Burning discharge during pregnancy
Vaginal itching during pregnancy: Causes and treatments
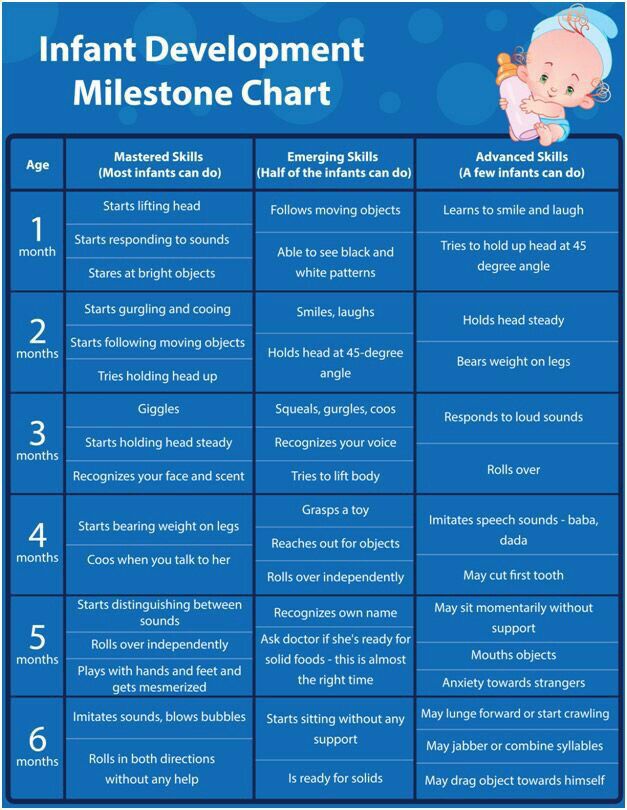
Vaginal itching in pregnancy is a common experience. Potential causes include changes to the vagina during this period, or an infection. Identifying the cause can help with treatment and prevention.
Scientific studies have looked at the prevalence of conditions that may cause vaginal itching in a pregnant woman.
A 2015 study found that women are more likely to have vaginal yeast during pregnancy. Another 2019 study of women in Ghana found that 56.4% had a vaginal infection during pregnancy, while a 2017 analysis of women in Nigeria put the figure at 60.8%.
Some medications to treat vaginal infections are unsafe for pregnant women. For this reason, it is important to see a doctor or midwife to diagnose and treat vaginal pain or itching during pregnancy.
Vaginal itching may have a range of symptoms, including:
- pain at the entrance to the vagina
- itching and pain in and around the vulva
- itching and pain inside the vagina
- pain or itching that worsens after sexual intercourse
- burning in or around the vagina
- pain when urinating
Some people also notice an increase or change in vaginal discharge.
Similarly, some infections may cause a change in the smell of vaginal discharge.
Yeast infections do not typically cause a bad smell, though some people may notice an odor that resembles that of bread, beer, or something sweet.
Trichomoniasis and bacterial vaginosis may cause a fishy odor.
The most common reasons for vaginal itching during pregnancy include:
Bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis is a bacterial infection of the vagina. In some cases, it may transmit from one sexual partner to another. In others, it may happen when something causes the normal bacterial balance of the vagina to change.
Bacterial vaginosis can cause pain and itching. One of the most noticeable symptoms, however, is a fishy odor that gets worse after sex.
Without treatment in pregnant women, the infection can cause preterm birth and low birth weight.
Vaginal yeast infection
A vaginal yeast infection causes too much yeast to grow in the vagina. Symptoms include intense itching and burning.
Symptoms include intense itching and burning.
Some people also notice a thick, cottage cheese-like discharge. Severe cases can cause swelling in the vagina, or lead the skin to crack. This increases the risk of other infections.
Vaginal yeast tends to grow in warm, moist areas. Wearing cotton underwear and keeping the vagina dry, especially after exercise or sex, may reduce the risk.
Women who are pregnant, have diabetes, use hormonal contraceptives, or who have recently used antibiotics are more likely to get yeast infections.
Trichomoniasis
A parasite causes a contagious sexually transmitted infection (STI) called trichomoniasis.
Only about 30% of people with the infection have symptoms. When symptoms are noticeable, they include vaginal itching and pain when urinating.
