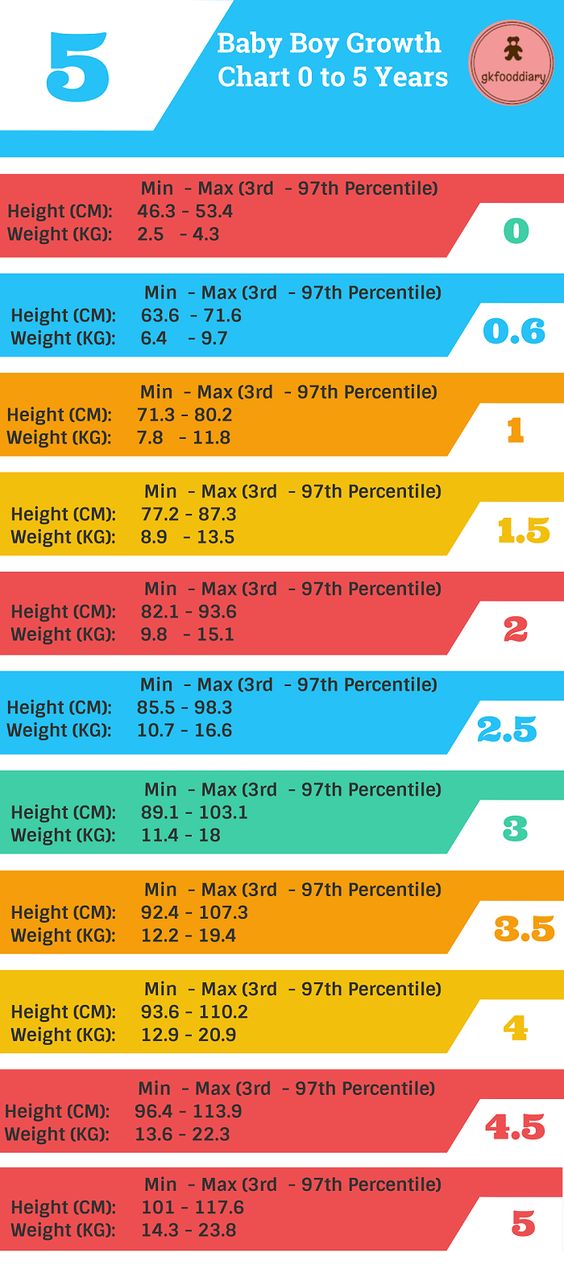
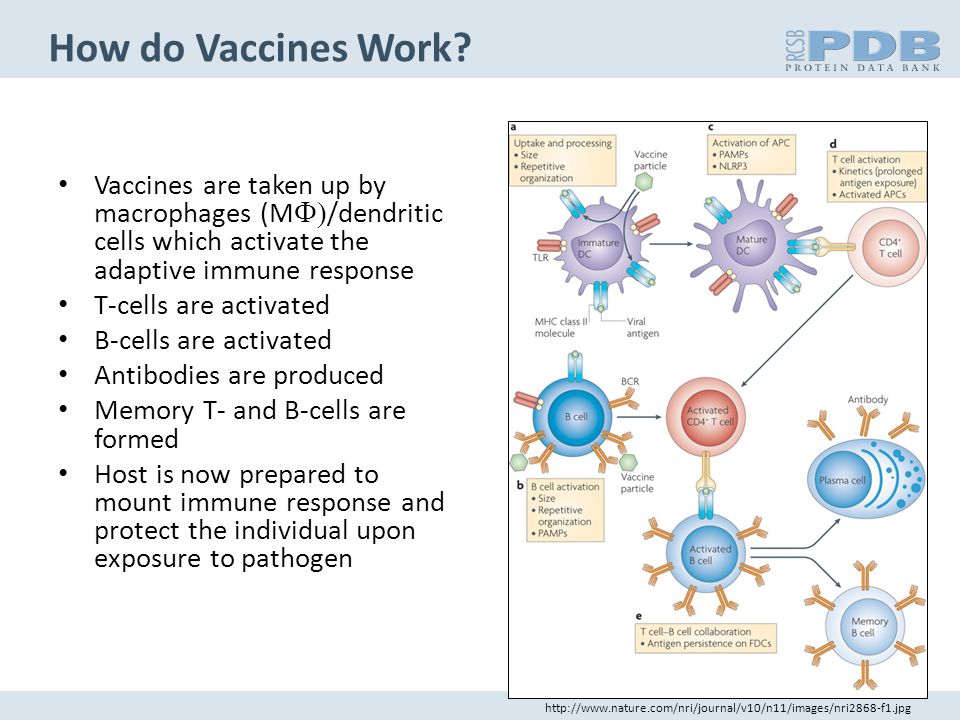
Can you pass blood clots and still be pregnant
Blood clots during pregnancy: Symptoms and prevention
There is nothing quite like the feeling of not being able to catch your breath. When I was 22 years old, I had trouble breathing. I eventually went to the hospital where they diagnosed me with a pulmonary embolism—a blood clot in the lung, a rare condition for a person of my age. I later learned that I had a genetic condition that increased my likelihood of developing a blood clot.
My clot was broken up and I was treated for some time afterward with blood thinners, but I knew that in the future I would need to take proactive measures if I were to become pregnant or have surgery. Blood clots during pregnancy are a concern for many expectant mothers, but as I learned, it is possible to manage your high risk.
What is a blood clot?
