Blood clots in vomit during pregnancy
Vomiting Blood During Pregnancy: Causes and Treatment
Vomiting is so common in pregnancy that some women first discover they’re expecting when they suddenly can’t hold down their breakfast.
In fact, up to 90 percent of pregnant women have nausea and vomiting, usually in the first trimester. Fortunately, this so-called “morning sickness” (which can happen at any time of day) typically goes away by week 12 to 14.
So you’re used to the vomiting, but one morning you spot a red to brown tinge in your vomit — blood.
While vomiting blood during pregnancy (or any time) isn’t a good sign, it does happen. It even has a medical name, hematemesis.
There are several common health reasons for why you may be vomiting blood during pregnancy. Most of these will go away on their own after your first trimester or after you’ve had your baby. But all require a check-in with your doctor.
While vomiting is normal during pregnancy, vomiting blood is not. See your doctor right away if you see blood in your vomit.
![]()
We’ll give you the bottom line first: See your doctor right away if you have blood in your vomit.
Some of the causes for vomiting blood have to do with the upper part of your digestive tract — your mouth, throat, esophagus (the tube from your mouth to your stomach), and stomach. Your doctor may take a closer look at your esophagus with an endoscopy.
Your doctor might also recommend some other tests and scans, such as:
- oxygen readings
- blood tests
- ultrasounds
- an MRI
- a CT scan
- an X-ray
Is vomiting blood a sign of miscarriage or pregnancy loss?
Vomiting blood on its own is not a sign of a miscarriage. Your pregnancy is likely still fine. However, if you have other specific symptoms along with vomiting blood, there might be cause for concern.
Get urgent medical attention if you also have:
- severe nausea and vomiting
- severe stomach cramps
- mild to severe back pain
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- a serious headache
- heavy spotting
- period-like bleeding
- vaginal discharge of fluid or tissue
Bleeding gums
Some women get sore, swollen, and bleeding gums while they’re pregnant. This is also called pregnancy gingivitis.
This is also called pregnancy gingivitis.
Your gums might be more sensitive and bleed because pregnancy hormones increase the flow of blood to the gums.
You might have other symptoms like:
- red gums
- swollen or puffy gums
- tender or inflamed gums
- sensitivity when you eat and drink
- receding gums (your teeth look a bit longer)
- bad breath
You may not notice it, but all the pregnancy vomiting might make your sensitive gums even more irritated and sore. This can lead to gum bleeding, and the blood can show up when you vomit. Not a pretty mix.
While pregnancy gingivitis can happen even if you have good dental health, brushing your teeth at least twice a day and flossing once a day can help keep your gums healthy — and prevent the bleeding.
Nosebleeds
Pregnancy increases blood flow everywhere, even in your nose. This can make the blood vessels inside your nose swell up.
More blood and wider blood vessels can make you more likely to have a nosebleed while you’re pregnant — even if you don’t normally get them.
Depending on where in your nose the bleed is, or if you’re lying down, the blood may not trickle out of one or both nostrils. Instead, the blood may flow to the back of your throat or mouth and come out if you happen to throw up shortly after.
Blood from a nosebleed may be bright red to dark red. You’ll likely also have a stuffy nose — another fun part of pregnancy!
Mouth or throat irritation
If you’re seeing small bits of blood, or dark, dried blood in your vomit, it might be from your throat or mouth.
Too much vomiting can irritate the lining and back of your throat. This is because vomit is usually mixed with acidic stomach juices.
You’ve probably felt the acid burn at the back of your throat if you’ve ever had bad heartburn. This can lead to bleeding, or crusting, that’s carried out when you vomit again.
Your throat and mouth might also feel sore, raw, and swollen.
Esophageal irritation or tear
The esophagus tube runs from the mouth and throat down to the stomach. Vomiting a lot can irritate the lining of the esophagus. This can lead to small amounts of blood or dried blood in your vomit.
Vomiting a lot can irritate the lining of the esophagus. This can lead to small amounts of blood or dried blood in your vomit.
More serious bleeding might be caused by an esophageal tear. This condition is rare — but serious — and can happen any time during pregnancy. Fortunately, it’s a less common cause of bleeding while vomiting in your first trimester.
An esophageal tear happens when there’s too much pressure inside the stomach or esophagus. In rare cases, this can happen later in the third trimester of pregnancy. This might be because of a combination of carrying more weight and having other health conditions.
More common causes of an esophageal tear include:
- alcohol misuse
- bulimia
- a hernia
- high blood pressure
- preeclampsia
- severe coughing
- stomach infections
If you have an esophageal tear, you’ll likely see a lot of bright red blood in your vomit. You might also have other serious symptoms, such as:
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- difficulty breathing
- serious heartburn
- severe stomach pain
- back pain
- abnormal tiredness
- dark or tarry poop
Stomach ulcer
Stomach ulcers are open sores in the lining of your stomach. Sometimes, these tiny wounds can bleed and you might see bright red or dark blood in your vomit.
Sometimes, these tiny wounds can bleed and you might see bright red or dark blood in your vomit.
If you’ve had stomach ulcers before, they might cause problems again while you’re pregnant.
Stomach ulcers are usually caused by:
- a bacterial infection (called H. pylori)
- taking medications like aspirin and ibuprofen
- too much stress
A stomach ulcer can worsen nausea and vomiting while you’re pregnant. You might also have symptoms like:
- stomach pain or discomfort
- heartburn
- burping
- bloating
- feeling full easily
- weight loss
Medical treatment for blood in your vomit depends on the cause.
If you have a stomach ulcer, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic to clear it up. Changing your diet and avoiding over-the-counter medications like aspirin (unless your OB-GYN advises it as part of your pregnancy regimen) can also help.
Your doctor may recommend medication to help ease the nausea and vomiting. Check with your doctor before taking over-the-counter medication. Some common drugs for nausea might not be right for you during pregnancy.
Check with your doctor before taking over-the-counter medication. Some common drugs for nausea might not be right for you during pregnancy.
More serious causes of blood in your vomit — like an esophageal tear — may need medications and even surgery to repair.
Home remedies for vomiting
Until you talk to your doctor about the cause of the blood in your vomit — which you should do right away — don’t pursue home remedies for throwing up blood.
If you get treatment for the cause but are still struggling with difficult morning sickness, again talk to your doctor about solutions.
Remember, even natural remedies and herbs are powerful drugs. Some may even give you more heartburn or stomach irritation, which could worsen the issue!
A tried and tested home remedy for nausea and vomiting is ginger. In fact, a 2016 medical review found that ginger helped improve nausea and vomiting in pregnant women who took 250 milligrams (mg), 4 times a day.
