Can you get pregnant with cysts on your ovaries
How to Get Pregnant with Ovarian Cysts?
- How to Get Pregnant with Ovarian Cysts?
- How does an ovarian cyst form?
- Infertility due to cysts
- Follicular cysts and pregnancy
- Chocolate cysts and pregnancy
- Types of an ovarian cyst (Broadly divided according to fertility) -
- Cysts which don’t interfere with fertility/pregnancy
- Cysts, which interfere with fertility/pregnancy
- How to conceive with ovarian cysts?
- Ovarian cyst success story
- Doctor’s suggestion on ovarian cyst
- How can medicover fertility help women with fertility issues caused by ovarian cyst?
- Can you ovulate with an ovarian cyst?
- Can you get pregnant with cyst on ovary?
- How soon after ovarian cyst removal can you get pregnant?
- Can a cyst stop you from getting pregnant?
- Can ovarian cysts cause infertility?
- Does ovarian cyst removal affect fertility?
- Do ovarian cyst causes infertility?
- Can you get pregnant with large ovarian cyst?
- Will para-ovarian cyst affect pregnancy?
- Will ovarian torsion affect pregnancy?
- I have dermoid cyst, will it affect my pregnancy?
- Tissues from one of my ovaries is removed due to cyst.
Can I still get pregnant?
- What are the chances of a successful IUI with a cyst?
Medicover Fertility
-
- ✓ State-of-The-Art Technology
- ✓ Patient Centric Approach
- ✓ Cost Effective Treatment
- ✓ 26+ Years of Experience
Book An Appointment
How to Get Pregnant with Ovarian Cysts?
To increase your chances of getting pregnant with ovarian cysts, one needs to have good health, and a healthy lifestyle, and must eat a balanced diet. Several health conditions may upset the plans of having a baby by affecting fertility. One such health condition may be the presence of ovarian cyst. Ovarian cyst can be associated with decreased fertility, but it depends on the type of ovarian cyst. There is also an increased chance of pregnancy success after cyst removal.
Ovarian cysts are common in females who have regular periods, and they usually form during ovulation.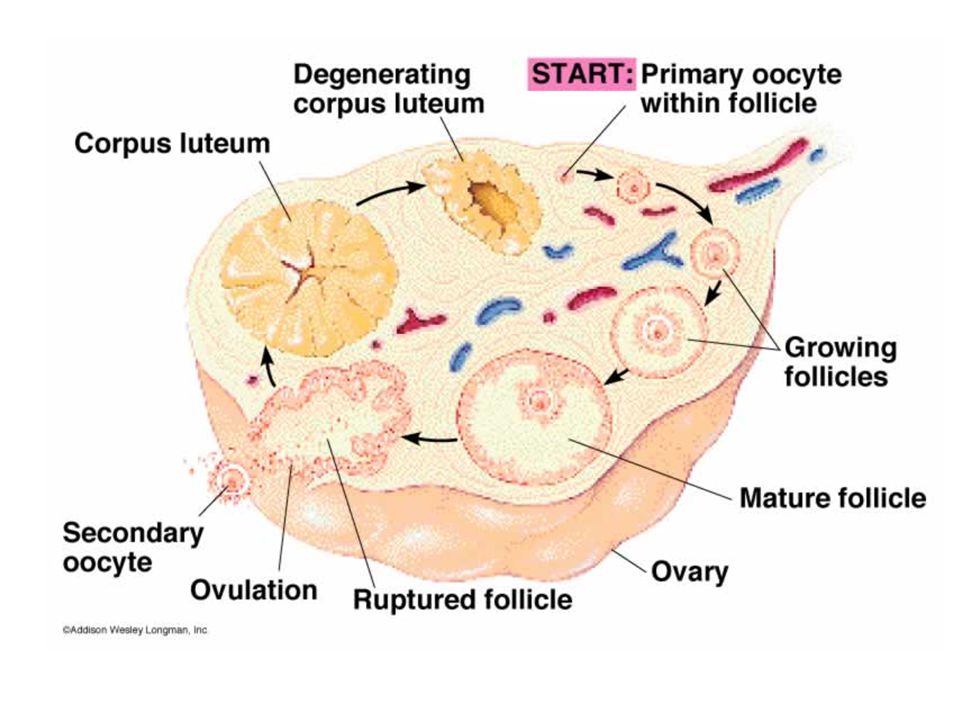 Hence females must keep a regular check on their fertile window, and for this purpose, they can use an ovulation calculator. It monitors your most fertile days and helps you analyse whether you are not prone to any other related health concern by calculating your fertility window.
Hence females must keep a regular check on their fertile window, and for this purpose, they can use an ovulation calculator. It monitors your most fertile days and helps you analyse whether you are not prone to any other related health concern by calculating your fertility window.
How Does an Ovarian Cyst Form?
Each month the brain stimulates the ovary to make (an) egg by releasing a hormone that stimulates a follicle to grow. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) causes a fluid collection around an egg to enlarge. Once the egg is mature, a second hormone is released by the brain to get the ovary to release the egg. After the egg comes out (Ovulation), the follicular cyst converts to a cyst that has a yellow pigment called lutein. So, during each monthly cycle, there is a cyst normally present in the ovary.
For the first two weeks, the growing follicular cyst contains the maturing egg, and for the second two weeks, the corpus luteum makes a hormone to help promote pregnancy. In rare cases, fluid accumulates within a thin membrane inside the ovary, and there is no egg inside and forms a cyst. If a cyst grows larger than 5 centimetres, one must have check-ups in a month or two to see if it will continue to grow. If it gets larger, then one might need surgery to remove the cyst. Even though these types of cysts always don’t have a negative effect on fertility.
In rare cases, fluid accumulates within a thin membrane inside the ovary, and there is no egg inside and forms a cyst. If a cyst grows larger than 5 centimetres, one must have check-ups in a month or two to see if it will continue to grow. If it gets larger, then one might need surgery to remove the cyst. Even though these types of cysts always don’t have a negative effect on fertility.
Infertility Due to Cysts
In some cases, when women are on birth control pills or hormone medications, they will not be able to conceive. The contraceptive medication prevents ovulation and hence inhibits pregnancy. Oral contraceptive is prescribed to those women who are currently not considering family planning.
Some cysts like functional cysts, dermoid and cystadenomas do not affect the fertility of a woman or the normal functioning of the ovaries. Cysts like endometriomas can cause infertility and prevent a woman from being able to conceive naturally. Women whose ovaries continue to make lots of small cysts are known to have a condition called polycystic ovaries.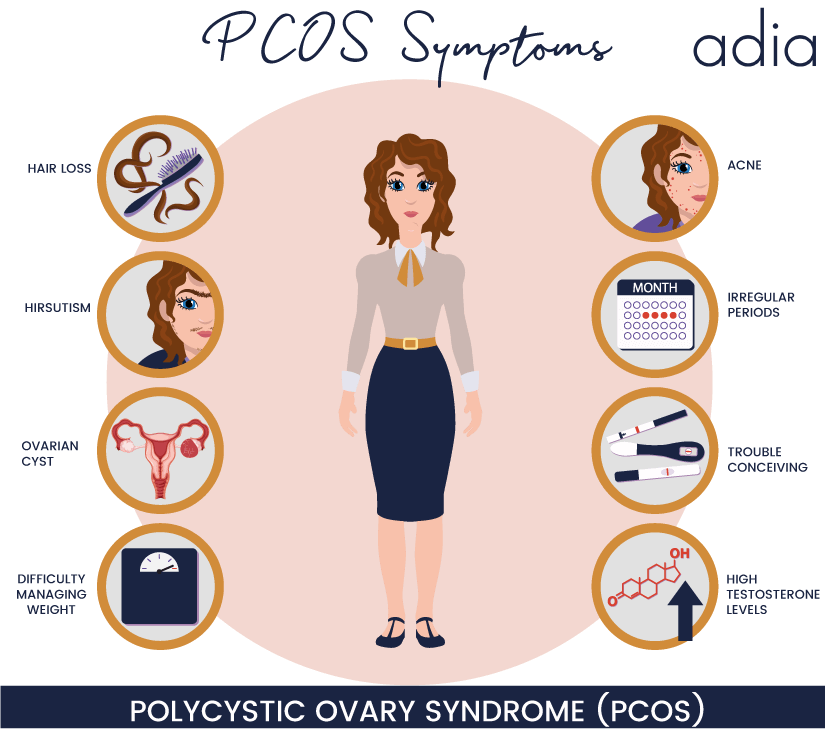 These are a non-functional cyst and do not go on their own. The ovarian cyst infertility prevents a woman from getting pregnant by causing a hormonal imbalance and restricting follicle maturation.
