Bright red spotting 32 weeks pregnant
Vaginal bleeding in late pregnancy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
One out of 10 women will have vaginal bleeding during their 3rd trimester. At times, it may be a sign of a more serious problem. In the last few months of pregnancy, you should always report bleeding to your health care provider right away.
You should understand the difference between spotting and bleeding:
- Spotting is when you notice a few drops of blood every now and then on your underwear. It is not enough to cover a panty liner.
- Bleeding is a heavier flow of blood. With bleeding, you will need a liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your clothes.
When labor begins, the cervix starts to open up more, or dilate. You may notice a small amount of blood mixed in with normal vaginal discharge, or mucus.
Mid- or late-term bleeding may also be caused by:
- Having sex (most often just spotting)
- An internal exam by your provider (most often just spotting)
- Diseases or infections of the vagina or cervix
- Uterine fibroids or cervical growths or polyps
More serious causes of late-term bleeding may include:
- Placenta previa is a problem of pregnancy in which the placenta grows in the lowest part of the womb (uterus) and covers all or part of the opening to the cervix.
- Placenta abruptio (abruption) occurs when the placenta separates from the inner wall of the uterus before the baby is born.
To find the cause of your vaginal bleeding, your provider may need to know:
- If you have cramping, pain, or contractions
- If you have had any other bleeding during this pregnancy
- When the bleeding began and whether it comes and goes or is constant
- How much bleeding is present, and whether it is spotting or a heavier flow
- The color of the blood (dark or bright red)
- If there is an odor to the blood
- If you have fainted, felt dizzy or nauseated, vomited, or had diarrhea or a fever
- If you have had recent injuries or falls
- When you last had sex and if you bled afterward
A small amount of spotting without any other symptoms that occurs after having sex or an exam by your provider can be watched at home. To do this:
- Put on a clean pad and recheck it every 30 to 60 minutes for a few hours.

- If spotting or bleeding continues, call your provider.
- If the bleeding is heavy, your belly feels stiff and painful, or you are having strong and frequent contractions, you may need to call 911 or your local emergency number.
For any other bleeding, call your provider right away.
- You will be told whether to go to the emergency room or to the labor and delivery area in your hospital.
- Your provider will also tell you whether you can drive yourself or you should call an ambulance.
Baeseman ZJ. Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2021. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2021:1227-1229.
Francois KE, Foley MR. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
Hull AD, Resnik R, Silver RM. Placenta previa and accreta, vasa previa, subchorionic hemorrhage, and abruptio placentae. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 46.
In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 46.
Salhi BA, Nagrani S. Acute complications of pregnancy. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 178.
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Center for Fertility, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Browse the Encyclopedia
9 Reasons for Bleeding And Spotting During Pregnancy
Are you pregnant? Have you experienced some spotting or bleeding and are wondering what it means?
While it can be alarming and distressing to notice blood in the bathroom when you least expect it, there are some rational explanations — and not all of them are as dire as you may think. In fact, while not experienced by every mom, some level of bloody discharge during pregnancy is actually pretty common.
In fact, while not experienced by every mom, some level of bloody discharge during pregnancy is actually pretty common.
Read on to learn what bleeding or spotting during pregnancy can mean, what other symptoms to watch for, and when to worry.
Table of Contents
- The Differences Between Bleeding and Spotting
- What Does Bleeding During Pregnancy Mean?
- How Common is Bleeding During Pregnancy?
- 9 Causes Of Bleeding or Spotting During Pregnancy
- When Should I Seek Medical Help?
- The Bottom Line
The Differences Between Bleeding and Spotting
Any bleeding that occurs outside your menstrual period is commonly referred to as breakthrough bleeding (1).
However, there are different levels of breakthrough bleeding, often differentiated by the terms “bleeding” and “spotting.”
Spotting:
- Blood that is visible on your underwear or the toilet paper when you wipe after urinating.

- Appears as light brown or pink spots — as you see at the beginning or end of your menstrual period.
- Does not require a pad or panty liner.
Bleeding:
- Is bright red.
- Is heavier than spotting, more similar to a menstrual period.
