Diet plan while pregnant
Healthy diet during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Healthy diet during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content9-minute read
Listen
Why diet is important during pregnancy for you and your baby
Your diet during pregnancy helps to support your own wellbeing and supplies the nutrition your baby needs to develop and grow.
As a general guide, pregnant mothers need to eat a healthy diet, high in nutrients and low in sugar, salt and saturated fats.
It’s normal for a pregnant mother to gain weight — however, gaining too much or too little weight increases the risk of complications for you and your baby.
Healthy weight gain depends on a mother’s weight before pregnancy. Evidence supports using Body Mass Index (BMI) as a guide for how much weight gain is recommended during pregnancy.
A well balanced diet is usually enough to meet your nutritional needs during pregnancy. However, some foods contain higher concentrations of certain nutrients which are specifically recommended during pregnancy.
Folate, iron, iodine and vitamin D are nutrients needed to support a growing baby’s health and development and can prevent certain conditions. If you are planning a pregnancy, you should start taking a folic acid supplement at least one month before you fall pregnant and for 3 months after conception. Folic acid supplements have been proven to help protect against neural tube defects.
If you are considering taking or currently taking any supplements, please discuss this with your doctor or midwife, as doses can vary depending on your individual circumstance.
What is a 'balanced diet'?
A healthy, balanced diet includes a wide variety of nutritious foods from the five food groups. It’s also advisable to drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Wholegrains and cereals
- Vegetables and legumes/beans
- Lean meats and poultry, fish, eggs, tofu, nuts and seeds as well as legumes/beans
- Fruit
- Dairy foods including mostly reduced fat milk, cheese and yoghurt
Most of us have days when we eat well, and days where our intake of ‘treat’ foods may be higher. Pregnancy cravings can also make this harder to manage, especially when they’re for foods which are high in sugar, salt or fat.
Pregnancy cravings can also make this harder to manage, especially when they’re for foods which are high in sugar, salt or fat.
If you are suffering from morning sickness or severe vomiting during pregnancy, it is important to eat what you can at the time. You should contact you doctor or midwife if you are concerned.
What about pregnancy cravings?
It used to be thought that pregnancy food cravings were a sign of nutrient deficiencies in a pregnant mother’s diet; however, there is no evidence to support this link. Pregnancy can also cause changes in a mother’s tastes, and foods once found appealing can take on a completely different flavour. Food aversions can develop during pregnancy, due in part to hormonal influence.
Are there any foods I should avoid during pregnancy?
There are some foods which need to be avoided during pregnancy, due to their risk of carrying specific bacteria or parasites. An infection with listeria, salmonella or toxoplasmosis when pregnant can cause serious complications to your baby and increase the risk of pregnancy loss.
Some types of fish contain high levels of mercury, including shark/flake, marlin or broadbill/swordfish, orange roughy and catfish. Being selective about what type of fish to eat is important during pregnancy.
It’s also important to check ‘use-by’ dates and to make sure that food has been stored correctly. If in doubt about the safety of a particular food, the safest option is to not eat it.
Food and drink guide
Useful guide to food and drink during pregnancy
Do I need to prepare and cook food differently when I’m pregnant?
It’s important to be careful about food preparation and safety during pregnancy. Food poisoning is generally caused by contamination of food with certain bacteria or viruses. Sometimes it’s easier to suspect food has been contaminated because it smells ‘off’ or looks different to what it should. But it’s not always obvious that food may not be safe. When preparing food, you should always:
- defrost frozen meat, especially poultry, in the fridge or in the microwave
- wash your hands before preparing food and eating
- use different cutting boards for vegetables and meat
- wash benches, cutting boards and utensils with hot, soapy water
- change dishcloths frequently — if they smell, this is a sign of contamination
- cook food thoroughly and don’t eat raw or ‘rare’ meats or fish
- reheat foods to at least 60° Celsius and until it’s steaming hot
What can I drink during pregnancy?
The safest drinks during pregnancy are water and milk. Current evidence supports the recommendations that you should avoid drinking alcohol if you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy. Even small amounts can harm a baby’s development and may have lifelong effects.
Current evidence supports the recommendations that you should avoid drinking alcohol if you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy. Even small amounts can harm a baby’s development and may have lifelong effects.
Water and milk are considered to be safe to drink when pregnant. Low sugar soft drinks, small amounts of juice and soda or mineral water are also fine to drink. Likewise, small amounts of caffeine in tea and coffee are thought to be safe. During pregnancy and when breastfeeding, consuming up to 200 mgs/day is considered safe for a mother and her baby.
As a guide the approximate amounts of caffeine found in food and drinks are:
- 1 cup of instant coffee – 60mg
- 1 shot of espresso coffee – 100mg
- 1 cup of plunger coffee – 80mg
- 1 cup of tea – 30mg
- 375ml can of cola – 49mg
- 250ml can of energy drink – 80mg
- 100g bar of milk chocolate – 20mg
What foods should I limit during pregnancy?
Processed foods tend to be high in sugar, fat and salt. Although they can taste good and are often convenient, they don’t meet the daily requirements for nutrition. The Australian Dietary Guidelines recommend that during pregnancy, you should limit the amount of foods that contain saturated fat, added salt and sugars as well as alcohol.
Although they can taste good and are often convenient, they don’t meet the daily requirements for nutrition. The Australian Dietary Guidelines recommend that during pregnancy, you should limit the amount of foods that contain saturated fat, added salt and sugars as well as alcohol.
During pregnancy, you will have extra energy requirements and needs more serves from the five food groups. It’s important to understand that the ‘serving size’ doesn’t change, but instead the variety of food and serves per day increases to meet the mother and baby’s needs.
| Food group | Serves per day |
|---|---|
| Vegetables and legumes/beans | 5 |
| Fruit | 2 |
| Grains and cereals, mostly wholegrain and/or high fibre cereals | 8 |
| Lean meat/fish/poultry/eggs/tofu/nuts | 3. 5 5 |
| Milk/dairy foods | 3.5 |
Speak with your maternity care provider. If necessary, they can refer you to a dietician who specialises in pregnancy eating support.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Australian Government Department of Health (Alcohol during pregnancy and breastfeeding), Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) (Folic acid/folate and pregnancy), NSW Food Authority (Foods to eat or avoid when pregnant), Eat for Health (Healthy eating during your pregnancy poster), Queensland Health (Healthy eating for gestational diabetes mellitus), Eat For Health (Healthy Eating When You’re Pregnant or Breastfeeding), Eat For Health (Australian Guide to Healthy Eating), The Royal Women's Hospital (Food & nutrition in pregnancy)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: April 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Food preparation and safety
- Food cravings during pregnancy
- Alcohol and pregnancy
- Guide to food and drink during pregnancy
- Foods to avoid when pregnant
- Vitamins and supplements during pregnancy
- Appetite changes and food aversions during pregnancy
Need more information?
