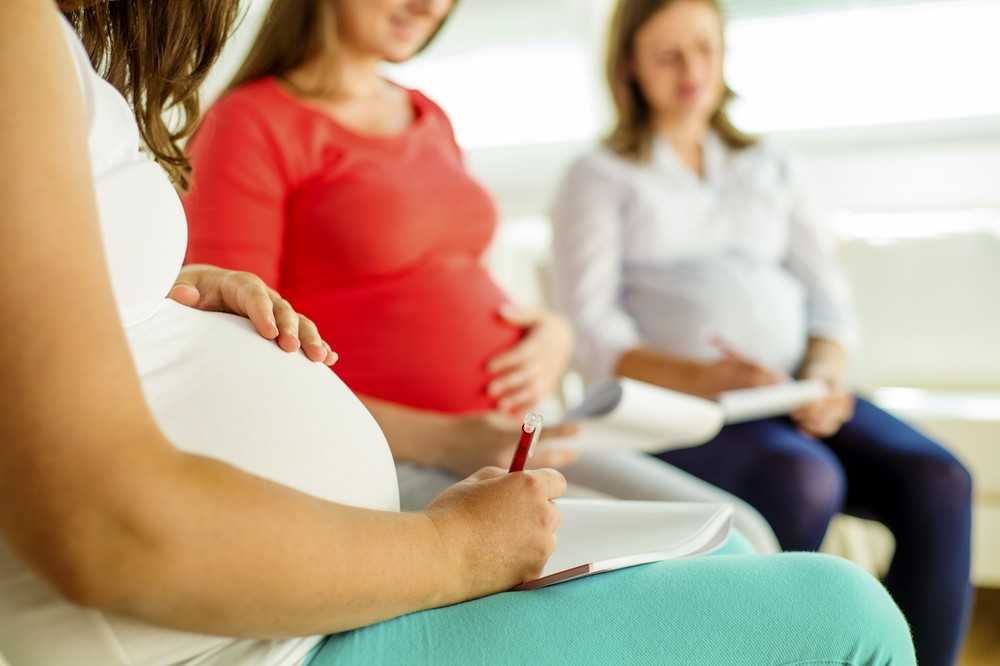
First thousand days
The first 1,000 days | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
The first 1,000 days | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content7-minute read
Listen
Key facts
- The first 1,000 days refers to a child's life from the moment they are conceived until they reach 2 years of age (24 months).
- A baby's experiences in their first 1,000 days of life can have a lifelong effect on their health and wellbeing.
- Stress, trauma, poverty and violence experienced during the first 1000 days can have long term adverse health effects on a baby.
- It is important to provide your baby with good nutrition, safety and security and a loving home environment, especially during the first 1000 days.
What is 'the first 1,000 days'?
The first 1,000 days refers to a child's life from the moment they are conceived until they reach 2 years of age (24 months). This is a time when their brain, body and immune system grows and develops significantly.
During pregnancy, your health, nutrition and stress levels can have an effect on your baby’s future. After your baby is born, their physical environment, nutrition and relationships can have a lifelong impact on their health and wellbeing.
In their first 1,000 days, your baby will need:
- healthy food
- loving relationships
- safety and security
- time to play
- a healthy environment — including in the womb
How does my baby's brain grow in the first 1,000 days?
Your baby's brain develops more quickly during the first 1,000 days than at any other time of life. The way their brain adapts to its environment contributes to the sort of person they will grow into.
The right diet (nutrition) during pregnancy and in early childhood will help your baby's learning, physical skills and emotions to develop properly.
Being hungry or exposed to stress or abuse during this time can have a lifelong effect on a child's development. An unsafe or unhealthy environment in the first 1,000 days can affect a child's physical health in later life too.
An unsafe or unhealthy environment in the first 1,000 days can affect a child's physical health in later life too.
Why is good nutrition in the first 1,000 days important?
Receiving good nutrition in the womb and through early life is essential for your child's future health. When you’re pregnant, your weight and lifestyle habits can influence how your baby's metabolism, immune system and organs develop. Poor nutrition during pregnancy and early life can lead to obesity, heart disease and stroke later on.
To give your baby the best possible start in life, it's important to eat a healthy diet while you're pregnant and to breastfeed if possible. Once your baby starts solids, you can help them develop healthy eating habits for life.
Do stress and trauma in the first 1,000 days have an effect?
If you experience a lot of stress while pregnant, your baby's nervous system and growth can be affected. This can lead to health problems later in life, including heart disease, high blood pressure, obesity and diabetes.
Of course, often stress and trauma are unavoidable. It's not your fault if you experience trauma, and help is available. If you are facing a very stressful situation when you're pregnant or you have a young child, speak to your doctor or child health nurse.
Why are safety and security important for my child in the first 1,000 days?
Loving, secure relationships are vital for your child's development. It's through their relationships that babies learn to think, understand, communicate, show emotions and behave. Relationships affect how they see the world and help them understand how they fit into society.
Playing, singing, reading and talking to your baby are all important ways to help them to feel safe and loved.
Stress caused by violence in the home can affect babies. Parents who are experiencing family (domestic) violence may have difficulty forming a loving attachment with their baby.
Call 1800RESPECT (1800 737 732) at any time of the day or night if you or someone close to you are experiencing emotional abuse or violence.
How can I address poverty during my child’s first 1,000 days?
There is a link between poverty in infancy and adverse health and wellbeing outcomes later in life. This may be partly because the stress on parents caused by financial hardship can prevent them from providing the level of care their baby needs.
If you are experiencing poverty, there are things you can do to help your baby build resilience in the first 1,000 days:
- Asking for help and accepting practical support. Learn about government-funded financial benefits for families here.
- Manage your own stress — for example, by avoiding fighting or using drugs or alcohol to cope.
- Make your baby feel secure and loved.
- Do fun, low-cost activities together as a family.
What can I do to give my baby the best start?
To ensure the best possible first 1,000 days for your baby:
- Eat a healthy diet when you're pregnant
- Avoid smoking, alcohol or drugs
- If you're experiencing violence or trauma, seek help
- Breastfeed for at least 6 months, if you can
- Make sure your baby has a healthy diet
- Give your baby lots of love and attention so they feel secure
Where can I go for help?
For more information about the first 1,000 days, visit these websites:
- Raising Children
- First 1,000 Days Australia (for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander families)
- Australian Research Alliance for Children and Youth (ARACY)
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Centre for Community Child Health (The First Thousand Days - An Evidence Paper), First 1000 Days Australia (Why First 1000 Days?), Trauma and Grief Network (Supporting your child through times of financial hardship)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: June 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Payments for families
- Healthy eating habits for children
- Healthy diet during pregnancy
- Stress and pregnancy
- How your baby’s brain develops
- Your baby’s growth and development – first 12 months
Need more information?
First 1000 days: conception to two years | Raising Children Network
The first 1000 days of life are key to lifelong health and wellbeing.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Your baby's growth and development - 12 months old
At 12 months, your baby is now a toddler. If they haven’t already, it won’t be long now before they take their first steps, develop a sense of humour, and tell you they love you.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Your baby's growth and development - 10 months old
A 10-month-old will be very active. As a parent, you’ll probably be chasing them around as they crawl, and be learning more about their developing personality.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Baby's development in the womb - MyDr.com.au
A month by month guide to pregnancy and your baby's development in the womb. Starting at the first month, myDr.com.au brings you all the milestones.
Starting at the first month, myDr.com.au brings you all the milestones.
