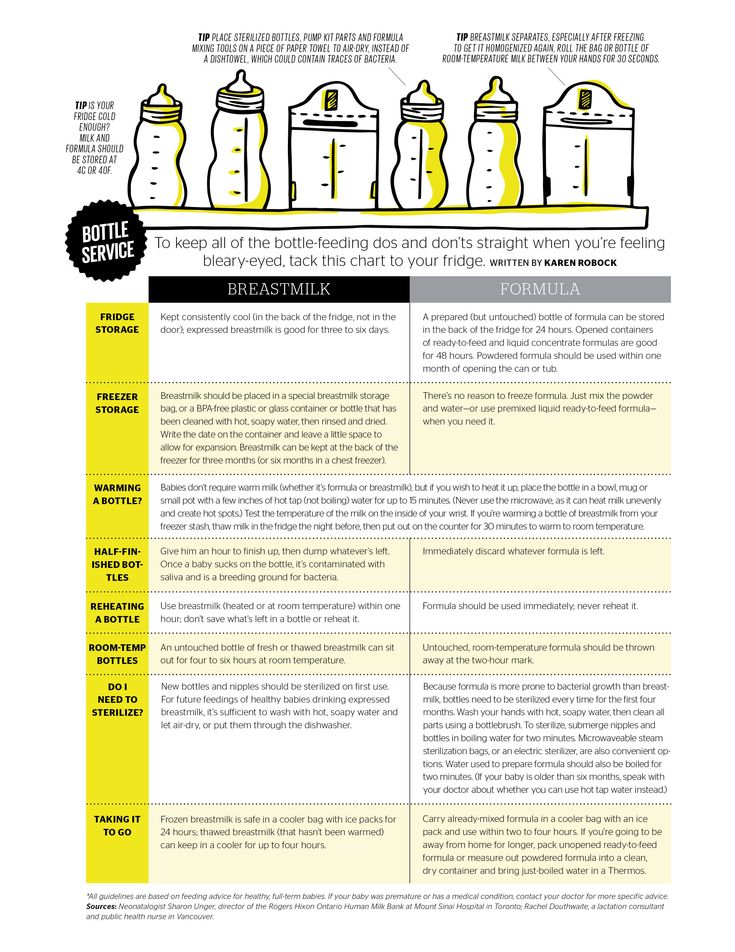
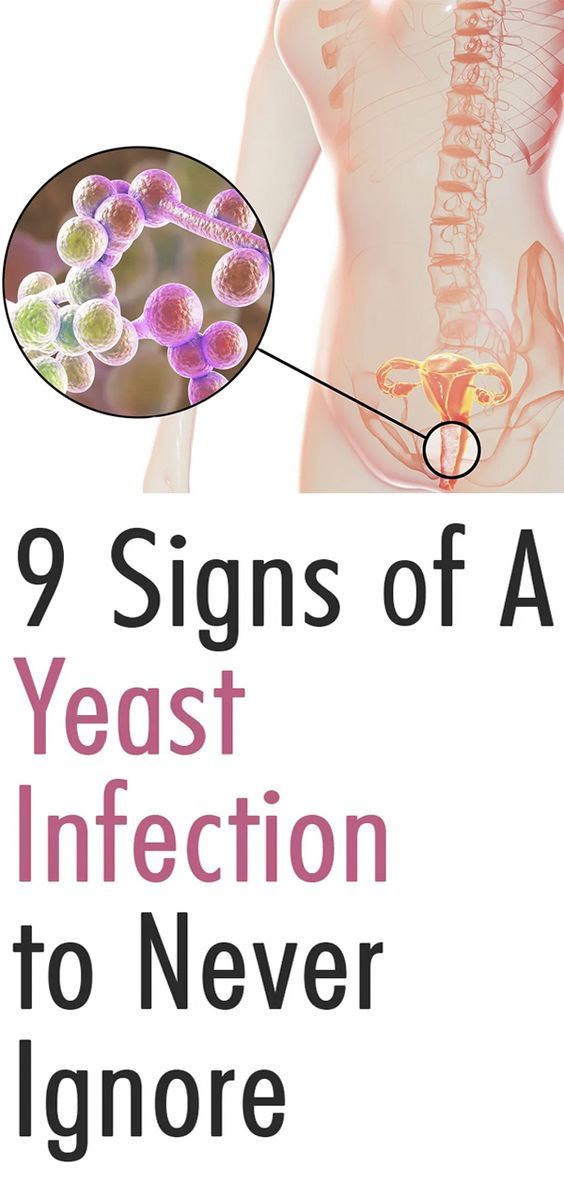
Can i get thrush from my baby
Causes, Treatment and When to See a Doctor
Nationwide Children’s Hospital
Thrush is an infection caused by a fungus called candida (CAN-did-ah). Candida is naturally present in the mouth and body and is usually harmless. But, if conditions are right, it can grow out of control and cause an infection.
