Bleeding during end of pregnancy
Bleeding during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Bleeding during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content6-minute read
Listen
Contact your doctor or midwife if you notice bleeding from your vagina at any time during your pregnancy. If you have very heavy bleeding, strong pain or feel very unwell, call triple zero (000) immediately and ask for an ambulance.
Is it normal to bleed during pregnancy?
Bleeding during pregnancy, especially in the early stages, is quite common. About 1 in 4 women will experience vaginal spotting or bleeding during the first trimester. Many of these women will go on to have healthy pregnancies.
However, vaginal bleeding may be the first sign of a problem, so it’s important to contact your doctor or midwife if you experience vaginal bleeding at any stage of your pregnancy for advice on what to do next.
What are the causes of bleeding during pregnancy?
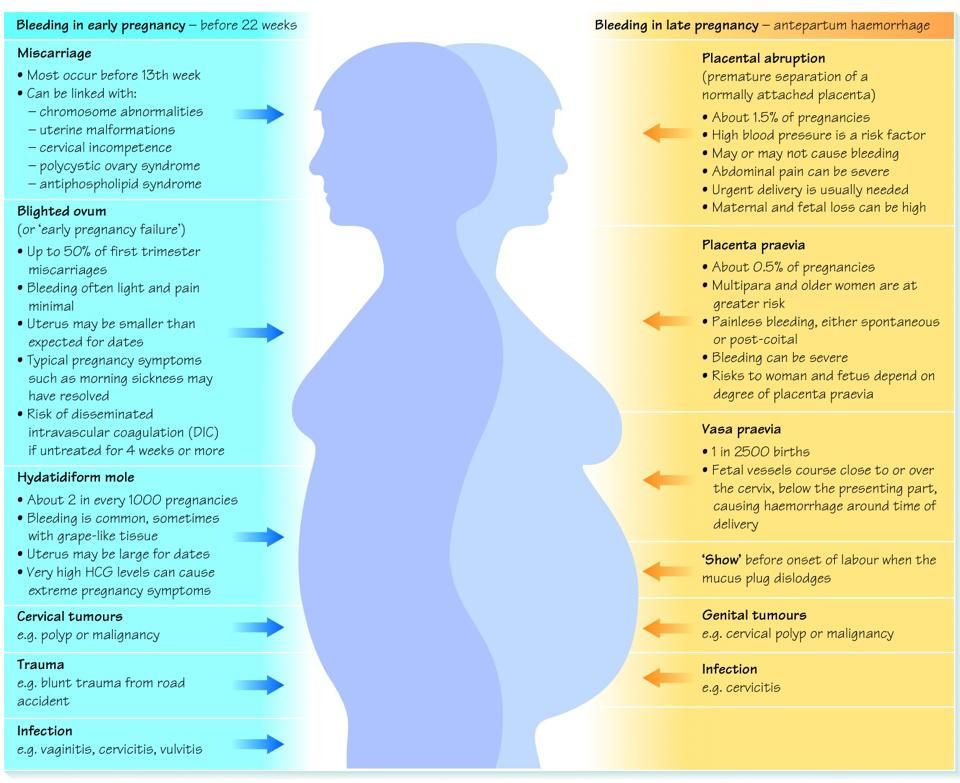
The causes of bleeding during pregnancy are generally divided into two categories — bleeding before 20 weeks and bleeding after 20 weeks gestation.
Before 20 weeks gestation, causes of bleeding may include:
- Implantation bleeding — in very early pregnancy (4 to 5 weeks gestation) some women may experience bleeding when the pregnancy implants itself in the lining of the uterus (womb).
- Miscarriage — bleeding may be the first sign of a miscarriage. About 1 in 15 women who experience bleeding in early pregnancy end up having a miscarriage.
- Ectopic pregnancy — a rare but serious cause of bleeding when a fertilised egg starts growing outside the uterus (womb). An ectopic pregnancy can rupture (burst) and cause heavy bleeding, and may be life-threatening.
Bleeding in later pregnancy (after 20 weeks) is usually caused by problems with the placenta such as:
- Placenta previa — also known as a 'low lying placenta', when the placenta implants close to the cervix (neck of the uterus).
 If the cervix starts to open or the uterus contracts, this can cause bleeding.
If the cervix starts to open or the uterus contracts, this can cause bleeding. - Placental abruption — when the placenta starts to separate from the uterus during pregnancy but before birth, causing bleeding from the place where the placenta has peeled away. Bleeding caused by placental abruption is usually associated with sudden, severe abdominal pain.
