Folic rich foods list
15 Healthy Foods That Are High in Folate (Folic Acid)
Folate, also known as vitamin B9, is a water-soluble vitamin that has many important functions in your body.
In particular, it supports healthy cell division and promotes proper fetal growth and development to reduce the risk of birth defects (1).
Vitamin B9 is found naturally in many foods, as well as in the form of folic acid in fortified foods.
It’s recommended that healthy adults get at least 400 mcg of folate per day to prevent a deficiency (2).
Here are 15 healthy foods that are high in folate or folic acid.
Legumes are the fruit or seed of any plant in the Fabaceae family, including:
- beans
- peas
- lentils
Although the exact amount of folate in legumes can vary, they’re an excellent source of folate.
For example, one cup (177 grams) of cooked kidney beans contains 131 mcg of folate, or about 33% of the Daily Value (DV) (3).
Meanwhile, one cup (198 grams) of cooked lentils contains 358 mcg of folate, which is 90% of the DV (4).
Legumes are also a great source of protein, fiber, and antioxidants, as well as important micronutrients like potassium, magnesium, and iron (5).
SUMMARYLegumes are rich in folate and many other nutrients. One cup (198 grams) of cooked lentils contains 90% of the DV, while one cup (177 grams) of cooked kidney beans contains about 33% of the DV.
Asparagus contains a concentrated amount of many vitamins and minerals, including folate.
In fact, a half-cup (90-gram) serving of cooked asparagus contains about 134 mcg of folate, or 34% of the DV (6).
Asparagus is also rich in antioxidants and has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties (7).
What’s more, it’s an excellent source of heart-healthy fiber, knocking out up to 6% of your daily fiber needs in just one serving (6).
SUMMARYAsparagus is high in fiber and contains a good amount of folate, with about 34% of the DV per half-cup serving.

Adding eggs to your diet is a great way to boost your intake of several essential nutrients, including folate.
Just one large egg packs 22 mcg of folate, or approximately 6% of the DV (8).
Including even just a few servings of eggs in your diet each week is an easy way to boost your folate intake and help meet your needs.
Eggs are also loaded with protein, selenium, riboflavin, and vitamin B12 (8).
Furthermore, they’re high in lutein and zeaxanthin, two antioxidants that may help reduce the risk of eye disorders like macular degeneration (9, 10).
SUMMARYEggs are a good source of folate, with about 6% of the DV in just one large egg.
Leafy green vegetables such as spinach, kale, and arugula are low in calories yet bursting with many key vitamins and minerals, including folate.
One cup (30 grams) of raw spinach provides 58.2 mcg, or 15% of the DV (11).
Leafy greens are also high in fiber and vitamins K and A. They’ve been associated with a host of health benefits.
They’ve been associated with a host of health benefits.
Studies show that eating more cruciferous vegetables, such as leafy greens, may be associated with reduced inflammation, a lower risk of cancer, and increased weight loss (12, 13, 14).
SUMMARYLeafy green vegetables are high in many nutrients, including folate. One cup (30 grams) of raw spinach contains about 15% of the DV.
In addition to providing a burst of color to main dishes and desserts alike, beets are rich in many important nutrients.
They contain much of the manganese, potassium, and vitamin C that you need throughout the day.
They’re also a great source of folate, with a single cup (136 grams) of raw beets containing 148 mcg of folate, or about 37% of the DV (15).
Besides their micronutrient content, beets are high in nitrates, a type of plant compound that has been associated with many health benefits.
One small study showed that drinking beetroot juice temporarily lowered systolic blood pressure by 4–5 mmHg in healthy adults (16).
SUMMARyBeets are high in nitrates and folate. One cup (136 grams) of raw beets contains 37% of the DV for folate.
Besides being delicious and full of flavor, citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruit, lemons, and limes are rich in folate.
Just one large orange contains 55 mcg of folate, or about 14% of the DV (17).
Citrus fruits are also packed with vitamin C, an essential micronutrient that can help boost immunity and aid disease prevention (18).
In fact, observational studies have found that a high intake of citrus fruits may be associated with a lower risk of breast, stomach, and pancreatic cancer (19, 20, 21).
SUMMARYCitrus fruits are high in vitamin C and folate. One large orange contains about 14% of the DV.
