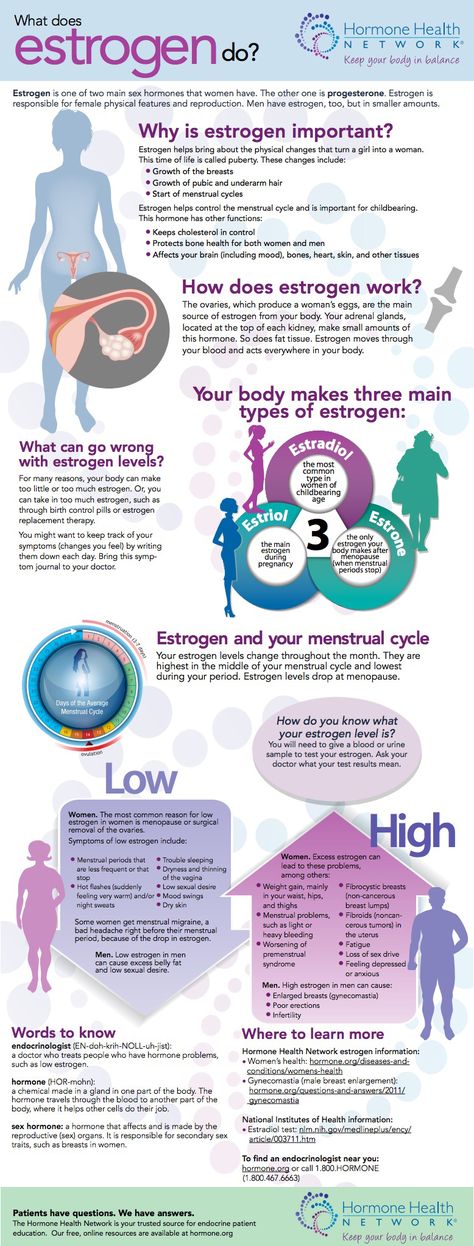
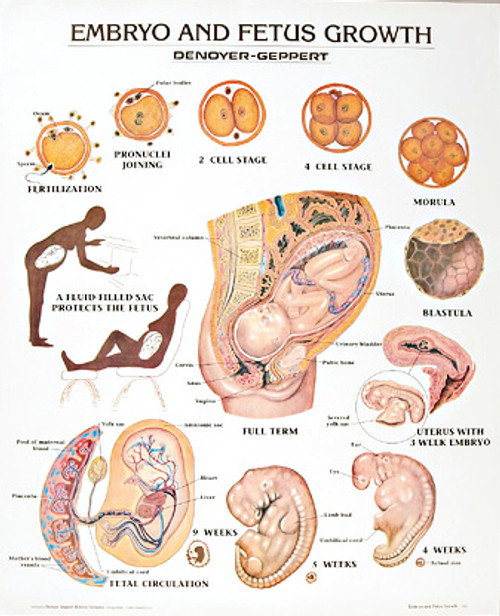
What is pregnancy hormone called
Six key pregnancy hormones and their roles – Compound Interest
Click to enlargePregnancy is a rollercoaster of shifting hormone levels which can have numerous effects. This graphic looks at six key hormones during pregnancy, their roles in the development of the baby, and other effects.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
hCG is an important hormone in early pregnancy. It’s produced by the placenta after implantation, and supports the function of the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum is a temporary structure in the ovaries which produces other key hormones during early pregnancy.
hCG is also the hormone detected by pregnancy tests. Its concentration increases from conception and peaks 8–11 weeks after. For the first few days after conception its levels are too low to detect with pregnancy tests, but after implantation its levels double every 48 hours. There’s more on hCG and pregnancy tests in this previous graphic.
Progesterone
During the early weeks of pregnancy, the corpus luteum produces progesterone. After 8-12 weeks, the placenta takes over.
Progesterone stimulates growth of the blood vessels that supply the womb lining. It also stimulates the lining to release nutrients, providing nourishment for the early embryo. Additionally, progesterone inhibits contraction of the smooth muscle of the uterus so that it grows as the baby does.
Progesterone levels continue to rise as the pregnancy progresses. Along with oestrogen, it promotes the growth of breast tissue and milk duct development. Progesterone prevents lactations during pregnancy, which only starts when levels drop after birth. This hormone also plays an important role in preparation for birth: it strengthens the pelvic wall muscles required for labour.
Noticing increased hair growth during pregnancy? That’s also due to progesterone!
