Breech position definition
Causes, Complications, Turning & Delivery
Overview
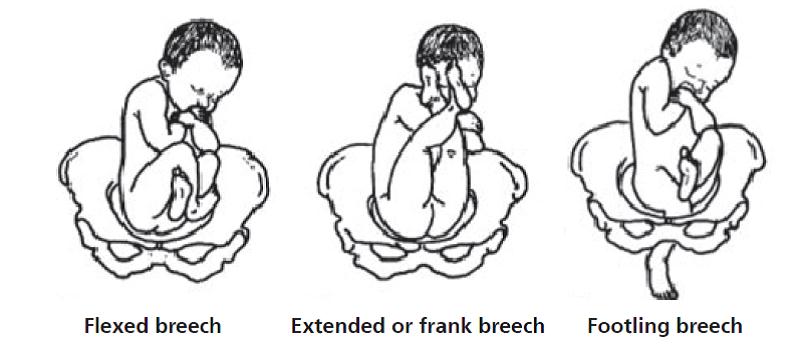
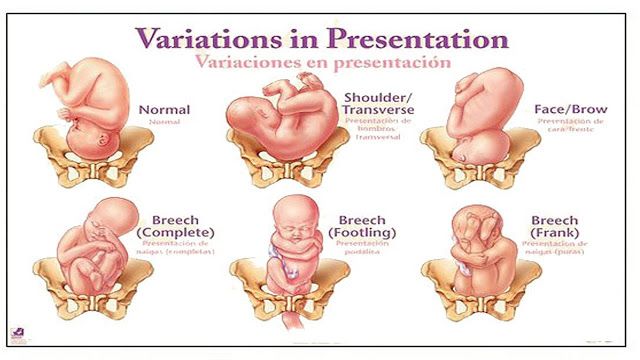
Types of breech positions during pregnancy.What is a breech baby?
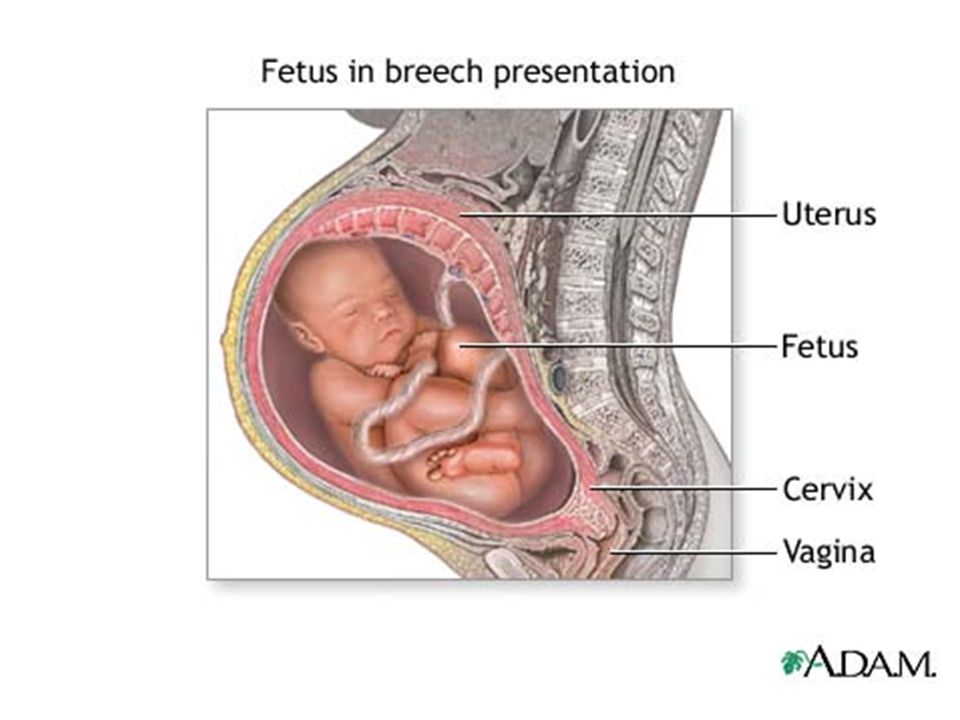
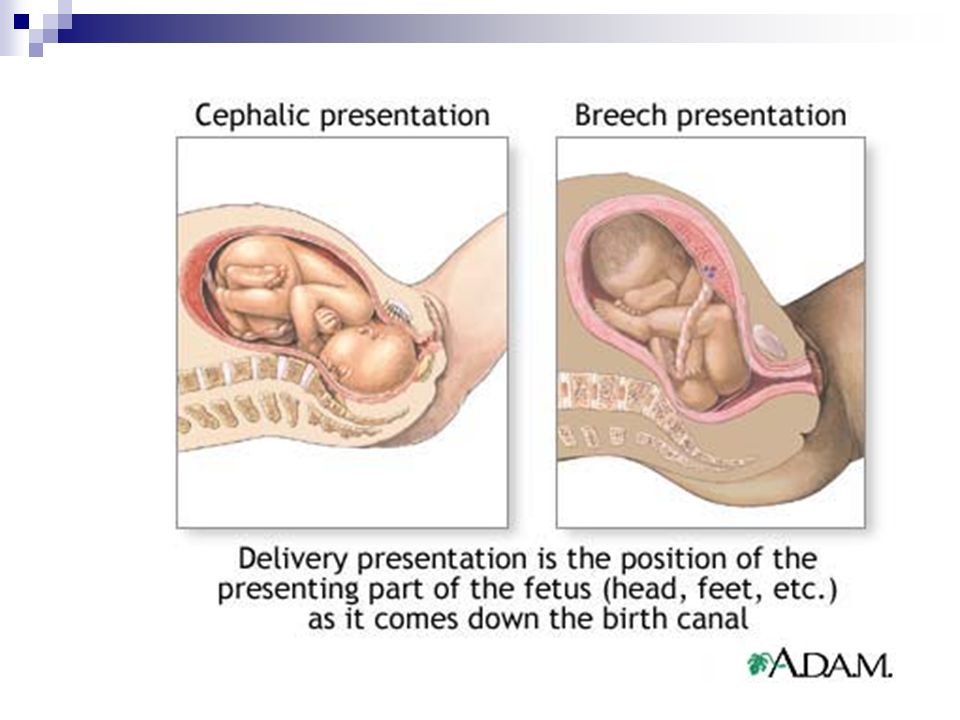
A breech baby, or breech birth, is when your baby’s feet or buttocks are positioned to come out of your vagina first. Your baby’s head is up closest to your chest and its bottom is closest to your vagina. Most babies will naturally move so their head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. Breech is common in early pregnancy and most babies will move to a head-first position by 36 weeks of pregnancy. This head-first position is called vertex presentation and is the safest position for birth.
How common is a breech baby?
There is a small chance that your baby will not move into a head-first position before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Breech babies account for about 3% to 4% of all full-term pregnancies.
What are the types of breech position a baby can be in?
There are several fetal positions your baby may present in. Ideally, your baby is positioned head-down, facing your back, with their chin tucked to their chest.