Less common causes of bleeding, which may happen at any stage of pregnancy, may include:
- genital tract infections
- injuries to the genital tract
- growths or tumours of the reproductive system
- bleeding from vulvovaginal varicosities (varicose veins in the vulva or vagina)
What should I do if I bleed during pregnancy?
If you bleed during pregnancy, contact your doctor or midwife. Your antenatal care provider can give you advice about what to do next.
It can be helpful to note down details about what you have been experiencing. This may include:
This may include:
- the amount and colour of any discharge
- whether you have passed any clots
- whether you have had any abdominal pain
If you are having heavy bleeding, it’s a good idea to keep your pads or stained clothes to show your doctor or midwife.
How will my doctor or midwife diagnose the cause of my bleeding?
Your doctor or midwife will ask you questions about the bleeding, any other symptoms you have been having and about your pregnancy and general health. Your doctor or midwife may also perform a vaginal examination to check the bleeding and look for any visible cause.
You may be referred for a blood test to check your human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level. hCG is a hormone made by the placenta that can be found in your blood and urine. Your hCG level can give your doctor important information about how your pregnancy is progressing.
You may also be referred for an ultrasound scan, which may be used to:
- check your baby’s heartbeat
- check for signs of a miscarriage
- look for signs of an ectopic pregnancy
- check the position and health of the placenta
It may take some time to work out what is causing your bleeding. You may need to have several blood tests or ultrasound scans over a few days or weeks. This can be a stressful time, so consider seeking support from your partner or someone else you trust.
You may need to have several blood tests or ultrasound scans over a few days or weeks. This can be a stressful time, so consider seeking support from your partner or someone else you trust.
In some situations, your bleeding may resolve on its own without your doctor or midwife finding a cause.
When should I seek medical attention?
If you have bleeding at any stage of pregnancy, contact your doctor or midwife for advice and support.
You should contact your doctor urgently, or visit the nearest emergency department, if:
- your bleeding becomes very heavy
- you have strong pains
- you feel dizzy or faint
- you feel short of breath
If you have very heavy bleeding, strong pain or feel very unwell, call triple zero (000) immediately and ask for an ambulance.
Does bleeding mean I am having a miscarriage or might lose my baby?
Bleeding in early pregnancy is very common and does not necessarily mean you are having a miscarriage.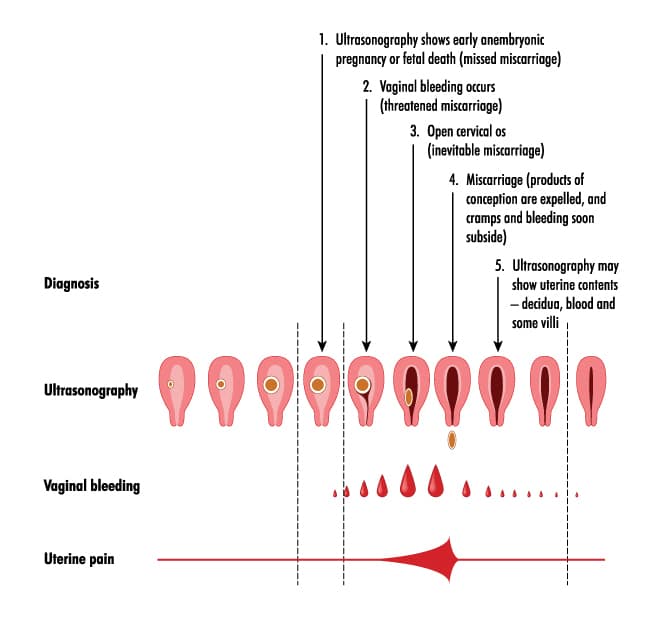 Many women who experience bleeding in early pregnancy go on to have healthy babies.
Many women who experience bleeding in early pregnancy go on to have healthy babies.
In some cases, bleeding can be the first sign of a miscarriage. If you are experiencing bleeding in early pregnancy, contact your doctor or midwife for advice.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
The Royal Women's Hospital (Bleeding in early pregnancy), Safer Care Victoria (Bleeding in early pregnancy), Royal Women's Hospital (Placenta problems), Safer Care Victoria (Antepartum haemorrhage: assessment and management), Australian Family Physician (Early pregnancy bleeding)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: June 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Check-ups, tests and scans available during your pregnancy
- Questions to ask your doctor about tests and scans
- Health professionals involved in your pregnancy
Need more information?