- A candida infection in the mouth is called oral thrush; in the diaper area, a yeast diaper rash; in other places on or in the body, a yeast infection.
- Candida is the same fungus that causes vaginal yeast infections.
- Oral thrush is more common in infants and toddlers, but older children can get it too.
- Thrush is contagious (catching) and can be passed to others.
Risk Factors for Getting Thrush Are:
- Age – born early (premature) or younger than 6 months or low birth weight
- Getting it during birth from the parent who has an unknown vaginal yeast infection
- Breastfeeding with an untreated yeast infection of the breast
- Using human milk from a pump that has not been properly sterilized
- Sucking on a pacifier or bottle too often and for too long
- Using an inhaler for asthma without rinsing the mouth after use
- Recent history of child or nursing parent taking antibiotic medicine to treat a bacterial infection
- A weakened immune system
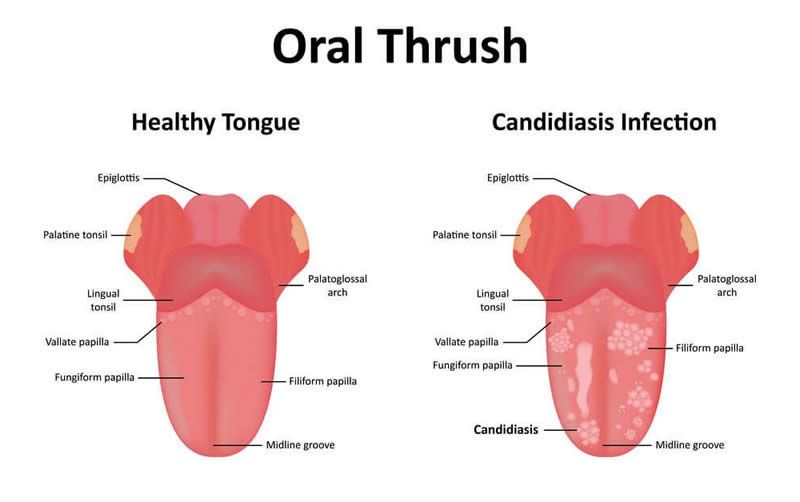
Signs and Symptoms
- Thrush in the mouth:
- Can be on the tongue, gums, roof of the mouth, or inside of the cheeks.
- Begins as tiny, flat, white, or creamy yellow spots. These spots come together and form cheesy patches that look like cottage cheese. The spots are often mistaken for milk patches. Sometimes it looks like a white coating.
- Cannot be removed with a soft cloth or a cotton-tipped swab without causing bleeding.
- May cause pain while sucking or swallowing. Your child may not drink or eat as much as usual.
- Can be on the tongue, gums, roof of the mouth, or inside of the cheeks.
- Yeast infections in the diaper area look like diaper rash. The skin can have:
- Small or big red patches, be entirely bright red, or have raised edges or small bumps
- Pimples that ooze pus
- A vaginal yeast infection can cause the skin to be red, itchy, and burn. Often, there is a creamy discharge from the vagina.
Treatment
- Thrush is easily treated with an antifungal medicine such as nystatin (Mycostatin®), fluconazole (Diflucan®), or itraconazole (Sporanox®).
 Your child may get these medicines as a syrup or a pill.
Your child may get these medicines as a syrup or a pill. - Thrush usually clears up in 4 to 5 days. It is important to use all of the medicine for the length of time that is recommended.
- An antifungal cream is usually recommended for yeast infections in the diaper area, in the vagina, or other places on the skin. You can buy some of these medicines without a prescription.
- Avoid using any home remedies without asking your child’s health care provider first.
How to Give Oral Drops
- A liquid medicine comes with a dropper in the box. Use it to give the oral drops.
- You will put the drops directly in the mouth on the sores. The medicine needs to stay in the mouth for a while. It will not hurt your child to swallow it.
- Plan to give the drops right after you feed your baby.
Follow These Steps:
- Wash your hands well.
- For an infant or young child, place them on their back.
