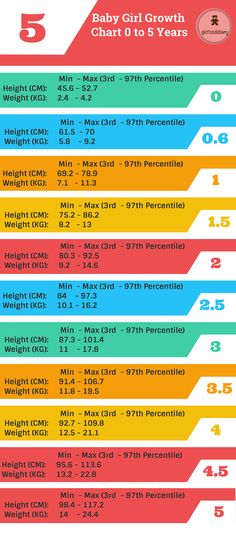
Fetal weight and height chart
Fetus size by week: Your baby's weight throughout pregnancy
Find out how big your baby is during each week of their development with our fetal growth chart. From early in pregnancy, babies grow at different rates, so your baby's actual size by week may vary substantially – but look how they grow! At 20 weeks your baby may be just over 10 inches long and weigh less than 12 ounces, but by 32 weeks they'll reach almost 17 inches and top 4 pounds. At 33 weeks they may be over 17 inches and closer to 5 pounds, and by 37 weeks they'll reach 19 inches and about 6.5 pounds.
How do you determine fetus size by week?
There are different methods for estimating how big a fetus is, which is why you'll find different numbers depending on the source.
Experts have formulas they use to come up with the estimated fetal weight (EFW) and height of a fetus, and the formulas aren't always the same. The measurements that are used in equations to estimate weight usually include biparietal (head) diameter (BPD), head circumference (HC), abdominal circumference (AC) and femur (thigh bone) length (FL).
Height is a straightforward measurement, but the method of measuring it changes after the first trimester. For the first 13 weeks, the height measurement is taken from the top of the head to the baby's bottom. After the first 13 weeks, the measurement is taken from the top of the head to the baby's heel – explaining why, on the chart below, your baby appears to grow 3 inches from week 13 to week 14!
Hadlock, the main source we use in our fetal growth chart, provides one of the most commonly used – and most accurate – equations for estimating fetal height and weight. The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG) and the Society for Maternal and Fetal Medicine (SMFM) use Hadlock's figures to diagnose and manage fetal growth conditions, such as intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
The numbers on our chart should coincide with the numbers your healthcare provider will be checking against when they measure your baby using ultrasound. (Providers don't measure height after 13 weeks, however, so don't expect to get those numbers at your ultrasound appointments. )
)
Note that the data used by Hadlock was gathered from middle-class Caucasian women with no history of maternal diseases known to affect fetal growth and no evidence of congenital anomalies. Your provider may make adjustments based on your individual circumstances.
Fetal growth chart
Wondering how big your baby is during each week of pregnancy? The numbers in our chart below can give you a sense of your baby's size. Keep in mind that your baby may be much smaller or larger than these averages. That's okay – after all, healthy babies can weigh less than 5 pounds or more than 9 pounds at birth.
Boy's measurements are different than girl's measurements, even this early. For the numbers on our chart, we've taken an average of boys and girls. And remember, the height measurements up to 13 weeks are head-to-bottom estimates, while the height measurements starting at week 14 are head-to-toe estimates.
(head to toe)
| Gestational age | Length (US) | Weight (US) | Length (cm) | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (head to bottom) | (head to bottom) | |||
| 8 weeks | 0. 62 inches 62 inches | 0.71 ounces | 1.57 cm | 20 grams |
| 9 weeks | 0.91 inches | 0.95 ounces | 2.30 cm | 27 grams |
| 10 weeks | 1.22 inch | 1.23 ounces | 3.1 cm | 35 grams |
| 11 weeks | 1.61 inch | 1.59 ounces | 4.1 cm | 45 grams |
| 12 weeks | 2.13 inches | 2.05 ounces | 5.4 cm | 58 grams |
| 13 weeks | 2.64 inches | 2.58 ounces | 6.7 cm | 73 grams |
| (head to toe) | (head to toe) | |||
| 14 weeks | 5.79 inches | 3.28 ounces | 14.7cm | 93 grams |
| 15 weeks | 6.57 inches | 4.13 ounces | 16.7 cm | 117 grams |
| 16 weeks | 7. 32 inches 32 inches | 5.15 ounces | 18.6 cm | 146 grams |
| 17 weeks | 8.03 inches | 6.38 ounces | 20.4 cm | 181 grams |
| 18 weeks | 8.74 inches | 7.87 ounces | 22.2 cm | 223 grams |
| 19 weeks | 9.45 inches | 9.63 ounces | 24.0 cm | 273 grams |
| 20 weeks | 10.12 inches | 11.68 ounces | 25.7 cm | 331 grams |
| 21 weeks | 10.79 inches | 14.07 ounces | 27.4 cm | 399 grams |