This nutritious vegetable belongs to the cruciferous family of vegetables and is closely related to other greens like kale, broccoli, cabbage, and kohlrabi.
Brussels sprouts are brimming with many vitamins and minerals and especially high in folate.
A half-cup (78-gram) serving of cooked Brussels sprouts can supply 47 mcg of folate, or 12% of the DV (22).
They’re also a great source of kaempferol, an antioxidant associated with numerous health benefits.
Animal studies show that kaempferol can help to reduce inflammation and prevent oxidative damage (23, 24).
SUMMARYBrussels sprouts contain a good number of antioxidants and micronutrients. One-half cup (78 grams) of cooked Brussels sprouts provides about 12% of the DV for folate.
Well known for its multitude of health-promoting properties, adding broccoli to your diet can provide an array of essential vitamins and minerals.
When it comes to folate, one cup (91 grams) of raw broccoli contains around 57 mcg of folate, or about 14% of the DV (25).
Cooked broccoli contains even more folate, with each half-cup (78-gram) serving providing 84 mcg, or 21% of the DV (26).
Broccoli is also high in manganese and vitamins C, K, and A.
It likewise contains a wide variety of beneficial plant compounds, including sulforaphane, which has been studied extensively for its powerful anti-cancer properties (27).
SUMMARYBroccoli, especially when cooked, is rich in folate. One cup (91 grams) of raw broccoli provides 14% of the DV, while one-half cup (78 grams) of cooked broccoli can supply 21% of your daily needs.
There are plenty of reasons to consider upping your intake of nuts and seeds.
In addition to containing a hearty dose of protein, they’re rich in fiber and many of the vitamins and minerals that your body needs.
Incorporating more nuts and seeds into your diet can also help you meet your daily folate needs.
The amount of folate in various types of nuts and seeds can vary slightly.
One ounce (28 grams) of walnuts contains about 28 mcg of folate, or around 7% of the DV, while the same serving of flax seeds contains about 24 mcg of folate, or 6% of the DV (28, 29).
SUMMARYNuts and seeds supply a good amount of folate in each serving. One ounce (28 grams) of almonds and flax seeds provides 7% and 6% of the DV, respectively.
Beef liver is one of the most concentrated sources of folate available.
A 3-ounce (85-gram) serving of cooked beef liver packs 212 mcg of folate, or about 54% of the DV (30).
In addition to folate, a single serving of beef liver can meet and exceed your daily requirements for vitamin A, vitamin B12, and copper (30).
It’s also loaded with protein, providing a whopping 24 grams per 3-ounce (85-gram) serving.
Protein is necessary for tissue repair and the production of important enzymes and hormones.
SUMMARYBeef liver is high in protein and folate, with about 54% of the DV of folate in a single 3-ounce (85-gram) serving.
Wheat germ is the embryo of the wheat kernel.
Although it’s often removed during the milling process, it supplies a high concentration of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Just one ounce (28 grams) of wheat germ provides 78.7 mcg of folate, which equals about 20% of your daily folate needs (31).
It also contains a good chunk of fiber, providing up to 16% of the fiber you need per day in a single ounce (28 grams) (31).
Fiber moves slowly through your digestive tract, adding bulk to your stool to help promote regularity, prevent constipation, and keep blood sugar levels steady (32, 33).
SUMMARYWheat germ is high in fiber, antioxidants, and micronutrients. One ounce (28 grams) of wheat germ contains about 20% of the DV for folate.
Papaya is a nutrient-dense tropical fruit native to southern Mexico and Central America.
Besides being delicious and full of flavor, papaya is jam-packed with folate.
One cup (140 grams) of raw papaya contains 53 mcg of folate, which is equal to about 13% of the DV (34).
Additionally, papaya is high in vitamin C, potassium, and antioxidants like carotenoids (34).
Pregnant women should consider avoiding eating unripe papaya.
Researchers speculate that eating high amounts on unripe papaya might cause early contractions in pregnant women, but the evidence is weak (35).
SUMMARYPapaya is rich in antioxidants and folate. One cup (140 grams) of raw papaya provides approximately 13% of the DV for folate.
Rich in a wide variety of vitamins and minerals, bananas are a nutritional powerhouse.
They’re especially high in folate and can easily help you meet your daily needs when paired with a few other folate-rich foods.