These are a non-functional cyst and do not go on their own. The ovarian cyst infertility prevents a woman from getting pregnant by causing a hormonal imbalance and restricting follicle maturation.
Follicular Cysts and Pregnancy
The functional cysts such as follicular cysts or corpus luteum cysts – are the most common type of ovarian cysts and get developed during the normal menstrual cycle. They don’t contribute to infertility. In-fact the necessary functions leading to fertility are taking place.
Chocolate Cysts and Pregnancy
Chocolate cysts actually are the scars containing old blood. They attach to the ovaries and may adversely affect the ovarian function. In some cases, these cysts can prevent ovaries from functioning and affect conceiving.
Types of an Ovarian Cysts (Broadly Divided according to Fertility)
1) Cysts, which don’t affect fertility/pregnancy
2) Cysts, which interfere with fertility/pregnancy
1) Cysts which Don’t Interfere with Fertility/Pregnancy
These ovarian cysts, even though they may bleed and cause pain, will not affect one’s fertility unless their size increases significantly.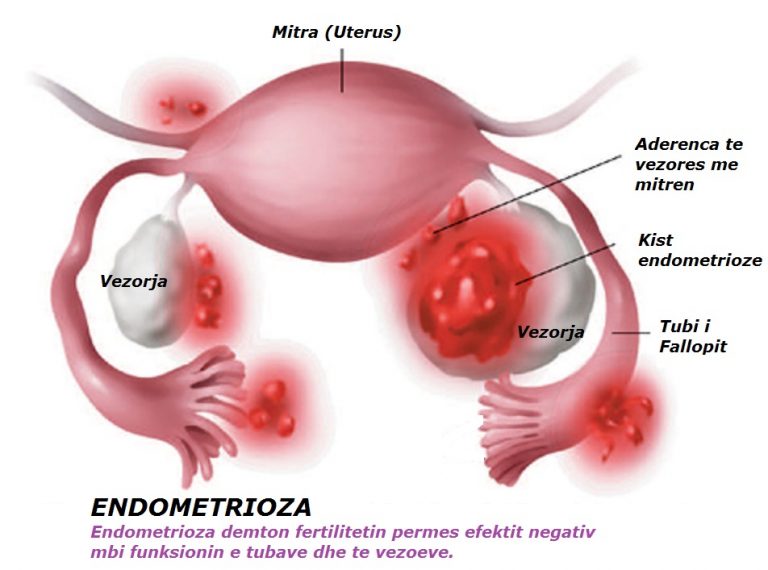
- FUNCTIONAL OVARIAN CYSTS
A functional cyst is either follicular or luteal cyst that develops on the surface of the ovary during the menstrual cycle. They usually hold a developing egg. In a normal case, the sac becomes small and dissolves once the egg is released. This sac may swell up with fluid, if an egg is not released, or if the sac closes again after the egg is released. These cysts do not show any signs or symptoms. They usually dissolve without any treatment after a couple of menstrual cycles. Functional cysts do not cause infertility, and pregnancy can easily be achieved with a functional cyst.
However, if a cyst becomes too large, it can get ruptured and bleed, and ovarian torsion can happen that can cause extreme pain. Ovarian torsion happens in cases of enlarged ovaries. The incidence of ovarian torsion rises 5-6-fold during pregnancy. If not diagnosed in time, it can cause foetal death and even potential loss of fertility of the woman.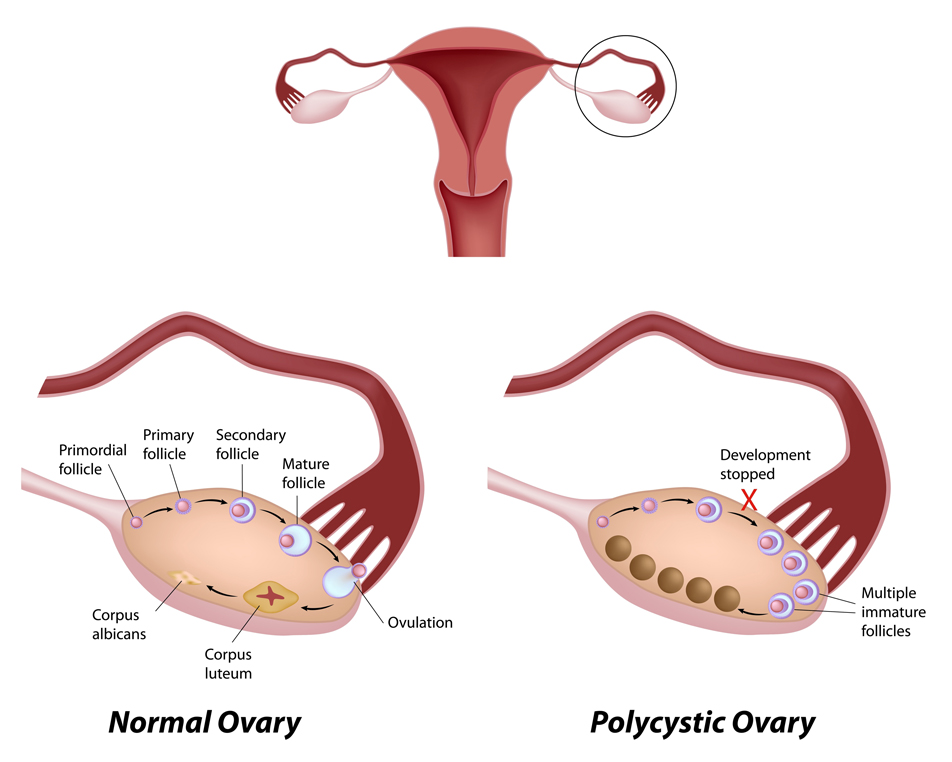 So, a large cyst should be monitored to avoid any fatal consequence. Ruptured cysts can cause pelvic infection, which may scar the fallopian tubes and can affect getting pregnant.
So, a large cyst should be monitored to avoid any fatal consequence. Ruptured cysts can cause pelvic infection, which may scar the fallopian tubes and can affect getting pregnant.
- CYSTADENOMAS
They are a kind of benign tumour. They are growths in the ovary that develop from the tissues at the surface of the ovary. Although they require treatment, cystadenomas do not affect fertility.
- DERMOID CYSTS
A strange type of tumour, generally harmless found in the ovary that typically contains different types of tissues, including neural tissue, hair, teeth, bone, instead of fluid. Dermoid cysts do not cause infertility.
- HEMORRHAGIC CYSTS
A hemorrhagic cyst is a functional cyst that develops when the bleeding occurs in the cyst. Its symptoms include abdominal cyst in one side of the body. They do not lead to or interfere with infertility.