| 22 weeks | 11.42 inches | 1.05 pounds | 29.0 cm | 478 grams |
| 23 weeks | 12.05 inches | 1.25 pounds | 30.6 cm | 568 grams |
| 24 weeks | 12.68 inches | 1.48 pounds | 32.2 cm | 670 grams |
| 25 weeks | 13. 27 inches 27 inches | 1.73 pounds | 33.7 cm | 785 grams |
| 26 weeks | 13.82 inches | 2.01 pounds | 35.1 cm | 913 grams |
| 27 weeks | 14.41 inches | 2.33 pounds | 36.6 cm | 1055 grams |
| 28 weeks | 14.80 inches | 2.67 pounds | 37.6 cm | 1210 grams |
| 29 weeks | 15.47 inches | 3.04 pounds | 39.3 cm | 1379 grams |
| 30 weeks | 15.95 inches | 3.44 pounds | 40.5 cm | 1559 grams |
| 31 weeks | 16.46 inches | 3.86 pounds | 41.8 cm | 1751 grams |
| 32 weeks | 16.93 inches | 4.30 pounds | 43.0 cm | 1953 grams |
| 33 weeks | 17.36 inches | 4.77 pounds | 44.1 cm | 2162 grams |
| 34 weeks | 17. 84 inches 84 inches | 5.24 pounds | 45.3 cm | 2377 grams |
| 35 weeks | 18.23 inches | 5.72 pounds | 46.3 cm | 2595 grams |
| 36 weeks | 18.62 inches | 6.20 pounds | 47.3 cm | 2813 grams |
| 37 weeks | 19.02 inches | 6.68 pounds | 48.3 cm | 3028 grams |
| 38 weeks | 19.41 inches | 7.13 pounds | 49.3 cm | 3236 grams |
| 39 weeks | 19.72 inches | 7.57 pounds | 50.1 cm | 3435 grams |
| 40 weeks | 20.08 inches | 7.98 pounds | 51.0 cm | 3619 grams |
| 41 weeks | 20.39 inches | 8.35 pounds | 51.8 cm | 3787 grams |
Thanks to Dr. Mark Curran, maternal-fetal medicine specialist, for his help preparing this chart.![]()
Advertisement | page continues below
Fetal weight by week: How it changes
Your baby steadily gains weight over the course of your pregnancy, but it's not always at the same rate. If you're having one baby (not twins or multiples), your baby's rate of growth accelerates until 35 weeks, then decelerates.
Here are some highlights, based on estimations:
- Up until 16 weeks, a fetus grows an average of about 19 grams per week, gradually increasing from 7 grams per week at 8 weeks to 15 grams per week at 12 weeks and 29 grams per week at 16 weeks.
- By 20 weeks, a fetus is gaining about 59 grams per week (just over 2 ounces).
- By 30 weeks, a fetus is gaining about 175 grams each week (more than 6 ounces).
- At 35 weeks, a fetus is gaining about 215 grams each week, or about 7.5 ounces. At this point their growth rate peaks.
- After 35 weeks, growth slows to about 188 grams per week, or 6.6 ounces. (Twins slow earlier, at around 28 weeks, and then average about 170 grams each week.
 )
) - In the last few weeks of pregnancy, the growth rate continues to gradually slow to about 168 grams (a little less than 6 ounces) per week by week 40.
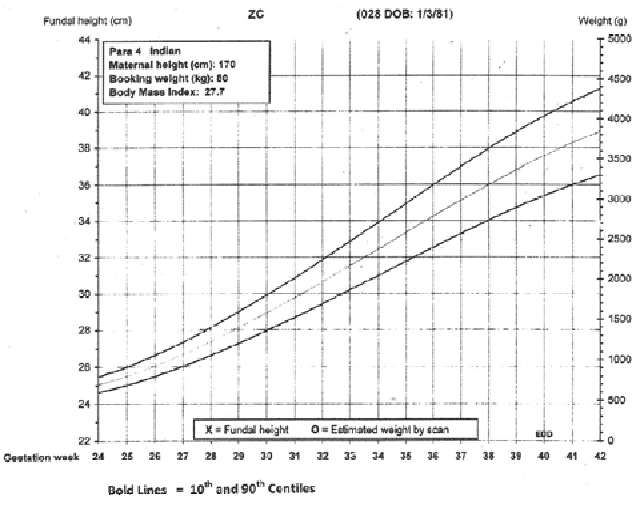
Using a tape measure stretched over your belly, your provider will use a fundal height measurement to check your baby's size at your prenatal visits. Beginning at about 24 weeks, the measurement in centimeters should roughly match the gestational age of your baby. If you're 26 weeks pregnant, for example, your fundal height should be about 26 cm, give or take a centimeter in each direction.
If your provider is concerned that your baby is too small, they'll monitor your baby's size with ultrasound, which is more accurate. Using ultrasound, your practitioner can take various measurements (head circumference and diameter, abdomen circumference, femur length) and use them to estimate your baby's size. They may also use a Doppler ultrasound to look at the blood flow to your placenta.
If your baby's estimated weight is less than the 10th percentile for their gestational age, they may be diagnosed with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), also called fetal growth restriction (FGR). IUGR can happen at any time during pregnancy. Some babies with IUGR just turn out to be small for their age, but sometimes there's a problem that's preventing the baby from growing properly.
IUGR can happen at any time during pregnancy. Some babies with IUGR just turn out to be small for their age, but sometimes there's a problem that's preventing the baby from growing properly.
At birth, a baby with IUGR is called "small for gestational age." While most SGA babies who are otherwise healthy grow just fine, some (especially those born prematurely) are at higher risk of problems such as c-section, jaundice, low blood sugar, and even long-term developmental and health problems.