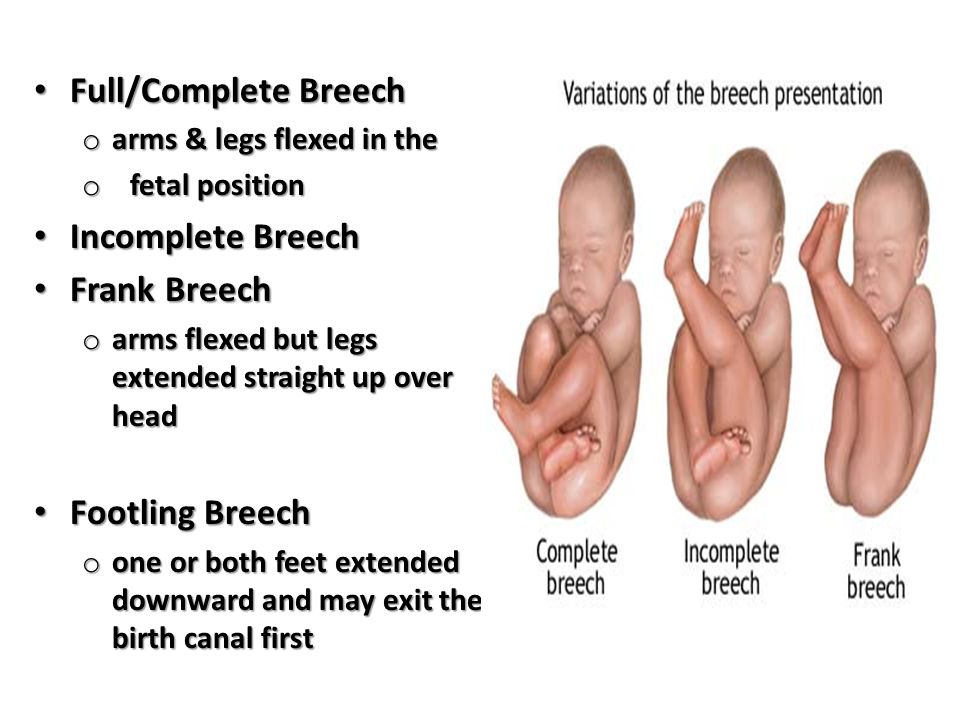
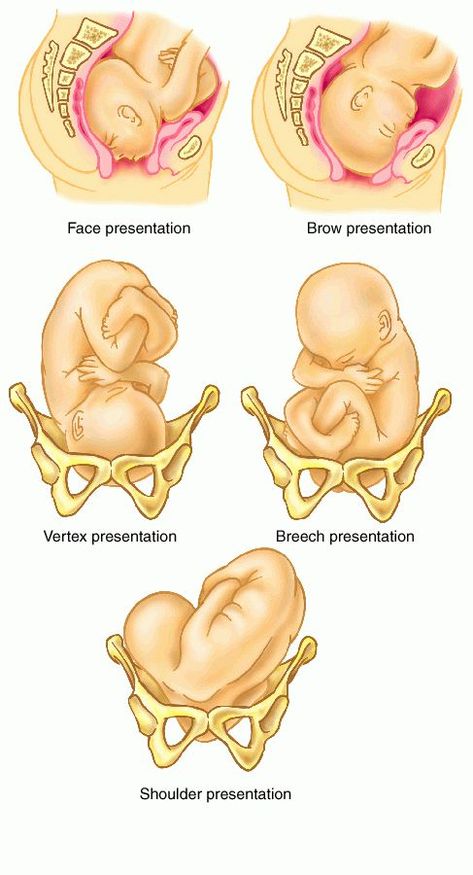
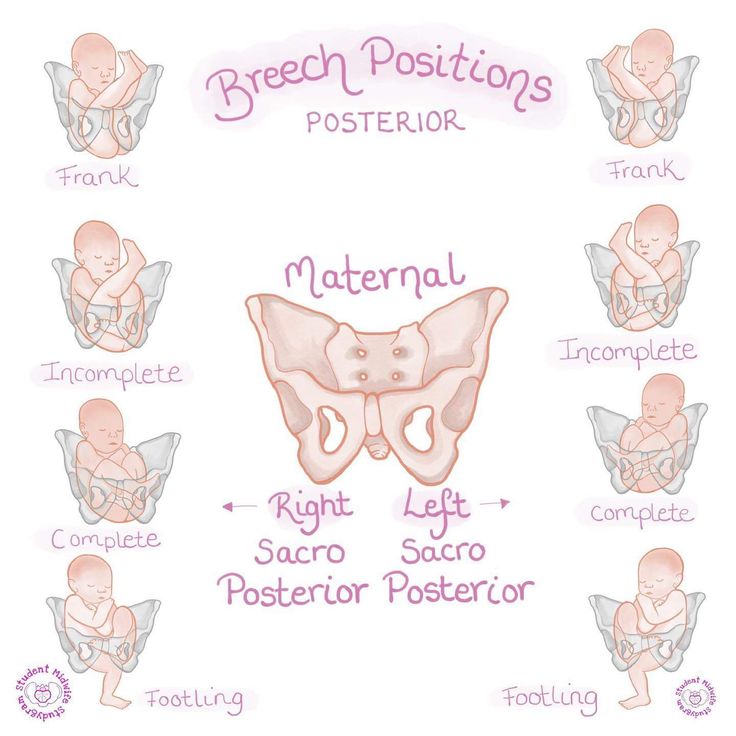
Breech babies can be in a few different positions:
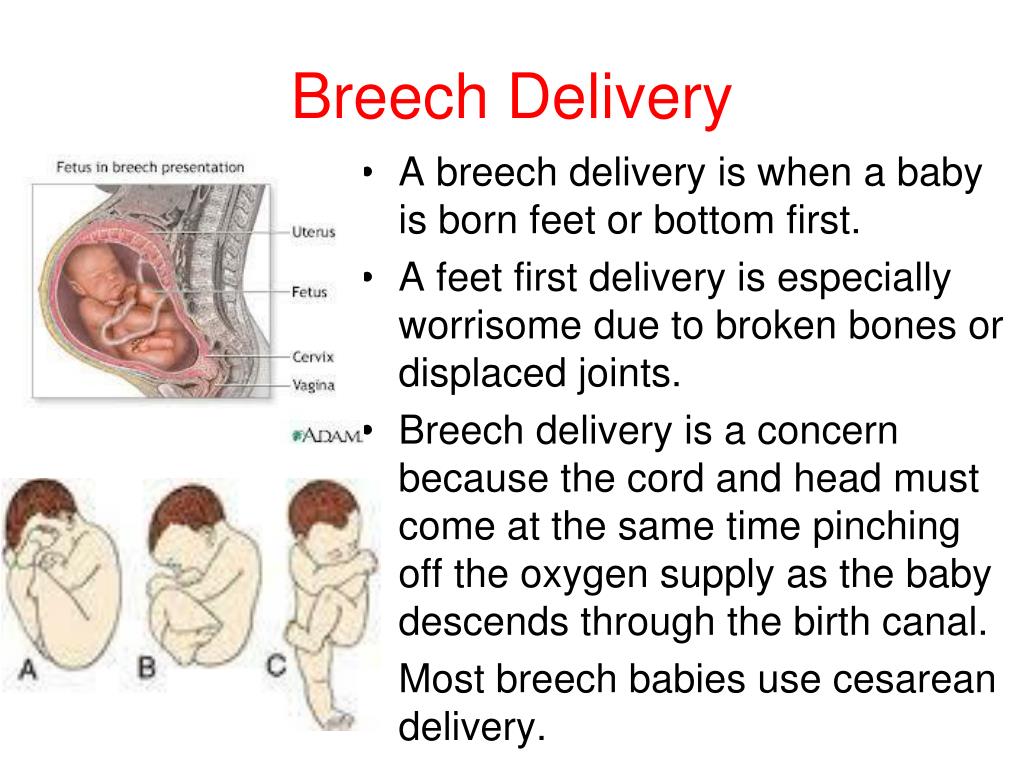
- Frank breech: The baby’s buttocks are aimed at the vaginal canal with its legs sticking straight up in front of their body and the feet near their head.
- Complete breech: The baby’s buttocks are pointing downward and both the hips and the knees are flexed (folded under themselves).
- Footling breech: One or both of the baby’s feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of their body.