Trichomoniasis increases the risk of preterm labor and low birth weight.
Vaginal dryness
Most people experience an increase in vaginal discharge and moisture during pregnancy. However, after delivery, vaginal dryness is common.
However, after delivery, vaginal dryness is common.
This dryness may cause itching and pain in the immediate postpartum period. The itching may get worse if a person uses soap to clean the area, as soap can dry the skin.
Treatment depends on the reason for the vaginal itching. The wrong treatment will not help and may even make the infection worse.
Yeast infections, for example, sometimes appear or get worse after a person uses antibiotics. People should see a doctor instead of self-diagnosing for effective diagnosis and treatment.
Bacterial vaginosis sometimes goes away on its own, or with home remedies. However, it is essential to treat it promptly with antibiotics because it increases the risk of negative pregnancy outcomes.
Many antibiotics are safe during pregnancy. Make sure the doctor or midwife knows about the pregnancy, so that they can select the right drug.
Vaginal yeast infections usually get better with antifungal treatment. Oral antifungal treatments are typically safe during pregnancy and often work better than over-the-counter remedies.
A woman should speak to a doctor before trying home remedies during pregnancy.
Learn about some home remedies for yeast infections here.
Medication to treat trichomoniasis involves killing the parasite that causes the condition. This medication is safe during pregnancy.
People who experience dryness-related itching after pregnancy may find relief from using vaginal lubricants during sex or trying long-term vaginal moisturizers.
As a person’s hormones return to normal, and their vagina recovers from any tears or injury during delivery, the itching usually goes away. If moisturizers do not help, it is advisable to see a doctor, as there could be an infection.
It is a myth that bad hygiene causes vaginal infections or vaginal itching during pregnancy. Frequent washing or showers will not prevent infections. Douching and perfumed soaps may even increase the risk of some infections.
Strategies that may help prevent vaginal itching during pregnancy include:
- wearing breathable cotton underwear
- keeping the vaginal area dry by not sitting in wet bathing suits or sweaty underwear
- taking antibiotics only when necessary
- using condoms or protection against STIs during sex
- limiting sexual partners
A person should see a doctor for any signs or symptoms of a vaginal infection. It is also important to see a doctor in the following circumstances:
It is also important to see a doctor in the following circumstances:
- A person develops new symptoms after treating an infection.
- The symptoms get worse or do not improve after a few days of treatment.
- A person develops another vaginal infection after treatment.
- A woman has multiple vaginal infections during pregnancy.
Call a doctor right away, and go to the emergency room if the doctor does not answer, if:
- The baby stops moving.
- There are signs of labor, such as leaking fluid or contractions.
- There is bleeding from the vagina.
Vaginal itching during pregnancy is a common if painful experience. It is rarely dangerous, but having a diagnosis can help ensure the safety of the pregnant woman and developing fetus.
Vaginal infections are highly treatable, and treatment is usually safe for anyone who is pregnant.
Pregnant women experiencing persistent or severe vaginal itching should speak to a doctor.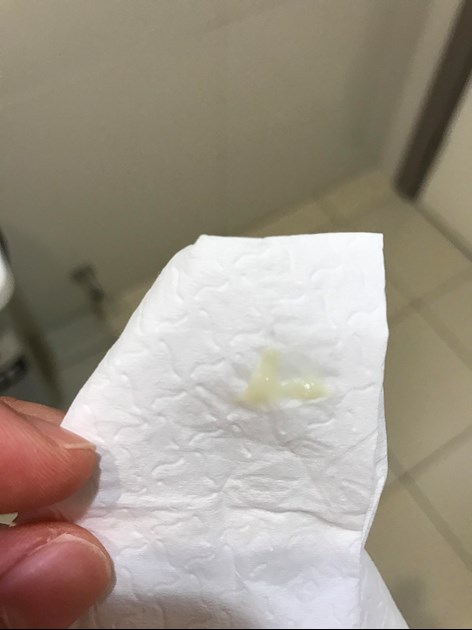 They can advise on safe treatments and prevention of future itching.
They can advise on safe treatments and prevention of future itching.
Vaginal thrush during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Vaginal thrush during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
Most women experience occasional bouts of a common yeast infection known as vaginal thrush. It causes itching, irritation and swelling of the vagina and surrounding area, sometimes with a creamy white cottage cheese-like discharge.
