Can pushing too hard to poop hurt the baby
Can straining to go when pregnant hurt the baby?
Can straining to go when pregnant hurt the baby?
June 08, 2021
For many people, pregnancy and digestive issues go hand-in-hand. A real question that many have is, will straining when you go to the bathroom hurt the baby? Zachary C. Hamilton, MD, Ob/Gyn at ARC Medical Plaza Specialty weighs in on this topic in an article on Romper.com.
Will straining during pregnancy hurt the baby?
For most pregnancies that are progressing without any issues, straining isn’t a huge concern. “Straining won’t harm the baby, but it can lead to hemorrhoids and anal fissures which can be very painful and uncomfortable for mom,” says Dr. Hamilton. Although not a serious health risk, hemorrhoids can be quite painful. There are ways to help avoid hemorrhoids during pregnancy, however, such as getting enough fiber and staying hydrated. If you do get them, hemorrhoids are generally not difficult to treat, and even a simple sitz bath can help improve them considerably.
Some other potential health issues.
Straining a lot or for long duration can reduce blood flow to the pregnant person's heart and head and cause dizziness. Further, for those with certain pregnancy complications, straining could potentially be more dangerous. Those include:
- Placenta previa
- Preterm labor
- Problems with the cervix such as women who have a cerclage
“Move around! Staying active can help keep your bowels active. Eat a balanced diet that includes fiber. Stay well hydrated and if you’re still having trouble with bowel movements, talk to your doctor,” says Dr. Hamilton. “A stool softener might help move everything along as well and is generally considered safe in pregnancy.” In other words, don’t hesitate to talk to your doctor about issues with straining while you poop during pregnancy, because it’s often a common and manageable issue.
If you have more questions, make an appointment with Dr. Hamilton online at ARCBookNow.com or by calling 512-260-1581.
Related Items:
- Dr. Zachary Hamilton in Doctors
- ARC Medical Plaza Specialty in Locations
- Obstetrics/Gynecology (Ob/Gyn) in Specialties
Tags: pregnancy
July 07, 2022
Dr. Crystal Berry-Roberts answers your questions about women's health care, birth control, and options now available in Texas. More.
October 27, 2021
ARC’s Dr. Crystal S. Berry-Roberts, MBA, FACOG, Obstetrics/Gynecology (Ob/Gyn) talks openly about challenges facing Black mothers and their babies.
Crystal S. Berry-Roberts, MBA, FACOG, Obstetrics/Gynecology (Ob/Gyn) talks openly about challenges facing Black mothers and their babies.
August 30, 2021
If you’re worried about getting in that massage chair while you are pregnant, get the 411 from an expert! See the whys and why nots from Romy Ghosh, MD.
May 03, 2021
ARC physician, Dr. Rose Chang-Jackson, Ob/Gyn, joined other local doctors encouraging pregnant women to get their COVID-19 vaccine. Book your COVID-19 vaccine appointment today.
April 14, 2021
Can’t wait to start expecting? Talk to your ARC doctor for a healthy start. Check out this quick guide on what doctor to see and when to see them when you are planning a pregnancy.
Will Straining When I Poop Hurt My Baby?
Symptoms
Srinrat Wuttichaikitcharoen / EyeEm / Getty images
Will it affect your baby at all?
by Lindsay E. Mack
Updated:
Originally Published:
For plenty of people, pregnancy and digestive issues seem to go hand-in-hand, sometimes to a concerning degree. So to put it bluntly, will straining when you poop hurt the baby? It’s a real question for many people who are expecting a baby and experiencing serious gastro issues.
Will straining during pregnancy hurt the baby?For most pregnancies that are progressing without any issues, it isn’t a huge concern. “Straining won’t harm the baby, but it can lead to hemorrhoids and anal fissures which can be very painful and uncomfortable for mom,” Dr. Zachary Hamilton, board certified OB/GYN at Austin Regional Clinic in Austin, Texas, tells Romper in an email.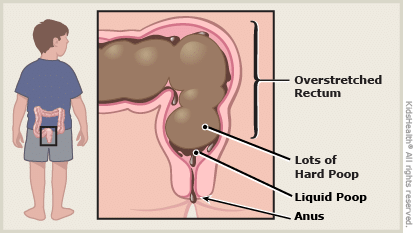 Although not a serious health risk, hemorrhoids can be quite painful. There are ways to help avoid hemorrhoids during pregnancy, however, such as getting enough fiber and staying hydrated. If you do get them, hemorrhoids are generally not difficult to treat, and even a simple sitz bath can help improve them considerably, according to a study in Women and Birth: Journal of the Australian College of Midwives.
Although not a serious health risk, hemorrhoids can be quite painful. There are ways to help avoid hemorrhoids during pregnancy, however, such as getting enough fiber and staying hydrated. If you do get them, hemorrhoids are generally not difficult to treat, and even a simple sitz bath can help improve them considerably, according to a study in Women and Birth: Journal of the Australian College of Midwives.
There are some other potential health issues associated with difficult trips to the bathroom, however. For instance, “straining a lot or for long duration actually can reduce blood flow to the pregnant person's heart and head and cause dizziness,” Dr. Rebecca Levy-Gantt, Premier ObGyn Napa Inc., author of Womb With A View: Tales from the Delivery, Emergency and Operating Rooms , tells Romper. Pregnant people who experience low blood pressure, or a history of heart problems, may want to be especially aware of this possibility, as Dr. Levy-Gantt further explains.
And even if you are experiencing difficulty going to the bathroom, remember that your baby is in a whole other part of the body. “The rectum sits beneath the vagina and would not transmit too much pressure to the placenta,” Dr. Kim Langdon, MD, an OB/GYN, tells Romper. “Furthermore, the intrauterine contents are a closed system and do not experience the intra-abdominal pressure changes associated with bearing down or straining.” Even if you’re having a *bad* time, the baby probably won’t even know.
Those with certain health conditions, however, may want to know more about whether straining could be potentially harmful. “There are certain pregnancy complications that make straining more dangerous. Those include placenta previa (when the placenta low and is over the cervix) because it could cause bleeding, preterm labor, or problems with the cervix such as women who have a cerclage,” Dr. Kelly Culwell, board certified OB/GYN tells Romper. If you are experiencing these or any other complications during pregnancy, then talk about whether straining may potentially be problematic with your physician.
“Bowel problems like constipation are common because the hormones of pregnancy (especially Progesterone, which relaxes the smooth muscles in the body) often slow down metabolism, and that causes the intestines also to be more sluggish,” says Dr. Levy-Gantt. “That can cause gas to build up, and cause constipation.” You’re hardly the first pregnant person to deal with stomach issues, if that’s any consolation.
What can you do to help ease the stomach issues caused by pregnancy?Thankfully, the doctors have some advice about easing your stomach issues while expecting. “Move around! Staying active can help keep your bowels active. Eat a balanced diet that includes fiber. Stay well hydrated and if you’re still having trouble with bowel movements, talk to your doctor,” says Dr. Hamilton. “A stool softener might help move everything along as well and is generally considered safe in pregnancy. ” In other words, don’t hesitate to talk to your doctor about issues with straining while you poop during pregnancy, because it’s often a common and manageable issue.
” In other words, don’t hesitate to talk to your doctor about issues with straining while you poop during pregnancy, because it’s often a common and manageable issue.
Studies Referenced:
Shirah BH, Shirah HA, Fallata AH, Alobidy SN, Hawsawi MMA. Hemorrhoids during pregnancy: Sitz bath vs. ano-rectal cream: A comparative prospective study of two conservative treatment protocols. Women Birth. 2018 Aug;31(4):e272-e277. doi: 10.1016/j.wombi.2017.10.003. Epub 2017 Oct 18. PMID: 29055673.
Experts:
Dr. Kelly Culwell (AKA Dr. Lady Doctor) Board Certified OB/GYN
Dr. Zachary Hamilton, board certified OB/GYN, Austin Regional Clinic in Austin, Texas
Dr. Kim Langdon, MD, an OB/GYN
Dr. Rebecca Levy-Gantt, Premier ObGyn Napa Inc., author of Womb With A View: Tales from the Delivery, Emergency and Operating Rooms
This article was originally published on
Discolored stool gray white causes diagnosis treatment
Changes in the color of the stool are an important diagnostic sign indicating a violation of digestive functions. Depending on the stool, you can guess the location and nature of the problem, choose additional testing programs, and judge the need for treatment. Gray or white stools (discoloration) are a common symptom requiring detailed tests and a fundamental cause.
When is white stool considered normal?
A change in voicing in infants can be seen by changing the type of milk speech and the introduction of new complementary products. In most cases, the color and hardness of the stool will return to the original within a few days.
In the digestive tract (GIT) x-ray shooting using oral contrast agents, the stool may be temporarily discolored. Barium sulfate solutions, which patients drink before surgery, are gradually discharged from the intestine after 1-2 days. The color of the stool becomes white or pale, is in good physical condition, and there are no other signs of digestive diseases.
The color of the stool becomes white or pale, is in good physical condition, and there are no other signs of digestive diseases.
Pathological causes of colorless stools
The presence of stelcobyrin and stele-cosilinogen, a product of the conversion of bilirubin in the intestine from the bile duct, recognizes brown in the feces. If bile production and secretion are obstructed, the stool becomes lighter (stool).
Typical disease of the hepatic pancreas, with discoloration of the stool.
- Biliary movement. Functional pathology of the gallbladder and bile duct is considered a common cause of fecal and painful pain. In this state, symptoms periodically appear due to stress, physical overwork and nutritional shifts. When the aggravation is resolved, the stool returns to its normal color and texture.
- Mechanical blockage of bilious bile, accompanied by complete disappearance of intestinal bile, and the pigment which is characteristic of stool is lost.
 At the same time, urine becomes darker due to the metabolic product bilirubin. In the case of gallstones, it often appears with intense cramps, nausea and vomiting of the right ribs.
At the same time, urine becomes darker due to the metabolic product bilirubin. In the case of gallstones, it often appears with intense cramps, nausea and vomiting of the right ribs. - Hepatitis All damage to the liver causes bile production and secretion, resulting in constipation. Human white stools are common in chronic diseases such as viral hepatitis, hepatitis B and C, alcoholic hepatitis, toxic hepatitis, and autoimmune hepatitis.
- Non-obstructive disease in the liver. A change in the color and hardness of the stool is a characteristic feature of severe organic diseases with the loss of all functions of these organs. Khefir o-stools appear in cirrhosis, polycystic liver and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gray stools may be caused by pancreatitis, which is inflammation of the pancreas. In this disease, the structure of the stool changes because the production of digestive enzymes is reduced and the digestion of food becomes more difficult. Pancreatitis is characterized by Steatororhoea, indicated by the discharge of gray, greasy, and strong-smelling feces. In addition, those who are worried about pain in the upper left abdomen, diarrhea, buoyobio and bowel intestines.
In addition, those who are worried about pain in the upper left abdomen, diarrhea, buoyobio and bowel intestines.
Diagnostic methods
The examination begins with an examination by a gastroenterologist. Doctors learn about complaints, their causes, diseases and chronic conditions. Physicians are certainly interested in dietary changes, stress, and infections as causes of white stools in adults.
The function of the gastrointestinal tract can be assessed using special examination methods.
- Slanderous color - gray stools appear dripping with a lot of triglycerides, undigested dietary fiber, mucus and inflammatory cellular components.
- Analysis of stool elasticity - the study of this indicator is used for screening in the diagnosis of pathological conditions.
- Biochemical blood tests - violations of the hepatobiliary system are indicated by elevated levels of bilirubin and bile acids, as well as the production of transaminase enzymes (ALT and AST) also indicate lesions.

