Can anything be done to stop a miscarriage
Miscarriage - Prevention - NHS
In many cases, the cause of a miscarriage is not known and you would not have been able to prevent it.
However, there are ways to lower your risk of miscarriage, including:
- not smoking during pregnancy
- not drinking alcohol or using illegal drugs during pregnancy
- eating a healthy, balanced diet with at least 5 portions of fruit and vegetables a day
- making attempts to avoid certain infections during pregnancy, such as rubella
- avoiding certain foods during pregnancy, which could make you ill or harm your baby
- being a healthy weight before getting pregnant
Your weight
Obesity increases your risk of miscarriage. A person is obese when they have a body mass index (BMI) of over 30. You can check your BMI using the healthy weight calculator. If you're pregnant, your midwife or doctor may be able to tell you your BMI.
The best way to protect your health and your baby's wellbeing is to lose weight before you become pregnant. By reaching a healthy weight, you cut your risk of all the problems associated with obesity in pregnancy. Contact your GP for advice about how to lose weight. They may be able to refer you to a specialist weight loss clinic.
As yet, there's no evidence to suggest losing weight during pregnancy lowers your risk of miscarriage, but eating healthily, and activities such as walking and swimming, are good to do during pregnancy.
If you were not active before becoming pregnant, you should consult your midwife or doctor before starting a new exercise regimen while you're pregnant.
Read more about obesity and pregnancy and exercise in pregnancy.
Treating an identified cause
Sometimes the cause of a miscarriage can be identified. In these cases, it may be possible to have treatment to prevent this causing any more miscarriages.
Antiphospholipid syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), also known as Hughes syndrome, is a condition that causes blood clots. It can be treated with medication.
Research has shown that a combination of aspirin and heparin (a medicine used to prevent blood clots) can improve pregnancy outcomes in women with the condition.
Read more about treating antiphospholipid syndrome.
Weakened cervix
A weakened cervix, also known as cervical incompetence, can be treated with an operation to put a small stitch of strong thread around your cervix to keep it closed.
This is usually carried out after the first 12 weeks of your pregnancy.
Page last reviewed: 09 March 2022
Next review due: 09 March 2025
How to Prevent Miscarriage: Is It Possible?
A miscarriage cannot be prevented in most cases. A miscarriage is a pregnancy that ends unexpectedly in the early weeks or months. This is also called a spontaneous abortion.
The factors that lead to most miscarriages are unavoidable. These issues include chromosomal abnormalities and fetus development problems.
Miscarriages are not uncommon. About 10 percent of early pregnancies end in a miscarriage before the twentieth week. The real number of miscarriages may actually be higher, too, as many people miscarry before knowing they’re pregnant.
While you cannot prevent a miscarriage, you can take steps to have a healthier pregnancy. This may lower the risk of a miscarriage by reducing the risk of possible causes of the premature end of the pregnancy.
Pinpointing an exact cause for a miscarriage is difficult. In most cases, the cause is something you couldn’t have prevented, meaning you couldn’t have prevented the miscarriage, either.
Rarely, doctors are able to find an issue that increases the risk for a miscarriage. In that case, treating the issue may help prevent a future miscarriage.
First trimester
Around 80 percent of miscarriages occur in the first trimester. The first trimester refers to the time between weeks 1 and 13.
Common causes of miscarriage in the first trimester include:
- Genetic abnormalities. More than half of all first trimester miscarriages are the result of problems with the fetus’s chromosomes. If your body detects the fetus has damage or missing chromosomes, it will end the pregnancy.
- Blood clots. A condition called antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) causes blood clots that can end a pregnancy. This condition can be treated with medications to prevent a miscarriage.

- Ectopic pregnancy. This potentially serious but rare type of pregnancy occurs when the fetus begins developing outside the womb. Ectopic pregnancies cannot be saved and are a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment.
- Placental problems. If the fetus and placenta are not compatible, the pregnancy may be lost. Likewise, uterine defects, including an abnormal shape, may also cause the sudden end of a pregnancy.
Second trimester
A miscarriage in this later stage of pregnancy, weeks 13 to 24, is much less common. If it does occur, the cause is likely related to external health conditions, or problems with the mother’s health.
These second trimester issues that may lead to pregnancy loss include:
- Infection. Infections within the uterus or cervix can lead to a miscarriage. Likewise, food-borne illnesses may put a woman at risk for a miscarriage.
- Chronic conditions. Chronic conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure increase a woman’s risk of having a miscarriage.
 The risk is higher if the condition isn’t properly treated or managed.
The risk is higher if the condition isn’t properly treated or managed. - Thyroid disease. Untreated thyroid conditions increase risk of miscarriage.
- Autoimmune conditions. Lupus, as well as other autoimmune conditions, can lead to a miscarriage.