Oestrogen
As with progesterone, the corpus luteum produces oestrogen in the early stages of pregnancy before the placenta takes over. Oestrogen is actually a collective group of similar compounds: oestrone, oestradiol, and oestriol.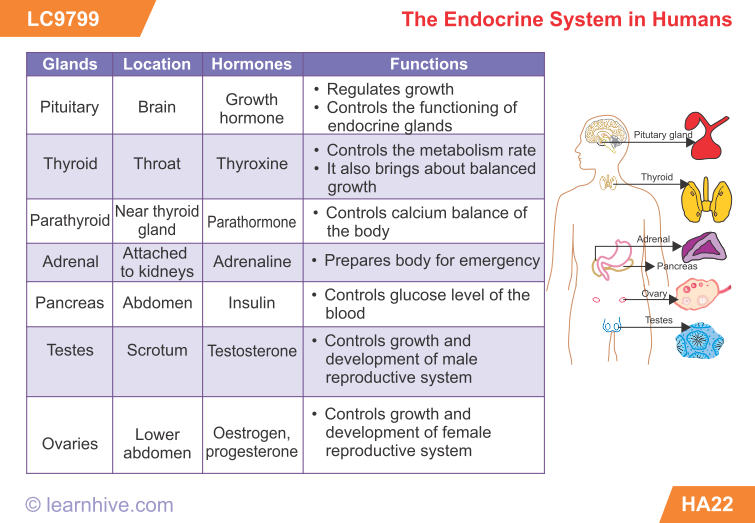
Oestrogen helps the uterus grow and maintains its lining. It supports foetal development, including the development of organs and bodily systems. It also activates and regulates the production of other important pregnancy hormones.
Prolactin
Prolactin is the main hormone needed to trigger the production of breast milk. It enlarges the mammary glands to prepare for this (though as previously noted progesterone levels prevent lactation until the baby is born).
Prolactin has other roles unrelated to milk production. It contributes to the development of the foetal lungs and brain, and also to the mother’s immune system tolerating the foetus.
Relaxin
Relaxin levels are highest during the first trimester of pregnancy, but it is present throughout. It has several roles, including prohibiting contraction of the uterine muscles to prevent premature birth.
Relaxin’s name gives a clue to its more important roles.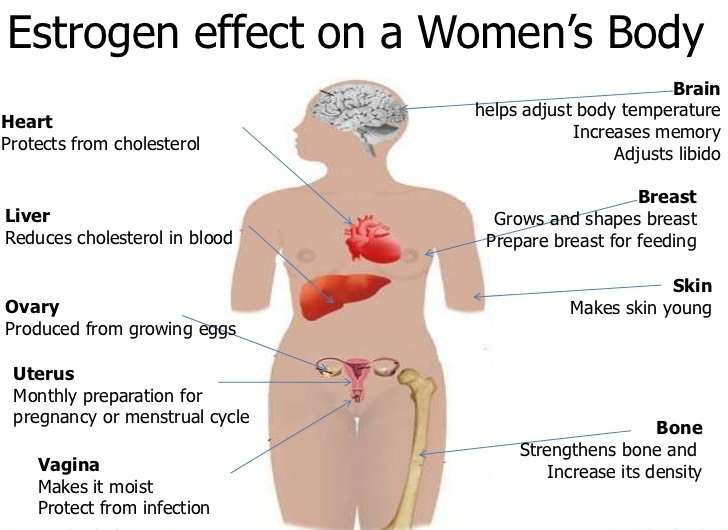 It relaxes blood vessels, increasing blood flow to the placenta and kidneys. This helps the mother’s body cope with the increased demand for oxygen and nutrients from the developing baby.
It relaxes blood vessels, increasing blood flow to the placenta and kidneys. This helps the mother’s body cope with the increased demand for oxygen and nutrients from the developing baby.
Relaxin also helps the mother’s body prepare for birth. It relaxes joints in the pelvis and softens and widens the cervix to make delivery of the baby easier.
Oxytocin
Oxytocin only appears in significant amounts towards the end of pregnancy, though it is present in lower amounts before this. Its levels rise when labour starts, triggering contractions.
If labour doesn’t start naturally, oxytocin (or synthetic equivalents) can be used to induce it.
The graphic in this article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. See the site’s content usage guidelines.
Enjoyed this post? Support Compound Interest’s graphics on Patreon!
References & Further Reading
- Hormones of pregnancy and labour – The Society of Endocrinology
- HPL, relaxin and oxytocin – What to Expect
- Oxytocin in pregnancy and the post-partum – M Prevost and others
- A review of the hormone prolactin during lactation – K M Ostrom
- Renal physiology of pregnancy – K L Cheung & R A Lafayette
Like Loading. ..