 Turn their head sideways so that the cheek with the white patches faces down toward the bed (Picture 1).
Turn their head sideways so that the cheek with the white patches faces down toward the bed (Picture 1). - Gently open your child’s mouth and drop half of the medicine inside the cheek. Turn your child’s head the other way and repeat squirting the medicine inside the other cheek.
- Using a cotton-tipped swab, spread the medicine inside the mouth over the white patches.
- For an older child, have them swish the medicine in their mouth for 30 seconds and then swallow.
- Wait 30 minutes before giving your child anything to eat or drink.
- Always wash your hands well before and after touching your child’s mouth or things that have touched their mouth. This is so you do not pass the infection to others.
- Be sure your child drinks plenty of liquids so that they do not get dehydrated (lose too much fluid).
- Sterilize baby bottle nipples after each use.
 Do this by placing the nipples in boiling water for 10 minutes. Let the nipples cool before using them.
Do this by placing the nipples in boiling water for 10 minutes. Let the nipples cool before using them. - Limit breastfeeding and bottle feeding to 20 minutes. Sucking for a long time can increase irritation.
- If your baby uses a pacifier:
- Let them use it only when they cannot be calmed in any other way.
- Buy several extras that can be sterilized between uses. Sterilize pacifiers the same way as the bottle nipples.
- Do not put your child’s pacifier in your mouth or let other children do this.
- Do not share bottles, cups, or toys that your child has used with others.
- If you are breastfeeding:
- Clean each breast with water and air-dry after each feeding.
- If your breasts show any signs of infection, such as soreness or redness, call your health care provider. You may need to be treated at the same time.
- If using human breast milk from a pump, all pump parts need to be sterilized.

Treatment of a Yeast Rash
If your baby has a yeast diaper rash or yeast infection on the skin, the health care provider will prescribe a cream or recommend an over-the-counter one.
- Wash your hands well before and after treating your child’s yeast infection.
- To help the skin heal, keep it clean and dry.
For a Yeast Diaper Rash:
- Change the diaper as soon as your baby pees or poops. You may also want to change the diaper once during the night.
- Rinse your baby’s bottom after each diaper change. Gently clean the diaper area from front to back and inside the skin folds with warm water and a soft washcloth (Picture 2).
- Try to avoid baby wipes, but especially those with alcohol, propylene glycol, and fragrances.
- Use mild soap and water only if the poop (stool) does not come off easily.
- Avoid scrubbing or rubbing. It can damage the skin more.
- If the rash is severe, use a squirt bottle of water to clean and rinse without rubbing.
 Or you can soak your baby’s bottom in a tub of warm water after each diaper change.
Or you can soak your baby’s bottom in a tub of warm water after each diaper change. - Pat the skin dry and let it air dry fully.
- Apply a thin layer of antifungal cream. Most should be used only 2 to 3 times a day.
- You can also use an over-the-counter skin barrier or zinc oxide cream over the antifungal cream on the baby’s bottom and in the skin folds. Apply a thick layer each time the diaper is changed. Popular ones are petroleum jelly (Vaseline®) or a cream with zinc oxide like Desitin®, Triple Paste®, A+D®, or Balmex®. These creams do not have to be completely washed off with each diaper change.
- Do not use steroidal creams, corn starch, talc, or baby powder on your baby’s bottom.
- Let your baby play or nap with their diaper off. The air helps dry and heal the rash (Picture 3).
- Avoid rubber pants or plastic liners over the diaper.
- Put the diaper on loosely so it does not rub against the skin as much.

- Call your child’s health care provider if thrush gets worse after 3 days of treatment, if it lasts more than 10 days, or you have any questions.
Thrush and Yeast Infections (PDF), Somali (PDF), Spanish (PDF)
HH-I-117 6/90, Revised 3/22 Copyright 1990, Nationwide Children's Hospital
Thrush in newborns Information | Mount Sinai
Candidiasis - oral - newborn; Oral thrush - newborn; Fungal infection - mouth - newborn; Candida - oral - newborn
Thrush is a yeast infection of the tongue and mouth. This common infection can be passed between a mother and baby during breastfeeding.
Causes
Certain germs normally live in our bodies. While most germs are harmless, some can cause infection.
While most germs are harmless, some can cause infection.
Thrush occurs when too much of a yeast called Candida albicans grows in a baby's mouth. Germs called bacteria and fungi naturally grow in our bodies. Our immune system helps keep these germs in check. But babies do not have fully-formed immune systems. That makes it easier for too much yeast (a type of fungus) to grow.