Try adding fresh ginger to tea, water, or juice. You can also use ginger powder, syrup, juice, capsules, or tablets, as well as candied ginger and dried ginger.
You can also use ginger powder, syrup, juice, capsules, or tablets, as well as candied ginger and dried ginger.
Other home and natural remedies for nausea and vomiting include:
- vitamin B-6 (likely already in your prenatal vitamin)
- peppermint
- certain juices, like cranberry or raspberry
Vomiting blood during pregnancy has more to do with you than your baby. But it can cause health concerns for both of you. Tell your doctor if you spot any amount of blood in your vomit. Don’t ignore it.
You may not need any treatment at all. If you do, the right treatment can help prevent complications.
Serious bleeding inside your body can lead to health complications like too much blood loss and shock. Signs and symptoms that something might not be quite right include:
- severe nausea and vomiting
- fast, shallow breathing
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- blurred vision
- confusion
- cold or clammy skin
- not peeing enough
- dark poop or blood in your poop
Blood in your vomit is definitely not nice to see. However, there are several simple reasons that you might be vomiting blood.
However, there are several simple reasons that you might be vomiting blood.
The vomiting and retching itself could be causing it. Other side effects of pregnancy may also be to blame.
Let your doctor know if you see blood in your vomit. A checkup is important, just in case there’s another cause for the blood.
You may need medication or other medical treatments. Treating the cause quickly and properly can help keep you and your baby healthy.
Cuases, Signs & Home Remedies
A common yet relatively unknown problem that many women experience in their pregnancy is vomiting blood. Although vomiting blood in the early stages of pregnancy is normal, it could be a sign of an underlying condition. Experiencing morning sickness or vomiting for a long period of time could cause vomiting of blood during pregnancy. If you are pregnant and vomit severely, it could rupture your oesophagus lining, and the blood may spew out. There is no reason to panic as it could be treated. However, there are some serious conditions which could lead to vomiting of blood during pregnancy. These conditions could be a sign of worry and must be diagnosed and treated appropriately.
However, there are some serious conditions which could lead to vomiting of blood during pregnancy. These conditions could be a sign of worry and must be diagnosed and treated appropriately.
Also Read: Home Remedies for Vomiting in Pregnancy
What Is Hematemesis (Vomiting Blood)?
Vomiting blood during pregnancy is known as hematemesis and it may happen because of various medical reasons ranging from a small nosebleed or serious bleeding of the intestine. Hematemesis is not characterized by the presence of streaks of blood in the bile. In this condition, the blood looks black or dark brown in colour similar to ground coffee. Vomiting blood in the first trimester of pregnancy is common, as morning sickness is at its worst then. The bleeding occurs due to a tear in the oesophagus and the bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract is primarily caused by the force of the previous vomiting.
Also Read: Vomiting in Third Trimester while Pregnant
Facts About Hematemesis
Here’s what may happen when you vomit blood during pregnancy.
- Bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract is one of the main causes of hematemesis during pregnancy.
- Vomiting continuously can increase the risk of melaena – a condition which leads to black and tarry stools with the presence of blood.
- Haematin acid is the main cause of the presence of blood in vomit.
- When some large blood vessels bleed heavily, fresh blood appears in the vomit.
- Vomiting of blood causes dizziness and slight abdominal pain.
- Vomiting blood could lead to a drop in blood pressure levels.
- Vomiting forcefully leads to a sudden mucosal tear in the oesophagus (called the Mallory-Weiss tear), which can also lead to hematemesis.
Causes of Hematemesis During Pregnancy
Vomiting blood during pregnancy has several factors associated with it. Some of the common causes of vomiting of blood during pregnancy are as follows:
- Gastritis: An inflammation of the stomach causes harmful bacteria, Helicobacter pylori, to infect the inner lining of the stomach, which leads to gastritis.
 Acute gastritis leads to minor inflammation whereas chronic gastritis causes chronic inflammation. This disorder may eventually lead to excessive vomiting of blood, which is often red in colour. It may also be accompanied by abdominal pain and weakness.
Acute gastritis leads to minor inflammation whereas chronic gastritis causes chronic inflammation. This disorder may eventually lead to excessive vomiting of blood, which is often red in colour. It may also be accompanied by abdominal pain and weakness. - Dehydration: One of the main reasons why you may vomit blood during pregnancy is dehydration. When the body runs out of fluid, it exerts excess pressure causing the vomit to spew bile pigments and blood. Lack of fluids causes nausea and lead to vomiting.
- Starvation: It is a known fact that an expectant woman needs to have smaller meals at regular intervals to satisfy her hunger. If you starve yourself during pregnancy, your empty stomach could make you feel sick and you might vomit blood. It may sound strange, but if you don’t eat enough during pregnancy, your body may rebel by vomiting.
- Rupture of the Oesophagus: It is very common to feel nauseous and vomit repeatedly during pregnancy.
 But constant episodes of vomiting, especially forceful ones could cause a rupture in the oesophagus. This injury could result in stains of blood in the vomit.
But constant episodes of vomiting, especially forceful ones could cause a rupture in the oesophagus. This injury could result in stains of blood in the vomit. - Unhealthy Diet: A lack of a well-balanced diet during pregnancy can also lead to vomiting of blood. It is not uncommon if you feel like throwing up after meals or early in the morning if you are not following the diet chart. The body has its own way to fight back against things that it cannot accept.
- Hypertension: Pregnancy usually leads to hypotension but if the woman has hypertension, then it may lead to vomiting of the blood, but this happens rarely. Portal hypertension can also lead to hematemesis. Doctors always suggest pregnant women to take ample rest and stay in a peaceful and happy environment. Stress can lead to an upset stomach, eventually leading to vomiting of blood.
- Food Poisoning: Food poisoning is a gastrointestinal problem. Eating stale or toxic food can put you at an added risk during pregnancy.
 Ensure that you are cautious about hygiene and wash your fruits and vegetables well before eating them. Stay away from foods that could trigger allergies and complications.
Ensure that you are cautious about hygiene and wash your fruits and vegetables well before eating them. Stay away from foods that could trigger allergies and complications. - Medications: Taking over-the-counter medicines for pain like aspirin and Ibuprofen can lead to irritation and bleeding. Taking these medicines reduce the production of mucus and irritate the lining of the stomach. Aspirin is known to clot the blood and interfere with the function of blood platelets. Prenatal vitamins are also known to cause nausea and vomiting.