- Microbiological analysis of stool - stool may contain pathogenic bacteria, protozoa and helminths, which can aggravate the patient's condition.
- Urinalysis. With jaundice, it is usually not possible to determine a large amount of bilirubin pigment in the urine.
Given the epidemiological history of diagnosing the cause of white stools, the doctor may prescribe tests for antibodies to viral hepatitis A, B, C and E.
In addition to laboratory tests, a gastroenterologist performs instrumental imaging to assess the structure and functional activity of internal organs. A typical diagnostic program includes the following tests:
- Intra-abdominal ultrasonography: the main method for diagnosing the digestive system, which allows you to examine the liver, pancreas, gallbladder and spleen.
- Sample-based gallbladder ultrasonography is an extensive follow-up procedure performed after sampling on a choleretic breakfast to assess gallbladder contractility.

- Duodenoscopy - this study allows you to take different portions of bile for microscopy or baxev to assess the state of the function of the biliary tract.
- Pancreatography. Invasive imaging diagnostics provides the most accurate information about the anatomy of the biliary tract and the sphincter of Oddi.
Treatment of discolored stools
Treatment is based on the elimination of the underlying cause of discoloration of the stool. This allows you to achieve a complete cure and save the patient from unpleasant symptoms. Since all digestive functions are blocked in the liver and pancreas, diet must be followed to improve health. In your diet, limit fatty and spicy foods and completely eliminate alcohol, fast food and carbonated drinks. The diet should have enough calories and vitamins, and the recommended methods of preparing the product are boiling, tempering and baking.
The second step in the treatment of gray or white stools in adults is the selection of the drug.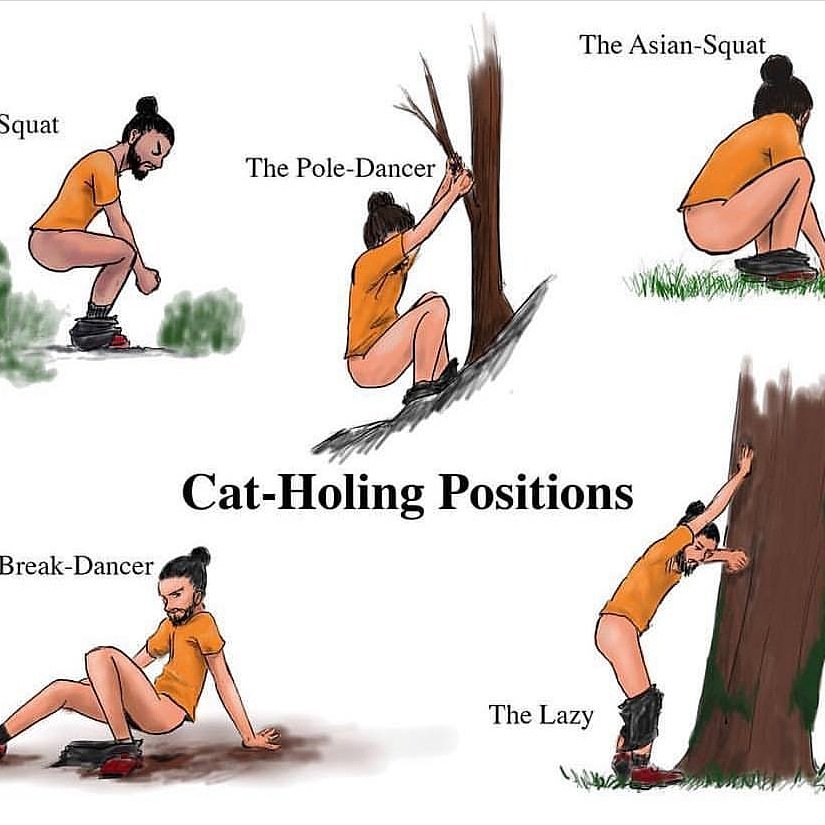 This group of drugs is most commonly used in gastroenterology.
This group of drugs is most commonly used in gastroenterology.
- Characteristics of the drug - improves the outflow of bile into the intestines, accelerates the breakdown of fats, ensures that a sufficient amount of bilirubin metabolites enters the feces.
- Enzymes. When the pancreas is underfunctioning, enzyme replacement therapy is indicated to improve absorption of all types of nutrients and remove staters.
- This is because anticonvulsants are effective in hepatobiliary dysfunction of the pancreas by relieving spasms and promoting the excretion of bile into the intestinal tract.
- Probiotics - a mixture of beneficial bacteria restores the normal flora of the large intestine, prevents the processes of fermentation and spoilage, normalizes the frequency and consistency of the stool.
- Antibacterial agents - for viral, bacterial and parasitic lesions of the liver, special etypic drugs are used.
Most cases are successfully treated conservatively, so that after a few days the shadow of the stool begins to heal, and the symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases also decrease. In severe cases or with delayed manifestation, they are treated surgically. These include removing large gallstones and draining the bile ducts.
In severe cases or with delayed manifestation, they are treated surgically. These include removing large gallstones and draining the bile ducts.
Patients are advised not to delay visiting a gastroenterologist in order to avoid complications and traumatic treatments. By contacting a medical institution in a timely manner, you can cope with the symptoms of the disease and regain a full life.
In the Medproosvet clinic, a qualified gastroenterologist will understand the causes of fecal discoloration and draw up an individual program for examining and treating the identified pathologies. You can make an appointment with a gastroenterologist by phone by leaving a request request on the main page.
Hepatitis A is an acute disease with a cyclical course of onset and then rapid resolution of symptoms such as poisoning and liver dysfunction. Hepatitis A is classified into the following types according to the international classification.
- Hepatitis A with hepatic coma
- acute hepatitis A
- Hepatitis A without hepatic coma.

