First trimester pains
Uterus Pain in Early Pregnancy: Causes and Seeking Help
During early pregnancy, you may experience mild twinges or cramping in the uterus. You may also feel aching in your vagina, lower abdomen, pelvic region, or back. It may feel similar to menstrual period cramps.
These minor pains may be caused by different factors like implantation, constipation or gas, or the womb expanding and your ligaments stretching to make room for your baby.
If the pain is mild and goes away on its own, it’s likely nothing to worry about. But any pain along with spotting or heavy bleeding should be reported to your doctor.
Seek emergency care if you experience sharp or chronic pain along with faintness, nausea, high fever or chills, or dizziness.
Read on to learn more about the causes for uterus pain in early pregnancy and when to seek help.
During the first weeks of pregnancy, you likely won’t notice your uterus growing or expanding. But by the 12th week, your uterus stretches and grows to about the size of a grapefruit. If you’re pregnant with twins or multiples, you may feel your uterus stretching sooner.
Symptoms of your uterus stretching may include twinges, aches, or mild discomfort in your uterine or lower abdominal region. This is a normal part of pregnancy and a sign that everything is progressing normally.
Watch for spotting or painful cramping. Report these symptoms to your doctor.
Gas and constipation are common during the first trimester of pregnancy. Levels of hormones in the body increase during pregnancy, which can slow down digestion and relax muscles in the bowels. You may feel additional pressure in the uterus as a result.
Symptoms also include hard, dry stools, or fewer bowel movements than usual.
Some women also experience bloating or gas in the first trimester. This is considered a normal part of pregnancy.
Drink at least 10 cups of water per day to help relieve gas pain and bloating.
For constipation, eat plenty of fiber-rich foods. You can also talk to your doctor about taking a pregnancy-safe stool softener.
Miscarriage is the loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks.
Possible symptoms include:
- vaginal spotting or bleeding
- uterine or pelvic pain
- low back pain
- abdominal pain
- passing tissue or discharge through the vagina
Let your doctor know if you’re experiencing miscarriage symptoms. Once a miscarriage has started, there is no treatment for saving the pregnancy, but in some cases medication or surgery is needed.
Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg attaches itself in a place other than the inside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes. You may feel sharp, stabbing, or chronic pain on one or both sides of the uterus or abdomen.
Other symptoms include:
- vaginal bleeding that’s heavier or lighter than your normal period
- weakness, dizziness, or fainting
- gastrointestinal or stomach discomfort
Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency. Seek immediate emergency medical help if you think you’re experiencing an ectopic pregnancy.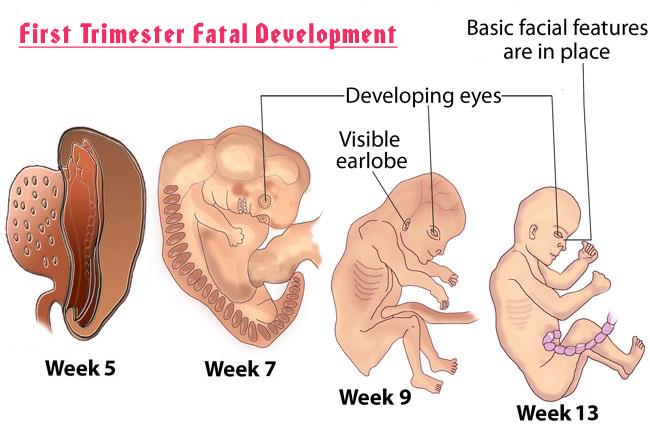
Round ligament pain usually starts in the second trimester, so it’s unlikely to be the cause of pain in early pregnancy. The round ligaments are located in the pelvis and hold the uterus in place. As your belly grows, they stretch.
With round ligament pain, you may experience what feels like a spasm on the right side of your abdomen or right hip. Some pregnant women do feel round ligament pain on both sides, though.
The pain should only last a few seconds or minutes, though it may return when you laugh or do certain movements like standing or bending down.
If you continue to experience round ligament pain, it may be helpful to try light stretching, prenatal yoga, or prenatal massage. Always check with your doctor before trying these treatments, though.
Treatment for uterine pains depends on your symptoms. Mild uterine pain that goes away after a few minutes or hours is likely nothing to worry about.