..
6 Hormones to Help You Make a Baby
According to the Cleveland Clinic, hormones manage the functions of the various systems in your body by sending chemical messages. Even when you’re not pregnant, they control basically everything from your appetite and sleep to your sex drive. When you get pregnant, your pregnancy hormones ready your body to have a baby, and they come with some fun side effects too.
What are the Main Pregnancy Hormones?
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HcG)
What does HcG do?
HcG is the hormone that tells the rest of your body that you’re pregnant. It’s also the indicator that over-the-counter pregnancy tests use. HcG is the most likely pregnancy hormone behind morning sickness because higher levels are correlated with more intense vomiting and nausea. Another key task: increasing production of estrogen and progesterone so they can do their part to grow the baby.
When will HcG matter?
For the first two months of your pregnancy, your HcG levels will continue to rise very quickly, doubling every other day, then plateau for the rest of your pregnancy.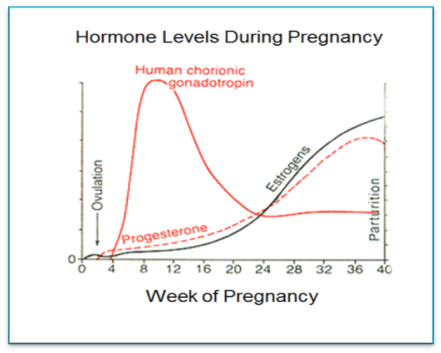
Progesterone
What does progesterone do?
This hormone, released by the ovaries, plays a key role in supporting your pregnancy. During the first trimester, progesterone relaxes your uterus, slows down your metabolism and signals breast tissue to get ready for milk production. It is also responsible for pregnancy symtoms such as bloating, constipation and fatigue.
When will progesterone matter?
Progesterone plays a key role in overall fertility, so it’s kind of a big deal. When you concieve, its levels skyrocket during the first trimester. During pregnancy, the placenta also produces progesterone. After your baby is born and placenta is delivered, progesterone levels fall which can contribute to mood swings.
Estrogen
What does estrogen do?
During pregnancy, estrogen helps the uterus grow and jumpstarts fetal development. It also increases blood flow, which heightens your sense of smell and gives you that pregnancy “glow.” Side effects: spider veins and increased appetite.
When will estrogen matter?
Estrogen levels continue to rise through your pregnancy and peak in the third trimester. Since this pregnancy hormone is also generated by the placenta during pregnancy, estrogen levels crash postpartum.
Relaxin
What does relaxin do?
The name says it all. Relaxin keeps your uterus relaxed during the first trimester and helps with the growth of your placenta. It also makes your ligaments relax, helping your body adjust to the physical changes it’ll experience as your baby grows. When the time comes to give bith, relaxin allows your pelvis to open so your baby can be born. The downside of relaxin? Since it causes your ligaments to become more flexible, this hormone is behind some of the aches and pains you may experience during your pregnancy.
When will relaxin matter?
Relaxin levels are highest during the first trimester as your body gears up for pregnancy.
Oxytocin
This isn’t Oxycontin. That’s an opioid pain medication. This is nature’s version.
This is nature’s version.
What does oxytocin do?
Oxytocin (pronounced oxy-toh-son) is our favorite hormone. This so-called love hormone floods your brain during sex, childbirth and breastfeeding and gives you an overall feeling of wellbeing.
When will oxytocin matter?
This hormone starts your contractions, keeps going through labor and makes your uterus contract after birth (which helps with bleeding once the placenta is delivered). Once your baby is born, oxytocin helps you bond with baby. Every time you nurse, cuddle, kiss and smell your baby, your body produces more oxytocin.
Prolactin
What does prolactin do?
As its name suggests, prolactin helps your body produce milk.
When will prolactin matter?
When you’re pregnant, prolactin levels go up 10 to 20 times to prep your mammary glands for milk production and then levels stay high if you start breastfeeding. Prolactin levels are highest when you’re sleeping and in the early morning (which may be why many people experience their highest levels of milk production around that time).
Hormones in the fourth trimester
The hormones that carried you through pregnancy are still hard at work once you give birth. While progesterone and estrogen levels decrease, oxytocin and prolactin are busy helping you bond with your baby, produce milk and heal. The dramatic shift in hormones can cause some people to experience baby blues. If you feel sad or down for longer than two weeks, you’ll want to contact your doctor for some support. While there isn’t a definitive link between hormone level changes in the fourth trimester and perinatal mood and anxiety disorders, it’s a good idea to have support in place before you give birth–whether that looks like lining up a therapist, asking friends and family to drop off homecooked meals or setting boundaries around visitors in the first weeks after baby arrives. Most importantly, keep in mind that adding a new member to your family comes with a lot of change so be gentle with yourself!