Read more on myDr website
Your baby's growth and development - 9 months old
Your 9-month-old will, by now, really be developing their personality. They will form stronger attachments with a few people, preferring some over others.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Your baby's growth and development - 11 months old
At 11 months old, your baby is almost a toddler – you’ll probably be surprised at how quickly they can move around your home and how independent they are becoming.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Your baby's growth and development - 8 months old
At 8 months old, your baby will start to explore their little world. It might mean more running around for you, but it's a great time to watch them learn.
It might mean more running around for you, but it's a great time to watch them learn.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
The First 1000 Days | Department of Social Services, Australian Government
Improving the lifetime wellbeing of people and families in Australia.
Read more on Department of Social Services website
Your baby in the first few days
Find out what you can expect from your newborn, like how often they feed and sleep, as well as other things you need to know.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Screening tests in the first 3 months of pregnancy
You may wish to find out early in your pregnancy if your baby is at increased risk of a serious health condition by having a screening test in your first trimester (the first 3 months of pregnancy).
Read more on WA Health website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Building Health - 1,000 Days
Loading..
The 1,000 days between a woman’s pregnancy and her child’s second birthday provide the foundation for lifelong health. It is a time when our external environments—from the food we eat to our exposures to stress and adversity—shape our future health in powerful ways. In recent years, science has shed new light on how nutrition in the first 1,000 days impacts how our bodies and our immune systems develop, and how it influences our predisposition to diseases later in life. There is even evidence suggesting that the health effects of poor nutrition and adverse experiences early in life can pass down from one generation to the next.
There is even evidence suggesting that the health effects of poor nutrition and adverse experiences early in life can pass down from one generation to the next.
Throughout the first 1,000 days, the well-being of a mother and the well-being of her child are closely linked. It is why it is essential that women have the nutrition, care and support they need for the healthiest possible future—for themselves and for their children.
Brain development begins before birth.
A child’s brain begins to grow very early on in pregnancy and develops at an astonishing speed. At the 4th week of pregnancy, the brain has an estimated 10,000 cells—by the 24th week, it contains 10 billion. The nutrition that a baby gets from his mother through her diet is the fuel that drives much of this incredible transformation.
Nutrients such as folic acid, iron, zinc and iodine, as well as protein and fatty acids play a vital role in building a baby’s brain during pregnancy. When one or more of these is absent during pregnancy, a baby could be at risk for developmental delays, birth defects and cognitive deficits.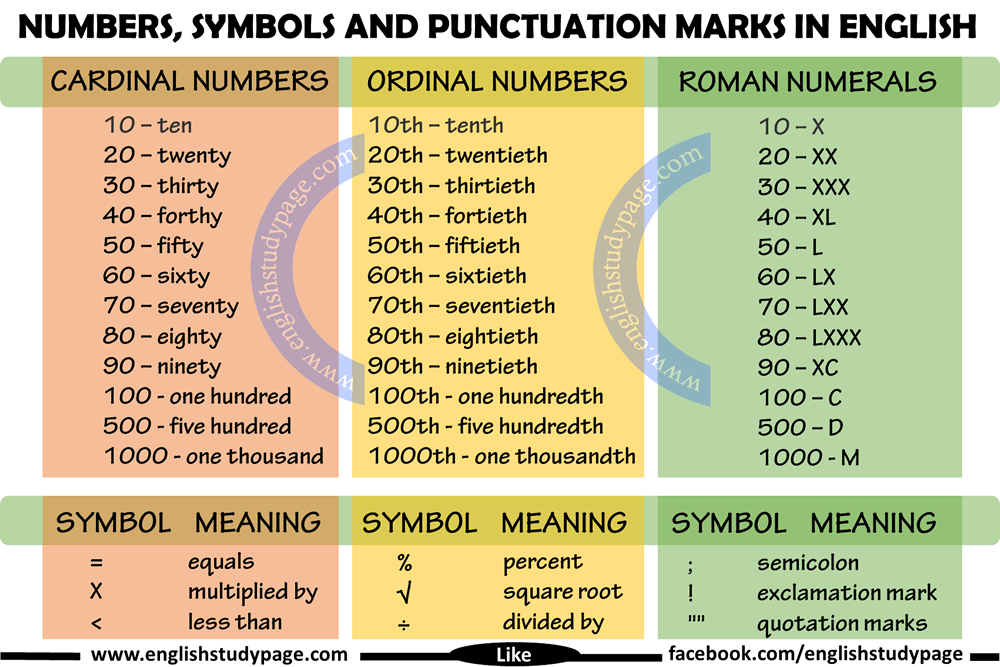 Because a mother’s diet and her nutrient stores are the only source of nutrition for a developing baby, it is critical that women get the health care and nutritious food they need before and during pregnancy.
Because a mother’s diet and her nutrient stores are the only source of nutrition for a developing baby, it is critical that women get the health care and nutritious food they need before and during pregnancy.
Photo credit: United States Breastfeeding Committee
Mother’s milk is the food that builds a baby’s immunity and protects her health.
When it comes to giving babies the healthiest start to life, breastfeeding is unmatched. Packed with antibodies, stem cells and other unique properties, breastmilk acts as babies’ first vaccine. It builds their immunity, protecting them from infections, conditions such as sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), and diseases like diarrhea and pneumonia which kill hundreds of thousands of young children every year. Breastfeeding also lowers a child’s risk of developing obesity later in life. The health effects of breastfeeding for mothers are just as powerful, reducing a woman’s risk of heart disease, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, diabetes and depression. Researchers estimate that breastfeeding has the potential to save the lives of over 820,000 young children and 20,000 women each year.
Researchers estimate that breastfeeding has the potential to save the lives of over 820,000 young children and 20,000 women each year.
Because of the impact breastfeeding has on child health and survival, leading health authorities including the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommend that for their first six months, babies be exclusively breastfed—i.e. fed only breastmilk with no solids or other liquids. WHO recommends that babies continue to breastfeed, along with eating nutritious foods, for at least 24 months as this provides both mom and baby with the greatest health benefits. Unfortunately, too many mothers lack the support they need to meet these recommendations and as a result, they and their children aren’t able to reap the extraordinary health benefits of breastfeeding.
A window of opportunity to shape lifelong health.
Early childhood is when lifelong eating habits are established. To fuel their growth, older infants and toddlers need to eat a variety of protein-rich foods, fruits and vegetables, whole grains, unsweetened milk and other dairy products. A healthy diet is essential to ensuring a young child grows well and gains an appropriate amount of weight.
A healthy diet is essential to ensuring a young child grows well and gains an appropriate amount of weight.
Over the past several years, there has been a dramatic increase in the number of pre-school age children with overweight and obesity—an emerging epidemic driven by unhealthy diets and poor eating and feeding practices in the first 1,000 days. Obesity can harm a young child’s body, impacting the healthy functioning of his organs as well as the hormones that control blood sugar. But the consequences of obesity in young children also reach far into the future. Studies show that children who develop overweight or obesity early in life are more likely to be obese as adults and are at greater risk for heart disease, type 2 diabetes, cancer and other illnesses later in life.
- Pregnancy
- Infancy
- Early Childhood
Pregnancy
Healthy futures start here.
During pregnancy, a person’s diet, the rate at which they gain weight, their physical and mental well-being, their environment and lifestyle habits have a powerful effect on a child’s future health. These factors influence how a child’s metabolism, immune system, and organ functioning begin to develop. They can also affect whether a child is born prematurely or at a low birthweight—outcomes that have a lasting impact on a child’s health well into adulthood.
These factors influence how a child’s metabolism, immune system, and organ functioning begin to develop. They can also affect whether a child is born prematurely or at a low birthweight—outcomes that have a lasting impact on a child’s health well into adulthood.