Vaginal thrush is fairly harmless, but it can be uncomfortable and it can keep coming back, which is known as recurrent thrush.
Thrush is a yeast infection, usually caused by a yeast-like fungus called 'Candida albicans'.
Many women have Candida in their vagina without it causing any symptoms. Hormones in vaginal secretions and 'friendly' vaginal bacteria keep the fungus under control. Problems arise when the natural balance in the vagina is upset and Candida multiplies.
Hormones in vaginal secretions and 'friendly' vaginal bacteria keep the fungus under control. Problems arise when the natural balance in the vagina is upset and Candida multiplies.
Vaginal thrush can sometimes be passed on during sex but is not considered a sexually transmitted infection (STI). However, if you have thrush it’s best to avoid having sex until you’ve completed a course of treatment and the infection has cleared up.
During pregnancy
You are more at risk of getting thrush while you're pregnant. Changes in the levels of female hormones, such as oestrogen, increase your chances of developing thrush and make it more likely to keep coming back.
There is no evidence that thrush affects your chances of getting pregnant.
If you're pregnant or breastfeeding and you have thrush, you should avoid taking oral anti-thrush treatments. Instead, use vaginal pessaries, plus an anti-thrush cream if necessary.
Treatment
If you have thrush and you're pregnant or breastfeeding, you should always visit your doctor rather than buying anti-thrush medication over the counter from a pharmacy.
You won’t be prescribed oral treatment because it may affect your baby. An anti-thrush pessary, such as clotrimazole, nystatin or miconazole will probably be prescribed to be used for about 3 to 7 days.
If you're pregnant, take care when inserting a pessary because there's a risk of injuring your cervix (neck of the womb). To reduce the risk, it may be better to insert the pessaries by hand instead of using the applicator.
If you have symptoms around your vulva, such as itching and soreness, you may also be prescribed an anti-thrush cream.
Not all of these products are safe to use at different stages of pregnancy, so it's important to talk to your doctor and pharmacist before using any products.
What can I do to prevent vaginal thrush?
There are a number of simple things you can do:
- Wear cotton or silk underwear rather than synthetics and change daily. Wear tights or stockings for as short a time as possible.
- Wash underwear in hot water and pure soap and double rinse to make sure any irritants are removed before you wear them.

- Change out of damp swimming costumes or sports clothes as soon as possible after swimming or exercise.
- If using pads, change them regularly and avoid perfumed or deodorised pads.
- Avoid tight fitting clothes such as jeans as this creates a moist, warm environment that encourages the overgrowth of bacteria and yeasts.
- Never douche — except if it is specifically prescribed by a doctor to treat an infection. Douching increases your risk of vaginal irritation and is not recommended during pregnancy. A healthy vagina does not need a vaginal deodorant.
- Avoid using soaps, bubble baths, bath salts, perfumes and perfumed talcs around the vaginal area. And never ever use anything harsh such as disinfectants — even diluted, near your vagina.
- A gentle moisturiser like aqueous cream may be advised. Use water or soap substitutes to wash the area.
- Always wipe from the front to the back after going to the toilet since this stops bowel organisms being swept into the vagina.
 Don’t use perfumed toilet paper because it can cause irritation.
Don’t use perfumed toilet paper because it can cause irritation.
Sources:
Mater Mother’s Hospital (Pregnancy – information for women and families), MotherSafe: NSW Medications in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Service (Thrush in pregnancy), Women and Children’s Health Network (Common health problems in pregnancy – vaginal thrush)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: November 2020
Back To Top
Need more information?
Thrush | SA Health
Thrush or Candidiasis is a common vaginal infection, caused by an overgrowth of yeasts and is not considered to be a sexually transmitted infection
Read more on SA Health website
Vaginal discharge during pregnancy
Almost all women have more vaginal discharge in pregnancy as it helps prevent any infections travelling up from the vagina to the womb.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Contraception: vaginal ring - MyDr.com.au
The vaginal ring (brand name NuvaRing) is a type of hormonal contraception. When used properly, the vaginal ring is an effective and safe way of preventing pregnancy.