EXPERT SOURCES
Cleveland Clinic Hormones: What They Are, Functions & Types
University of North Carolina School of Medicine Perinatal Mood and Anxiety Disorders
About Babylist
Looking for the best items for your growing family? Add all your favorite baby products to ONE registry with Babylist.
This information is provided for educational and entertainment purposes only. We do not accept any responsibility for any liability, loss or risk, personal or otherwise, incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, from any information or advice contained here. Babylist may earn compensation from affiliate links in this content. Learn more about how we write Babylist content and the Babylist Health Advisory Board.
hCG, human chorionic gonadotropin, indications for the appointment, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
Confirm More
- INVITRO
- Library
- Laboratory...
- HCG, Chorionic...
Miscarriage
Pregnancy
2088 July 29
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0025 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable, the information below is for reference only.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, β-hCG, beta-hCG, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin): indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators. nine0031
Chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone produced by the outer shell of the embryo, and is normally determined in the blood and urine of a woman only when pregnancy occurs.
Chorionic gonadotropin consists of two subunits - alpha and beta. The beta subunit (β-hCG) used for the immunometric determination of the hormone is unique. To monitor the course of pregnancy, the determination of the beta subunit of hCG is used. The level of beta-hCG in the blood as early as 6-8 days after conception makes it possible to diagnose pregnancy (the concentration of β-hCG in the urine reaches the diagnostic level 1-2 days later than in the blood serum). nine0003
nine0003
HCG has a multifaceted effect on the body of a pregnant woman: it affects the development of the embryo and fetus, stimulates the synthesis of estrogens and androgens by ovarian cells, promotes the functional activity of the chorion and placenta, and ensures the successful course of pregnancy.
The introduction of hCG into the body of non-pregnant women stimulates ovulation and the synthesis of sex hormones necessary for conception. In men, this hormone enhances the formation of seminal fluid, activates the production of gonadosteroids. nine0003
In early pregnancy and up to the 2nd trimester, β-hCG supports the production of hormones necessary to maintain pregnancy, and in male fetuses it stimulates cells responsible for the formation and development of the male reproductive system.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, beta-hCG, b-hCG, Human Chorionic)
Synonyms: Beta-hCG general.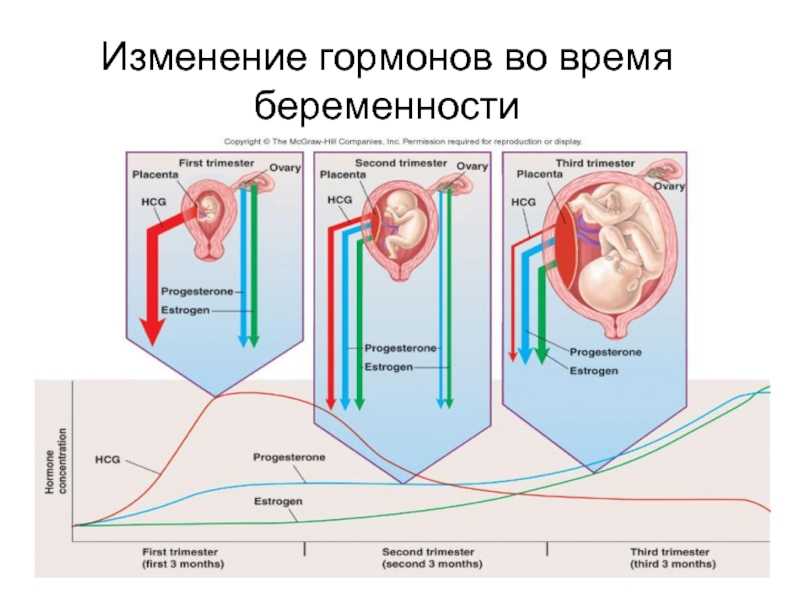 Human Chorionic Gonadotropin; hCG; Pregnancy Quantitative hCG; Beta hCG; Total beta hCG. Brief description of the analyte Human chorionic gonadotropin ...
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin; hCG; Pregnancy Quantitative hCG; Beta hCG; Total beta hCG. Brief description of the analyte Human chorionic gonadotropin ...
Up to 1 business day
Available with home visit
RUB 685
In garbage
Indications for determining the level of hCG in women
- Absence of menstruation (amenorrhea).