Bleeding or pain in early pregnancy
One in 4 women will experience bleeding and/or pain during their first 12 weeks of pregnancy. Unfortunately half of these pregnancies may also end in miscarriage, which cannot be prevented.
Read more on WA Health website
Natural/Expectant management - Miscarriage Australia
Natural or expectant management is when you wait for your body to miscarry naturally without the use of medicines or physical treatment.
Read more on Miscarriage Australia website
The Pink Elephants Support Network - Types of Miscarriage
A chemical pregnancy is a very early miscarriage that normally ends before 5 weeks
Read more on The Pink Elephants Support Network website
Types of miscarriage - Miscarriage Australia
We explain the different types of miscarriages. Your doctor or specialist may discuss the kind of miscarriage you have experienced with you.
Read more on Miscarriage Australia website
Late miscarriage - Miscarriage Australia
Late miscarriage is a pregnancy loss between 13-20 weeks gestation. It is much less common, occurring in 1-2 in 100 women.
Read more on Miscarriage Australia website
Week by week pregnancy- antenatal care at 7 weeks pregnant
Your doctor can look at your foetus’s features to determine how old they are – find out how. You need to talk to your doctor if you experience very severe morning sickness as you may not be getting all the nutrients you and your baby need or early pregnancy spotting (spot bleeding) as you may be at risk of miscarriage.
Read more on Parenthub website
Having a miscarriage - Miscarriage Australia
Here you can find information about the common symptoms of miscarriage, what happens during a miscarriage, and where to go for help.
Read more on Miscarriage Australia website
Recurrent miscarriage - Miscarriage Australia
Recurrent miscarriage is defined as 3 or more miscarriages in a row. Around 1-2% of women experience recurrent miscarriage.
Around 1-2% of women experience recurrent miscarriage.
Read more on Miscarriage Australia website
Medical management - Miscarriage Australia
Medical management of miscarriage involves taking medication (mifepristone or misoprostol) to bring on the miscarriage.
Read more on Miscarriage Australia website
Am I having a miscarriage? - Miscarriage Australia
We describe the common signs or symptoms of miscarriage. Sometimes there are symptoms, but sometimes there aren't.
Read more on Miscarriage Australia website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.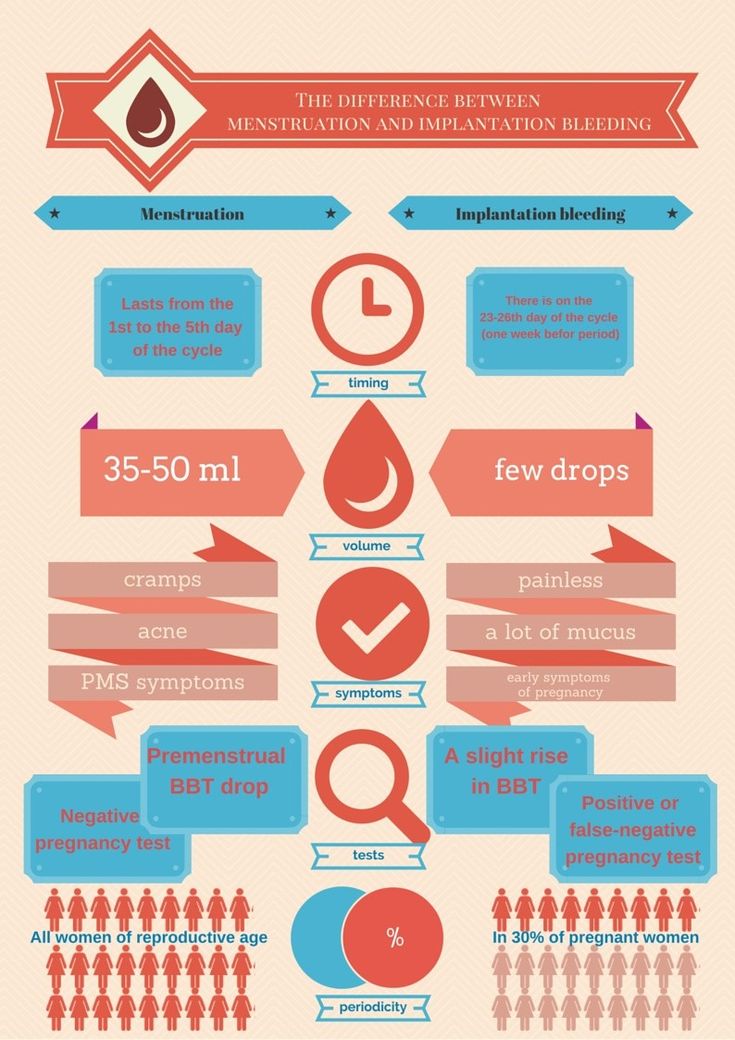
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Vaginal bleeding in late pregnancy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
One out of 10 women will have vaginal bleeding during their 3rd trimester. At times, it may be a sign of a more serious problem. In the last few months of pregnancy, you should always report bleeding to your health care provider right away.