epidemiology
Children often get hepatitis. Outbreaks manifest themselves in the form of isolated periodic cases or small epidemics. More than 60% of people with hepatitis A are children. This disease affects children between the ages of 3 and 7 years. Transplantation immunity protects children up to a year from diseases.
Only humans are susceptible to hepatitis. Infections can be carried and transmitted by humans, regardless of their form, overt or covert, and also as virus carriers. Epidemics are caused mainly by patients with atypical hepatitis A. It remains undiagnosed because the infected person continues to live a normal life and unconsciously spreads the infection.
The patient's virus "lives" in his feces, blood and urine. In the case of urine, it develops before symptoms appear. Hepatitis A is classified as a classic intestinal infection. transmission path. Hepatitis is not transmitted by airborne droplets. It can also be transmitted by blood transfusion, but the virus is not stable in the blood, so the risk is very, very low. The path of infection through transplantation is excluded.
The path of infection through transplantation is excluded.
The human body is very sensitive to this virus. Antibodies are produced in most adults. The incidence of hepatitis A is highest in autumn and winter, and lowest in summer. It is found in kindergartens and schools. After an illness, the body develops immunity to protect a person from hepatitis and survive it for the rest of their lives.
Hepatitis A is classified according to type, severity and course.
Typical cases of hepatitis are all in the skin and visible mucous dye. Usually be classified into three types: mild, moderate and severe. Atypical cases include hepatitis, seeding hepatitis, and sullen hepatitis. Falling hepatitis hepatitis A is not classified and because of the severity and belongs to the mild type.
The severity is determined by how remarkable the general malaise and jaundice are. We also consider the results of biochemical studies.
Lightweight. This form is used by about 50% of children.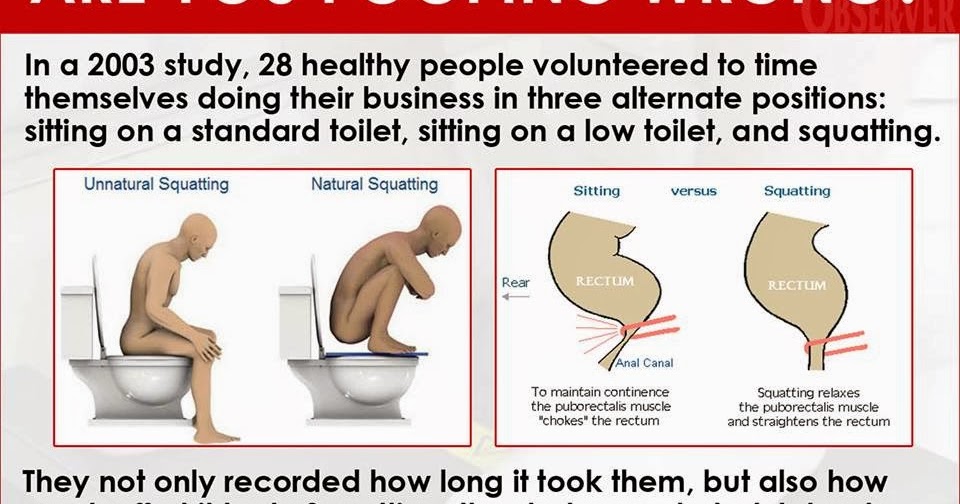 The peculiarity lies in the fact that the body temperature rises moderately (short period). Drunk is hardly expressed. The liver is moderately enlarged.
The peculiarity lies in the fact that the body temperature rises moderately (short period). Drunk is hardly expressed. The liver is moderately enlarged.
Periodically reaches benign. The capture period lasts from one week to 10 days. The liver is normal from the 2nd 5th to the 3rd 5th day. 5% of children have a long period of time.
30% of patients are moderate hepatitis, and the symptoms of poisoning are noticeable from mild, mild jaundice. The edge of the liver is dense, and the organs themselves hurt. The amount of urine is greatly reduced. In addition, the spleen is often enlarged. At 10-14 days of illness, when the disease progresses smoothly, the symptoms of poisoning continue. Yellowing does not disappear within 2-3 weeks. The liver returns to normal, 40-460 days after onset. Only 3% will extend the course.
Severe cases are rare, reported only in a ratio of 100 people to 100 people. The phenomenon of drunkenness is very noticeable, like jaundice. There is intense and frequent vomiting, lethargy and anorexia. The appearance of jaundice does not relieve the symptoms of general poisoning, but rather the opposite. Children are lethargic and depressed. Symptoms include dizziness, nosebleeds, bradycardia, decreased remarkable diuretic effects, and bleeding rashes.
The appearance of jaundice does not relieve the symptoms of general poisoning, but rather the opposite. Children are lethargic and depressed. Symptoms include dizziness, nosebleeds, bradycardia, decreased remarkable diuretic effects, and bleeding rashes.
In severe hepatitis A, the liver is large and the spleen is enlarged. There is severe pain on palpation.
Menstrual sutras pass without jaundice on the skin and strong film. Approximately 20% of patients with hepatitis A are affected, and other symptoms are similar to hepatitis A. The temperature may rise temporarily. Appetite is lost, and the whole body is weak and sluggish. There may be nausea and vomiting, but within 3-5 days.
The main symptoms of the menstrual sutra are swelling of the acute liver with a feeling of pressure and pain during palpation. You may also see swelling of the spleen, dark urine and slightly discolored.
A su-formal type is also called a su-reveal type. There are no clinical symptoms. In this case, it is possible to diagnose hepatitis A in a biochemical test for children in contact with the patient. If a TGM antibody for HAV is detected in the serum, the diagnosis is definite. The children of this disease support the fashion process with the help of the cluster.
In this case, it is possible to diagnose hepatitis A in a biochemical test for children in contact with the patient. If a TGM antibody for HAV is detected in the serum, the diagnosis is definite. The children of this disease support the fashion process with the help of the cluster.
Cholestatic type. The main symptom is obstructive jaundice. The pathogenesis of this disease is bile retention at the level of the intrahepatic bile ducts. The main symptom is prolonged and widespread jaundice, which resolves in 30-40 days. The skin can be not only yellow, but also green or saffron. In such cases, itching of the skin predominates. Symptoms of poisoning are absent, there is a slight increase in the liver. Urine dark, stool whitish. However, the course of the cholestatic form of hepatitis A is long and favorable. There is no chronic hepatitis.
The course of hepatitis A
The disease can be acute or protracted, smooth without exacerbations or with exacerbations. Complications from the biliary tract and adhesions of intercurrent diseases are also possible.
Acute course occurs in 95/100 cases. In some cases, the symptoms disappear very quickly, in 2-3 weeks. During this time, the liver will return to normal. In children, this usually corresponds to the duration of acute hepatitis (2-3 months), but some complaints may persist for 6-8 weeks after resolution of jaundice. Such cases can be seen as recalled recruits.
With a long course, hepatitis is diagnosed and lasts more than 3-6 months. In the period after the onset of jaundice, a violation of the periodicity of the disease is detected. The liver remains elevated for a long time, sometimes even the spleen. The persistent form of hepatitis A ends with recovery.
Current with exacerbations. An overdose can be understood as an increase in the clinical manifestations of hepatitis or a deterioration in liver function tests in situations where pathological processes in the liver persist. An exacerbation, in contrast to a recurrence of hepatitis A, is understood as a relapse that begins after a complete cure (no visible symptoms). Relapses may not be accompanied by the development of jaundice.
Relapses may not be accompanied by the development of jaundice.
In children, the addition of different types of hepatitis with the onset of relapse is observed. Aggravated by a weakened immune system.
Biliary tract infections usually develop in a moderate form. In this case, the disease often proceeds without distinct symptoms and is diagnosed according to the results of laboratory tests. A condition in which hepatitis A is cured and the disease progresses without specific treatment.
Currently intermittent infections. The diseases involved usually do not exacerbate the severity of the symptoms. However, in some cases, it can lead to liver enlargement.
As a result, the structure of the liver is expected to recover and fully recover. Recovery may be accompanied by anatomical defects, in which case the liver continues to grow throughout life. Complications may also occur. Biliary tract injury is thought to be related to complications of hepatitis and microbiota activation rather than sequelae.
When injured bile ducts complain of pain under the right rib, nausea and vomiting. Also, vague complaints begin 2-3 months after recovery.
What provokes / Causes of Hepatitis A in children:
The hepatitis A virus was discovered in 1970 by S. Feinstone et al. The virus contains RNA with a diameter of 27-30 nm. Caused by enteroviruses. VG can be "killed" with solutions of formalin, chloramine, ultraviolet. Also, when the medium temperature reaches 85 ° C, the virus dies in the first minute. But VGA is insensitive to the air.
Pathogenesis (what happens?) during Hepatitis A in children:
Hepatitis A has a direct effect of cellular disorder on viruses in the liver. The virus invades the stomach with saliva, food and water. It returns from the stomach to the small intestine, which is likely taken up by the portal circulation, enters the hepatocytes through the appropriate receptor, and interacts with the biological polymer involved in the detoxification process.
At this time, a free radical is generated that contributes to the oxidation of cell membrane lipids. The tissue structure of the lipids that make up the membrane changes. A hole opens in the hydrophobic barrier of the biofilm and eventually becomes transparent. The hepatitis A condition has a central relationship with the cellular syndrome.
In the body, the replacement of protein, lipids, carbohydrates, pigments, etc. As a result, albumin synthesis, blood coagulation capacity and various vitamins are reduced, and glucose utilization is also impaired. Restore the liver in the relocated facility.
Pathological morphology. Intravenous piercing data in the hope of examining the liver were studied form of hepatitis A. All organizational components are changing. With hepatitis, there is no large-scale liver necrosis.
Symptoms of Hepatitis A in children:
The disease follows periodic progress, including incubation period, early (farm front), onset (yellowing), layer period and hiring period. Number five.
Number five.
If a child becomes infected with hepatitis A, the incubation period will be 10 to 45 days, but in many cases it is 15 to 30 days. Viral antigen at this time can already be detected from the blood of an infected child. In addition, the activity of hepatocellular enzymes is also high.
In specialized literature, the initial period is also called the injection period. The disease is acute and body temperature rises to 38-39°C, causing symptoms such as decreased physical strength, headache, anorexia, nausea, and vomiting. The lower right ribs may complain of pain, and there are cases where there is no specific local area.
Infants become frustrated and irritated, no interest in play and no sleep disturbances. In many cases, there are special digestive diseases: thinner, constipation and more rare cases, and a few rare stools appear.
A few days later, or after the first day, the body temperature returns to a flat fever, and the symptoms improve, but the whole body is still debilitated. The most important objective symptoms at this time are liver enlargement, tenderness, and pain during palpation.
The most important objective symptoms at this time are liver enlargement, tenderness, and pain during palpation.
In mild hepatitis A hepatitis, it is not as dependent as above, but also due to changes in the shades of urine and stool. The precursor period lasts from 3 to 8 days.
During height, the expression of jaundice is characteristic. The whole state of the body improves. First yellow solid, face skin, torso, palate and then skin. Yellow appears very quickly.
Yellowing and due to hepatitis A in children does not always appear strongly. The period is one to two weeks, with an average of 9 to 13 days. Skin folds, auricles and scoliopathy are almost yellow. In jaundice, the liver grows to its maximum and feels pain on palpation. Lower blood pressure, weak heart sounds, tone impurities, and slight shrinkage at the top.
Above the maximum, jaundice begins to subside, which occurs 7-10 days after the onset of the disease. Symptoms of intoxication disappear, appetite increases, diuretic effect increases. Stool color returns to normal. If it follows a cyclical course, it will disappear in a week (maximum 10 days). Then the postictal phase begins. Despite the good state of health, the functional tests of the liver were changed, the liver was enlarged (rarely, the spleen).
Stool color returns to normal. If it follows a cyclical course, it will disappear in a week (maximum 10 days). Then the postictal phase begins. Despite the good state of health, the functional tests of the liver were changed, the liver was enlarged (rarely, the spleen).
The fifth stage is called the recovery period. It is characterized by the normalization of the size of the liver and the restoration of its function. The general condition of the child is good. However, children often complain of fatigue and abdominal pain during exercise. The fifth period lasts 2-3 months.
Diagnosis of hepatitis A in children:
Diagnosis of hepatitis A in children is based on clinical, epidemiological and laboratory data. Experimental methods are important. Test drug markers are divided into specific and non-specific. Specificity makes it possible to detect HAV RNA in the blood (PCR method) and to detect specific antibodies against HAV JgM (ELISA method).
Non-specific tests help determine the extent of liver damage and evaluate the severity, course, and prognosis of the disease. Among many clinical and biochemical tests, the most effective are the activity of hepatocyte enzymes (APAT, AST, F-1-FA, etc.), markers of pigment metabolism and measurement of the function of protein synthesis in the liver.
Among many clinical and biochemical tests, the most effective are the activity of hepatocyte enzymes (APAT, AST, F-1-FA, etc.), markers of pigment metabolism and measurement of the function of protein synthesis in the liver.
Treatment of Hepatitis A in children:
Most cases are treated at home. Moderate/minimum physical activity is recommended. The more severe the disease, the better to refrain from physical activity.
If jaundice is severe, mild bed rest is recommended if jaundice is detected.
In severe to moderate cases, bed rest should be observed during the first 3-5 days of jaundice. Bed rest can be introduced as soon as the symptoms of intoxication begin to subside.
Physical education is released for 3-6 months, and sports for 6-12 months. Depending on the individual case, it is recommended to introduce increased physical activity.
A sick child needs physiological nutrition, complete and high-calorie, preferably with a protein:fat:carbohydrate ratio of 1:1:4-5.
Healthy protein intake for children with hepatitis A includes low-fat dairy products, lean meats, lean fish, and eggs. Carbohydrates are included in the diet in the form of bread, rice, semolina, oatmeal, buckwheat, pasta, sugar, potatoes, etc.
The diet of a child with hepatitis A should include plenty of raw and cooked vegetables, green leafy vegetables, juices and fruits. Ingestion of extracts should be avoided. According to this concept, organic substances that have entered the solution during the cooking of the product are hidden. Examples include creatine, xanthine, creatinine, tyrosine, urea and leucine.
Fat, margarine and flame retardants contained in compound oils are also not recommended for children. Avoid fatty sausages, canned meats, pork, ham, fatty chicken, fatty fish, marinades, hot sauces, legumes, spicy cheeses, radishes, garlic, and radishes. Cakes, chocolate, pastries, pastries, spicy condiments (mustard, mayonnaise, pepper, etc.), smoked meats, nuts, fish, wasabi, etc. Such
Such
dried apricots, raisins), jellies, mousses, salads, vinaigrettes, fish jellies, pickled herring, etc. can be used for hepatitis A.
Pediatric hepatitis A is not treated with drugs, but bile acid drugs are prescribed. In the acute phase, it is desirable to use drugs that promote bile secretion (magnesium sulfate, falmin, bellflower, etc.) and during the convalescence period, a drug that promotes bile secretion (Allocall, Coenzyme, etc.).
In the case of hepatitis A, doctors prescribe composite vitamins, vitamin C and PP in group B. During the recovery period, especially if hepatitis A is prolonged, LIV52 K tablets (for 2 years and older) and LIV52 can be prescribed. Alternatively, you can follow the progress of the legal appeal.
In bile, bile is removed with ursodoroxycolic acid (ursozan). The dose is 10-15 mg/kg/day. If hepatitis A prolongs, the progress of ursosan will be prolonged, by 3 to 6 months. Ursosan may be replaced with Phosphogliv or Essential or Legalon for 2-4 weeks (as directed by your doctor). In severe cases (including moderate cases), infusion therapy is performed.
In severe cases (including moderate cases), infusion therapy is performed.
1.5% solution of leopilicin, gmodese and 10% glucose solution are injected into a vein at a weight ratio of 10 ml/kg.
After the acute phase of the disease, children are under medical supervision. We have a special office in the hospital. If such an office cannot be arranged, the local pediatrician will consult with the pediatric clinic.
The first consultation will take place 45-60 days after the start and will be reviewed after three months. If you do not have clinical symptoms, you will be removed from registration.
Intestinal absorption therapy should be administered during the treatment period, regardless of the form and severity of the disease. Drugs such as enterosgel and endodes are used.
If the elderly child lives in a village or town, the infection department or pediatric clinic will consult with the pediatric hospital in the central region.
Hepatitis A Prevention in Children:
The measure to prevent the spread of hepatitis A infection is to respond to sources of infection, routes of infection, and bacterial susceptibility.
Early diagnosis can be isolated to the sick, and you can avoid the tendency of organized children in groups. Children in contact with the patient are examined on a strong film and skin every day and palpation of the liver. In some cases, the color of urine and stool can be checked.
Laboratory tests are recommended to identify an atypical type with hepatitis A focus. This test is done every 10-15 days until the hepatitis A trend ends.
Public food and drink management, drinking water quality control, and public health and personal hygiene are essential to prevent the spread of infection. If hepatitis A patients are confirmed at the infection center, ongoing and final decontamination will be implemented.
Prophylaxis is to administer normal immunoglobulin. This may stop the outbreak. Immunoglobulin (1:10,000 or more) that has a high antibody count for hepatitis A virus is usually used. Also a fashion sign. From the beginning of autumn August to September, the planned falls for prevention and will be implemented in case of multiple hepatitis e-type, which affects 12 out of 1000 children.
The most effective prevention of hepatitis A is possible only through universal vaccination. The following vaccines are registered and licensed in Russia:
- Hepatitis C vaccine Polyoxidonium hep-a-in-vak-p-p L, Russia.
- Hep-a-ine-VAK vaccine Purified concentrated adsorbent inactivation solution. Russia?
- Havricks 720 from GlaxoSmithKline UK Ltd. 1440 GlaxoSmithKline Ltd (UK).
- Twinrix Hepatitis A and B Vaccine, Glaxso Smith Klein Company, UK. 25 (and 50). Merk Sharp and UM, USA, USA Sanofi Pasteur (France).
Intramuscular hepatitis A vaccine for children over 1 year of age. Hepatitis A vaccine can be given at the same time as hepatitis B vaccine if vaccinations at different sites overlap. 95% of vaccinations give a protective level of immunity.
Side effects from the vaccine are almost rare. In rare cases, it can be manifested by pain at the injection site, hyperglycemia, and edema. Perhaps an increase in body temperature, chills, allergic rashes.
Which doctors should you contact if you have Hepatitis A in children:
Do you have any concerns? For more information about hepatitis and children, including causes, symptoms, treatments and prevention, the course of the disease, and follow-up nutrition, click here. Or want an overview? You can make an appointment to see a doctor.
Normal brown stool is associated with the presence of bile pigment storms and stercetinogen derivatives. Green stools often indicate problems with the digestive system. Therefore, it is necessary to quickly find out the cause of the pathological symptoms and get the necessary treatment.
Causes of green stool
A change in the color of the stool does not necessarily indicate a pathological process. People who follow a plant-based diet suffer from this disease even if they don't have the disease. Green vegetables, such as spinach, contain large amounts of a pigment called chlorophyll, which is partially shed from feces and turns green. In this case, there are no other gastrointestinal symptoms, and the stool quickly acquires a natural color with a change in the intensity of nutrition.
In this case, there are no other gastrointestinal symptoms, and the stool quickly acquires a natural color with a change in the intensity of nutrition.
Another physiological cause is iron therapy. Some components of this drug are excreted from the body through the intestines and turn dark green or black with feces. This symptom begins to appear immediately after the start of correction of anemia and persists until the end of the course of treatment. Green feces do not cause discomfort to a person, so this is not a reason to stop taking iron supplements.
Dysbacteriosis
The main cause of green stool in children, adolescents and adults is dysbacteriosis, disordered composition of the intestinal flora and the predominance of pathogens. The color change in this case can be explained by two mechanisms. First, because the stool passes quickly, bilirubin, which is normally green, does not have time to turn into brown sterbilin in the intestine. Second, the stool contains mucus, inactive foods, and harmful bacteria, which also affect the color of the stool.
People who are concerned about nausea, heaviness in the stomach after eating, bloating, flatulence, etc., and changes in bowel movements. The number of bowel movements increases to 3-4 or more times a day, discomfort after defecation decreases.
Other causes
Green stool may indicate a digestive tract disorder. Similar mechanisms are possible in such diseases.
- Green stools such as intestinal infections such as "bogs" are typical symptoms of a salmonella infection. Stool color may change with rotavirus, enteritis, atchetitis, and shigella infections.
- Allergic reactions to food allergies are often also due to indigestion and changes in stool color. Patients complain of diarrhea, abdominal convulsions, nausea and vomiting. The relationship between experienced symptoms and exposure to the allergen can usually be clearly identified.
- Chronic enteritis. Inflammation of the mucous membrane in the small intestine and large intestine is said to be a frequent cause of stool disorders.
 As the disease worsens, green stools often appear, accompanied by pain in the abdomen, intestines, and intestines.
As the disease worsens, green stools often appear, accompanied by pain in the abdomen, intestines, and intestines. - Inflammatory bowel disease. In rare cases, green stools may appear to be signs of clonal disease and ulcerative colitis. They are often accompanied by bleeding from the intestines and are dangerous.
- Gluten intolerance in celiac disease is associated with chronic diarrhoea, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting with bile. The symptoms were also worsened by the consumption of foods high in gluten, such as cereals, and suffered by patients for many years.
- Disease of the gallbladder. With cholecystitis, chili pipitis, dyskinesia, etc., abnormal colors may appear. Patients are also concerned about abdominal pain, pain in the right ribs, nausea and vomiting.
Which doctor to contact
If you change the color of the link, you must first analyze your diet. If you don't have other symptoms and are overdosing on specific foods, don't worry. In addition, if the stool is green is one of the signs of gastrointestinal disorders, it is necessary to consult a gastrointestinal doctor. A doctor who handles the diagnosis and treatment of digestive problems. If you are not an expert, you cannot study the root cause of the decline in health and choose the appropriate method to improve it.
In addition, if the stool is green is one of the signs of gastrointestinal disorders, it is necessary to consult a gastrointestinal doctor. A doctor who handles the diagnosis and treatment of digestive problems. If you are not an expert, you cannot study the root cause of the decline in health and choose the appropriate method to improve it.
Diagnostic methods
Firstly, a consultation with a gastrointestinal tract doctor will be carried out, collecting complaints, establishing the possibility of triggering factors and clarifying the life history. Then, palpate the abdomen (look at the tip of the intestine, tip of the liver, and stomach) to confirm the possibility of gastrointestinal involvement.
Tests to be done for green stool complaints.
- SI N-SAMER microscopy can confirm contamination of undigested food particles, large amounts of mucus, leukocytes and erythrocytes in the stool.
- Microbial diagnostics to detect typical pathogenic intestinal infections that change the appearance and amount of stool.