Pregnancy health & wellbeing | Raising Children Network
Pregnant? Here’s all you need to stay healthy during pregnancy, including tips for healthy diet and lifestyle and a guide to pregnancy health care.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Having a healthy pregnancy
Having a healthy pregnancy means following a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, knowing what to avoid and making sure your vaccinations are up to date. Find out more here.
Find out more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy and Healthy Eating
It’s especially important to eat healthy food during pregnancy and while breast feeding.
Read more on Healthy Eating Active Living NSW website
Pregnancy healthy eating in pictures | Raising Children Network
Healthy eating for pregnancy means lots of fruit, vegetables and foods with calcium, protein and iron. Avoid sugary, fatty foods, and drink plenty of water.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Pregnancy: illustrated guides | Raising Children Network
Parenting in pictures provides step-by-step guides to pregnancy topics such as healthy eating, pelvic floor exercises and more.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Appetite changes and food aversions during pregnancy
It’s common to experience food cravings or a food aversion during pregnancy. Find out how to ensure you continue to eat healthily if this affects you.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Healthy Eating When You’re Pregnant or Breastfeeding | Eat For Health
Eating well during pregancy and while breastfeeding has health benefits for you and your baby.
Read more on NHMRC – National Health and Medical Research Council website
Gi and Pregnancy | GI Foundation
Home / Gi Health Benefits / Gi and Pregnancy Gi and Pregnancy Following a healthy low Gi diet during pregnancy helps protect your child’s future health and improves health and wellbeing for lifelong benefits
Read more on Glycemic Index Foundation website
Losing weight after birth safely
Tips for losing weight after birth, including how to enjoy a healthy lifestyle, setting realistic goals, breastfeeding and weight loss and when to seek help.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Male fertility and conception- tips for getting pregnant by improving sperm health
Male fertility is vital for conception and a healthy pregnancy. Couples trying to get pregnant need to pay attention to factors which increase the chances of infertility in men. In addition to a healthy diet and regular exercise, treating sexual problems and avoiding recreational drugs helps boost male fertility.
Read more on Parenthub website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Pregnancy Diet Guide & Meal Plan | Nourished Natural Health
To learn more about how to eat during pregnancy to balance your hormones, check out my Hormone Harmony Academy program when you come along to my free Heal Your Cycle webinar.
So, you’ve found out you’re pregnant – congratulations! After getting over the initial excitement and shock, you are probably wondering what you can do to support this new life. Doctors may have warned you about foods to avoid, not to drink alcohol and to reduce caffeine, but so far, my guess is no one has told you what you should be eating. Much of the preparation for pregnancy and birth is focussed on avoiding risks, but did you know that the way you eat throughout pregnancy can boost your baby’s IQ, lower their future disease and obesity risk, make birth easier and less painful and help you recover faster post-birth? Read on to find out how to give your baby the best start in life.
Doctors may have warned you about foods to avoid, not to drink alcohol and to reduce caffeine, but so far, my guess is no one has told you what you should be eating. Much of the preparation for pregnancy and birth is focussed on avoiding risks, but did you know that the way you eat throughout pregnancy can boost your baby’s IQ, lower their future disease and obesity risk, make birth easier and less painful and help you recover faster post-birth? Read on to find out how to give your baby the best start in life.
Table Of Contents:
Why Should I Eat Well During Pregnancy?
What Should I Eat During Pregnancy?
Do I Need To Take Supplements During Pregnancy?
Month By Month Pregnancy Chart
Month 1 Pregnancy Diet
Month 2 Pregnancy Diet
Month 3 Pregnancy Diet
Month 4 Pregnancy Diet
Month 5 Pregnancy Diet
Month 6 Pregnancy Diet
Month 7 Pregnancy Diet
Month 8 Pregnancy Diet
Month 9 Pregnancy Diet
Why Should I Eat Well During Pregnancy?
Optimal nutrition throughout pregnancy is crucial for growing a healthy baby, minimising complications, and also beyond birth. Studies have shown that a healthy diet during pregnancy can reduce the chances of your baby developing obesity, diabetes and heart disease later in life. Eating well and taking certain probiotics throughout your pregnancy can also dramatically reduce the chances of your baby developing asthma, eczema and hay fever after they are born (more on this later).
Studies have shown that a healthy diet during pregnancy can reduce the chances of your baby developing obesity, diabetes and heart disease later in life. Eating well and taking certain probiotics throughout your pregnancy can also dramatically reduce the chances of your baby developing asthma, eczema and hay fever after they are born (more on this later).
This month by month pregnancy diet guide and chart gives you key foods to focus on for baby’s development each month, along with common physical symptoms experienced at this time, and nutritional and lifestyle strategies to manage these. Before jumping in to each specific month, let’s have a look at some general guidelines for healthy eating throughout your whole pregnancy.
Can’t see the image? Download my PCOS Repair Protocol eBook here.
What Should I Eat During Pregnancy?GENERAL GUIDELINES FOR EATING THROUGHOUT ENTIRE PREGNANCY
Focus on nutrient dense whole-foods: this means minimally processed and as close to the natural form as possible. When buying packaged foods – a good rule of thumb is if there are ingredients on the packet you don’t recognise – don’t buy it.
When buying packaged foods – a good rule of thumb is if there are ingredients on the packet you don’t recognise – don’t buy it.
Good quality protein: most women require around 80 grams (2.8 oz.) of protein during pregnancy. Good quality proteins are minimally processed and from high quality sources e.g. grass fed/free range/organic where possible. To calculate your estimated protein requirement, times your pre-pregnancy weight by 1.2 - this is the amount in grams suggested to eat daily. (E.g. 65 kg woman requires ~78g protein per day).
Adequate healthy fats: contrary to much of the now outdated government advice to reduce fats, modern research is demonstrating the importance of healthy fats for all body systems. During pregnancy, adequate fat intake is crucial for the development of baby’s organs and brain. Healthy sources of fats include: olive oil, avocado, nuts and seeds, eggs, oily fish, meats (if you choose to consume them).
An abundance of fresh vegetables and fruit: fruit and veg are full of vitamins, minerals and fibre. Eating a wide variety of fruit and veg will act as a cover-all in providing your body with many of the nutrients it needs, as well as plenty of fibre to avoid constipation. Focus on including plenty of leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale, collard greens, parsley etc) for a good quality source of folate.
do you have a hormone imbalance?
At least 10 cups of fluid a day. As blood volume increases rapidly during pregnancy, adequate water levels are crucial for replenishing baby’s amniotic fluid and can prevent morning sickness and constipation. Ideally, most of this fluid comes from water, herbal tea and occasionally juices. Stay away from soda/soft drinks, alcohol and high intake of tea and coffee.
Steer clear of processed/packaged/high sugar foods: processed foods offer very little nutrition and often contain chemicals which can be harmful to you and your baby. Don’t waste space with low nutrient foods – crowd them out with nutritious, satisfying wholefoods and you won’t feel deprived.
Don’t waste space with low nutrient foods – crowd them out with nutritious, satisfying wholefoods and you won’t feel deprived.