- Exclusion/confirmation of pregnancy, including ectopic (ectopic). nine0006
- Diagnosis of the state of the fetus at different stages of pregnancy.
- Assessment of the state of the placenta at different stages of pregnancy.
- Dynamic monitoring of fetal development during pregnancy, including in the diagnosis of malformations.
- Suspicion of the presence of neoplastic diseases of the reproductive system, such as hydatidiform mole (a rare pathology of the fetal egg, in which instead of the development of the embryo, chorionic villi grow), chorionepithelioma (a malignant tumor that develops from the epithelium of the villi of the fetal egg). nine0006
- Performing artificial termination of pregnancy.
Indications for determining the level of hCG in men:
The presence of suspicion of tumors of the testicles.
Deadline for this test is 1 working day, excluding the day of taking the biomaterial.
Rules for preparing for a blood test to determine the level of hCG
non-specific: it is enough to refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol on the eve of the procedure, limit stress and intense physical activity for a week; blood donation is carried out on an empty stomach. nine0003
nine0003
The determination of hCG in the blood is possible already on the 6-8th day after conception. The use of urinary test systems (rapid pregnancy tests) will be informative starting from the 7th day after the fertilization of the egg. To confirm the result, it is recommended to re-determine the level of the hormone a few days after the first analysis.
You can take a blood test for hCG (thyroid-stimulating hormone, thyrotropin, Thyroid StimulatingHormone, TSH) at the nearest INVITRO medical office. The list of offices where biomaterial for laboratory testing is accepted is presented in the "Addresses" section. nine0003
Reasons leading to high levels of β-hCG
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Incorrect timing of pregnancy.
- Pathological pregnancy: the appearance of edema, increased blood pressure, loss of protein in the urine (preeclampsia), convulsions (eclampsia), toxicosis.

- The presence of a pregnant woman with chronic diseases (for example, diabetes mellitus). nine0006
- Multiple fetal malformations (in such a situation, the determination of the level of β-hCG is used together with other indicators, the so-called "triple test". This study is used as a screening, and not for diagnosis.).
Reasons for fixing a decrease in the level of β-hCG
- Incorrectly established terms of pregnancy.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Frozen pregnancy. nine0006
- Threat of miscarriage.
- Fetal or placental disorders (including placental insufficiency).
- Intrauterine fetal death (in this case, it is informative to determine the level of the hormone in the first and second trimesters).
During abortion, the level of β-hCG is also monitored, the dynamics of growth / fall of which can be used to judge the completeness of the manipulation.
Determining the level of hCG, in addition to establishing the fact of pregnancy in the early stages, is part of the screening examination of pregnant women in the first trimester, along with ultrasound. nine0003
1st trimester prenatal screening for trisomies, PRISCA-1 (1st trimester biochemical screening - 1st trimester “double test”, risk calculation using PRISCA software)
Synonyms: Prenatal Screening Markers for Down Syndrome; PRISCA-1. Brief description of the study "Prenatal screening for trisomies of the 1st trimester of pregnancy, PRISCA-1)" Test run...
Up to 1 business day
Available with home visit
2 040 RUB
In garbage
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
Examination necessary to monitor the growth and development of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy.
RUB 2,790 Sign up nine0003
In gynecological practice, human chorionic gonadotropin is used to treat infertility, stimulate ovulation, and synthesize sex steroids. In urology, it is used in the treatment of cryptorchidism (undescended testicles) and infertility associated with impaired spermatogenesis.
Quantitatively, β-hCG is determined in the blood, for a qualitative determination, special test systems (pregnancy tests) are used, and in this case, urine serves as a biomaterial.
Quantitative determination of the level of hCG allows you to monitor the course of pregnancy in dynamics. To do this, obstetrician-gynecologists have developed tables for increasing the level of hCG, depending on the duration of pregnancy in weeks. The sensitivity of the determination is in the range of 1.2-1125000 mU/ml. nine0025
Reference values of hCG levels in dynamics by gestational age
| Pregnancy (weeks from conception) | HCG level (mU / ml) |
| 2 | 25–300 |
| 3 | 1500–5000 | nine0195
| 4 | 10000–30000 |
| five | 20000–100000 |
| 6–11 | 20000–>225000 |
| 12 | 19000–135000 |
| 13 | 18000–110000 | nine0195
| fourteen | 14000–80000 |
| fifteen | 12000–68000 |
| 16 | 10000–58000 |
| 17–18 | 8000–57000 |
| nineteen | 7000–49000 | nine0195
| 20–28 | 1600–49000 |
| Men and non-pregnant women | 0–<5 mU/ml |
Values ranging from 5 to 25 mU / ml do not allow unambiguous confirmation or denial of pregnancy, therefore, a second study is required after two days.