Read more on myDr website
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) during pregnancy
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most common bacterial infection women get in pregnancy, but there are ways to lower the risk of developing one.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Gestational diabetes: Q and A - MyDr.com.au
Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is different from having known diabetes before pregnancy and then getting pregnant.
It is different from having known diabetes before pregnancy and then getting pregnant.
Read more on myDr website
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth - perineum and pelvic floor
The perineum – the skin between the vagina and anus - stretches during childbirth and can sometimes tear. Learn here how to prepare the perineum for the birth.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy - signs and symptoms - Better Health Channel
All women experience pregnancy differently, and you will experience different symptoms at different stages of your pregnancy.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
STIs and pregnancy
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), if left untreated, can cause serious problems for both mother and child.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Episiotomy
An episiotomy is a procedure performed during labour to assist with the delivery of your baby.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Menstrual cycle: normal - MyDr.com.au
All you need to know about periods, including what's normal and what's not. Plus, see what happens inside your body during the different phases of a normal menstrual cycle.
Read more on myDr website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Pregnancy discharge | What are the discharge during pregnancy? | Blog
In the absence of menstruation, girls usually suspect that conception has occurred. However, during pregnancy, the female body may continue to secrete a secret of a different color and character. We recommend that you keep a close eye on everything that happens so as not to miss the development of adverse events. We will talk about how to recognize problem situations during pregnancy in the article.
What discharge can occur during conception
Many women note that immediately after the delay and in the later stages, the nature of the secretion changes. It can be:
It can be:
- With or without scent.
- Depending on the color - transparent, white, cream, yellow, greenish, bloody.
- By consistency - thick, liquid, cheesy.
- As a symptom for assessing the state of health - threatening, safe.
During ovulation, the egg is released from the ovary, its membrane is deflated, a small amount of fluid is released - so it becomes ready for fertilization. At this time, the thick mucus that fills the cervical canal of the cervix becomes less viscous. This makes it easier for the spermatozoa to penetrate and move further into the tubes for fertilization. At this time, you may notice an abundance of clear mucous secretion.
After the fusion of the egg with the spermatozoon, movement into the uterus begins, which should end with implantation in the inner layer. During penetration, its slight detachment may occur - this causes damage to the blood vessels that abundantly penetrate the muscular layer of the uterus. You may see light brown discharge, which is common during pregnancy. The color is due to the fact that the blood has time to clot.
You may see light brown discharge, which is common during pregnancy. The color is due to the fact that the blood has time to clot.
Sometimes the discharge is brightly colored and some women mistake it for a period that has started too early. But in this case, a short duration is characteristic, a different shade (dark or scarlet), a slight mark on the linen.
With some features of the structure of the female genital organs (for example, with a bicornuate uterus), after implantation of the embryo in one part, rejection of the endometrium may begin in the other, as usually occurs during menstruation. This rarely happens.
Characteristics of discharge in the event of a threatened miscarriage
Spontaneous abortion is the rejection of an embryo in the early stages after conception. If at the first signs of pregnancy, you notice spotting, there is a high probability that a miscarriage begins.
Also, miscarriage symptoms include:
- pulling or pressing on the lower abdomen, sacrum, lower back;
- the muscles of the uterus are tense.

The woman may feel cramps. This continues all the time or intermittently. From the vagina there are scarlet or brown discharge during pregnancy, which was previously confirmed. Sometimes the period may be still small, and the first signs did not have time to appear.
After 22 weeks, this phenomenon is called preterm labor. The child in this case is still weak, the organs are not sufficiently developed, and there is little chance of survival.
The following factors increase the risk of miscarriage:
- various diseases;
- progesterone deficiency;
- nervous and physical overexertion;
- pathologies in the genitals;
- fetal developmental defects.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound scan. If it shows that the fetal heart rate is disturbed, the tone of the uterus is increased, its size differs from normal for this period, hospitalization will be recommended to maintain pregnancy.
What discharge during pregnancy is considered normal
This secretion does not pose a threat to health:
- transparent;
- whitish;
- yellowish;
- odor free;
- mucous;
- without itching, burning, redness of the genitals.
Clear fluid on underwear is a symptom of ovulation. During pregnancy, the activity of ongoing processes in the body increases, so the amount of secretion secreted may increase. However, a violation of the norm is the leakage of amniotic fluid. You can determine the problem with the help of special diagnostic tests that the doctor will prescribe if he has suspicions.