Moderate levels of grains/starch: when eating grains, go for whole-grains such as brown rice, whole oats, quinoa or whole-grain pasta. Nutrient dense starches include sweet potato, pumpkin, parsnip and beetroot. High consumption of carbohydrates (particularly refined carbs and sugars) during pregnancy can imbalance blood sugar levels and contribute to gestational diabetes, so aim to include moderate serves each meal. To make your grains more digestible and higher in available nutrients, read this article about soaking grains.
Do I Need To Take Supplements When I’m Pregnant?SUPPLEMENTS WORTH CONSIDERING DURING PREGNANCY:
This is a general guide – please talk to your health care provider before beginning any of the suggested supplements.
High quality pregnancy multivitamin that contains at least 400 mcg folic acid (to help prevent neural tube defects) - this supplement is most important in the very early stages of pregnancy as the spinal cord is developed 4 weeks after conception. It is important to start as soon as you know you are pregnant, or ideally before you start trying to conceive. If you know you have an MTHFR gene mutation (which is responsible for the conversion of folic acid to other compounds required by the body), you may benefit from supplementing folinic acid and/or 5-MTHF instead.
Lactobacillus Rhamnosus probiotic. If both parents have a history of eczema, the chances of their baby developing eczema is around 60-80%. Probiotics containing lactobacillus strains have been shown to reduce the chances of the child developing allergies by almost 80%. One of the most studied strains: lactobacillus rhamnosus has been shown that when taken in the final trimester of pregnancy (and in some cases postnatally as well), it greatly reduces the chances of the baby developing atopy (asthma, eczema, hay fever). If you or your partner have a history of allergies, talk to your health care provider about whether this probiotic might be helpful for you.
If you or your partner have a history of allergies, talk to your health care provider about whether this probiotic might be helpful for you.
Magnesium is essential for foetal bone and teeth development and can prevent premature contraction of the uterus. It’s also a great supplement to take throughout pregnancy as it helps muscles to relax, so can help with constipation, assist your tissue growth and promote restful sleep.
Fish oil/omega 3’s are essential for neurological and visual development in your baby, and in the production of breast milk. Studies have shown that supplementing with omega 3 during pregnancy can increase the cognitive development of your baby and boost future IQ. Other studies have also shown that a higher intake of omega 3’s may decrease the risk of allergy development in the baby. Furthermore, omega 3’s have been shown to reduce premature labour, lower the risk of preeclampsia and mother’s risk of depression. Talk to your doctor about whether an omega 3 supplement may be beneficial for you but please note – quality of these supplements varies widely. Choose brands that have proven purity and appropriate storage – not the cheap brand off your chemist’s shelf.
Talk to your doctor about whether an omega 3 supplement may be beneficial for you but please note – quality of these supplements varies widely. Choose brands that have proven purity and appropriate storage – not the cheap brand off your chemist’s shelf.
Print the following chart (right click the image to open in a new window and print from there) and follow along each month of your pregnancy for the most important foods to focus on that month. Read on to learn more about each specific month of pregnancy: what physical symptoms to expect and how to overcome them, your baby’s month-by-month development, and key foods to focus on in each month and trimester.
How Should I Eat In Each Month of Pregnancy?Month By Month Pregnancy Diet ChartPrint the following chart (right click the image to open in a new window and print from there) and follow along each month of your pregnancy for the most important foods to focus on that month. Read on to learn more about each specific month of pregnancy: what physical symptoms to expect and how to overcome them, your baby’s month-by-month development, and key foods to focus on in each month and trimester.
Read on to learn more about each specific month of pregnancy: what physical symptoms to expect and how to overcome them, your baby’s month-by-month development, and key foods to focus on in each month and trimester.
Click here to expand and download checklist
FIRST TRIMESTER
Month 1 Pregnancy Diet
BABY’S DEVELOPMENT:
In the first month of pregnancy your baby is an embryo consisting of two layers of cells. All the organs and body parts will develop from here. This month, the neural tube is developed which is the reason a supplement containing folic acid (or folinic acid or 5-MTHF if you know that you have an MTHFR gene mutation) is crucial to prevent neural tube defects.
YOUR PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS:
Morning sickness is common in the first few months of pregnancy. It is not experienced by all women, but can be extremely severe for some. The good news is that most women find their nausea disappears by the beginning of their second trimester. In the meantime, here are some strategies to decrease nausea (which can occur at any time of the day, not just in the morning):
In the meantime, here are some strategies to decrease nausea (which can occur at any time of the day, not just in the morning):
Have a carbohydrate-rich snack 15-20 minutes before you get out of bed in the morning – this can help to settle the stomach before you start to move about. Try storing some plain crackers or bread by your bed for when you wake up
Consume smaller meals, more frequently (i.e. 6 meals a day, rather than 3). Don’t let yourself get too hungry between meals
Focus on foods that are easy to digest
Try to consume liquids between meals rather than with food
Stay away from high fat, fried and spicy foods as these can aggravate nausea
Sip plain soda water throughout the day when you feel nauseous
IMPORTANT FOODS TO FOCUS ON IN MONTH 1 OF PREGNANCY:
Folate-rich foods: green leafy vegetables (spinach, rocket, parsley), whole-grains and legumes (lentils, beans, chickpeas)
Vitamin B6: 40 mg taken twice daily has been shown to be an effective, natural treatment at reducing early pregnancy nausea and vomiting.
 Talk to your healthcare provider about taking this supplement if you feel it might be useful
Talk to your healthcare provider about taking this supplement if you feel it might be useful
FOODS TO AVOID DURING PREGNANCY:
Raw/undercooked meats
Cold cuts of cured meat
Raw fish (sashimi/sushi)
Soft cheeses
Salad bars
Raw eggs (and foods that contain them e.g. mayonnaise and raw cake batter)
Unwashed fruit and veg
High levels of caffeine (coffee, black tea)
Can’t see the image? Download my PCOS Repair Protocol eBook here.
Month 2 Pregnancy Diet
BABY’S DEVELOPMENT:
In the second month of pregnancy your baby is around the size of a kidney bean and has distinct, slightly webbed fingers.
YOUR PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS:
Nausea and fatigue are common in the second month. Have a read of this article for some natural remedies for morning sickness. Need your partner to understand what you’re going through? Get him to read this funny male perspective on nausea.
IMPORTANT FOODS TO EAT IN MONTH 2 OF PREGNANCY:
Ginger for nausea: ginger has been demonstrated to provide the same relief from nausea as the leading anti-nausea drugs. Try grating 2 Tbsp. into hot water as a tea, chewing on crystallised ginger sweets throughout the day or adding powdered ginger to cooking
Vitamin E: this study demonstrated a link between low vitamin E status and increased miscarriage risk
Some good sources of vitamin E include:
raw almonds
avocado
olive oil
sunflower seeds
hazelnuts
egg yolk
Month 3 Pregnancy Diet
BABY’S DEVELOPMENT:
In the third month of pregnancy, your baby is around 7 to 8 cm (3 inches) long and weighs the same as a pea pod. Tiny, unique fingerprints are now distinct.