Since the hormone is produced by the placenta, during normal pregnancy, with placental pathology (for example, with fetoplacental insufficiency - a violation of the development of the fetus and placenta), with multiple pregnancies, the values of β-hCG will differ. With a normal pregnancy until the fifth week, the level of the hormone rises exponentially: every two days its concentration doubles, reaching a peak by the 11th week of gestation. Accordingly, in a multiple pregnancy, the level of β-hCG will be even higher than in a single pregnancy. nine0003
If the indicator deviates from the norm, additional ultrasound of the pelvic organs (uterus, appendages) is required.
US examination of pelvic organs (uterus, adnexa)
Ultrasound scanning of the organs of the female reproductive system to assess the shape and size, as well as exclude pathology.
RUB 2,390 Sign up nine0003
However, with a normal hCG value, additional examinations may also be needed:
- Ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy (required to confirm pregnancy, clarify the term).
Ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy
Examination to confirm pregnancy and determine the place of attachment of the ovum (to exclude ectopic pregnancy).
RUB 2,290 Sign up nine0003
- Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days) - to assess the characteristics and confirm the normal development of the fetus.
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
Examination necessary to monitor the growth and development of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy.
RUB 2,790 Sign up nine0003
- Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of multiple pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days) - to confirm the presence of several fetuses, determine their characteristics; It is necessary for planning the subsequent actions of the doctor and the management of pregnancy.
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of multiple pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
A study that allows you to assess the growth and development of fetuses, their position in the uterus, and make a plan for further pregnancy management. nine0003
RUB 3,840 Sign up
- Fetal ultrasound according to indications (before the 20th week) - performed in case of suspected ectopic pregnancy.
Fetal ultrasound according to indications (before the 20th week)
Additional ultrasound, which is prescribed in the presence of concomitant pathologies to monitor the condition of the fetus.
RUB 2,540 Sign up nine0003
- Laboratory tests to be performed in the first trimester are collected in the Pregnancy: 1st trimester (1-13 weeks) profile.
For professional assistance in interpreting the results, contact
obstetrician-gynecologist
.
Sources:
- www.invitro.ru
- Clinical guidelines "Ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians-Gynecologists, Association of Obstetric Anesthesiologists-Resuscitators. – 2021.
- Clinical guidelines "Premature birth". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians-Gynecologists, Association of Obstetric Anesthesiologists-Resuscitators. – 2020.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0025 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
Recommendations
-
PSA (prostate specific antigen) test
7731 may 13 nine0003
-
Human papillomavirus
11946 04 May
-
Alkaline phosphatase
3773 16 April
Similar articles
ECO
Hypogonadism
Menopause
Climax
nine0020 Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH, AMH, anti-Mullerian hormone) Anti-Mullerian hormone: indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.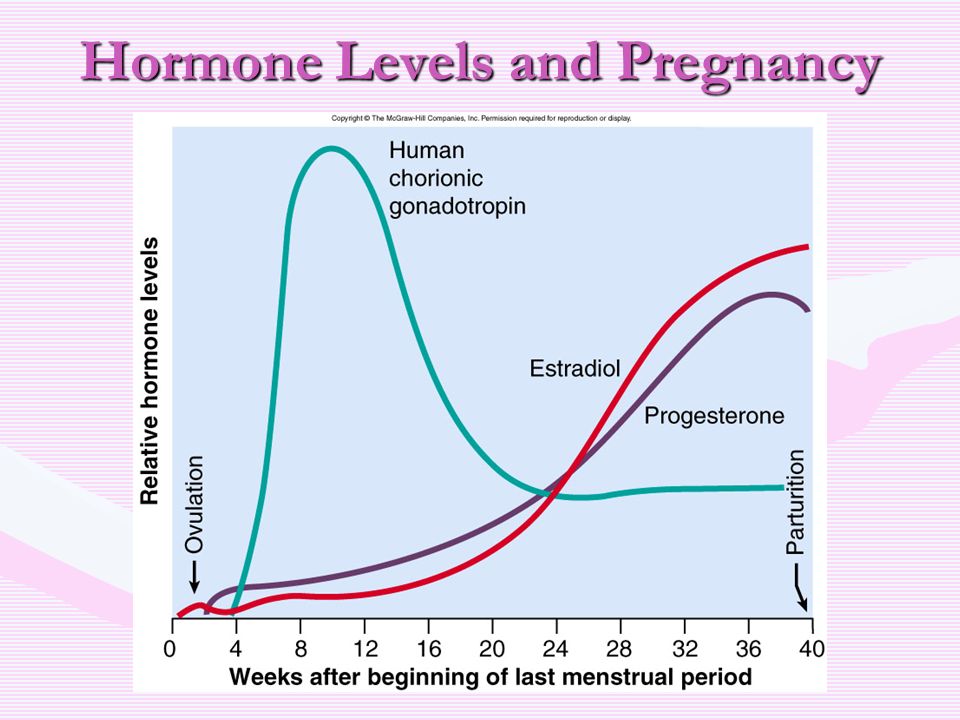
More
ECO
Thrombophilia
nine0002 PregnancyThrombosis: extended panel 114GP
Thrombosis, extended panel: indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the analysis, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
More
Malabsorption syndrome
Pregnancy
Vegetarianism
Celiac disease
Crohn's disease
Osteoporosis
Tuberculosis
25-OH vitamin D
25-OH vitamin D: indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
More
ECO
Blood transfusion
nine0002 PregnancyRh-affiliation (Rh-factor, Rh)
Rh-affiliation: indications for the appointment, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and indicators of the norm.