- The in-flight PCP P-test is the fastest and most accurate method for diagnosing intestinal infection by detecting the pathogen gene contained in stool.
- Rattle egg assay and - Baseline tests that can rule out the most common pathogen in perigeres (three tests are required for high reliable results).
- Serrinistic blood test and blood test that examines antibodies for common pathogens in intestinal infections.
- Clinical blood chemistry tests are standard tests for detecting signs of inflammatory processes in the body and metabolic disorders.
In the case of green stools, diagnostics must be supplemented by instrumental visualization. As a screening study, ultrasound of the abdominal organs is prescribed, which provides basic information about the state of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and pancreas. To clarify the diagnosis, endoscopy (EGD, colonoscopy), CT or MRI of the abdominal organs can be prescribed. The diagnostic program "MedProsvet" is individual for each patient, and only those studies are assigned that help to make a final diagnosis.
Principles of treatment
In case of constipation, treatment begins with dietary modification. For intestinal infections and inflammatory diseases with diarrhea, a strict diet is required, consisting of pureed boiled vegetables, warm soups, cereals, dry white bread, low-fat meat soups. As the condition of the gastrointestinal tract improves, you can gradually increase the range of your diet, and after a few weeks return to your usual diet. Some chronic diseases require a special diet, such as avoiding gluten in celiac disease and limiting fatty foods in cholecystitis and pancreatitis.
Various types of drugs are prescribed to treat green stool disorders.
- Enterobacteria are effective drugs that help during periods of exacerbation of food poisoning, various poisonings, and chronic diseases of the digestive tract.
- Enzymes - drugs to improve digestion in gastritis, hepatitis, pancreatitis and other chronic diseases.
- Probiotics - preparations containing lactobacilli and bifidobacteria are used to restore the intestinal flora in bacterial diseases.

