Does yeast infection cause itching
What is a Yeast Infection?
In This Section
- Vaginitis (yeast infection & bacterial vaginosis)
- How do I get checked and treated for vaginitis?
- How do I prevent vaginitis?
- What is a yeast infection?
- What is bacterial vaginosis?
Most healthy vaginas have yeast. But sometimes your yeast grows too much and leads to an infection. Yeast infections can be very irritating and uncomfortable.
What causes yeast infections?
A vaginal yeast infection, which is also sometimes called vulvovaginal candidiasis, happens when the healthy yeast that normally lives in your vagina grows out of control. It often leads to itching and other irritating symptoms. The medical name for a yeast infection is "candidiasis," because they’re usually caused by a type of yeast called candida.
If your vaginal chemistry gets thrown off balance, the normal yeast that live in your vagina can grow too much and lead to an infection. Some things that can cause changes in your vagina’s environment are:
-
normal changes in hormone levels (like during your menstrual cycle)
-
antibiotics, cortisone, and other drugs
-
pregnancy
-
diabetes
-
a weak immune system
-
a natural reaction to another person's genital chemistry
Yeast infections can happen on penises and scrotums too, but it’s not as common. They can cause redness and irritation on your penis or scrotum.
They can cause redness and irritation on your penis or scrotum.
Yeast infections aren’t an STD. They aren’t contagious, and can’t spread to another person during sex. But sexual contact sometimes leads to yeast infections — your body chemistry can have a bad reaction to another person’s natural genital yeast and bacteria, which causes yeast to grow.
People can also get a yeast infection on their mouth, throat, or tongue — that’s called "thrush."
What are yeast infection symptoms?
Yeast infections often cause thick, white, clumpy vaginal discharge that usually doesn’t smell (or only smells slightly different than normal). You might also have a creamy, whitish coating in and around your vagina.
Most yeast infections lead to itching, burning, and/or redness in or around the vagina. Vaginal itching usually gets worse the longer you have the infection. Sex may be uncomfortable or painful. In extreme cases, you can get fissures or sores on your vagina or vulva.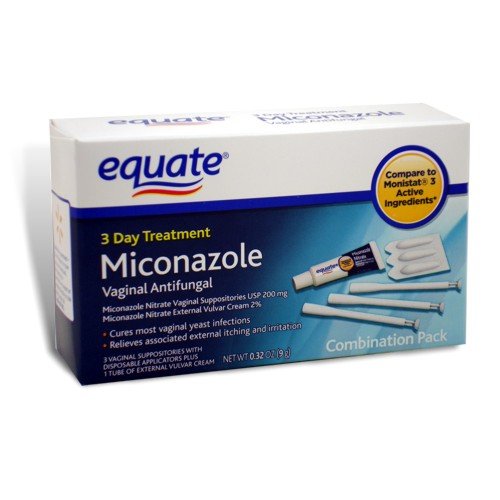 If you have lots of irritation, it may sting when you pee.
If you have lots of irritation, it may sting when you pee.
How do I treat yeast infections?
Yeast infections can usually be cured easily in a few days with anti-fungal medicine. You can get medicated creams or suppositories for yeast infections (like Monistat and other brands) at a drugstore, over-the-counter without a prescription.
Make sure you follow the directions and use all of the medicine, even if your symptoms go away before you finish. You can also treat yeast infections with a single pill that you swallow (called Diflucan or Fluconazole). You need a prescription from your doctor to get the yeast infection pill.
Don’t have vaginal or oral sex, or put anything into your vagina, until you’ve finished treatment and your infection goes away. Friction from sex can cause more irritation or make it harder to heal. And some medicines that you use in your vagina have oil in them, which can cause condoms to break.