YOUR PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS:
Nausea usually starts to disappear at the end of this month. To get you through, have a read of this cute article on one women’s experience on debilitating morning sickness and the lessons she learned along the way.
To get you through, have a read of this cute article on one women’s experience on debilitating morning sickness and the lessons she learned along the way.
IMPORTANT FOODS TO FOCUS ON IN MONTH 3 OF PREGNANCY:
Could a hormone imbalance be affecting your ability to fall pregnant? Take my FREE 3-minute quiz to find out
Month 4 Pregnancy Diet
BABY’S DEVELOPMENT:
Welcome to your second trimester! In the fourth month of pregnancy, your baby is around 13 cm (5.5 inches) long and weighs 140g (5oz). The skeleton is starting to harden from rubbery cartilage into bone. Your baby bump will usually begin to show this month.
YOUR PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS:
Nausea usually disappears by this month and you may start to notice much of your energy returning.
IMPORTANT FOODS TO INCLUDE IN YOUR DIET IN MONTH 4 OF PREGNANCY:
Iron-rich foods: your blood volume is rapidly increasing (and will increase by 50% by the time you give birth).
 Increase your intake of good quality proteins like eggs and free-range meats (organic/grass fed where possible). If you are vegetarian, make sure you are consuming iron-rich plant foods such as leafy greens and legumes with every meal, along with a source of vitamin C (such as a squeeze of lemon juice or some capsicum/peppers) as this enhances the body’s uptake of iron from non-animal sources. Iron deficiency during pregnancy can cause fatigue for the mother and low birth weight, iron-deficient infants so keep on top of your iron intake, or talk to your healthcare provider about supplementation if this might be an issue or you have been feeling very fatigued.
Increase your intake of good quality proteins like eggs and free-range meats (organic/grass fed where possible). If you are vegetarian, make sure you are consuming iron-rich plant foods such as leafy greens and legumes with every meal, along with a source of vitamin C (such as a squeeze of lemon juice or some capsicum/peppers) as this enhances the body’s uptake of iron from non-animal sources. Iron deficiency during pregnancy can cause fatigue for the mother and low birth weight, iron-deficient infants so keep on top of your iron intake, or talk to your healthcare provider about supplementation if this might be an issue or you have been feeling very fatigued.
Month 5 Pregnancy Diet
BABY’S DEVELOPMENT:
In the fifth month of pregnancy, your baby’s elbows and eyelids will now be visible. Baby is around 27cm (10.5inches) long. Your energy usually increases this month and your baby bump is probably obvious by this point. You may start to feel baby’s kicks in this month!
You may start to feel baby’s kicks in this month!
YOUR PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS:
Bloating and fluid retention can become an issue around this month. To manage this, avoid excess salt (and processed foods) and make sure you are keeping up your hydration.
IMPORTANT FOODS TO INCLUDE IN YOUR DIET IN MONTH 5 OF PREGNANCY:
Calcium: is vital during pregnancy for your developing baby’s teeth and bones, as well as helping your baby grow a healthy heart, nerves and muscles.
Some good sources of calcium (aim to include at least 2 daily):
Small bony fish such as sardines
Almonds
Tahini
Green leafy vegetables
Dairy (if tolerated)
Vitamin C: your body does not store vitamin C so it’s important to have daily food sources such as broccoli, oranges and tomatoes.
 Vitamin C is needed throughout pregnancy to make collagen – a protein that provides structure to cartilage, tendons, bones and skin, as well as helping your body to fight infections
Vitamin C is needed throughout pregnancy to make collagen – a protein that provides structure to cartilage, tendons, bones and skin, as well as helping your body to fight infections
Month 6 Pregnancy Diet
BABY’S DEVELOPMENT:
In the sixth month of pregnancy, your baby weighs around 660g (1.5 lb). Their wrinkled skin is starting to stretch out as baby puts on some fat.
YOUR PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS:
Hunger often increases this month. While you do need more calories to support your rapidly growing baby, make sure to choose nutrient-dense rather than calorie-dense foods to give you and your baby optimal nutrients for growth.
Constipation is common around this time. Constipation commonly occurs during pregnancy as the body is literally slowing down the speed to digestion to ensure maximum uptake of nutrients to support the growth of your baby. Therefore, focussing on a whole food, nutrient-dense diet will likely prevent constipation as the body’s nutritional needs are being met. If you do struggle with constipation, focus on getting plenty of whole-grains, fibre-rich vegetables, fruits and legumes, as well as drinking enough water throughout the day.
If you do struggle with constipation, focus on getting plenty of whole-grains, fibre-rich vegetables, fruits and legumes, as well as drinking enough water throughout the day.
IMPORTANT FOODS TO EAT IN MONTH 6 OF PREGNANCY:
Whole-grains, fruits, vegetables and legumes to prevent constipation. Aim for 25-30g fibre each day. This roughly equates to 5 large apples, 2 cups of legumes or 2 cups of wheat bran.
Use this counting tool which gives fibre of common foods to estimate your daily intake
For a natural relief of constipation, try taking 1 Tbsp. of psyllium mixed into a glass of water before bed, to promote a healthy bowel movement the following morning
Month 7 Pregnancy Diet
BABY’S DEVELOPMENT:
Welcome to your third trimester! In the seventh month of pregnancy your baby is now more than 40cm (15 inches) long. They can open and close their eyes and see what is around them.
YOUR PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS:
Heartburn: due to your enlarging uterus, it is common for pressure to be placed on the stomach, causing acid to creep up the oesophagus.
Here are some tips to avoid heartburn:
Eat small meals regularly
Avoid high-fat, fried foods and spicy foods
Don’t eat until you are completely full (stop at 80%)
Avoid laying down for 45 minutes after eating
Try to eat dinner earlier so that you don’t go to bed right after eating
Try elevating the head of your bed at night
IMPORTANT FOODS TO EAT IN MONTH 7 OF PREGNANCY:
Protein: Adequate protein throughout pregnancy is crucial for the development of the foetus. Most women need around 80 grams of protein (2.8 oz) every day for a healthy pregnancy. Consuming this much protein each day has been linked with a lower risk of developing preeclampsia, morning sickness and other complications.
 Low protein diets can increase the chances of the baby developing high blood pressure later in life, so it is crucial that you are consuming enough good quality protein.
Low protein diets can increase the chances of the baby developing high blood pressure later in life, so it is crucial that you are consuming enough good quality protein.
Try this printable protein counter to make sure you are meeting your daily needs
This blog shares some ideas on how to get enough protein in your day and gives sample menus of healthy choices
which hormonal imbalance do you have?
Month 8 Pregnancy Diet
BABY’S DEVELOPMENT:
Baby now weighs around 2.4kg (4.7lb). Layers of fat are filling out and lungs are well developed.