- Prebiotics are ingredients necessary for the growth and reproduction of beneficial bacteria in the colon.
- Antibiotics. Antibiotics are prescribed for severe bacterial enteritis.
- Anthelmintic drugs are used to target and eliminate helminthic infestations.
- Antidiarrheals are drugs used for constipation associated with chronic gastrointestinal disease, not for infectious diarrhea.
- Antispasmodics are medicines used to relieve symptoms of abdominal pain.
Given green stool disorders, gastroenterologists may prescribe additional drugs. In liver diseases, choleretic, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective agents are effective. Strong anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agents are used to improve conditions in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Patients with chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract should be regularly observed by a specialist to check the dynamics and effectiveness of treatment.
Prevention
To avoid green stools, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Try to eat a balanced diet that includes not only plant foods, but also products of animal origin.

- Avoid eating food from questionable catering establishments; - Avoid eating food from food outlets.
- Drink bottled or boiled water.
- observe personal hygiene
- Do not take antibiotics or other medicines unless directed by a doctor.
Many chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract progress gradually, so regular check-ups are recommended, even if you do not complain.
The clinic "Medproosvet" employs a gastroenterologist who provides support on the principles of evidence-based medicine. Our specialists tailor individual examinations and treatment plans to obtain the best possible treatment results. Call +7 (812) 374-84-00 or use the feedback form to book a convenient time for you!
Stagnation of bile is a condition called cholestasis. Normally, it is associated with the accumulation in the blood of substances secreted by bile. Cholestasis is not an independent disease, but a syndrome of dysfunction of the liver and biliary tract.
What happens in cholestasis?
With cholestasis, the process of outflow of bile from the intrahepatic or extrahepatic ducts noticeably slows down or stops completely. Although these syndromes can occur at any age, they are most common in men over 40 years of age who do not adhere to the principles of a healthy lifestyle. In children, bile stasis occurs very rarely.
Separately, consider such disorders as gestational cholestasis. This syndrome is less common and is characterized by complete recovery of the biliary tract after childbirth.
Due to stagnation of bile, its components (lipids, bilirubin) enter the bloodstream and accumulate in hepatocytes and bile ducts. It is toxic to hepatocytes and causes hepatocyte dysfunction.
Prolonged cholestasis increases the risk of developing biliary fibrosis and biliary cirrhosis.
Causes of bile stasis
Bile stasis is associated with the following causes:
- Liver infection (viral hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis).

- Congenital metabolic disorders (cystic fibrosis, galactocarcinoma).
- Penetration of helminths into the bile ducts. Common parasites here are insects such as ramuria and opistarchia.
- In the presence of stones in the gallbladder or ducts that affect patency.
- Tumor or cyst compressing the gallbladder or bile ducts.
- Anatomical features of the gallbladder and ducts (extraordinary, congenital, acquired infections).
- Abuse of fatty or spicy foods
- Toxic damage to the liver (poisoning with poisons, heavy metals).
- alcoholism
In case of inhibition of the outflow of bile, there are such concerns as indigestion, secondary inflammation of the liver and bile ducts, and a decrease in pancreatic function.
Forms and types of cholestasis
Cholestasis manifests itself in two forms: intrahepatic and extrahepatic. Violation of the outflow of bile may be associated with a decrease in capillary production and excretion of bile, blockage of the bile ducts by stones, or compression by a tumor.
Intrahepatic cholestasis according to the degree of damage is divided into intrahepatic (hepatic duct) and interhepatic.
These cholestases differ in their mechanism of occurrence.
- Partial. Partially.
- General bile does not enter the duodenum.
- split. In the body, the substances necessary for the full production of bile are reduced.
A distinction is made between acute and chronic cholestasis.
Consider the residence of bile during pregnancy separately. This syndrome usually occurs in the third period of pregnancy. Itching is not very strong. Pretty shapes are simple and bile effects occur independently two weeks after birth. In rare cases, if biliary stagnation develops early (between 25 and 27 weeks of pregnancy) and severe jaundice, you may have complications during childbirth.
Manifestations
Residential stay accompanied by these symptoms.
- There is severe itching of the skin mainly at night and after bathing.

- Frustrated and insomnia and itching.
- Frustrated with excitement, disappointment, disappointment, pain, etc.
- Bloating.
- Nausea and vomiting
- Skin appearance of the back and chest Zante-brown and yellow rough parts become thicker.
- The color of the skin and visible mucous membranes turns dark yellow (direct bilirubin in the blood is excessive).
- The color of urine becomes darker.
- Stool whitening
- Feeling that my mouth is bitter
- The amount of stool increases, becomes moist and emits a particularly unpleasant odour.
- Increased bleeding and due to impaired assimilation of fatty vitamins (especially vitamin K).
If bile secretion is inhibited, vitamins are not absorbed, causing symptoms of hypopro-vitaminemia such as fatigue, poor performance, dry skin and decreased muscle strength.
Complications
If bile treatment is not timely, bile stasis can become chronic.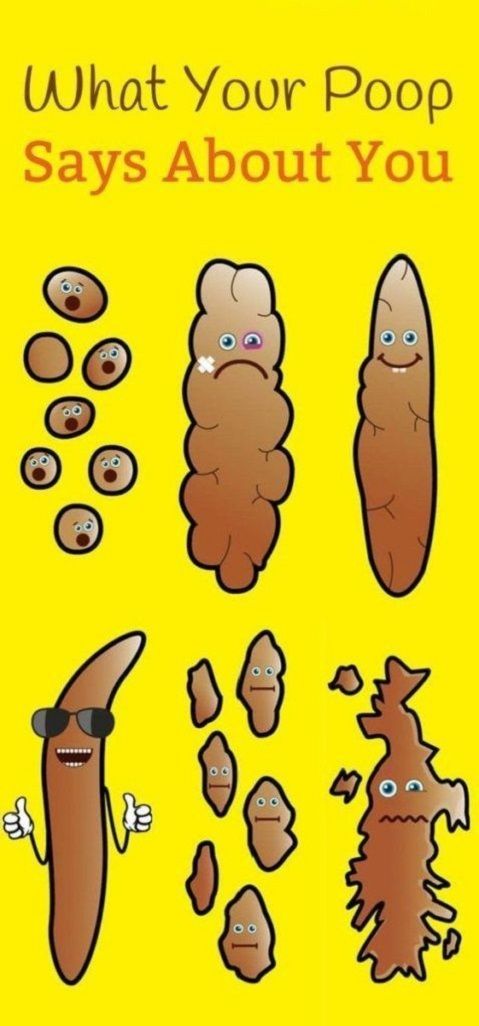 This indicates that the syndrome has continued for more than 6 months.
This indicates that the syndrome has continued for more than 6 months.
As a result of bile stagnation, the following occurs.
- Gastrointestinal disease
- Liver encephalopathy
- Hiken Zhou; Kanfuten
- Internal bleeding
- Cirrhosis
- Sepsis
The prognosis when bile leakage is inhibited depends largely on the cause of the cause. For example, if there is a stone in the jurisdiction, the prognosis is good, but the prognosis is inferior if the cause of the bile is a tumor that presses on the bile organs.
Diagnosis
If bile stasis is suspected, vision is performed for the first time. After that, we assign such a diagnostic method.
- Complete blood count, biochemical blood test
- Urinalysis.
- Bile analysis
- Sinomography
- Bile duct endoscopy with contrast agent.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
- CT or MRI of the abdomen.

Diagnosis cannot be obtained using the procedure listed separately. In this case, perform a liver biopsy.
Treatment
The first thing the doctor does when deciding on treatment is to choose the appropriate method against diseases and conditions that caused bile leakage. For example, in the case of stone syndrome, the stone is crushed or removed.
The following group drugs are indicated for the treatment of biliary stagnation.
- Protection hides what protects hepatocytes from damage (basic lipid phosphorus, lipid peroxide, amino acid).
- Dosing agent for the elimination of bile duct spasms.
- Bile secretion accelerator (when stones are not allowed into the gallbladder or tube).
- An antihistamine agent that suppresses skin itching.
During treatment, you need to provide dietary therapy. Table 5 is displayed in the issue of bile removal. From the diet, it is necessary to completely eliminate fried foods, spicy, smoked and canned foods.
In some cases, surgery may be required. Conducted patients whose bile leakage is decreasing.
- External bile duct drain.
- Opening of the gallbladder.
- Remove the gallbladder.
If there is a large stone in the bile duct, it is functionally removed.
What is considered normal adult stool
The body of each of us is different. Human stool depends on your diet and health. This time I will tell you in detail what an ordinary chair is.
Co-author, editor, medical expert-krimovich Elina Valivenna Khlimovich.
Number of views: 540 times 746 times
Last update: April 27, 2022
Average reading time: 9 minutes day or twice a day with long without strong strength. After a bowel movement, the intestines are completely empty and the urge completely disappears. Some external environments, such as resting in bed, changing the usual environment, the need for judgment, and the association of strangers, can slow or speed up this process. 。
。
No stool for 3 days (constipation) or more than 5 times a day (diarrhea), etc. (diarrhea) will deviate from the standard.
Daily stool count
In the case of mixed meals, the number of daily flights may change significantly. The average value is about 150-400 g. If you eat mostly vegetable products, the amount of stool may increase and animal products may decrease.
A remarkable increase or decrease in flight is a kind of anxiety. The main causes of Polycall (increased amount of stool) include the following:
- Use plenty of dietary fiber.
- Stomach disease with protein digestion.
- Intestinal diseases with decreased absorption of food and moisture, remarkable peristalsis, inflammatory exudate in the intestinal cavity and secretion of mucus (enteritis, polyp).
- Liver, gastric bladder and biliary diseases reduce the secretion and absorption of bile in the large intestine.
- Disease of the pancreas with extrinsic division function (protein and fat indigestion).