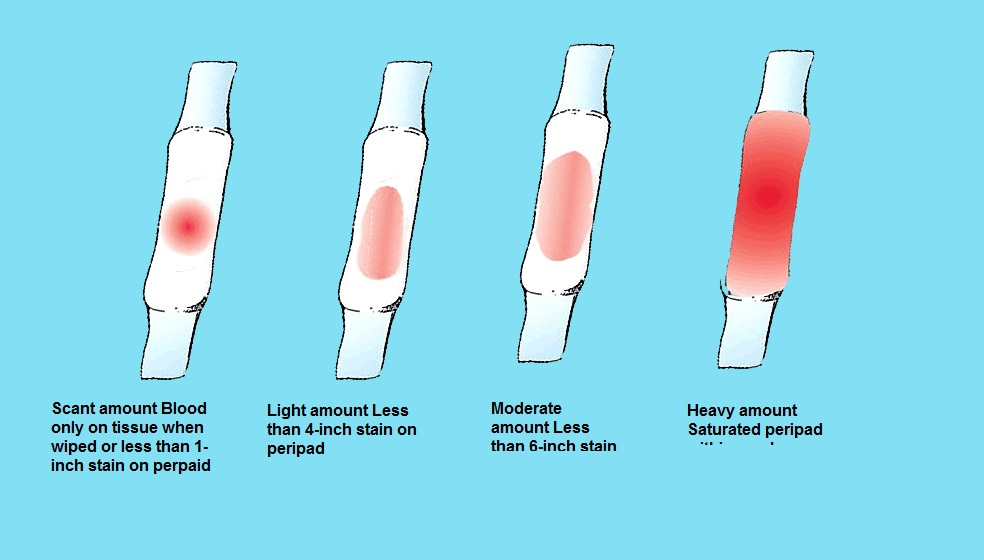
You should understand the difference between spotting and bleeding:
- Spotting is when you notice a few drops of blood every now and then on your underwear.
 It is not enough to cover a panty liner.
It is not enough to cover a panty liner. - Bleeding is a heavier flow of blood. With bleeding, you will need a liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your clothes.
When labor begins, the cervix starts to open up more, or dilate. You may notice a small amount of blood mixed in with normal vaginal discharge, or mucus.
Mid- or late-term bleeding may also be caused by:
- Having sex (most often just spotting)
- An internal exam by your provider (most often just spotting)
- Diseases or infections of the vagina or cervix
- Uterine fibroids or cervical growths or polyps
More serious causes of late-term bleeding may include:
- Placenta previa is a problem of pregnancy in which the placenta grows in the lowest part of the womb (uterus) and covers all or part of the opening to the cervix.
- Placenta abruptio (abruption) occurs when the placenta separates from the inner wall of the uterus before the baby is born.

To find the cause of your vaginal bleeding, your provider may need to know:
- If you have cramping, pain, or contractions
- If you have had any other bleeding during this pregnancy
- When the bleeding began and whether it comes and goes or is constant
- How much bleeding is present, and whether it is spotting or a heavier flow
- The color of the blood (dark or bright red)
- If there is an odor to the blood
- If you have fainted, felt dizzy or nauseated, vomited, or had diarrhea or a fever
- If you have had recent injuries or falls
- When you last had sex and if you bled afterward
- If you're feeling the baby move
- If you've had other complications during the pregnancy
A small amount of spotting without any other symptoms that occurs after having sex or an exam by your provider can be watched at home. To do this:
- Put on a clean pad and recheck it every 30 to 60 minutes for a few hours.
- If spotting or bleeding continues, call your provider.
- If the bleeding is heavy, your belly feels stiff and painful, or you are having strong and frequent contractions, you may need to call 911 or your local emergency number.