- Requires a sanitary pad to manage.
What Does Bleeding During Pregnancy Mean?
When you experience any amount of vaginal bleeding during pregnancy, your mind always jumps to the worst. We’ve been there, too, so we understand the fear.
It’s alarming, it’s unexpected, and it’s scary — especially when you feel so helpless and want to know what’s going on inside your body.
Try To Relax
While bleeding or spotting could signal there is a problem with your pregnancy, rest assured it’s not the only possible explanation.
So before you freak out, remember that many changes are going on in your body. Hormones are shifting, tissues are stretching, and blood flow to your uterus is increasing. So bleeding during pregnancy may also be due to a physiological process.
So bleeding during pregnancy may also be due to a physiological process.
How Common is Bleeding During Pregnancy?
Bleeding is relatively common during pregnancy. How often it occurs and the reasons behind it differ throughout the trimesters. Up to 30% of women experience bleeding during their first trimester (2), and as many as 20 percent of women — that’s one in five — have bleeding at some point during their pregnancy (3).
You’re most likely to experience bleeding at certain points in your pregnancy — like toward the beginning to middle of the first trimester or toward the end of the third. Report to your doctor any bleeding you might notice at any point during pregnancy.
9 Causes Of Bleeding or Spotting During Pregnancy
There are many reasons you may experience bleeding or spotting during pregnancy. Some of these are:
1. Implantation Bleeding
When fertilization occurs, it happens in the fallopian tubes — well before the egg reaches the uterus. Meanwhile, the uterine walls have become thick-lined with blood and tissue, preparing for a potential pregnancy, should it happen.
Meanwhile, the uterine walls have become thick-lined with blood and tissue, preparing for a potential pregnancy, should it happen.
If pregnancy does not occur, this uterine lining is shed and is what comprises the menstrual period. If a pregnancy does occur, the fertilized egg needs to burrow its way into the lining, which can cause light bleeding. This is known as implantation bleeding.
About one-third of women experience implantation bleeding. While the timing for women varies based upon their fertility cycles, it typically occurs about 3 to 7 days before an expected period.
For this reason, it can often be mistaken as the start of a woman’s period, although it is usually of a much shorter duration and differs in color and amount.
How Long It Lasts
Implantation bleeding can be a one-time occurrence or last for up to three days.
The bleeding is not heavy and resembles spotting. It is usually pink or dark brown and does not include clots like menstrual blood.
2. Miscarriage
When you notice bleeding or spotting during pregnancy, miscarriage is typically the first thing you think of — after all, it’s a much-feared worst-case scenario. And while it is a very real possibility, try to remember it’s not the only possible explanation.
A miscarriage is the loss of a pregnancy within the first 20 weeks of gestation. However, most miscarriages occur within the first three months (4).
As many as one in five pregnancies ends in miscarriage, primarily due to genetic abnormalities. Other miscarriages occur for no known reason.
If you do experience a miscarriage, bleeding is one of the primary symptoms. The blood may appear brown or bright red and may be accompanied by clots or tissue (5). There may also be a gush of clear or pink fluid or discharge, which is actually amniotic fluid.
If you suspect you are experiencing a miscarriage, your doctor will likely order an ultrasound and a blood test.
The ultrasound will examine the inside of your uterus to try to determine whether there is a fetus and detectable heartbeat. A blood test can measure HCG levels, also known as the “pregnancy hormone.”
A blood test can measure HCG levels, also known as the “pregnancy hormone.”
The levels of HCG in your bloodstream rise rapidly during early pregnancy, and if a downward trend is detected in your blood, it could indicate a miscarriage. Remember, though, HCG levels alone are not an indicator that everything is 100% OK, as they can rise and double as expected even in some cases of ectopic pregnancy. That’s why your doctor will always do an ultrasound too.
It usually takes two HCG levels to diagnose a problem with the pregnancy (6). While the absolute value varies greatly from one woman to the next, two tests 48-72 hours apart should show a doubling of the HCG level in the early first trimester.