- Transverse lie: This is a form of breech presentation where your baby is positioned horizontally across your uterus instead of vertically. This would make their shoulder enter the vagina first.
How does a breech baby affect pregnancy?
Your pregnancy is usually not affected. Most breech babies are born healthy, although there is a slightly elevated risk for certain birth defects. Your baby’s movements may feel a little different. You will feel your baby’s kicks lower in your belly. You may feel a hard lump closer to your ribs. This is your baby’s head.
Your baby’s movements may feel a little different. You will feel your baby’s kicks lower in your belly. You may feel a hard lump closer to your ribs. This is your baby’s head.
If you planned a vaginal delivery, a breech baby could change these plans. When your baby is breech, a vaginal delivery can be complicated and dangerous. Your healthcare provider may feel comfortable attempting a vaginal breech delivery, but in most cases, they will recommend a Cesarean birth (C-section).
How does a breech baby affect delivery?
If your baby presents in a breech position after 36 weeks of pregnancy, your birthing plan will likely change. It's usually unsafe for a breech baby to be born vaginally due to risks of injury. In most cases, a planned C-section is the safest way to deliver your baby. Some healthcare providers may be comfortable with a vaginal breech birth. In some cases, turning your baby to a head-down position while they are still inside your uterus is an option. Your baby is then born head first.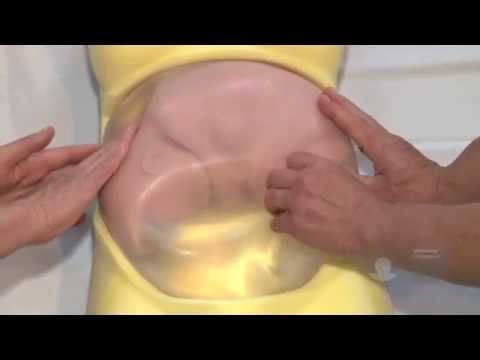
Symptoms and Causes
How can you tell if your baby is breech?
You may be able to tell if your baby is breech, especially if you have had past pregnancies where your baby was head-first. The places where you feel lumps and kicks might indicate that your baby is breech. Let your healthcare provider know where you feel movement. They will feel your belly or do an ultrasound to confirm that your baby is breech.
What causes a baby to be breech?
It’s not always known why a baby is breech. Some factors that may contribute to this position are:
- You are expecting multiples (twins or more). This makes it harder for each baby to get into the right position.
- There is too much or too little amniotic fluid.
- The uterus is not normal in shape or has abnormal growths such as fibroids. Most of the time, the uterus is shaped like an upside-down pear. If it's shaped differently, there might not be enough room for a full-grown baby to move into position.
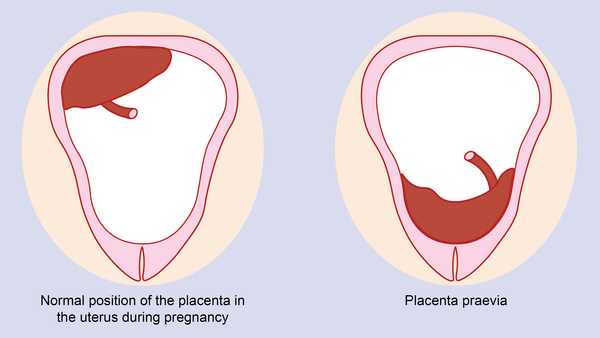
- The placenta covers all or part of the cervix (a condition called placenta previa).
- The baby is preterm. This means they are less than 37 weeks gestation and may not have turned to a head-first position.
- Your baby has a birth defect that causes them to not turn head-down.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is a breech baby diagnosed?
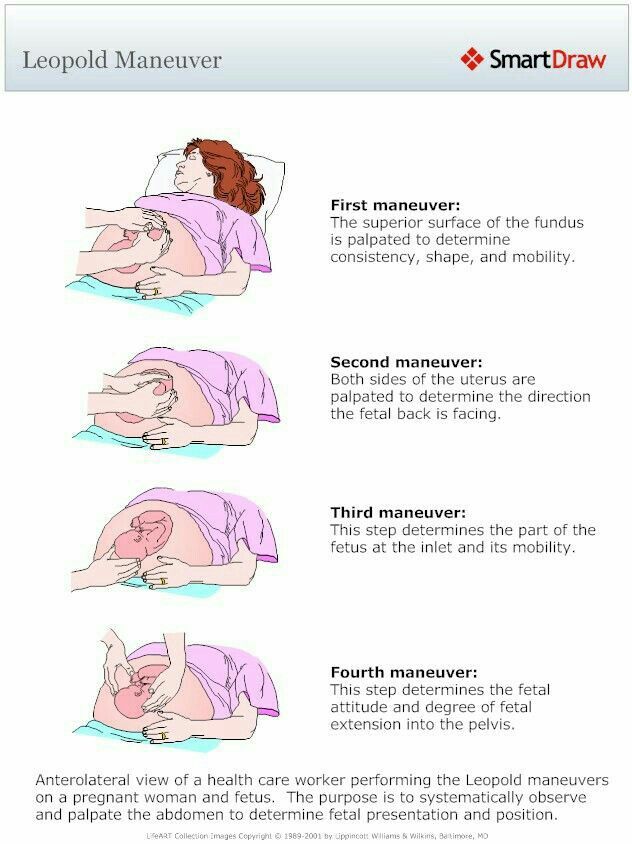
Your healthcare provider may be able to tell which way your baby is facing by placing their hands at certain places on your abdomen. By feeling where the baby’s head, back and buttocks are, it’s usually possible to find out what part of the baby is positioned to come out of the vagina first. An ultrasound may be used to confirm the baby’s position.
When is a breech baby diagnosed?
Almost all babies are breech at some point. As your pregnancy progresses, your baby will naturally move to a head-down position — probably between 32 and 36 weeks. Your healthcare provider will feel your belly and determine where your baby is positioned. This will happen during most of your appointments in the third trimester. After 37 weeks, a breech baby usually does not turn on their own. Your healthcare provider will discuss delivery options with you.
This will happen during most of your appointments in the third trimester. After 37 weeks, a breech baby usually does not turn on their own. Your healthcare provider will discuss delivery options with you.
Management and Treatment
What are the options for treating a breech baby?
If your baby is breech at 37 weeks of pregnancy, your healthcare provider may:
- Try turning your baby in your uterus into the head-first position.
- Plan a C-section birth.
- Plan a vaginal breech birth.
What are some complications of having a breech baby?
The complications of having a breech baby usually do not occur until it's time to deliver. Some breech babies can be safely delivered through the vagina.
The risks of attempting a vaginal breech birth are:
- Injuries to your baby’s legs or arms such as dislocated or broken bones.
- Umbilical cord problems. The umbilical cord can be flattened or twisted during delivery. This can cause nerve or brain damage due to a lack of oxygen.
Will my doctor try to flip my baby if it's breech?
If your baby is breech, your healthcare provider may consider turning your baby so that you can have a vaginal delivery. In some cases, trying to turn your baby may not be safe or the risks outweigh the benefits.
Flipping your baby may not be safe if you have any of the following:
- Bleeding from your vagina.
- Placenta previa. This is when your placenta covers all or part of your cervix.
- A nonreactive nonstress test.
- An abnormally small baby.
- Low level of amniotic fluid.
- Low or high fetal heart rate.
- Premature rupture of the membranes.
- Twins or multiples.