Your baby's size by week
Here are some highlights of your baby's growth during pregnancy:
At 20 weeks, about the midpoint in your pregnancy, your baby is transmitting taste signals to their brain. And you may feel them hiccupping. Your baby's weight at 20 weeks is about 11.68 ounces, and they're about the length of a (10.12-inch) banana.
At 32 weeks, your baby's lungs are developing fast, and your baby's storing minerals like iron for their first 6 months of life. Your baby's weight at 32 weeks is 4. 30 pounds, and their length is 16.93 inches, about the size of a jicama.
30 pounds, and their length is 16.93 inches, about the size of a jicama.
At 33 weeks, things are getting snug in there! Your baby's skin is becoming less wrinkled as they fill in – your baby's weight at 33 weeks is about 4.77 pounds. At 17.36 inches, your baby is now about the size of a pineapple.
At 37 weeks, your baby's brain and lungs are still maturing, and they're still moving a lot, despite the close quarters. Your baby's weight at 37 weeks is about 6.68 pounds, and they're about the length of a bunch of Swiss chard, 19.02 inches.
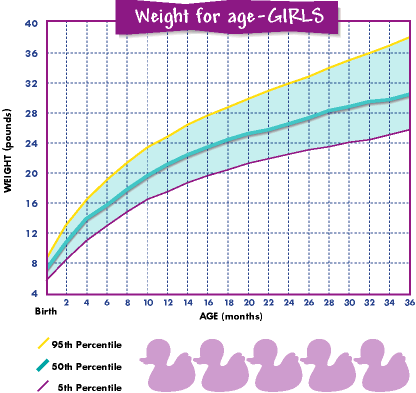
Once your baby is born, they'll be weighed and measured, and your provider will continue to monitor their growth. While the average newborn weight is a little over 7 pounds, most newborns lose about 5 to 10 percent of their weight in the first days. No worries – they gain it back by the time they're about 2 weeks old, and by 4 months they usually double their birth weight.
Learn more:
- To-do lists for the first, second, and third trimesters
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator
- How to understand pregnancy weeks, months, and trimesters
Fetal Chart from Baby My Baby
Free info for you and your baby! Text BABY to 511411
Search
Search for:
(crown to rump measurements)
| Gestational Age | Length (inches) | Weight (oz/lb) | Length (cm) | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 weeks | 0. 63 63 | 0.04 oz | 1.6 | 1 |
| 9 weeks | .9 | 0.07 oz | 2.3 | 2 |
| 10 weeks | 1.22 | 0.14 oz | 3.1 | 4 |
| 11 weeks | 1.61 | 0.25 oz | 4.1 | 7 |
| 12 weeks | 2.13 | 0.49 oz | 5.4 | 14 |
| 13 weeks | 2.19 | 0.81 oz | 7.4 | 23 |
| 14 weeks | 3.42 | 1.52 oz | 8.7 | 43 |
| 15 weeks | 3.98 | 2.47 oz | 10.1 | 70 |
| 16 weeks | 4.57 | 3.53 oz | 11.6 | 100 |
| 17 weeks | 5.12 | 4.94 oz | 13 | 140 |
| 18 weeks | 5.59 | 6.70 oz | 14.2 | 190 |
| 19 weeks | 6.02 | 8.47 oz | 15.3 | 240 |
| 20 weeks | 6.46 | 10. 58 oz 58 oz | 16.4 | 300 |
| 21 weeks | 10.51 | 12.70 oz | 26.7 | 360 |
| 22 weeks | 10.94 | 15.17 oz | 27.8 | 430 |
| 23 weeks | 11.38 | 1.10 lb | 28.9 | 501 |
| 24 weeks | 11.81 | 1.32 lb | 30 | 600 |
| 25 weeks | 13.62 | 1.46 lb | 34.6 | 660 |
| 26 weeks | 14.02 | 1.68 lb | 35.6 | 760 |
| 27 weeks | 14.41 | 1.93 lb | 36.6 | 875 |
| 28 weeks | 14.80 | 2.22 lb | 37.6 | 1005 |
| 29 weeks | 15.2 | 2.54 lb | 38.6 | 1153 |
| 30 weeks | 15.71 | 2.91 lb | 39.9 | 1319 |
| 31 weeks | 16.18 | 3.31 lb | 41.1 | 1502 |
| 32 weeks | 16. 19 19 | 3.75 lb | 42.4 | 1702 |
| 33 weeks | 17.20 | 4.23 lb | 43.7 | 1918 |
| 34 weeks | 17.72 | 4.73 lb | 45 | 2146 |
| 35 weeks | 18.19 | 5.25 lb | 46.2 | 2383 |
| 36 weeks | 18.66 | 5.78 lb | 47.4 | 2622 |
| 37 weeks | 19.13 | 6.30 lb | 48.6 | 2859 |
| 38 weeks | 19.61 | 6.80 lb | 49.8 | 3083 |
| 39 weeks | 19.96 | 7.25 lb | 50.7 | 3288 |
| 40 weeks | 20.16 | 7.63 lb | 51.2 | 3462 |