- Problems with the uterus or cervix. Fibroids or an abnormally shaped womb may cause a miscarriage.
- Lifestyle factors. Smoking, second-hand smoke, consuming alcohol, and drug use can interfere with a fetus’s development. High caffeine consumption may also be problematic.
- Environmental factors. Exposure to certain chemicals or hazards can cause a miscarriage. These include mercury, solvents, paint thinners, pesticides, and heavy metals. Air pollutants have also been linked to an increased risk of miscarriage.
Third trimester
At this late stage of a pregnancy, a miscarriage is more commonly called stillbirth. The same issues that can cause a miscarriage in the first two trimesters of a pregnancy can also be responsible for a pregnancy loss in the third trimester. But, understanding the exact cause is often difficult.
The same issues that can cause a miscarriage in the first two trimesters of a pregnancy can also be responsible for a pregnancy loss in the third trimester. But, understanding the exact cause is often difficult.
These issues may include:
- Pregnancy complications. This includes preterm labor or the separation of the placenta from the womb.
- Birth defects. One in 10 stillbirths are the result of a genetic or structural birth defect.
- High blood pressure. Preeclampsia occurs in 5 to 8 percent of all pregnancies. While the greatest risks of this condition are to the mother, preeclampsia can cut off the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus. Preeclampsia can also progress to eclampsia, a very serious condition that can be fatal to the fetus and woman.
- Uncontrolled diabetes.
- Infection. An infection in the placenta or in the fetus can cause the end of the pregnancy.

- Problems with the umbilical cord. If this cord is knotted or squeezed, it can cut off the flow of blood and oxygen to the fetus.
- Problems with the placenta. Insufficient blood flow to the placenta can end in a miscarriage.
Miscarriage cannot be prevented in most cases. However, you can improve your chances of a healthy pregnancy and possibly reduce your risk for miscarriage with these tips.
Take folic acid
Research suggests that taking 400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid daily might reduce the risk of birth defects that can lead to miscarriage.
Start taking this B vitamin every day before you intend to get pregnant. Continue taking it during pregnancy for the greatest benefits.
Follow a healthy lifestyle
Avoid unhealthy risk factors, such as:
- smoking
- second-hand smoke
- alcohol consumption
- drug use
You should also limit your caffeine intake to 300 milligrams (mg) or less per day.
In addition to avoiding risks, you may also be able to improve your pregnancy health by:
- getting regular exercise
- getting adequate sleep
- eating a healthy, well-balanced diet during all three trimesters
Maintain a healthy weight
Being overweight, obese, or underweight may increase your risk for complications during pregnancies. This includes miscarriage.
Take precautions against infections
Wash your hands frequently. This can help you avoid illnesses like the flu and pneumonia, which are easily spread.
Make sure your immunizations are all up to date, too. Talk with your doctor about any other immunizations you might need during pregnancy, including the flu shot.
Manage chronic conditions
If you have a health issue, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or an autoimmune disease, work with your doctor to properly treat or manage it. This can help prevent miscarriages when you become pregnant.
Practice safe sex
Some sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can lead to complications during pregnancy. Get tested before you try to get pregnant. If you’re already pregnant, get tested as soon as possible.
Get tested before you try to get pregnant. If you’re already pregnant, get tested as soon as possible.
During pregnancy, use barrier methods properly in every sexual encounter, including oral or anal sex, to reduce your risk for STD.
The most common signs of a miscarriage include:
- spotting that lasts longer than three days
- bleeding that may include clots or tissue
- mild to severe pain and cramping in your back and abdomen
- weight loss
- fluid or mucus discharge from the vagina
- a decrease in signs of pregnancy, such as breast tenderness, nausea, and vomiting
If you think you’re experiencing signs of a miscarriage, seek emergency treatment. Your doctor can perform a physical exam to determine the cause of the symptoms.
In most cases, you cannot stop a miscarriage once it has started, no matter the trimester you are currently in. The symptoms of a miscarriage typically indicate the pregnancy is already over.
In some cases, the symptoms may be a sign of a condition called threatened miscarriage. This can occurs in people who are less than 20 weeks pregnant. You may experience heavy bleeding and assume your pregnancy is ending.
This can occurs in people who are less than 20 weeks pregnant. You may experience heavy bleeding and assume your pregnancy is ending.
However, if a fetal heartbeat is still present, the pregnancy can continue, despite what appears to be signs of an impending miscarriage. It’s important, however, that you work with your doctor to help prevent a full miscarriage.
Treatment for a threatened miscarriage includes:
- bed rest
- avoiding sexual intercourse
- treatment for any underlying conditions that may be causing the bleeding
- an injection of the hormone progesterone
- an injection of Rh immunoglobulin if your baby has Rh-positive blood and you have Rh-negative blood
There is no shortage of misunderstandings and myths about the unexpected end of a pregnancy. Here, learn more about several common miscarriage misconceptions and the truth behind them.