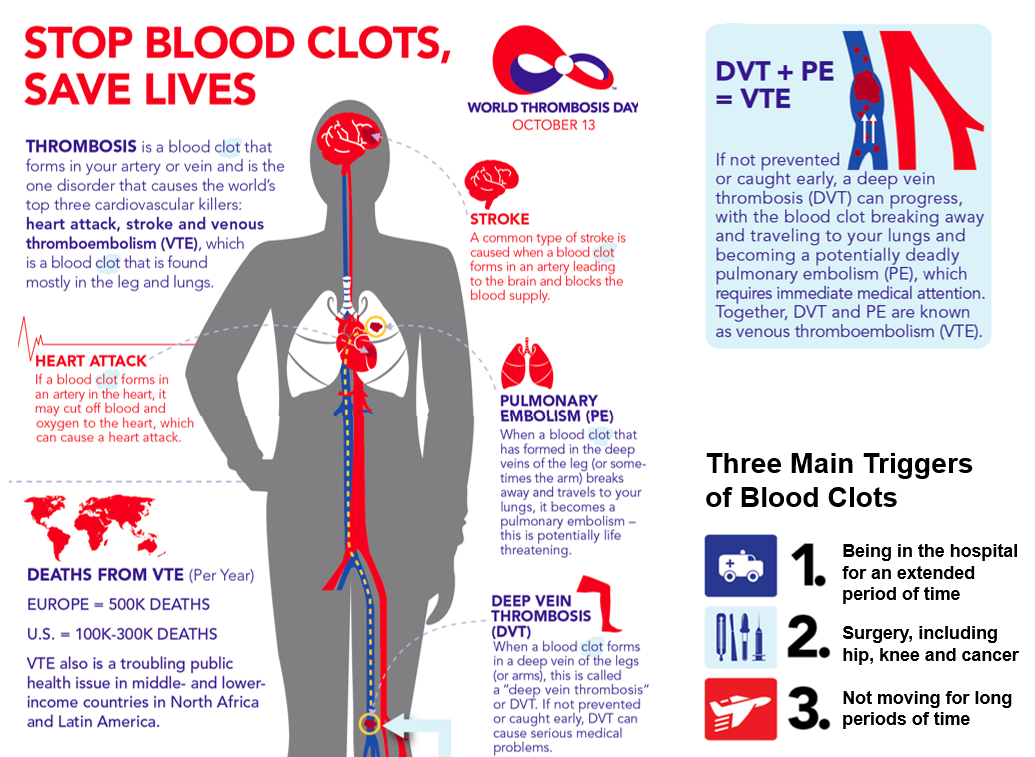
Blood clotting is a natural process that occurs when blood clumps together to form a gelatinous mass. This process protects your body from bleeding too much when you’ve been injured, as clotting can seal off the wound. Blood clotting (called thrombosis) can also cause complications, especially when it happens internally in your blood vessels.
This can happen in any blood vessel in the body. However, the most common place for abnormal blood clots to occur is in the deep veins of your legs. This is called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The major concern is that the clot can break free and travel to other parts of the body (lungs are most common), which can lead to serious complications or even death.
Why are pregnant women at greater risk of blood clots?
In pregnancy, the body is primed to clot to prevent blood loss during delivery. While this is important, it also increases the risk of clotting problematically.
It is estimated that pregnant women may be up to five times more likely to experience blood clots than non-pregnant women. There are several reasons for this uptick. Higher-than-normal levels of estrogen during pregnancy are known to increase clotting risk, although the exact mechanism by which this happens is unknown.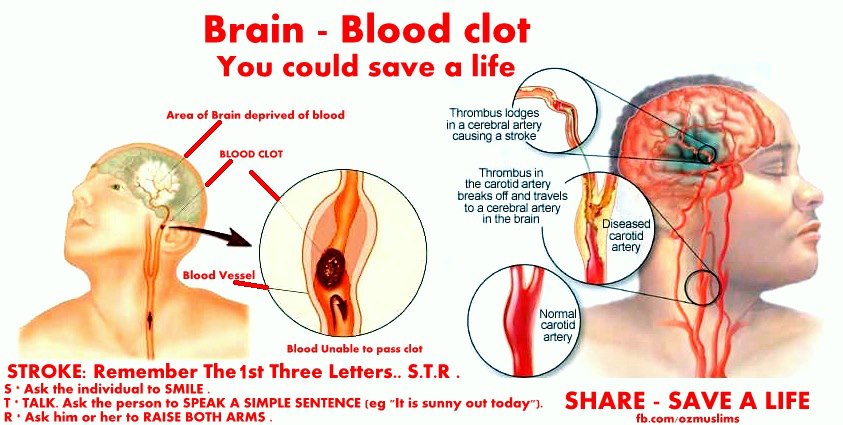 Also, a woman’s blood clots more easily in preparation for childbirth in order to reduce blood loss at delivery. Restricted blood flow may also raise the likelihood of blood clots. As the baby gets larger during pregnancy, it places more pressure on the blood vessels in the pelvic region, resulting in a restriction of blood flow that can also cause blood clots. If bed rest is required, lack of movement can decrease blood flow to the arms and legs, also increasing risk.
Also, a woman’s blood clots more easily in preparation for childbirth in order to reduce blood loss at delivery. Restricted blood flow may also raise the likelihood of blood clots. As the baby gets larger during pregnancy, it places more pressure on the blood vessels in the pelvic region, resulting in a restriction of blood flow that can also cause blood clots. If bed rest is required, lack of movement can decrease blood flow to the arms and legs, also increasing risk.
A blood clot in the lung, also known as a pulmonary embolism, is a leading cause of maternal death for pregnant women in the U.S., according to the CDC. And the risk of developing blood clots isn’t just during the pregnancy—it continues to be a concern for approximately three months after giving birth. Delivery by cesarean section (C-section) nearly doubles your risk after birth.