White color, small amount, homogeneous structure should also not cause concern. The increased volume of fluid in this case is associated with increased hormonal activity.
One of the variants of the norm is mucous discharge, which smells of slight sourness. If there is no pain, discomfort, there is nothing to worry about.
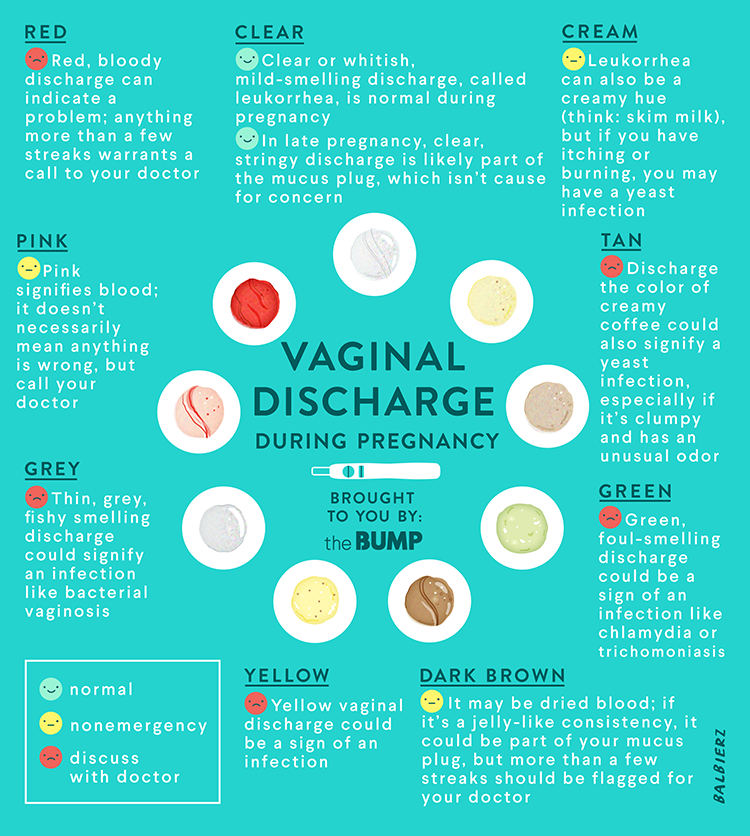
Yellow discharge, there are signs of pregnancy, there is no unpleasant odor - you are all right. Some women had this color before conception, only they did not pay attention. Now there are more of them, therefore more noticeable.
Sometimes a woman observes that the laundry gets wet and there is a smell of urine. This may indicate incontinence due to the constant pressure of the growing uterus. In this case, it is recommended to go to the toilet more often, change underpants twice a day.
What discharge during pregnancy is considered a sign of infection?
White discharge during pregnancy with a cheesy texture is a symptom of thrush (candidiasis). In pregnant women, it is diagnosed quite often - the reason is a change in hormonal levels. The disease is accompanied by itching, redness of the vulva, a strong sour smell. Sometimes external manifestations are not detected, then treatment is not carried out.
Infection is indicated by pain, pain, skin irritation, ulcers, smell of rot or fish, gray or green color, frothy discharge, increased nervousness, large inguinal lymph nodes. The reason may lie in sexually transmitted infections. This includes syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and others. They are dangerous because they cause premature birth and fetal developmental defects.
The reason may lie in sexually transmitted infections. This includes syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and others. They are dangerous because they cause premature birth and fetal developmental defects.
What kind of discharge during pregnancy should I pay special attention to and should I consult a doctor?
The following indicates that pregnancy is at risk:
- Severe pain in the perineum, bleeding, difficulty defecation, convulsions - these may be injuries to the vaginal mucosa.
- Nausea, profuse vomiting, edema, headaches, cough, hypertension, bright red secretion are symptoms of hydatidiform mole (abnormal development of the embryo).
- A drop in blood pressure, pallor, weakness, sweating, pulling sensations, bleeding during pregnancy against the background of a lack of growth of hCG in the blood - this is how ectopic attachment manifests itself.