Myth: Miscarriage is rareTruth: Miscarriages are not rare. About 10 percent of known pregnancies end in miscarriage, though the number of total miscarriages is likely higher. That’s because many people have a miscarriage very early in the pregnancy before they realize they are expecting and mistake the miscarriage for their menstrual period.
About 10 percent of known pregnancies end in miscarriage, though the number of total miscarriages is likely higher. That’s because many people have a miscarriage very early in the pregnancy before they realize they are expecting and mistake the miscarriage for their menstrual period.
Truth: Exercise will not cause a miscarriage. In fact, regular exercise during a pregnancy is important. However, you may need to take precautions to avoid injuring yourself.
Talk with your doctor about the healthiest way to continue getting movement while you’re expecting.
Myth: Bleeding always means you’re having a miscarriageTruth: Spotting is common in the early weeks of a pregnancy. If you experience bleeding, talk with your doctor about what is normal and what is a possible sign of miscarriage.
Myth: A miscarriage is the mother’s faultTruth: The majority of miscarriages occur early in a pregnancy and are the result of a chromosomal abnormality. This is the fault of neither parent.
This is the fault of neither parent.
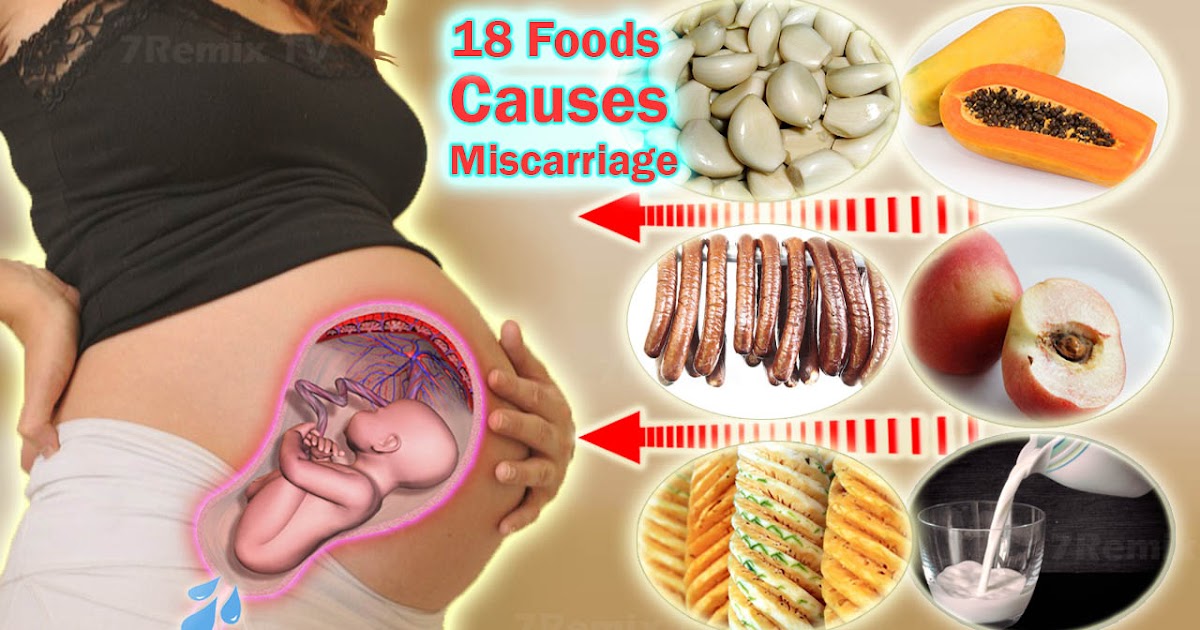
Truth: If you’re expecting, there are certain foods you should avoid because they may contain harmful bacteria that can increase risk for miscarriage, such as Listeria and Salmonella. Food to avoid include:
- shellfish
- raw fish (such as sushi)
- undercooked or raw meat
- processed meats (such as hot dogs and lunch meat)
- unpasteurized milk and cheese
- raw eggs
In almost every case, a miscarriage cannot be prevented. It’s most likely the result of a chromosomal abnormality that prevents the fetus from developing properly.
Repeated miscarriages are not common. Only about one percent of people will have a second miscarriage after having a first. If a specific cause for a miscarriage is identified, your doctor can help you treat the condition to prevent a future pregnancy loss.
Taking care of yourself and trying to maintain a healthy pregnancy through diet, exercise, and regular prenatal checkups can help reduce your risk of a miscarriage.
Miscarriage, how to avoid - Planning and management of pregnancy in the gynecology of the Literary Fund polyclinic after a miscarriage
- Gallery
- News
- Blog
- Reviews
- Jobs
- Licenses
- Insurance partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule of reception of citizens on personal appeals
- What you need to know about coronavirus infection?