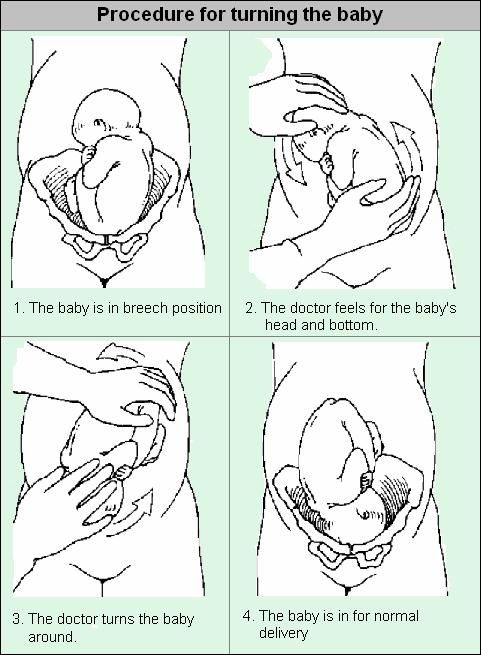
The most common method used to turn a breech baby is called external cephalic version (ECV). It's performed by your healthcare provider around 37 weeks of pregnancy. This procedure is performed in the hospital just in case an emergency occurs. It involves placing hands on your abdomen and applying firm pressure to turn your baby to a head-down position while your baby is still in your uterus. It is about 65% effective and carries some risks.
It is about 65% effective and carries some risks.
What are the risks of turning my breech baby?
The risks of ECV include the following:
- Premature labor.
- Premature rupture of the amniotic sac.
- Blood loss for either you or your baby.
- Emergency C-section.
- Your baby might turn back to the breech position.
Although the risk of having these complications is small, some healthcare providers prefer not to try to flip a breech baby.
Will my breech baby flip on their own?
Most babies will flip to a head-down position before they reach full term (37 weeks). If your baby is still in a breech position at this time, your healthcare provider will determine if you can deliver vaginally or if you will need a C-section.
How can I flip my baby if it's breech?
Some women will try at-home methods to flip their baby to a head-first position. They may help, but there is no scientific evidence that they work.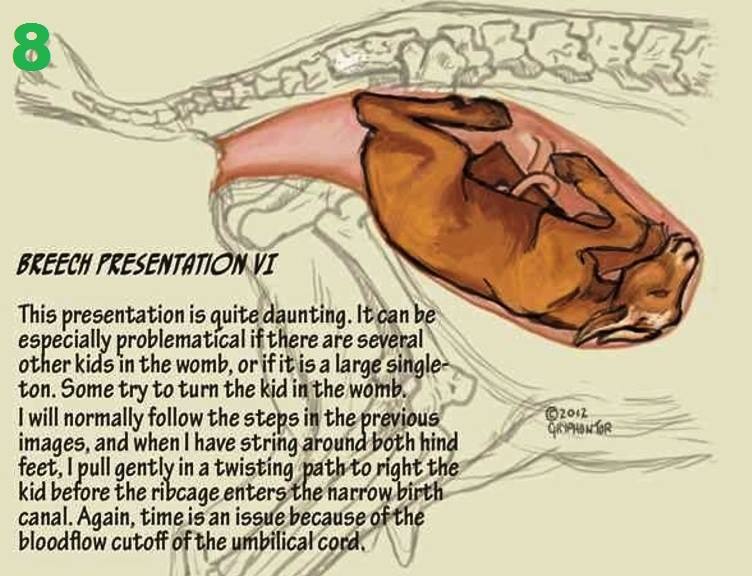
- Bridge position: Lie on the floor with your legs bent and your feet flat on the ground. Raise your hips and pelvis into a bridge position. Hold this position for 10 or 15 minutes several times a day.
- Child’s pose: Rest in the child’s pose for 10 to 15 minutes. It can help relax your pelvic muscles and uterus. You can also rock back and forth on your hands and knees or make circles with your pelvis to promote activity.
- Music: Place headphones or a speaker at the bottom of your uterus to encourage your baby to turn.
- Temperature: Try placing something cold at the top of your stomach where your baby’s head is. Then, place something warm at the bottom of your stomach.
A chiropractic technique, called the Webster technique, can also help your uterus relax. Some providers even recommend acupuncture. Both of these techniques need to be done by a professional that your healthcare provider has recommended.
Prevention
How can I reduce my risk of having a breech baby?
There is nothing you can do to prevent your baby from being in a breech position. If your baby is in a breech position, it’s not because you did anything wrong.
Outlook / Prognosis
Can you deliver vaginally with a baby breech?
It's possible to deliver a breech baby vaginally. It can be more dangerous for the baby and the risk of injury is much higher. If the umbilical cord is compressed during birth, the baby could be deprived of oxygen and this could harm their brain and nerves. The cord could also slip around the baby’s neck or arms, causing injury. Healthcare providers have various levels of comfort with vaginal deliveries of breech babies. Talk to your provider about the risks and benefits of different types of birth for a breech baby.
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following symptoms during pregnancy:
- Severe cramping or contractions.
- Vaginal bleeding.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
Learning your baby is breech may give you concerns about your delivery. It’s completely natural to have questions. Some questions to ask your doctor can include:
- How can I tell if my baby is breech?
- Is my baby OK?
- What are the benefits and risks of turning my baby?
- What are my options for delivery if my baby remains in the breech position?
- What are the health risks to my baby and me if they are born breech?
Frequently Asked Questions
Do birth defects cause breech position?
Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies. It might be the reason that the baby didn’t move to the head-down position. Most babies who are breech at delivery are born without any health complications.
Will I need a C-section if my baby is breech?
Most of the time, a C-section is the safest way to deliver a breech baby. Your risks of developing complications are much higher if you try to deliver a breech baby through the vagina. However, some healthcare providers may feel comfortable performing a vaginal breech birth.
However, some healthcare providers may feel comfortable performing a vaginal breech birth.
How does labor start if your baby is breech?
Having a breech baby doesn’t change some of the first signs of labor like contractions or rupturing of your membranes. In most cases, your healthcare provider will recommend a planned C-section. If your delivery is planned, you may not have any labor symptoms.
If you are in labor and go to the hospital for delivery, your provider will confirm your baby’s position a final time. Your provider could attempt a vaginal delivery, but it's more likely they will proceed with a C-section to be safe.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Having a breech baby can be unexpected and change the vision you had for childbirth. Talk to your healthcare provider about what to expect during a breech delivery. They can help you understand the risks and benefits of a breech birth so that you and your baby are kept safe.
Causes, Complications, Turning & Delivery
Overview
Types of breech positions during pregnancy.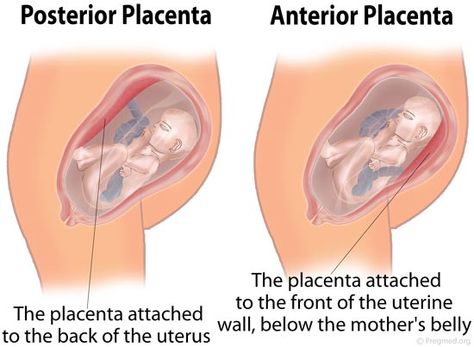
What is a breech baby?
A breech baby, or breech birth, is when your baby’s feet or buttocks are positioned to come out of your vagina first. Your baby’s head is up closest to your chest and its bottom is closest to your vagina. Most babies will naturally move so their head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. Breech is common in early pregnancy and most babies will move to a head-first position by 36 weeks of pregnancy. This head-first position is called vertex presentation and is the safest position for birth.
How common is a breech baby?
There is a small chance that your baby will not move into a head-first position before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Breech babies account for about 3% to 4% of all full-term pregnancies.
What are the types of breech position a baby can be in?