- Rupture of the Gastrointestinal Tract: Vomiting puts pressure on the chest, oesophagus, and abdomen. The sudden increase in pressure causes a rupture in the intestinal tract. This results in vomiting causing chest inflammation. You might experience chest pain, sweating, and shortness of breath if there is a rupture in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Cirrhosis: Drinking alcohol excessively or autoimmune diseases like hemochromatosis (absorption of the excess amount of iron in the blood) leads to cirrhosis.
 Cirrhosis leads to the dilation of blood vessels, which start rupturing and affect the oesophagus too. Cirrhosis is a serious condition affecting the health of the liver, and people affected with this disease tend to vomit large quantities of bright red blood.
Cirrhosis leads to the dilation of blood vessels, which start rupturing and affect the oesophagus too. Cirrhosis is a serious condition affecting the health of the liver, and people affected with this disease tend to vomit large quantities of bright red blood.
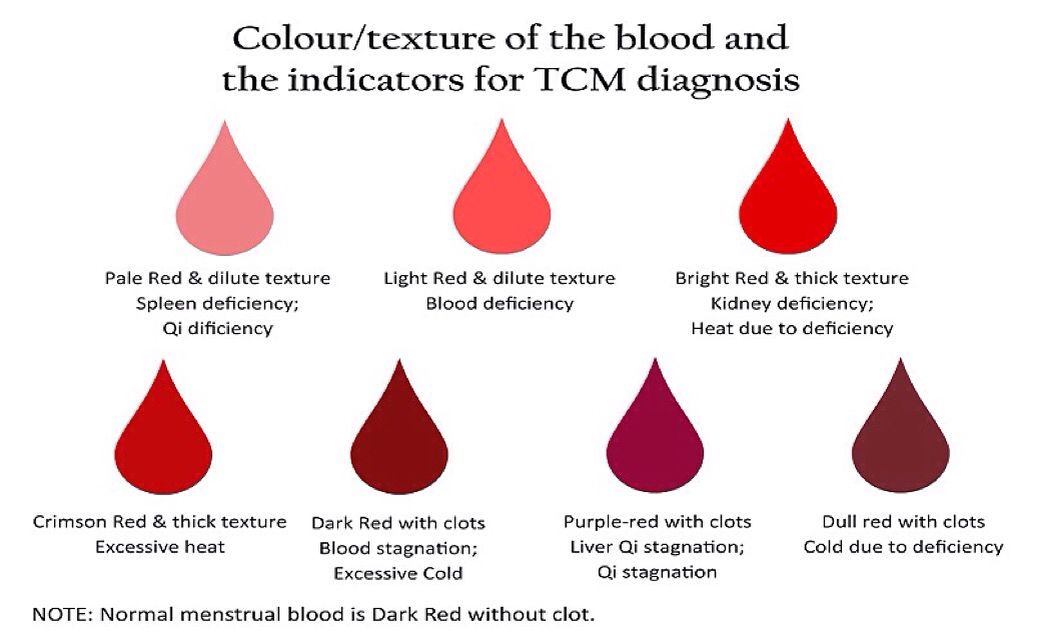
What Is the Colour of the Blood in the Vomit?
Here’s how the blood may appear if you vomit during pregnancy.
- If the bleeding is caused by an injury to the stomach or duodenum (first part of the small intestine), then the blood in the vomit may appear maroon or dark brown.
- If bleeding is caused by a tear in the oesophagus, the blood will appear red and fresh.
The colour and consistency of the blood vomited differs as per the cause of bleeding. Apart from bleeding, pregnant women also experience other symptoms which need to be given attention. Some of the common symptoms associated with vomiting of blood during pregnancy are:
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain and discomfort
- Enlargement of pupils
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
How Is the Diagnosis Done?
For diagnosis, the doctor may ask you questions about the colour of the blood discharged or any injuries that you may have had in the past or present.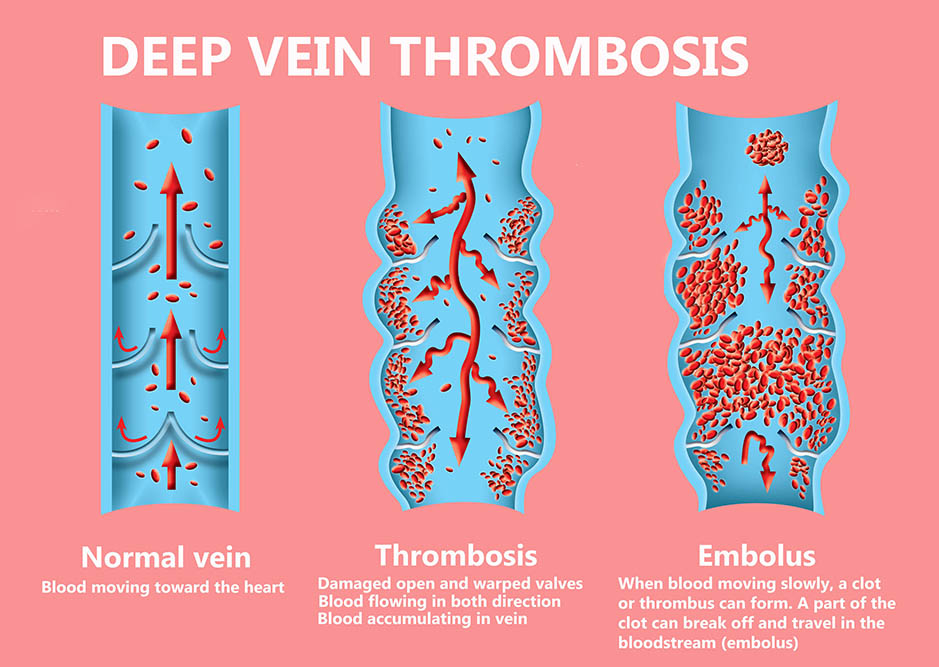 To diagnose any internal causes, the doctor may need to conduct imaging tests to look deeper. Scans determine the injury and the extent of the damage caused to suggest appropriate treatment. Common imaging tests used by gynaecologists include:
To diagnose any internal causes, the doctor may need to conduct imaging tests to look deeper. Scans determine the injury and the extent of the damage caused to suggest appropriate treatment. Common imaging tests used by gynaecologists include:
- Ultrasound tests
- X-ray
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
- Nuclear medicine scan
- Endoscopy
- Blood tests
Complications Associated With Hematemesis While Pregnant
A few complications that arise because of vomiting blood during pregnancy are mentioned below.
- Choking: You may often find yourself struggling to swallow food after an episode of vomiting or if you vomit continuously.