- Rules for patients
- Online doctor's consultation
- to corporative clients
- The documents
A miscarriage is always associated with severe consequences for the whole body of a woman and for her reproductive organs in particular, it also affects the family situation, disrupts the woman's work schedule. An unfavorable outcome of pregnancy requires great mental and physical costs on the part of parents. Therefore, contacting doctors to find out the causes of the problem is the very first and correct step towards the birth of a child.
Any competent gynecologist will tell you that the problem of miscarriage can be solved. With proper preparation for pregnancy and its management, the next time you will have a successful pregnancy. Most girls after a miscarriage go to extremes: they try to get pregnant again as soon as possible. And if this succeeds, then the miscarriage is very often repeated. And you need to give the body a rest for 2-3 months, then identify and eliminate the cause. And only then try.
Causes of miscarriage
Many are convinced that miscarriages are due to a fall, bruise, or some other physical shock. Any woman who has had a miscarriage can remember that not long before she either fell or lifted something heavy. And I am sure that she lost her unborn child precisely because of this. However, those women whose pregnancy was normal also fall and lift heavy things. Most sudden miscarriages do not occur for this reason. The reason is in violations of the pregnancy itself. Approximately half of miscarriages are due to abnormal genetic development of the fetus, which can be hereditary or accidental. Merciful nature, following the principles of natural selection in everything, destroys the defective and unviable fetus. But you should not be afraid of this. The fact that there is a defect in one embryo does not mean at all that all the others will be the same.
Merciful nature, following the principles of natural selection in everything, destroys the defective and unviable fetus. But you should not be afraid of this. The fact that there is a defect in one embryo does not mean at all that all the others will be the same.
The woman's body is almost always to blame for the other half of miscarriages. They are caused by various known and unknown factors, such as: acute infectious diseases suffered in the first trimester of pregnancy, poor environment or difficult working conditions, excessive psychological or physical stress, abnormal development of the uterus, radiation, alcohol, smoking and certain types of drugs.
The causes of early and late miscarriage may differ, although they may overlap. The most important thing is to find out and eliminate or compensate for your own cause of miscarriage. Having discovered the cause, the gynecologist will tell you how to avoid another loss.
Miscarriage
Miscarriage statistics also include “missed pregnancy”. Sometimes it happens that the embryo dies and lingers in the uterine cavity. Most often, this fact is detected by ultrasound. The dead fetus may begin to decompose, and this, thereby, will lead to poisoning of the mother's body.
Sometimes it happens that the embryo dies and lingers in the uterine cavity. Most often, this fact is detected by ultrasound. The dead fetus may begin to decompose, and this, thereby, will lead to poisoning of the mother's body.
Doctors resort to surgical curettage, which is associated with a risk of inflammation and complications. With such a miscarriage, the next pregnancy is planned after the body is fully restored - not earlier than a year. During this year, you will have to find out the cause of the missed pregnancy and treat it.
Miscarriage up to 6 weeks
The main causes of miscarriage on this line are malformations of the embryo itself. Statistics say that from 70-90% of embryos had chromosomal abnormalities: they are random and will not occur in other pregnancies. You may have been ill, taken medication, or were under the influence of other harmful factors. Fate saved you from a child with malformations.
The human body is perfect and finds a way to correct the situation by miscarriage. Today is a tragedy for you. The real tragedy would be the preservation and birth of a sick, non-viable child. So don’t cry and understand: everything is for the best, you won’t help grief with tears ... And after three months, try again - it will almost certainly turn out to be successful.
Today is a tragedy for you. The real tragedy would be the preservation and birth of a sick, non-viable child. So don’t cry and understand: everything is for the best, you won’t help grief with tears ... And after three months, try again - it will almost certainly turn out to be successful.
It should also be noted that the fact of a miscarriage does not mean that you have lost something. So for a period of 7-8 weeks, the absence of an embryo in the fetal egg is found - "anembryony". It is believed that in 80-90% of cases, miscarriages are undiagnosed non-developing pregnancies.
Miscarriage between 6 and 12 weeks
Miscarriage in this period is also considered early. Its most common causes are:
Endocrine disorders
Endocrine disorders, when the ovaries do not synthesize enough hormones to keep the fetus in the womb, or the amount of male sex hormones is increased, is one of the most common causes of miscarriage and miscarriage.
Imbalance of hormones in a woman's body is very likely to lead to an early termination of pregnancy. With a lack of the main hormone progesterone produced by the ovaries, this happens most often. Another hormonal problem is an increase in the tone of the uterus, which provokes the expulsion of the fetus.
With a lack of the main hormone progesterone produced by the ovaries, this happens most often. Another hormonal problem is an increase in the tone of the uterus, which provokes the expulsion of the fetus.