Thrush often occurs when mother or baby has taken antibiotics. Antibiotics treat infections from bacteria. They can also kill "good" bacteria, and this allows yeast to grow.
The yeast thrives in warm, moist areas. The baby's mouth and the mother's nipples are perfect places for a yeast infection.
Babies can also get a yeast infection on the diaper area at the same time. The yeast gets in the baby's stool and can cause a diaper rash.
Symptoms
Symptoms of thrush in the baby include:
- White, velvety sores in the mouth and on the tongue
- Wiping the sores may cause bleeding
- Redness in the mouth
- Diaper rash
- Mood changes, such as being very fussy
- Refusing to nurse because of soreness
Some babies may not feel anything at all.
Symptoms of thrush in the mother include:
- Deep-pink, cracked, and sore nipples
- Tenderness and pain during and after nursing
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can often diagnose thrush by looking at your baby's mouth and tongue. The sores are easy to recognize.
Treatment
Your baby might not need any treatment. Thrush often goes away on its own in a few days.
Thrush often goes away on its own in a few days.
Your provider may prescribe antifungal medicine to treat thrush. You paint this medicine on your baby's mouth and tongue.
If you have a yeast infection on your nipples, your provider may recommend an over-the-counter or prescription antifungal cream. You put this on your nipples to treat the infection.
If both you and your baby have the infection, you both need to be treated at the same time. Otherwise, you can pass the infection back and forth.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Thrush in babies is very common and can easily be treated. Let your provider know if thrush keeps coming back. It may be a sign of another health issue.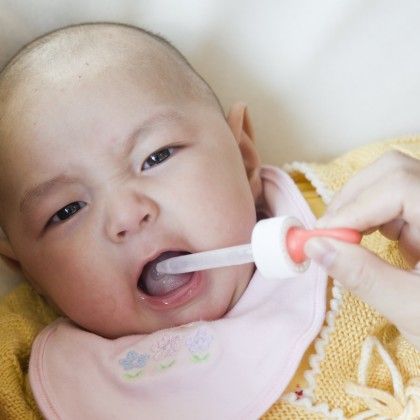
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- Your baby has symptoms of thrush
- Your baby refuses to eat
- You have symptoms of a yeast infection on your nipples
Prevention
You may not be able to prevent thrush, but these steps may help:
- If you bottle feed your baby, clean and sterilize all equipment, including nipples.

- Clean and sterilize pacifiers and other toys that go in baby's mouth.
- Change diapers often to help prevent yeast from causing diaper rash.
- Be sure to treat your nipples if you have a yeast infection.
Balest AL, Riley MM, O'Donnell B, Zarit JS. Neonatology. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 2.
Harrison GJ. Approach to infections in the fetus and newborn. In: Cherry JD, Harrison GJ, Kaplan SL, Steinbach WJ, Hotez PJ, eds. Feigin and Cherry's Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 66.
Last reviewed on: 12/12/2021
Reviewed by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
How thrush is transmitted - Healthy family
Thrush is a disease caused by the fungus Candida. From this came the medical name of this disease - candidiasis, most common in women. A fungal infection affects the mucous membranes of the vagina and causes the growth of pathogenic microflora.
Causes of thrush:
- Taking antibiotics that destroy the normal microflora;
- climate change;
- Change of sexual partner;
- Wearing tight synthetic underwear;
- Use of poor quality tampons and pads;
- Pregnancy;
- Severe stress;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Malnutrition, abuse of sweets;
- Use of hormonal contraceptives;
- Non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
Unfortunately, if a woman has thrush, she can infect her family members as well. When asked if thrush is transmitted to a child, the answer is unequivocal: it is transmitted. This happens frequently during childbirth. Older children, just like men, can become infected by household means: through a towel, bed linen, etc.
When asked if thrush is transmitted to a child, the answer is unequivocal: it is transmitted. This happens frequently during childbirth. Older children, just like men, can become infected by household means: through a towel, bed linen, etc.
How is thrush transmitted from woman to man?
Is thrush transmitted orally? Definitely yes. Candidiasis in men most often occurs through oral sex. If a woman is sick, then the fungus settles on the mucous membrane of the man's mouth, and later, through a kiss, through saliva, it can infect other people. At the same time, it is unambiguously difficult to answer the question of whether thrush is sexually transmitted. Men, as a rule, are not at risk of contracting candidiasis even after unprotected intercourse, since the stronger sex has better health and a stable hormonal background. However, in some cases, the disease can be transmitted. Therefore, it will not be superfluous at the time of illness to completely refrain from sexual intercourse or to protect yourself. A fungal infection will not penetrate through a condom.