There are several fetal positions your baby may present in. Ideally, your baby is positioned head-down, facing your back, with their chin tucked to their chest.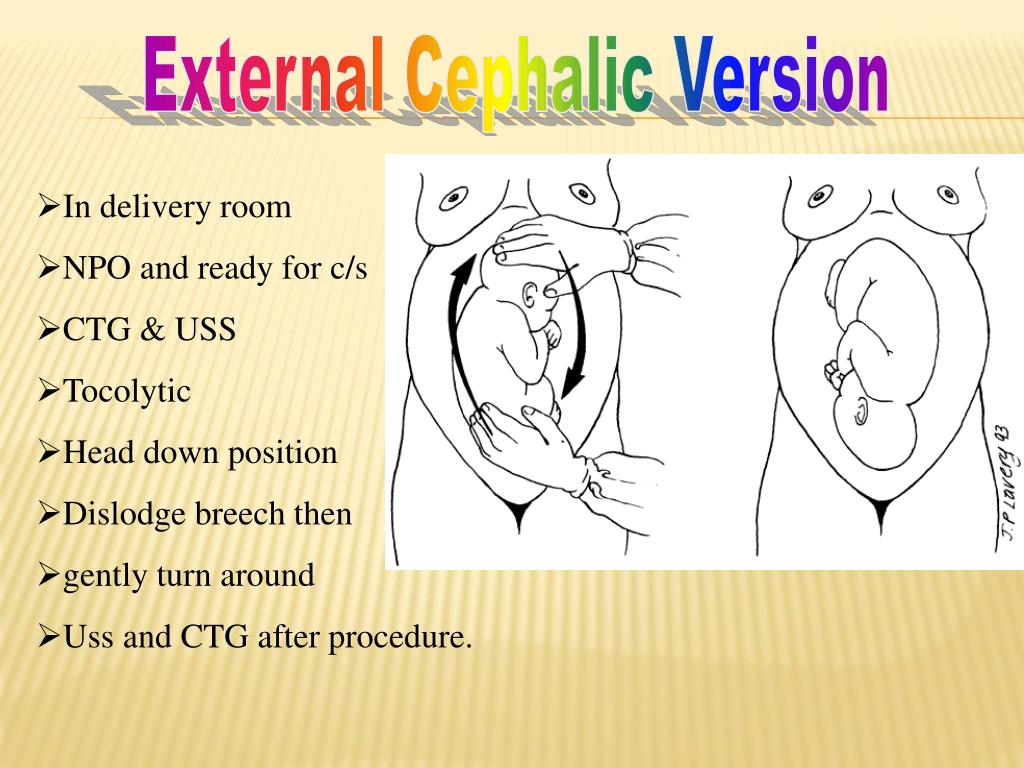
Breech babies can be in a few different positions:
- Frank breech: The baby’s buttocks are aimed at the vaginal canal with its legs sticking straight up in front of their body and the feet near their head.
- Complete breech: The baby’s buttocks are pointing downward and both the hips and the knees are flexed (folded under themselves).
- Footling breech: One or both of the baby’s feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of their body.
- Transverse lie: This is a form of breech presentation where your baby is positioned horizontally across your uterus instead of vertically. This would make their shoulder enter the vagina first.
How does a breech baby affect pregnancy?
Your pregnancy is usually not affected. Most breech babies are born healthy, although there is a slightly elevated risk for certain birth defects. Your baby’s movements may feel a little different.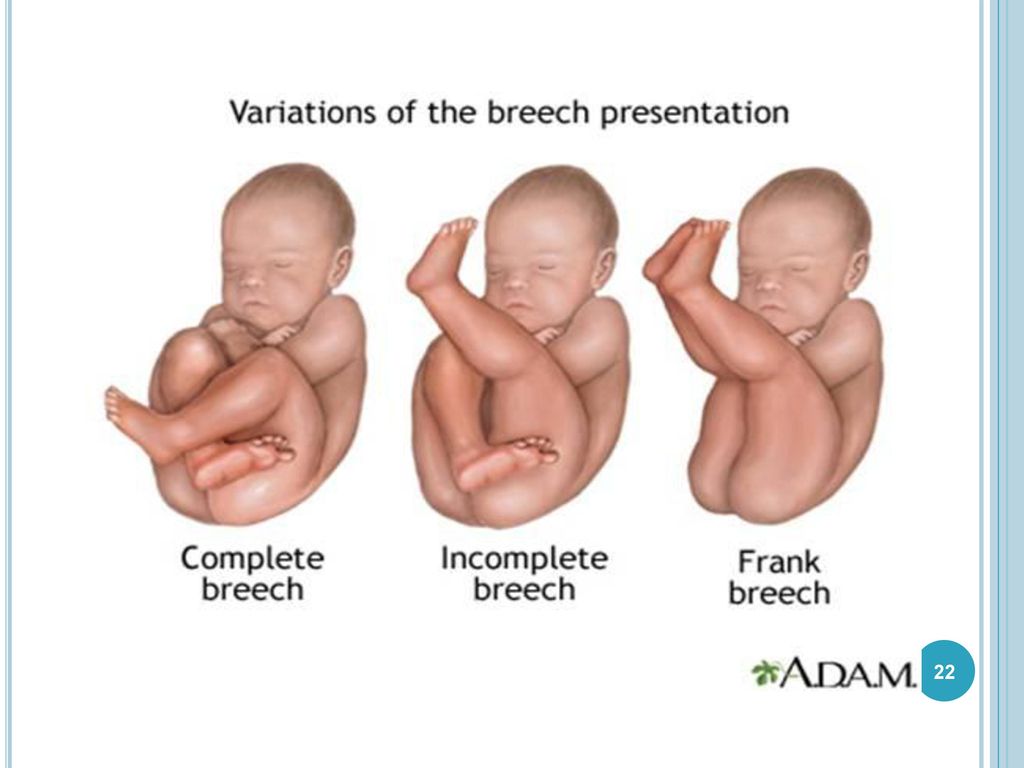 You will feel your baby’s kicks lower in your belly. You may feel a hard lump closer to your ribs. This is your baby’s head.
You will feel your baby’s kicks lower in your belly. You may feel a hard lump closer to your ribs. This is your baby’s head.
If you planned a vaginal delivery, a breech baby could change these plans. When your baby is breech, a vaginal delivery can be complicated and dangerous. Your healthcare provider may feel comfortable attempting a vaginal breech delivery, but in most cases, they will recommend a Cesarean birth (C-section).
How does a breech baby affect delivery?
If your baby presents in a breech position after 36 weeks of pregnancy, your birthing plan will likely change. It's usually unsafe for a breech baby to be born vaginally due to risks of injury. In most cases, a planned C-section is the safest way to deliver your baby. Some healthcare providers may be comfortable with a vaginal breech birth. In some cases, turning your baby to a head-down position while they are still inside your uterus is an option. Your baby is then born head first.
Symptoms and Causes
How can you tell if your baby is breech?
You may be able to tell if your baby is breech, especially if you have had past pregnancies where your baby was head-first. The places where you feel lumps and kicks might indicate that your baby is breech. Let your healthcare provider know where you feel movement. They will feel your belly or do an ultrasound to confirm that your baby is breech.
The places where you feel lumps and kicks might indicate that your baby is breech. Let your healthcare provider know where you feel movement. They will feel your belly or do an ultrasound to confirm that your baby is breech.
What causes a baby to be breech?
It’s not always known why a baby is breech. Some factors that may contribute to this position are:
- You are expecting multiples (twins or more). This makes it harder for each baby to get into the right position.
- There is too much or too little amniotic fluid.
- The uterus is not normal in shape or has abnormal growths such as fibroids. Most of the time, the uterus is shaped like an upside-down pear. If it's shaped differently, there might not be enough room for a full-grown baby to move into position.
- The placenta covers all or part of the cervix (a condition called placenta previa).
- The baby is preterm. This means they are less than 37 weeks gestation and may not have turned to a head-first position.