Sometimes, women experience a miscarriage, and after the initial symptoms of pain and bleeding, and after they notice tissue passing, they can start feeling their symptoms disappear and might not want to see their doctor. This can potentially be very dangerous for the woman since there are different types of miscarriages, and they can happen due to an ectopic pregnancy.
So if you feel you are having a miscarriage, you should always see your doctor.
Editor's Note:
Dr. Irena Ilic, MD
3. Placenta Previa
The placenta is the major organ that delivers blood, oxygen, and nutrients to your baby, and it grows throughout your pregnancy. It is typically attached high in your uterine wall, where it gets the best blood flow and will stay well out of the baby’s way when it comes time to deliver.
Sometimes, the placenta develops close to or directly over the cervix. This is called placenta previa (7). There are different types, depending on its position, including partial, low-lying, marginal, and major or complete placenta previa.
This is typically detected in an ultrasound during the second trimester and is closely monitored for the duration of pregnancy.
Placenta previa can cause a good amount of vaginal bleeding and must be monitored, but with lifestyle modifications and modern medical procedures, you will more than likely deliver a healthy baby. Also, not all cases of placenta previa will be accompanied by heavy bleeding; it can be minimal to none. As the uterus continues to grow, it’s common for the placenta to shift out of the way of the cervix, leading to a normal delivery.
What Placenta Previa Means For Your Pregnancy
If you have placenta previa, you will probably have to go on pelvic rest for the remainder of your pregnancy, which means you can’t have sex or vaginal exams, and you may have to avoid vigorous exercise. If it doesn’t resolve by the end of your pregnancy, you will have to deliver your baby by C-section since the placenta is blocking your baby’s exit from the womb. Also, after the delivery, you might experience more bleeding than usual or bleeding that is harder to control, so your doctor will monitor you closely.
Placenta previa is relatively common, occurring in 1 of 200 pregnancies. Most of these, up to 90%, resolve by the time of delivery. It’s more likely to occur if this is not your first pregnancy, if you’re pregnant with multiples, or if you’ve had any previous procedures on your uterus.
4. Placental Abruption
Placental abruption occurs when the placenta separates from your uterine wall before your baby is born (8). It is a serious condition as it affects your baby’s oxygen and blood supply, and there is no medical treatment to reattach the placenta. It happens most commonly in the third trimester.
Placental abruption usually develops suddenly and is accompanied by abdominal and back pain and heavy bleeding. However, occasionally it occurs slowly over time, which can result in light, occasional bleeding. This can be the case with chronic placental abruption, and in these cases, the baby’s growth progress might be slowed.
If you have occasional bleeding, your doctor will also monitor your amniotic fluid levels and your baby’s growth rate to determine how the condition is affecting your pregnancy.
It’s important to note the severity of your bleeding does not always directly correlate with the severity of your placental abruption. This means that even if sometimes there is little blood seen on the outside, there could be more blood trapped inside the uterus. Your doctor will examine your uterus and order an ultrasound to diagnose your placental abruption and its severity.
When
If you have any signs or symptoms of placental abruption, you should call your doctor right away.
If you have a placental abruption, you may have to deliver your baby immediately if you are near the end of your pregnancy. If you are earlier in your pregnancy and your bleeding stops, you will be closely monitored for the duration of your pregnancy as there is a risk of premature labor.
5. Hematoma
The chorion membrane is contained between your placenta and the uterine wall. Sometimes, blood collects in the folds of the chorion and results in a condition called subchorionic bleeding, or subchorionic hematoma (9). Subchorionic hematomas can be of different sizes, with larger ones causing heavier bleeding, but with smaller ones being the most common.
Sometimes, blood collects in the folds of the chorion and results in a condition called subchorionic bleeding, or subchorionic hematoma (9). Subchorionic hematomas can be of different sizes, with larger ones causing heavier bleeding, but with smaller ones being the most common.
If you experience bleeding during pregnancy, your doctor will likely order an ultrasound to screen for the presence of a hematoma. However, some hematomas are accidentally detected through routine ultrasounds with no accompanying bleeding.
There is no specific treatment for subchorionic hematoma except possible pelvic rest, depending on the severity of your condition. The good news is that it frequently resolves on its own. Your doctor might also start you on medication to prevent miscarriage.