A growing body of research suggests that diseases such as diabetes, hypertension and stroke have their origins in pregnancy—and that prenatal nutrition plays an important role in whether a child becomes susceptible to these and other illnesses later in life. There is also research showing that babies start to develop food preferences in the womb with implications for lifelong eating habits.
Infancy
Mother’s milk is the food that builds a baby’s immunity and protects her health.
When it comes to giving babies the healthiest start to life, breastfeeding is unmatched. Packed with antibodies, stem cells and other unique properties, breast milk acts as babies’ first vaccine. It builds their immunity, protecting them from infections, conditions such as sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), and diseases like diarrhea and pneumonia which kill hundreds of thousands of young children every year. Breastfeeding also lowers a child’s risk of developing obesity later in life. The health effects of breastfeeding for mothers are just as powerful, reducing a woman’s risk of heart disease, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, diabetes and depression. Researchers estimate that breastfeeding has the potential to save the lives of over 820,000 young children and 20,000 women each year.
Breastfeeding also lowers a child’s risk of developing obesity later in life. The health effects of breastfeeding for mothers are just as powerful, reducing a woman’s risk of heart disease, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, diabetes and depression. Researchers estimate that breastfeeding has the potential to save the lives of over 820,000 young children and 20,000 women each year.
Because of the impact breastfeeding has on child health and survival, leading health authorities including the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommend that for their first six months, babies be exclusively breastfed—i.e. fed only breastmilk with no solids or other liquids. WHO recommends that babies continue to breastfeed, along with eating nutritious foods, for at least 24 months as this provides both mom and baby with the greatest health benefits. Unfortunately, too many mothers lack the support they need to meet these recommendations and as a result, they and their children aren’t able to reap the extraordinary health benefits of breastfeeding.
Photo credit: United States Breastfeeding Committee
Early Childhood
A window of opportunity to shape lifelong health.
Early childhood is when lifelong eating habits are established. To fuel their growth, older infants and toddlers need to eat a variety of protein-rich foods, fruits and vegetables, whole grains, unsweetened milk and other dairy products. A healthy diet is essential to ensuring a young child grows well and gains an appropriate amount of weight.
Over the past several years, there has been a dramatic increase in the number of pre-school age children with overweight and obesity—an emerging epidemic driven by unhealthy diets and poor eating and feeding practices in the first 1,000 days. Obesity can harm a young child’s body, impacting the healthy functioning of his organs as well as the hormones that control blood sugar. But the consequences of obesity in young children also reach far into the future. Studies show that children who develop overweight or obesity early in life are more likely to be obese as adults and are at greater risk for heart disease, type 2 diabetes, cancer and other illnesses later in life.
Stay in Touch
Get news and updates from 1,000 Days
Sign Up
The first 1000 days of the baby. How not to miss the most important?
Pediatrics
Tags:
Tatyana Butskaya:
Friends, good morning! I am Tatyana Butskaya, the author and host of the program "Parents' Choice", and today we will talk about the first 1000 days of your child's life. You thought it was a birthday? No! It turns out that everything is not so simple. A child is born when two cells just connect with each other - it is at this moment that the future of your baby is laid. And all 9months, while a woman walks pregnant, something is laid that will then be almost impossible to change. And that's what I'm going to talk about today with my guest. Svetlana Gennadievna Makarova - Head of the Preventive Pediatrics Department of the Scientific Medical Research Center for Children's Health of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. We will now move on to your center, because only the parent company, which unites the entire pediatrics of the country, can deal with such global issues that are still not so relevant for many now, in fact, how to cure a specific acute respiratory disease in a child, how to cure specific allergy, but everything is laid before. What is this institution?
And that's what I'm going to talk about today with my guest. Svetlana Gennadievna Makarova - Head of the Preventive Pediatrics Department of the Scientific Medical Research Center for Children's Health of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. We will now move on to your center, because only the parent company, which unites the entire pediatrics of the country, can deal with such global issues that are still not so relevant for many now, in fact, how to cure a specific acute respiratory disease in a child, how to cure specific allergy, but everything is laid before. What is this institution?
Svetlana Makarova:
This institution was formed from the Institute of Pediatrics of the Academy of Medical Sciences, which everyone knows very well. Even then it was the leading pediatric institution, and now the Ministry of Health of Russia, in fact, the Government of Russia has given the status of our institution as the National Medical Research Center.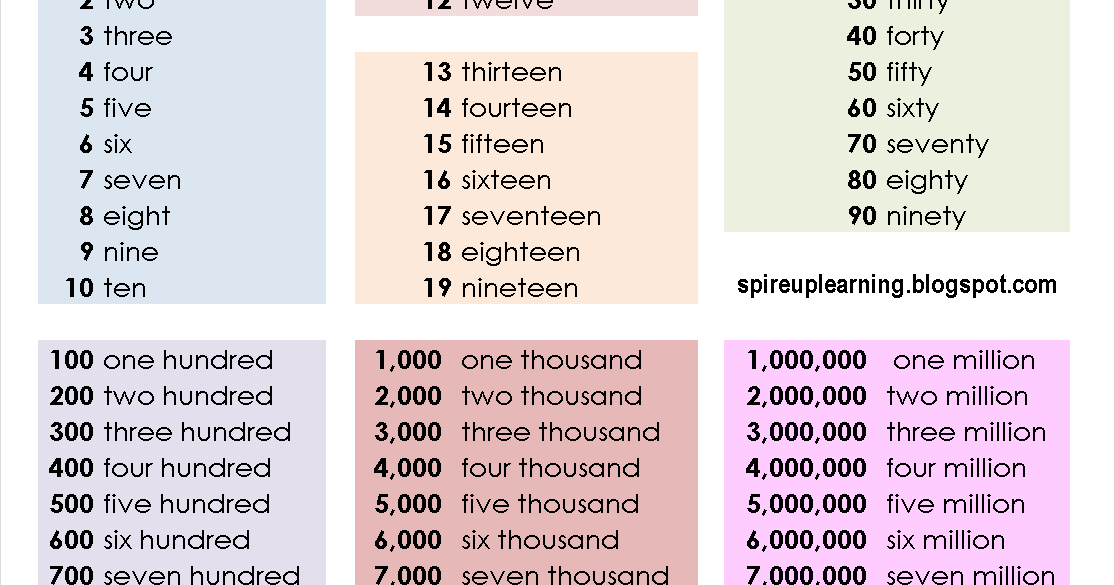 This is indeed a very high status, and all pediatrics are entrusted to us, that is, we are legally appointed as the leading leading center. Therefore, on the one hand, this is a great honor, on the other hand, a very big responsibility, because we deal with all the problems of pediatrics and pediatric surgery. Only 2 children's centers have been named national medical research centers - this is the Kulakovskaya Center for Gynecology, Obstetrics and Perinatology, but they have their own specialization, and the Dima Rogachev Center. nine0003
This is indeed a very high status, and all pediatrics are entrusted to us, that is, we are legally appointed as the leading leading center. Therefore, on the one hand, this is a great honor, on the other hand, a very big responsibility, because we deal with all the problems of pediatrics and pediatric surgery. Only 2 children's centers have been named national medical research centers - this is the Kulakovskaya Center for Gynecology, Obstetrics and Perinatology, but they have their own specialization, and the Dima Rogachev Center. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
Do you only examine or also treat children?