- Your baby has a birth defect that causes them to not turn head-down.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is a breech baby diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider may be able to tell which way your baby is facing by placing their hands at certain places on your abdomen. By feeling where the baby’s head, back and buttocks are, it’s usually possible to find out what part of the baby is positioned to come out of the vagina first. An ultrasound may be used to confirm the baby’s position.
When is a breech baby diagnosed?
Almost all babies are breech at some point. As your pregnancy progresses, your baby will naturally move to a head-down position — probably between 32 and 36 weeks. Your healthcare provider will feel your belly and determine where your baby is positioned. This will happen during most of your appointments in the third trimester. After 37 weeks, a breech baby usually does not turn on their own. Your healthcare provider will discuss delivery options with you.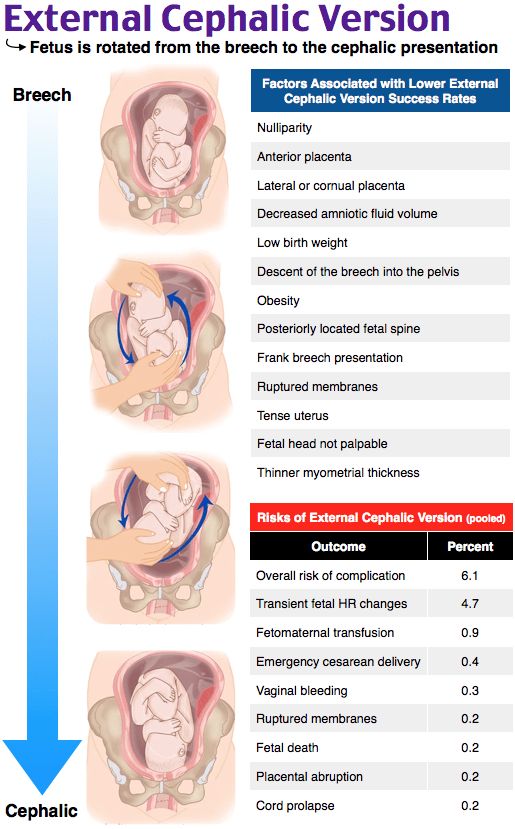
Management and Treatment
What are the options for treating a breech baby?
If your baby is breech at 37 weeks of pregnancy, your healthcare provider may:
- Try turning your baby in your uterus into the head-first position.
- Plan a C-section birth.
- Plan a vaginal breech birth.
What are some complications of having a breech baby?
The complications of having a breech baby usually do not occur until it's time to deliver. Some breech babies can be safely delivered through the vagina.
The risks of attempting a vaginal breech birth are:
- Injuries to your baby’s legs or arms such as dislocated or broken bones.
- Umbilical cord problems. The umbilical cord can be flattened or twisted during delivery. This can cause nerve or brain damage due to a lack of oxygen.
Will my doctor try to flip my baby if it's breech?
If your baby is breech, your healthcare provider may consider turning your baby so that you can have a vaginal delivery. In some cases, trying to turn your baby may not be safe or the risks outweigh the benefits.
In some cases, trying to turn your baby may not be safe or the risks outweigh the benefits.
Flipping your baby may not be safe if you have any of the following:
- Bleeding from your vagina.
- Placenta previa. This is when your placenta covers all or part of your cervix.
- A nonreactive nonstress test.
- An abnormally small baby.
- Low level of amniotic fluid.
- Low or high fetal heart rate.
- Premature rupture of the membranes.
- Twins or multiples.
The most common method used to turn a breech baby is called external cephalic version (ECV). It's performed by your healthcare provider around 37 weeks of pregnancy. This procedure is performed in the hospital just in case an emergency occurs. It involves placing hands on your abdomen and applying firm pressure to turn your baby to a head-down position while your baby is still in your uterus. It is about 65% effective and carries some risks.
What are the risks of turning my breech baby?
The risks of ECV include the following:
- Premature labor.
- Premature rupture of the amniotic sac.
- Blood loss for either you or your baby.
- Emergency C-section.
- Your baby might turn back to the breech position.
Although the risk of having these complications is small, some healthcare providers prefer not to try to flip a breech baby.
Will my breech baby flip on their own?
Most babies will flip to a head-down position before they reach full term (37 weeks). If your baby is still in a breech position at this time, your healthcare provider will determine if you can deliver vaginally or if you will need a C-section.
How can I flip my baby if it's breech?
Some women will try at-home methods to flip their baby to a head-first position. They may help, but there is no scientific evidence that they work.
- Bridge position: Lie on the floor with your legs bent and your feet flat on the ground. Raise your hips and pelvis into a bridge position. Hold this position for 10 or 15 minutes several times a day.

- Child’s pose: Rest in the child’s pose for 10 to 15 minutes. It can help relax your pelvic muscles and uterus. You can also rock back and forth on your hands and knees or make circles with your pelvis to promote activity.
- Music: Place headphones or a speaker at the bottom of your uterus to encourage your baby to turn.
- Temperature: Try placing something cold at the top of your stomach where your baby’s head is. Then, place something warm at the bottom of your stomach.
A chiropractic technique, called the Webster technique, can also help your uterus relax. Some providers even recommend acupuncture. Both of these techniques need to be done by a professional that your healthcare provider has recommended.
Prevention
How can I reduce my risk of having a breech baby?
There is nothing you can do to prevent your baby from being in a breech position. If your baby is in a breech position, it’s not because you did anything wrong.
Outlook / Prognosis
Can you deliver vaginally with a baby breech?
It's possible to deliver a breech baby vaginally. It can be more dangerous for the baby and the risk of injury is much higher. If the umbilical cord is compressed during birth, the baby could be deprived of oxygen and this could harm their brain and nerves. The cord could also slip around the baby’s neck or arms, causing injury. Healthcare providers have various levels of comfort with vaginal deliveries of breech babies. Talk to your provider about the risks and benefits of different types of birth for a breech baby.
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following symptoms during pregnancy:
- Severe cramping or contractions.
- Vaginal bleeding.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
Learning your baby is breech may give you concerns about your delivery. It’s completely natural to have questions.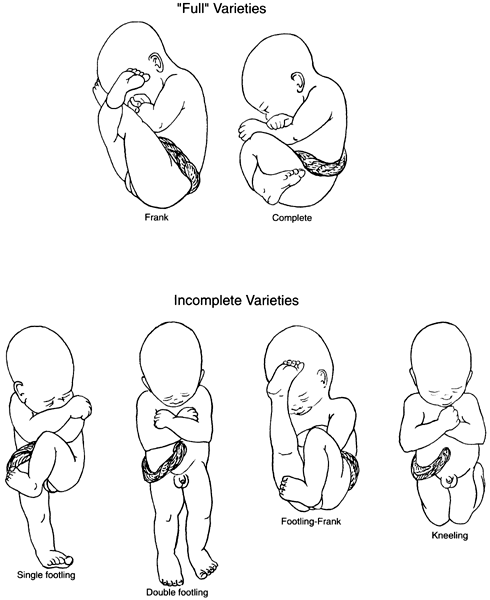 Some questions to ask your doctor can include:
Some questions to ask your doctor can include:
- How can I tell if my baby is breech?
- Is my baby OK?
- What are the benefits and risks of turning my baby?
- What are my options for delivery if my baby remains in the breech position?
- What are the health risks to my baby and me if they are born breech?
Frequently Asked Questions
Do birth defects cause breech position?
Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies. It might be the reason that the baby didn’t move to the head-down position. Most babies who are breech at delivery are born without any health complications.
Will I need a C-section if my baby is breech?
Most of the time, a C-section is the safest way to deliver a breech baby. Your risks of developing complications are much higher if you try to deliver a breech baby through the vagina. However, some healthcare providers may feel comfortable performing a vaginal breech birth.
How does labor start if your baby is breech?