A medium banana can supply 23.6 mcg of folate, or 6% of the DV (36).
Bananas are high in other nutrients as well, including potassium, vitamin B6, and manganese (36).
SUMMARYBananas contain a good amount of folate. One medium banana contains about 6% of the DV.
Avocados are incredibly popular due to their creamy texture and buttery flavor.
In addition to their unique taste, avocados are an excellent source of many important nutrients, including folate.
One-half of a raw avocado contains 82 mcg of folate, or about 21% of the amount you need for the entire day (37).
Plus, avocados are rich in potassium and vitamins K, C, and B6 (37).
They’re also high in heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, which may protect against heart disease (38).
SUMMARYAvocados are high in heart-healthy fats and folate, with one-half of a raw avocado providing about 21% of the DV for folate.
Many types of grains, such as bread and pasta, have been fortified to boost their folic acid content.
The amounts can vary between different products, but one cup (140 grams) of cooked spaghetti supplies approximately 102 mcg of folic acid, or 25% of the DV (39).
Interestingly, some studies have demonstrated that the folic acid in fortified foods may be more easily absorbed than the folate found naturally in foods.
For example, one study concluded that the folate in foods such as fruits and vegetables is only about 78% as bioavailable as the folic acid in fortified foods (40).
Conversely, other research suggests that the specific enzyme the body uses to break down folic acid in fortified foods is not as efficient, which can result in a buildup of unmetabolized folic acid (41).
A well-balanced diet that’s rich in natural sources of folate and includes a moderate number of fortified foods can ensure you’re meeting your needs, all while minimizing potential health concerns.
SUMMARYFortified grains contain added amounts of folic acid. One cup (140 grams) of cooked spaghetti contains about 26% of the DV.
Folate is an important micronutrient found in abundance throughout your diet.
Eating a variety of healthy foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, as well as fortified foods, is an easy way to increase your folate intake.
These foods are not only rich in folate but also high in other key nutrients that can improve other aspects of your health.
8 Healthy Foods High in Folate and Why It’s Important
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- Why You Need Folate
- Foods with Folate
Folate is another name for B9, one of the eight B vitamins. It occurs naturally in a wide range of foods. A synthetic version of the vitamin, known as folic acid, is often added to fortified cereals and vitamins. You can also find folic acid supplements. The human body absorbs folic acid more easily than it does natural folate, but you can get all the folate you need from your diet.
Like other B vitamins, folate plays an important role in protein metabolism and helps to form DNA. It’s also necessary for the production of healthy red blood cells. Folate is an important nutrient. While it’s particularly important for pregnant women, everyone needs it for their overall health and wellness.
Why You Need Folate
Folate, like other B vitamins, is water-soluble, meaning that, rather than storing it, your body excretes any excess through your urine. Since your body doesn’t store it, you need to make sure you’re getting enough every day.
The daily recommended intake of folate for teens and adults is 400mcg. Pregnant women need at least 600mcg per day, and breastfeeding women need 500mcg.
Insufficient folate intake can lead to a deficiency. Too little of the vitamin can lead to megaloblastic anemia, which has symptoms such as:
- Fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
- Heart palpitations
- Changes in your hair, nails, and skin
In addition to preventing a deficiency, getting enough folate is necessary for many reasons:
Healthy Pregnancy
While folate is important for everyone, it’s especially important for women who are pregnant. Getting enough before and during early pregnancy helps to prevent neural tube defects such as anencephaly and spina bifida. The CDC recommends that all women get at least 400mcg of folate a day, whether or not they plan on becoming pregnant. Some studies suggest that sufficient folate intake may also help to prevent autism spectrum disorder, but there isn’t enough research out there to say for certain.
The CDC recommends that all women get at least 400mcg of folate a day, whether or not they plan on becoming pregnant. Some studies suggest that sufficient folate intake may also help to prevent autism spectrum disorder, but there isn’t enough research out there to say for certain.
Heart Health
Both folate and vitamin B12 play an essential role in converting homocysteine, an amino acid in your blood, into methionine, which is one of the essential building blocks of new proteins. Without enough folate, the process becomes inefficient, which leads to increased homocysteine in the blood and an increased risk of heart disease.
Reduced Cancer Risk
High homocysteine levels and low folate levels are also associated with an increased risk of cancer. Large amounts of the vitamin after a cancer diagnosis, however, may speed up the progression of the disease, so those with cancer should be careful about taking folic acid supplements.