A fungal infection will not penetrate through a condom.
What are the symptoms of thrush?
There are a lot of photos on the net where you can see how the fungus affects the mucous membrane of a woman's intimate organs. With this disease, an increased amount of vaginal discharge appears, which is a white curdled mass, has an unpleasant smell of rotten fish and causes itching and burning in the vulva. The asymptomatic form of thrush is also rare, when a woman does not experience any discomfort, and candidiasis is detected after taking smears at a gynecologist's appointment. What consequences in men and women can occur if you do not pay attention to the symptoms of the disease and leave it without treatment? The infection will multiply rapidly in the body and can cause other concomitant diseases, such as cystitis in women, urethritis and prostatitis in men, and in the most advanced cases, candidiasis can cause infertility. And although many treat thrush negligently and believe that if left untreated, no consequences can arise, this is an erroneous opinion.
Women often develop thrush during pregnancy due to hormonal fluctuations. While carrying a child, it is useless to fight it, but on the eve of childbirth, treatment for this disease is mandatory. After all, thrush during childbirth and its consequences for the child can be deplorable. During childbirth, a child will get sick with candidiasis, in which case a white coating appears on the mucous membrane in the baby's mouth, which gives the newborn discomfort. He cannot breastfeed and cries all the time.
As for the symptoms of thrush in men, most often it is redness of the foreskin of the penis, dryness and peeling of the skin, itching.
How to treat thrush?
Candidiasis is treated in two stages: the first stage is to get rid of the fungal infection. The doctor usually prescribes vaginal suppositories or tablets to the woman, which bring relief after only a few applications. Pimafucin, livarol, polygynax - the pharmaceutical industry provides a wide range of drugs to get rid of this disease. The course of treatment for women is from three to seven days. At the second stage of treatment of thrush, an important role is played by the colonization of the mucosa with beneficial lactobacilli. For this, there are preparations in the form of suppositories. It is undesirable to have sex with thrush, because during this period it is easy to damage the vaginal mucosa, which is deprived of natural protection.
The course of treatment for women is from three to seven days. At the second stage of treatment of thrush, an important role is played by the colonization of the mucosa with beneficial lactobacilli. For this, there are preparations in the form of suppositories. It is undesirable to have sex with thrush, because during this period it is easy to damage the vaginal mucosa, which is deprived of natural protection.
In men, treatment consists of an antifungal cream applied to the penis. Thrush in the mouth is treated with antifungal agents, vitamins, mouth rinses with disinfectant and alkaline solutions, resorption of lozenges with bactericidal properties, and the use of dental gels. If you answer the question of how to treat chronic thrush, then first of all it is important to observe the correct lifestyle and hygiene. You should wash yourself with water using special means for intimate hygiene, wear only cotton underwear, consume more fermented milk products, and limit sweets in the diet. And the last thing: how to treat thrush during breastfeeding, only a doctor can answer, because not only the health of the mother, but also the child depends on the choice of treatment.
And the last thing: how to treat thrush during breastfeeding, only a doctor can answer, because not only the health of the mother, but also the child depends on the choice of treatment.
ways of transmission and prevention of infection
Thrush is common in women and less common in men. It does not apply to sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). But since it is an infection, the possibility of transmission through intimate intercourse cannot be ruled out.
Differences between candidiasis in men and women
Candidiasis or thrush is an infectious and inflammatory disease of the skin and mucous membranes caused by Candida yeast. Numerous representatives of this genus are often found in nature. Some species, mainly Candida albicans, live in the human body and form part of the normal microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, oral cavity, vagina, skin [1] .
The fungus does not cause symptoms in healthy men and women. Candida peacefully coexist with beneficial microbes, the immune system does not allow them to multiply uncontrollably.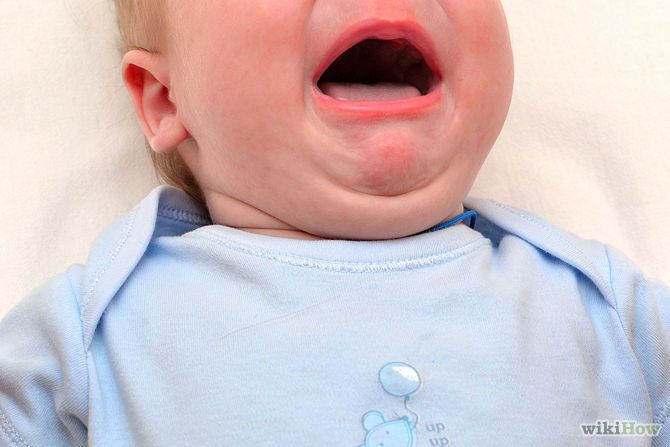 But as soon as the natural defense fails, the fungus becomes active and displaces the healthy microflora. In this case, candidiasis develops.