You can treat mild uterine discomfort at home by taking a warm (not hot) shower or bath, resting, and drinking plenty of water and other fluids. Tell your doctor about your symptoms, as they may recommend another form of treatment that’s safe for your pregnancy.
Tell your doctor about your symptoms, as they may recommend another form of treatment that’s safe for your pregnancy.
Sharp, stabbing, or chronic pain along with symptoms like bleeding, shortness of breath, or fever or chills likely requires emergency medical care.
Let medical staff know you’re pregnant and report any symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, or faintness right away. The medical staff will assess your symptoms and may perform an ultrasound.
Seek help if you’re experiencing sharp or chronic uterine pain along with other symptoms like:
- vaginal bleeding
- dizziness
- high fever
- chills
If the pain goes away on its own, it likely isn’t a reason for concern, but you should still let your doctor know.
You should also let your doctor know about any mild uterine pain during pregnancy. They can decide if you need to be seen right away or if you can wait until your next scheduled prenatal appointment.
Also, tell your doctor if you’re experiencing uterine pain along with spotting or bleeding. These may be symptoms of a miscarriage. Your doctor can assess your symptoms and determine next steps.
These may be symptoms of a miscarriage. Your doctor can assess your symptoms and determine next steps.
Mild uterine pain during early pregnancy doesn’t always mean something is wrong with the pregnancy. However, pain accompanied by spotting or bleeding should be reported to your doctor. These may be signs that a miscarriage is starting.
Your doctor can assess your symptoms at any point during your pregnancy to determine if you need medical care.
Uterus Pain in Early Pregnancy: Causes and Seeking Help
During early pregnancy, you may experience mild twinges or cramping in the uterus. You may also feel aching in your vagina, lower abdomen, pelvic region, or back. It may feel similar to menstrual period cramps.
These minor pains may be caused by different factors like implantation, constipation or gas, or the womb expanding and your ligaments stretching to make room for your baby.
If the pain is mild and goes away on its own, it’s likely nothing to worry about. But any pain along with spotting or heavy bleeding should be reported to your doctor.
But any pain along with spotting or heavy bleeding should be reported to your doctor.
Seek emergency care if you experience sharp or chronic pain along with faintness, nausea, high fever or chills, or dizziness.
Read on to learn more about the causes for uterus pain in early pregnancy and when to seek help.
During the first weeks of pregnancy, you likely won’t notice your uterus growing or expanding. But by the 12th week, your uterus stretches and grows to about the size of a grapefruit. If you’re pregnant with twins or multiples, you may feel your uterus stretching sooner.
Symptoms of your uterus stretching may include twinges, aches, or mild discomfort in your uterine or lower abdominal region. This is a normal part of pregnancy and a sign that everything is progressing normally.
Watch for spotting or painful cramping. Report these symptoms to your doctor.
Gas and constipation are common during the first trimester of pregnancy. Levels of hormones in the body increase during pregnancy, which can slow down digestion and relax muscles in the bowels.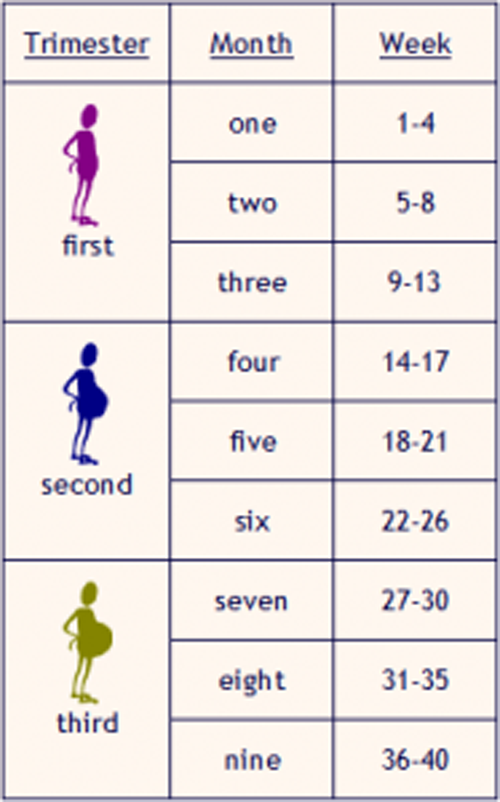 You may feel additional pressure in the uterus as a result.
You may feel additional pressure in the uterus as a result.