For any other bleeding, call your provider right away.
- You will be told whether to go to the emergency room or to the labor and delivery area in your hospital.
- Your provider will also tell you whether you can drive yourself or you should call an ambulance.
Baeseman ZJ. Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, Heidelbaugh JJ, Lee EM, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2023. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2023:1273-1276.
Francois KE, Foley MR. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
Henn MC, Lall MD. Complications of pregnancy.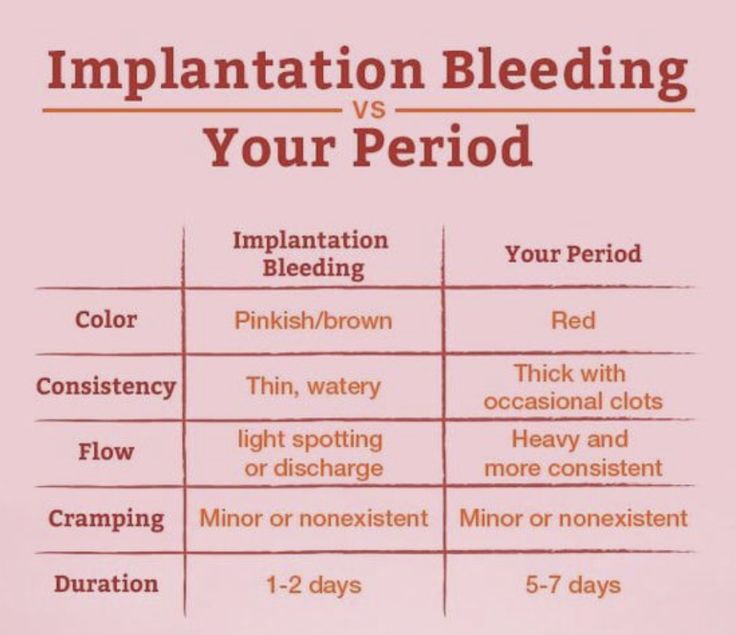 In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 173.
In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 173.
Hull AD, Resnik R, Silver RM. Placenta previa and accreta, vasa previa, subchorionic hemorrhage, and abruptio placentae. In: Lockwood CJ, Copel JA, Dugoff L, et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 43.
Updated by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Browse the Encyclopedia
Bleeding during pregnancy. What is Bleeding During Pregnancy?
IMPORTANT
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Bleeding during pregnancy is a sign that can occur regardless of the period of embryogenesis and indicates ongoing changes in the woman's body. It can be observed with spontaneous miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, Rh conflict, placenta previa and other conditions. This manifestation can develop against the background of general well-being or be accompanied by painful sensations in the lower abdomen, lower back, and sacrum. Diagnosis of bleeding during pregnancy is carried out on the basis of data from a gynecological examination, an ultrasound assessment of the condition of the patient and the fetus. The treatment of this pathological symptom is determined by its cause and is prescribed exclusively by a specialist.
- Causes of bleeding during pregnancy
- Classification and symptoms of bleeding during pregnancy
- Diagnosis and treatment of bleeding during pregnancy
- Prognosis and prevention of bleeding during pregnancy
- Prices for treatment
General
Bleeding during pregnancy is an obstetric symptom, indicating the possible development of a number of disorders, the cause of which can be both physiological changes in the body of a woman after conception, and pathological conditions. Only an obstetrician-gynecologist can finally find out the etiology of such a manifestation after a complete examination. Bleeding during pregnancy occurs in about one in five patients. In 50%, they indicate pathological changes and end in spontaneous miscarriage. In half of the patients, the symptom is physiological in nature. Bleeding occurs more often in the first and third trimester of embryogenesis.
Only an obstetrician-gynecologist can finally find out the etiology of such a manifestation after a complete examination. Bleeding during pregnancy occurs in about one in five patients. In 50%, they indicate pathological changes and end in spontaneous miscarriage. In half of the patients, the symptom is physiological in nature. Bleeding occurs more often in the first and third trimester of embryogenesis.
The danger of bleeding during pregnancy lies in the fact that a variety of factors can provoke them, including those that pose a threat to the mother and fetus. In some situations, there are no other pathological signs. Any bleeding during pregnancy should be a reason for immediate medical attention. Only a specialist is able to assess the danger to the health of a woman and the fetus, as well as decide on further tactics. Timely assistance provided even with an abnormal course of pregnancy allows you to continue its management and save the life of the child.