| 41 weeks | 20.35 | 7.93 lb | 51.7 | 3597 |
| 42 weeks | 20.28 | 8.12 lb | 51.5 | 3685 |
| 43 weeks | 20.20 | 8.19 lb | 51.3 | 3717 |
English
Table of norms for the size of the fetus by weeks of pregnancy
The size of the child by weeks of pregnancy is the average data by which doctors monitor the development of the fetus in the tummy of the expectant mother.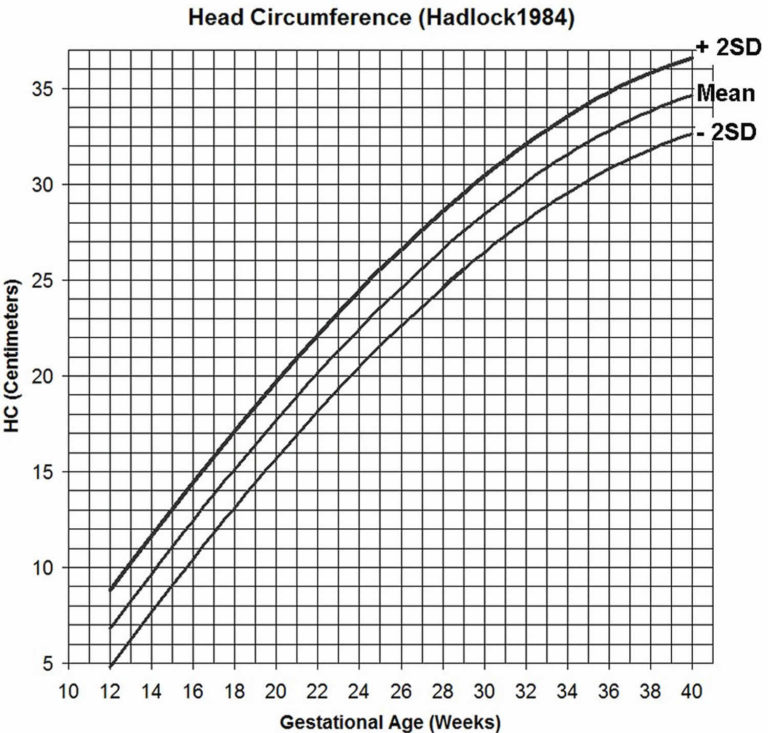 These figures are influenced by the genetic predisposition, the physical and emotional state of the woman.
These figures are influenced by the genetic predisposition, the physical and emotional state of the woman.
Dimensional indicators by which changes in the fetus are determined, and where to get them
The growth of the baby in the mother's tummy, its changes in weight and length are important indicators of its development and health. By 7-8 weeks, the baby weighs about a gram. But every day it grows and gains mass. Up to 15 weeks there is a rapid mass gain, after which it slows down. From the 2nd trimester, the weekly increase is about 80 grams and from 28 to 30 weeks, the increase goes up to 300 grams per week.
There are two ways to find out the weight of a child during pregnancy - calculated and by ultrasound.
- Estimated. Before ultrasonic examination (ultrasound) was tightly included in the everyday life of doctors, the mass of the baby in the abdomen was determined by the calculation method. How they did it: the gynecologist measured the height of the fundus of the uterus and the circumference of the abdomen of the expectant mother with a centimeter tape.
 These values were multiplied among themselves and received the approximate weight of the baby. This method did not take into account the amount of amniotic fluid, the constitution of the mother, the genetic predisposition and the presentation of the child. This calculation method gives fairly accurate readings after the 32nd week of pregnancy. Before this period, the error of the method is up to 200 grams.
These values were multiplied among themselves and received the approximate weight of the baby. This method did not take into account the amount of amniotic fluid, the constitution of the mother, the genetic predisposition and the presentation of the child. This calculation method gives fairly accurate readings after the 32nd week of pregnancy. Before this period, the error of the method is up to 200 grams.
- ultrasound. Ultrasound examination is planned for each woman 3 times during pregnancy (1 time per trimester). Unscheduled ultrasound is prescribed according to indications.
Doctors in polyclinics and antenatal clinics are guided by the data of ultrasound examinations. On ultrasound, the exact gestational age is established and the main indicators of the development of the baby in the mother's tummy are recorded.
By what indicators does an ultrasound specialist determine the intrauterine development of a child (abbreviation in English is given in brackets):
- MP (FW) - fetal weight.
- KTP (CRL) is the coccyx-parietal size. It determines the exact gestational age and size of the baby.
- BPD (BPD) is the biparietal head size.
- OFD is the distance from the frontal bone to the center of the occipital bone. According to the BPR and LZR indicators, the child's growth and development are assessed.
- DB (FL) - the length of the femur.
- OG (HC) - head circumference.
- coolant (AC) - abdominal circumference.