Symptoms also include hard, dry stools, or fewer bowel movements than usual.
Some women also experience bloating or gas in the first trimester. This is considered a normal part of pregnancy.
Drink at least 10 cups of water per day to help relieve gas pain and bloating.
For constipation, eat plenty of fiber-rich foods. You can also talk to your doctor about taking a pregnancy-safe stool softener.
Miscarriage is the loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks.
Possible symptoms include:
- vaginal spotting or bleeding
- uterine or pelvic pain
- low back pain
- abdominal pain
- passing tissue or discharge through the vagina
Let your doctor know if you’re experiencing miscarriage symptoms. Once a miscarriage has started, there is no treatment for saving the pregnancy, but in some cases medication or surgery is needed.
Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg attaches itself in a place other than the inside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes.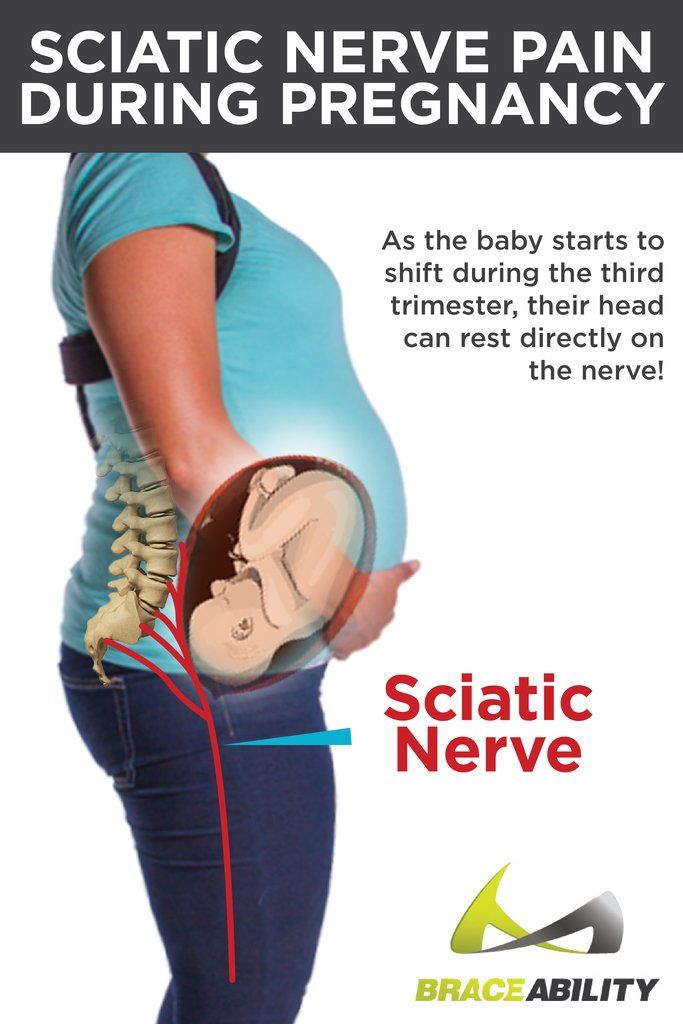 You may feel sharp, stabbing, or chronic pain on one or both sides of the uterus or abdomen.
You may feel sharp, stabbing, or chronic pain on one or both sides of the uterus or abdomen.
Other symptoms include:
- vaginal bleeding that’s heavier or lighter than your normal period
- weakness, dizziness, or fainting
- gastrointestinal or stomach discomfort
Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency. Seek immediate emergency medical help if you think you’re experiencing an ectopic pregnancy.
Round ligament pain usually starts in the second trimester, so it’s unlikely to be the cause of pain in early pregnancy. The round ligaments are located in the pelvis and hold the uterus in place. As your belly grows, they stretch.
With round ligament pain, you may experience what feels like a spasm on the right side of your abdomen or right hip. Some pregnant women do feel round ligament pain on both sides, though.
The pain should only last a few seconds or minutes, though it may return when you laugh or do certain movements like standing or bending down.
If you continue to experience round ligament pain, it may be helpful to try light stretching, prenatal yoga, or prenatal massage. Always check with your doctor before trying these treatments, though.
Treatment for uterine pains depends on your symptoms. Mild uterine pain that goes away after a few minutes or hours is likely nothing to worry about.