- Too much dietary fiber
The main reasons for the amount of stool are as follows.
- Many meals are digested.
- In case of constipation, stool remains in the large intestine for a long time and water absorption is maximized, reducing the amount of stool.
- It will be easier to get a stool.
Stool excretion and floating in water
If the stool is not sinking and the flow is very bad, it may contain a lot of undigested fat or a lot of gas.
In the case of mixed meals, the color of the stool is brown.
Stool color
If your stool is dark brown, you may be abnormal in eating food such as stomach, colitis, sepsis and indigestion. In addition, this color dominates and due to constipation and carnivores.
Light brown is observed by activation of bowel movement and compliance with dairy products.
Orange colors attract attention using β-carotene and many foods (eg pumpkin, carrots, etc. ).
).
Bleeding from the lower intestine (anus line of pregnancy, hemorrhoids, ulcerative colitis, etc.) and redness appears when eating beets.
If you use a lot of oxalic acid, spinach or lettuce, if the bowel movement increases or if there is a bacterial abnormality, it will be green.
Light yellow stool indicates that the speed of the stool passing through the intestines is very fast.
Black from the upper gastrointestinal tract (cirrhosis, digestive force ulcer, colorectal cancer), blood consumption during bleeding in the lungs and nose, the acquisition of activated carbon and the preparation of bimas, cranberries and edema.
If you take an iron, the color of the stool may turn green and black.
Gray stool indicates that there is too little or no bile in the intestines (acute pancreatitis, bile duct obstruction, cirrhosis, hepatitis, etc.).
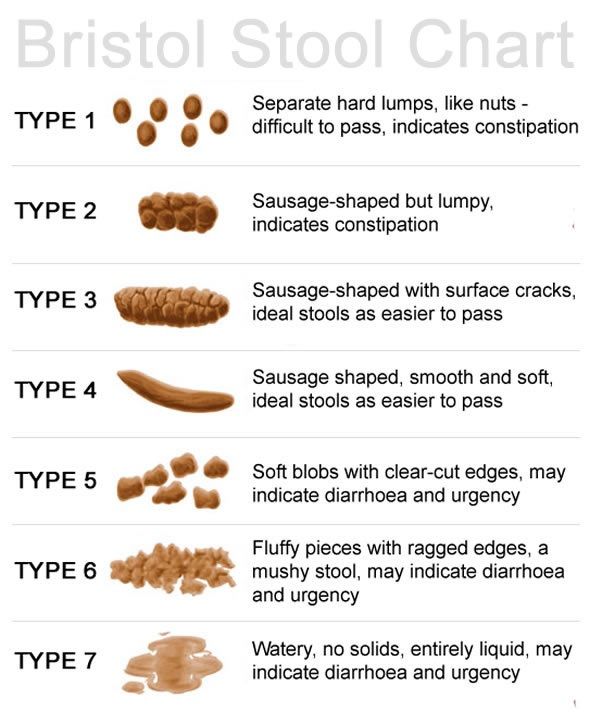
The chairs are usually softly decorated. 70% of stool is water and 30% is made up of processed food residues, intestinal cells and dead bacterial.
Stool consistency (density)
Determine the presence or absence of lesions on wet stool, foam polished stool, sebum stool, molecular stool, semi-loose stool, excessive thick stool, and pulmonary TB.
Flying in the form of Hyog o- with increased peristalsis, inflammation of the intestinal inflammation or excretion and may be associated with a large consumption of vegetable products.
- Very dark "sheep" flight, seen in constipation and dehydration, may indicate mechanical obstruction of the rectum.
- MAEI D-deserved in pancreatic diseases, this may be due to a rapid decrease in bile stores and an increase in the use of fat-based products the day before. Frequent stools of sebum can be a symptom when there is pancreatic disease and insufficient bile secretion.
- Liquid covered with digestion absorption in small intestine foods, process disturbances and stool acceleration, it is a symptom of poisoning, acute intestinal infection and poisoning.
- Foaming - the process of intestinal fermentation is observed when dominated.
- Adult stools must be cylindrical sausage shaped.
Shape of feces
And due to stenosis of the large intestine, convulsions, intestinal adenoids and lack of moisture or tightly spherical stools such as tape.
The smell of stool is unpleasant, like herbs and not spicy. It depends on the severity of the fermentation and decomposition processes and the composition of the food.
Smell of feces
If the digestive system is abnormal, what you eat may rot in the intestines or feed on pathogens. Some of them generate hydrogen sulfide and emit a unique rotten smell.
Fermentation of indigestion caused by an overdose of carbohydrates (flour products, sugar, beans, fruits, etc.). And fermentation (KWAS, etc.).
Explanation e-There is pancreatic dysfunction, over-secretion of the large intestine and a decrease in the flow of bile in the intestine. The cause of excessive stimulating stools may be the spread of pathogens.
The cause of excessive stimulating stools may be the spread of pathogens.
Stretching e-conditioning, colitis, gastric force of the stomach and marked by sufficient suffocation of saffron.
Smell weak when excretion from the small intestine is progressing or constipation.
Based on the smell of oil, punctuated by the bacterial decomposition of fat in the intestines.
Ga s is a product that occurs naturally during digestion and fermentation as food moves through the digestive tract. In adults, from 0.2 to 0.5 liters of gas are excreted.
Intestinal gases
Gas is also generated due to the vital activity of microorganisms that live in the intestines during the digestive process of the stomach. Dismantling of nutrients and the release of hydrogen sulfide, methane, carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
To increase the gas is considered normal.
When eating large amounts of carbohydrates and dietary fiber.
- ingestion during meals, high intake of air
- Consumption of foods that stimulate the fermentation process, as well as dairy products for lactose intolerance.

- Increased gas formation can be observed in such pathologies as:
deterioration of the intestinal environment
- celiac disease.
- About irritable bowel syndrome.
- I'm sick.
- Violation of pancreatic enzymes.
- Chronic liver diseases: hepatitis, cholecystitis, cirrhosis.
- Chronic bowel disease (enteritis, colitis).
- Dysfunction of the stomach and duodenum, gastritis.
- Normal faecal acidity for mixed feeding should be around pH 6.8-7.6. Because there is life in the intestinal microflora.
Fecal acidity
Be aware of abnormalities.
Acidity (pH 6.7 or less) is due to the presence of fermentative digestive disorders, the result of the predominance in the diet of simple carbohydrates, fermented foods, vegetables and fruits that promote fermentation in the intestines.
- Alkalinity (pH 8.0 and above) is observed in the presence of decay decomposition.
 This may be caused by excessive intake of dietary protein. Malabsorption of fats and proteins, digestive disorders and chronic bowel diseases are also manifested by alkaline reactions.
This may be caused by excessive intake of dietary protein. Malabsorption of fats and proteins, digestive disorders and chronic bowel diseases are also manifested by alkaline reactions. - The elimination process depends on the diet, the quantity and quality of products, the regularity of meals. If you notice problems with the stool, do not put off going to the doctor. Timely treatment helps to avoid complications.
The information in this article is for guidance only and does not replace the advice of a professional physician. Consult a qualified physician for diagnosis and treatment.
Discoloration of the stool is an important diagnostic sign indicating a malfunction of the digestive system. The appearance of the stool allows you to identify and consider the nature of the problem, as well as decide on the need for further research, program selection and treatment. Gray or white stools (white stools) are a common symptom and require careful examination to determine the underlying cause.
White stools in infants may be seen when the type of dairy product is changed or when a new diet is introduced. In most cases, stool color and consistency will return to normal after a few days.
When is white stool considered normal?
Temporary changes in stool color may occur in patients undergoing gastrointestinal x-rays using oral contrast agents. The barium sulfate solution you drink before surgery is gradually eliminated from the intestines over 1 to 2 days. The stool is white or light gray, but feels good and has no other signs of gastrointestinal distress.
Bilirubin entering the intestine through the bile ducts has a product of acidylin and sterbilinogen, which turns the stool brown. When blocking the formation and secretion of bile, the stool becomes lighter (astolic).
Pathological causes of colorless stools
A typical disease of the hepatobiliary system of the pancreas, accompanied by cloudy stools.
Biliary dyskinesia Dysfunction of the gallbladder and bile ducts is a well-known cause of halitosis in stool. In this state, the symptoms appear cyclically against the background of stress, physical exertion, malnutrition, etc. As the condition worsens, the president acquires a normal color and stickiness.
In this state, the symptoms appear cyclically against the background of stress, physical exertion, malnutrition, etc. As the condition worsens, the president acquires a normal color and stickiness.
- Obstructive jaundice. Blockage of the bile discharge tube accompanies the dying of intestinal bile, which is worse. At the same time, urine becomes darker due to the metabolic product bilirubin. It is common in gallstones, with intense cramps, nausea and vomiting in the right ribs.
- Hepatitis All types of liver damage can cause bile production and secretion and ascites. Human white stool most often develops in chronic diseases such as viral hepatitis, hepatitis B and C, alcohol, liver, and autoimmune inflammation.
- Anal liver disease. A change in the color and hardness of the stool is a typical example of serious organic diseases accompanied by loss of all organs. Sweet and white stools include cirrhosis, hepatic liver, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Gray stool is caused by pancreatitis, which is inflammation of the pancreas.
 In this condition, digestive enzymes are reduced and digestion of food interferes with the digestion of feces. In the case of pancreatitis, Steator, which releases gray bowel movements with a glow of fat and pungent odor, is typical. In addition, some people are concerned about pain, diarrhea, flickering and bowel movements in the upper left abdomen.
In this condition, digestive enzymes are reduced and digestion of food interferes with the digestion of feces. In the case of pancreatitis, Steator, which releases gray bowel movements with a glow of fat and pungent odor, is typical. In addition, some people are concerned about pain, diarrhea, flickering and bowel movements in the upper left abdomen.
The patient's consultation begins with a consultation with the gastrointestinal department. Doctors learn about complaints, prescriptions for their appearance, disease, and chronic condition. Doctors are always interested in the background of white stools in adults, such as changes in dietary habits, stress, and infectious diseases.
Diagnostic methods
The function of the gastrointestinal tract can be assessed using a special test method.
Gray color shows a large amount of triglycerides, sliced e-i n-a - A-A - a-Loss of dietary fiber, mucus and inflammatory cellular components, are discharged in large quantities.
- Stool Elasticity Analysis-Study This index is used for screening in pathological diagnosis.
- Biochemical analyzes of blood and disorders a-infrator disorders are indicated by an increase in bilirubins and bile acids, and the development of transformer enzymes (ALT and AST) also indicates lesions.
- Microbial analysis of field cullets may have pathogenic bacteria, protozoa and developers that worsen the patient's condition.
- Test jaundice has a large amount of bilirubin pigments in the urine, but this cannot be assessed normally.
- Physicians may order antibody tests for viral hepatitis A, B, C, and E, taking into account the epidemiological history, to diagnose the cause of white flying.
In addition to testing in the laboratory, image diagnosis is performed by devices to assess the structure of internal organs and functional activity. The standard diagnostic program includes the following surveys:
Intonal cavity ultrasound test: a basic method for diagnosing the digestive system can be tested for the liver, pancreas, gallbladder and spleen.
- The Gallbladder Specimen Ultrasound Test is a wide range of examinations performed after collection of specimens with a choletic breakfast to assess gallbladder shrinkage.
- Duodenal test e-In this test, different parts of bile can be collected for microscopy and bakseve to assess the state of the function of the biliary tract.
- Cholangiopancreatography. Invasive imaging diagnostics provides the most accurate information about the anatomy of the bile ducts and the sphincter of Oddi.
- The main principle of treatment is to eliminate the underlying cause of discoloration of the stool. This allows you to achieve a complete cure and save the patient from unpleasant symptoms. In diseases of the liver and pancreas, all digestive functions are reduced, therefore, in order to improve health, it is necessary to follow a diet. Limit fatty and spicy foods, completely eliminate alcohol, fast food and carbonated drinks. The diet should be high-calorie and fortified.
 Cooking methods such as simmering, boiling, and baking have been proposed.
Cooking methods such as simmering, boiling, and baking have been proposed.
Treatment of discolored stools
The second step in the treatment of gray stools and white stools in adults is the selection of a drug. In gastroenterology, the following groups of drugs are commonly used:
Cholesecretory - improves the outflow of bile into the intestine, promotes the breakdown of fats, removes a sufficient amount of bilirubin metabolites with feces.
- Enzymes. Enzyme replacement therapy is indicated in cases of insufficient pancreatic function to improve the absorption of all types of nutrients and eliminate fatty liver.
- Antispasmodics - this drug relieves spasms and promotes the excretion of bile into the duodenum, therefore it has a good effect on the dysfunction of the hepatobiliary system.
- Probiotics - a mixture of beneficial bacteria restores the normal flora of the large intestine, prevents the processes of fermentation and putrefaction, normalizes the frequency and consistency of the stool.