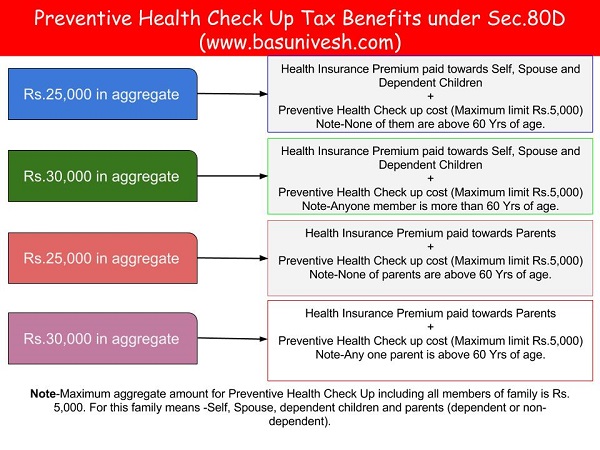
Even though yeast infections can be really itchy, try not to scratch. It can make irritation worse or cause cuts in your skin, which can spread germs and lead to more infection. There are over-the-counter creams that you can use on your vulva to help calm the irritation. Your doctor can also give you tips on relieving burning and itching.
It can make irritation worse or cause cuts in your skin, which can spread germs and lead to more infection. There are over-the-counter creams that you can use on your vulva to help calm the irritation. Your doctor can also give you tips on relieving burning and itching.
If you finish your treatment and your symptoms persist for more than a week, talk to your nurse or doctor to see what’s going on. You may require further treatment or something else may be causing the irritation. You can always schedule an appointment at your local Planned Parenthood health center.
Was this page helpful?- Yes
- No
Help us improve - how could this information be more helpful?
How did this information help you?
Please answer below.
Are you human? (Sorry, we have to ask!)
Please don't check this box if you are a human.
You’re the best! Thanks for your feedback.
Thanks for your feedback.
Do I Have a Yeast Infection or Something Else?
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- Some STDs
- Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
- Allergies or Other Skin Conditions
- Hemorrhoids
- Not Enough Estrogen
Yeast infections can be uncomfortable, but they’re usually not serious. You may have itching or irritation in or around your vagina, as well as a thick, white discharge. In many cases, an antifungal treatment will clear up your symptoms.
If you’re not sure whether you have a yeast infection or something else, it’s important to see a doctor for the right diagnosis and treatment. This is important. If you don’t really have a yeast infection, antifungals won’t help you get better. They can actually prolong the real problem, because while you’ll think you’re treating the issue, the real cause will continue to develop.
There are several reasons you might have symptoms that are like a yeast infection.
Some STDs
Herpes, genital warts and trichomoniasis (trich) can also cause irritation, itchiness, and discharge that has a slight odor. With other sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea, you don’t always have symptoms, but you might experience pain and burning when you pee.
STDs often need a different kind of treatment than a yeast infection. For example, trich isn’t caused by a fungus. It’s caused by bacteria. To treat it, you’ll usually need to take strong antibiotics for a short period of time.
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
This is an infection that’s caused by an overgrowth of bacteria. There’s no specific cause for it, but along with redness and itchiness, you might notice discharge that’s gray or white and has a fishy odor.
If you have BV, your doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics like metronidazole or tinidazole, or vaginally applied antibiotic creams or gels with metronidazole or clindamycin.
Allergies or Other Skin Conditions
Cleaning products can trigger symptoms if you’re allergic to one or more of their ingredients. Soaps and feminine hygiene products can sometimes do this, as can laundry detergents.
Certain skin conditions can also cause itching and other symptoms. They sometimes require treatment with steroid ointments like hydrocortisone.
Small cuts can even feel itchy and irritated while they’re healing.
Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids may be itchy. They can affect the area in and around the vagina. too. Typical home treatments are a sitz bath (warm water you sit in to help relieve pain in your bottom or around your private parts) or witch hazel wipes to soothe the symptoms.
Not Enough Estrogen
As you get older, your level of estrogen goes down. This can cause changes in your body, like thinner skin. That can lead to uncomfortable symptoms like itching and discharge.