- PARAOVARIAN CYSTS
Paraovarian cysts are the fluid filld cysts in the adnexa, adjacent to the fallopian tube and ovary.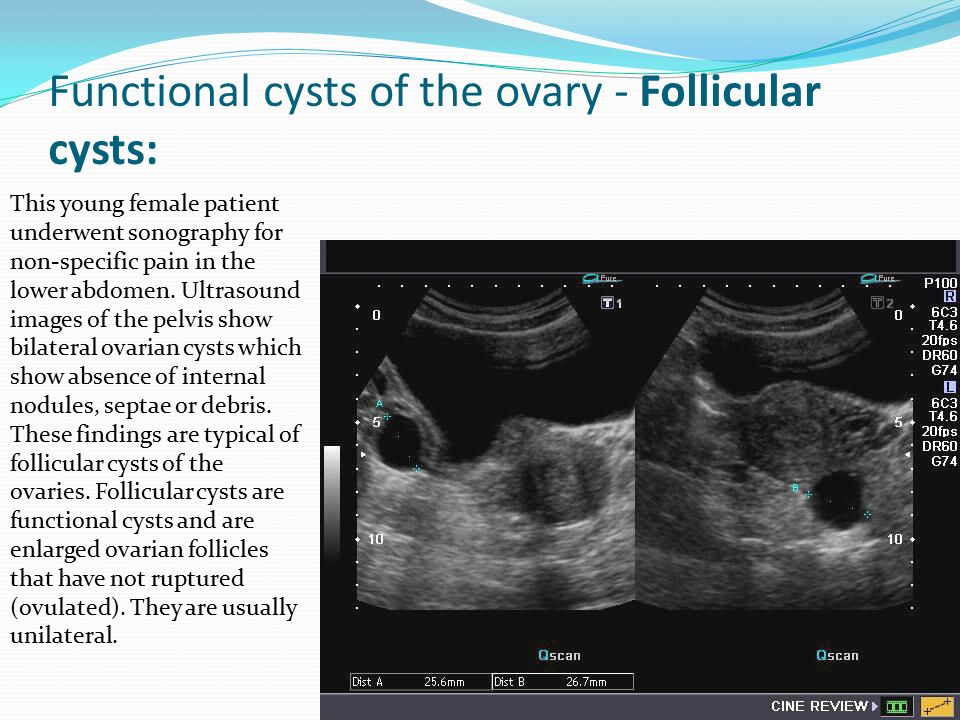 It is a type of cyst that does not affect fertility. However, if grown large, it might require surgeries to treat these cysts.
It is a type of cyst that does not affect fertility. However, if grown large, it might require surgeries to treat these cysts.
2) Cysts which Interfere with Fertility/Pregnancy
Two types of cysts that are most harmful to fertility are ovarian cysts resulting from polycystic ovary syndrome, and endometriomas – caused by endometriosis. These cysts need treatment because they may cause fertility issues.
ENDOMETRIOMA
They are also known as an endometrial cyst, it is a type of cyst formed when endometrial tissue, abnormally grows in the ovaries. The endometrium is the mucous membrane that lines the inner layer of the uterine wall. It affects pregnancy and causes chronic pain in the pelvic area during periods. Endometrial cysts are more often packed with dark, reddish-brown blood and may vary in size. They are also called chocolate cysts and causes infertility.
EndometriomaEndometriosis affects 5-10% of all women, and not all of them have fertility problems. A woman with endometrioma may not experience any issues or pain. It is only discovered during a routine gynaecological examination through a vaginal ultrasound or X-ray. An endometrioma or chocolate cysts begin as a small lesion on the ovaries. It may remain very small (just a few millimetres in size) and is not a cause for concern. However, some cysts grow large (over 10 cm) or become very painful with the menstrual cycle.
A woman with endometrioma may not experience any issues or pain. It is only discovered during a routine gynaecological examination through a vaginal ultrasound or X-ray. An endometrioma or chocolate cysts begin as a small lesion on the ovaries. It may remain very small (just a few millimetres in size) and is not a cause for concern. However, some cysts grow large (over 10 cm) or become very painful with the menstrual cycle.
Larger cysts tend to be the most problematic for fertility. If an endometrioma ruptures, its contents can enter the pelvic cavity. This can cause ovaries to adhere to the fallopian tubes creating fertility blockages and pain. Endometriomas disturb the normal tubo-ovarian relationship. In severe cases, endometriomas can affect ovarian reserve, damage the ovaries, or even require oophorectomy (removal of the infected ovary, and keeping the other ovary intact) which makes a female infertile.
CYSTS RESULTING FROM PCOS (POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME)Polycystic ovarian syndrome or PCOS is the most common cysts that create problems in a woman trying to get pregnant.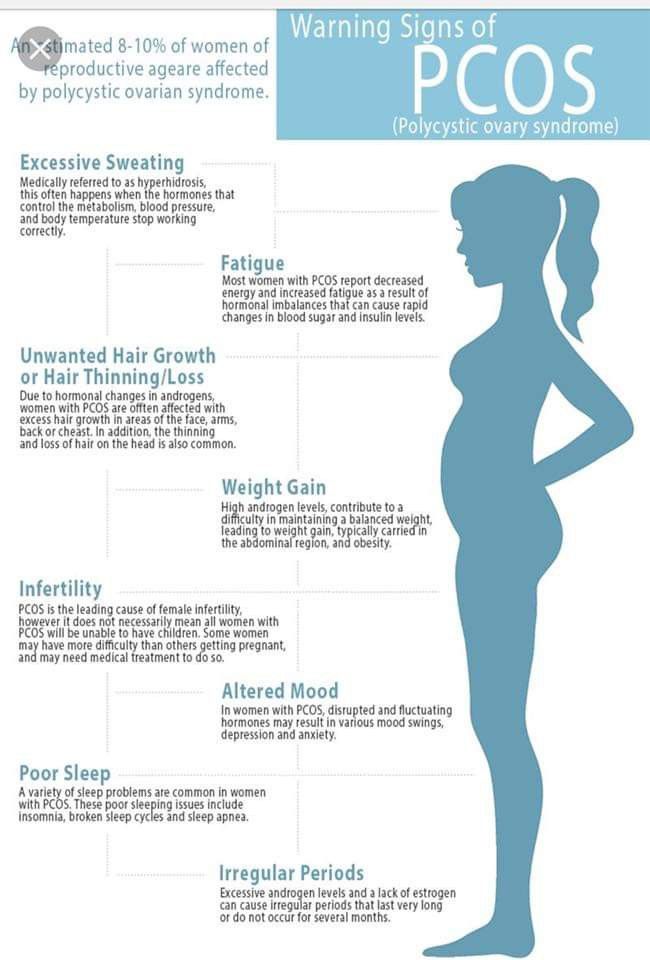 They can cause enlarged ovaries and the development of small ovarian cysts due to hormonal imbalance. Many small cysts in ovaries along with irregular periods, excess hair growth, acne, insulin resistance and obesity are all symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome. Hence conceiving with polycystic ovary syndrome becomes problematic by hampering fertility, causing a hormonal imbalance and restricting follicle maturation.
They can cause enlarged ovaries and the development of small ovarian cysts due to hormonal imbalance. Many small cysts in ovaries along with irregular periods, excess hair growth, acne, insulin resistance and obesity are all symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome. Hence conceiving with polycystic ovary syndrome becomes problematic by hampering fertility, causing a hormonal imbalance and restricting follicle maturation.
Women with PCOS can struggle to become pregnant and are at higher risk of developing complications during pregnancy. However, by managing the symptoms, many women with PCOS can become pregnant and have a healthy baby. It is important for patients to visit a doctor if they experience any symptoms related to PCOS. This will reduce the risk of complications when a woman decides to become pregnant. PCOS women struggle to get pregnant because of the presence of high levels of the male hormone androgen which prevents the release of an egg (ovulation).
While conceiving with a polycystic ovary, certain things need to be followed, such as a woman should maintain a healthy weight, healthy eating, exercise regularly, monitoring ovulation and plan sexual intercourse accordingly. A doctor might prescribe fertility medicines, if medications don’t work, the doctor might suggest surgery to remove a tiny amount of tissue that produces the excess male hormone in the ovaries. Otherwise, complications during pregnancy might increase such as miscarriages, high blood pressure induced by the pregnancy, gestational diabetes and even premature birth.