Bleeding during pregnancy
Causes of bleeding during pregnancy
Bleeding during pregnancy can occur at any time of embryogenesis, develops both against the background of physiological changes in the woman's body, and as a result of the formation of a certain obstetric pathology.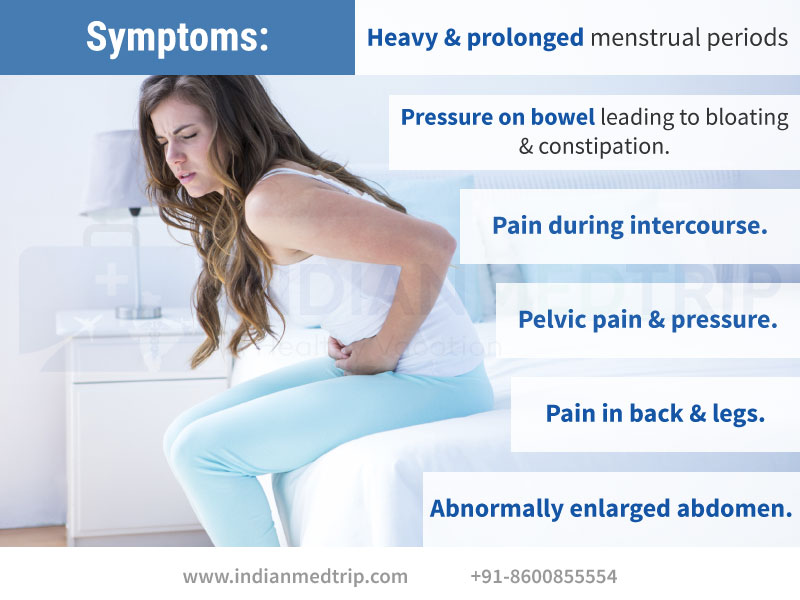 In the early stages, half of the women have a slight separation of blood due to the implantation of the fetal egg in the uterine cavity. Such bleeding during pregnancy is often regarded by the patient as menstrual, so she does not seek medical help, which in the future may make it difficult to determine the timing of embryogenesis. A similar symptom is possible with insufficient production of progesterone in the early stages of gestation.
In the early stages, half of the women have a slight separation of blood due to the implantation of the fetal egg in the uterine cavity. Such bleeding during pregnancy is often regarded by the patient as menstrual, so she does not seek medical help, which in the future may make it difficult to determine the timing of embryogenesis. A similar symptom is possible with insufficient production of progesterone in the early stages of gestation.
The most common cause of abnormal bleeding during pregnancy in the first trimester is spontaneous miscarriage. This symptom appears both with a just-started and with a complete abortion. Approximately 6 weeks after conception, the symptom occurs with an ectopic attachment of the fetal egg. Also, bleeding during pregnancy at this time may indicate an Rhesus conflict, fetal fading. Similar manifestations are characteristic of women suffering from varicose veins that feed the uterus. In this case, bleeding during pregnancy is due to increased blood supply to the tissues.
Bleeding during pregnancy in the second trimester is diagnosed much less frequently, in about 5-10% of all cases of gestation. As a rule, the symptom is caused by pathological changes and in most cases indicates spontaneous late abortion or isthmic-cervical insufficiency. Sometimes the separation of blood from the genital tract is observed during intrauterine death of the fetus. Bleeding during pregnancy in the third trimester also always speaks of the development of gestation pathology. The most common cause is placenta previa. In this case, the embryonic organ completely or partially covers the uterine os, while due to the high load on the lower segment, placental micro-ruptures occur, which causes a similar sign.
Less commonly, bleeding during pregnancy in the third trimester is due to premature detachment of a normally located placenta. In this situation, there is a high threat to the life of the fetus. The danger also lies in the fact that initially internal bleeding develops during pregnancy or the formation of a hematoma, and only then the blood flows out. The rarest, but most dangerous for the life of the mother and child, the cause of the development of this symptom is uterine rupture. Such a complication is diagnosed in the presence of a scar on the myometrium and tissue overstretching, provoked by polyhydramnios, large fetuses or multiple pregnancies. It is extremely rare that bleeding during pregnancy occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the membranes or umbilical cord vessels.
The rarest, but most dangerous for the life of the mother and child, the cause of the development of this symptom is uterine rupture. Such a complication is diagnosed in the presence of a scar on the myometrium and tissue overstretching, provoked by polyhydramnios, large fetuses or multiple pregnancies. It is extremely rare that bleeding during pregnancy occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the membranes or umbilical cord vessels.