Brain Health
Too little folate could lead to an increased risk of depression.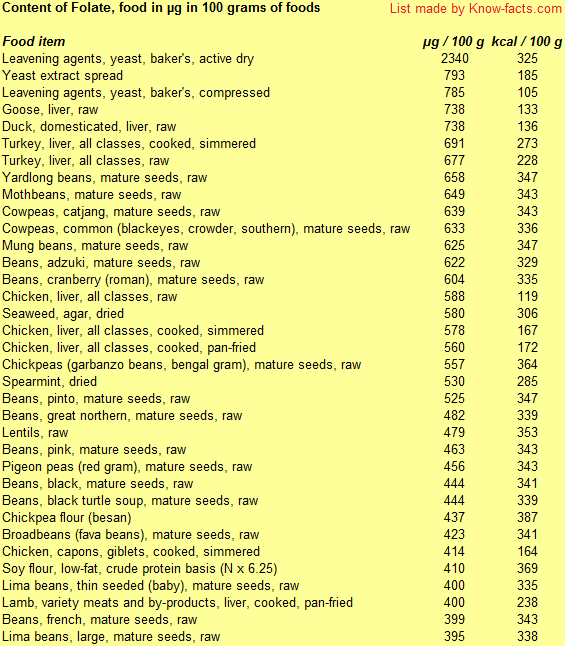 People with depression and low folate levels may also not respond as well to antidepressants as people with adequate levels of the vitamin in their blood. Some studies show that increasing folate (or taking a folic acid supplement) in addition to an antidepressant may help to increase the effectiveness of the medication.
People with depression and low folate levels may also not respond as well to antidepressants as people with adequate levels of the vitamin in their blood. Some studies show that increasing folate (or taking a folic acid supplement) in addition to an antidepressant may help to increase the effectiveness of the medication.
Foods with Folate
Many foods, particularly dark, leafy greens, are full of folate, which helps to make it easy to get all of the vitamin B9 you need from your diet. You can also find fortified cereals that contain the vitamin. Some of the foods with the most folate include:
1. Beef Liver
Most meats are low in folate. Beef liver, however, is one of the most concentrated sources available. In addition to providing 215mcg of folate per 3-ounce serving, beef liver also provides a decent amount of protein and more than 100% of your recommended daily intake of vitamin A, vitamin B12, and copper.
2. Dark, Leafy Greens
Dark, Leafy Greens
Many types of dark, leafy greens have high concentrations of folate. Spinach, a powerhouse of nutrients, provides 58mcg in a 1-cup serving of raw leaves and 131mcg in a half-cup serving of cooked. A half-cup of boiled mustard greens has 52mcg. A cup of raw collards has 46.4mcg.
3.Legumes
Legumes, which include beans, peas, and lentils, are an excellent source of plant protein, as well as fiber, iron, magnesium, and antioxidants. They’re also high in folate, with different varieties providing different amounts. A half-cup of kidney beans has 46mcg and black-eyed peas have 105mcg. A half-cup of peas has 47mcg.
4.Asparagus
Asparagus is high in many important nutrients, including folate. Four spears have 89mcg. The vegetable also provides anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
5.Broccoli
Like many other vegetables, broccoli is high in many essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, vitamin K, and vitamin A. A 1-cup serving of raw broccoli has 57mcg of folate. The folate content is even higher when you cook broccoli, with a half-cup serving providing 84mcg.
A 1-cup serving of raw broccoli has 57mcg of folate. The folate content is even higher when you cook broccoli, with a half-cup serving providing 84mcg.
6.Oranges
Oranges, and other citrus fruits, are most well-known for their vitamin C content. They also contain a decent amount of folate. One small fresh orange provides 39mcg of the vitamin.
7.Bananas
Bananas are typically known best for their potassium content. They’re high in carbohydrates, and they’re easily digestible. Add the fact that they’re highly portable, and they’re a perfect pre-workout snack. One medium banana also contains 24mcg of folate.
8.Eggs
Eggs are a common breakfast food, high in many essential vitamins and minerals. Along with protein, selenium, riboflavin, and vitamin B12, one hardboiled egg contains 22mcg of folate. While eggs are generally considered healthy, the yolks are high in cholesterol. If you have high cholesterol or heart disease, or you’re trying to watch your cholesterol intake, you may want to limit the number of eggs you eat per week.