A doctor might prescribe fertility medicines, if medications don’t work, the doctor might suggest surgery to remove a tiny amount of tissue that produces the excess male hormone in the ovaries. Otherwise, complications during pregnancy might increase such as miscarriages, high blood pressure induced by the pregnancy, gestational diabetes and even premature birth.
How to get pregnant with ovarian cyst syndrome? From the above article, we understand that women suffering from conditions like polycystic ovaries and endometriomas might face fertility issues. However, they can be managed with lifestyle changes or infertility treatments or minor surgery (removal of endometrioma). If medications or any other treatment doesn’t work, and the existing cyst has caused any scarring, the last option that would be available for these women would be IVF (In vitro fertilisation), which would offer the best chance of conception. IVF is an assisted reproductive technology in which the ovaries are artificially stimulated by administering hormonal injections, and when the eggs are mature, they are extracted directly from the ovaries and fertilised in a lab and then the embryo is transferred in a woman’s uterus.
Tina (34) was trying to conceive for a long time, but each time a negative urine pregnancy test broke her heart.
I was diagnosed with polycystic ovarian syndrome at the age of 17. I always knew I would have trouble conceiving. After trying naturally when I couldn’t conceive, I decided to visit a fertility clinic. After much research and going by high success rate, I decided to visit Medicover Fertility. There, I saw an advertisement of Dr Lavi Sindhu, who is the Clinical Incharge at Medicover. The first question I asked her was “How to conceive with Ovarian Cyst?” and she recommended Ovulation Induction Therapy, a process that would increase the number of eggs ovulating each month.also recommended me to see an Endocrinologist, where I was told to lose weight, a diet plan was charted out, and some medicines were given. I worked hard, but it didn’t help me with my fertility issue. I had even one unsuccessful IUI (Intrauterine insemination).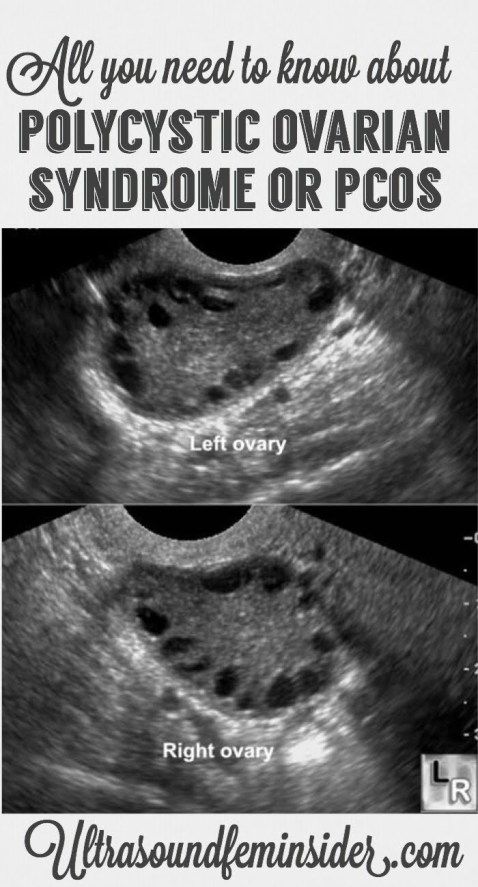 After a failed IUI Dr recommended IVF. My first cycle of IVF was cancelled due to low egg production, and my second cycle was successful as all other things were kept in mind. Moreover, thank you Medicover Fertility I have beautiful twin boys today.
After a failed IUI Dr recommended IVF. My first cycle of IVF was cancelled due to low egg production, and my second cycle was successful as all other things were kept in mind. Moreover, thank you Medicover Fertility I have beautiful twin boys today.
PCOS treatment is often focused on reducing the symptoms of the disorder and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Focus should be on weight reduction. Drugs are given to induce egg formation in each menstrual cycle and when one mature egg forms, timed intercourse or intrauterine insemination is advised. Some PCOS patients are resistant, and it is difficult to induce egg formation with oral drugs.
How can Medicover Fertility Help Women with Fertility Issues Caused by Ovarian Cyst?Medicover Fertility is a fertility clinic that enables couples with severe infertility problems to successfully conceive and take home a healthy baby. Medicover uses advanced fertility treatments to help couples in dealing with different kinds of infertility complications. Infertility caused due to ovarian cysts can be successfully treated at Medicover.
Medicover uses advanced fertility treatments to help couples in dealing with different kinds of infertility complications. Infertility caused due to ovarian cysts can be successfully treated at Medicover.
Women who go through cyst removal (endometrioma) procedure, which is minimally invasive, might face the risk of getting a scar tissue, which worsens the cyst or damages healthy ovarian tissue. Women with PCOS might face a severe problem with conceiving due to their hormonal imbalance, where medications, lifestyle management is not helping to solve infertility. For these women, IVF (In vitro fertilisation) is the safest option available to conceive.
Here in Medicover, we genuinely follow international standards and facilitate the latest methods to treat infertility. In addition, we have a team of highly experienced and internationally certified doctors at our IVF centre in Delhi to help patients with different fertility concerns.
FAQs
Q) Can you ovulate with an ovarian cyst?- A) Well, the very question that “can you ovulate with an ovarian cyst?” has a straightforward answer that cysts like the polycystic ovary are associated with irregular ovulation as ovulation problems account for about 25% of all cases of female infertility.

- A) An ovarian cyst does not usually affect a woman’s ability to conceive, but the only condition in which a cyst is linked with difficulty in getting pregnant is polycystic ovary syndrome.
- A) It is recommended by doctors that you should wait until your incision is fully healed before resuming intercourse, including other physical activities such as exercise. It may take anywhere between 3-5 days to several weeks.
- A) Ovarian cyst usually doesn’t affect a woman’s ability to conceive. If you were pregnant before, there’s a good chance that you can still be pregnant. Only women linked with PCOS, endometriomas can be linked with difficulty in conceiving.
- A) Most ovarian cysts do not cause infertility.
 Cysts that become infected and cause a pelvic infection can sometimes lead to infertility due to scarring of the fallopian tube. However, this condition is very rare. Ovarian cysts that contain endometriosis can be associated with infertility.
Cysts that become infected and cause a pelvic infection can sometimes lead to infertility due to scarring of the fallopian tube. However, this condition is very rare. Ovarian cysts that contain endometriosis can be associated with infertility.
- A) Yes! In most of the cases the surgical treatment of ovarian cyst affects infertility as it invariably damages the healthy eggs.
- A) Depends on the type of cyst. Infertility is usually diagnosed after a couple has been unable to get pregnant even after 12 months. Ovarian cysts that contain endometriomas and polycystic ovaries may be associated with infertility.
- A) Functional cysts usually do not affect fertility unless they are very large. However, it should also be noted that women who have polycystic ovarian syndrome can experience fertility challenges too.

- A) If a woman is trying to conceive and has a paraovarian cyst, and it is big enough, a doctor might recommend getting it removed laparoscopically as it might be difficult to conceive with a paraovarian cyst, and these cysts do not get affected by birth control pills.
- A) Women who are treated with fertility drugs develop ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome and are at higher risk of ovarian torsion during pregnancy than those who do not become pregnant. Ovarian torsion during pregnancy can cause extreme pain, and it should be removed, otherwise can cause haemorrhage or necrosis.
(*necrosis – Death of most or all of the cells in an organ or tissue, due to failure of blood supply)
Q) I have dermoid cyst; will it affect my pregnancy?- A) The very commonly asked question in this regard is, can ovarian cyst affect pregnancy? The course of pregnancy of patients with dermoid cysts is favourable.
 The cysts should be managed conservatively if possible, with routine ultrasound follow up during pregnancy since complications are extremely rare.
The cysts should be managed conservatively if possible, with routine ultrasound follow up during pregnancy since complications are extremely rare.