Changes by week (with tables): norms
To monitor the intrauterine development of the baby, doctors use the norms of the child's weight by weeks of pregnancy, in which averaged data are used.
| Gestational age (weeks) | Approximate length of the child, (cm) | Approximate weight of the child, (g) |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | 3 | |
| 8 | 5 | |
| 9 | 7 | |
| 10 | 9 | |
| 11 | 4.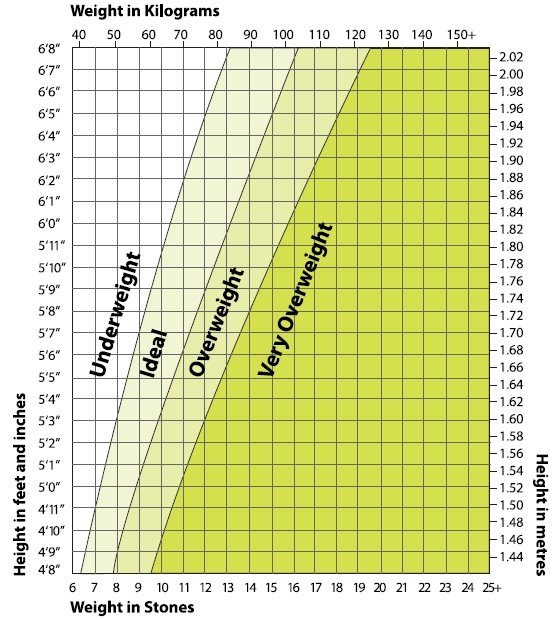 1 1 | 11 |
| 12 | 5.4 | 19 |
| 13 | 7.4 | 31 |
| 14 | 8.7 | 52 |
| 15 | 10.1 | 77 |
| 16 | 11.5 | 118 |
| 17 | 13 | 160 |
| 18 | 14.2 | 217 |
| 19 | 15.3 | 270 |
| 20 | 25.8 | 345 |
| 21 | 26.7 | 410 |
| 22 | 27.8 | 506 |
| 23 | 28.9 | 607 |
| 24 | 30 | 733 |
| 25 | 34.6 | 844 |
| 26 | 35.6 | 969 |
| 27 | 36.6 | 1 135 |
| 28 | 37.6 | 1 319 |
| 29 | 38.6 | 1482 |
| 30 | 39. 9 9 | 1636 |
| 31 | 41.1 | 1 779 |
| 32 | 42.4 | 1930 |
| 33 | 43.8 | 2088 |
| 34 | 45 | 2 248 |
| 35 | 46.2 | 2414 |
| 36 | 47.4 | 2612 |
| 37 | 48.6 | 2820 |
| 38 | 49.8 | 2992 |
| 39 | 50.7 | 3 170 |
| 40 | 51.2 | 3 373 |
Parents receive more accurate data on the intrauterine development of their baby by ultrasound.
First trimester
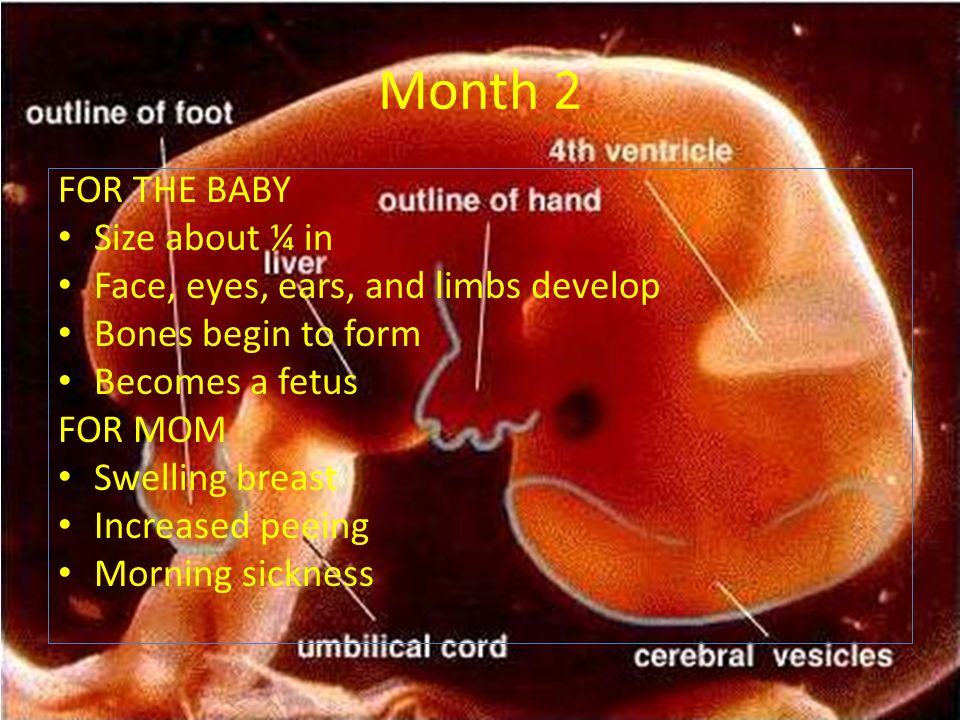
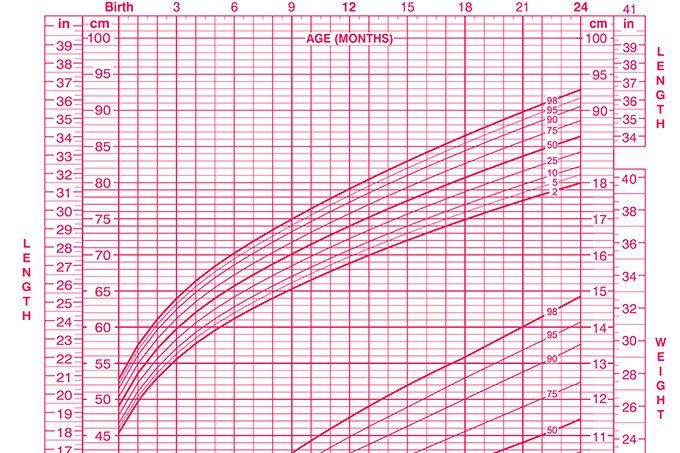
The first trimester is the period from weeks 1 to 13. By ultrasound, the size of the fetus is estimated from 10 to 11 weeks (before this period, ultrasound is not informative).