Progesterone prepares the uterine mucosa for implantation and is the hormone for maintaining pregnancy in the first months. If conception occurs, the fetus cannot properly establish itself in the uterus. As a result, the fertilized egg is rejected. But pregnancy can be saved with the help of progesterone preparations if this problem is detected in time.
An excess of male sex hormones that suppress the production of estrogen and progesterone can also be the cause of an early miscarriage. Often, the cause of recurrent miscarriages are androgens that affect the formation and development of pregnancy; as well as thyroid and adrenal hormones. Therefore, a change in the function of these glands can lead to miscarriage.
Undertreated sexual infections
This problem must be solved before conception. Often the cause of miscarriage is sexually transmitted infections: syphilis, trichomoniasis, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, cytomegalovirus and herpetic infections. Their effect on the fetus and the course of pregnancy is different for each woman and depends on the timing of infection, the activity of the microorganism, the degree of immune protection and the presence of other adverse factors. Depending on the situation, they can lead to the formation of fetal malformations, intrauterine infection, feto-placental insufficiency, early miscarriage or premature birth. Infection of the fetus and damage to the membrane of the fetus leads to miscarriage. To avoid this, infections should be treated before pregnancy. The use of therapy is possible during pregnancy as prescribed by a doctor.
Often the cause of miscarriage is sexually transmitted infections: syphilis, trichomoniasis, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, cytomegalovirus and herpetic infections. Their effect on the fetus and the course of pregnancy is different for each woman and depends on the timing of infection, the activity of the microorganism, the degree of immune protection and the presence of other adverse factors. Depending on the situation, they can lead to the formation of fetal malformations, intrauterine infection, feto-placental insufficiency, early miscarriage or premature birth. Infection of the fetus and damage to the membrane of the fetus leads to miscarriage. To avoid this, infections should be treated before pregnancy. The use of therapy is possible during pregnancy as prescribed by a doctor.
Viral infections and other diseases
Any disease accompanied by intoxication and fever above 38 about C can lead to a miscarriage. Rubella, influenza and viral hepatitis occupy a leading position in this list. At a period of 4-10 weeks for pregnancy, ordinary tonsillitis can also become tragic, pneumonia carries a more serious risk. Pyelonephritis and appendicitis can cause early labor. When planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to undergo a medical examination in order to identify and treat foci of infections.
At a period of 4-10 weeks for pregnancy, ordinary tonsillitis can also become tragic, pneumonia carries a more serious risk. Pyelonephritis and appendicitis can cause early labor. When planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to undergo a medical examination in order to identify and treat foci of infections.
Extremely dangerous during pregnancy rubella - it leads to severe fetal malformations, so infection during pregnancy is an indication for medical abortion.
Any disease during pregnancy can lead to non-viability of the fetus. And the body, through a miscarriage, insures you against unwanted offspring. With such a miscarriage, the next pregnancy has every chance of going well.
Immune causes of miscarriage
Sometimes antibodies that are hostile to the fetus are formed in the blood of a pregnant woman. This cause can be predicted and eliminated in advance. Most often, the conflict occurs when the embryo inherits the positive Rh factor of the father, and the negative Rh factor, the mother's body rejects the embryonic tissues that are alien to it. Constant monitoring of antibody titer and the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins allows you to maintain and maintain pregnancy. In case of an immune conflict, progesterone preparations are also used to prevent miscarriage, which in this case has an immunomodulatory effect.
Constant monitoring of antibody titer and the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins allows you to maintain and maintain pregnancy. In case of an immune conflict, progesterone preparations are also used to prevent miscarriage, which in this case has an immunomodulatory effect.
Reduced immunity
Reduced immunity during pregnancy also refers to immune causes. The body is simply not able to grow a new life in itself. You need to take care of yourself and recover before the next conception.
Anatomical causes of miscarriage
Anatomical causes of miscarriage are the most intractable. Malformations of the uterus are a serious reason for miscarriage. Sometimes you just have to deal with it.
Miscarriage between 12 and 22 weeks
Such a miscarriage is considered late. Its causes coincide with the causes of miscarriages in the early stages (anatomical, immune, infectious, endocrine).
At this time, miscarriage also occurs due to isthmic-cervical insufficiency - a weak cervix cannot hold the fetus and opens. For this reason, a miscarriage can occur in the 2nd or 3rd trimester. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is observed in 15.0-42.7% of women suffering from miscarriage. Careful monitoring of the pregnant woman allows you to identify the problem in time and make surgical correction of the cervix before the onset of childbirth.
For this reason, a miscarriage can occur in the 2nd or 3rd trimester. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is observed in 15.0-42.7% of women suffering from miscarriage. Careful monitoring of the pregnant woman allows you to identify the problem in time and make surgical correction of the cervix before the onset of childbirth.