“Pregnant women are at a higher risk of DVT for several reasons,” says Nisha Bunke, MD, a vein specialist and diplomate of the American Board of Venous and Lymphatic Medicine, “a hypercoagulable state (proteins in the blood make it thicker, and more likely to form clots), an enlarged uterus may put pressure on the veins in the lower abdomen, and the hormones decrease venous tone.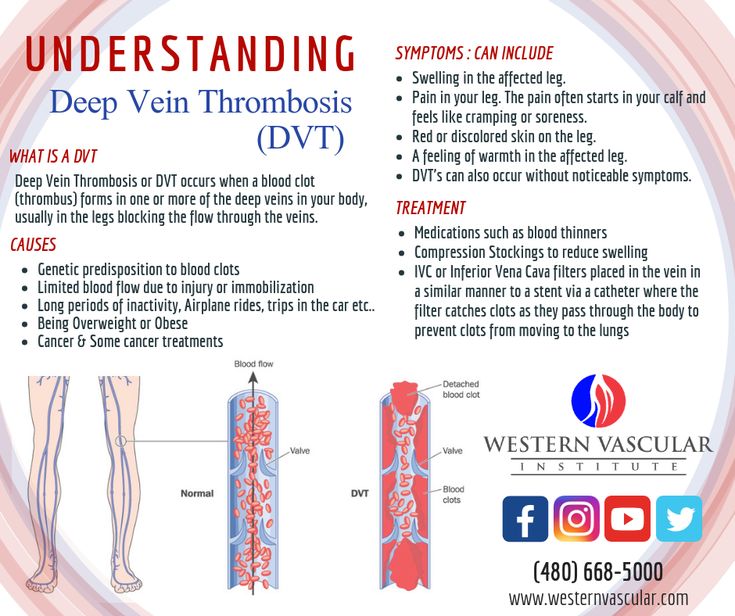 ”
”
Anyone can develop a blood clot during pregnancy, however it is more likely under certain conditions, or for those who already have some risk factors. Dr. Bunke adds that “some women have risk factors that increase their risk of DVT even more during pregnancy, like inherited blood clotting disorders, medical conditions such as lupus and sickle cell disease, obesity, immobility and age over 35.”
Other factors that may increase the risk of clotting during pregnancy are:
- Family history of blood clots
- Multifetal gestation (twins or more)
- Being dehydrated
- Traveling long distances (sitting for long time periods)
- Prolonged stillness, like bed rest during pregnancy
- Other medical conditions
- Transfusion at delivery
- Peripartum cardiomyopathy
- Postpartum hemorrhage
- Pre-eclampsia
What are other risk factors for blood clots?
In addition to pregnancy, the following risk factors can increase your risk of developing a blood clot.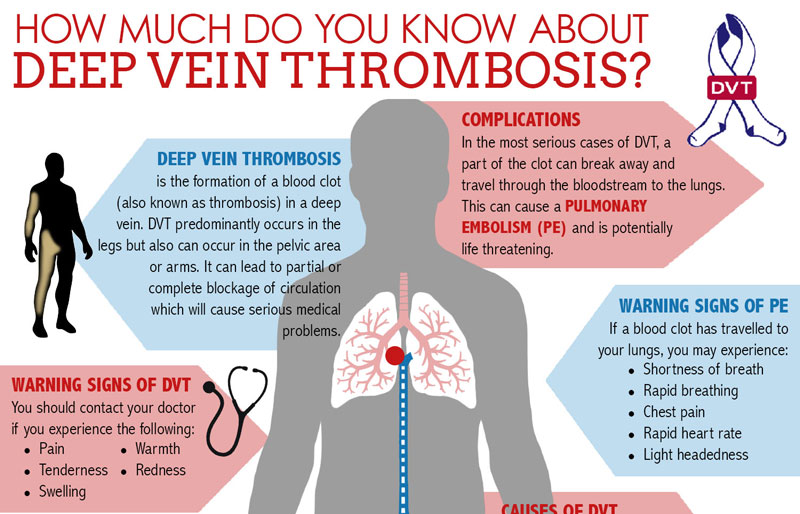
Acquired:
- Smoking
- Being overweight or obese (a BMI of 30 or greater)
- Having a surgery, hospitalization or illness that necessitates prolonged bed rest
- Traveling for long stretches by car or plane with little movement
- Being on estrogen-containing contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy
- Having cancer
Genetic:
- Having a family member who’s had a blood clot
- Having a personal history of blood clots
- Having a personal history of unexplained miscarriages
Condition-related:
- Atherosclerosis
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Vasculitis
- Heart failure
- Irregular heartbeat
- Metabolic syndrome
Additionally, some people may be predisposed to getting blood clots if they have thrombophilias, a group of disorders that increase a person’s risk of thrombosis (abnormal blood clotting). This was my case, with a condition known as Protein C Deficiency.
This was my case, with a condition known as Protein C Deficiency.
Symptoms of blood clots during pregnancy
“The most obvious symptom of DVT is swelling and heavy pain or extreme tenderness in one of your legs,” says Kendra Segura, MD, a board-certified OB-GYN in Southern California. Other symptoms include:
- Swelling
- Pain in the legs while in motion
- Skin feels warm or tender
- Redness, usually behind the knee
- A heavy, painful sensation
Dr. Segura says if you are experiencing these symptoms you must seek medical attention immediately. Your healthcare provider may require further testing because “it’s not always easy to diagnose DVT in pregnancy from symptoms alone,” she says.
What problems are associated with blood clots during pregnancy?
Blood clots during pregnancy can increase your risk of complications including:
- Blood clots in the placenta that can inhibit blood flow to your baby, causing damage to a developing fetus.
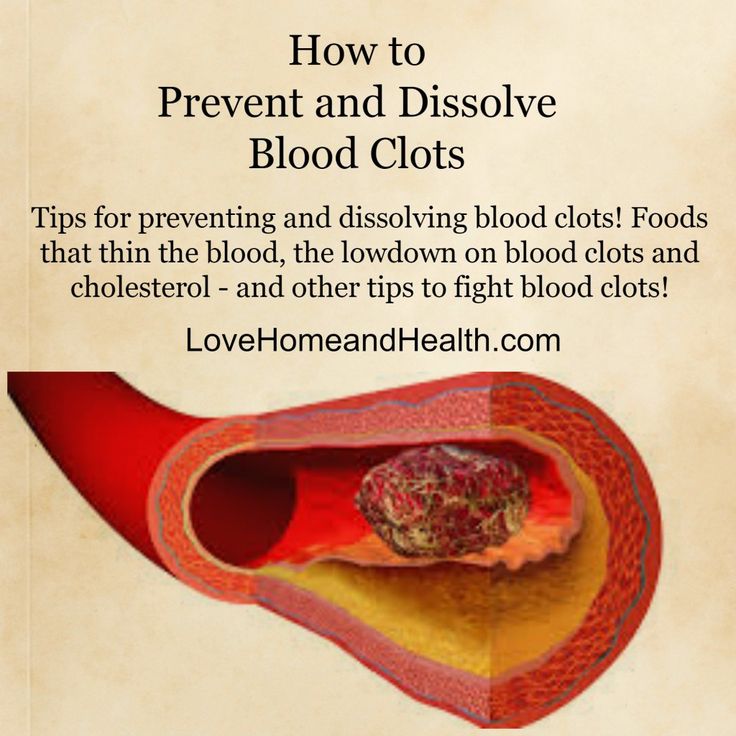
- Heart attack can occur if a blood clot blocks blood flow to the heart.
- Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or when your baby does not grow as expected, may occur.
- Miscarriage can occur before week 20 of your pregnancy.
- Placental insufficiency may occur, reducing the supply of necessary food and oxygen to your baby.
- Preeclampsia, a dangerous condition marked by high blood pressure and high levels of protein in the urine, may occur after week 20 in your pregnancy or immediately after childbirth. This can be fatal if not treated.
- Premature birth, in which your baby is born prior to week 37 of pregnancy, may occur.
- Pulmonary embolism, or a blood clot that moves to the lung, can potentially lower your blood oxygen levels and damage your organs, even leading to death.
- Stillbirth, or death of a baby after week 20 of pregnancy, may occur.

- Stroke can occur if a blood clot blocks one of the blood vessels that supplies blood to the brain or causes a blood vessel in the brain to burst.
- Sudden death
- Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot inside of a blood vessel impedes blood flow. Central vein thrombosis (CVT) occurs in the brain, and deep vein thrombosis usually occurs in the leg.
- Venous thromboembolism occurs if a blood clot travels to the brain, lungs, or heart.
Bleeding during early pregnancy
Sometimes during pregnancy, women pass blood clots vaginally, which is an understandable cause of concern.
In the first trimester of pregnancy (first three months), women may bleed as a result of implantation (where the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine wall) or due to early pregnancy loss (miscarriage). Implantation bleeding is usually light and not enough to soak a pantiliner. While not all cases of passing clots within the first 12 weeks of pregnancy are indicative of a loss, vaginal bleeding during pregnancy can be indicative of a complication.
For example, bleeding during the first trimester of pregnancy may be caused by a cervical infection, subchorionic hematoma (bleeding from the membranes surrounding the fetus), cervical polyps, ectopic pregnancy, or molar pregnancy (in which a fertilized egg develops into abnormal tissue). That’s why if you experience bleeding of any kind–including blood clots, it’s best to follow up with your obstetrician, gynecologist, or another healthcare professional.
Blood clots that develop in the body can increase the risk of miscarriage, or loss of a fetus prior to 20 weeks of pregnancy. Signs of a miscarriage include vaginal spotting or bleeding, abdominal cramping, back pain, and passing fluid, tissue or blood clots from the vagina. Light vaginal bleeding often occurs during the first trimester, but if you are bleeding or passing blood clots or tissue, seek immediate medical attention and bring the discharge to your provider.
Bleeding in the second and third trimesters
In the second and third trimesters, bleeding could be caused by a variety of factors. These may include miscarriage, preterm labor, or obstetric abnormalities including placenta previa, or placental abruption. Bleeding and especially passing clots during pregnancy can be a sign of miscarriage, preterm labor, or other complications, so make sure to contact your healthcare provider if you experience bleeding.
These may include miscarriage, preterm labor, or obstetric abnormalities including placenta previa, or placental abruption. Bleeding and especially passing clots during pregnancy can be a sign of miscarriage, preterm labor, or other complications, so make sure to contact your healthcare provider if you experience bleeding.
How to prevent and treat blood clots in pregnancy
When it comes to DVT in pregnancy, prevention is key. In my own case, I was known to have a higher risk due to a thrombophilic disorder, as well as a history of previous clots. This meant that I was given an injectable low-molecular-weight Heparin (LMWH) drug (Fragmin coupons | Fragmin details) for the duration of my pregnancy as a preventive measure.
There are also other preventative measures that can help lower your risk of clots, Dr. Segura says, including:
- Wearing compression stockings
- Keeping well-hydrated
- Staying active (“Regular exercise improves circulation,” Dr.
 Segura notes.)
Segura notes.) - Avoid prolonged sitting or bed rest, travel can also be considered prolonged bed rest
- Avoiding smoking
- Communicating any other medical conditions to your doctor
- Keep your blood pressure normal
Although the development of blood clots during pregnancy can be dangerous, they are still fairly uncommon—and treatable. Due to associated risks to you and your developing baby, getting diagnosed and treated as soon as possible is crucial.
Anticoagulant medications (also known as blood thinners) can be prescribed to help to break up the clot and get the blood moving again. Dr. Segura says that both Heparin and low-molecular-weight Heparin are safe in pregnancy for mother and baby. The main side effect of taking blood thinners is an increased risk of bleeding, so your doctor will monitor you as the pregnancy progresses.
Vaginal Bleeding and Blood Clots During Pregnancy
Written by Stephanie Watson
In this Article
- Bleeding in the First Trimester
- Bleeding in the Second and Third Trimesters
- What to Do If You Have Abnormal Bleeding During Pregnancy
Bleeding during pregnancy is common, especially during the first trimester, and usually it's no cause for alarm.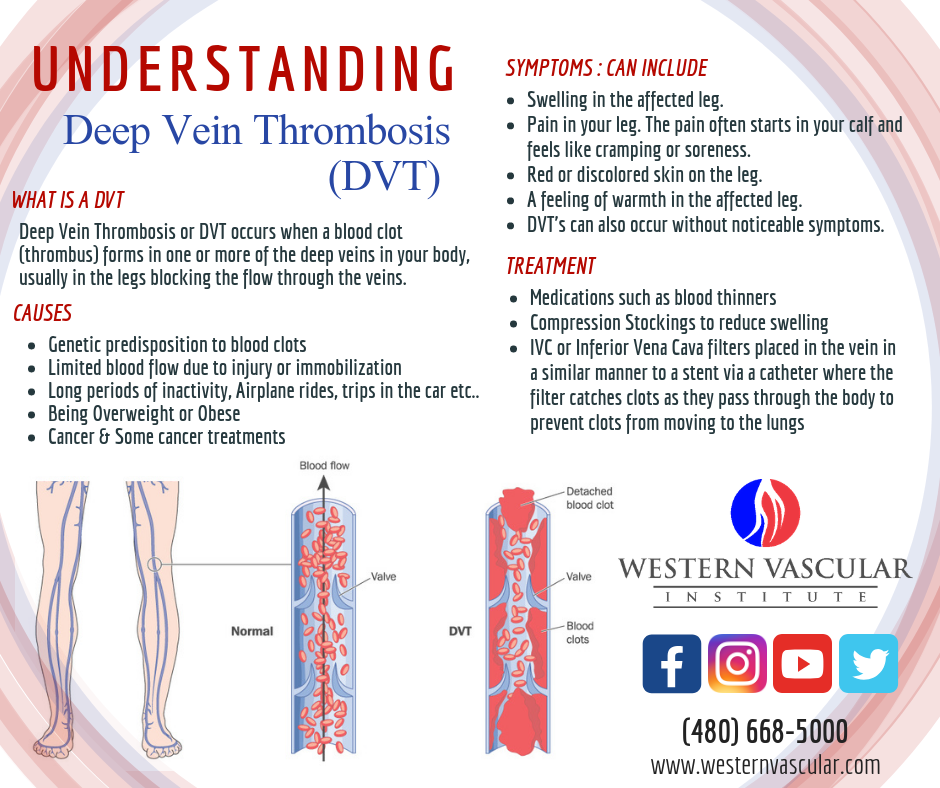 But because bleeding can sometimes be a sign of something serious, it's important to know the possible causes, and get checked out by your doctor to make sure you and your baby are healthy.