Table of normal development of the baby in the 1st trimester according to the results of ultrasound
| Gestational age (weeks) | Height, cm | Weight, g | dB, mm | DGK, mm | BPR, mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 6. 8 8 | 11 | 7 | 20 | 18 |
| 12 | 8.2 | 19 | 9 | 24 | 21 |
| 13 | 10.0 | 31 | 12 | 24 | 24 |
Second trimester
The second trimester is the 14th to 27th week of gestation.
Average fetal weight by week of pregnancy in the table (according to ultrasound results)
| Gestational age (weeks) | Height, cm | Weight, g | dB, mm | DGK, mm | BPR, mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 12.3 | 52 | 16 | 26 | 28 |
| 15 | 14.2 | 77 | 19 | 28 | 32 |
| 16 | 16.4 | 118 | 22 | 34 | 35 |
| 17 | 18.0 | 160 | 24 | 38 | 39 |
| 18 | 20.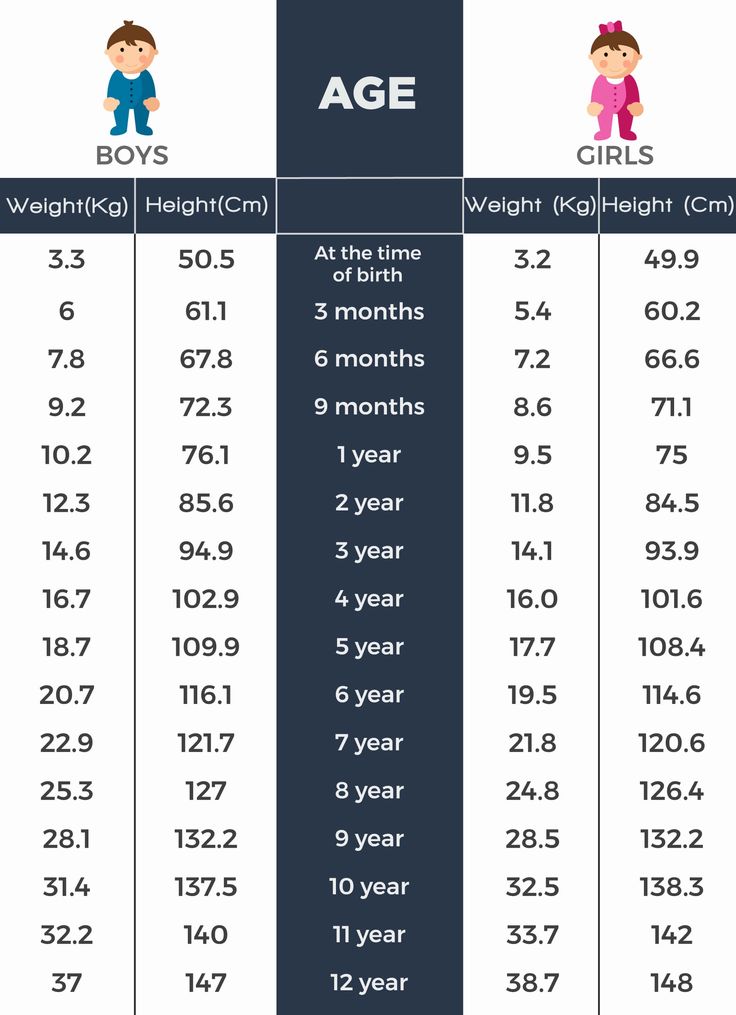 3 3 | 217 | 28 | 41 | 42 |
| 19 | 22.1 | 270 | 31 | 44 | 44 |
| 20 | 24.1 | 345 | 34 | 48 | 47 |
| 21 | 25.9 | 416 | 37 | 50 | 50 |
| 22 | 27.8 | 506 | 40 | 53 | 53 |
| 23 | 29.7 | 607 | 43 | 56 | 56 |
| 24 | 31.2 | 733 | 46 | 59 | 60 |
| 25 | 32.4 | 844 | 48 | 62 | 63 |
| 26 | 33.9 | 969 | 51 | 64 | 66 |
| 27 | 35.5 | 1 135 | 53 | 69 | 69 |
Third trimester
The third trimester is the gestation period from the 28th week.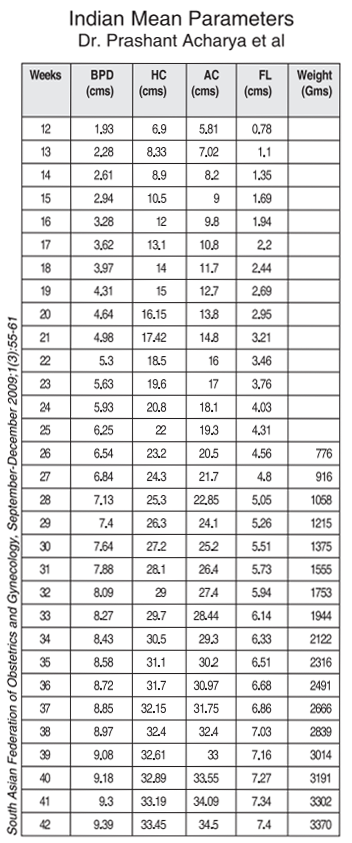
Approximate height and weight of the child by weeks of pregnancy in the table (determined by ultrasound results)
 8
8 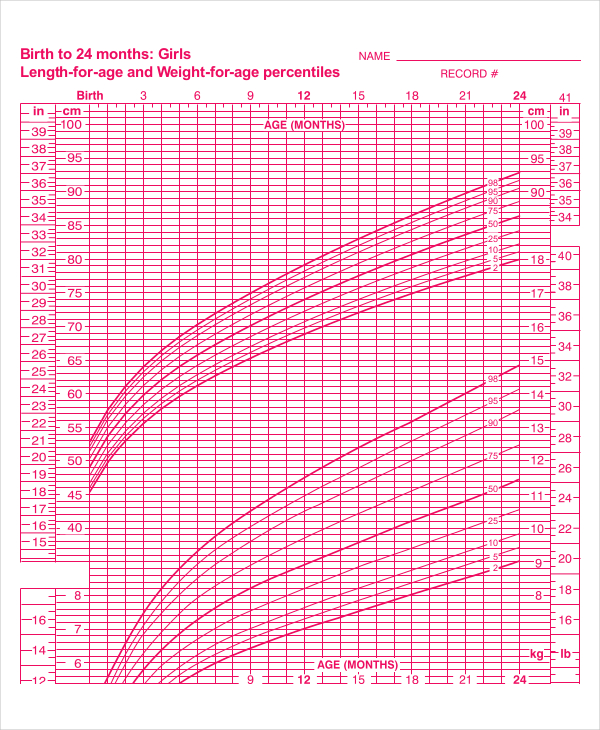 6
6
Is it possible to increase the weight of the fetus during pregnancy?
Let's figure out what determines the weight of the fetus during pregnancy, and how the expectant mother can correct the underweight of the crumbs:
- Nutrition.
 If the mother is malnourished, then the baby also receives less nutrients and slows down in development.
If the mother is malnourished, then the baby also receives less nutrients and slows down in development.