- A) If the other ovary is intact and if there is no problem in ovulating, then a woman should not have any problem in conceiving.
- A) When a couple is recommended IUI treatment, it is advisable not do it in the presence of a simple cyst because during ovulation induction, It will be difficult to differentiate between an actual growing follicle and the clear cyst. So, a cyst might be misdiagnosed as a follicle, and exact timing of IUI might go wrong.
References
1) https://www.todaysparent.com/getting-pregnant/trying-to-conceive/fertility-myths-that-are-hurting-your-chances-of-getting-pregnant/
2) https://www.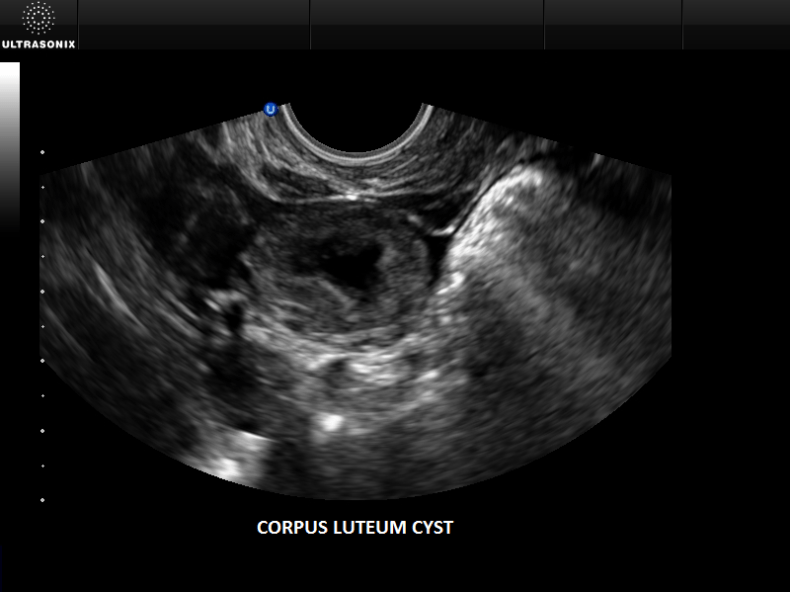 mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ovarian-cysts/expert-answers/ovarian-cysts-and-infertility/faq-20057806
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ovarian-cysts/expert-answers/ovarian-cysts-and-infertility/faq-20057806
3) https://www.beingtheparent.com/ovarian-cysts-affect-pregnancy/
4) https://www.romper.com/p/how-do-you-get-pregnant-if-you-have-ovarian-cyst-expert-explains-71880
5) http://natural-fertility-info.com/chocolate-cysts.html
6) https://www.pregnancybirthbaby.org.au/pcos-and-pregnancy
7) http://www.ivflite.org/article.asp?issn=2348-2907;year=2015;volume=2;issue=3;spage=99;epage=101;aulast=Shah
8) https://trmbaby.com/library/conditions/ovarian-cysts/
9) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19554342
10) https://www.steadyhealth.com/topics/dermoid-cyst-and-pregnancy
How do ovarian cysts affect fertility?
Two types of cysts are common byproducts of ovulation:
- Follicular cysts form when, instead of breaking open to release the egg, the follicle stays intact and the cyst continues to grow.
- Corpus luteum cysts, or luteal cysts, sometimes form after ovulation.
 Normally, once the egg has broken free, the follicle shrinks into a mass of cells known as the corpus luteum, which produces hormones to prepare for the next cycle. Luteal cysts form when, instead of shrinking, the follicle reseals itself and fluid builds up inside.
Normally, once the egg has broken free, the follicle shrinks into a mass of cells known as the corpus luteum, which produces hormones to prepare for the next cycle. Luteal cysts form when, instead of shrinking, the follicle reseals itself and fluid builds up inside.
Both of these cysts are typically harmless and disappear within 1–3 months without treatment. And for pregnant women, corpus luteum cysts are actually super important: they produce progesterone, a hormone that’s essential for the first 8–10 weeks of pregnancy.
Which ovarian cysts affect fertility, and how?
There are a few types of cysts associated with lower fertility. How do ovarian cysts affect fertility? In actuality, it’s not these cysts themselves that make it harder to get pregnant—they are simply symptoms of larger illnesses that may compromise fertility.
Endometriosis is one example of an illness that can cause ovarian cysts that affects fertility. Endometriosis occurs when endometrial tissue—the lining of the uterus—begins to grow in other places, like on the outside of the uterus or the fallopian tubes. One result of endometriosis is ovarian cysts known as “endometriomas,” formed when this tissue grows in the ovaries. Endometriomas can range in size from less than an inch to over 6 inches, and are often filled with dark blood.
One result of endometriosis is ovarian cysts known as “endometriomas,” formed when this tissue grows in the ovaries. Endometriomas can range in size from less than an inch to over 6 inches, and are often filled with dark blood.
While doctors aren’t 100% sure how these ovarian cysts affect fertility, they do know that endometriosis is closely tied to infertility; some studies demonstrate that women with even mild cases of endometriosis have only a 2–4% chance of getting pregnant each month (compared to the 15–20% chance healthy women have). Dr. Iris Orbuch, OB/GYN and endometriosis specialist, estimates that “40% of unexplained infertility is due to endometriosis,” which both “decreases a woman’s ovarian reserve [and] decreases fertility by either an anatomical distortion or via inflammation.”
Learn more about endometriosis.
Secondly, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a hormone imbalance that causes many tiny ovarian cysts, affects fertility by a higher rate than almost any other condition (besides age).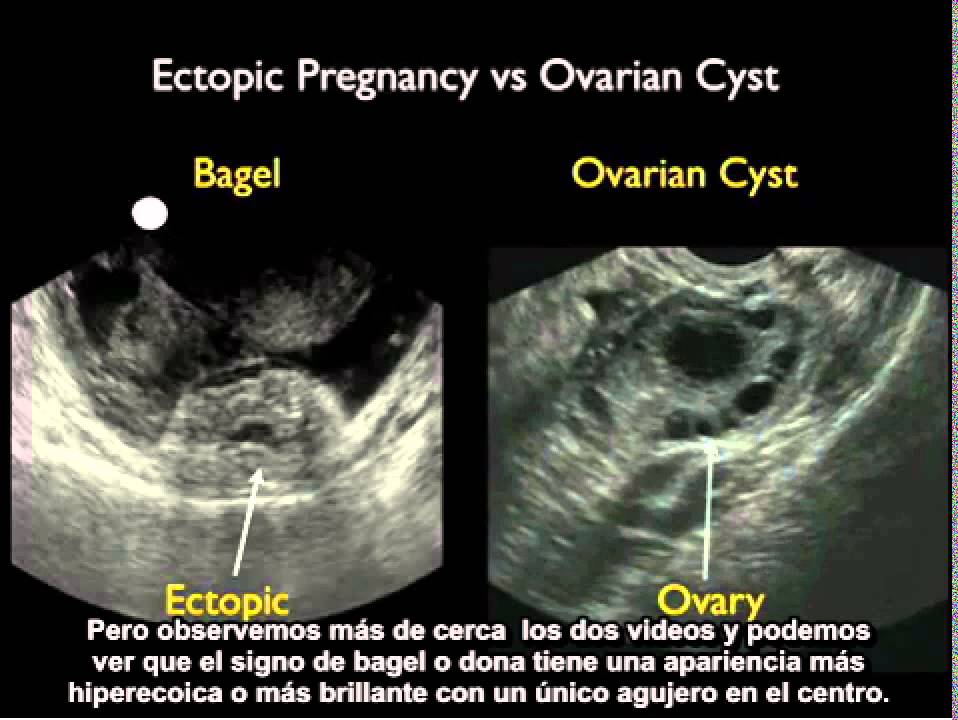 In PCOS, the eggs that begin to develop during the ovulation cycle never mature enough to prompt ovulation, so none of them are released from the ovary. The immature follicles, each containing an immature egg, then cause the ovary to become “polycystic,” filled with these tiny cysts.