But because bleeding can sometimes be a sign of something serious, it's important to know the possible causes, and get checked out by your doctor to make sure you and your baby are healthy.
Bleeding in the First Trimester
About 20% of women have some bleeding during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. Possible causes of first trimester bleeding include:
Implantation bleeding. You may experience some normal spotting within the first six to 12 days after you conceive as the fertilized egg implants itself in the lining of the uterus. Some women don't realize they are pregnant because they mistake this bleeding for a light period. Usually the bleeding is very light and lasts from a few hours to a few days.
Miscarriage. Because miscarriage is most common during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, it tends to be one of the biggest concerns with first trimester bleeding. However, first trimester bleeding does not necessarily mean that you’ve miscarried or will miscarry. In fact, if a heartbeat is seen on ultrasound, over 90% of women who experience first trimester vaginal bleeding will not miscarry.
In fact, if a heartbeat is seen on ultrasound, over 90% of women who experience first trimester vaginal bleeding will not miscarry.
Other symptoms of miscarriage are strong cramps in the lower abdomen and tissue passing through the vagina.
Ectopic pregnancy. In an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized embryo implants outside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. If the embryo keeps growing, it can cause the fallopian tube to burst, which can be life-threatening to the mother. Although ectopic pregnancy is potentially dangerous, it only occurs in about 2% of pregnancies.
Other symptoms of ectopic pregnancy are strong cramps or pain in the lower abdomen, and lightheadedness.
Molar pregnancy (also called gestational trophoblastic disease). This is a very rare condition in which abnormal tissue grows inside the uterus instead of a baby. In rare cases, the tissue is cancerous and can spread to other parts of the body.
Other symptoms of molar pregnancy are severe nausea and vomiting, and rapid enlargement of the uterus.
Additional causes of bleeding in early pregnancy include:
- Cervical changes. During pregnancy, extra blood flows to the cervix. Intercourse or a Pap test, which cause contact with the cervix, can trigger bleeding. This type of bleeding isn't cause for concern.
- Infection. Any infection of the cervix, vagina, or a sexually transmitted infection (such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, or herpes) can cause bleeding in the first trimester.
Bleeding in the Second and Third Trimesters
Abnormal bleeding in late pregnancy may be more serious because it can signal a problem with the mother or baby. Call your doctor as soon as possible if you experience any bleeding in your second or third trimester.
Possible causes of bleeding in late pregnancy include:
Placenta previa. This condition occurs when the placenta sits low in the uterus and partially or completely covers the opening of the birth canal. Placenta previa is very rare in the late third trimester, occurring in only one in 200 pregnancies. A bleeding placenta previa, which can be painless, is an emergency requiring immediate medical attention.
A bleeding placenta previa, which can be painless, is an emergency requiring immediate medical attention.
Placental abruption. In about 1% of pregnancies, the placenta detaches from the wall of the uterus before or during labor and blood pools between the placenta and uterus. Placental abruption can be very dangerous to both the mother and baby.
Other signs and symptoms of placental abruption are abdominal pain, clots from the vagina, tender uterus, and back pain.
Uterine rupture. In rare cases, a scar from a previous C-section can tear open during pregnancy. Uterine rupture can be life-threatening, and requires an emergency C-section.
Other symptoms of uterine rupture are pain and tenderness in the abdomen.
Vasa previa. In this very rare condition, the developing baby's blood vessels in the umbilical cord or placenta cross the opening to the birth canal. Vasa previa can be very dangerous to the baby because the blood vessels can tear open, causing the baby to bleed severely and lose oxygen.
Other signs of vasa previa include abnormal fetal heart rate and excessive bleeding.
Premature labor. Vaginal bleeding late in pregnancy may just be a sign that your body is getting ready to deliver. A few days or weeks before labor begins, the mucus plug that covers the opening of the uterus will pass out of the vagina, and it will usually have small amounts of blood in it (this is known as "bloody show"). If bleeding and symptoms of labor begin before the 37th week of pregnancy, contact your doctor right away because you might be in preterm labor.
Other symptoms of preterm labor include contractions, vaginal discharge, abdominal pressure, and ache in the lower back.
Additional causes of bleeding in late pregnancy are:
- Injury to the cervix or vagina
- Polyps
- Cancer
What to Do If You Have Abnormal Bleeding During Pregnancy
Because vaginal bleeding in any trimester can be a sign of a problem, call your doctor. Wear a pad so that you can keep track of how much you're bleeding, and record the type of blood (for example, pink, brown, or red; smooth or full of clots). Bring any tissue that passes through the vagina to your doctor for testing. Don't use a tampon or have sex while you are still bleeding.
Bring any tissue that passes through the vagina to your doctor for testing. Don't use a tampon or have sex while you are still bleeding.