- Indolent diseases. If a mother has exacerbated chronic diseases during pregnancy, then her general condition can negatively affect the weight gain of the baby.
- Smoking. According to research by experts from the World Health Organization (WHO), smoking mothers increase the risk of having babies with underweight.
- Stress, emotional overload of the mother reduce her appetite, metabolic rate and overall body tone. This directly affects the absorption of nutrients by the child. The more harmonious and calmer the emotional state of a woman, the easier the gestation and intrauterine development of the child.
If the expectant mother takes care of her health, she will notice that from the 28th week her weight (and the weight of the baby) is growing rapidly. The average indicators of how much a child gains in the last weeks of pregnancy are reduced to 250 - 300 grams weekly.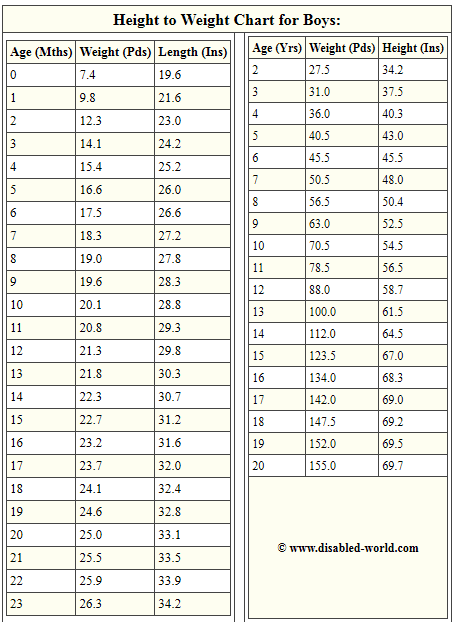
Supervision by a specialist will help to keep the development of the baby under control, to ensure that it is within the normal range. If a pregnant woman develops preeclampsia, swelling, high blood pressure, the doctor will prescribe drugs and procedures that will help to go through a difficult period easier.
Remember that heredity affects the weight and height of a child, whether it is the first pregnancy or not, the physical and emotional state of the mother.
Be healthy and have an easy pregnancy!
Weekly pregnancy weight calculator
The weight of the expectant mother is very important for the development of the fetus. It is desirable to have a normal body weight before pregnancy. Lack of weight is a serious risk factor, as a result of which a child may be born too small.
Being overweight increases the likelihood of having an oversized baby. In such situations, only a timely caesarean section made by obstetricians can help.