You can treat mild uterine discomfort at home by taking a warm (not hot) shower or bath, resting, and drinking plenty of water and other fluids. Tell your doctor about your symptoms, as they may recommend another form of treatment that’s safe for your pregnancy.
Sharp, stabbing, or chronic pain along with symptoms like bleeding, shortness of breath, or fever or chills likely requires emergency medical care.
Let medical staff know you’re pregnant and report any symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, or faintness right away. The medical staff will assess your symptoms and may perform an ultrasound.
Seek help if you’re experiencing sharp or chronic uterine pain along with other symptoms like:
- vaginal bleeding
- dizziness
- high fever
- chills
If the pain goes away on its own, it likely isn’t a reason for concern, but you should still let your doctor know.
You should also let your doctor know about any mild uterine pain during pregnancy. They can decide if you need to be seen right away or if you can wait until your next scheduled prenatal appointment.
Also, tell your doctor if you’re experiencing uterine pain along with spotting or bleeding. These may be symptoms of a miscarriage. Your doctor can assess your symptoms and determine next steps.
Mild uterine pain during early pregnancy doesn’t always mean something is wrong with the pregnancy. However, pain accompanied by spotting or bleeding should be reported to your doctor. These may be signs that a miscarriage is starting.
Your doctor can assess your symptoms at any point during your pregnancy to determine if you need medical care.
Pain in the first trimester of pregnancy
General information
The first trimester of pregnancy is the period from conception to the end of the 12th week of pregnancy. During the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the fertilized egg becomes an embryo, and embryo becomes a fetus.
During the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the fertilized egg becomes an embryo, and embryo becomes a fetus.
The first trimester is an important time, expectant mothers need to be especially careful and attentive to themselves. After all, the health of the child will depend on the nutrition of the mother, her emotional and physical condition.
In the first twelve weeks, almost all vital organs are formed in the unborn child, and the body of the future mother gets used to her pregnancy and begins to work for the child.
Pain in the first trimester in pregnancy
Physiological pain and symptoms in the first trimester not requiring treatment:
- 2 weeks) feel a metallic taste in the mouth.
- There is swelling and pain in the breasts.
- Accumulation of blood in the pelvic organs makes the color of the vulva bluish or purple and may also cause frequent urination.
- The pregnant woman feels that she has started to get tired more quickly than usual; she may experience dizziness, nausea, vomiting (especially in the morning, but it happens throughout the day).
- Sense of smell becomes very acute; for example, some strong or pungent odors (tobacco, fried foods, alcohol) can cause nausea.
Pregnancy by week
At week 6, many pregnant women begin to suffer from constipation and occasional abdominal pain. This is easy to fix if you drink enough water (up to 2 liters per day), and also include foods rich in fiber and fiber, lots of vegetables and fruits in the diet.
At 7 weeks, the uterus is about 8-10 cm in diameter. The breast continues to swell, the nipples may change color to a darker one. The growing uterus creates constant pressure on the bladder, squeezing it, which leads to pain in the lower abdomen and frequent urination.
At 12 weeks, a woman may feel mild pain in the lower abdomen due to tension in the ligaments that support the growing uterus.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, women usually suffer from pain in the lumbar region. However, this pain can absolutely disappear after the twentieth week of pregnancy.
However, this pain can absolutely disappear after the twentieth week of pregnancy.
Most women suffer from lower back pain in the first trimester due to softening of the supporting ligaments and discs and due to an increase in the hormone progesterone. If during pregnancy a woman gets sick with any infectious disease of the bladder, then this can also be the cause of lower back pain. Constant back pain in pregnant women is due to the fact that the center of gravity of the abdomen is changing, in which the child grows and develops.
If something goes wrong during the first trimester, there are two main scenarios: miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. If you find yourself experiencing one of the symptoms discussed below, call your gynecologist immediately, or better yet, call an ambulance.
Threatened miscarriage
Miscarriage can be caused by various reasons. Some studies suggest that about 60% of all miscarriages during the first trimester are due to genetic abnormalities. Over 90% of women who have had a single miscarriage go on to give birth safely. However, it is worth waiting three to six months before trying again.
Over 90% of women who have had a single miscarriage go on to give birth safely. However, it is worth waiting three to six months before trying again.