In isthmic-cervical insufficiency, there is only one method of treatment - mechanical narrowing of the cervical canal. To do this, the neck is either sewn up or a special ring is put on it. However, the latter method is less efficient, because the ring can easily slide off the neck, then it will no longer hold back the process of opening it.
After suturing, if necessary, it is possible to use antibiotics and drugs that normalize the microflora of the vagina. The treatment of the vagina and the control of the state of the seams are carried out daily for 5 days. Stitches are removed at 37-38 weeks and with premature onset of labor.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency may be primary (for no apparent reason), may be the result of abortion or hormonal disorders (increased levels of androgens - male sex hormones or their precursors).
Miscarriage after 22 weeks
Such a loss is hard to forget. Obstetricians talk about premature birth after the 28th week of pregnancy. Traditionally, a child born after this period is considered viable. But medicine knows many cases when it was possible to save the life of earlier children.
We recommend that you be carefully examined for miscarriage, check the above factors. In addition to them, the cause of a miscarriage can be antiphospholipid syndrome, while the woman's body perceives the child as something alien and rejects it. This disease, like the others listed, can be corrected; you have a very real chance of bearing a child.
Miscarriages due to hemostasis disorders
All of the above causes account for only 30-40%. Up to 70% of miscarriages are caused by disorders in the blood coagulation system (hemostasis).
Blood coagulation disorders leading to pregnancy loss can be divided into thrombophilic (increased clotting) and hemorrhagic (bleeding tendencies). Both of these extremes are dangerous to the fetus. Various disorders leading to the formation of small blood clots lead to the fact that the fetus loses sufficient blood supply, development is disturbed and the fetus is rejected.
Both of these extremes are dangerous to the fetus. Various disorders leading to the formation of small blood clots lead to the fact that the fetus loses sufficient blood supply, development is disturbed and the fetus is rejected.
The main hemorrhagic changes can appear even in childhood in the form of increased bleeding during cuts, tooth extractions, the onset of menstruation. But sometimes they declare themselves only during pregnancy and are the cause of a miscarriage. Bleeding in the early stages and detachment of the chorion is difficult to stop.
You may not guess, but incomprehensible headaches, weakness, fatigue, temporary loss of smell or hearing may be symptoms of disorders in the blood coagulation system.
When planning a pregnancy, a genetic examination should be carried out and, if necessary, treatment should be initiated.
It is advisable to be examined for hidden hemostasis defects even for those who consider themselves healthy. This will allow you to predict the occurrence of complications and prevent loss. Early therapy can prevent miscarriage at 98% of cases. If defects in hemostasis are already detected during pregnancy, it can be difficult to maintain it.
Early therapy can prevent miscarriage at 98% of cases. If defects in hemostasis are already detected during pregnancy, it can be difficult to maintain it.
What to do after a miscarriage?
Find the cause! The ideal option is to be examined by future parents: it is much more reasonable to postpone conception and spend two or three months to identify the causes than to risk getting pregnant again, spend two months waiting, and then lose everything again and still go to the doctors.
Until you understand the reason, it will not evaporate. In most cases, the answers lie on the surface. Take care of your health and your future baby.
Sign up for a consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist by phone +7 (495) 150-60-01
Tyan Oksana Alexandrovna
Head of the department, obstetrician-gynecologist Doctor of the highest category Work experience: 26 years
Volkova Polina Dmitrievna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of ultrasound diagnostics Doctor of the highest category Experience: 35 years
Postnikova Nadezhda Anatolyevna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound specialist Work experience: 35 years
Moiseeva Alla Vitalievna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of ultrasound diagnostics Doctor of the first category Work experience: 37 years
Zabolotnova Olga Valentinovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist Doctor of the first category Experience: 25 years
Shchelokova Elena Nikolaevna
Obstetrician-gynecologist Doctor of the highest category Work experience: 38 years
Pass or medical card number:
Contact phone: *
Select the day of your appointment:
Additional information:
I am not a robot
By clicking the "Submit Application" button, you agree to the terms Privacy Policy and User Agreement
Early Miscarriage Help
- home /
- Blog /
- How to avoid early miscarriage
A miscarriage occurs when the fetus is shed from the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus. According to experts, two out of 10 clinically established pregnancies end in spontaneous abortion. It is necessary to understand in more detail the causes, symptoms and methods of dealing with miscarriage.
How an early miscarriage occurs
There are three steps in this process. First, the fetus dies, after which it detaches from the endometrial layer. This is manifested by the fact that bleeding begins.
At the third stage, everything that has exfoliated is removed from the uterine cavity. The process may be complete or incomplete. In the early stages - five to six weeks - the process resembles ordinary menstruation. They are characterized by painful and much more unpleasant sensations. You can find out that it was just an early miscarriage by taking tests for the ratio of hCG in the blood.
You can find out that it was just an early miscarriage by taking tests for the ratio of hCG in the blood.