But as soon as the natural defense fails, the fungus becomes active and displaces the healthy microflora. In this case, candidiasis develops.
The inflammatory process can occur anywhere, for example, in the mouth, in skin folds. But the most common localization in women is the external genitalia. It is vulvovaginal candidiasis that is commonly referred to as thrush.
Thrush in men is less common than in women, because the fungus does not take root so well on the mucous membrane of the male genital organs.
The infection affects the head of the penis and the foreskin. The disease is called candidal balanoposthitis.
Can a woman get thrush from a man
Unlike trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections, thrush is not considered a sexually transmitted disease [2] . The causative agents of STDs are disease-causing microbes that enter the body only through sexual contact. But candida are conditional pathogens, that is, healthy people also have them in small quantities. Therefore, it is not entirely correct to talk about infection with thrush. The infection activates the opportunistic flora against the background of weak immunity or other predisposing factors.
Therefore, it is not entirely correct to talk about infection with thrush. The infection activates the opportunistic flora against the background of weak immunity or other predisposing factors.
“Nevertheless, infection from a man is possible, but very rare. Most often, the opposite happens: women infect their sexual partners. And in this case, I suggest prophylactically using Gepon for men, which, when applied topically, will protect against the development of candidiasis. Women should use Gepon in combination with any antifungal drugs.
Tsaturova Kristina Ashotovna, LLC Clinic for Assisted Reproductive Technologies "Children from Test Tube", chief physician, obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist, candidate of medical sciences
Causes of thrush in men
In about 15% of healthy men, Candida fungi are found on the skin and mucous membrane of the genitals. However, most patients are infected sexually from women with vaginal candidiasis [3] . The main part of patients are men from 18 to 30 years old, leading an active sexual life [4] .
The main part of patients are men from 18 to 30 years old, leading an active sexual life [4] .
Contact with the pathogen does not necessarily lead to disease. Thrush in men, as in women, occurs under the influence of predisposing factors. Intensive reproduction of the fungus and the development of balanoposthitis contribute to:
-
inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
-
metabolic and endocrine disorders - diabetes mellitus, obesity, hypothyroidism;
-
long-term use of antibiotics, hormonal drugs;
-
chronic somatic diseases;
-
anatomical features - elongated foreskin, narrowing of the foreskin;
-
external factors - irritation and injury to the skin, neglect of hygiene, abuse of alkaline detergents;
-
immunodeficiency states - primary, for example, with HIV infection; secondary - against the background of taking immunosuppressants, cytostatics, radiation and chemotherapy.

Symptoms of disease in men and women
Thrush in women is manifested by severe itching of the external genitalia and white or yellowish discharge with a characteristic smell of sour milk. Most often they are curdled, flaky, but can also be liquid, of a homogeneous consistency. The mucous membrane of the genital organs turns red, swells, a white coating appears on it. Cracks form on the skin in the intimate area. When urinating, a woman feels a burning sensation, sexual intercourse is painful.
In 10% of women, the disease becomes chronic, recurring more than 4 times a year [5] . Symptoms in this case are less pronounced than in the first acute candidiasis. Itching and discharge usually increase a few days before menstruation, then subside again.
In men, the disease manifests itself with similar symptoms: itching, redness and swelling of the glans penis, rashes, cracks in the skin, curdled discharge from the urethra. Patients complain of burning sensation during urination and pain during intercourse.
Patients complain of burning sensation during urination and pain during intercourse.
Can the disease be asymptomatic
Women and men can be asymptomatic carriers of Candida. In such cases, laboratory tests show the presence of a fungus on the genital mucosa, but patients do not feel any discomfort. This condition is not considered a disease and does not require treatment [6] .
Diagnostic methods
Laboratory tests are needed for an accurate diagnosis. When a woman suspects thrush, she should see a gynecologist. For a man - to a urologist or dermatovenereologist.