The risk of miscarriage increases with age. In women under 30, it is 10%, after 45 it rises to 50%. After two miscarriages, it's best to stop trying to conceive and have diagnostic tests done to understand what's causing the miscarriage. Among the possible causes of miscarriage at this stage:
- hormonal deficiency preventing fetal development;
- anomalies in the structure of the uterus;
- genetic failures;
- Rhesus conflict.
However, the reasons often remain unknown, and the woman safely bears her third pregnancy. After two miscarriages, there is a 70% chance that the third pregnancy will pass without pathologies.
It is very important that women know that the probability of miscarriage is quite high in the first trimester of pregnancy were ready for it and did not panic. Miscarriages recur only in a small number of women; if you have had one miscarriage, the chances that the next pregnancy will be successful is very high.
Miscarriages recur only in a small number of women; if you have had one miscarriage, the chances that the next pregnancy will be successful is very high.
The main symptom of threatened interruption is bleeding . However, it is important to remember that not all bleeding indicates a threatened miscarriage. However, although some spotting in early pregnancy is quite common, it is still not normal. Severe bleeding requiring frequent pad changes for heavy flow should be reported to the doctor immediately. Bleeding is usually accompanied by other symptoms: colic, pain in the lower abdomen, fever, weakness, and sometimes vomiting. There may be clots in the blood. You may also notice an unusual smell. Others are possible types of bleeding :
- brown simultaneous or continuous discharge from the vagina;
- minor bleeding accompanied by severe pain in the abdomen or shoulders.
If minor bleeding does not stop for more than three days, this is a bad symptom.
Severe bleeding and colic between the end of the second and the end of the third month: classic symptoms threatened miscarriage. A sharp pain in the lower abdomen, not accompanied by bleeding, is also an alarm signal. Bleeding can reach such intensity that you have to change several pads within an hour, or it can be "bearable" - as during heavy menstrual bleeding. A thick discharge may appear: dark red clots that look like small pieces of raw beef liver.
Occasional gray or pink discharge. In the first trimester, the threat of miscarriage may also be indicated by persistent minor bleeding or mild abdominal pain. In the hospital, the doctor will be able to tell if it is really a threat of miscarriage, and if so, how far the process has gone. He will perform a careful examination of the abdominal organs, may prescribe an ultrasound.
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fetus does not implant in the uterine cavity, but begins to develop in the fallopian tube. It is very dangerous. In the event of a pipe rupture, there may be a threat to life. Classic symptoms ectopic pregnancy : severe pain in the abdomen or side.
It is very dangerous. In the event of a pipe rupture, there may be a threat to life. Classic symptoms ectopic pregnancy : severe pain in the abdomen or side.
The pain may start as a dull ache and get worse. Pain in the neck and shoulders is also common. Along with pain, you may also have menstrual-type bleeding, but pain is the main symptom.
The problem with ectopic pregnancy is that women often do not realize they are pregnant until these symptoms appear. So if you are trying to get pregnant or are simply not using protection, contact a specialist as soon as possible if you experience incomprehensible abdominal pain.
Why does the stomach pull in early pregnancy?
Why does the stomach pull in early pregnancy? This question often worries expectant mothers, and at times leads to panic. When is discomfort pathology, and when is it normal?
Pregnancy is a special time for a mother and her baby. After all, the connection between them is inextricable, and every negative influence or stress affects both of them.
Possible causes of pain
Every woman dreams of having an easy pregnancy and no cause for alarm. However, a very common complaint among pregnant women is pain in the lower abdomen of a pulling or aching nature.
Complaints are so common that it is necessary to clearly understand when pulling sensations during pregnancy are pathological and require immediate medical attention, and when they are quite physiological and require only general recommendations.
Of course, pain in the lower abdomen can appear at any stage of pregnancy, however, most often women notice their appearance in the early stages of pregnancy.
Painful sensations in the abdomen during pregnancy are very diverse both in subjective sensations, and in their localization, in intensity of occurrence. Pain can appear both at rest and after any physical activity. Unpleasant sensations can manifest themselves in one place, or radiate to other areas.
Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen are rarely avoided during pregnancy. These sensations can occur not only in pathology. During pregnancy, the uterus increases in size, there is a tension in its ligaments and muscles. In addition, there is a displacement of the pelvic organs. All this leads to the appearance of pulling or aching sensations in the abdomen. All these phenomena are manifestations of physiological changes that occur to a woman during pregnancy.