Symptoms of a miscarriage
Signs of miscarriage are abdominal cramps, cramps or bloody discharge. However, they do not always appear. It is necessary to note the most typical manifestations of the presented state and their main characteristics.
Temperature
For a short period of time, hyperthermia may well not be observed. Fever is not the most common symptom. In some cases, the thermometer readings really rise to 38 degrees or more.
At the same time, when hyperthermia is accompanied by a number of additional symptoms, septic miscarriage is likely. These are its symptoms:
- severe pain in the abdomen and deep in the vagina;
- increase in the tone of the uterus, which is felt by jerks inside;
- pungent, pungent and unpleasant odour.
All this indicates that the infection has joined. In such a case, emergency hospitalization is strongly recommended to stop the development of the process. It is better not to engage in self-medication or the use of folk recipes.
In such a case, emergency hospitalization is strongly recommended to stop the development of the process. It is better not to engage in self-medication or the use of folk recipes.
Discharge
Early miscarriage can indeed be accompanied by discharge. They may be habitual, as during menstruation. Also, the discharge may be smearing, insignificant.
Secretion brown, scanty, much less likely to end in spontaneous abortion. Most often, this is indicated by abundant and bright red discharge. It is blood that normally appears when the fetus is rejected from the inner layer of the uterus.
Pain
The severity of unpleasant and specific sensations may differ from each other depending on the duration of pregnancy. Probably the accession of pain, similar to menstruation. Most often, a similar symptom indicates an early miscarriage - no more than six weeks.
Probably cramping pains in the abdomen, pulling in the back. Their strength can vary from subtle to much more pronounced. In the rarest cases, when the clinical picture is complicated by a long course, this leads to a state of shock.
In the rarest cases, when the clinical picture is complicated by a long course, this leads to a state of shock.
Another typical manifestation of pain is discomfort in the back or abdomen. Only then are the discharges identified. A similar situation is most typical for spontaneous abortion at the seventh or eighth week of pregnancy.
Causes of miscarriage
The first factor is genetic abnormalities in the development of the fetus. It is they who most often lead to miscarriage in the early stages. Violations can be expressed in qualitative or quantitative failures in chromosomes. In this regard, the female body recognizes the defect, and therefore does not allow such a fetus to develop further. Most often, such rejection is noted in the third week of pregnancy.
The next reason that an early miscarriage has developed may be disturbances in the work of the endocrine gland. Hormones determine not only the success and regularity of the cycle, but also how well the fetus is attached to the mucous surface of the uterus. If, due to a malfunction of the thyroid gland, the endometrium is not able to provide the fetus with all the necessary components, the pregnancy will not go well. Most often, a miscarriage occurs at the beginning or at the end of the fourth week.
If, due to a malfunction of the thyroid gland, the endometrium is not able to provide the fetus with all the necessary components, the pregnancy will not go well. Most often, a miscarriage occurs at the beginning or at the end of the fourth week.
Other reasons why pregnancy is terminated:
- Rhesus conflict. If the parents have different Rh factors, then the risk that a miscarriage will occur after the first weeks of pregnancy increases significantly. This happens if a woman has a negative Rh, and the child has a positive, inherited from the father. In such a situation, the female body recognizes the fetus as a foreign object. Therefore, it is excreted from the uterus. Timely diagnosis allows you to save the child through full-fledged drug therapy.
- Sexually transmitted diseases, other infections. Similar problematic conditions also lead to spontaneous abortion. In this case, the embryo is infected at a very early stage. That is why the body will perceive it as a foreign object.
 In this regard, a miscarriage will occur already in the fifth week.
In this regard, a miscarriage will occur already in the fifth week. - Previous abortions. Another common reason why a miscarriage occurred. Abortion is a huge stress for the reproductive system, which leads to thinning of the lining of the uterus. That is why the risk of miscarriage may be greater.
Abdominal injuries should not be excluded from the list. Sharp pressure on the peritoneum, including when lifting weights, can provoke an abortion. Also on the list are severe stress, anxiety and depression. Anything that violates the normal state of a woman can lead to serious consequences.