- Anaemia: Due to the loss of blood, your body may become deficient in healthy red blood cells. You may suffer from loss of energy or anaemia. It is advisable to intake healthy and nutritious food to restore blood loss.
- Stress or Depression: Vomiting blood during pregnancy can make you feel stressed or depressed.
 Stress may lead to further complications like pale skin, rapid breathing, dizziness, and low urine discharge.
Stress may lead to further complications like pale skin, rapid breathing, dizziness, and low urine discharge.
Prolonged episodes of choking, stress or low levels of anaemia must not be ignored. It is best to consult a doctor to avoid any complication.
Treatment
The treatment begins after ascertaining the cause of bleeding and administering the appropriate line of treatment.
- After vomiting, there is a deficiency in optimum fluid levels. A pregnant woman will need to stay hydrated.
- If severe dehydration occurs, the patient would need to be admitted to a hospital to ensure she gets body fluids and supplements through intravenous saline.
- A healthy and nutritious diet will be suggested to ensure that the right amount of nutrients and minerals are being supplied to the mother and the baby.
If there is a huge amount of blood loss caused by vomiting, a doctor may prescribe the following treatments:
- Blood transfusions
- Administering oxygen
- Endoscopic treatment to determine any rupture and treat it accordingly
- Extraction of fluids through veins
- A surgical procedure in case of several internal haemorrhage or ulcer
Prevention
Prevention is better than cure, and it certainly stands true in case of vomiting of blood during pregnancy. A few steps that could help prevent vomiting of blood are:
A few steps that could help prevent vomiting of blood are:
- Avoid intake of alcohol as it causes inflammation of the stomach.
- Quit smoking.
- Avoid eating spicy food as it causes irritation of the stomach and acid reflux during pregnancy.
- Limit your intake of medicines especially painkillers, aspirin, etc.
Home Remedies
If you vomit blood and notice blood clots, you must consult a doctor. Loss of blood can make you feel weak. Vomiting blood may also leave an unpleasant taste in your mouth. Apart from medical advice, there are a few tips that you can follow to treat nausea and vomiting while pregnant.
- Drink Fruit Juice: Regular intake of water and fruit juice can help you stay hydrated and recover from spells of dehydration. Electrolyte solutions are also a good alternative to combat dehydration. Keep yourself hydrated by drinking at least 2-3 litres of water in a day. Drinking water will help flush out the toxins from the body and also balance the production of urine in your body.

- Follow a Balanced Diet: Unarguably, a diet which is well planned, balanced and proportionate in vital nutrients and minerals will go a long way in maintaining optimum energy levels and reducing nausea. So eat healthy foods and drink lots of water.
- Opt for Small and Light Meals: Nausea is more common in the morning. Avoid having heavy meals at night and have a light breakfast to prevent nausea. Don’t overeat – stick to a fixed pattern of eating. For example, eat at a 3-4 hour interval to give yourself enough time to digest the food. Eating a lot at once might make you feel full and cause vomiting.
- Avoid Oily Food: Curb your urge to gorge on fatty or spicy foods. Foods high in fat and spice can cause the stomach lining to swell and cause acidity. Stick to boiled foods which are low on spice.
- Drink Ginger Juice: Drinking ginger juice is an age-old remedy for nausea and morning sickness.
 It is highly recommended to have ginger juice in the morning.
It is highly recommended to have ginger juice in the morning. - Prenatal Yoga: Prenatal yoga exercises or even light exercises have proven to be good for curing nausea.
- Sleep Well: Get enough sleep at night and ensure that you do not feel suffocated or claustrophobic where you sleep. Ensure that you breathe well at night for a good night’s sleep.
- Take Adequate Rest: Avoid stressing yourself – take ample rest and allow your body to relax and unwind to stay healthy during pregnancy.
Opt for natural remedies in case you suffer from nausea. If you find that your vomiting spells are not getting controlled by home remedies, then seek medical advice. If you do vomit blood, try and consult a doctor to rule out any issue in the beginning itself. Your doctor will guide you the best, so consult her if needed. Have a happy and healthy pregnancy!
Also Read: Everything You Need to Know About Vomiting in Pregnancy
Vomiting with blood during pregnancy: causes, treatment
Everyone knows that during pregnancy almost all girls have vomiting associated with toxicosis. But if vomiting appears with blood during pregnancy, then this is no longer an ordinary situation. Of course, ordinary vomiting has nothing to do with any abnormalities, but if there are bloody impurities or even clots in the vomit, then this situation requires urgent action, because this phenomenon may indicate the development of a serious pathology. nine0003 Do not ignore poor health, it can be a disturbing sign
But if vomiting appears with blood during pregnancy, then this is no longer an ordinary situation. Of course, ordinary vomiting has nothing to do with any abnormalities, but if there are bloody impurities or even clots in the vomit, then this situation requires urgent action, because this phenomenon may indicate the development of a serious pathology. nine0003 Do not ignore poor health, it can be a disturbing sign
Content
- The concept and danger of
- What is the vomiting of blood
- Causes of vomiting
- Intoxication
- GIT of the Pathology
- Excessive food consumption
- Oncological processes
- if vomiting appeared at the beginning of pregnancy
- Vomiting with blood at later stages
- First aid
Concept and danger
The appearance of vomiting containing bloody inclusions, in the language of physicians, is referred to as hematomesis. This process involves damage to the upper gastrointestinal tract, causing blood to mix with the vomit as it passes through the esophagus. The patient at the same time notes the appearance of mucus and bloody streaks. With increased bleeding, blood also penetrates into the feces, melena develops - when the patient has frequent bowel movements with black feces.
The patient at the same time notes the appearance of mucus and bloody streaks. With increased bleeding, blood also penetrates into the feces, melena develops - when the patient has frequent bowel movements with black feces.
Vomiting with blood during pregnancy is always caused by some traumatic damage to the mucous and vascular tissues. Such traumatic lesions can occur against the background of many factors such as peptic ulcer. Frequent vomiting of bile can also provoke the appearance of bloody impurities, because the bile secretion damages the mucous tissues of the esophagus, corroding them and causing bleeding.