Having a breech baby doesn’t change some of the first signs of labor like contractions or rupturing of your membranes. In most cases, your healthcare provider will recommend a planned C-section. If your delivery is planned, you may not have any labor symptoms.
In most cases, your healthcare provider will recommend a planned C-section. If your delivery is planned, you may not have any labor symptoms.
If you are in labor and go to the hospital for delivery, your provider will confirm your baby’s position a final time. Your provider could attempt a vaginal delivery, but it's more likely they will proceed with a C-section to be safe.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Having a breech baby can be unexpected and change the vision you had for childbirth. Talk to your healthcare provider about what to expect during a breech delivery. They can help you understand the risks and benefits of a breech birth so that you and your baby are kept safe.
Legal status of the municipal state institution \ Acts, samples, forms, contracts \ Consultant Plus
- Main
- Legal resources
- Collections
- Legal status of the municipal government institution
A selection of the most important documents upon request Legal status of the municipal government institution (legal acts, forms, articles, expert advice and much more).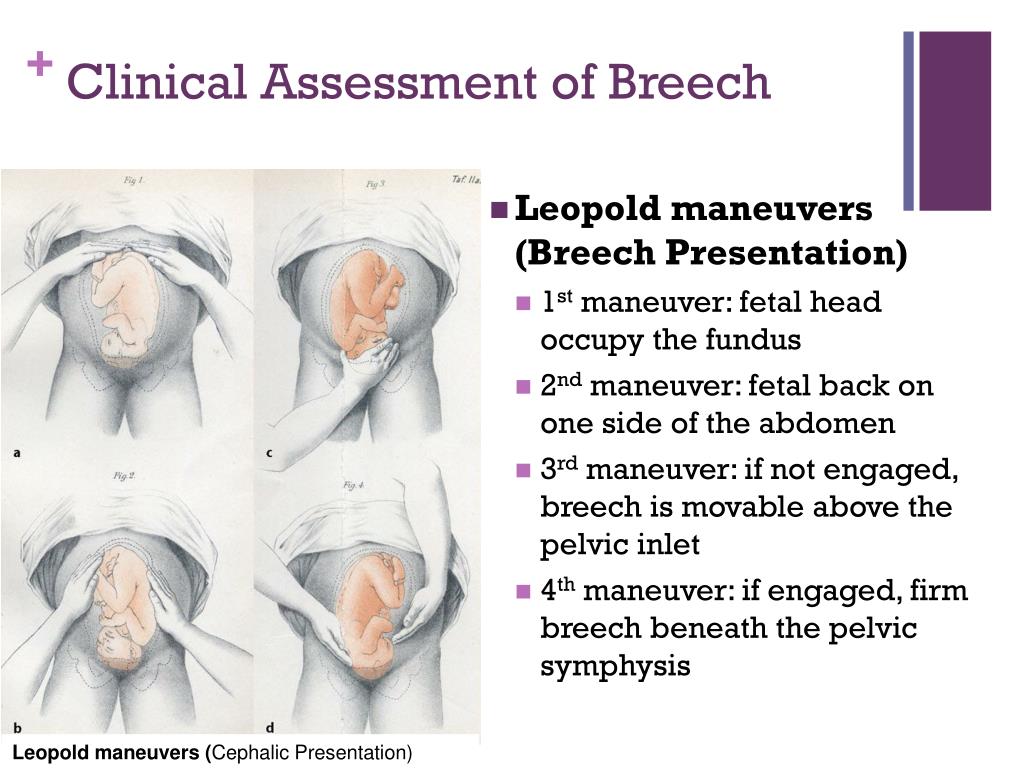
- State institution:
- Bus GOV RU
- Bus.gov.ru
- Bankruptcy of the Institution
- Budget organization is
- Budget estimate is
- Show all →
- Kazakh:
- Bus GOV RU
- Bus.gov.ru
- Bankruptcy of an institution
- Budget organization is
- Budget estimate is
- Show all →
Judicial practice
Register and receive trial access
to the ConsultantPlus system free for 2 days
Determination of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated 12.12.2020 N 306-ESP20-18969 in the case N A12-776/2019
Require cassation of judicial acts in the case of recovery of unjust enrichment in the form of overpayment under a land lease agreement, interest for the use of other people's money.
Decision: The transfer of the case to the Judicial Collegium for Economic Disputes of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation was denied, since the court of appeal came to the conclusion that during the disputed period, it was the committee that was the body authorized to dispose of land on behalf of the state, and it was he who was the administrator of income, produces calculation of rent. In accordance with clause 19Decree No. 13, the monetary obligations of state institutions within the meaning of the concepts enshrined in Article 6 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation include, among other things, their obligations to pay certain funds from the budget in accordance with the fulfilled conditions of a civil law transaction or in accordance with the provisions law, other legal act, the terms of the contract, agreement, in connection with this, in the indicated order, judicial acts are executed on the recovery of funds from a state institution under state (municipal) contracts, unjust enrichment, on the return of overpaid payments on transactions or by virtue of the law .
Articles, comments, answers to questions
Register and get trial access
to the ConsultantPlus system free of charge for 2 days
.G.)
("Perm Legal Almanac. Annual Scientific Journal", 2018, N 1) The projection of this norm on the norms of civil legislation, whose regulatory burden has always included establishing the status of participants in property relations acting on the basis of equality, allows achieving legal certainty only in the status of a state treasury institution and a municipal treasury institution. The rest of the categories of state customers from the point of view of civil legal identification are in the position of unidentified. Some - state corporations created in the form of an independent organizational and legal form, as well as management bodies of extra-budgetary funds - are not displayed at all within the boundaries of civil law, others are public authorities, despite the presence of Art. 125 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation on the procedure for the participation of the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipalities in civil legal relations, are named in the legislation on the contract system through concepts that are for civil law to a greater extent the concepts of "secondary order".
Register and get trial access
to the ConsultantPlus system free of charge for 2 days
"Rent (leasing)"
(4th edition, revised and supplemented)
(dia99ross V.V.) ", "Rosbuh", 2020) The definition of a public institution is contained in Article 6 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the RF BC), according to which a public institution is a state (municipal) institution that provides state (municipal) services, performs work and (or ) performance of state (municipal) functions in order to ensure the implementation of the powers of state authorities or local self-government bodies provided for by law, the financial support of which is carried out at the expense of the relevant budget on the basis of the budget estimate.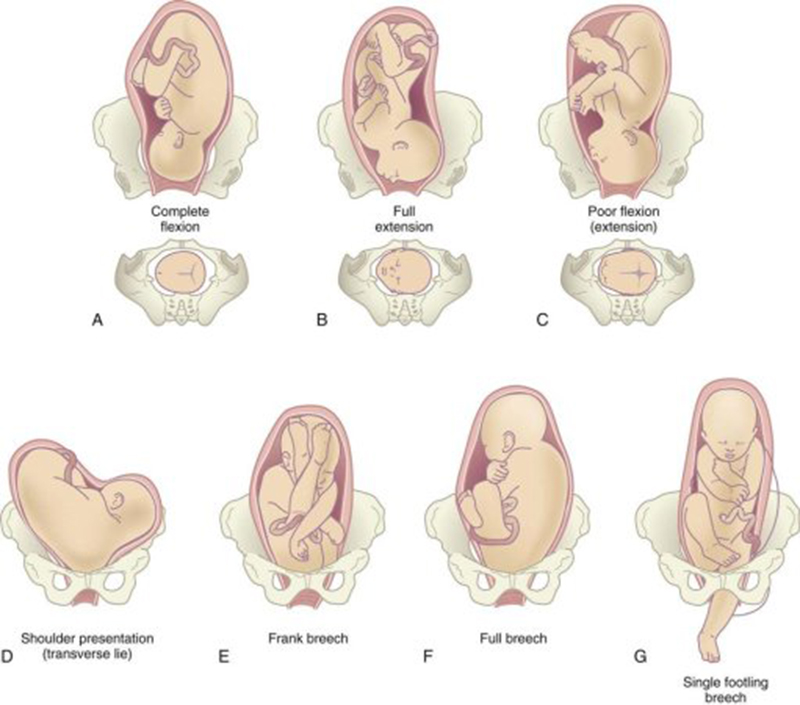 At the same time, in accordance with paragraph 11 of Article 161 of the RF BC, the norms establishing the specifics of the legal status of state-owned institutions apply to state and municipal bodies, taking into account the provisions of the budget legislation of the Russian Federation that establish the powers of these bodies.