Svetlana Makarova:
We are a huge multidisciplinary children's clinic where they receive medical care, consultations, and see children with a variety of diseases. In fact, there are no areas of pediatrics and pediatric surgery that are not represented here, so we are a very well organized clinical center where a child can receive the multidisciplinary care that many children need. nine0003
nine0003
Prophylactic work at our institute has always been of great importance, and 3 years ago a department of preventive pediatrics was formed, which I am the head of. I like these 3 years, because we have outgrown the age of the first 1000 days a little, that is, we are still quite small, but we continue the research that was conducted at the center, we consolidated it in our department, and I hope that we will be of great benefit. Indeed, right now the preventive direction is given great importance, because it has become clear that prevention is not only easier and more pleasant than treating, it is also much cheaper, so now all this work is supported at the state level, and we are working on the most modern wave. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
Then let's go back to 1000 days. Where did the theory of the first 1000 days of life come from? Is this our Russian theory, or did it come to us from other countries?
Svetlana Makarova:
The theory of 1000 days originally arose as a scientific hypothesis, which found a lot of confirmation, and it is well known to medical specialists.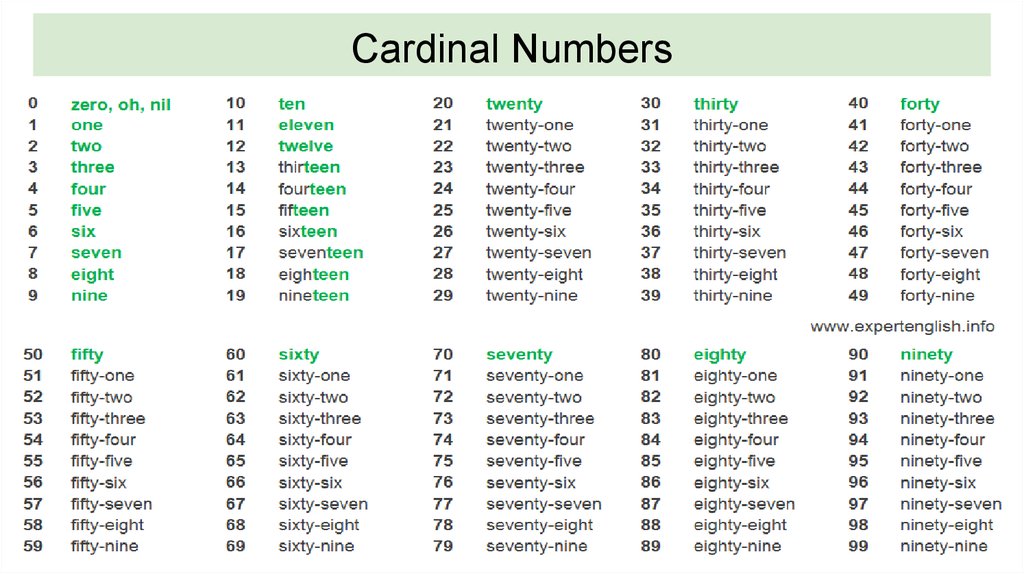 What is 1000 days? We count 1000 days from the moment of conception of a child - this is 270 days of pregnancy plus 2 more times of 365, here the math clearly converges, this is another 2 years of a child's life. It became clear on the basis of scientific research that it is at this moment that the foundation of a child's health is laid. Now this hypothesis is submitted for wide discussion. UNICEF initiated this campaign to polarize this hypothesis, because not only doctors should know about this, parents should understand very well that it is during this period that opportunities in prevention are laid that will never be provided to them again. nine0003
What is 1000 days? We count 1000 days from the moment of conception of a child - this is 270 days of pregnancy plus 2 more times of 365, here the math clearly converges, this is another 2 years of a child's life. It became clear on the basis of scientific research that it is at this moment that the foundation of a child's health is laid. Now this hypothesis is submitted for wide discussion. UNICEF initiated this campaign to polarize this hypothesis, because not only doctors should know about this, parents should understand very well that it is during this period that opportunities in prevention are laid that will never be provided to them again. nine0003
What happens during these 1000 days? It's just incredible to imagine! From one cell, which was obtained from two cells (maternal and paternal), during this time 500 trillion cells of the body are formed, and each cell knows what to do, each cell in its place - this is a fantastic process! Of course, this is a very fast growth process, an incredibly fast process of brain development, 70% of all brain development occurs in the prenatal period, and 80% of all cognitive activity, cognition of the world falls on the first 2 years of life. It seems incredible, but it's true. Cognitive processes go so fast that in this period the formation of neural connections, that is, connections between brain cells that just provide mental activity, is formed from 700 to 1000 neural connections per second. That is, this is something incredible, and this will never happen again in my life, this is such a period. nine0003
It seems incredible, but it's true. Cognitive processes go so fast that in this period the formation of neural connections, that is, connections between brain cells that just provide mental activity, is formed from 700 to 1000 neural connections per second. That is, this is something incredible, and this will never happen again in my life, this is such a period. nine0003
Tatiana Butskaya:
Because when you understand that in one second there is a huge number of cell divisions, connections, and if something goes wrong, then everything will go wrong.
Svetlana Makarova:
You are absolutely right. And so UNICEF literally says in its campaign that parents are responsible, they are responsible not only for their child, but also for the future of mankind. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
Is each of us responsible for the future of humanity?
Svetlana Makarova:
Yes.
Tatyana Butskaya:
Is dad also responsible?
Svetlana Makarova:
Of course, both mom and dad must understand that it is the first 1000 days that give them the opportunity to influence the whole future life of the child and their own lives.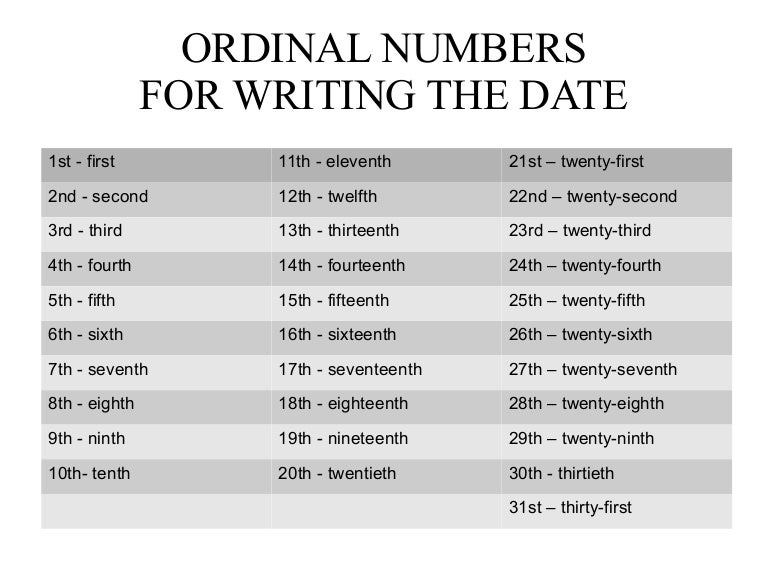 You need to understand that your child's life is your life. nine0003
You need to understand that your child's life is your life. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
What can be done and what should never be done?