- Isolation of clots, sharp pain, vomiting, diarrhea may indicate a frozen fetus.

If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
It is also necessary to go to the clinic if you have been physically abused, had rough sex, had an accident, fell, hit. The likelihood that the situation will be resolved successfully is much higher if you do not delay the visit, listen to the symptoms and take good care of your health.
Remember, despite the fact that pregnancy is a normal state of health of the female body, the diagnosis and treatment tactics are still different, due to the many restrictions on manipulations and medications during pregnancy. That is why diagnosis and treatment during pregnancy should take place only under the supervision of a physician. By ignoring the symptoms or self-medicating, a pregnant woman risks not only her health, but also the health of her child.
Doctors of the Leleka maternity hospital manage pregnancies of any complexity, including those aggravated by infections, pathologies, and the threat of miscarriage. Our own diagnostic laboratory allows us to accurately and in the shortest possible time to obtain the results of the tests. Thanks to constant medical supervision throughout the entire period, the chances of a successful birth are greatly increased.
Our own diagnostic laboratory allows us to accurately and in the shortest possible time to obtain the results of the tests. Thanks to constant medical supervision throughout the entire period, the chances of a successful birth are greatly increased.
Trust the life and health of your child to Leleka doctors, and we will make sure that you are satisfied.
Vaginal discharge: types, causes, deviations
The article was checked by a doctor: Sokolova Marina Olegovna
Consultation with a specialist:
Vaginal discharge is the result of the work of glands located in the mucous membrane of the vagina. By the nature of the discharge, it is possible to assess the state of the organs of the female genital area.
Normal vaginal discharge is not considered a disease, as it is necessary for the normal functioning of the reproductive system. In the vestibule of the vagina and near the cervix, there are secretory glands that produce mucus, which is necessary to moisturize the mucous membrane and form a healthy microflora. Healthy secretions are formed in a small volume, they are transparent, odorless and are not accompanied by pain and itching. When the type of discharge changes, this indicates the presence of a pathological process in the organs of the female genital area.
Healthy secretions are formed in a small volume, they are transparent, odorless and are not accompanied by pain and itching. When the type of discharge changes, this indicates the presence of a pathological process in the organs of the female genital area.
Types of vaginal discharge
Depending on the amount of mucus produced, the discharge is divided into scanty, abundant and normal.
Meager is called discharge, which is not enough for the normal functioning of the vagina and external genital organs. The mucous membranes begin to dry out and crack. During sexual intercourse, friction and pain are felt. Scanty discharge is the result of hormonal changes due to age, endocrine disease, or taking hormonal drugs.
Abundant discharge is called, which leads to a constant feeling of moisture in the vagina. They are visible on underwear. Abundant discharge can be diagnosed in young women during ovulation in the middle of the menstrual cycle, they are transparent and do not have an unpleasant odor. During pregnancy, especially before childbirth, the discharge also becomes more abundant. These are healthy secretions, they should not be feared. If the consistency, volume, color or smell of the discharge changes, this indicates the beginning of the pathological process.
During pregnancy, especially before childbirth, the discharge also becomes more abundant. These are healthy secretions, they should not be feared. If the consistency, volume, color or smell of the discharge changes, this indicates the beginning of the pathological process.
Discharge is considered natural if it sufficiently moisturizes the vagina and does not cause anxiety. In the presence of normal discharge, additional moistening of the vagina before intercourse is not required.
According to the consistency, the discharges differ in watery, mucous, cheesy and foamy.
- Fluid discharge - watery and mucous - odorless and color appear normal. Watery discharge is noted in the middle of the cycle during the period of ovulation, mucous membranes appear during intercourse and serve as a lubricant.
- Thick curdled discharge indicates the presence of a fungal infection. Doctors usually diagnose candidiasis. The secretions resemble liquid cottage cheese, they are not uniform in consistency.

- Foamy discharge indicates the presence of a bacterial infection. This is especially dangerous if they have an unpleasant odor or a pronounced color. Foamy discharge is a hallmark of trichomoniasis.
The color of the discharge distinguishes between transparent (normal), white, bloody, yellow, green and brown.
- Clear discharge is normal. Usually they are invisible on underwear and on the body.
- Thick white discharge indicates the presence of candidiasis (thrush). In a healthy state, white discharge may appear before childbirth.