Your doctor might recommend that you rest as much as you can and avoid exercise and travel.
You should expect to receive an ultrasound to identify what the underlying cause of your bleeding may be. Vaginal and abdominal ultrasounds are often performed together as part of a full evaluation.
Go to the emergency room or call 911 right away if you have any of the following symptoms, which could be signs of a miscarriage or other serious problem:
- Severe pain or intense cramps low in the abdomen
- Severe bleeding, with or without pain
- Discharge from the vagina that contains tissue
- Dizziness or fainting
- A fever of more than 100.4 or more degrees Fahrenheit and/or chills
Health & Pregnancy Guide
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor and Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Guide Topics
Pregnancy and menstruation | Kotex®
The question “Am I pregnant?” probably occurred at least once to the vast majority of heterosexual women who are sexually active.
Although the absence of periods is the most noticeable early symptom of pregnancy, many women have many questions when it comes to whether menstruation is possible during pregnancy.
Is it possible to have periods during pregnancy?
No, they can't. If you have your period, it means that you are not pregnant.
Menstruation occurs only if the monthly egg that comes out of the ovaries has not been fertilized.
If the egg is not fertilized, it leaves the uterus and is excreted along with the menstrual blood through the vagina.
The difference from pregnancy seems obvious at first glance, because during pregnancy there are no periods, and if you are not pregnant and in reproductive age, then you have periods.
But some women have doubts about this, which are related to the fact that about 20-30% of pregnant women have irregular spotting, which in essence is not menstruation and differs from it: most often they have light pink or brown shade and not so abundant. Sometimes women confuse them with menstruation if they occur around the same time that menstruation is expected.
Sometimes women confuse them with menstruation if they occur around the same time that menstruation is expected.
-
normal menstrual bleeding is light at first and then increases, and the blood becomes more saturated red
-
normal menstrual bleeding becomes less intense towards the end of menstruation, the color also becomes less intense
What can cause bleeding during early pregnancy?
Bloody discharge during pregnancy can be associated with many factors, each of which is a reason to urgently visit a doctor to rule out pathology.
Main causes of bleeding in the first trimester of pregnancy:
-
bleeding after attachment of the egg to the wall of the uterus
-
signs of threatened miscarriage
-
infections
-
ectopic pregnancy
Many women who experience this light bleeding go on to have normal pregnancies and give birth to healthy children, but in about a third such bleeding becomes more intense over time and eventually leads to a miscarriage.
Unfortunately, there is no way to determine at home what caused such bleeding, so whenever such light bleeding occurs during pregnancy, you should consult your gynecologist for advice to rule out the possibility of pathology.
Important: if you are pregnant and have bleeding that becomes more intense and does not stop, accompanied by pain in the abdomen and lower back, you should immediately consult a doctor.
When do periods start after pregnancy?
Both after caesarean section and after vaginal delivery, women experience vaginal bleeding.
In the first weeks after childbirth, the blood may clot and be more intense than normal periods, but then they become brown, light red and finally whitish.
This discharge is called lochia and usually lasts no more than 45 days after vaginal delivery and up to 60 days in women after caesarean section. Lochia begins immediately after childbirth, and menstruation occurs only when the level of the hormone prolactin in the woman's body drops, which causes the appearance of breast milk.
If you are not breastfeeding, your periods usually return 6-8 weeks after delivery.
If you are breastfeeding, you may not have your period for as long as you are breastfeeding your baby.
During lochia, it is recommended to use pads rather than tampons.
Abortion and menses
Many questions about menstruation also arise in women who have experienced an unplanned pregnancy and have decided to have an abortion.
How this procedure will affect the body depends on many factors, primarily on whether the abortion was medical or surgical. Bleeding after an abortion is normal, but in the truest sense of the word, menstruation is not.
Medical abortion
During a medical abortion, the doctor gives you two pills.
Usually, the first tablet is taken under the supervision of a doctor, in the clinic. After taking this pill, the endometrium of the uterus, to which the fertilized egg is attached, ceases to thicken, and pregnancy can no longer develop. Some women begin to bleed at this point.
Some women begin to bleed at this point.
The woman then leaves the clinic and takes the second pill at home. After taking it, the endometrium begins to separate from the walls of the uterus and exit through the vagina. Such bleeding usually begins 0.5-4 hours after taking the pill. Usually, at 4-5 hours of bleeding, it becomes more intense, then its intensity decreases, and it becomes similar to normal menstruation.
Surgical abortion
In the case of a surgical abortion, bleeding may begin immediately after the procedure, but in some women it begins after 3-5 days. Usually such bleeding is weaker than normal menstruation. Bleeding may stop or last until the next menstruation.
How long does bleeding last after an abortion?
Bleeding after any type of abortion often lasts 1-2 weeks. Most often, after this period, it becomes quite insignificant, and in some women it completely disappears until the next menstruation.
What should be the bleeding after an abortion?
Bleeding after an abortion is similar to normal menstruation, but the blood itself is often brown rather than red. After a medical abortion, it is usually more intense than after a surgical one.
You may notice blood clots and most of the time this is not a cause for concern, but if they continue to stand out against the background of heavy bleeding and continue for more than two hours, then your doctor should be contacted.
Many doctors do not recommend the use of tampons for at least two weeks after an abortion, during this period it is better to use hygienic gaskets.
First period after abortion
Abortion restarts the menstrual cycle.
Periods after it usually return to normal within 1-1.5 months after the procedure. The timing depends, among other things, on how long the pregnancy was terminated—as a rule, the longer the term, the more time it may take for the body to restore the usual level of hormones.
Pathological and physiological causes of bleeding during early pregnancy
The gestation period is a complex process that does not always go well. Every second woman has various complications. Most often, women go to the doctor with complaints of spotting. Why does bleeding occur during early pregnancy, how dangerous is it?
Causes of bleeding in pregnancy
Blood in the first trimester of pregnancy in the vaginal secretion is observed in 30% of expectant mothers. Bleeding can be weak, spotting, plentiful.
Most often, blood during early pregnancy is observed during implantation of the fetal egg. When the egg is attached, the vessels are often damaged, which leads to the appearance of blood secretions. They are similar to menstruation, last 1-2 days. This process is considered natural, does not indicate any pathologies.