Svetlana Makarova:
Here we need to talk about all this time aspect, starting from the beginning. We will only start not from the period of conception, but even before the conception of a child, because now studies say that prevention should be started even before conception, which is why gynecologists say: preconceptually, preconceptually, a mother should prepare herself for pregnancy. What might this preparation be? If a young girl, a woman takes care of her health, goes in for sports, leads an active lifestyle, eats right, attaches great importance to healthy nutrition, makes sure that she is provided with micronutrients, then no special preparation is needed. But if a woman does not particularly attach importance to a healthy lifestyle, then the stage of planning a child is the time to think about the health of the unborn child and about yourself too.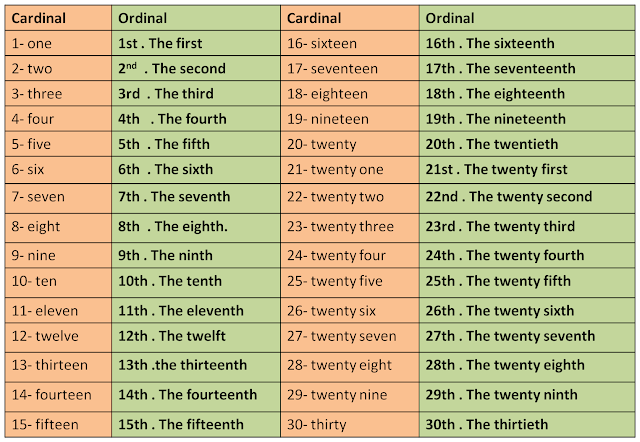 Because if a mother enters pregnancy with a normal body mass index, of course, chubby women are beautiful, maybe there will be fashion for them, but from the point of view of the health of the unborn child, the ideal body mass index is better than overweight . If she enters pregnancy with a good supply of vitamins and minerals, then this is not only an opportunity to endure pregnancy better and maintain her health, these are already the first bricks in the foundation of the baby's health. nine0003
Because if a mother enters pregnancy with a normal body mass index, of course, chubby women are beautiful, maybe there will be fashion for them, but from the point of view of the health of the unborn child, the ideal body mass index is better than overweight . If she enters pregnancy with a good supply of vitamins and minerals, then this is not only an opportunity to endure pregnancy better and maintain her health, these are already the first bricks in the foundation of the baby's health. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
I want to be very specific, because everyone understands the concepts of “healthy lifestyle”, “healthy diet”, “healthy regimen” in their own way. For some, a healthy lifestyle is running marathons. On the other hand, not always a woman who runs marathons can get pregnant at all. Where is that edge? Are there any life hacks, 5 useful tips for a woman who is going to become a mother?
Svetlana Makarova:
Even when I said “going in for sports”, I myself doubted this wording, because sports are not always about health. Physical activity, physical activity for at least an hour a day.
Physical activity, physical activity for at least an hour a day.
Tatyana Butskaya:
Physical activity at the level of physical education?
Svetlana Makarova:
At the level of physical education.
Tatyana Butskaya:
And if a woman lifts weights, goes in for fitness, can this somehow affect her reproductive system? nine0003
Svetlana Makarova:
If it doesn't go beyond fitness, then no. And if there are already high physical loads that occur when playing sports (say, in professional sports, or, as they say now, sports of high achievements), then we, doctors, admit that this is not about health. And such high physical activity for women can indeed adversely affect reproductive health. Although this is absolutely not a rule, I do not want to be such a hypocrite here. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
Good. What do we say to future dads? What features do they have? Do they need to take folic acid?
Svetlana Makarova:
Dad doesn't have to take folic acid, but it's good if dad is also well provided for and drinks. You know, taking vitamin-mineral complexes constantly or intermittently is also a separate issue. The fact is that if nutrition is important, and parents receive a well-balanced diet - with enough protein (including animal protein), with enough dairy products (sources of calcium), with enough vegetables, fruits. For example, in some countries they don’t sit down at the table until there are 3 types of vegetables on the table. nine0003
You know, taking vitamin-mineral complexes constantly or intermittently is also a separate issue. The fact is that if nutrition is important, and parents receive a well-balanced diet - with enough protein (including animal protein), with enough dairy products (sources of calcium), with enough vegetables, fruits. For example, in some countries they don’t sit down at the table until there are 3 types of vegetables on the table. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
Beautiful countries!
Svetlana Makarova:
I'm talking about the Netherlands, it's so traditional here that you just can't start eating.
Tatyana Butskaya:
Is this for breakfast, lunch and dinner?
Svetlana Makarova:
For breakfast, lunch and dinner. Here we do not have such a habit, but we are now working on it. Studies show that even if everything is done correctly, vitamins and minerals may still be lacking in the diet. This is especially true for our country, we cannot fully transfer the experience of other countries to our country, because there are countries where common products are fortified. Flour, for example, in the United States of America, vitamins of group B are added to it, and people, eating even just baked goods, improve their status in vitamins of group B. In our country ...
This is especially true for our country, we cannot fully transfer the experience of other countries to our country, because there are countries where common products are fortified. Flour, for example, in the United States of America, vitamins of group B are added to it, and people, eating even just baked goods, improve their status in vitamins of group B. In our country ...
Tatyana Butskaya:
Iodized salt?
Svetlana Makarova:
Absolutely right. In some countries it is not possible to buy non-iodized salt in a grocery store, non-iodized there just to sprinkle the streets or for household needs.
Tatyana Butskaya:
So it's not harmful? Someone started rumors that it is harmful - iodized salt, excess iodine ...
Svetlana Makarova:
No, there will be no excess of iodine, we live in an iodine-deficient region. Iodine deficiency adversely affects the physical and mental development of children, so you need to use iodized salt.
Tatyana Butskaya:
And even pregnant women who are restricted from taking salt?
Svetlana Makarova:
Yes, even for pregnant women. But in the amount in which salt is needed, it is not necessary to increase the dosage. But there is iodized salt, low sodium salt, potassium and magnesium are added, there is such a preventive salt. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
Where is it for sale?
Svetlana Makarova:
In pharmacies.
Tatyana Butskaya:
What is it called, prophylactic salt?
Svetlana Makarova:
Prophylactic salt with reduced sodium content and with the addition of potassium and magnesium.
Tatyana Butskaya:
How interesting, friends! Be sure to go to the pharmacy today and buy prophylactic salt. That is, it can be used like ordinary salt. nine0003
Svetlana Makarova:
Just do not pickle the cucumbers.
Tatyana Butskaya:
That is, minus edema plus iodine, magnesium and potassium - just what you need. How do you feel about multivitamins during pregnancy? Now there are a lot of discussions on this subject, that a child grows too much from multivitamins, then it is difficult to give birth, complications during childbirth, and all this does not end very well.
Svetlana Makarova:
Yes, I have heard about this idea, but studies have not confirmed this, including this idea that large fetuses are more common when taking multivitamins during pregnancy. Studies conducted in our country by the staff of the Institute of Nutrition showed that there is no such connection. One isolated case or several isolated cases is one thing, but when they recruit a group and begin to compare, then this is another.