Sometimes, using a vaginal lubricant to reduce friction can help.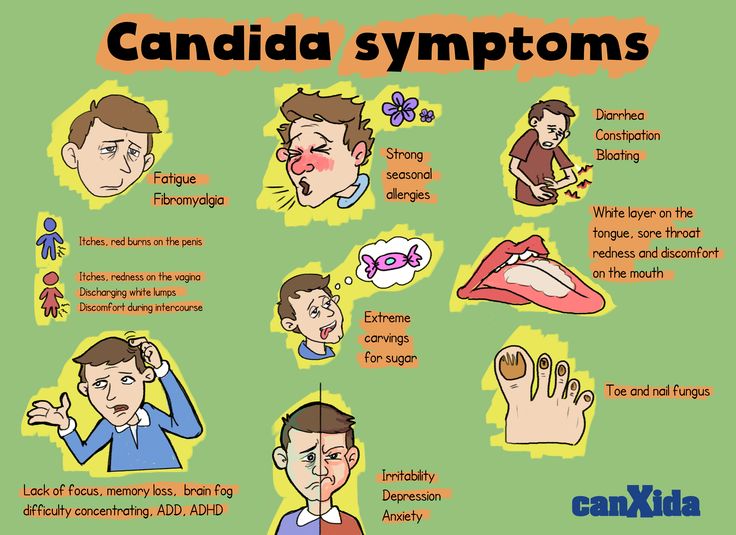 You may also want to talk to your doctor about taking a small dose of estrogen.
You may also want to talk to your doctor about taking a small dose of estrogen.
Women's Health Guide
- Screening & Tests
- Diet & Exercise
- Rest & Relaxation
- Reproductive Health
- Head to Toe
Dermatomycosis (fungal diseases) - infectious lesions of the skin and its appendages. Allocate pathological changes in smooth surfaces, folds, hands, feet and scalp. These lesions occur in 20-30% of the world's population. The frequency of diseases increases with age. Recently, not only adults, but also children suffer from them.
Causes of ringworm
The causative agents of lesions are dermatophyte fungi.
The main reasons for the development of diseases include a number of factors, including:
- Dermatoses.
 Often, fungal skin diseases are diagnosed in people with psoriasis, eczema, and neurodermatitis. The development of pathology is facilitated by permanent injuries of the skin, as well as the use of corticosteroids for therapy and impaired local immunity. High risks of infection are when corns and diaper rash occur, as well as with excessive sweating
Often, fungal skin diseases are diagnosed in people with psoriasis, eczema, and neurodermatitis. The development of pathology is facilitated by permanent injuries of the skin, as well as the use of corticosteroids for therapy and impaired local immunity. High risks of infection are when corns and diaper rash occur, as well as with excessive sweating - Occupational factors. Fungal skin diseases are often found in athletes, miners and military personnel. This is due to the fact that the wearing of special shoes and clothing, closed areas and the presence of a large number of common areas contribute to lesions
- Non-observance of hygiene rules. Dermatomycosis is usually diagnosed with improper cleansing of the skin, neglect of the usual hand washing, violation of the rules for washing common areas
The risks of fungal diseases also increase with some chronic pathologies. Among them: chronic leg ischemia, diabetes mellitus, venous insufficiency. Against the background of a decrease in general immunity, an exacerbation of the infection occurs.
Classification of fungal diseases of the skin
In dermatology, there are several approaches to the systematization of pathologies. Basically, the following main forms of dermatomycosis are distinguished:
- Scalp
- Large skin folds
- Hands and feet
- Nail
- Smooth leather
The treatment of each fungal skin disease in this classification requires an individual and comprehensive approach.
Important! You should contact your doctor as soon as possible. Otherwise, serious complications may develop, which may complicate therapy. Self-medication is strictly prohibited! It can lead to deterioration not only of the skin, but of the whole organism.
Symptoms of fungal skin diseases in which you should consult a doctor
Clinical manifestations of the pathology largely depend on the location of the lesion.
Mycosis of the scalp, for example, is characterized by the appearance of bright red plaques, covered with gray scales on top. In some cases, deep foci of inflammation are formed. The pathology is characterized by breaking off of the hairs at the root, at a height of about 5–8 mm. Patients usually complain of severe itching and rapid hair contamination.
In some cases, deep foci of inflammation are formed. The pathology is characterized by breaking off of the hairs at the root, at a height of about 5–8 mm. Patients usually complain of severe itching and rapid hair contamination.
Mycoses of skin folds are characterized by edematous pink rounded spots with a smooth surface and clear contours. If timely therapy is not carried out, individual foci merge into a single one with the formation of vesicles and crusts. Patients complain of excruciating itching.
With mycosis of the feet, peeling is noticeable on their surfaces. Usually cracks do not become inflamed and do not bleed. In some cases, plaques and calluses form on the feet.