Any bloody discharge during early pregnancy is a reason for an urgent appeal to a gynecologist. Even if there is no additional discomfort. At a remote consultation, our doctor will collect an anamnesis, draw up a clinical picture in order to identify the cause of bleeding. And he will select effective methods to eliminate the problem.
At a remote consultation, our doctor will collect an anamnesis, draw up a clinical picture in order to identify the cause of bleeding. And he will select effective methods to eliminate the problem.
Blood during pregnancy - other common causes
In addition to the main ones, there are some other reasons why pathology can develop.
| No. | Cause |
| one | Excessive exercise, deep penetration during intercourse. If the cervix is damaged, slight red discharge occurs, which disappears within two hours. |
| 2 | Progesterone deficiency. With a low level of the hormone, the body starts the process of menstruation. Bloody discharge during pregnancy appears when the uterine mucosa is exfoliated. The situation may adversely affect the implantation of the fetal egg. |
| 3 | Miscarriage - occurs in 2-8% of pregnant women. It is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen, which is rapidly increasing, bloody discharge at the beginning of pregnancy. The causes of the pathological condition can be different - infectious diseases, fetal malformations that are incompatible with life, dehydration, abdominal trauma, taking certain drugs. |
| four | Ectopic pregnancy. Dangerous condition, urgent hospitalization is required. |
| 5 | A failed miscarriage. Blood discharge during pregnancy, abdominal pain are the main manifestations of intrauterine development of the fetus. |
| 6 | Infections. To avoid dangerous complications, it is necessary to treat diseases. Parents of both sexes should be tested. |
| 7 | Full or partial hydatidiform mole. |
| eight | Cervical cancer. Pregnant women are rarely diagnosed. The risk group includes women with a large number of abortions and childbirth, often changing sexual partners. |
| 9 | Subchorionic hematoma. Hemorrhage around the placenta most often resolves on its own. But it increases the risk of preterm birth and other complications. |
| ten | Cervical erosion. Detected in 50% of women. For pregnant women, the disease is not dangerous, but constant medical supervision is needed. |
Bleeding in the first trimester can be caused by causes that appear at any gestational age. These are fibroids, polyps in the uterus and cervical canal, cardiovascular pathologies that are associated with a weakening of the endothelium.
Physiological or pathological bleeding during gestation - differences
Clinical manifestations of bleeding in pregnant women depend on the causes. Physiological discharge of blood from the genital tract in the early stages of gestation proceeds without deterioration in well-being. With bleeding caused by erosion, fibroids and polyps, there are also no additional discomfort. In this case, only a few drops of blood are released, it bleeds for a short time.
Abundant bleeding, similar to menstruation, against the background of a general satisfactory condition, occurs with a deficiency of progesterone.
Bleeding with spontaneous interruption is accompanied by constant or periodic pain in the lumbar region, abdomen. Disturbed by nausea, bouts of dizziness, slightly increased body temperature. Bleeding can be weak or intense, and clots are often observed in the discharge.
Disturbed by nausea, bouts of dizziness, slightly increased body temperature. Bleeding can be weak or intense, and clots are often observed in the discharge.
When a fertilized egg is fixed outside the uterus, internal bleeding often occurs, and discharge from the genital tract may appear much later. Characteristic manifestations - acute pain in the abdomen radiates to the anal region, right or left side, blood pressure decreases, cold sweat appears, fainting is possible. Significant blood loss leads to the development of a state of shock with a high probability of death.
Learn more about implantation bleeding
Why does it bleed at the initial stages of gestation? Most often, the appearance of spotting during pregnancy is associated with the implantation of the embryo. They occur 6-12 days after conception and are often one of the first signs of conception.
Usually, the appearance of spotting at the beginning of pregnancy coincides with the time of the onset of menstruation, if the cycle is regular. But discharge in pregnant women is not as abundant as menstrual bleeding. Duration - from several hours to three, with the first pregnancy up to 5 days.
But discharge in pregnant women is not as abundant as menstrual bleeding. Duration - from several hours to three, with the first pregnancy up to 5 days.
How does implantation bleeding manifest?
- weak, pulling pain in the lower abdomen;
- headache, dizziness;
- sudden change of mood;
- bouts of nausea;
- increased sensitivity, swelling of the mammary glands;
- fatigue, drowsiness.
Important! When the embryo is implanted, little blood is released, usually these are small specks. The discharge may be pink, brown, orange, and there should be no clots.
Possible causes of early bleeding by week
The first months of pregnancy are the most difficult and dangerous. It is in the early stages that various pathologies and complications often appear.
Why blood may appear in the early stages during pregnancy:
- At the 4th week of pregnancy, discharge with an admixture of blood may appear - this is implantation bleeding.
 Heavy bleeding is a dangerous sign, most often indicates a miscarriage. Spontaneous abortion can be caused by exercise, fever, infections, drugs or alcohol. Such bleeding is profuse, painful, blood clots are present.
Heavy bleeding is a dangerous sign, most often indicates a miscarriage. Spontaneous abortion can be caused by exercise, fever, infections, drugs or alcohol. Such bleeding is profuse, painful, blood clots are present. - The appearance of sanious discharge at the 5th week of pregnancy may be a sign of a missed pregnancy. The reasons are overwork, Rh conflict, bad habits, bacterial and viral diseases of the reproductive system, genetic disorders in the embryo. Symptoms - causeless fever, severe pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, the disappearance of signs of toxicosis.
- Blood in the discharge at the 6th week of pregnancy appears with an ectopic attachment of the fetal egg, fetal fading, Rhesus conflict. Discharge with blood at 6 weeks of pregnancy is a reason for an urgent visit to the gynecologist.
- At the 7th week of pregnancy, discharge with blood is not the norm. May indicate a miscarriage, missed or ectopic pregnancy.
- From the 8th week of pregnancy, one of the most dangerous periods of pregnancy begins.
 The formation of the placenta begins, the hormonal background changes. Bloody discharge appears with the threat of miscarriage or spontaneous abortion. Pregnancy is often not saved.