Tatyana Butskaya:
I live in social networks in the evenings, and when I read the posts of different mothers who have 1, 2, 3, 4 children, and based on their 4 children, they draw conclusions that tens of thousands can follow , and even millions of subscribers, it becomes scary. Therefore, I once again want to draw attention to the words of a respected specialist that even if there were 2 cases in a row, or if three of your children were sick every time they put on a red hat, this does not mean that the red hat and SARS have some kind of relationship. So multivitamins and large fetal size are an unproven correlation? nine0003
Therefore, I once again want to draw attention to the words of a respected specialist that even if there were 2 cases in a row, or if three of your children were sick every time they put on a red hat, this does not mean that the red hat and SARS have some kind of relationship. So multivitamins and large fetal size are an unproven correlation? nine0003
Svetlana Makarova:
Unproven correlation. We, doctors, are now moving into the field of evidence-based medicine, probably many have already heard this term. The fact is that some time ago you could read various studies in the scientific medical literature of the type: children were given this, and they grew up. That is, no one considered that children, in general, grow up. Now, in order to prove that this works and improves the growth of the child, we need to take a comparison group and see how children grow up without it? Therefore, evidence-based medicine arose, that is, only those studies that correspond to these principles are taken into account. There should be comparison groups, ideally they should be randomized. There are even special randomization methods to make it completely random. There should be comparison groups, there should be statistically significant differences - not just any, but statistically significant. The results of meta-analyses are taken into account. nine0003
There should be comparison groups, ideally they should be randomized. There are even special randomization methods to make it completely random. There should be comparison groups, there should be statistically significant differences - not just any, but statistically significant. The results of meta-analyses are taken into account. nine0003
Meta-analysis is generally an incredible thing when, for example, all studies over the past 10 years in the world are analyzed, but each study is initially analyzed whether it corresponds to the principles of evidence-based medicine or not. And then, when a group of studies is selected that are worthy of this analysis, a conclusion is made on the basis of this. Huge cohort studies are taken into account. That is, now even medical research has very high requirements. But such, as you said, with a red cap - this is a coincidence. There is a lot of work to be done to distinguish coincidence from relationship. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
We are trying to do one such work, we are trying to take the first step towards a very big job, that is, to solving a big issue called the diet of a nursing mother, because not only parents, but also doctors - everyone understands this phrase in their own way. From completely polar opinions that there is or is not a diet for a nursing mother, and inside there are another 150 million options for what you can eat, what you can’t eat. And until we come to a common denominator, until we understand that there are some products that have been proven to affect the child's body, if the mother ate them and fed the child with milk, until that moment everyone will understand something by this phrase own. Let's finish with the preparation for pregnancy. It seems to me that everything is already clear, you just need to think that if you are not pregnant yet, and you are of reproductive age, then you can have a child, and every day you live, every cigarette you smoke, every glass of wine you drink, every serving you eat french fries fried in strange oil, sleepless nights, stress…
From completely polar opinions that there is or is not a diet for a nursing mother, and inside there are another 150 million options for what you can eat, what you can’t eat. And until we come to a common denominator, until we understand that there are some products that have been proven to affect the child's body, if the mother ate them and fed the child with milk, until that moment everyone will understand something by this phrase own. Let's finish with the preparation for pregnancy. It seems to me that everything is already clear, you just need to think that if you are not pregnant yet, and you are of reproductive age, then you can have a child, and every day you live, every cigarette you smoke, every glass of wine you drink, every serving you eat french fries fried in strange oil, sleepless nights, stress…
Svetlana Makarova:
You have listed everything perfectly.
Tatyana Butskaya:
Or a man who thinks: “But I won’t bear a child,” but those very cells are ripening in you, from which a child will be born later, therefore you are responsible for your future every day of your life generation and for our nation as a whole. Okay, got pregnant. Are there any other life hacks for pregnant women during pregnancy? Should I eat for two?
Okay, got pregnant. Are there any other life hacks for pregnant women during pregnancy? Should I eat for two?
Svetlana Makarova:
I expected this question, is it necessary to eat for two. Certainly not for two, because studies show that the need for all macronutrients and energy does not increase as much. According to our recommendations, at the end of pregnancy, the need for energy increases by 15-16%. Now European pediatricians say that even less - only 10%, because at the end of pregnancy, the mother reduces physical activity. Not for two, of course, but you need to eat for two, because the need for various substances increases disproportionately, the need for protein increases more. It is important to get complete protein, that is, protein of animal origin, here you need to add about 20 grams, but this is not so much, it is about 100 grams of meat, these are not such large amounts. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
100 grams of meat?
Svetlana Makarova:
Yes, it's not that much, you don't need to be overloaded with protein.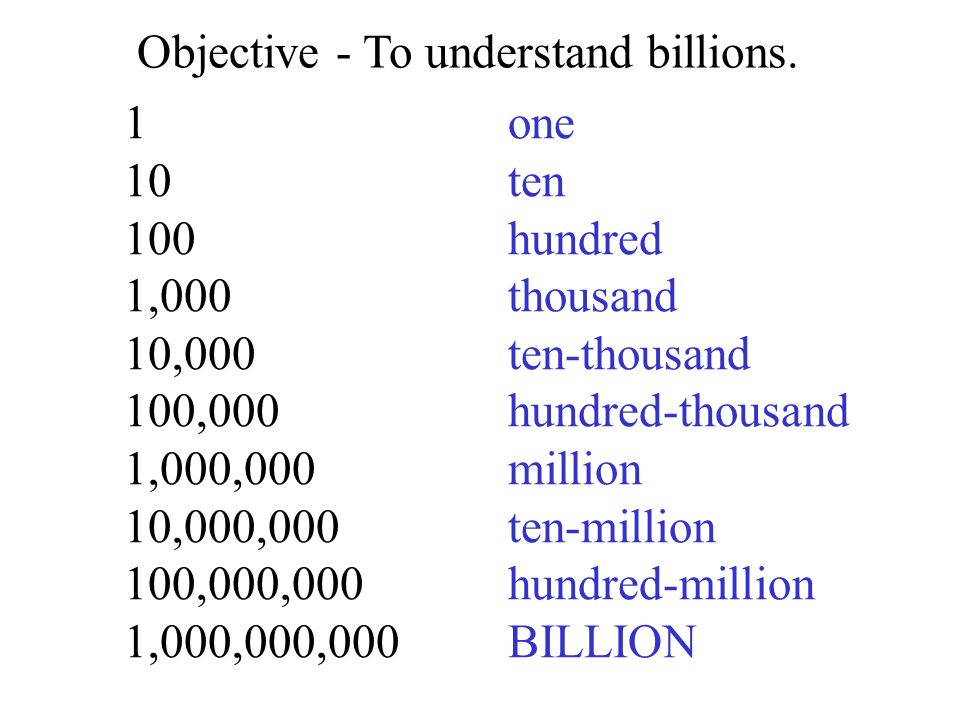 The need for carbohydrates increases little because physical activity decreases, especially towards the end of pregnancy. And the need for calcium, iron, folic acid increases. In iodine, by the way, the need also increases during pregnancy.
The need for carbohydrates increases little because physical activity decreases, especially towards the end of pregnancy. And the need for calcium, iron, folic acid increases. In iodine, by the way, the need also increases during pregnancy.
Tatyana Butskaya:
But is it possible then just to eat more protein and multivitamins? nine0003
Svetlana Makarova:
Practically so, but fat also needs to be slightly increased, and carbohydrates, but it will simply increase disproportionately - only 10-15%.
Tatyana Butskaya:
Literally half a sandwich?
Svetlana Makarova:
Yes, literally half a sandwich, and a little more carbohydrates (bun).
Tatyana Butskaya:
Although the tsunami of the 21st century is diabetes, and it seems to me that now all buns are excluded from pregnant women. Juices are still considered harmful, although we have always considered them useful. nine0003
nine0003
Svetlana Makarova:
Juice and a bun are slightly different things. A bun contains long carbohydrates, and free sugar is often added to juice, especially if it is not freshly squeezed juice, and now there are a lot of questions with juices for both adults and children, because it is a source of fast sugar, fast carbohydrates.
Tatyana Butskaya:
So you need to stop treating juices as healthy food?
Svetlana Makarova:
Unfortunately, yes.
Tatyana Butskaya:
Does this only apply to the juices that we buy, or freshly squeezed ones too?
Svetlana Makarova:
It is better to give preference to a whole fruit, so that there is fiber, which slows down absorption. The process of digestion is going on, the juice is not a very physiological product, there are a lot of acids, and free sugar immediately puts a load on the pancreas, and a glycemic jump is made.