With onychomycosis (nail lesions), grayish-yellow stripes appear on the plates. In this case, the nails become brittle and prone to deformation. If the pathology is running, itching and discomfort occur. In some cases, the transparency of the nails is reduced, and their edges are thickened, may be bent.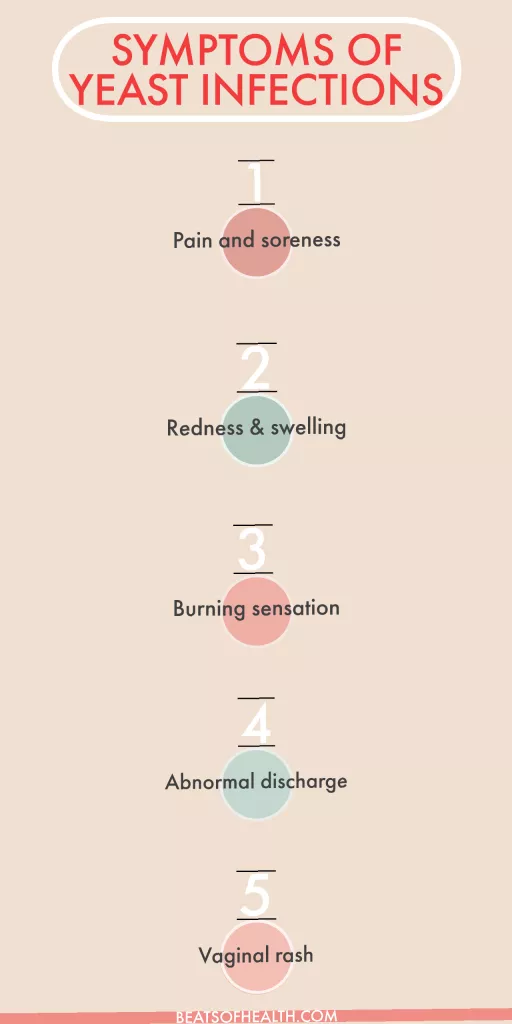
Mycosis of smooth skin is characterized by the formation of scaly flat pink and red spots. Inflamed areas may appear along their borders. Due to increased pigmentation, the central parts of the spots turn brown. Patients complain of pain, itching and burning of the affected areas.
Diagnostics
The examination is organized by a dermatologist. It begins with a skin examination, for which a dermatoscope and a Wood's lamp are used. The doctor also collects an anamnesis. Thanks to him, the specialist can identify the causes of fungal skin lesions.
Comprehensive diagnostics includes:
- Scrapings. They are performed from the affected areas. The microscopic method allows you to quickly detect fungal spores or mycelium. To clarify the pathogen, a mycological study is carried out
- Complete blood count. It allows to identify concomitant diseases of internal organs
- Biochemical blood test. It also allows you to assess the general condition of the patient
If necessary, the patient is referred for consultations with narrow specialists. Such consultations are relevant, since dermatomycosis often develops against the background of chronic diseases of internal organs.
Such consultations are relevant, since dermatomycosis often develops against the background of chronic diseases of internal organs.
Possible complications
Cracks and erosions that appear on the skin with fungal infections are the entrance gate for bacteria. Therefore, this pathology can provoke:
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Plantar warts, etc.
When patients self-medicate, the risk of more serious complications increases. Therefore, it is not worth delaying a trip to the doctor. Only he can timely prescribe the necessary therapy and prevent the deterioration of the patient's condition.
Methods for the treatment of fungal skin diseases
Conservative therapy
Always carried out in a complex and individual way. Means are selected taking into account a number of factors, including not only the type of pathology, but also the personal characteristics of the patient, his secondary diseases.
The treatment of any fungal skin disease is impossible without the elimination of the pathogenic fungus. For this purpose, antimycotics are prescribed. When selecting them, the dermatologist takes into account the general condition of the patient, the depth of the lesion and other factors.