The formation of the placenta begins, the hormonal background changes. Bloody discharge appears with the threat of miscarriage or spontaneous abortion. Pregnancy is often not saved.
Pay attention! In the second trimester, bleeding occurs only in 5-10% of women. Most often this is due to late spontaneous abortion, isthmic-cervical insufficiency. The appearance of blood in the third trimester mainly occurs with presentation, placental abruption.
Early bleeding after IVF
The appearance of blood discharge during pregnancy on the 8-10th day after IVF is not considered a pathology, provided that the woman feels normal. After the introduction of the embryo into the uterine cavity, minor damage to the small uterine vessels often occurs. Brown, dark cream, pale pink, odorless discharge most often indicates a successful transplant, pregnancy.
If spotting after IVF is observed for 1-2 days, slight pulling pains in the lower abdomen are disturbing, this may be due to a progesterone deficiency. After the examination, the doctor will adjust the hormonal maintenance therapy.
After the examination, the doctor will adjust the hormonal maintenance therapy.
Pink discharge on the 16th day after the transfer is a dangerous symptom. It may be a sign of detachment of the fetal egg, the threat of termination of pregnancy.
According to studies, uterine bleeding in the first trimester is a common occurrence in pregnancy after IVF. Discharge does not affect the incidence of adverse reproductive outcomes. The number of embryo rejections in women with and without uterine bleeding is approximately the same. Consult with our doctors by phone for more details.
Diagnostics
If blood has gone from the genitals of a pregnant woman, the doctor conducts an external and gynecological examination.
Analyzes and examinations:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- tests for hCG, other hormones;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- CTG is performed to assess the vital activity of the fetus.

Treatment
Methods of treatment depend on the results of the examination.
Bloody discharge in the first trimester - causes and therapeutic measures:
| The reasons | Treatment |
| Miscarriage | Cleansing the uterus. |
| Ectopic pregnancy | Diagnostic laparoscopy, removal of residual fetal tissues, antibiotic therapy. |
| Risk of miscarriage | Hospitalization, bed rest, prescribing drugs to maintain pregnancy, sedatives and tocolytics to reduce uterine tone. |
| bubble skid | Curettage of the uterine cavity. |
| Cervical cancer | Operational intervention. |
| Polyp injury, cervical erosion | Expectant management, if the condition does not worsen, removal and cauterization is carried out after childbirth. |
| progesterone deficiency | hormone therapy. |
| Damage to the uterus | Complete bed rest. |
| Infectious pathologies | Depending on the type of pathogen - antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs. |
Complications and consequences
It is impossible to ignore bloody impurities in vaginal discharge during pregnancy. Without proper and timely assistance, the following complications may occur:
- miscarriage;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- the development of an infectious process, sepsis due to the remainder of dead tissues in the uterine cavity;
- profuse blood loss can lead to death.
Important! Urgent medical attention is needed in case of heavy bleeding, bright scarlet blood, presence of blood clots in the discharge. In life-threatening and fetal conditions, severe pain in the abdomen, lower back, convulsions, profuse cold sweat, and loss of consciousness are disturbing.
In life-threatening and fetal conditions, severe pain in the abdomen, lower back, convulsions, profuse cold sweat, and loss of consciousness are disturbing.
Methods of prevention
If there is blood in the first trimester, it is important to remain calm. Stress and anxiety will only exacerbate the situation. But any health problem is easier to prevent than to treat.
How to avoid bleeding during childbearing - recommendations from a gynecologist:
- eat right and balanced, give up junk and junk food, eat more fresh vegetables and fruits;
- observe the drinking regime;
- in the absence of contraindications, moderate physical activity is indicated - yoga, swimming, special gymnastics for pregnant women;
- more time to walk in the fresh air;
- avoid stress, overwork, observe the daily routine, get enough sleep;
- give up bad habits, do not be in smoky rooms;
- timely visit a gynecologist;
- according to the doctor's prescription, take vitamin complexes for pregnant women;
- do not self-medicate.

The prognosis for bleeding during gestation depends on the causes and timely visit to the doctor. Properly provided medical care can save the life of the fetus and the woman.
FAQ
Why is there blood from the genital tract during gestation?
+
The causes of bleeding in early pregnancy are different. Most often, spotting appears when the fetal egg is fixed, progesterone deficiency, with erosion of the cervix and polyps. Dangerous causes - ectopic, molar, miscarriage, miscarriage.
What to do if there is bleeding during pregnancy?
+
Much depends on the amount of blood released, general well-being. If the bleeding is not strong, not for long, the general condition is normal, it is enough to lie down and rest. Write down the date of the attack, inform the doctor at the next visit. But if even slight spotting during early pregnancy lasts more than 72 hours, is accompanied by cramping or acute pain, fever, you should immediately visit a gynecologist or call an ambulance.
How can you recognize a miscarriage?
+
With the threat of interruption, spotting is scanty, pain in the lower abdomen is absent or may be dull, aching. The condition is considered reversible, with timely treatment, pregnancy can be saved. If a miscarriage has begun, bleeding intensifies, cramping pain appears. The general condition is satisfactory. Urgent hospitalization is required, the probability of maintaining pregnancy is decided on an individual basis.
Expert opinion:
Bleeding during pregnancy is a dangerous symptom. Sometimes spotting can be caused by physiological reasons. But often such a symptom appears in life-threatening conditions for the woman and the fetus.
We publish only verified information
Article author
Menshikova Maria Viktorovna obstetrician-gynecologist
Experience 38 years
Consultations 1816
Articles 46
Specialist with extensive practical experience.

 Pathology of the chorion, in which the size of the villi increases, bubble expansions form. The risk group includes women with ovarian dysfunction, inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, and a history of cystic mole. Bleeding is profuse and constant, characteristic blisters are present. The symptoms of early toxicosis are very pronounced, the size of the uterus, the hCG indicators do not correspond to the gestational age.
Pathology of the chorion, in which the size of the villi increases, bubble expansions form. The risk group includes women with ovarian dysfunction, inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, and a history of cystic mole. Bleeding is profuse and constant, characteristic blisters are present. The symptoms of early toxicosis are very pronounced, the size of the uterus, the hCG indicators do not correspond to the gestational age.