appearance of new pimples is caused by the ingestion of a product to which there is an increased sensitivity.
Often the cause of these allergic reactions is toothpaste or other oral care products, even if they are recommended for use in children.
Angina
A bacterial infection that affects the tonsils in children can also spread to the lymphoid tissue, which is located at the root of the tongue closer to the throat. This is accompanied by the appearance of white acne with a purulent coating in the area of the tongue. When the pus is removed, areas with redness and slight swelling are exposed. The formations are painful, interfere with normal swallowing and significantly worsen the child's well-being: he becomes capricious, refuses to eat, his body temperature rises. Often, in the presence of such pimples near the throat, enlarged lymph nodes can be felt.
Herpes infection
Infection with the herpes virus most often occurs in childhood and with a decrease in the body's immune defenses, the infection can worsen. At the same time, watery small pimples appear on the tongue on a red background, which can also be on the lips and throat of the child. They are very painful and after opening them, shallow sores appear that prevent the child from eating and talking normally.
They are very painful and after opening them, shallow sores appear that prevent the child from eating and talking normally.
Dysbacteriosis and unbalanced nutrition
Errors in the nutrition of a child, especially of a younger age, as well as violations of the normal composition of the intestinal microflora can lead to glossitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue. This leads to the fact that the epithelium of the papillae begins to actively divide, they take the form of inflamed red or whitish pimples. They rarely bother the child, the sensitivity to hot, cold or sour food can only change.
Treatment
In the treatment of pimples on the tongue, regardless of the reasons that caused their appearance, there are common points:
- Compulsory meticulous oral hygiene. After each meal, it is desirable to treat pimples with an antiseptic solution.
- Exclusion from the child's diet of any irritants: spicy, hot or sour food.
 It is desirable that the food be soft and not cause additional injury to the mucosa.
It is desirable that the food be soft and not cause additional injury to the mucosa. - In no case should you squeeze or open pimples, this can lead to the development of complications in the child and the aggravation of his condition.
- Dr. Komarovsky recommends in such cases to consume a large amount of liquid, which will help to eliminate toxins and allergens from the child's body.
If pimples cause pain and discomfort in a child, the doctor may prescribe topical agents with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects (Solcoseryl, Metrogyl denta).
If the cause of pimples is a sore throat or stomatitis, then it may be recommended to take antibacterial agents in combination with antiseptics. Treatment of allergic manifestations consists in eliminating the action of the allergen and taking antiallergic medications. With herpetic lesions of the mucous membranes of the tongue, antiviral drugs give a good effect, and with candidiasis, antifungal agents.