However, in more severe cases, if it does not resolve, it may result in a placental abruption, which can be a serious threat to your pregnancy.
If you are diagnosed with a subchorionic hematoma, you will likely be monitored more closely by your doctor and have more frequent ultrasounds. You should avoid standing for long periods of time, having sex, and exercising. And make sure to follow any bed rest instructions your doctor prescribes.
You should avoid standing for long periods of time, having sex, and exercising. And make sure to follow any bed rest instructions your doctor prescribes.
The Bottom Line
Subchorionic hematoma is found in up to 11% of pregnancies and is more common after IVF (10), but with a timely diagnosis, most women go on to have healthy pregnancies and normal deliveries.
6. Vaginal Infection
The cervix is considered a blood-rich organ, which means it can easily bleed if inflamed or irritated. An infection such as a yeast infection or bacterial vaginosis can cause cervical irritation and bleeding.
These conditions are completely unrelated to pregnancy, but with the increased blood flow to your reproductive organs and cervix during this time, bleeding may be a symptom you don’t experience as frequently when you’re not pregnant.
Vaginal bleeding may be due to an infection if it’s accompanied by foul-smelling or abnormal discharge, if you have redness, itching, or vaginal wall irritation, or if you are experiencing a burning sensation when you pee (11).
What To Look For
The bleeding you experience as a result of infection is most similar to spotting and will not likely be bright red or heavy.
Vaginal infections are easily treated with antibiotics, and your doctor will prescribe those safe to use in pregnancy.
7. Sex
Sex is safe during pregnancy, so unless you’ve been given explicit instructions from your doctor to avoid it, enjoy getting your groove on while you’re expecting.
However, the act of sex has the potential to irritate the cervix — especially if the penis bumps up against it. This can cause you to notice some very light bleeding the next day, most likely so light that you’ll only notice it on toilet paper after going to the bathroom.
This does not indicate there is a problem and is completely normal.
Don’t be shy about discussing sex during pregnancy with your partner and with your health care provider. There are some cases when your doctor might suggest you avoid sex, such as having an incompetent cervix, placenta previa, or unexplained bleeding.
Even then, nine months will pass soon, and in the meantime, there are other ways to maintain intimacy with your partner, so don’t feel discouraged.
Editor's Note:
Dr. Irena Ilic, MD
8. Losing Your Mucus Plug
During pregnancy, your body develops a mucus plug at the opening of your cervix. Sounds lovely, I know, but it has a very important purpose. It helps protect your baby and uterus from bacteria (12).
Toward the end of your pregnancy, as your cervix begins to open, the mucus plug will release, and you may experience spotting in your underwear. However, it looks different from typical spotting in that it’s mixed with stringy or thick mucus.
Some women experience the loss of their mucus plug throughout several days and may notice it as pink-tinged bloody spots or streaks on the toilet paper when they wipe after going to the bathroom. Other women experience the loss of their mucus plug all at once. In this case, the volume of blood will be greater and the loss of the mucus plug will be more noticeable. It can also happen without you noticing it. But, if you see discharge which might or might not be your mucus plug, and it is bright red in color and not just a few drops you should contact your doctor right away, especially if you are feeling any pain.
In this case, the volume of blood will be greater and the loss of the mucus plug will be more noticeable. It can also happen without you noticing it. But, if you see discharge which might or might not be your mucus plug, and it is bright red in color and not just a few drops you should contact your doctor right away, especially if you are feeling any pain.
The loss of the mucus plug usually signals that labor is imminent, though it can be up to two weeks before labor begins. Some women don’t lose their mucus plug until they’re in active labor. It is also known as bloody show.
If you are near the end of your pregnancy and start seeing blood in your underwear or on toilet paper, don’t panic — especially if it is mixed with discharge. It is a normal part of your body preparing for labor.
On the other hand, if you’re not nearing your due date and notice some blood-tinged mucus, contact your doctor. They will check your cervix to see if it is opening too early. If it is, you may be going into premature labor or have an incompetent cervix (13).
If either of these are diagnosed, they can be treated with labor-stopping medications or a cerclage.