Weight in the first trimester
In addition to body weight before conception, weight during pregnancy by weeks and its constant control play an important role.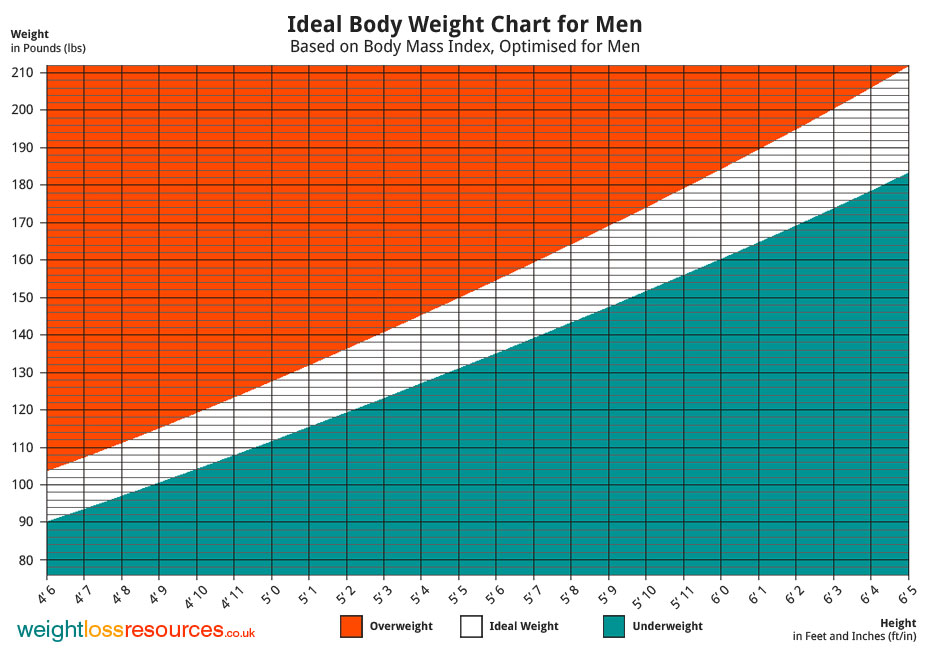 In the first couple of months, it increases slowly, the baby and mother only adapt to each other. During this period, there are frequent cases of toxicosis, which additionally reduces weight. During the first trimester of pregnancy, a woman gains about 1.5 kg.
In the first couple of months, it increases slowly, the baby and mother only adapt to each other. During this period, there are frequent cases of toxicosis, which additionally reduces weight. During the first trimester of pregnancy, a woman gains about 1.5 kg.
Weight in the second half of pregnancy
Intensive weight gain occurs in the second half of the term. Most women gain only 40% in the first 4 months, and the remaining 60% in the second half. However, it also happens the other way around - in some women, weight during pregnancy is gained week by week faster in the first months, there is no pathology in this.
The increase is distributed as follows:
| Fat | 28% |
| Water | 13% |
| Fruit | 27% |
| Blood | 10% |
| Uterus | 8% |
| amniotic fluid | 6% |
| Placenta | 5% |
| Mammary glands | 3% |
Permissible weight gain
If we take the allowable value of weight gain in women, then it is 350 g per week (50 g per day), with a maximum of 500 g per week. Using the weight calculator during pregnancy, you can find out what it should be at different times. To exceed this norm, it is desirable to lead an active life and monitor nutrition. Although an extra increase is undesirable, in no case should you exhaust yourself with hunger strikes. And there is nothing good in the abuse of flour products in an attempt to get to the norm either. You need to eat something that will benefit not only you, but also the child.
Using the weight calculator during pregnancy, you can find out what it should be at different times. To exceed this norm, it is desirable to lead an active life and monitor nutrition. Although an extra increase is undesirable, in no case should you exhaust yourself with hunger strikes. And there is nothing good in the abuse of flour products in an attempt to get to the norm either. You need to eat something that will benefit not only you, but also the child.
To obtain an accurate calculation, enter the following digital data into the pregnancy weight calculator:
- initial weight;
- growth;
- approximate gestational age in weeks.
What causes the difference in weight in different women at the same time?
The difference can be due to several reasons. One of them is age; with increasing age, the tendency to be overweight also increases. More weight is gained by women with a lack of mass before pregnancy and who have undergone early toxicosis. The body thereby tries to compensate for the losses.
The body thereby tries to compensate for the losses.
An important factor is the peculiarity of the constitution, the difference with the indications of the weight calculator during pregnancy by weeks may be due to a tendency to thinness or fullness. It also depends on the size of the baby: the larger it is, the larger the placenta will be. Sometimes a sharp increase in the appetite of the expectant mother leads to intensive weight gain, it is quite difficult to deal with it.
How is the weight gained distributed?
The normal weekly weight gain during pregnancy is as follows:
- the uterus accounts for 0.9 kg;
- adipose tissue of the order of 2.2 kg;
- the child weighs about 3.3 kg;
- tissue fluid - 2.7 kg;
- amniotic fluid approximately 1.2 kg;
- mammary glands increase by 0.5 kg
- circulating blood - per 1.2 kg.
Approximately 12.1 kg. In case of multiple pregnancy, at least 2-4 kg must be added to the figures obtained.