In PCOS, the eggs that begin to develop during the ovulation cycle never mature enough to prompt ovulation, so none of them are released from the ovary. The immature follicles, each containing an immature egg, then cause the ovary to become “polycystic,” filled with these tiny cysts.
The chronic lack of ovulation alters the levels of hormones that play an important role in the ovulation process, and PCOS is often associated with higher levels of male hormones known as “androgens.” It’s not the ovarian cysts themselves that affect fertility in cases of PCOS—it’s the fact that women with PCOS don’t ovulate, and ovulation is essential for getting pregnant naturally.
Can ovarian cysts have other side effects?
While it’s not typical for ovarian cysts to affect fertility, larger or multiple cysts can have other side effects or symptoms, such as bloating, needing to urinate more often, pelvic pressure or pain, or abnormal vaginal bleeding. If your cyst(s) doesn’t go away on its own after a few months, continues to grow, or causes you pain, your doctor might recommend surgery to remove it.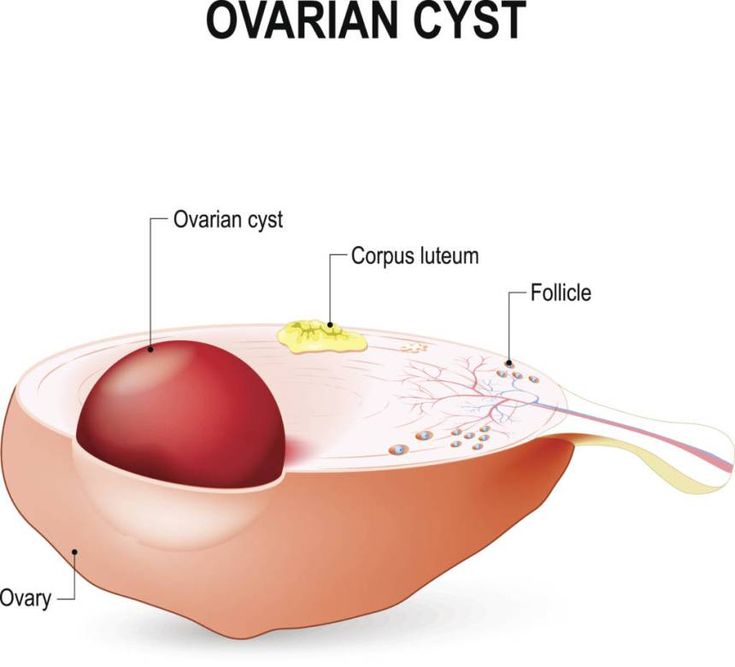 With larger ovarian cysts, there is the concern for a rare condition of twisting of the ovary, called ovarian torsion, which—if not corrected promptly with surgery—can lead to loss of an ovary. Alternative treatments for benign cysts include hormonal birth control—such as the pill, vaginal ring, shot, or patch—which prevent ovulation and lower your chances of getting more cysts. Malignant (cancerous) cysts are very rare in young women.
With larger ovarian cysts, there is the concern for a rare condition of twisting of the ovary, called ovarian torsion, which—if not corrected promptly with surgery—can lead to loss of an ovary. Alternative treatments for benign cysts include hormonal birth control—such as the pill, vaginal ring, shot, or patch—which prevent ovulation and lower your chances of getting more cysts. Malignant (cancerous) cysts are very rare in young women.
Can treatment for ovarian cysts affect fertility?
That depends on the treatment. Hormonal birth control doesn’t have a long-term effect on fertility (learn more about birth control and fertility). Surgery almost invariably damages some healthy eggs, and complications can (rarely, but sometimes) mean doctors need to remove an entire ovary. Both situations result in a lower egg count, which is one factor in fertility.
Should women with ovarian cysts freeze their eggs?
While not all ovarian cysts affect fertility by way of reproductive illness, there are cases in which a woman may want to consider egg freezing to preserve fertility.
Women with endometriosis who aren’t yet ready to get pregnant are excellent candidates for egg freezing. During endometriosis, the abnormally growing endometrial tissue can cause inflammation, scarring, cysts, and organ damage, including damage to the ovary. And if the ovary is damaged, it can mean impaired egg production or ovulation—or none at all.
Additionally, while surgical treatment of endometriosis offers long-term pain relief, studies show that it may actually reduce ovarian reserve (and therefore fertility) by inadvertently removing healthy ovarian tissue or cutting off blood supply to the ovary. Freezing eggs before endometriosis progresses too far is the best way to preserve fertility options for later in life.
And surgical treatment of other ovarian cysts affects fertility by damaging healthy eggs. Women who have had ovarian cysts surgically removed will typically have a lower egg count. For that reason, women who are considering surgery for ovarian cysts should also consider freezing their eggs—prior to the surgery, if possible, or after the removal of the cyst, if the size or location of the cyst will make egg freezing too risky or complicated.
Learn more about how ovarian cysts affect fertility—and how egg freezing can help:
Contact our healthcare team
Ovarian cyst during pregnancy. You can get pregnant with an ovarian cyst.
There are several types of cysts. Among the most common are functional ones (their other name is “normal”), since they develop against the background of natural ovulation processes and pass on their own over time.
Others - abnormal cysts - can cause the development of various complications, up to their degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Many women do not attach much importance to this problem, but if you are suddenly planning a pregnancy or are already in an "interesting position", then you should pay closer attention to this problem. In this regard, expectant mothers are interested in several questions, we list them below.
Is it possible to get pregnant with an ovarian cyst?
An ovarian cyst in itself can cause difficulties with conception, that is, cause secondary infertility.
With a long existence and lack of adequate treatment, an ovarian cyst can give complications: there is a "torsion" of its legs, hemorrhages and ruptures, and poor health.
If you have been diagnosed with an ovarian cyst and you are wondering if it is possible to get pregnant, then be sure to contact an experienced ON CLINIC gynecologist who will help dispel all your doubts!
Can pregnancy occur after removal of an ovarian cyst?
With the right approach, timely diagnosis and treatment, an ovarian cyst is only a temporary phenomenon. And even if the doctor had to resort to surgical intervention, thanks to modern organ-preserving technologies and equipment, pregnancy successfully occurs after removal of the ovarian cyst.
Is an ovarian cyst dangerous during pregnancy?
An ovarian cyst during pregnancy is not dangerous if the woman is under close medical supervision.
In relation to a pregnant woman, the doctor, as a rule, takes a wait-and-see attitude, monitors her well-being and conducts control ultrasounds.
The danger for a pregnant woman is represented by large cysts and cysts "on legs" (because the leg can be twisted, as a result of which necrosis of the cyst may develop, manifested by severe pain in the abdomen).
There is also a possibility that the cyst will rupture, allowing its contents (mucus, watery fluid, or bloody substance) to enter the abdominal cavity. This situation already belongs to the category of urgent and requires emergency intervention of doctors!
Operations to remove an ovarian cyst during pregnancy are prescribed according to strict indications.
Can a cyst occur during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, a woman may face various problems, and the appearance of an ovarian cyst is no exception; no expectant mother is immune from this.