The patient may be advised:
- Special antifungal ointments. They are applied directly to the affected areas several times a day. Ointments are used in courses until the symptoms of the disease are eliminated
- Antifungal varnishes. They are convenient for damage to the nail plates. Such products are distinguished not only by ease of use, but also by a pronounced therapeutic effect
- Fungicidal solutions. They are used for the purpose of antiseptic treatment of affected areas
- Systemic preparations. Such remedies are especially effective in moderate and severe cases of the disease. Usually these drugs are combined with topical
Antihistamine therapy is given to reduce swelling and itching. In case of circulatory disorders, the doctor may recommend drugs that improve microcirculation processes.
In case of circulatory disorders, the doctor may recommend drugs that improve microcirculation processes.
Also used in complex therapy:
- Vitamin and mineral preparations
- Herbal remedies
- Adaptogens
In some cases, for lesions of the nail plates, hands and feet, procedures such as medical manicure and pedicure are relevant. They involve the treatment of nails and skin with an antiseptic, the removal of dead areas with cutters, the application of special preparations to saturate tissues with valuable nutrients.
The patient may also be advised to undergo a course of physiotherapy. Treatment of fungal diseases of the skin is carried out using the methods of ultraviolet radiation, amplipulse, diathermy.
Surgical interventions
Usually they are carried out for lesions of the nail plates. In this case, the nail is simply removed with a laser, radio frequency or standard scalpel. Surgical treatment is also relevant for abscesses and phlegmon. It allows you to open and drain the bacterial focus.
It allows you to open and drain the bacterial focus.
Prevention
The basis for preventing the development of pathology is the observance of personal hygiene rules. It is important to accustom yourself to the use of personal towels, combs and other items. You should also wash your hands regularly and refrain from walking barefoot in public places.
Important measures to prevent fungal skin diseases include:
- Elimination of excessive dryness of the skin
- Correction of excessive sweating
- Timely removal of diaper rash
If irritation and cracks or other damage appear on the skin, you should immediately contact a dermatologist and not start the problem.
Benefits of contacting MEDSI
- Modern expert class equipment. It allows you to quickly identify the problem, its cause, stage of development and other features
- Multidisciplinary approach. It allows you to provide complex therapy.
 Our specialists understand that dermatomycosis is often provoked not only by external, but also by internal factors, and they are able to successfully eliminate them. Each patient is guaranteed to receive an individual set of funds
Our specialists understand that dermatomycosis is often provoked not only by external, but also by internal factors, and they are able to successfully eliminate them. Each patient is guaranteed to receive an individual set of funds - Treatment according to the latest recommendations (including international ones). The therapy is carried out with high efficiency and in the shortest possible time. This allows you to return to a full life, forgetting about itching and other unpleasant symptoms of pathology
- Minimally invasive techniques. Thanks to them, the risk of complications is reduced and the rehabilitation period is shortened
To clarify the conditions for the treatment of fungal skin diseases or make an appointment with a dermatologist, just call +7 (495) 7-800-500. Our specialist will answer all questions. Recording is also possible through the SmartMed application.
Do not delay treatment, see a doctor now:
- Dermatologist appointment
- Treatment of nail diseases, care and restoration
- Pediatric dermatologist consultation
Fungal infections
According to official international statistics on the prevalence of in the world, fungal infections have been ranked second among all skin diseases for many years in a row. They not only reduce the quality of life and cause discomfort, but also provoke allergic reactions, chronic inflammatory processes and many other pathologies.
They not only reduce the quality of life and cause discomfort, but also provoke allergic reactions, chronic inflammatory processes and many other pathologies.
Analyzes
Microscopic examination of the discharge of the urinary organs of men (urethra)
1-2 days
from 325 ₽
Add to cart
Microscopic examination of the discharge of the urinary organs of women (vagina, cervical canal) 90-02 9002 2 days
from 315 ₽
Add to cart
Candida albicans
1-2 days
from 200 ₽
Add to cart
Due to the peculiarities of their microbiological nature, fungal diseases can be actively transmitted from the carrier to a healthy person, and in addition to the skin, affect the nail plates, hair, internal organs and cause their various pathogenic changes. Some fungi are prone to recurrence, have a fairly long incubation period and very similar external manifestations. At the same time, some types of mycoses are treated only with oral preparations, others with cutaneous forms, therefore it is absolutely impossible to self-medicate and contact specialists at the first symptoms.