- Bloody and brown discharge is the most dangerous, as it indicates the presence of blood in the vagina. Normally, they occur only during menstruation. When taking hormonal contraception, especially in the first months, the appearance of intermenstrual spotting is acceptable, this is considered normal and reports the adaptation of the body to artificial hormones. In other cases, bleeding indicates the presence of a serious pathology or the onset of bleeding.

- Yellow and green discharge indicates the presence of an infectious and inflammatory process.
Odorless secretions, with a sweetish odor, with a sour odor, with an unpleasant odor are differentiated by smell.
- The phrase “odorless discharge” is arbitrary, since all human discharge is characterized by some odor. In a healthy state, this smell is pleasant and barely perceptible. It is individual for each person. Since a person constantly feels it, he eventually ceases to feel it. If a woman does not smell the discharge, it can be said that the discharge is odorless.
- Discharge with a sweetish or sour smell most often speaks of thrush. Candida fungi use sugar for food, love it and settle in a sugar-rich environment.
- Foul-smelling discharge is caused by a bacterial infection. They often smell like stale fish. Anaerobic bacteria give the characteristic smell of fish. The stronger the smell, the stronger the infection.
Call now
+7 (495) 215-56-90
Sign up
Causes of vaginal discharge
Intimate secretions serve as a kind of indicator of the health of the female sphere.
With natural secretions that do not cause discomfort, we can conclude that the organs of the female reproductive system are healthy. However, regular examinations by a gynecologist at the beginning of the cycle are still necessary. Many pathological processes pass without symptoms; only a gynecological examination and laboratory tests can show their presence.
Several factors can affect the type of discharge in a healthy woman. These are stress, climate change, taking hormonal drugs, taking potent drugs, and allergic reactions. Also, the nature of the discharge can be affected by personal hygiene.
A woman should be concerned when the discharge changes in consistency, acquires a strange color or smell, or changes in intensity. Often, such discharge is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, itching, pain in the perineum, irritation of the external genital organs, and discomfort during urination.
There are some symptoms by which you can preliminarily determine the disease. Of course, an accurate diagnosis is possible only with a doctor after an examination and laboratory diagnosis, but the appearance of some can give a more or less accurate picture of the disease.
Of course, an accurate diagnosis is possible only with a doctor after an examination and laboratory diagnosis, but the appearance of some can give a more or less accurate picture of the disease.
Curdled discharge white with a sweetish or sour smell indicates candidiasis. Other symptoms of candidiasis are:
- burning, itching in the vagina and external genitalia;
- swelling of the vagina after intercourse;
- pain during urination and during intercourse.
Profuse yellow or bloody discharge with an unpleasant odor may indicate bacterial vaginitis. This is an inflammation of the vagina caused by a violation of the microflora. This means that local immunity cannot restrain the growth of pathogenic bacteria, they attack the cells of the vagina, and the inflammatory process begins. Typical symptoms of bacterial vaginitis:
- redness, itching and swelling of the genitals;
- drawing pains in the lower abdomen;
- painful intercourse;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- weakness and fatigue;
- frequent urination.
Abundant frothy leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor may indicate trichomoniasis. The causative agent of the disease are Trichomonas. The following symptoms are also observed:
- irritation of the genitals and inner thighs;
- erosion of the mucous membranes of the intimate area;
- pain when urinating;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during sexual contact.
Homogeneous yellow-green discharge with an unpleasant odor may be a sign of gonorrhea. This is an acute infectious disease caused by gonococcus and sexually transmitted. The symptoms of gonorrhea are:
- itching and pain in the urethra and vagina;
- fever;
- discharge of pus from the vagina;
- frequent painful urination;
- swollen and sore lymph nodes;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- violation of appetite.
Serous-purulent discharge with blood often indicates the presence of a cyst in the uterus or its appendages. Symptoms of a cyst, in addition to spotting, are:
Symptoms of a cyst, in addition to spotting, are:
- vaginal discomfort;
- pain in lower abdomen;
- pain during intercourse;
- increase in menstrual flow;
- menstrual disorders;
- painful menstruation.