- Antibacterial agents - special Ethiopian drugs are used for viral, bacterial and parasitic lesions of the liver.
- In most cases, conservative treatment is successful, and after a few days the color of the stool begins to return, and the symptoms of digestive problems decrease. In severe cases or when you are late to see a doctor, surgical treatment is possible, including the removal of large gallstones and drainage of the bile ducts.
Patients are advised not to delay their visit to a gastroenterologist in order to avoid complications and traumatic procedures. By contacting a medical institution in a timely manner, you can cope with the symptoms of the disease and regain a full life.
A qualified gastroenterologist will meet you at the MedProsvet clinic. They understand what causes stool discoloration and create a customized program for testing and treating local conditions. You can sign up for gastroenterological medicine by phone or by clicking the "feedback" button on the website.
The normal brown color of the stool is associated with the presence of the bile pigment stercovirin and stercobilinogen derivatives. Green stools often indicate problems with the digestive system. Therefore, it is necessary to quickly find out the cause of the pathological symptoms and get the necessary treatment.
A change in the color of the stool does not necessarily indicate a pathological course. People who follow a plant-based diet suffer from this disease even if they don't have the disease. Green vegetables such as spinach are high in the pigment chlorophyll, some of which is excreted in the stool and turns green. At the same time, the patient has no symptoms of other digestive disorders, and the stool quickly acquires a natural color when the nature of the diet changes.
Causes of green stools
Another physiological cause is iron therapy. Some components of the drug are excreted from the body through the intestines, and the stool turns dark green or black. This symptom begins to appear immediately after the start of correction of anemia and persists until the end of the course of treatment. Green feces do not cause discomfort to a person, so this is not a reason to stop taking iron supplements.
This symptom begins to appear immediately after the start of correction of anemia and persists until the end of the course of treatment. Green feces do not cause discomfort to a person, so this is not a reason to stop taking iron supplements.
The main cause of green stool in children, adolescents and adults is dysbacteriosis, disordered composition of the intestinal flora and the predominance of pathogens. The color change in this case can be explained by two mechanisms. First, because the stool passes quickly, bilirubin, which is normally green, does not have time to turn into brown sterbilin in the intestine. Second, the stool contains mucus, inactive foods, and harmful bacteria, which also affect the color of the stool.
Dysbacteriosis
People who are concerned about nausea, heaviness in the stomach after eating, bloating, flatulence, etc., as well as changes in defecation. The number of bowel movements increases to 3-4 or more times a day, discomfort after defecation decreases.
Green stools may indicate a disorder in the digestive tract. Similar mechanisms are possible in such diseases.
Other causes
Intestinal infection A typical symptom of salmonellosis is green bowel movements resembling "swamp mud". Rotavirus infection, enteroviral enteritis, echotosis, and silicosis can also cause discoloration of feces.
- People with food allergies Allergic reactions are often manifested by indigestion or discoloration of the stool. Patients also complain of diarrhea, abdominal pain, cramps, nausea and vomiting. It is usually possible to clearly identify the relationship between symptoms and exposure to the allergen.
- chronic enteritis. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the small and large intestines is considered a well-known cause of stool disorders. Green stool appears most often during exacerbations of the disease and is accompanied by abdominal pain, flatulence and intestinal flicker.
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
 Sometimes green stools can be a sign of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. They are often accompanied by bleeding from the intestines and are dangerous conditions.
Sometimes green stools can be a sign of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. They are often accompanied by bleeding from the intestines and are dangerous conditions. - celiac disease. Gluten intolerance is manifested by chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting with an admixture of bile. Symptoms haunt the patient for many years and are aggravated after eating cereals and other plutin - plutin.
- Diseases of the biliary system. Abnormal colors can occur with cholecystitis, cholangitis, dyskinesia, etc. Patients also complain of chills with bitterness, pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, and vomiting.
- If you change the color of the intestines, you should first analyze your diet. If you overuse a certain product and have green stools without other symptoms, don't worry. Also, if a greenish stool is one of the signs of gastrointestinal disorders, you should contact a gastroenterologist. A doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
 Only a specialist can find the root cause of poor health and choose the appropriate methods to improve it.
Only a specialist can find the root cause of poor health and choose the appropriate methods to improve it.
Which doctor to contact
First, a consultation with a digestive doctor is carried out, collecting complaints, finding out the causative factors that are considered to be occurring, and finding out the life history. In addition, palpation of the abdominal cavity (intestine, tip of the liver, stomach) is performed to determine the possibility of damage to the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnostic methods
What test should I do if I have green stools?
SUMI is the observation of a bowel movement pattern with a microscope and can be confirmed to contain food particles, large amounts of mucus, white blood cells and red blood cells in the stool.
- Carabaxef is a microbial diagnosis that examines typical pathogens in intestinal infections that alter the state and amount of bowel movements.
- PTS stool R-test is a method for a faster and more accurate intestinal infection by detecting the pathogen gene contained in the stool.
- Analysis of test trials with rattle eggs that can remove the most typical pathogen in the perierate (triple test required for reliable results).
- Serrinism blood test is a blood test that tests for antibodies against common pathogens in intestinal infections.
- Clinical blood chemistry tests are standard tests that can detect signs of inflammation and metabolic disorders in the body.
- If a green stool comes out, you will inevitably make up for the diagnosis using the organic image diagnostic method. As a screening test, abdominal ultrasonography is prescribed to obtain basic information about the state of the gastrointestinal, liver and pancreas. To clarify the diagnosis, endoscopy (FGD, colonoscopy), abdominal organs, and MRI may be prescribed. Medoprosbeth creates a diagnostic program for each patient and prescribes only tests that are useful for a definitive diagnosis.
In the event of a flight disturbance, read the Treatment for Nutritional Correction. Strict dietary restrictions are needed for intestinal infections and inflammatory diseases with diarrhea. Seasoned boiled vegetables, slimy soup, porridge rice, dry white bread, low base meat soup. As your gastrointestinal tract improves, you can gradually expand your food intake and return to regular meals after a few weeks. For example, specific chronic diseases require specific dietary therapies, such as elimination of gluten for celiac disease and restriction of high-fat foods for gallatin and pancreatitis.
Strict dietary restrictions are needed for intestinal infections and inflammatory diseases with diarrhea. Seasoned boiled vegetables, slimy soup, porridge rice, dry white bread, low base meat soup. As your gastrointestinal tract improves, you can gradually expand your food intake and return to regular meals after a few weeks. For example, specific chronic diseases require specific dietary therapies, such as elimination of gluten for celiac disease and restriction of high-fat foods for gallatin and pancreatitis.
Principles of treatment
Various types of drugs are prescribed to treat green stool disease.
Intestinal suckers such as food poisoning, various drug addicts and exacerbation of chronic digestive diseases.
- Enzyme: Pharmaceuticals that improve digestive functions and chronic diseases such as gastritis, hepatitis and pancreatitis.
- Probiotic and pharmaceutical preparations, including lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria, are used to restore abnormal intestinal flora.