At the same time, some types of mycoses are treated only with oral preparations, others with cutaneous forms, therefore it is absolutely impossible to self-medicate and contact specialists at the first symptoms.
When tests for fungal infections are ordered
By external signs, it is only possible to initially diagnose a fungal disease. Therefore, with redness of the skin, focal lesions of the smooth and hairline, as well as with itching in the foot or skin folds, changes in the shape and color of the nail plate, dermatologists prescribe laboratory tests. This allows you to correctly diagnose the nosological form, and, therefore, to select the most effective set of therapy, take the necessary measures to localize the infection and minimize possible side effects.
Types of fungal diseases
Microscopic pathogenic fungi in medical practice have a common name - mycosis (Greek mycosis). Today, more than 100 species of parasitic and pathogenic microfungi are classified, and we will single out the main infections that affect adults and children.
Dermatomycosis
Common fungal diseases that affect the skin, nails and hair. The source of infection can be a person or an animal. They manifest themselves with various symptoms, we will only indicate the most common diseases in our geographical area:
- rubromycosis is a disease caused by the anthropophilic fungus Trichophyton rubrum. Differs in a variety of clinical manifestations and localization of foci on any part of the body, can affect smooth skin, hair follicles and nails;
- Mycosis of the foot (epidermophytosis), also affecting the interdigital folds. Very similar to candidal lesion, and sometimes there is a polymycotic infection;
- favus - a rare form accompanied by severe baldness of the head. Can be transmitted through combs, underwear, and shaving and haircutting tools;
- microsporia - trichomycosis caused by the microsporum fungus. On smooth skin it appears as red spots of a clear shape with a peripheral roller, and on the scalp - with small scaly foci;
- trichophytosis (synonymous with ringworm).
 Outwardly, it is manifested by pink-red focal lesions of the skin on any part of the body;
Outwardly, it is manifested by pink-red focal lesions of the skin on any part of the body; - Athlete's skin folds . Accompanied by itching, redness and peeling.
Keratomycosis
Mycoses predominantly of the stratum corneum. Among them, the most famous are piedra, erythrasma and bran lichen.
Superficial mycoses are often ignored by many ordinary people, because if multi-colored lichen can be primarily identified by yellowish-brown spots covered with pityriasis scales, then erythrasma is often perceived as age-related darkening of the skin. This is due to the fact that the disease progresses slowly and is localized on the inner surface of the thighs, in the inguinal folds and under the mammary glands in women. The dim darkening of the skin affected by erythrasma is covered with small scaly scales, and although the disease almost does not cause itching, it sharply reduces the protective properties of the skin and spoils the appearance of the infected.
Candidiasis
Diseases caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candidosis, which includes more than 150 varieties. They are considered the most dangerous and most common, as they are found throughout the world and can be transmitted from people, birds and pets. In this case, in addition to skin manifestations of candidiasis can:
- affect mucous membranes;
- penetrate deeply into tissues and organs;
- cause septic diseases and allergic changes in the body.
Candidiasis can manifest as a localized and widespread rash on the hands and feet, lesions of the nail folds and scalp, in the form of stomatitis, cheilitis and gingivitis. With internal infection, they cause vulvovaginitis, urethritis, pleuropneumonia, endocrites, meningitis and other diseases.
Visceral and systemic mycoses
Fungal lesions of internal organs caused by infection with taxonomic microfungi and accompanied by severe lesions of the skin, visceral (internal) organs, subcutaneous tissue, nervous system, and even the musculoskeletal system. This group includes more than two dozen fungi, among which there are pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic. The most common are actinomycosis, aspergillosis, histoplasmosis, coccidiodiasis, sporotrichosis, chromomycosis and others.
This group includes more than two dozen fungi, among which there are pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic. The most common are actinomycosis, aspergillosis, histoplasmosis, coccidiodiasis, sporotrichosis, chromomycosis and others.
As a rule, deep mycoses are transmitted indirectly and are difficult to diagnose. Some pathogens demonstrate amazing survivability and resistance to drug therapy, high pathogenicity and significant contagiousness, and can lead to disability and death. Most systemic mycoses act as opportunistic infections in patients with hepatitis and AIDS.