YOUR PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS:
Frequent urination, backaches, shortness of breath, trouble sleeping are common as you head towards the end of your pregnancy. Try having a warm shower before bed and buying a long pillow that allows you to support your belly while you sleep on your side.
IMPORTANT FOODS TO FOCUS ON EATING IN MONTH 8 OF PREGNANCY:
Month 9 Pregnancy Diet
BABY’S DEVELOPMENT:
Baby is almost ready to come out. At birth, they are usually more than 51cm (20.5 inches) long from head to toe and weight around 3.4kg (7.5lb).
At birth, they are usually more than 51cm (20.5 inches) long from head to toe and weight around 3.4kg (7.5lb).
YOUR PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS:
Swollen hands and feet are common in your final month. To reduce this, avoid excess salt intake and increase your water consumption. Try some gentle exercise such as walking or swimming to help promote the movement of fluid.
IMPORTANT FOODS TO EAT IN MONTH 9 OF PREGNANCY:
Garlic: “high” garlic intake during the final month of pregnancy has been correlated with a significantly reduced risk of preterm labour. This is thought to be related to the antimicrobial properties of garlic, which help to reduce infections of the urinary and genital tract, which can increase premature delivery. The best part? “High” intake of garlic in this study equated to 1 single garlic clove per week – pretty manageable!
Dates: consumption of 6 dates daily for the final 4 weeks before the estimated due date was found to dramatically increase the chances of spontaneous labour (i.
 e. reduce the need to be induced), encourage greater cervical dilation, faster first stage of labour and decreased need for medical and pharmaceutical intervention. Another more recent study confirmed the results of the earlier study and concluded that “dates consumption in late pregnancy is a safe supplement to be considered as it reduced the need for labour intervention without any adverse effect on the mother and child”. Try snacking on fresh dates throughout the day or use in cooking as a delicious natural sweetener
e. reduce the need to be induced), encourage greater cervical dilation, faster first stage of labour and decreased need for medical and pharmaceutical intervention. Another more recent study confirmed the results of the earlier study and concluded that “dates consumption in late pregnancy is a safe supplement to be considered as it reduced the need for labour intervention without any adverse effect on the mother and child”. Try snacking on fresh dates throughout the day or use in cooking as a delicious natural sweetener
Raisins: an intake of around 2 handfuls of dried raisins per week has been correlated with a reduction in chances of premature labour, demonstrating a similar effect to garlic Try snacking on raisins as well, or add to salads or rice dishes for a sweet flavour burst
Eating well throughout your pregnancy can have huge and lasting effects on your baby’s health and development, as well as your experience of pregnancy and birth. With so little reliable information around about how to eat well in pregnancy, I was inspired to create this guide to help you give your baby the best start in life, based on the facts.
With so little reliable information around about how to eat well in pregnancy, I was inspired to create this guide to help you give your baby the best start in life, based on the facts.
Keen to dig your teeth into even more hormone-loving content?
Take my free Hormone Imbalance Quiz to find out which imbalance is most likely for you
In need of a hormone reset? Join my 7 Day Hormone Reset Challenge now
Sign up for my free Heal Your Cycle 60 minute webinar
Ready to supercharge your fertility and reverse hormone imbalances? Enrol in the next intake of my Hormone Harmony Academy 8 week digital program
Other blogs you might enjoy…
Tamika Woods | Nutritionist
For a decade, Tamika battled chronic acne, irregular cycles, mood swings, hair loss, painful periods, severe digestive issues and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). You name it - she's been there!
You name it - she's been there!
Tam was finally able to clear her skin, regulate her cycle, be free of period pain and fall pregnant naturally with her daughter in 2020. It took Tam 10 years and tens of thousands of dollars in tertiary education to get the answers she needed to get better. She didn’t want other women to suffer as long as she did which is why she has dedicated her life to helping women in the same position as she was.
Tam helps women interpret what their bodies are trying to communicate through frustrating symptoms, and then develop a step-by-step roadmap to find balance again. She's here to help you get on track!
Tamika Woods holds a Bachelor of Health Science degree (Nutritional Medicine) as well as a Bachelor of Education, graduating with Honours in both. She is a certified Fertility Awareness Method (FAM) Educator and a certified member of the Australian Natural Therapists Association (ANTA).
Tamika Woods18 Comments
0 LikesNutrition for pregnant women: menu TEA.
 RU
RU Nutrition for pregnant women is of particular importance. Before pregnancy, not many of us think about what is healthy and proper nutrition. From the very moment when a woman finds out about her “interesting position”, the realization comes that now you need to “eat for two”. And this does not mean at all that the menu for a pregnant woman should contain more calories and, accordingly, food. This means that proper nutrition during pregnancy leads to the correct development of the fetus in terms of anatomy and physiology.
Numerous research data have shown that malnutrition during pregnancy can not only lead to anatomical underdevelopment of the fetus, but can also affect the future cognitive abilities, memory and other developmental features of the baby.
Surprisingly, malnutrition during pregnancy is one of the underlying factors in the development of obesity. Even at the intrauterine level, the child turns on a gene that ensures the maximum absorption of all nutrients from any, even a limited, amount of food. In the future, even if the child's nutrition is sufficient, his body will still try to "accumulate" calories "with a margin."
In the future, even if the child's nutrition is sufficient, his body will still try to "accumulate" calories "with a margin."
In addition, malnutrition of a pregnant woman can cause problems in the future:
• with the psychomotor development of the child;
• with the immune system;
• with the endocrine system;
• with metabolism;
• lead to impaired memory, attention and even behavior of the child.
For this and other reasons, a balanced diet is a very important component, along with the psycho-emotional state. The diet of pregnant women should be carefully thought out and conscious so that the child from the moment of conception to the very birth develops as harmoniously and correctly as possible.
Pregnancy menu: what will be useful?
The dietary menu for pregnant women should include a full range of vitamins, nutrients and minerals. In addition, such a menu should include immunonutrients and micronutrients. What is it and what is the significance of these substances in the formation of the fetus?
What is it and what is the significance of these substances in the formation of the fetus?
The main task of micronutrients is the direct protection of the fetus from any adverse external influences. These impacts include both environmental factors and exposure to various chemicals that are abundant in the environment. Micronutrients are involved in almost all biochemical processes in the body of the mother and fetus.
Immunonutrients are chemicals that have a direct impact on the formation of a child's immunity, the ability of his body to resist various bacterial, viral and other attacks of pathogens. These substances include amino acids, probiotics, nucleotides, fatty acids and some other elements.
Not only the lack of such elements in the future mother's diet is dangerous, but also their excess. For example, vitamin A is useful for the formation of the organs of vision in the fetus, but in large doses this vitamin can be toxic and lead to the development of intrauterine pathologies. For this reason, it is better to choose a menu for every day during pregnancy, taking into account the recommendations of a specialist leading your pregnancy. Any "amateur", in this case, it is better to exclude.
For this reason, it is better to choose a menu for every day during pregnancy, taking into account the recommendations of a specialist leading your pregnancy. Any "amateur", in this case, it is better to exclude.