Usually during gestation, vomiting reactions are observed with the content of small bloody particles, such vomiting is also called coffee grounds. Such a condition is safe and does not require treatment, if there are no other pathological signs. This is quite possible with minor blood loss. nine0003
What is vomiting with blood
Depending on the type and nature of the vomit, the origin of bloody vomiting can be assumed.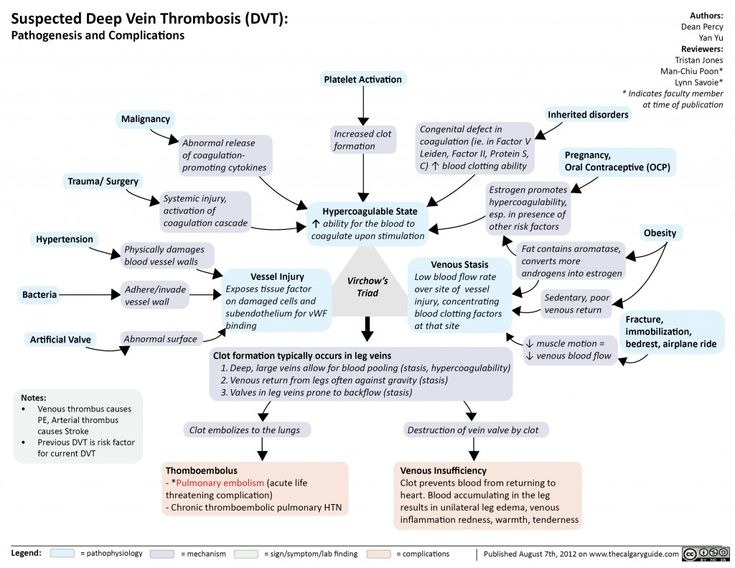
- Dark vomiting occurs not only due to bleeding, but also due to eating specific foods such as dark chocolate or beets, some dark berries and other foods that have not had time to digest.
- Scarlet blood in the vomit indicates that it has not undergone a hydrochloric acid reaction, which means that its source is the esophagus; nine0008
- Vomiting with bloody foam indicates pulmonary hemorrhage;
- Vomit resembling coffee grounds indicates gastric origin of the blood, and it was released about 3-4 hours earlier. Such vomiting is often accompanied by dark, almost black feces.
- Fountain-like vomiting of blood is caused by an esophageal varicose vein in which a blood clot has ruptured.
- Small single thread-like bloody blotches are usually observed in patients suffering from severe, acute toxicosis or esophageal hernia. nine0008
If blood appears in the vomit of pregnant women quite often, then you need to urgently contact a gastroenterologist.
Causes of vomiting
Any woman dreams of giving birth to a healthy childIn general, pregnancy cannot be a direct cause of bloody vomiting, therefore the etiology of this condition is associated with the same factors as in other people. Although in the state of pregnancy, such factors are provoked more often.
Usually, blood in the vomit appears in pregnant women during the first trimester, when patients in position suffer from toxic manifestations. With complicated toxicosis, accompanied by severe emetic reactions, ruptures of various esophageal sections often develop (Mallory-Weiss syndrome). nine0003
But not only toxicosis can cause bloody vomit. There are other factors against which pregnant women vomit with blood. Moreover, the appearance of blood in the masses of vomiting is always associated with digestive damage, in which the vessels burst and lose their functional significance. The root cause of blood in vomiting always takes place, and most often they are pathological in nature.
Intoxication
Mothers with toxicosis often experience a state when they want to eat something unusual, and immediately, immediately. They are ready to eat incongruous foods and even dishes of dubious quality. If you are so illegible about food, then you can easily get poisoned. The cause of toxic poisoning can be the use of fruits containing nitrates or pesticides, and infectious poisoning is diagnosed due to the use of a stale product. nine0003
Against the background of poisoning, a pregnant woman inevitably develops an emetic reaction. At the same time, such vomiting will differ markedly from ordinary toxicosis in the presence of undigested pieces of food, profuse salivation and the occurrence of about an hour and a half after eating food. Moreover, toxic vomiting is usually accompanied by acute diarrhea and cutting pain in the pancreas and umbilical region.
This condition is also dangerous because profuse vomiting and diarrhea quickly leads to dehydration, i. e. dehydration, which is extremely dangerous for pregnancy and can provoke its termination, regardless of the duration of gestation. Therefore, in case of any poisoning, mom needs to seek specialized medical help. nine0003
e. dehydration, which is extremely dangerous for pregnancy and can provoke its termination, regardless of the duration of gestation. Therefore, in case of any poisoning, mom needs to seek specialized medical help. nine0003
Gastrointestinal pathology
Often, vomiting with bloody impurities is provoked by digestive pathologies. Usually the cause is gastric ulcer, although other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract are quite possible. Characteristic symptoms accompanying such vomiting are jumps in blood pressure, abdominal pain that tends to increase after eating or on an empty stomach, belching and heartburn, causeless nausea and dark stool. In general, bloody vomiting may be accompanied by such gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Acute gastritis. With such a pathology, blood can be released from the lesions of the mucous membrane. Bleeding can be provoked by the use of alcohol or spicy food, any medications (usually anti-inflammatory). To avoid vomiting blood, you must follow a diet.
- Perforation of an ulcerative lesion. The disease is characterized by the presence of acute pain at the site of the ulcer, a decrease in blood pressure, loss of consciousness or an excessively frequent pulse. Such a condition is dangerous for the patient, without appropriate assistance can lead to peritonitis and even death. nine0008
- Esophageal varicose veins. In pregnant women, it appears in the presence of hepatic pathologies. On the portal vein, located in the abdominal cavity, bleeding thrombotic formations are formed. They are extremely dangerous and require immediate treatment.
- Esophageal hernia lesions. They are usually formed under the influence of the progesterone hormone, which relaxes muscle tissues, as well as under the influence of increased intra-abdominal pressure, which occurs against the background of an increase in the size of the uterine body. Because of this, the entrance to the stomach is stretched, esophagitis occurs, which is manifested by heartburn, painful symptoms, vomiting with bloody impurities.
 nine0008
nine0008 - Duodenitis can also cause a condition such as hematomesis. Inflammation of the duodenum is characterized by bloody vomiting, heartburn, weakness, etc. During the diagnosis, Helicobacter pylori is detected, which determines further treatment tactics.
These pathologies most often become etiological factors that provoke vomiting of blood in pregnant women.
Excessive food intake
Excessive eating habits often lead to gluttony, which overloads the digestive system and provokes emetic reactions. Indigestible foods seriously impede the enzymatic breakdown of the food bolus. Moreover, the enlarged uterus exerts a certain pressure on the intraorganic structures, displacing them from their place. If vomiting torments too often, then the esophageal vessels are damaged, provoking the appearance of blood. Cramps in the stomach also break the mucous membranes, causing blood loss. These processes are accompanied by severe nausea reactions, severe malaise, etc.