Bright yellow and green discharge in copious amounts with a very unpleasant odor indicate endometritis. This is an inflammation of the uterus caused by bacteria or trauma. Symptoms of endometritis:
- acute pain in the abdomen, in its lower part;
- fever with chills;
- increased heart rate;
- painful urination;
- weakness;
- enlargement of the uterus due to tissue inflammation;
- profuse and painful periods;
- infertility.
Brown discharge during delayed menstruation may indicate an abnormal course of pregnancy, such as an ectopic pregnancy. You can judge the likelihood of this pathology by the following symptoms:
- absence of menstruation;
- sharp or cramping pain in the lower abdomen, usually on the side;
- toxicosis and other signs of pregnancy.
This is a very dangerous condition that requires immediate medical attention. Even if the pregnancy is uterine, but spotting is present, you should immediately consult a doctor, as this is a sign of a threatened abortion.
Which doctor should I contact for unhealthy vaginal discharge?
If the discharge is unnatural in color, smell or consistency, you should visit a gynecologist. The doctor will ask about the symptoms, conduct a visual examination, take a swab from the vagina and make a diagnosis based on the results of the studies. Analysis of vaginal discharge will show if there is a bacterial, viral or fungal infection, what is the degree of infection. After that, an ultrasound examination of the organs of the reproductive system is prescribed. Ultrasound will show the size of the organs of the female system, their position, the presence of neoplasms, such as cysts or tumors, and will help to specify the diagnosis. In addition, the doctor prescribes a complete blood count, cytological examination and / or colposcopy.
With a cyst or tumor, an additional consultation with an oncologist will be required. If there is a heavy discharge due to stress, it is useful to consult a psychologist. If sexually transmitted diseases are detected, an immunologist's consultation will be required. With a long course of diseases, it is useful to contact an immunologist and assess the immune status. In case of abundant discharge against the background of allergies, it is recommended to consult an allergist. In children, unhealthy discharge is evaluated by a pediatric gynecologist and pediatrician.
Treatment of abnormal vaginal discharge
Treatment of problematic discharge should always be carried out with the participation of a doctor after a thorough diagnosis.
In case of a bacterial infection and inflammation against its background, antimicrobial drugs are prescribed. Antibiotics are prescribed orally and topically in the form of suppositories, creams, ointments.
For fungal infections, antifungal drugs are prescribed. It is worth remembering that thrush is a local manifestation of extensive damage to the body by a fungus, and its treatment is not limited to suppositories and creams. The bulk of the fungus is in the intestines, so the whole body as a whole, and not just the vagina, should be treated.
It is worth remembering that thrush is a local manifestation of extensive damage to the body by a fungus, and its treatment is not limited to suppositories and creams. The bulk of the fungus is in the intestines, so the whole body as a whole, and not just the vagina, should be treated.
With a viral infection, antiviral drugs are prescribed. Viruses are dangerous organisms, and doctors have not yet learned how to treat them effectively. This is where immunity plays an important role.
When neoplasms appear, their conservative treatment or removal is possible. Here the decisive role is played by the nature of the neoplasm - benign or malignant - and the rate of its development.
In case of uterine pregnancy with a threat of miscarriage, the patient is sent to a hospital, the condition of the uterus, placenta, and fetus is examined. In case of an ectopic pregnancy, the immediate removal of the fetal egg from the woman's body is required.
In any case, when an unhealthy discharge appears, very careful hygiene is required, since many pathological discharges corrode the skin of the genitals. Sometimes the doctor prescribes baths with therapeutic solutions and douching.
Sometimes the doctor prescribes baths with therapeutic solutions and douching.
There are many folk methods for treating discharge. They sometimes help, but sometimes they can blur the clinical picture and make it difficult to diagnose and treat the disease. Of the folk methods, washing with decoctions of herbs is considered safe and useful. Chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort relieve inflammation, increase local immunity and soothe irritated skin. In no case should foreign objects be introduced into the vagina, as some folk recipes advise. This can harm the microflora and injure the already irritated vaginal mucosa.
How to prevent abnormal vaginal discharge?
The first rule of preventing painful discharge is regular hygiene. It is necessary to wash yourself every time after visiting the toilet and in the evening before going to bed. Washing is carried out with clean warm water with special means for intimate hygiene. Ordinary soap can destroy the natural microflora and promote the growth of pathogenic bacteria.