The doctor does:
-
Smear microscopy is the main method for diagnosing urogenital candidiasis. Biological material taken from the vagina in women or from the urethra in men is stained and examined under a microscope. Budding cells and other structural elements of the fungus indicate thrush. But this basic analysis does not give an idea of the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to drugs.

-
Cultural research - sowing of biological material on a nutrient medium. The method allows not only to verify the presence of a fungus, but also to accurately determine its type. This information is needed to select the appropriate antifungal drug. A culture study is mandatory for recurrent thrush, which may be caused by rare Candida species that are resistant to conventional treatment [7] .
-
Molecular biological analysis (PCR) is a method for determining fungal DNA fragments in a biomaterial. This highly sensitive examination helps to identify pathogens even when they are not visible under a microscope and do not grow on a nutrient medium. But PCR is a laborious method, so it is rarely used [8] .
To identify predisposing factors and concomitant diseases, additional diagnostics are carried out. It includes:
-
general blood and urine tests - including determining the level of glucose to exclude diabetes mellitus;
-
research on STIs;
-
HIV test;
-
consultation with an endocrinologist in case of recurrent thrush [9] .

Treatment of thrush in men
Candidiasis is treated with antifungal agents - antimycotics. More often, broad-spectrum drugs are prescribed: they are active against different types of fungus. If the results of the tests showed that the causative agent of thrush is not C. albicans, but a rarer representative of the genus Candida, its sensitivity to antimycotics is examined.
Antifungal drugs for the treatment of thrush in men exist in the form of creams for external use, tablets for oral administration. Therefore, there are two treatment regimens. Local remedies are used 2 times a day for 14 days. Systemic drugs are most often used once - one tablet is enough to destroy the fungus. The doctor [10] will select the appropriate antifungal agent and treatment regimen.
As well as a new tool - a lyophilisate for preparing a solution for local and external use. This is a Gepon drug for the chronic treatment of candidiasis of any strain. It increases the functional activity of cells responsible for protecting the body from viruses, bacteria and fungi. It has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antifungal effects, does not cause allergic reactions. The course of treatment requires three bottles. Solutions are used at intervals of 1 to 3 days. The effect is noticeable after two days: itching, pain, dryness, swelling and inflammation disappear.
It increases the functional activity of cells responsible for protecting the body from viruses, bacteria and fungi. It has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antifungal effects, does not cause allergic reactions. The course of treatment requires three bottles. Solutions are used at intervals of 1 to 3 days. The effect is noticeable after two days: itching, pain, dryness, swelling and inflammation disappear.
Simultaneously with the main treatment, attention should be paid to hygiene - daily baths with a solution of potassium permanganate should be taken. Erosions and cracks on the skin of the penis are treated with an antiseptic solution [11] .
For the period of treatment, it is better to refuse sexual intercourse. Both partners must undergo antifungal therapy, otherwise re-infection cannot be avoided.
What happens if candidiasis is not treated
Without treatment, thrush in women can cause adnexitis, cervicitis and other inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs. They lead to chronic pelvic pain syndrome, problems with conception, miscarriage [12] .
They lead to chronic pelvic pain syndrome, problems with conception, miscarriage [12] .
In men, untreated candidal balanoposthitis is most often complicated by phimosis - cicatricial narrowing of the foreskin [13] .
Prophylaxis
To reduce the likelihood of developing thrush, eliminate the predisposing factors:
-
avoid casual sex, use condoms;
-
observe the rules of intimate hygiene - daily shower or bath, clean underwear,
-
discard daily sanitary pads and synthetic underwear;
-
do not abuse soap and other alkaline detergents;
-
take antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor and always in combination with antifungal drugs;
-
treat diseases in time;
-
strengthen immunity, avoid stress, get enough sleep.
“No one has canceled the standard prevention schemes. In the first place is the observance of the well-known basic rules of hygiene. And an important point that today is in the arsenal of both doctors and patients is the drug Gepon, which is sold without a prescription, and it can be used independently to activate the local immunity of the genital organs.”
In the first place is the observance of the well-known basic rules of hygiene. And an important point that today is in the arsenal of both doctors and patients is the drug Gepon, which is sold without a prescription, and it can be used independently to activate the local immunity of the genital organs.”
Tsaturova Kristina Ashotovna, LLC Clinic for Assisted Reproductive Technologies "Children from Test Tube", chief physician, obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist, candidate of medical sciences
Main
-
Thrush (urogenital candidiasis) affects both men and women. But women are more common.