At the same time, in accordance with paragraph 11 of Article 161 of the RF BC, the norms establishing the specifics of the legal status of state-owned institutions apply to state and municipal bodies, taking into account the provisions of the budget legislation of the Russian Federation that establish the powers of these bodies.
Normative acts
Register and receive trial access
to the ConsultantPlus system free for 2 days
of the Russian Federation of 25.04.2011 N 02-06-07/1546
1. In the inter-reporting period-in the inter-report reflection by a budgetary institution on the accounts of budgetary accounting of operations to close account indicators within the framework of the end of 2010 and before reflection on the accounts of the Unified Chart of Accounts of Accounts operations in 2011, are formed on the basis of the Certificate (f. 0504833) incoming balances on the accounts of the Unified Chart of Accounts of Accounts and Instructions for its application, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation N 157n dated 01.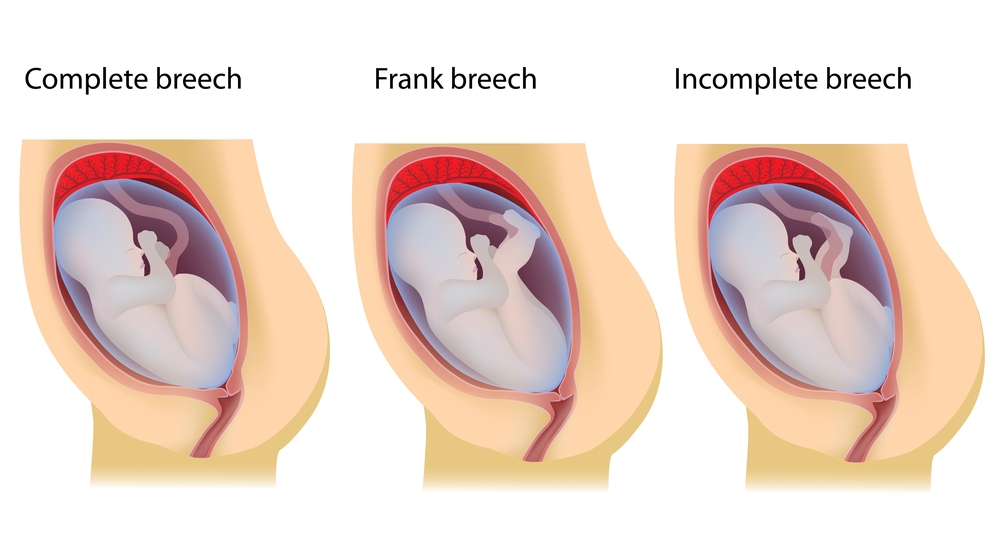 12.2010 (hereinafter the Unified Chart of Accounts, Instruction 157n), taking into account the specifics of the legal status of state (municipal) state institutions (hereinafter - state institutions).
12.2010 (hereinafter the Unified Chart of Accounts, Instruction 157n), taking into account the specifics of the legal status of state (municipal) state institutions (hereinafter - state institutions).
Documents - Government of Russia
Site search optionsClose
Next news
Previous news
- Small font size
- Normal font size
- Large font size
- Enable/disable image display On Off
Government of Russia
-
- Demographics
- Health
- Education
- Culture
- Society
- State
-
- Employment and labor
- Technological development
- Economics.
 Regulation
Regulation - Finance
- Social services
-
- Ecology
- Housing and cities
- Transport and communications
- Energy
- Industry
- Agriculture
-
- Regional development
- Far East
- Russia and the world
- Security
- Law and justice
- Selected documents with references to them
- Search across all documents
Document type
Decree of the Government of the Russian FederationOrder of the Government of the Russian FederationOrder of the President of the Russian FederationDecree of the President of the Russian FederationFederal LawFederal Constitutional LawCode
Number
Title or text of the document
Signing date
Monday 13 February
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 13, 2023 No.
 206
206 On introducing amendments to paragraph 6-1 of the Rules for investing the funds of the National Wealth Fund in securities of Russian issuers related to the implementation of self-sustaining infrastructure projects, and recognizing as invalid a separate provision of the act of the Government of the Russian Federation
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 13, 2023 No. 204
On Amendments to Clause 4 of the Procedure for the Creation, Reorganization, Change of Type and Liquidation of Federal State Institutions, as well as Approval of Charters of Federal State Institutions and Amendments to Them
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 13, 2023 No.
 205
205 On amendments to the Rules for the provision of financial support at the expense of the state corporation - the Fund for Assistance to the Reform of Housing and Communal Services for the modernization of communal infrastructure systems that are state-owned or municipally owned by a constituent entity of the Russian Federation
Saturday, February 11
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 11, 2023 No. 199
On amendments to paragraph 12-1 of the Regulation on payment of additional expenses for medical, social and professional rehabilitation of insured persons who have received health damage due to accidents at work and occupational diseases
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 11, 2023 No.
 202
202 On amendments to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2011 No. 1121
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 11, 2023 No. 198
On amendments to paragraph 6 of the Rules for the provision and distribution of other interbudgetary transfers for the implementation of social development plans for economic growth centers of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation that are part of the Far Eastern Federal District and the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 11, 2023 No.
 200
200 On Amendments to the Annex to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2016 No. 1487
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 11, 2023 No. 195
On Amendments to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 804 of August 8, 2012 and Recognizing the Provisions of Certain Acts of the Government of the Russian Federation as Invalid
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 11, 2023 No.
 197
197 On amendments to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated August 28, 2015 No. 899
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 11, 2023 No. 201
On amendments to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 19, 2017 No. 986
Friday February 10
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 10, 2023 No.
 191
191 On amendments to the Rules for determining the amount of rent, as well as the procedure, conditions and terms for paying rent for land owned by the Russian Federation
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 10, 2023 No. 192
On amendments to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 12, 2020 No. 1816
Thursday, February 9
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 09.
 02.2023 No. 189
02.2023 No. 189 On Amendments to the Rules for State Registration of the Disposition of the Exclusive Right to an Invention, Utility Model, Industrial Design, Trademark, Service Mark, Registered Integrated Circuit Topology, Computer Program, Database under an Agreement and Transfer of the Exclusive Right to Them Without an Agreement
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 09.02.2023 No. 182
On Amendments to Certain Acts of the Government of the Russian Federation
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 09.
 02.2023 No. 188
02.2023 No. 188 On the approval of the Rules for the direction by the governing bodies of the Pension and Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund in 2023 to the National Welfare Fund of income from the receipt of insurance premiums, the payment deadline for which, in accordance with the decision of the Government of the Russian Federation in 2022, was extended by 12 months, by amending the consolidated budget breakdown of the budget of the Pension and Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation and the budget of the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 09.02.2023 No. 185
On amendments to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 27, 2008 No. 795
795
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 09.02.2023 No. 187
On Amendments to the Regulation on Licensing Activities for the Production of Biomedical Cellular Products
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 09.02.2023 No. 183
On amendments to the Regulations on the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation
February 8, Wednesday
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 08.