Tatyana Butskaya:
Remember: we buy salt in a pharmacy, we don't buy juices. If you're pregnant right now, you're eating for two, which is just a little meat and half a sandwich. How do you feel about vegetarians?
Svetlana Makarova:
In our center, we are summing up the results of a study on vegetarian children. Why don't I want to say that it's finished? I want this direction to continue with us, and we plan to give recommendations. Now the results are being analyzed, and I will briefly say that we are a little upset by the results of this study, because the younger the child, the more important this vegetarianism is for the child. And the greatest concern is the earliest age - vegetarianism during pregnancy and lactation. It's not just us. Indeed, it has become very popular, and that is why in recent years a huge amount of research has appeared. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
As a result, what did you find?
Svetlana Makarova:
We have found something to agree with the European Pediatric Society, which has formulated that parents must be made aware that they are exposing their child to high nutritional risks. We must accept vegetarianism as an objective reality, respect the choice of parents, but parents must be aware that these are very high nutritional risks. It is written in the documents that it is possible to organize a vegetarian diet for a child, but supplementation is required, that is, the addition of various micronutrients, a doctor's supervision is required. If parents are very determined to do this, then this can only be done in collaboration with pediatricians. I invite you to our center, we are doing this, make an appointment. First of all, I recommend that mothers reconsider these principles during pregnancy and feeding, include at least some amount of animal protein in the diet. And if the principles are so serious, then contacting specialists so that all micronutrient needs are fully compensated in general is extremely important. nine0003
We must accept vegetarianism as an objective reality, respect the choice of parents, but parents must be aware that these are very high nutritional risks. It is written in the documents that it is possible to organize a vegetarian diet for a child, but supplementation is required, that is, the addition of various micronutrients, a doctor's supervision is required. If parents are very determined to do this, then this can only be done in collaboration with pediatricians. I invite you to our center, we are doing this, make an appointment. First of all, I recommend that mothers reconsider these principles during pregnancy and feeding, include at least some amount of animal protein in the diet. And if the principles are so serious, then contacting specialists so that all micronutrient needs are fully compensated in general is extremely important. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
I communicate with vegetarians, with mothers who have not betrayed themselves during pregnancy, they say: “We drink vitamins, we have enough of everything, and we also eat a lot of soy protein. ”
”
Svetlana Makarova:
Protein – yes, I'm talking about micronutrients. There are macronutrients and there are micronutrients. Macronutrients are big nutrients: protein, fats and carbohydrates. Dietary fiber is also needed, as it turned out, but they are not nutrients, although they provide some energy. Soy protein is about protein. If there is a lot, then all the essential amino acids can be obtained, this is true. But there are micronutrients - these are vitamins and vitamin-like substances, these are minerals and polyunsaturated fatty acids. They are few, but their role in the body is huge. And it is even more huge for children who are going through their first 1000 days - this is critically important. nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
That's what mothers say: “On the one hand, we eat soybeans, and on the other hand, we drink multivitamins – everything is fine with us, we give everything.”
Svetlana Makarova:
Such a nuance that the composition of multivitamins is formed in such a way as to cover the needs of a fairly ordinary diet, they are not for vegetarians.
Tatyana Butskaya:
That is, they need to select separately multivitamin complexes - it's not even just multivitamin complexes, is it like replacement therapy? nine0003
Svetlana Makarova:
There are targeted complexes. The most critical, of course, is vitamin B12, which is involved in the formation of the brain. And vitamin B12 deficiency in the early stages of a child's development is irreversible, a decline in IQ during adolescence.
Tatyana Butskaya:
Returning to the beginning of the program, remember that during pregnancy, every second, millions of cells divide, build connections, and if there is not enough vitamin B12, then these connections in our brain are not completed? nine0003
Svetlana Makarova:
Not completed.
Tatyana Butskaya:
A car with 3 wheels does not move, it needs a fourth, and then you can’t put on this fourth wheel if you didn’t give it at the moment when this car was assembled. It is very sad that not everyone understands this. And I hope that we will return to this issue once again, because we are now raising a lot of sensitive issues. We need to say every week, we need to take social advertising, we need to hang information at bus stops: “Do not think about yourself - think about the child!” – and then we can move something. But I really hope that we have taken the first small step today. We have very little time left, we must talk about the child when he was born. nine0003
It is very sad that not everyone understands this. And I hope that we will return to this issue once again, because we are now raising a lot of sensitive issues. We need to say every week, we need to take social advertising, we need to hang information at bus stops: “Do not think about yourself - think about the child!” – and then we can move something. But I really hope that we have taken the first small step today. We have very little time left, we must talk about the child when he was born. nine0003
Svetlana Makarova:
The way of birth is important, but then breastfeeding is of great importance. It is simply a factor that makes an incredibly large contribution to the health of the child. And for the remaining time we will not have time to discuss all aspects of the importance of breast milk, but I want to remember Academician Arshavsky Ilya Arkadievich - he was an absolutely incredible physiologist who studied age-related physiology, and I was very lucky to hear his lectures back in the 80s, when there were so many didn't talk about breastfeeding. He came out and said: “Understand, breastfeeding is a very special period in a child’s life.” He suggested isolating the lactotrophic type of nutrition after placental nutrition, and only then enteral. nine0003
He came out and said: “Understand, breastfeeding is a very special period in a child’s life.” He suggested isolating the lactotrophic type of nutrition after placental nutrition, and only then enteral. nine0003
A child, being born, is not separated from the mother in terms of nutrition, the umbilical cord remains in the form of breast milk, because breast milk is not only nutrition, it is an emotional relationship with the mother. Breast milk contains a huge amount of immune factors, contains immune cells, contains interleukins (and these are substances due to which immune cells speak to each other), contains immune cells themselves, bacteria (bifidobacteria) - this is something incredible, this is living tissue. And it is no coincidence that he understood that this is a stage that the child must go through. He is not adapted to receive anything other than breast milk. He also protested very much when pediatricians said: “The child still has an immature immune system, an immature gastrointestinal tract,” he said: “The child is mature for this period of his life, he is ripe to be born, to be attached immediately to the breast continue to breastfeed. " nine0003
" nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
And then I immediately remember the questions that I am often asked: “Tell me, which formula is best for a child? What kind of mixture, like breast milk?”
Svetlana Makarova:
Breast milk is just a space in which we discover new components every year. Therefore, I will not talk about which mixture is better. Because, by and large, this is not even a very bad substitute for breast milk, this is some kind of emergency action. Something went completely wrong, a catastrophe, and then we can give the baby formula. nine0003
This is food for the baby, but you need to understand that this is only in exceptional cases, when there are no opportunities to breastfeed the baby. But in fact, any healthy woman, even after a caesarean section, can feed, if there is a desire, there would be an initial attitude, support from the pope, support from the whole family. That is why you correctly said, Tatyana, that a lot of work is needed. We talk about this a lot at conferences, but we urgently need to endure it so that everyone understands how important the health of the mother is before pregnancy, during pregnancy, and how incredibly important it is for a child to receive breastfeeding. nine0003
We talk about this a lot at conferences, but we urgently need to endure it so that everyone understands how important the health of the mother is before pregnancy, during pregnancy, and how incredibly important it is for a child to receive breastfeeding. nine0003
Tatiana Butskaya:
What percentage of women cannot breastfeed?
Svetlana Makarova:
Various studies, but not more than 5%.
Tatyana Butskaya:
How much do they not breastfeed by the end of the first month?
Svetlana Makarova:
About 60.