Early pregnancy nutrition
In the early stages of pregnancy, experts say, the energy needs of a woman practically do not change. It is not necessary at this time to drastically change your lifestyle and diet. If your diet was balanced, then you can stick to it throughout the first trimester.
Attention should be paid to ensure that the diet includes:
• fresh seasonal vegetables and fruits;
• greens;
• berries;
• horse crops.
Numerous studies have found that early pregnancy menus often exclude this particular food group. These products are recommended to be consumed raw or with minimal heat treatment. When choosing a diet, it is worth considering the history in terms of the presence of allergies in the mother and a predisposition to the development of diabetes.
The norm of sugar consumption per day in the menu for pregnant women is no more than 60 gr. If you cannot do without sweets, and you also need to avoid foods that cause allergic reactions, it is recommended to include foods such as:
• jams and jams without sugar;
• chocolate without sugar;
• dark chocolate with a cocoa content of at least 70%;
• peanut butter without sugar, etc.
Contrary to popular belief, such products have not only beneficial properties for the body, but also excellent organoleptic characteristics. Foods that are low in sugar or do not contain sugar at all have a taste and aroma that are in no way inferior to similar products with sugar.
Otherwise, the menu for pregnant women in the 1st trimester should not differ from the usual. For the formation of the fetus in the early stages, "building materials" in high doses are not needed. Thus, all the calories that a woman receives are spent at the same rate as usual. Increasing the amount of food and its calorie content can lead to overweight and will not benefit the child at all.
Increasing the amount of food and its calorie content can lead to overweight and will not benefit the child at all.
So, what should pregnant women eat in the early stages? The same as usual, including a large amount of fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs and berries. Vegetables and fruits should be typical for your region, you should not give preference to exotic and new products for you. Dishes for pregnant women should be as simple and familiar as possible, there is no need to invent something new. Eat what you want most, but don't overeat.
Proper nutrition for pregnant women in the 2nd trimester
In the second half of pregnancy, there is an active growth of the fetus, as well as various changes in the organs of the woman's reproductive system themselves. It is during this period that the need for nutrients and microelements for the normal physiological development of the fetus may increase.
A sample menu during pregnancy should be such that the pregnant woman receives all groups of the following foods:
• Dairy products, including whole milk and lactic acid products. The approximate volume of this product group should be 500 ml.
The approximate volume of this product group should be 500 ml.
• Meat and poultry. The total amount of meat products should not be less than 170 gr. In the second trimester of pregnancy, 250 grams of any, but better - dietary, meat - this is the norm.
• Fish and seafood. It is enough to eat 70 grams daily.
• Cereals and bakery products in limited quantities. This group of products is simply necessary to prevent such problems in the gastrointestinal tract as constipation and bloating, which women often suffer from during the period of bearing a child.
• Vegetables, fruits and berries, as well as juices. Total quantity - up to 1000
• Sugar and confectionery. Preference should be given to marmalade, marshmallows, marshmallows and jams on a natural basis, as well as products with low or no sugar content.
• Fats. Dishes for expectant mothers are best cooked in butter. The amount of vegetable fats should not exceed 15 g per day.
In the second trimester, a large load falls on the liver and kidneys. The menu for pregnant women in the 2nd trimester should exclude a large number of any salty foods, smoked meats and excess fluids. You need to focus on the fact that a woman should normally gain no more than 300 grams per week, and for the entire pregnancy - no more than 10-12 kg. If you are gaining more, then the diet should be reconsidered.
The menu for pregnant women in the 2nd trimester should exclude a large number of any salty foods, smoked meats and excess fluids. You need to focus on the fact that a woman should normally gain no more than 300 grams per week, and for the entire pregnancy - no more than 10-12 kg. If you are gaining more, then the diet should be reconsidered.
Nutrition during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester: menus and recommendations
The diet for pregnant women in the third trimester also has its own characteristics. The menu for the 3rd trimester should include products that stimulate lactation. First of all, these are dairy and lactic acid products, such as kefir, milk, fermented baked milk, cheese and cottage cheese.
Breakfast for pregnant women should be 30-40% of the total diet. You can have oatmeal, a few slices of cheese, yogurt and tea for breakfast. It is good to use herbal teas, which not only have high taste, but also have the following properties:
• anti-inflammatory;
• immunostimulating;
• normalizing metabolism;
• restoring the optimal water-salt balance and other useful properties.
Herbal tea may contain chamomile, rose hips, berries or fruits, calendula, string, twigs and leaves of useful plants. For a woman during childbearing, in general, green and herbal teas are much more beneficial than black teas and their blends.
Late pregnancy diets should be high in protein and avoid heavily spiced foods, including salt. These foods retain water in the body and can cause swelling and other complications.
A sample menu for proper nutrition for pregnant women might look like this:
This is an approximate table of nutrition during the period of bearing a child. You can adjust it according to the season and the availability of seasonal fruits and vegetables, as well as your personal preferences. Recipes for pregnant women, menus for days or weeks today can be easily found in the public domain. Using these recommendations, you can create your own diet that will satisfy both the needs of the body and your own preferences.
Healthy nutrition during pregnancy
Category: Healthy food.
Happiness, agonizing expectation, anticipation and even fear - all these feelings inevitably accompany pregnant women. And it is very important during this period not to surrender to emotions, but to remember the responsibility that is an integral part of this time. It is during this period that it is important to follow the basics of a healthy lifestyle, taking into account the requirements of pregnancy. Proper nutrition during pregnancy is the most relevant, since what a woman eats largely determines how her child will develop. For example, whether a pregnant woman receives enough protein depends on whether the child will have enough building material.
It makes sense to take into account one important feature: proper nutrition in early pregnancy will be somewhat different from the diet of a pregnant woman in the last weeks.
Not everyone understands where such differences come from, but understanding the topic will be quite simple. Judge for yourself, important systems of the body are laid in the early stages, but the size of the fetus increases slightly. Therefore, in the early stages, a healthy diet for pregnant women is based on sufficient intake of minerals, vitamins, and the like.
Therefore, in the early stages, a healthy diet for pregnant women is based on sufficient intake of minerals, vitamins, and the like.
In the second trimester of pregnancy, nutrition should focus on increased protein intake, since it is now that the active growth of the child and its internal organs begins. All this requires a building material, that is, protein.
Nutrition in the third trimester of pregnancy is, first of all, vitamins and minerals that are necessary for the development of the internal systems of the child's body, especially calcium for bone growth and the development of the nervous system.
When planning a pregnancy, proper nutrition is also very important. The more healthy, hardy, strong the woman's body is at the time of conception, the greater the chances of successfully fixing the fetal egg in the uterus. And a certain set of vitamins in the body contributes to the proper development of the embryo.
As you can see, the difference in recommendations for proper nutrition of pregnant women by months, and sometimes even by weeks, is quite justified. However, there are, of course, general rules for proper nutrition during pregnancy, which will be discussed further.