More
Pregnancy
Abnormalities of the kidneys
nine0002 AnencephalyAlpha-fetoprotein (AFP, alfa-Fetoprotein)
Alpha-fetoprotein: indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
More
Nothing found
Try editing your query or select a doctor or service from the list.
Doctor not found
Try changing your query or select doctor from list
Medical office not found
Try changing your query or select medical office from the list
Therapist Traumatologist-orthopedist Endocrinologist Urologist Gynecologist Ultrasound doctor Cardiologist Pediatrician
Nothing found
Please try editing your query
Thank you!
You have successfully made an appointment
Detailed information has been sent to your e-mail
Subscribe to our newsletters
Enter e-mail
I give my consent to processing of personal data nine0003
Subscribe
Hormones during pregnancy: how does the female body change?
Nausea, chest pain, cravings for pickled cucumbers are all hormones. During pregnancy, you are under their strong influence.
How do they work? Until you became pregnant, most of the hormones in your body were produced by endocrine glands such as the thyroid gland. Now, many of them also form in the placenta, which is inside the uterus. Immediately after the birth of the baby, the placenta is excreted from the body and pregnancy hormones are no longer needed. nine0003
Hormones cause nausea during pregnancy.
The culprit is human chorionic gonadotropin , which is produced by the embryo and then by the placenta. It is the presence of this hormone in the urine that leads to a positive pregnancy test result. In addition, human chorionic gonadotropin increases the production of another hormone, progesterone , and stops the menstrual cycle.
Feeling of happiness.
Endorphins These hormones are your biggest allies. These are natural painkillers and calming hormones. They work like morphine. They are called happiness hormones because they are the reason you expect a baby with joy, regardless of nausea and other pregnancy ailments. The source of endorphins is in the brain, where they are produced until the end of labor. The highest concentration of endorphins at the time of childbirth. Thanks to them, the pain becomes weaker, and the stress associated with childbirth is not so tiring. After childbirth, the level of endorphins drops sharply. This is probably the cause of a mild form of postpartum depression. nine0003
Sexual attraction.
The estrogens that affect your sex drive are first produced by the ovaries and then by the placenta. Estrogen production rises rapidly at the beginning of pregnancy. Thanks to estrogen, you feel that the desire for intimacy in the first trimester of pregnancy increases. Estrogens increase the blood supply to the breasts, vagina, vulva, and clitoris, which become especially sensitive. It is interesting! Thanks to pregnancy hormones, sex in the second trimester of pregnancy can be the best in a lifetime, according to scientists! nine0003
They relax muscles and prevent spasms. This is the influence of one of the most important pregnancy hormones: progesterone . Before pregnancy, it was produced, like estrogens, by the ovaries, now this function has passed to the placenta. Progesterone is responsible for most of the changes in your body during pregnancy (including fever, increased breathing). It relaxes the smooth muscles of the uterus and protects against miscarriage.