9. Unknown Reasons
On rare occasions, some women will experience heavy breakthrough bleeding — almost like a regular period — intermittently throughout the course of their pregnancy with no known medical cause.
While this is not considered normal, if you are experiencing regular, heavy bleeding, your doctor will work with you to rule out all severe causes that may threaten your baby’s life and the viability of your pregnancy.
If this happens to you regularly, track the occurrences of breakthrough bleeding to see if you can notice a pattern and help your doctor identify the cause.
Cover Your Bases
Ask your doctor if you should take an additional iron supplement to compensate for the regular loss of blood, but don’t up your iron intake without your doctor’s guidance.
When Should I Seek Medical Help?
You should always mention any type of bleeding or spotting to your doctor at your next pregnancy appointment. If you want to get their opinion on whether they’d like to see you sooner, you can call them between appointments.
If you want to get their opinion on whether they’d like to see you sooner, you can call them between appointments.
If you experience any of the following symptoms along with your bleeding or spotting, ask your doctor for an immediate appointment or head to the local emergency room if they can’t fit you in:
- Severe, painful cramping.
- Bright red, heavy bleeding that soaks a pad.
- A rush of fluid in addition to blood.
- Severe nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
- Chills and high fever (100.4 degrees Fahrenheit or higher).
If you are experiencing heavy bleeding, use a sanitary pad to manage it until you can be seen by the doctor. If you do not have a pad on hand, you can stuff a baby diaper or washcloth in your underwear. Never use a tampon while pregnant.
The Bottom Line
While experiencing bleeding during pregnancy is alarming, rest assured that it often occurs due to a treatable condition, and most women can go on to deliver healthy babies.
However, because it may also signal a more severe condition, it’s always important to mention any level of vaginal bleeding or spotting to your doctor so they can evaluate you.
Feedback: Was This Article Helpful?
Thank You For Your Feedback!
Thank You For Your Feedback!
What Did You Like?
What Went Wrong?
Bloody discharge during pregnancy ᐈ Blood during early pregnancy
Seeing bloody discharge, a pregnant woman is always frightened. They are considered a symptom of miscarriage and other equally serious pathologies. At the same time, in some cases, the appearance of a small amount of blood is considered the norm and does not pose a threat to the life and health of the fetus or the expectant mother.
In early pregnancy, bloody discharge occurs in 25% of women. In most cases, they are associated with the implantation of the fetal egg to the wall of the uterus. Also, scanty spotting may appear on the dates of the expected menstruation.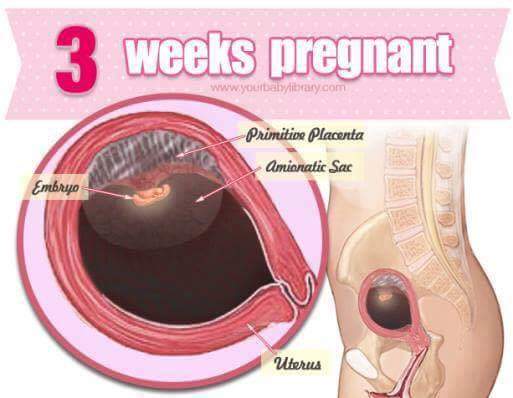 If they end quickly, are not accompanied by pain, and the woman has not had miscarriages or pregnancy complications before, most likely she has nothing to worry about. However, it is necessary to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist and undergo an examination.
If they end quickly, are not accompanied by pain, and the woman has not had miscarriages or pregnancy complications before, most likely she has nothing to worry about. However, it is necessary to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Why bloody discharge can appear and when it is dangerous, said Elena Petrovna Domnich, obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound specialist of the ADONIS medical center.
Elena Nikolaevna, tell me, can a woman have periods during pregnancy?
- Sometimes during pregnancy, a woman may experience spotting, but this should not be interpreted as menstruation. Menstruation occurs at the end of the menstrual cycle, during which the endometrium changes, first proliferative, then secretory. During the cycle, the endometrium prepares for pregnancy, and if it does not occur, then menstruation begins.