10 Sources of Folic Acid - The-Challenger.ru
Why does our body need folic acid, what foods should we look for it in and how much should we consume per day? Naturally, we know the answers to all these questions.
Benefits of folic acid
Women know that folic acid is especially necessary for the body during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Its main role is participation in the synthesis of various components of genetic material or DNA. Vitamin B 9 (another name for folic acid. - Ed. ) is essential in the formation and growth of cells, so it is very important to get enough of it for pregnant women and children.
But the beneficial properties of folic acid are not limited to this, because it is responsible for the health of the bone marrow and other tissues and cells of our body at any age. If there is a deficiency of vitamin B 9 megaloblastic anemia and other disorders may develop. nine0003
nine0003
When people think of folic acid, they usually talk about women's health. But men are also in dire need of this substance, because vitamin B 9 is required for the effective performance of the reproductive function. Folic acid is important for sperm quality.
Folic acid intake
As with other vitamins, long-term overdose or excessive intake of folic acid can be dangerous for human health. One of the most undesirable scenarios is the development of cancer. nine0003
That is why the World Health Organization has changed its recommendations to reduce the intake of folic acid supplements. If your doctor recommends 400 mg of folic acid per day, then most likely he is not aware of these changes. Therefore, we advise you to check his recommendations with the advice of WHO.
WHO recommended daily intake of synthetic folic acid:
- 0 to 12 months - 50 mcg; nine0046
- 1 to 3 years - 70 mcg;
- 4 to 6 years - 100 mcg;
- 6 to 11 years - 150 mcg;
- 11 years and older - 200 mcg;
- pregnant women - an additional 100 mcg;
- breastfeeding mothers - an additional 50 mcg.

10 products containing folic acid:
1. Poultry offal
100 g contains 345-770 micrograms of folic acid
Soup or stew with offal - traditional dishes of Slavic cuisine. Unfortunately, not everyone loves them. But in vain! Offal from duck, turkey, chicken or goose is very nutritious and there are many ways to cook delicious, for example, chicken hearts or goose liver.
WHAT TO COOK WITH OFFINGERS
2. Lamb or veal liver
100 g contains 330-400 micrograms of folic acid
Some people love this product, others hate it, so any advice and arguments will sound too flimsy for them. But the fact remains: the liver is an excellent source of B 9 , iron and other important biologically active substances.
3. Boiled legumes
100 g contains 230-370 micrograms of folic acid
Legumes are rich in dietary fiber, low in fat, high in high quality protein and a significant amount of folic acid. Add chickpeas, beans, lentils, and peas to salads, soups, and main dishes to replace some or all meats. nine0003
Add chickpeas, beans, lentils, and peas to salads, soups, and main dishes to replace some or all meats. nine0003
4. Pork liver
100 g contains 160-260 micrograms of folic acid
It has less folic acid, but it is more delicate in taste. If you do not like boiled or fried liver, then we advise you to try making homemade pate from it.
5. Spinach
125 ml boiled contains 140 micrograms of folic acid
Spinach is a delicate leafy green that contains important vitamins, minerals, including iron, plenty of fiber and a healthy dose of folic acid. Fresh herbs can be added to salads, scrambled eggs, stewed vegetables, soups, pasta sauce, etc.
6. Asparagus
Boiled 125 ml contains 130 micrograms of folic acid
This low-calorie food is an excellent source of iron and many other vitamins and minerals, and asparagus is rich in folic acid. Just five young stalks of asparagus on your plate is enough to provide about half of the daily folic acid requirement for the average person and a third for a woman during pregnancy or lactation. nine0003
Just five young stalks of asparagus on your plate is enough to provide about half of the daily folic acid requirement for the average person and a third for a woman during pregnancy or lactation. nine0003
7. Whole wheat products
125 ml boiled whole wheat pasta contains 125 micrograms of folic acid
dietary fiber. It is important to properly cook pasta, almost overcooking them - achieving an al dente consistency, in general. nine0003
8. Flaxseed oil
Contains 110 mcg of folic acid per 60 ml
Flax seeds contain the famous omega-3s and several other important chemical compounds, including soluble fiber and folic acid. Remember that you can't cook with linseed oil. But it can and should be added to salads, sauces, stewed or steamed vegetables.