-
The causative agent of the disease is the conditionally pathogenic fungus Candida, which is activated only when the body's defenses are weakened.
-
Thrush is not an STD, but sexual transmission is possible.
-
If one of the partners has candidiasis, both should be treated.
-
[1] Sokolova TV, Malyarchuk AP Doctors' mistakes in the choice of tactics of examination and treatment of patients with superficial candidiasis of the skin and mucous membranes // Clinical Dermatology and Venereology.
 — 2020. — №19(3). — S. 343–354. — URL: https://www.mediasphera.ru/issues/klinicheskaya-dermatologiya-i-venerologiya/2020/3/1199728492020031343
— 2020. — №19(3). — S. 343–354. — URL: https://www.mediasphera.ru/issues/klinicheskaya-dermatologiya-i-venerologiya/2020/3/1199728492020031343 -
[2] Savicheva AM, Shipitsyna EV Recurrent urogenital candidiasis: features of diagnosis and treatment // Medical Council. - 2015. - No. 9. — P. 15. — URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/retsidiviruyuschiy-urogenitalnyy-kandidoz-osobennosti-diagnostiki-i-lecheniya/viewer
-
[3] Mazo E. B., Popov S. V. Monodose therapy for candidal balanoposthitis // BC. - 06/07/2006. - No. 12. - S. 906. - URL: https://www.rmj.ru/articles/urologiya/Monodoznaya_terapiya_kandidoznogo_balanopostita/
-
[4] Nogay KG Features of candidal balanoposthitis // Journal of Siberian Medical Sciences. - 2007. - No. 5. — URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/osobennosti-kandidoznogo-balanopostita
-
[5] Savicheva AM, Shipitsyna EV Recurrent urogenital candidiasis: features of diagnosis and treatment // Medical Council.
 - 2015. - No. 9. — P. 15. — URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/retsidiviruyuschiy-urogenitalnyy-kandidoz-osobennosti-diagnostiki-i-lecheniya/viewer
- 2015. - No. 9. — P. 15. — URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/retsidiviruyuschiy-urogenitalnyy-kandidoz-osobennosti-diagnostiki-i-lecheniya/viewer -
[6] Savicheva AM, Shipitsyna EV Recurrent urogenital candidiasis: features of diagnosis and treatment // Medical Council. — 2015. — №9. — P. 15. — URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/retsidiviruyuschiy-urogenitalnyy-kandidoz-osobennosti-diagnostiki-i-lecheniya/viewer
-
[7] Savicheva AM, Shipitsyna EV Recurrent urogenital candidiasis: features of diagnosis and treatment // Medical Council. - 2015. - No. 9. — P. 15. — URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/retsidiviruyuschiy-urogenitalnyy-kandidoz-osobennosti-diagnostiki-i-lecheniya/viewer
-
[8] Karapetyan T. E., Naskhletashvili I. V., Tyutyunnik V. L. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: a modern view on the problem. — URL: https://www.eurolab-portal.ru/encyclopedia/565/46982/
-
[9] Mazo E.
 B., Popov S. V. Monodose therapy for candidal balanoposthitis // BC. - 06/07/2006. - No. 12. - S. 906. - URL: https://www.rmj.ru/articles/urologiya/Monodoznaya_terapiya_kandidoznogo_balanopostita/
B., Popov S. V. Monodose therapy for candidal balanoposthitis // BC. - 06/07/2006. - No. 12. - S. 906. - URL: https://www.rmj.ru/articles/urologiya/Monodoznaya_terapiya_kandidoznogo_balanopostita/ -
[10] Mazo E. B., Popov S. V. Monodose therapy for candidal balanoposthitis // BC. - 06/07/2006. - No. 12. - S. 906. - URL: https://www.rmj.ru/articles/urologiya/Monodoznaya_terapiya_kandidoznogo_balanopostita/
-
[11] Mazo E. B., Popov S. V. Monodose therapy for candidal balanoposthitis // BC. - 06/07/2006. - No. 12. - S. 906. - URL: https://www.rmj.ru/articles/urologiya/Monodoznaya_terapiya_kandidoznogo_balanopostita/
-
[12] Savicheva AM, Shipitsyna EV Recurrent urogenital candidiasis: features of diagnosis and treatment // Medical Council. - 2015. - No. 9. — P. 15. — URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/retsidiviruyuschiy-urogenitalnyy-kandidoz-osobennosti-diagnostiki-i-lecheniya/viewer
-
[13] Moscow Department of Health.