In the event of pregnancy, menstruation is not possible, although bleeding may occur at the expected time. Because of this, some women do not immediately know that they are pregnant. However, when the obstetrician-gynecologist at the reception asks them about the nature of the discharge, it always turns out that they are different from menstrual. As a rule, they are more scarce, pass faster and are not accompanied by other symptoms. Sometimes a woman says that her period was very recent, but at the time of examination and examination, we find that she is already 8 or 12 weeks pregnant.
How often does this happen? Is spotting during pregnancy an exception or a fairly common occurrence?
- Bloody discharge is not common in pregnant women, but still it cannot be said that these are exceptional cases.
Tell me, if a woman is planning to conceive a child, and during the expected period she has atypical discharge, should she take a pregnancy test?
– Yes, but it is better to visit an obstetrician-gynecologist. There are cases when a woman is pregnant, but the test strip shows a negative result. To accurately determine whether there is a pregnancy, allows a blood test for the level of hCG.
There are cases when a woman is pregnant, but the test strip shows a negative result. To accurately determine whether there is a pregnancy, allows a blood test for the level of hCG.
So bleeding during pregnancy is not menstruation, but bleeding? Why can it appear and why is it dangerous?
- Yes, that's right. This is bleeding, not menstruation. It can be a symptom of a miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or other pathology. For diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
Tell me more, if a woman has a discharge and thinks she is menstruating, but a previous pregnancy test came back positive, could it be wrong?
- A pregnancy test is sometimes positive even if it is not. This happens if a woman has formed luteal cysts or developed a thyroid disease.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy requires contacting the antenatal clinic or the medical center where the woman was registered for pregnancy management. Sometimes they may not be dangerous, but without diagnosis, it cannot be ruled out that this is a symptom of a serious disorder.
Sometimes they may not be dangerous, but without diagnosis, it cannot be ruled out that this is a symptom of a serious disorder.
Bleeding may occur with:
- threatened miscarriage;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- infectious diseases of the reproductive system;
- cysts;
- myomas;
- cervical erosion;
- placental abruption;
- threatened preterm birth.
You can watch the video version of Elena Petrovna Domnich's interview here. More helpful videos on our YouTube channel.
Pregnancy discharge | What are the discharge during pregnancy? | Blog
In the absence of menstruation, girls usually suspect that conception has occurred. However, during pregnancy, the female body may continue to secrete a secret of a different color and character. We recommend that you keep a close eye on everything that happens so as not to miss the development of adverse events. We will talk about how to recognize problem situations during pregnancy in the article.
What discharge can occur during conception
Many women note that immediately after the delay and in the later stages, the nature of secretion changes. It can be:
- With or without scent.
- Depending on the color - transparent, white, cream, yellow, greenish, bloody.
- By consistency - thick, liquid, cheesy.
- As a symptom for assessing the state of health - threatening, safe.
During ovulation, the egg is released from the ovary, its membrane is deflated, a small amount of fluid is released - so it becomes ready for fertilization. At this time, the thick mucus that fills the cervical canal of the cervix becomes less viscous. This makes it easier for the spermatozoa to penetrate and move further into the tubes for fertilization. At this time, you may notice an abundance of clear mucous secretion.
After the fusion of the egg with the spermatozoon, movement into the uterus begins, which should end with implantation in the inner layer. During penetration, its slight detachment may occur - this causes damage to the blood vessels that abundantly penetrate the muscular layer of the uterus. You may see light brown discharge, which is common during pregnancy. The color is due to the fact that the blood has time to clot.
Sometimes the discharge is brightly colored and some women mistake it for a period that has started too early. But in this case, a short duration is characteristic, a different shade (dark or scarlet), a slight mark on the linen.
With some features of the structure of the female genital organs (for example, with a bicornuate uterus), after implantation of the embryo in one part, rejection of the endometrium may begin in the other, as usually occurs during menstruation. This rarely happens.
Characteristics of discharge in the event of a threatened miscarriage
Spontaneous abortion is the rejection of an embryo in the early stages after conception. If at the first signs of pregnancy, you notice spotting, there is a high probability that a miscarriage begins.