- Prebiotic and ingredient required for the growth and growth of beneficial bacteria in the large intestine.
- Antibiotic and antibiotics are indicated for severe bacterial intestinal infections.
- Rubber preparation s-Drugs are used to eliminate the invasion of Perpapporo.
- Antidiarrheals are drugs used for constipation associated with chronic gastrointestinal disease, not for infectious diarrhea.
- Antispasmodics are medicines used to relieve symptoms of abdominal pain.
- Considering green stool disorders, gastroenterologists may prescribe additional drugs. In liver diseases, choleretic, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective agents are effective. Strong anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agents are used to improve conditions in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Patients with chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract should be regularly observed by a specialist to check the dynamics and effectiveness of treatment.
To avoid green stools, the following recommendations should be followed:
Prevention
Try to eat a balanced diet that includes not only plant foods, but also products of animal origin.
- Avoid food from questionable catering establishments; - Avoid eating food from food outlets.
- Drink bottled or boiled water.
- observe personal hygiene
- Do not take antibiotics or other medicines unless directed by a doctor.
- Many chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract progress gradually, so regular check-ups are recommended, even if you do not complain.
MedProsvet clinics employ qualified gastroenterologists who adhere to the principles of evidence-based medicine. Our specialists select an individual examination and treatment plan for the maximum possible therapeutic effect. Call +7 (812) 374-84-00 or use the feedback form to book in advance
Physical and chemical properties of faeces can tell a lot about human health, especially about the functioning of the digestive system. With a monotonous lifestyle and diet, the stool is stable and almost the same color, with slight variations in its shade. A sudden change in color can cause serious harm to your body, so be careful. In particular, caution is required if the color of the stool has changed to black. In some cases, this color is associated with serious pathologies of the digestive system. If treatment is delayed, it can be life-threatening.
With a monotonous lifestyle and diet, the stool is stable and almost the same color, with slight variations in its shade. A sudden change in color can cause serious harm to your body, so be careful. In particular, caution is required if the color of the stool has changed to black. In some cases, this color is associated with serious pathologies of the digestive system. If treatment is delayed, it can be life-threatening.
Fecal clumps are formed as a result of the enzymatic treatment of juices (food particles). The quality of food conversion and assimilation depends on the activity of digestion, which includes many factors (intestinal secretion activity, motility, food composition). The formation of stool is completed in the intestines. After processing, the excrement is excreted outside the body in the form of various colors from yellowish brown to blackish brown. It is usually released regularly (two to once every other day) every day.
What should be the feces of a healthy person?
Changes in diet and diet, excess consumption of certain food categories, consumption of exotic foods alter faecal values. It can change the color, texture, smell and appearance of small amounts of indigestible particles that are taken for granted. These phenomena are due to the peculiarities of the digestion of individual products.
It can change the color, texture, smell and appearance of small amounts of indigestible particles that are taken for granted. These phenomena are due to the peculiarities of the digestion of individual products.
Severe discoloration and stickiness suggest lack of digestive tract production, lack of digestive juice production (hydrochloric acid, pancreatic juice, bile) and unbalanced intestinal flora. Tests prescribed in gastrointestinal medicine can help determine the cause. First, you can get a lot of information from the Shin program (detailed flight analysis).
Very dark stools deviate from the normal standard. This symptom requires close attention and detailed interviews about why the stool is black. It is important to eliminate the causes of life as soon as possible.
The main causes of stool discoloration are as follows.
Possible causes of black stools?
Use specific product.
- Taking pharmaceuticals, using specific substances, using specific products, taking pharmaceuticals
- Side effects of specific drugs
- The beginning of a digestive illness.

- Next, we will consider the characteristics of symptom expression for each cause.
Mechanism that changes the color of the stool depending on the food
First of all, it is important to think about what it is, it is not dangerous even if the color of the stool is black. Dark stools are often associated with the consumption of a certain type of food, and the food changes directly or changes its properties during digestion. After eating the following foods, stools may become unusually thick.
Table bit; canteen bit; blows; bits; blows; blows; beats
- Side beans (beets, blackberries, raisins, blackberries).
- pomegranate?
- tomato?
- Fried and medium roast meat.
- I use a lever.
- When used, black stools occur after 1-2 days. This symptom lasts 1-3 days. Flight after the exclusion of this product will be normal color.
- In principle, Browning stool has no sudden change in stool viscosity and the stool remains formed.
 Various use of provocative products can cause laxatives and constipation. If the color of the stool is dark, the general condition of the patient will not change, and there are no other complaints if it is related to a particular meal or food preparation menu.
Various use of provocative products can cause laxatives and constipation. If the color of the stool is dark, the general condition of the patient will not change, and there are no other complaints if it is related to a particular meal or food preparation menu. - What drug can change the color of the stool?
- Some drugs may change the color of the stool and may be black. In fact, in the process of moving through the digestive tract, the drug is exposed to the digestive juice. This may affect the characteristics of pharmacological and active substances. If you are taking the following group medicines, there is a black change in stools.
Anemia (iron preparation).
Vitamins and metal complexes (including iron during formulation).
If you have a drug symptom, don't worry. Shortly after stopping the medication, the stool becomes a normal color. It is recommended to read the instructions to see if the product can change the color of the stool.
 In addition, it must be remembered that symptoms (other than symptoms of underlying diseases) did not appear.
In addition, it must be remembered that symptoms (other than symptoms of underlying diseases) did not appear. Activated carbon and preparations based on it may cause black fecal color. Staining is due to the release of a substance outside the body, as it is. As a rule, the color of the stool becomes normal one day after stopping.
- Pharmaceutical side effects
- The reason for the distribution of black stools is the consumption of drugs that can cause internal bleeding. These are the following.
- Non-steroidal ant and inflator.
Anti-hematopathic agent with acetylosalicylic acid as the main component.
There are also antibiotics.
This may change other physical properties of the stool (viscosity, frequency), as well as the general well-being of the patient. Signs of internal bleeding include weakness, drowsiness, dry skin, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite.
If you have recently taken any of these medicines and suddenly have dark stools, you should contact your doctor as soon as possible. Additional tests are ordered to diagnose internal bleeding. In such situations, urgent help is needed.
Additional tests are ordered to diagnose internal bleeding. In such situations, urgent help is needed.
- for which diseases the stool is black
- The most dangerous option is black stool as a symptom of an attack. Shows internal bleeding in the early stages from the esophagus, stomach and colon. In diseases of the ONT system, blood rarely enters the gastrointestinal tract. Clinically, hemoglobin in the blood is converted to hemin under the influence of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. In humans, black feces indicates a sufficiently large amount of bleeding (more than 60 ml), so it is imperative to consult a doctor.
- Bleeding stools not only change color but also become sticky. The stool becomes irregular, thick and sticky, resembling tar. This symptom may be accompanied by pathologies such as:
acute corrosive esophagitis
Acute purulent hypoxia of mucous membranes.
Ruptured aortic aneurysm into the lumen of the small intestine.

gastritis
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
- Meroli-Wise syndrome
- stomach cancer
- hemorrhagic fever
- Typhoid fever Typhoid fever.
- Electric shock fever?
- hemophilia;
- Thrombocytopenia
- hookworm
- histoplasmosis
- cirrhosis of the liver
- acute lymphoblastic leukemia, etc.
- Dangerous internal bleeding is accompanied by nausea and vomiting (red or brown mass), general weakness, decreased blood pressure and pulse. Internal bleeding in infections is accompanied by fever, sweating, chills.
- If you have any of the listed diseases or if your general condition worsens with the appearance of black stools, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
- Diseases that cause internal bleeding are rare in children. Serious health problems are indicated by the presence of other symptoms (fever, abdominal pain, weakness, vomiting, etc.
 ). In such situations, seek medical attention without delay.
). In such situations, seek medical attention without delay. - Dark stools in children are most often due to dietary habits or drug use. Digestion of certain foods may be incomplete due to reduced enzyme activity and color changes due to interaction with digestive juices. An example of a parent, as small black hairs in the feces are often mistaken for parasites. In fact, it is a particle made from undigested bananas.
- Newborn stools are usually black with greenish tinges. This is meconium (intestinal contents) produced during fetal development. With the introduction of milk mixtures and baby stool, the stool is stained with infant polychromy (mustard, light brown, yellowish).
If you are taking a multivitamin or iron supplement, don't worry about stool color. Changing the color of the stool in such a situation is also common.
Dark pregnancy stools may occur due to ironing and menu changes. This is completely normal and does not threaten the health of mothers and children.
Is black feces in a child normal or pathological?
When the black stool comes out, be careful if the girl's history has a digestive tract, liver, or blood disease. When you become pregnant, the burden on a woman's body may increase and chronic conditions may worsen. If you are unable to suddenly darken and have satisfactory stool results, you should consult with an obstetrician and gynecologist who monitors pregnancy.
Whether an adult or a child, a decorated black stool should not be a panic. This phenomenon can be dealt with at different stages.
At present, it is necessary to analyze the person's condition. If you have any problems, call an ambulance or take her to the hospital yourself.
If the patient is at home, it is necessary to remember whether to ask the last few weeks for health characteristics (regardless of symptoms, detection of disease or treatment). If the answer is yes, you need to contact the clinic. If you feel fine and normal, you can move on to the next step.
Pregnancy black stools
To clarify medications the patient is using regularly and recent medications. If you are using medicines that can cause internal bleeding, contact your doctor. Those who do not use medicine can proceed to the next step.
Analysis of the patient's diet for the last 2-3 days (there was a change in diet, unusual foods, seasonings and drinks were introduced, or foods on a certain list were used). If the relationship with food is confirmed, the cause of the product must be removed and this can be expected to normalize the flight within 1-3 days.
What to do if the feces turn black?
The following symptoms cannot be ignored in the presence of black stool.
- Violent cough
- Severe bleeding
- Does my stomach hurt?
- Pressure reduction
When do you need to see a doctor urgently?
Decreased heart rate
- Nausea, vomiting
- Loss of consciousness
- This is a weak point.

- Fatigue during known operation
- Increase body temperature
- Pot
- The skin is full.
- If you have one or more of these signs, you will not be allowed to delay your consultation.
- If the color of the stool is different, it is best to consult the gastrointestinal department. In difficult situations, the help of a surgeon is needed. If internal bleeding is suspected, test at the following steps:
- Blood tests (Coagulation tests are usually performed in addition to general clinical tests.)
- Faecal stool test in progress (celebration, coating test and bacterial tests)
- Endoscopy (esophagus, stomach, duodenum and colonoscopy can not only indicate the site of bleeding, but also collect hemorrhage and tissue).
- X-ray/MRI using a contrast agent (you can check the location of the bleeding deficit.)
People can add to the list of diagnostic methods.
What test should be done for black stools?
If your health is poor, you need to call the ambulance 112.


:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/2785562/original/028627600_1556001360-shutterstock_1019963743.jpg)