9. Soybeans
Boiled 125 ml contains 80 to 105 micrograms of folic acid
Soybeans are rich in protein, fiber, phytoestrogens and folic acid.
10. Broccoli
Boiled 125 ml contains 90 mcg of folic acid
Broccoli, like other green vegetables, contains folic acid. In addition, it contains a lot of ascorbic acid, vitamin K, antioxidants. Let broccoli become a traditional side dish on your menu. And don't ignore the stems, they are tasty and healthy. nine0003
Please note that prolonged cooking, canning and freezing reduce the content of vitamin B 9 .
Subscribe to The Challenger!
Share
Tags
- Product categories: vitamins nine0046
Table of Table of Contents
- Who needs folic acid
- Symptoms of deficiency
- Folic acid
- Is an overdose of
Please note that all information posted on the site Prowellness is provided for informational purposes only and is not a personal program, a direct recommendation for action, or medical advice. Do not use these materials for diagnosis, treatment, or any medical procedure. Consult your physician before using any technique or using any product. This site is not a specialized medical portal and does not replace the professional advice of a specialist. The Site Owner is not liable to any party who has suffered indirect or direct damage as a result of misuse of materials posted on this resource. nine0003
Do not use these materials for diagnosis, treatment, or any medical procedure. Consult your physician before using any technique or using any product. This site is not a specialized medical portal and does not replace the professional advice of a specialist. The Site Owner is not liable to any party who has suffered indirect or direct damage as a result of misuse of materials posted on this resource. nine0003
Where to find folic acid: foods and vitamins containing it
Folic acid (vitamin B₉) is important for a balanced diet. This substance is necessary for maintaining a beautiful and healthy complexion, strengthens muscles and healthy joints. You need to know which products contain it and who especially needs it.
Who needs folic acid
There are people who need more vitamin B₉. This is:
- pregnant women - scientists have proven that folic acid prevents various neural tube defects in the fetus;
- children and adolescents - a growing organism must develop correctly.

Attention! Folate deficiency is observed in people who take alcoholic beverages more than once a week. Actively remove it from the body and contraceptives, diuretics - this loss must be replenished.
nine0255
Deficiency symptoms
Symptoms of folic acid deficiency:
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- bad mood and frequent depression;
- sleep problems;
- excessive irritation;
- bad memory;
- lack of healthy ruddy skin;
- inflammatory processes on the gums;
- painful sensations of a neuralgic nature. nine0046
If you are among the categories of people who need an increased amount of this vitamin, or feel that its lack will affect your health, you need to take urgent action.
Foods with folic acid
The body does not produce folic acid on its own - it must be constantly replenished. It is possible to obtain this substance from special medical preparations. But there is also a huge list of products in which it is included:
It is possible to obtain this substance from special medical preparations. But there is also a huge list of products in which it is included:
- peas;
- beans;
- spinach;
- beets;
- cucumber;
- carrots;
- cereals;
- apricot;
- orange;
- banana;
- bow;
- greens.
Attention! From animal products, folates contain meat, fish, chicken, liver, eggs, cottage cheese, cheese. Of course, these foods cannot be eaten raw. But it is not recommended to expose them to a long heat treatment, otherwise you will destroy the supply of valuable substances. nine0253Folic acid is present in hazelnuts, almonds, walnuts. But the "champion" in terms of the amount of this useful element is peanuts - it contains approximately 240 mg of B₉ per 100 grams. Do not roast nuts, as this destroys the vitamin in their composition.

Folic acid degrades very quickly when exposed to sunlight and hot water. It also breaks down during long-term storage - that's why you need to eat fresh food.
Is it possible to overdose
An excess of folic acid in the body occurs only as a result of an overdose of synthetic drugs. And getting too much of this element from food so that it negatively affects well-being is almost impossible.
Another advantage of the substance is that it is non-toxic. Therefore, you can consume foods rich in vitamin B₉ without fear of dangerous consequences for the body.
Disclaimer
Please note that all information posted on the site Prowellness is provided for informational purposes only and is not a personal program, a direct recommendation for action, or medical advice. Do not use these materials for diagnosis, treatment, or any medical procedure. Consult your physician before using any technique or using any product.