These sensations can occur not only in pathology. During pregnancy, the uterus increases in size, there is a tension in its ligaments and muscles. In addition, there is a displacement of the pelvic organs. All this leads to the appearance of pulling or aching sensations in the abdomen. All these phenomena are manifestations of physiological changes that occur to a woman during pregnancy.
Of course, this state of fear does not cause and does not require any intervention on the part of the doctor. However, pulling pains in the lower abdomen are not always a physiological process. It happens that this indicates that the pregnancy proceeds with pathology and requires medical adjustment.
That is why, if there are pulling or aching pains in the lower abdomen, it is necessary to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist in order to accurately determine the cause of the pain.
Never self-medicate. Remember that you are responsible not only for yourself, but also for the little man that you carry under your heart.
Abdominal pain during pregnancy can be:
- obstetric;
- "non-obstetric".
Pain associated with pregnancy may be developmental:
- physiological changes during pregnancy;
- threatened miscarriage;
- missed pregnancy;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Pain not associated with pregnancy may occur with:
- inflammatory processes;
- pathologies of the digestive system;
- surgical diseases;
- diseases of other organs or systems.
Pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy as a variant of the norm
Not all pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy is a manifestation of pathology. Sometimes they can occur during the normal course of pregnancy.
As a physiological process, pain in the lower abdomen can occur in the following situations:
- sign of pregnancy;
- displacement of the pelvic organs by the growing uterus;
- sprains and muscles associated with uterine growth.

Abdominal pain is a sign of pregnancy
Finding out that you are pregnant is not difficult nowadays because there are pregnancy tests. In addition, a delay in menstruation can serve as evidence of pregnancy.
All this is good if the menses are regular and delayed by at least 14 days. In this case, the pregnancy test may be positive. However, do not forget that not all tests are highly accurate, so it can show two cherished strips much later than we would like.
Therefore, it is necessary to pay close attention to the sensations of your body, because it signals the onset of pregnancy long before the manifestation of a delay in menstruation.
If you assume that pregnancy is possible, then listen carefully to your body: it can send you a signal in the form of pulling pains in the lower abdomen. At the same time, the pains will differ in their intensity: one woman will say that the pains are unbearable, the other will not notice them at all. Each woman is individual.
Each woman is individual.
If each menstruation is preceded by unpleasant pain in the lower abdomen or lower back, you may not understand that once again they are associated with the onset of pregnancy.
Pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy may be associated with the implantation process. To do this, you need to remember the process of fertilization of the egg by the sperm. After their fusion in the fallopian tubes, the fertilized egg enters the uterus under the action of the movement of cilia in the fallopian tubes. The uterine endometrium is a loose mass where a fertilized egg is implanted.
The process of implantation is the introduction of a fertilized egg into the endometrium of the uterus. At this time, there is a violation of the integrity of the endometrium, which may be accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen. In addition, sometimes slight dark bloody discharge may appear from the genital tract, which can be perceived as the beginning of another menstruation.
Threatened miscarriage
A fairly common cause of pain in the lower abdomen is a threatened miscarriage. This condition is individual and does not depend on physical exertion or complete rest, but on the condition of the woman and her unborn child.
Causes that may cause miscarriage include:
- heavy physical exertion;
- sexual contact;
- malnutrition of the ovum;
- genetic disorders and other causes.
Of course, this is not evidence that a miscarriage will not occur with complete rest. Miscarriage can occur due to genetic abnormalities, and due to stress. No woman is immune from 90,003 threats of pregnancy loss.
That is why attention and sensitivity to the state of your body is so necessary, which will in every possible way send signals that the pregnancy is not going the way you want.
Threatened miscarriage is accompanied by:
- aching or pulling pains in the lower abdomen;
- Aching or drawing pains in the small of the back or sacrum.

- bloody discharge from the genital tract.
If you have pain in the lower abdomen, you should consult a doctor, as a threatened miscarriage, if medical assistance is not provided, can turn into an abortion that has begun, the treatment of which is much more difficult, if not completely useless.
An ambulance should be called if:
- pain in the lower abdomen gets worse;
- pains begin to radiate to other areas;
- painful sensations do not go away for a long time;
- bloody discharge from the genital tract appeared.
Increased pain
If the pulling pains in the lower abdomen are weak, do not increase and do not radiate to other areas, then you can come to the antenatal clinic in the daytime on your own. This will not threaten serious complications of your condition.