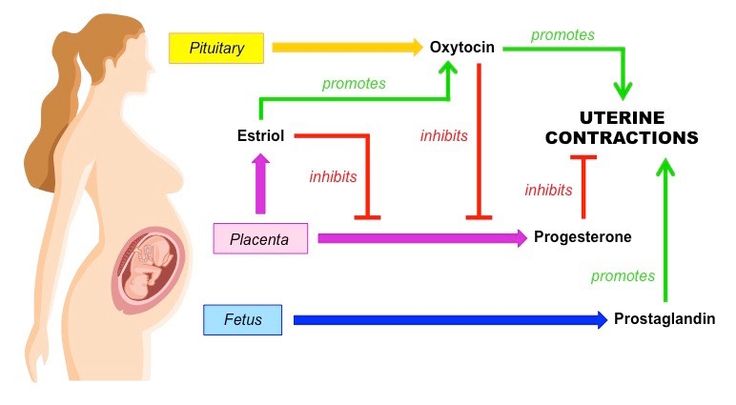
Pregnancy hormones prepare you for childbirth. nine0505
Preparing for childbirth is the merit of relaxin . Under its influence, the joints of the pelvic bones relax, soften the cervix and increase the elasticity of the surrounding ligaments, so that your uterus will grow, and your child will be able to pass through the birth canal.
Labor spasms.
Prostaglandins and oxytocin are the hormones that most support the final stages of pregnancy. The rising level of oxytocin is responsible for the development of the maternal instinct.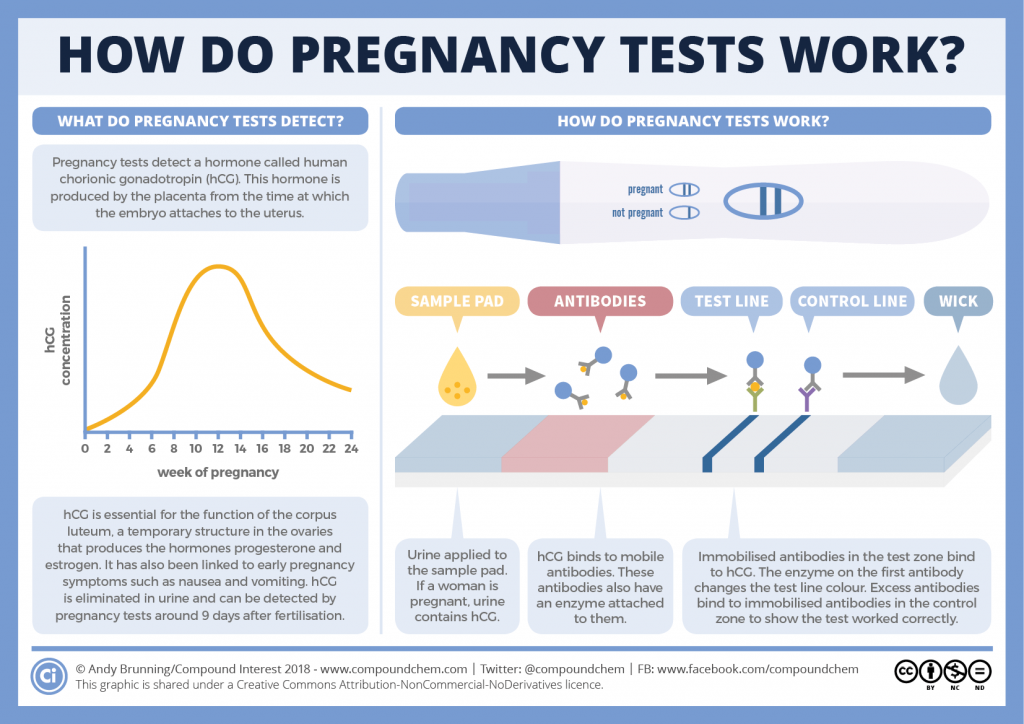 In the last trimester, you begin to feel uterine contractions stimulated by prostaglandins. If you have sex, you can speed up labor because prostaglandins are also found in male semen. Oxytocin stimulates predictive uterine contractions or Braxton-Hicks contractions and then the corresponding labor contractions. In some situations, it stimulates labor and accelerates the passage of the placenta. nine0003
In the last trimester, you begin to feel uterine contractions stimulated by prostaglandins. If you have sex, you can speed up labor because prostaglandins are also found in male semen. Oxytocin stimulates predictive uterine contractions or Braxton-Hicks contractions and then the corresponding labor contractions. In some situations, it stimulates labor and accelerates the passage of the placenta. nine0003
Help in the first days after childbirth.
Two more hormones, prolactin and placental lactogen , will allow you to breastfeed your baby. Thanks to them, the breasts begin to secrete colostrum (the first very nutritious food that can be excreted as early as the 19th week of pregnancy). Your body will produce it within days of giving birth. Later, milk will appear due to these hormones.
Pregnancy hormones also affect your appearance:
- Hair - at the end of the first trimester, they grow faster, they are thicker, thicker and stronger.