Oncological processes
Fast food and quick snacks have a bad effect on the functioning of the stomachOncopathology can appear at any time, and pregnancy, unfortunately, is no exception. On the contrary, some malignant tumors, against the background of hormonal changes that occur during gestation, begin to actively grow and develop. Similar oncoprocesses are malignant lesions of the stomach, intestines, esophagus and other gastrointestinal structures.
These pathologies are characterized by chronic weakness, decreased performance and constant fatigue. Patients complain of pain in the abdomen, sudden nausea, sudden onset of intolerance to any products or violations of defecation constipation. nine0003
But you should not panic and self-diagnose yourself with cancer when such symptoms appear. Such a disease can be confirmed only after a series of relevant studies, biopsy and fibrogastroduodenoscopy. Signs of oncology do not differ in specificity, they may be present in other diseases, albeit not so serious, but also unsafe, especially when carrying a baby.
If vomiting appeared at the beginning of pregnancy
If bloody impurities in the vomit appeared in the days of the first trimester, then they are attributed to manifestations of toxicosis characteristic of that period. In addition, the patient experiences a lack of appetite, she is constantly nauseous, she cannot bear some foods that she previously loved. Also, pregnant women complain of intolerance to pungent odors, drowsiness and constant weakness, she noticeably increases the secretion of salivary secretions. nine0003
It's no secret that sometimes pregnant women simply drive their household into a stupor with unusual gastronomic desires, managing to combine cucumbers with chocolate, and herring with strawberries. When a severe form of toxicosis develops, vomiting reactions become too frequent, mommy begins to suffer from dehydration and lose weight. Stomach acid corrodes the mucous membranes of the digestive system, which leads to the appearance of blood. Such conditions must be treated immediately.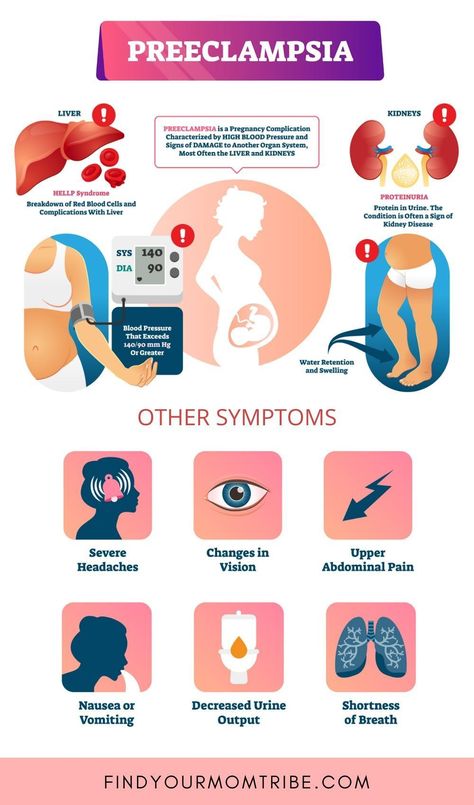
Vomiting blood in late pregnancy
In the later stages of gestation, vomiting reactions with bloody impurities are also possible. Sometimes this is possible after 36 weeks, when the gestation is coming to an end.
- At such times, hematomesis is usually caused by strong pressure of the uterine body on intraorganic structures, including the gastrointestinal tract.
- Even simple overeating can provoke vomiting of blood at this time.
- Particularly dangerous in this regard is gestosis, which develops due to the fact that the resources of the mother's body are not enough to fully provide the baby with oxygen and nutrition, which leads to hypoxia. nine0008
- In this condition, patients observe the appearance of hyperedema and hypertension, migraines and acute gastralgia or bloody vomiting.
- Pregnant women with gestosis are also worried about severe sleep disorders, visual disturbances, dangerous muscle contractions and convulsions.

Such a phenomenon at such a late date is extremely dangerous, because it can provoke fetal hypoxia, premature birth or complications during delivery, etc.
First aid
If vomiting with blood interspersed occurred once, then it does not pose any danger. Of course, you need to tell the doctor, but there is no need to panic. If the patient's condition is severe, bloody vomiting is profuse and does not go away, then it is necessary to call an ambulance. While the doctor is driving, you do not need to restrain the urge or cause an artificial emetic reaction.
Mommy should be placed under the covers with a pillow under her back to minimize esophageal stress. And thanks to the blanket, the pregnant woman will be able to avoid a drop in blood pressure and improve blood circulation. It is necessary to ensure that mom is conscious, and the doctors who arrive will decide for themselves what treatment tactics they should choose for a particular patient. nine0003
nine0003
Vomiting blood - causes, diagnosis and treatment
Vomiting blood is the sudden, uncontrolled discharge of bright red (hematemesis) or brown (coffee grounds) vomit through the mouth. The symptom is most characteristic of gastric ulcer, other factors include inflammatory or destructive diseases of the esophagus and gastroduodenal zone, liver damage, pathologies of the blood coagulation system, and taking certain medications. To clarify the causes of vomiting, endoscopic, radiological, ultrasound and laboratory research methods are used. Drugs are prescribed only after a clinical diagnosis has been made. nine0003
Causes of vomiting with blood
Peptic ulcer
Coffee grounds vomit is characteristic of massive bleeding from a damaged vessel at the bottom of the ulcer. The dark color is due to the reaction of blood hemoglobin with hydrochloric acid of the stomach, which is accompanied by the formation of hematin hydrochloride. A few days before bloody vomiting, there is an increase in dyspeptic disorders, abdominal pain. With the onset of bleeding, the pain subsides. The symptomatology caused by blood loss and hypoxia becomes the leading one: the patient feels dizzy, weak, the skin and visible mucous membranes become pale. nine0003
A few days before bloody vomiting, there is an increase in dyspeptic disorders, abdominal pain. With the onset of bleeding, the pain subsides. The symptomatology caused by blood loss and hypoxia becomes the leading one: the patient feels dizzy, weak, the skin and visible mucous membranes become pale. nine0003
In the case of a single discharge of more than 50 ml of blood, it can enter the intestines, which is manifested by black stools (chalky) on the next day after vomiting “coffee grounds”. With blood loss up to 15% of the BCC, the general condition is moderate, there is a sharp weakness, tachycardia, and a drop in blood pressure. There are complaints of dry mouth, intense thirst. With the loss of large volumes of blood, fainting, impaired consciousness are typical, the pulse becomes thready.