However, there are, of course, general rules for proper nutrition during pregnancy, which will be discussed further.
General principles of proper nutrition during pregnancy
First of all, it is worth remembering one simple thing: it is better to get up from the table slightly hungry than with heaviness in the stomach from overeating. In this regard, it is better to adhere to the principles of fractional nutrition at all: eat less, but more often. The ideal option would be to eat 5-6 times a day. The last meal should be 3 hours before bedtime. If the feeling of hunger is unbearable, you can drink a glass of milk or yogurt, eat an apple or a pear. It is this diet for pregnant women that will be most optimal.
Proper nutrition during pregnancy, like, in fact, any proper nutrition, involves the exclusion or maximum restriction of fried foods, pickled foods and smoked meats. Steamed, boiled, stewed or baked food will be much more useful. Food for pregnant women should be as fresh and natural as possible, should not contain preservatives, excess salt, and the like.
Food for pregnant women should be as fresh and natural as possible, should not contain preservatives, excess salt, and the like.
Obviously, canned foods, various sausages and other long-term storage products, if not banned, then require strict control of their use.
Of course, it is recommended to give up fast food. However, it is worth noting that if the choice arises - to remain hungry or eat something not very healthy, it is better to choose the latter. A pregnant woman should not starve. Another thing is, if you get suspiciously often before such a choice, then you should think about carrying fruit or sandwiches with you.
Of great importance is the balance between such important components of nutrition as proteins, fats, carbohydrates, as well as vitamins and minerals. Of course, a balanced diet for pregnant women at different times implies a different balance of these components, the fact itself remains unchanged.
Weekly meals
1-3 weeks pregnant
Gynecologists count pregnancy not from the day of conception, since it is almost impossible to calculate it, but from the first day of the last menstruation. Therefore, the first 2 weeks of the obstetric gestation period falls on the time before conception.
Therefore, the first 2 weeks of the obstetric gestation period falls on the time before conception.
Pregnancy planning is an extremely important period, on which, whatever one may say, both the health of the unborn child and the absence of any complications during pregnancy depend. So it turns out that proper nutrition before pregnancy is of paramount importance. At this stage, it is very important to increase the amount of folic acid. Doctors often recommend drinking it in the form of capsules, but it is much better to get all the vitamins from normal food. Folic acid is found in green leafy vegetables (spinach, lettuce, cabbage, etc.), asparagus, beans and legumes, seeds and nuts, citrus fruits.
It is equally useful to consume yellow fruits and vegetables. But it is better to refuse fatty and sweet foods. This will avoid problems with obesity, as well as reduce the risk of early toxicosis.
Approximately on the 10-14th day of the cycle, fertilization occurs and the movement of the fetal egg begins towards the uterus. From this time on, we can talk about the onset of pregnancy.
From this time on, we can talk about the onset of pregnancy.
3 week
Nutrition at the beginning of pregnancy is a very complicated topic, since literally every week new organs and systems appear in the fetus, which means that the need for vitamins and nutrients is constantly changing.
In the third week of pregnancy, the egg is implanted and the placenta begins to develop, as well as the fetal membrane. For their full development, calcium is needed, which is found in dairy products, nuts, fish, legumes, fruit juices and cereals; and manganese, it can be obtained from nuts, spinach, beets, mushrooms, animal liver.
4 week
For 4 weeks, the nutrition remains the same as for 3, but at this time it is especially important to give up coffee. However, drinking this certainly tasty, but not very healthy drink during pregnancy should be done with extreme caution. Especially coffee is contraindicated in the evening. As you can see, proper nutrition in the first month of pregnancy is not too difficult. Further it will be a little more difficult.
As you can see, proper nutrition in the first month of pregnancy is not too difficult. Further it will be a little more difficult.
5 week
As a rule, toxicosis of pregnant women begins around this time. To alleviate this condition, you can slightly change your daily menu. So, meat and eggs, as well as other animal proteins, can be replaced with nuts, soy and other legumes. Instead of milk, you can eat yogurt and cheese. It will not be superfluous to introduce carrots, mangoes, apricots into the diet.
6 week
Toxicosis is in full swing, so the morning should start with crackers or unsweetened crackers. It is better to eat them immediately after waking up, without getting out of bed. At this stage, it is better to drink plenty of fluids, at least 8 glasses a day (for example: water with lemon juice or tea with lemon). At night, you can eat a handful of raisins.
7 week
At this time, problems with the intestines may arise.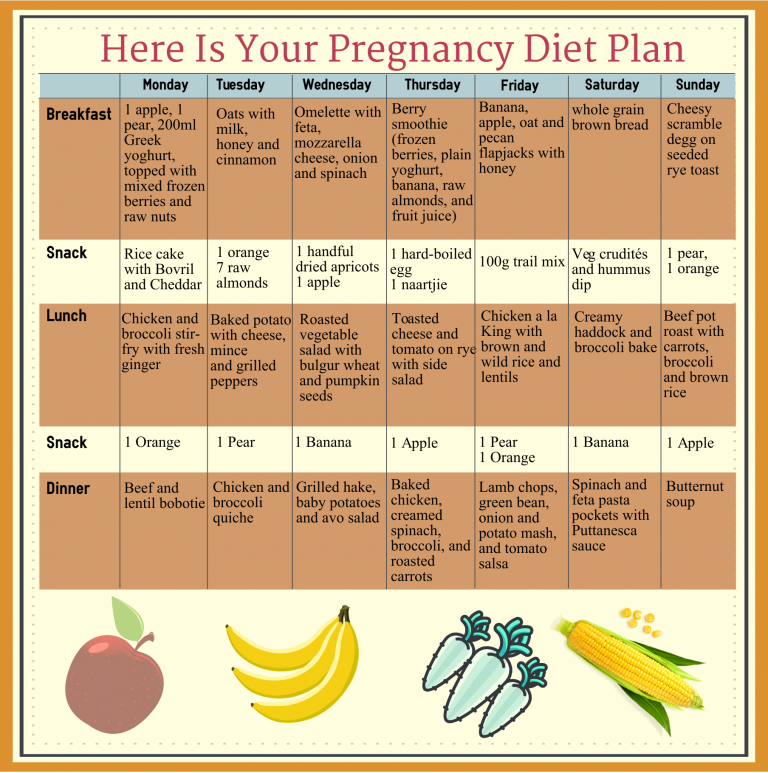 Therefore, you should avoid foods that promote gas formation, including cabbage. It will not be superfluous to refuse those products that strengthen. It is better to introduce prunes, fresh kefir and the like into the diet.
Therefore, you should avoid foods that promote gas formation, including cabbage. It will not be superfluous to refuse those products that strengthen. It is better to introduce prunes, fresh kefir and the like into the diet.
8 week
Ginger tea will help to cope with toxicosis, and do not forget about nuts.
9-10 weeks
Give preference to whole grain cereals and whole grain bread. Brown rice is better than white. In general, the body of a pregnant woman at this stage needs quite a lot of fiber.