Methods for the diagnosis of fungal infections
Microbiological methods
Microscopy is the most accessible and simple diagnostic method. The study is aimed at confirming infection with superficial mycosis, for which biological material is taken from the patient, which is potentially considered infected: scraping of a pathologically altered nail or skin, eyelash, hair. It refers to qualitative analyzes and allows only to establish or refute the fact of infection. The study takes several days: the resulting material is processed (stained) in a certain way and transferred to microscopic examination to identify elements of the fungus (spores, hyphae).
The study takes several days: the resulting material is processed (stained) in a certain way and transferred to microscopic examination to identify elements of the fungus (spores, hyphae).
Microscopy allows you to quickly confirm mycosis, but the type of pathogen and its quantitative concentration is established only for yeast-like and mold species. Therefore, it is often supplemented by cultural research (bakposev). The results of microbiological studies must be interpreted by the attending specialist.
ELISA
Enzyme immunoassay is a modern and highly reliable method for identifying fungi in a patient's venous blood. It is a qualitative and quantitative method and can be used as a primary diagnosis and act as a confirmatory analysis of superficial and visceral mycoses.
The method is based on the detection and identification of an immunoglobulin protein to a specific pathogen. Antibodies and antigens provide reliable information about infection with aspargillosis, candidiasis, cryptococcus and dimorphic microfungi. The result of the test is interpreted as "positive" (there is infection) or "negative" (no fungal infection). In some cases, the study may give a questionable result, as a rule, this happens if the patient has recently taken antibacterial drugs.
The result of the test is interpreted as "positive" (there is infection) or "negative" (no fungal infection). In some cases, the study may give a questionable result, as a rule, this happens if the patient has recently taken antibacterial drugs.
The study takes from 1 to 5 days. If it is required to reveal the dynamics of the disease, ELISA is carried out at intervals of 14 days.
PCR
High-precision research method based on polymerase chain reaction and taking no more than 3 days. It can be used to register any fungal pathogens, but has one drawback - directed research. This means that the laboratory must obtain information on the specific microfungal species whose spores and hyphae are to be identified.
Blood, sputum, prostate secretion or urine can be provided for analysis, but in the last three options it is necessary to ensure the maximum purity of the biological material. The most effective and expedient in the complex diagnosis of systemic and visceral forms of fungal diseases. The study gives qualitative and quantitative results that are interpreted only by the attending physician.
The study gives qualitative and quantitative results that are interpreted only by the attending physician.
Serological method
Classical studies, in which IgG-prepitins, enolase antigens, proteinases and mannoproteins are more often detected. The study is variable and may be based on the agglutination reaction, titration and RSK. They allow you to get information only about the fact of carrying a mycotic infection or testify to a previously transferred fungal disease.
The analysis may be based on the study of blood serum. With extensive serodiagnosis, the detection of a microfungus can also be carried out in other physiological fluids of the patient.
The results are interpreted by the treating specialist. At the same time, the serological method is often used as a control study for subsequent correction of therapy and determining the effectiveness of treatment.
Risk groups and prevention of fungal infections
Fungal pathogens in a minimal amount are found on the skin of any person. But the uncontrolled use of medicines, especially hormones and antibiotics, can provoke their active growth and subsequent lesions. It should also be noted that deep mycotic infections can enter the body through open wounds. Compliance with the sanitary rules for the treatment of any injuries associated with a violation of the skin minimizes the risks of disease with systemic and visceral microfungi.
But the uncontrolled use of medicines, especially hormones and antibiotics, can provoke their active growth and subsequent lesions. It should also be noted that deep mycotic infections can enter the body through open wounds. Compliance with the sanitary rules for the treatment of any injuries associated with a violation of the skin minimizes the risks of disease with systemic and visceral microfungi.
High humidity and a constant positive temperature are an ideal environment for the life and reproduction of microscopic fungi. Accordingly, the risk group a priori includes employees and visitors to swimming pools, fitness clubs, bath complexes, spas, as well as employees of laundries and catering establishments.
People with a weakened immune system, a depressed nervous system, a tendency to allergies, a critical underweight and metabolic disorders are also prone to fungal infections. Therefore, the most effective prevention is to strengthen the immune system, impeccable observance of the rules of personal hygiene and systematic examinations by a therapist and a dermatologist.