Blood-stained vomit is the first symptom of most stress ulcers with intense gastroduodenal bleeding. Hematemesis opens suddenly in the absence of pain in the epigastric region, which is associated with the predominance of symptoms of the underlying pathology. Weakness quickly increases, dizziness appears, the skin turns pale, the pulse quickens. Bloody vomiting after night and morning "hungry" pain in the abdomen is also complicated by Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, in which multiple bleeding ulcerative defects of the gastric mucosa are formed. nine0003
Weakness quickly increases, dizziness appears, the skin turns pale, the pulse quickens. Bloody vomiting after night and morning "hungry" pain in the abdomen is also complicated by Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, in which multiple bleeding ulcerative defects of the gastric mucosa are formed. nine0003
Diseases of the gastroduodenal zone
Inflammatory processes, anomalies in the structure of the upper digestive tract and tumor formations can serve as predisposing factors for "coffee grounds" vomiting. The symptom occurs when the pathology is long-standing, when the mucous membrane is totally affected and the vessels are involved in the process. The difference from bleeding in ulcerative defects is the persistence of pain after the release of vomit. Causes of hematemesis are:
- Acute erosive gastritis . Vomiting is preceded by moderate pain in the epigastric region, nausea, belching with air, loss of appetite. With small hemorrhages, streaks of blood are found in the contents of the vomit, with extensive damage to the organ and massive bleeding, vomiting of "coffee grounds" with a black tarry stool (chalky) begins.
 Similar symptoms are found in hyperplastic gastritis.
Similar symptoms are found in hyperplastic gastritis. - Hemorrhagic gastritis . Inclusions of blood in the vomit are characteristic of acute profuse bleeding. Vomiting develops against the background of pain in the epigastrium, which increases immediately after eating. Before an attack, severe nausea is felt for some time. With chronic blood loss, a metallic taste in the mouth, frequent dizziness, and shortness of breath when performing the usual physical activity are possible.
- Gastric diverticulum . Hematemesis is a late sign of diverticulosis. Such a complication, as a rule, occurs during the long-term existence of the disease and indicates an erosive process that damages the arteries. Before vomiting or simultaneously with it, there is a sharp pain in the epigastrium. The next day, the stool usually becomes dark, tarry. nine0008
- Acute gastric dilatation . Repeated vomiting of gastric contents, and then masses with an admixture of bile and blood, begins after the sudden onset of severe diffuse pain in the abdominal cavity and uncontrollable hiccups.
 More than 7-8 liters of vomit are released per day, while attacks occur spontaneously without the patient's conscious efforts. There is gas retention and bloating. The condition is somewhat relieved in the knee-elbow position.
More than 7-8 liters of vomit are released per day, while attacks occur spontaneously without the patient's conscious efforts. There is gas retention and bloating. The condition is somewhat relieved in the knee-elbow position. - Benign tumors . Vomiting of “coffee grounds” and melena are the first symptoms of massive bleeding in gastric leiomyoma, which, due to slow progression, is latent for a long time. Large bleeding polyps of the stomach are characterized by the presence of separate streaks of blood in the secreted vomit against the background of other dyspeptic disorders.
- Erosive bulbite . Hematemesis indicates severe bleeding from an eroded vessel in the wall of the duodenal bulb. Due to significant blood loss, general well-being disorders are possible - weakness, pallor, fainting. Unlike most other pathologies, tarry stools often precede vomiting, less often melena occurs after an attack. nine0008
Diseases of the esophagus
Esophageal pathology is accompanied by vomiting with the outflow of bright scarlet blood (hematemesis). The symptom is characteristic of inflammatory processes, in which the vulnerability of the mucous membrane increases, superficial or deep defects are formed. Hematemesis is provoked by traumatization of the esophageal wall by foreign bodies, iatrogenic injuries during medical procedures. Among the main reasons for the development of a symptom are:
The symptom is characteristic of inflammatory processes, in which the vulnerability of the mucous membrane increases, superficial or deep defects are formed. Hematemesis is provoked by traumatization of the esophageal wall by foreign bodies, iatrogenic injuries during medical procedures. Among the main reasons for the development of a symptom are:
- Mallory-Weiss syndrome . Bleeding is provoked by prolonged vomiting or hiccups, in which the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract wall and the abdominal muscles are strongly strained. Against the background of another vomiting urge, a sharp burning pain is felt in the area of the xiphoid process, after which profuse vomiting with blood begins. The symptom is also determined by ruptures of the esophagus of another etiology (with burns, thoracoabdominal injury).
- Acute esophagitis. The formation of erosions or ulcers of the esophagus due to a protracted course of the inflammatory process becomes a prerequisite for bleeding and vomiting.
 With the onset of an attack, the sharp pains behind the sternum, typical for lesions of the esophagus, that occur after eating and in a horizontal position, intensify. There are signs of posthemorrhagic anemia - weakness, fatigue, dizziness. Before vomiting, belching with air, heartburn, nausea are observed. nine0008
With the onset of an attack, the sharp pains behind the sternum, typical for lesions of the esophagus, that occur after eating and in a horizontal position, intensify. There are signs of posthemorrhagic anemia - weakness, fatigue, dizziness. Before vomiting, belching with air, heartburn, nausea are observed. nine0008 - Hiatus hernia . Vomiting with blood is one of the signs of infringement of the hernial sac. It occurs suddenly or against the background of nausea and is combined with a sharp retrosternal pain, which can radiate to the shoulder blades, neck. The general condition of the patient is severe - pronounced shortness of breath, the skin becomes cyanotic, the pulse quickens to 100 or more beats per minute, blood pressure drops.
- Esophageal perforation . With a through defect in the wall of the organ, repeated vomiting with impurities of fresh blood is characteristic, then the vomit takes the form of "coffee grounds". Severe pain is noted, which in intensity resembles a myocardial infarction or a perforation of a stomach ulcer.
 When air enters the cellular space of the mediastinum and neck, subcutaneous emphysema develops, breathing becomes difficult. nine0008
When air enters the cellular space of the mediastinum and neck, subcutaneous emphysema develops, breathing becomes difficult. nine0008 - Tracheoesophageal fistula . Hematemesis is provoked by the presence of an acquired anastomosis between the esophagus and the trachea, which contributes to the destruction of the vessels of the mucosa. The symptom is often accompanied by respiratory disorders - coughing, suffocation, hemoptysis. The possible presence of a three-esophageal fistula as a cause of vomiting is evidenced by moderate pain in the chest and epigastrium, coughing up pieces of food, and a tendency to frequent diseases of the lungs and bronchi.
- Cancer of the esophagus. Vomiting usually appears when the tumor is large, which partially closes the lumen of the organ. The symptom is combined with difficulty in swallowing solid food, a constant sensation of a foreign body (“lump”) behind the sternum, hoarseness, and a constant dry cough. The presence of streaks of blood in the composition of the vomit is characteristic of the late stage of the disease with ulceration and decay of neoplasia.