11-12 weeks
The first trimester of pregnancy is coming to an end, and nutrition at this time should be special. This is the most difficult time, and it is very important to listen to yourself, to your body. If you want to eat a particular dish, then it is precisely those substances that are contained in it that your baby lacks. Of course, you shouldn't go to extremes.
13-16 weeks
Nutrition in the 2nd trimester during pregnancy is characterized, as already mentioned, by abundant protein intake. In addition, it is necessary to increase the total daily caloric intake of food. If in the first trimester it will be enough to eat 2400-2700 kcal, then from this time it is necessary to eat 2700-2900 kcal.
In addition, it is necessary to increase the total daily caloric intake of food. If in the first trimester it will be enough to eat 2400-2700 kcal, then from this time it is necessary to eat 2700-2900 kcal.
16-24 weeks
Nutrition at 6 months of pregnancy should contribute to the development of the child's vision and hearing. That is, you need vitamin A and beta-carotene. It is better to eat cabbage, yellow peppers, carrots at this time. Keep in mind that vitamin A is absorbed only with fats.
24-28 weeks
It is at this time that fractional nutrition becomes especially relevant. The uterus is actively growing, taking up more and more space in the abdominal cavity, and begins to put pressure on the stomach. Accordingly, the stomach becomes smaller, and it is difficult for it to contain a large amount of food. Even when eating small meals, a pregnant woman may be bothered by heartburn. It is better to give up carbonated drinks and coffee, they also provoke heartburn. In general, the nutrition of a pregnant woman in the third trimester should be as diverse as possible, as the needs of the baby grow.
In general, the nutrition of a pregnant woman in the third trimester should be as diverse as possible, as the needs of the baby grow.
29-34 weeks
At the 8th month, bones are actively growing and teeth are being laid, therefore, it is very important to eat as many calcium-containing foods as possible. For brain development, fatty acids are simply necessary, and they contribute to the absorption of calcium. Iron deficiency at this time can lead to the development of anemia, both in the mother and in the child. Fatty fish, nuts, red meat, dark green vegetables and seeds are the foods to eat during this period of pregnancy.
35-40 weeks
Nutrition at the 9th, last month of pregnancy, should contribute to the overall strengthening of the mother's body. After all, she has a very difficult and time-consuming job ahead of her - childbirth. The main source of energy in the body is carbohydrates, and it is their consumption that should become the basis of the nutrition of a pregnant woman before childbirth. Cereals and vegetables are the foods that you should eat during this period.
Cereals and vegetables are the foods that you should eat during this period.
That's all that can be said about trimester nutrition. An example of a menu for pregnant women by trimesters may also be useful. Based on these menus and explanations for them, you can create a menu for yourself.
Sample menu for pregnant women for the 1st trimester
1. Breakfast: muesli with yogurt and freshly squeezed pear juice.
2. First snack: salmon sandwich.
3. Lunch: mushroom soup, cabbage salad, herbal tea.
4. Second snack: whole grain bread with cheese.
5. Dinner: carrot salad and vegetable risotto. You can drink everything with kefir.
In the first trimester, it is very important that a woman receives a large amount of folate and vitamin B6 from food.
An example of a menu for pregnant women for the 2nd trimester
In the second trimester for pregnant women, the presence of omega-3 acid, calcium, vitamin D and iron in the diet is important.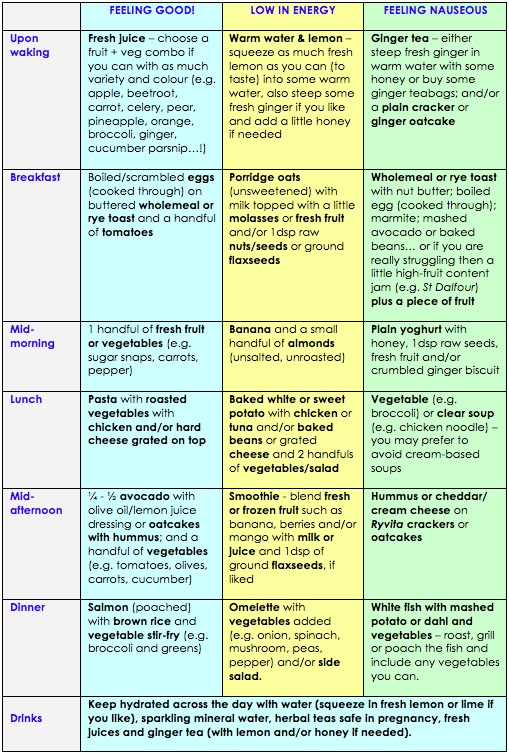
1. Breakfast: oatmeal in milk with apple and cinnamon, chamomile tea.
2. First snack: almonds with prunes.
3. Lunch: lentil soup, seaweed salad, cranberry juice.
4. Second snack: sandwich with herring.
5. Dinner: omelet with mushrooms and yogurt.
An example of a menu for pregnant women for the 3rd trimester
Carbohydrates and vitamin K play a special role here.
1. Breakfast: pancakes with cream cheese and curdled milk.
2. First snack: whole grain cheese sandwich.
3. Lunch: fish hodgepodge, tuna and green salad, rosehip broth.
4. Second snack: cheesecake.
5. Dinner: fish with rice and fermented baked milk.
Special nutrition for pregnant women
But this is not all the nutritional features of pregnant women. In some cases, women develop pathologies during pregnancy that require special nutrition. So, with anemia in pregnant women, special nutrition is simply necessary. A woman who has experienced pregnancy anemia should consult a doctor not only about drug treatment, but also about an appropriate diet. With such a disease, it is very important to increase the intake of foods containing iron. Iron can be obtained from animal products (lean red meat, fish, poultry) and vegetable (nuts, dried porcini mushrooms, spinach, buckwheat, legumes, etc.) origin. In addition, it is important not only to know which foods to use, but also in what combinations, as this affects the absorption of iron in the human body. Vitamin C increases the absorption of iron in the body, that is, the combination of products containing iron and vitamin C is favorable. Foods containing calcium (dairy products) and tannin (tea, coffee) prevent the absorption of iron in the intestine. Therefore, their use should be separated.
So, with anemia in pregnant women, special nutrition is simply necessary. A woman who has experienced pregnancy anemia should consult a doctor not only about drug treatment, but also about an appropriate diet. With such a disease, it is very important to increase the intake of foods containing iron. Iron can be obtained from animal products (lean red meat, fish, poultry) and vegetable (nuts, dried porcini mushrooms, spinach, buckwheat, legumes, etc.) origin. In addition, it is important not only to know which foods to use, but also in what combinations, as this affects the absorption of iron in the human body. Vitamin C increases the absorption of iron in the body, that is, the combination of products containing iron and vitamin C is favorable. Foods containing calcium (dairy products) and tannin (tea, coffee) prevent the absorption of iron in the intestine. Therefore, their use should be separated.
With obesity that has developed during pregnancy, there may be a need for dietary nutrition for pregnant women.