The first trimester of pregnancy is characterized by the appearance of a corpus luteum cyst. The corpus luteum during pregnancy contributes to the production of progesterone and the formation of the placenta.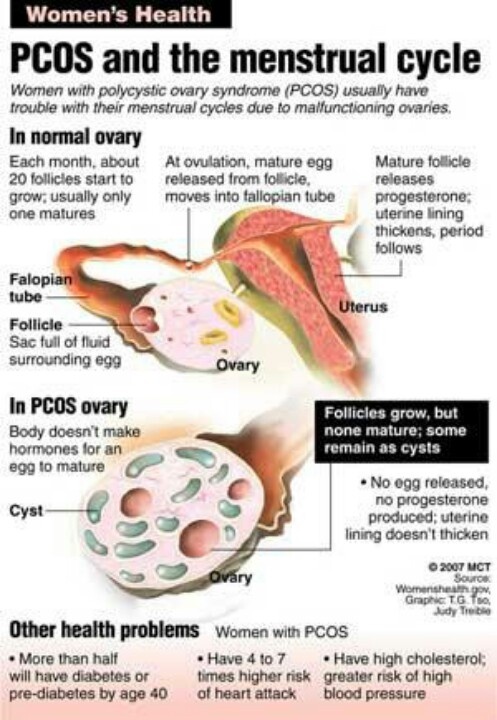 Often the corpus luteum turns into a cyst, but after about 12 weeks, when the placenta takes over the functions of providing the body with progesterone, it gradually regresses (disappears).
Often the corpus luteum turns into a cyst, but after about 12 weeks, when the placenta takes over the functions of providing the body with progesterone, it gradually regresses (disappears).
Other types of cysts, such as cystadenoma and endometrioid cyst, can be large and therefore very dangerous, and they cause severe pain.
Thus, a cyst of the left or right ovary during pregnancy, if it does not bother a woman, does not require special treatment, but only needs to be monitored by a doctor!
If the cyst does not resolve on its own for a long time, drugs are prescribed to speed up this process. In extreme cases, if the cyst reaches a large size and complications are noted, an intervention may be prescribed to preserve the pregnancy.
Many women diagnosed with ovarian cysts have successfully carried and given birth to healthy babies. The main thing is to be under the supervision of a highly qualified gynecologist and regularly undergo the necessary diagnostic tests.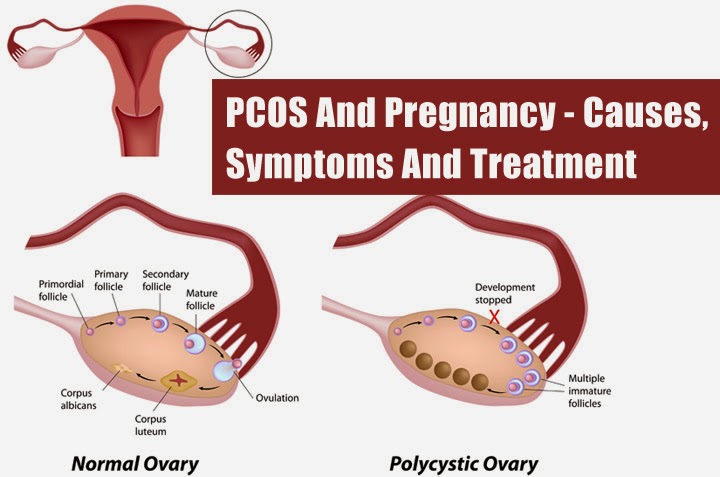
The most experienced gynecologists of ON CLINIC are especially attentive to pregnant patients with a diagnosis of ovarian cyst, conduct control examinations, closely monitor the condition and well-being of a woman.
Under the supervision of ON CLINIC gynecologists, every woman "in an interesting position" can be confident in the successful resolution of pregnancy. Contact professionals and feel the joy of healthy motherhood!
Author of article
Share
Different types of ovarian cysts - treatment of ovarian cysts before and during pregnancy
The first question that women with suspected cysts ask gynecologists is: is it possible to get pregnant if you have an ovarian cyst? And what types of cysts are incompatible with pregnancy? Patients who have already conceived a child and only after that they learned the diagnosis are concerned about another burning question: is an ovarian cyst dangerous for pregnancy? The answers to all these questions depend on many factors that are discussed in the article.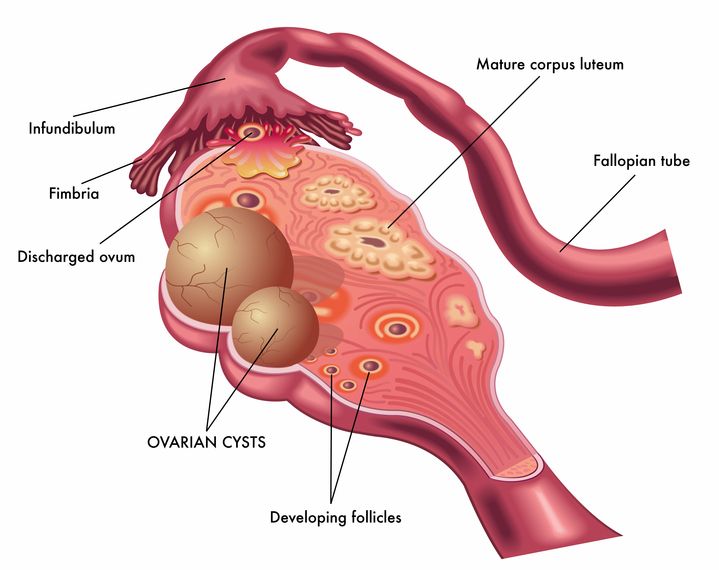
Different types of ovarian cysts: is it possible to get pregnant?
Theoretically, you can get pregnant even with an endometrioid ovarian cyst, which is considered the most dangerous option and in most cases blocks reproductive functions.
A functional cyst (follicular and corpus luteum cyst) in a patient is absolutely not an obstacle to conception and pregnancy. Moreover, often such cysts, without medical treatment, resolve on their own during pregnancy, when the body rearranges its hormonal levels. But still it is better to constantly be observed by a gynecologist.
The best option is to plan the conception of a child in advance, having previously passed all the gynecological examinations that will reveal a cyst.
To avoid unforeseen diagnoses, every woman must visit a gynecologist every six months with an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Is it possible to get pregnant with an endometrioid ovarian cyst?
The question of whether it is possible to get pregnant with an endometrioid ovarian cyst is especially relevant for those who want to conceive. Since this particular type of cyst is a very dangerous pathology.
Since this particular type of cyst is a very dangerous pathology.
An endometrioid cyst (“chocolate” cyst) is a neoplasm on the surface of the ovary that contains unrejected chocolate-colored menstrual blood (hence the name) in a sheath consisting of endometrial cells.
In the vast majority of cases, endometrioma causes infertility (although there are exceptions). Often, if the endometrioid cyst was asymptomatic, and the woman did not visit the gynecologist for preventive examinations, then infertility becomes the only symptom of endometrioma. With the problem of the impossibility of getting pregnant, the patient goes to the doctor, and only then is the true diagnosis established.
Significantly reduced (or no) possibility of getting pregnant with an endometrioid ovarian cyst is due to the following factors:
- Reduced ovarian reserve due to loss of follicles
- Hormonal disorders in the ovary and hypothalamic-pituitary system that develop against the background of a growing tumor
- The development of adhesive processes in the reproductive organs (fallopian tubes, ovaries), which make conception physically impossible, as they prevent sperm from reaching the egg
Also, many women are interested in the question of whether it is possible to get pregnant with an endometrioid ovarian cyst during the IVF procedure. Usually, doctors recommend starting the IVF procedure only after the cyst is completely cured, since it can have a negative impact not only on the process of conception, but also on the bearing of a child.
Usually, doctors recommend starting the IVF procedure only after the cyst is completely cured, since it can have a negative impact not only on the process of conception, but also on the bearing of a child.
However, there are cases when endometrioma was detected after a successful IVF procedure and the onset of pregnancy. In this case, an ultrasound examination is performed. If the tumor is small in size, does not compress the organs located nearby, then they do not touch it unless absolutely necessary, since the adhesive process may be aggravated. However, such a patient should be especially closely monitored.
In this case, hormonal, antispasmodic and sedative drugs are prescribed (conservative treatment is extremely important for maintaining early pregnancy). Significantly limited physical activity.