How to avoid miscarriage
The main goal of treatment is to relieve tension in the uterus. It will be equally important to stop the bleeding and prolong the pregnancy, but only on the condition that the fetus is viable. The sooner medical assistance is provided, the higher the likelihood of preserving the fetus, without the need to determine the expected timing of miscarriages.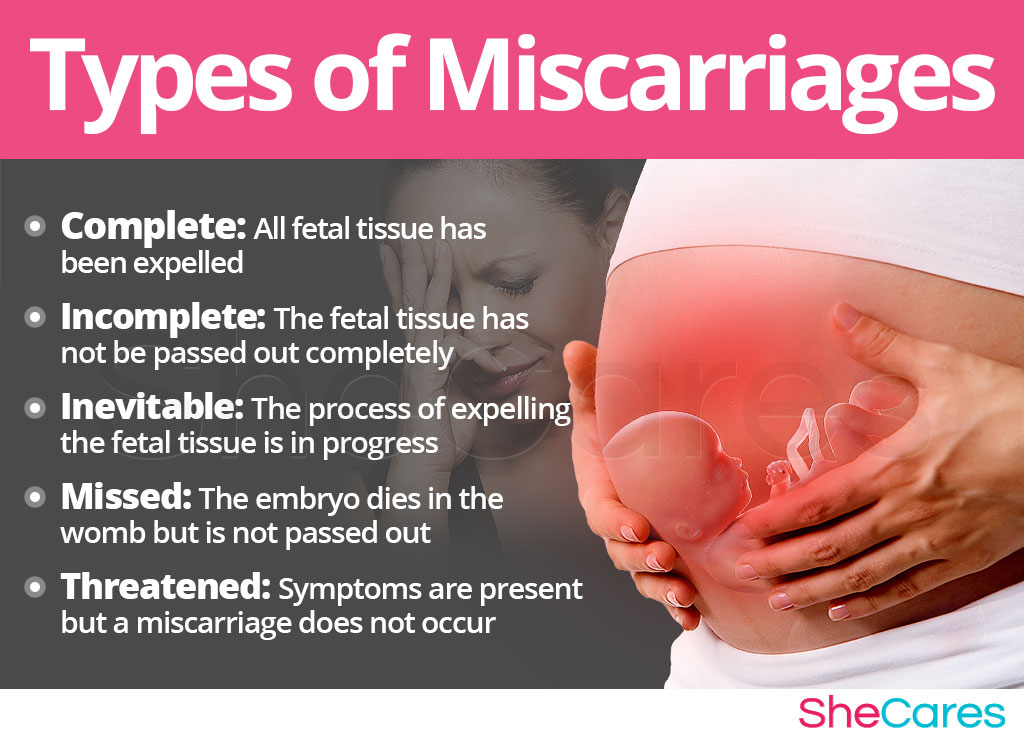
Our specialists will help you with this. Only we have the most qualified and experienced doctors who know exactly how to treat even the most difficult cases. They will conduct a full diagnosis and prescribe the most effective, effective medicines.
Drug treatment
Hormonal drugs are used. They at an early stage determine the normal course of pregnancy. Medicines based on the hormone progesterone are effective.
- The use of hemostatic drugs. In the case of pregnant women, droppers are used with drugs such as Dicinon or Tranexam. They are needed to stop bleeding.
- Antispasmodics. Experts recommend injections of Drotaverin, followed by a switch to painkillers such as No-shpa. Papaverine suppositories, droppers with the addition of magnesia are also used. All of them are necessary in order to remove a number of signs of a pathological condition, namely, an increased tone of the uterus and pronounced pain.
- Use of Tocopherol. Vitamin E is an indispensable component for women, including pregnant women.
 It ensures the normal and full functioning of the ovaries. Tocopherol also strengthens the vascular walls, eliminates the formation of blood clots.
It ensures the normal and full functioning of the ovaries. Tocopherol also strengthens the vascular walls, eliminates the formation of blood clots. - Sedative preparations. Use motherwort or valerian tincture. The presented measure is recommended for increased irritability or nervousness of a pregnant woman.
To prevent early miscarriage, the specialists of our clinic recommend glucocorticosteroids. Apply Dexamethasone or Metipred. They are prescribed to patients with diagnosed immune disorders that can lead to early termination of pregnancy.
A special relief ring can be fitted as an option. The presented procedure is carried out in the second trimester, or rather after the 20th week of gestation.
Remove this device not earlier than 38 weeks. It is necessary for a woman to maintain the correct position of the uterus. Also, the unloading ring helps to prevent premature birth.
Additional measures
To prevent early miscarriage, it is recommended to stop physical activity. Especially when it comes to jumping, lifting weights. Rest, lack of sudden physical activity and adherence to bed rest will help to keep the pregnancy.
Especially when it comes to jumping, lifting weights. Rest, lack of sudden physical activity and adherence to bed rest will help to keep the pregnancy.
Another preventive measure will be the exclusion of sudden movements. At any stage of pregnancy, they can provoke detachment of the embryo or lead to serious complications in its development.
To exclude an early miscarriage will allow:
- emotional peace and absence of stress;
- refusal to take a hot bath or visit a bath, sauna - this is due to the fact that high temperatures provoke increased bleeding, as well as detachment of the fetus;
- restriction of sexual intercourse - if there is a threat that an early miscarriage will occur, they refuse to have sex;
- exclusion of alcohol, nicotine addiction.
It is also important to stop eating certain foods. The ban applies to chocolate, coffee, and any other caffeinated drinks. In no case should you self-medicate.