If the pain becomes more intense, does not go away at rest, you should not self-medicate, take drugs without a doctor's prescription.
Do not put anything on the stomach. Both hot and cold application can contribute to the onset of a miscarriage. In addition, with the threat of termination of pregnancy, this manipulation will not remove the pain.
Localized pain
When a threatened miscarriage occurs, pain of a pulling or aching nature disturbs the pregnant woman in the lower abdomen.
If the pain has a clear localization in a certain place, most often on the right or left, then a mandatory consultation with a specialist is necessary, since an ectopic pregnancy or surgical pathology, such as appendicitis, may develop.
Bloody discharge from the genital tract
If bloody discharge from the genital tract has joined the pulling pain in the lower abdomen, urgent medical attention is needed. This phenomenon may indicate a miscarriage that has begun.
The discharge may be sparse, spotting or profuse, dark or bright. In any case, you can not do without consulting an obstetrician-gynecologist.
There are situations when there is no pain, but there is bloody discharge from the genital tract. This case also requires specialist advice.
Any bloody discharge from the genital tract may indicate a miscarriage. Only timely treatment can contribute to the preservation and prolongation of pregnancy.
In some cases, the appearance of bloody discharge from the genital tract may be a manifestation of a miscarriage, which requires immediate medical attention.
Miscarriage
A fertilized egg does not always develop correctly. In some cases, there is a cessation of its division and death. Most often, missed pregnancy occurs due to any mutations. At the same time, the woman does not suspect that the pregnancy has stopped.
However, the dead fetal egg begins to be rejected on its own. At the same time, there are pulling pains in the lower abdomen, which are soon joined by bloody discharge from the genital tract.
When a miscarriage is diagnosed, curettage of the uterine cavity may be indicated. Conservative management is also possible, but this can only be determined by a specialist after consultation.
Conservative management is also possible, but this can only be determined by a specialist after consultation.
Ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy most often occurs as a tubal pregnancy, when the fertilized egg does not reach the uterus, and the implantation process occurs in the fallopian tube. At the same time, the development of the fetal egg can continue for a long time without any manifestations, up to 12 weeks of pregnancy. However, most often such a pregnancy is interrupted at 6 to 8 weeks.
The fertilized egg develops and grows, which causes pain in the right or left side of the lower abdomen. The pains are unilateral, are obsessive, tend to increase.
In addition to pain in the lower abdomen, bloody discharge from the genital tract appears, and the pain begins to radiate to the leg from the side of the pain. There may be unpleasant sensations of pressure on the rectum. Medical surgery is the only way to save a woman's life. Preservation of pregnancy is impossible.
"Non-obstetric" causes of pain in the lower abdomen
Inflammatory processes
Among the "non-obstetric" causes, due to which there are pulling pains in the lower abdomen, inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs are most common. If earlier it was believed that there could be no inflammation in pregnant women, now it has been proven that a decrease in the immunity of a pregnant woman awakens all pathological processes in her body.
Pain in inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs differ in their intensity. At the same time, they occur in the lower abdomen and most often have a pulling or aching character.
Pathology of the digestive system
Very often, pulling pains in the lower abdomen can occur in a pregnant woman due to problems with the digestive tract. During pregnancy, there is a decrease in intestinal contractility. In addition, there are significant changes in the hormonal background of a woman. Therefore, very often pregnancy is accompanied by constipation and bloating. To normalize digestion, a change in diet is recommended and mild laxatives can be taken.
To normalize digestion, a change in diet is recommended and mild laxatives can be taken.
Surgical pathology
Of the surgical pathologies that may be accompanied by pulling pains in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, acute appendicitis is the most common.
In the early stages of pregnancy, it is obligatory to differentiate obstetric and gynecological diseases from appendicitis, since it has similar symptoms. There are pains in the lower abdomen, which most often occur in the navel or stomach, and then descend to the right iliac region. Nausea, vomiting, fever joins. The only treatment is surgery. In this case, the pregnancy is preserved.
Diseases of other organs or systems
In addition to obstetric and surgical causes, which can cause pulling pains in the lower abdomen in early pregnancy, other body systems may also be involved in the pathological process. The most common lesion is the urinary tract.
Cystitis
Cystitis due to the anatomical features of a woman can occur at any time and in any condition, so pregnant women are just as susceptible to it as non-pregnant women.