If the endometrioma has grown to a large size, it is better to remove it, because if the cyst is ruptured or torn, an emergency removal operation will be much more traumatic for the woman and her fetus (possible spontaneous abortion) than a planned removal.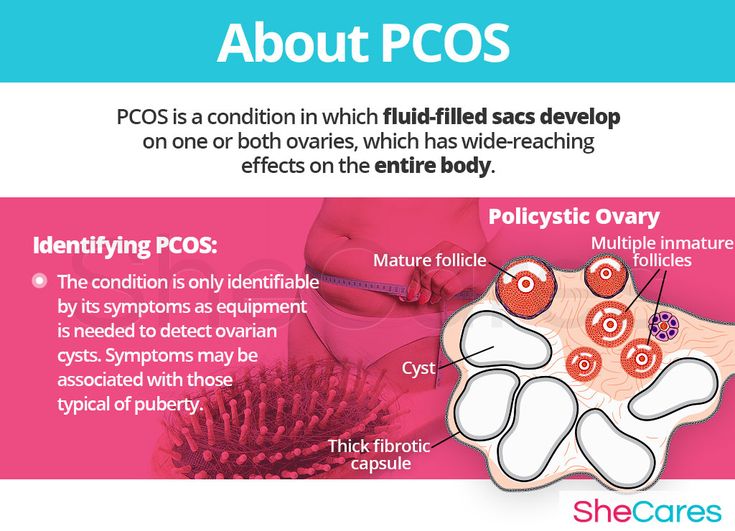 Laparoscopic removal is usually performed in the second trimester of pregnancy (14-25 weeks).
Laparoscopic removal is usually performed in the second trimester of pregnancy (14-25 weeks).
Removal of an endometrioid ovarian cyst during pregnancy is mandatory if:
- The size of the cyst reaches 6 cm (or more)
- Cyst gives pain syndrome
- The level of tumor markers exceeds the norm
In general, the detection of an endometrioid ovarian cyst already in a pregnant woman suggests that at the time of conception the tumor was at an early stage of development, so it did not have time to disrupt the hormonal balance and ovarian function.
If an endometrioid cyst is discovered during pregnancy planning, it is better to postpone the process of conception until a better time. First, it is recommended to remove the endometrioma by laparoscopy - a minimally invasive method. Then you will have to undergo a course of normalization of the hormonal background after the operation, which will help prevent the appearance of adhesions and the re-development of the tumor (this is possible, since endometrioma is a hormone-dependent formation).
Causes of the development of an endometrioid ovarian cyst during pregnancy:
- Hormonal disorders (excessive production of estrogen and prolactin against the background of a deficiency of progesterone - the hormone of the corpus luteum)
- Genetic mutations
- Immunodeficiencies
- Excess adipose tissue in the body
- Endocrine response to stress
- Menstrual abnormalities (so-called retrograde menstruation, in which blood flows back through the fallopian tubes to the ovaries), which may be due to surgery, abortion, or long-term contraception with an intrauterine device
If an ovarian cyst was found already after pregnancy
There are cases when an ovarian cyst is found already in a pregnant girl, and the patient's question is: "Is it possible to get pregnant if an ovarian cyst is present?" becomes completely irrelevant.
If the cyst is small and does not bother the woman, the patient is simply observed.
In this case, it is not uncommon for a cyst to involute during pregnancy - that is, a reverse reaction develops (the cyst decreases in size until it disappears completely).
This happens because the hormonal balance (due to violations of which the tumor develops) levels out, as the female body throws all its strength into maintaining the process of continuing life. The placenta surrounding the fetus produces a huge amount of progesterone (its lack also affects the formation of cysts). And the body of the expectant mother begins to produce hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which stimulates the thyroid gland and its production of hormones.
Pregnancy can proceed normally with an ovarian cyst if the following factors coincide:
- Cyst no larger than 8 cm (6 cm for endometrioma)
- Cyst stops growing
- The level of tumor markers is within the normal range
If at least one factor is disturbed, an operation to remove the cyst is recommended.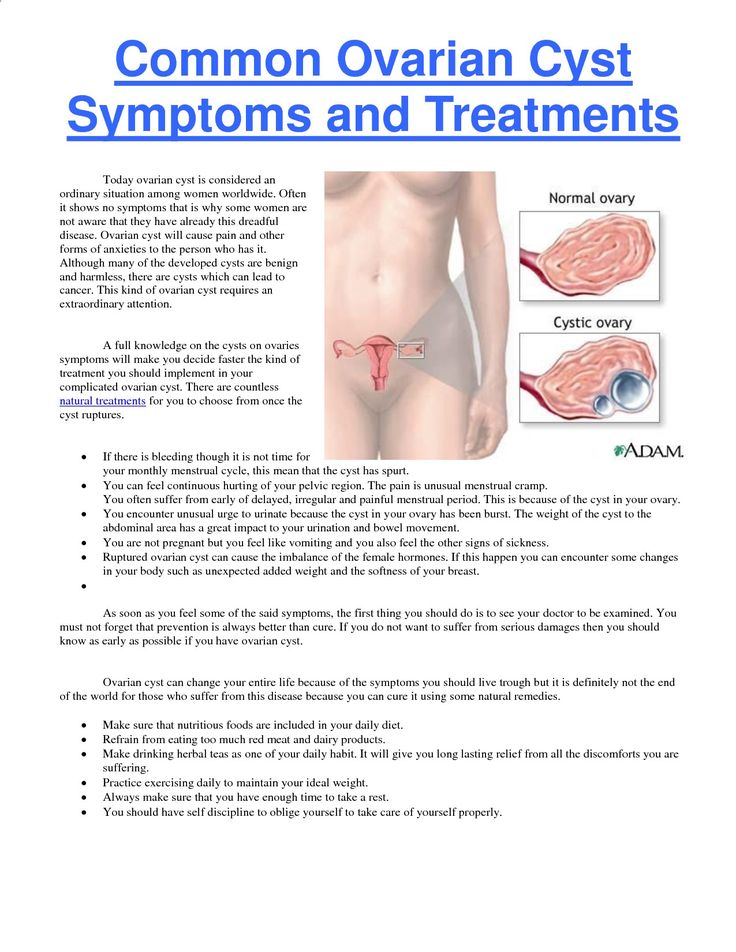
The situation is more complicated with patients diagnosed with an endometrioid ovarian cyst, since such a tumor can provoke a miscarriage or termination of pregnancy.
Medical practice records conflicting facts regarding the behavior of endometrioma during pregnancy. There are cases when, under the influence of hormonal changes in the body, the tumor stopped growing. But it happens that a hormonal surge, on the contrary, provoked rapid growth and subsequent rupture of the cyst, which led to an abortion. In addition, the risk of tumor transformation into a malignant form is high.
Treatment of ovarian cysts before and during pregnancy
If doctors detect ovarian cysts at a time when a woman is wondering if she can become pregnant, planned removal (except for small functional cysts) and subsequent long-term hormone therapy are indicated. After such treatment, in most cases, pregnancy successfully occurs.
Laparoscopy is recommended as a removal method, which allows removing the tumor while preserving the ovary, dissecting existing adhesions, and in parallel, diagnosing infertility and its causes.
After treatment of an ovarian cyst, the answer to the question: is it possible to get pregnant often depends on the woman herself, who must regularly see a gynecologist, lead a healthy lifestyle and maintain a positive attitude.
In the case of an acute pathology (rupture or torsion of an ovarian cyst) requiring radical surgical intervention, after surgery, a woman may have difficulty conceiving if adhesions occur in the fallopian tubes (as a complication after surgery) or if one damaged ovary has to be removed. However, if the operation is planned and carried out in a timely manner, then the answer to the question: is it possible to get pregnant after removal of the ovarian cyst, usually turns out to be positive.
Pregnant patients with an ovarian cyst (which happens when pregnancy is not planned) are usually only observed. But in the case of the development of acute pathologies, the medical consultation may prescribe an operation to remove the cyst during pregnancy.