Tatyana Butskaya:
Friends, here is your answer! And it happens so often when a woman says, "You know, I don't have milk." I want to say every time: “Imagine that you don’t have a store that sells breast milk substitute - either you will breastfeed your baby, or you will be hungry, without food at all.” It has to adjust itself. nine0003
nine0003
Svetlana Makarova:
It is a pity that we did not have time to talk about breastfeeding in more detail, but this, of course, is the mood. The mood of the whole family should be based on the understanding that the importance of breast milk for a child is incredibly high. This is even regardless of what mom eats, it's still a 25% reduction in the risk of obesity. Even if she does not follow any diet, moreover, this percentage depends on the duration of breastfeeding. This is higher than the IQ of children in adolescence. The most important thing is to breastfeed your baby! nine0003
Tatyana Butskaya:
I realized that today we talked about literally 270 out of the first 1000 days, so we have 2 more episodes ahead of us. We will have to talk about breastfeeding in the first year of life, in the second year of life. On my own behalf, I also want to say that our center "Parents' Choice" within the framework of a grant from the Mayor of Moscow conducted a national rating of maternity hospitals, and very soon you will be able to familiarize yourself with its results. There will be a film about how to choose the right maternity hospital, and we paid special attention there, of course, to breastfeeding. Therefore, there will be separate points where it will be seen in which maternity hospital breastfeeding support is at its best. Now remember that there is simply nothing better than breast milk for a child. Svetlana Gennadievna, thank you very much. nine0003
There will be a film about how to choose the right maternity hospital, and we paid special attention there, of course, to breastfeeding. Therefore, there will be separate points where it will be seen in which maternity hospital breastfeeding support is at its best. Now remember that there is simply nothing better than breast milk for a child. Svetlana Gennadievna, thank you very much. nine0003
Svetlana Makarova:
Thank you for inviting me. I really like to participate in such events that bring our knowledge to people.
Tatyana Butskaya:
Goodbye, see you next time!
Raising a healthy child. The concept of the first 1000 days of life.
Children are a small miracle! From the first day, when we can't see them yet, until the day when they finally come into the world, grow up, start walking and talking. nine0008
It is important for all parents to understand that the first 1000 days of a child's life, from conception to two years, are the most important for the formation of good health for the rest of his life .
Let's focus on the four stages of baby development that we can actually support with proper nutrition.
The first and most obvious is physical development. In the first 1000 days of life, babies grow faster than they will for the rest of their lives - from one cell to 500 trillion cells, tripling their weight from birth to one year and growing by 2 cm every month. This requires adequate nutrition both in quality and quantity, because if it is incorrect or insufficient during the mother's pregnancy and in infancy, then this negatively affects the future growth and development of the child. nine0003
The second and most interesting stage is mental development . In the first year of life, babies develop up to 80% of their adult mental abilities. The weight of the child's brain from birth and within 2 years increases by 3 times, and the baby learns up to 900 words by the age of three. Compared to those 600 words that make up 90% of all printed materials.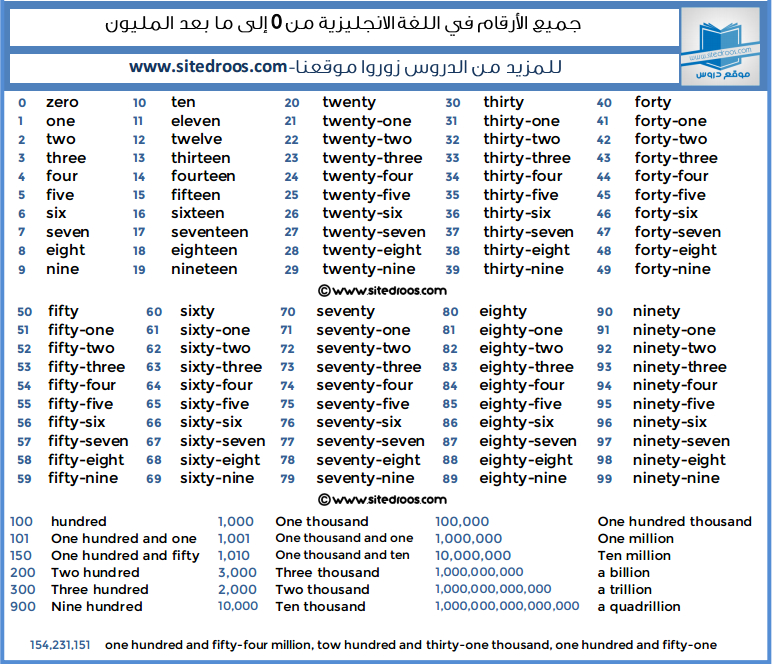 Therefore, proper nutrition for mother and baby is essential to unlock the full potential of the child.
Therefore, proper nutrition for mother and baby is essential to unlock the full potential of the child.
The third and most difficult stage is the formation of immunity . When babies are just born, their immune system is not yet capable of 100% protection. It takes 2 years to form an important organ responsible for immunity - the intestines. It is in it that a protective barrier is formed with trillions of protective bacteria. It takes the same amount of time for the immune cells of the intestine to learn to distinguish between friendly and aggressive proteins. It has already been proven that nutrition is one of the main factors that stimulate the development of immunity and has a powerful influence on the child's natural defense against infections and allergies. nine0003
The fourth most recently discovered stage is metabolic programming. Nutrition during pregnancy and in the first months of a child's life has a lifelong impact on the risk of becoming overweight and developing obesity-related diseases such as diabetes, hypertension and atherosclerosis.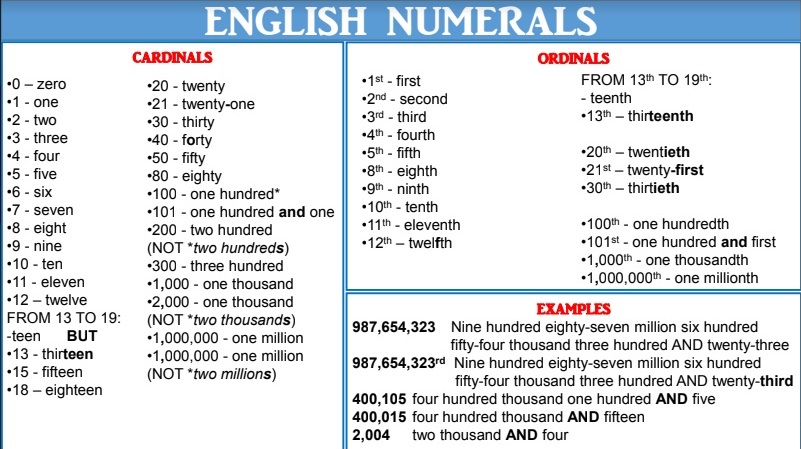 For example, children who are fully breastfed up to one year of age and do not consume excessive amounts of protein are 25% less likely to become overweight in the future.
For example, children who are fully breastfed up to one year of age and do not consume excessive amounts of protein are 25% less likely to become overweight in the future.
All these stages in a child's life are very important, and only when you understand how and how much nutrition during pregnancy and infancy affects health throughout the rest of your life, you can act correctly to raise a healthier generation.
It can be difficult for a modern mother to decide when and how to start introducing complementary foods, what foods to start with and in what sequence to introduce them. Diverse and not always reliable information does not add confidence in this matter. nine0003
Pediatricians at the Dobry Doktor medical center believe that every baby should grow up healthy from the first days, and therefore our pediatricians are ready to help parents with answers to questions about the nutrition of young children. To raise awareness among parents about the proper introduction of complementary foods, we are launching a long-term program with Nestlé.