Also, miscarriage symptoms include:
- pulling or pressing on the lower abdomen, sacrum, lower back;
- the muscles of the uterus are tense.
The woman may experience cramps. This continues all the time or intermittently. From the vagina there are scarlet or brown discharge during pregnancy, which was previously confirmed. Sometimes the period may be still small, and the first signs did not have time to appear.
After 22 weeks, this phenomenon is called preterm labor. The child in this case is still weak, the organs are not sufficiently developed, and there is little chance of survival.
The following factors increase the risk of miscarriage:
- various diseases;
- progesterone deficiency;
- nervous and physical strain;
- pathologies in the genitals;
- fetal developmental defects.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound scan. If it shows that the fetal heart rate is disturbed, the tone of the uterus is increased, its size differs from normal for this period, hospitalization will be recommended to maintain pregnancy.
What discharge during pregnancy is considered normal
This secretion does not pose a threat to health:
- transparent;
- whitish;
- yellowish;
- odor free;
- mucous;
- without itching, burning, redness of the genitals.
Clear fluid on underwear is a symptom of ovulation. During pregnancy, the activity of ongoing processes in the body increases, so the amount of secretion secreted may increase. However, a violation of the norm is the leakage of amniotic fluid. You can determine the problem with the help of special diagnostic tests that the doctor will prescribe if he has suspicions.
White color, small amount, homogeneous structure should also not cause concern. The increased volume of fluid in this case is associated with increased hormonal activity.
One of the variants of the norm is mucous discharge, which smells of slight sourness. If there is no pain, discomfort, there is nothing to worry about.
Yellow discharge, there are signs of pregnancy, there is no unpleasant odor - you are all right. Some women had this color before conception, only they did not pay attention. Now there are more of them, therefore more noticeable.
Sometimes a woman observes that the laundry gets wet and there is a smell of urine. This may indicate incontinence due to the constant pressure of the growing uterus. In this case, it is recommended to go to the toilet more often, change underpants twice a day.
What discharge during pregnancy is considered a sign of infection?
White discharge during pregnancy with a cheesy texture is a symptom of thrush (candidiasis). In pregnant women, it is diagnosed quite often - the reason is a change in hormonal levels. The disease is accompanied by itching, redness of the vulva, a strong sour smell. Sometimes external manifestations are not detected, then treatment is not carried out.
Infection is indicated by pain, pain, skin irritation, ulcers, smell of rot or fish, gray or green color, frothy discharge, increased nervousness, large inguinal lymph nodes. The reason may lie in sexually transmitted infections. This includes syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and others. They are dangerous because they cause premature birth and fetal developmental defects.
The reason may lie in sexually transmitted infections. This includes syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and others. They are dangerous because they cause premature birth and fetal developmental defects.
Which discharge during pregnancy should be paid special attention to and should I consult a doctor?
The following indicates that pregnancy is at risk:
- Severe pain in the perineum, bleeding, difficulty defecation, convulsions - these can be injuries to the vaginal mucosa.
- Nausea, profuse vomiting, swelling, headaches, cough, hypertension, bright red secretion are symptoms of hydatidiform mole (abnormal development of the embryo).
- A drop in blood pressure, pallor, weakness, sweating, pulling sensations, bleeding during pregnancy against the background of a lack of growth of hCG in the blood - this is how ectopic attachment manifests itself.
- Isolation of clots, sharp pain, vomiting, diarrhea may indicate a frozen fetus.

If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
It is also necessary to go to the clinic if you have been physically abused, had rough sex, had an accident, fell, hit. The likelihood that the situation will be resolved successfully is much higher if you do not delay the visit, listen to the symptoms and take good care of your health.
Remember, despite the fact that pregnancy is a normal state of health of the female body, the diagnosis and treatment tactics are still different, due to the many restrictions on manipulations and medications during pregnancy. That is why diagnosis and treatment during pregnancy should take place only under the supervision of a doctor. By ignoring the symptoms or self-medicating, a pregnant woman risks not only her health, but also the health of her child.
Doctors of the Leleka maternity hospital manage pregnancies of any complexity, including those aggravated by infections, pathologies, and the threat of miscarriage.