Portal hypertension
Esophageal varicose veins are the main cause of hematemesis with increased portal pressure. These vessels have a specific feature: they do not collapse, so blood loss is abundant (up to 30-40% of the BCC), which is life-threatening. Children may experience vomiting of a "fountain" with the release of bright red blood, which is a prognostically unfavorable sign. Portal hypertension with vomiting may be due to pylephlebitis, congenital liver fibrosis, abnormalities in the structure of large venous vessels in the abdominal cavity. nine0003
Bleeding from the esophageal veins is typical for the decompensated stage of the disease. At the same time, at the initial stages of portal hypertension, nausea, periodic heartburn or belching, and stool disorders are disturbing. With the progression of the pathological process, patients notice swelling in the lower extremities, an expanded venous network is clearly visible on the skin of the anterior abdominal wall. Dull pains are felt in the left hypochondrium, which are caused by an enlarged spleen.
Dull pains are felt in the left hypochondrium, which are caused by an enlarged spleen.
Communicable diseases
Vomiting blood occurs in the hemorrhagic form of dengue fever or yellow fever. These viral infections affect the vascular wall and disrupt the blood clotting system. Against the background of high temperature and general infectious syndrome, uterine, nasal, gastrointestinal bleeding occurs. Hematemesis can begin with the intestinal form of anthrax, in which case it is combined with melena, excruciating pain in the abdomen. Isolation of blood with vomit is typical of the initial period of the plague, which affects all organ systems. nine0003
Hemorrhagic syndromes
Regurgitation of vomit with blood is a typical sign of gastrointestinal bleeding in hemorrhagic diathesis. More often, vomiting of “coffee grounds” complicates the course of thrombocytopenic purpura and hemorrhagic vasculitis. In addition to dyspeptic disorders, such patients complain of a spotted or papular rash on the extremities and trunk. Massive nasal and intestinal bleeding, triggering a gag reflex, is pathognomonic for rare hereditary pathologies - Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome and Rendu-Osler-Weber disease. nine0003
Massive nasal and intestinal bleeding, triggering a gag reflex, is pathognomonic for rare hereditary pathologies - Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome and Rendu-Osler-Weber disease. nine0003
Acute conditions
In children, vomiting of blood may be a sign of systemic intoxication with extensive burns or neurotoxicosis. Such conditions, in addition to regurgitation, are characterized by an extremely serious condition of the child, impaired consciousness, dysfunction of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Repeated hematemesis, detected on the second or third day of postresuscitation illness, acute peritonitis, cardiogenic shock, indicates gastrointestinal bleeding due to the developed hemorrhagic syndrome. nine0003
Pathology of ENT organs
Vomiting of "coffee grounds" is noted in case of heavy nosebleeds, which are accompanied by swallowing of blood. In this case, dizziness, weakness, an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth, and nausea often occur. Massive blood loss provokes fainting, tachycardia, and a sharp pallor of the skin. Isolation of vomit in the form of "coffee grounds" is also characteristic of combined burns of the pharynx, which are combined with damage to the underlying sections of the gastrointestinal tract, ammonia poisoning (if taken orally), causing destruction of the mucosa. nine0003
Massive blood loss provokes fainting, tachycardia, and a sharp pallor of the skin. Isolation of vomit in the form of "coffee grounds" is also characteristic of combined burns of the pharynx, which are combined with damage to the underlying sections of the gastrointestinal tract, ammonia poisoning (if taken orally), causing destruction of the mucosa. nine0003
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Sometimes bloody vomiting is the result of gastrointestinal bleeding provoked by the so-called ulcerogenic drugs - drugs that contribute to the formation of erosive and ulcerative defects of the mucous membrane of the digestive organs. As a rule, patients report long-term, sometimes uncontrolled use or high doses of medications from the following groups:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) : aspirin, indomethacin, butadione.
- Glucocorticosteroids : prednisolone, dexamethasone.
- Direct acting oral anticoagulants : dabigatran, apixaban, rivaroxaban.

- Anti-gout preparations : atofan, cinchofen.
- Hypotensive sympatholytics : reserpine.
- Psychostimulants : caffeine, some drugs (cocaine, methamphetamines). nine0008
Examination
To identify the causes of vomiting with blood, a gastroenterologist prescribes a comprehensive examination, which is aimed at studying the morphological and functional features of the gastrointestinal tract. Instrumental studies have a high diagnostic value, laboratory tests help to establish the severity of hemodynamic and metabolic disorders. The examination plan includes:
- Endoscopic methods . To accurately determine the site of bleeding and visualize the defect in the mucous membrane of the upper gastrointestinal tract, endoscopy is performed. If necessary, during the procedure, coagulation of the affected vessel is performed, a biopsy is taken from pathologically altered tissue areas.
 nine0008
nine0008 - X-ray examination . X-ray with oral contrast is performed only after the cessation of vomiting and stabilization of the condition. The method is informative for the diagnosis of organic changes, hernial formations. Leakage of contrast outside the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract indicates perforation or fistulous tracts.
- Sonography . Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is prescribed for a quick assessment of the condition of the abdominal organs. Sonography is used to detect mass formations in the gastrointestinal tract, hernias, and to diagnose liver diseases. Doppler sonography is performed to assess linear blood flow in the hepatic and splenic veins. nine0008
- Laboratory methods . A general blood test is necessary to determine the degree of blood loss and the severity of the anemic syndrome. If hereditary defects in the hemostasis system are suspected, an extended coagulogram is performed with the determination of prothrombin time and other coagulation parameters.
 Serological tests are sometimes prescribed.
Serological tests are sometimes prescribed.
In case of possible primary disorders in the vascular system, contrast angiography is performed; radioisotope scintigraphy is recommended to assess the state of the liver parenchyma. Additionally, a macro- and microscopic analysis of feces is performed; to exclude intestinal bleeding, the Gregersen reaction to occult blood is informative. If bloody vomiting is combined with signs of hemorrhagic diathesis, a general infectious syndrome, consultations of other specialists are required. nine0003
Before arrival
Symptomatic therapy
The appearance of blood in the contents of the stomach indicates serious diseases of the digestive system or other organs, so self-treatment or delay in seeking medical help can harm your health. Patients with coffee grounds vomiting require rest and urgent hospitalization to determine the causes of the symptom and select a treatment regimen. At the preclinical stage, it is permissible to apply cold to the abdomen.