Also, bleeding during pregnancy can be triggered by causes that appear at any stage of embryogenesis. Such reasons include benign neoplasms - fibroids, polyposis growths in the cervical canal and uterine cavity. Often bleeding during pregnancy occurs in women with cervical erosion. Sometimes a sign occurs due to increased blood circulation in the pelvic organs. The risk of developing a symptom is also present with violent sexual intercourse, significant physical exertion, concomitant cardiovascular diseases associated with a weakening of the endothelium.
Classification and symptoms of bleeding during pregnancy
Depending on the origin of bleeding, two groups can be distinguished:
- Physiological bleeding during pregnancy - occurs due to the restructuring of the body, does not pose a threat to the health and life of the fetus or mother.
- Pathological bleeding during pregnancy - indicate its abnormal course, may be accompanied by a risk to the life and health of the woman and baby, require immediate medical attention.
The clinic of bleeding during pregnancy directly depends on the cause of this symptom. Isolation of blood from the genital tract in the early stages of embryogenesis, provoked by physiological changes, proceeds against the background of general well-being. Bleeding during pregnancy, which has developed due to the presence of polyps, erosion, fibroids in most cases also does not cause disturbances in well-being. In this case, there is a slight release of biological fluid - just a few drops, the symptom is of a short-term nature. More abundant, similar to menstrual, will be bleeding during pregnancy associated with a deficiency of progesterone.
More abundant, similar to menstrual, will be bleeding during pregnancy associated with a deficiency of progesterone.
In the case of bleeding during pregnancy associated with its spontaneous interruption, the patient is worried about constant or cramping pain in the lumbosacral region, abdomen. Additionally, nausea, dizziness, malaise, and a slight increase in body temperature may occur. Bleeding during pregnancy in this case can be of varying intensity, often in the discharge there are pieces of tissue. With an ectopic attachment of the fetal egg, as well as with a rupture of the uterus, a serious threat to the life of a woman arises. In such a situation, internal bleeding initially develops during pregnancy, and only then do pathological discharges from the external genital tract appear. There is acute pain in the abdomen with irradiation to the anal region, the lateral parts of the body. With significant blood loss, a state of shock occurs with a threat of death.
Bleeding during pregnancy in the later stages is also not always accompanied by a detailed clinical picture. In the case of placenta previa, this is the only symptom that should cause alertness in a woman and become a reason for contacting an obstetrician-gynecologist. As for the premature detachment of a correctly attached placenta, in this case, bleeding during pregnancy develops against the background of uterine hypertonicity, there is pain in the abdomen, deterioration in general well-being. During cardiac monitoring of the fetus, there is a violation of the heart rate, motor activity.
Diagnosis and treatment of bleeding during pregnancy
To identify the cause of bleeding during pregnancy, a gynecological examination of a woman is performed. With changes in physiological origin, no deviations from the norm can be detected. With pathological bleeding during pregnancy against the background of spontaneous abortion, an opening of the cervix is observed. An increase in the tone of the myometrium may indicate the onset of placental abruption. Of the laboratory diagnostic methods, an analysis is used to determine the concentration of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). With ectopic pregnancy and bleeding, this figure will be reduced. Instrumental diagnosis of bleeding during pregnancy is to conduct an ultrasound scan. Using this method, it is possible to assess the state of the myometrium and the embryo, the level of blood flow in the vessels, the exact localization of the placenta and (possibly) its incipient detachment. Using CTG, the diagnostician can make a conclusion about the vital activity of the fetus.
An increase in the tone of the myometrium may indicate the onset of placental abruption. Of the laboratory diagnostic methods, an analysis is used to determine the concentration of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). With ectopic pregnancy and bleeding, this figure will be reduced. Instrumental diagnosis of bleeding during pregnancy is to conduct an ultrasound scan. Using this method, it is possible to assess the state of the myometrium and the embryo, the level of blood flow in the vessels, the exact localization of the placenta and (possibly) its incipient detachment. Using CTG, the diagnostician can make a conclusion about the vital activity of the fetus.
Treatment of bleeding during pregnancy also depends on the cause of the symptom. If there are no pathological changes or the manifestation is provoked by damage to the polyp, medical attention is not required. In rare cases, the doctor recommends its removal. Expectant tactics are also used in case of cervical erosion.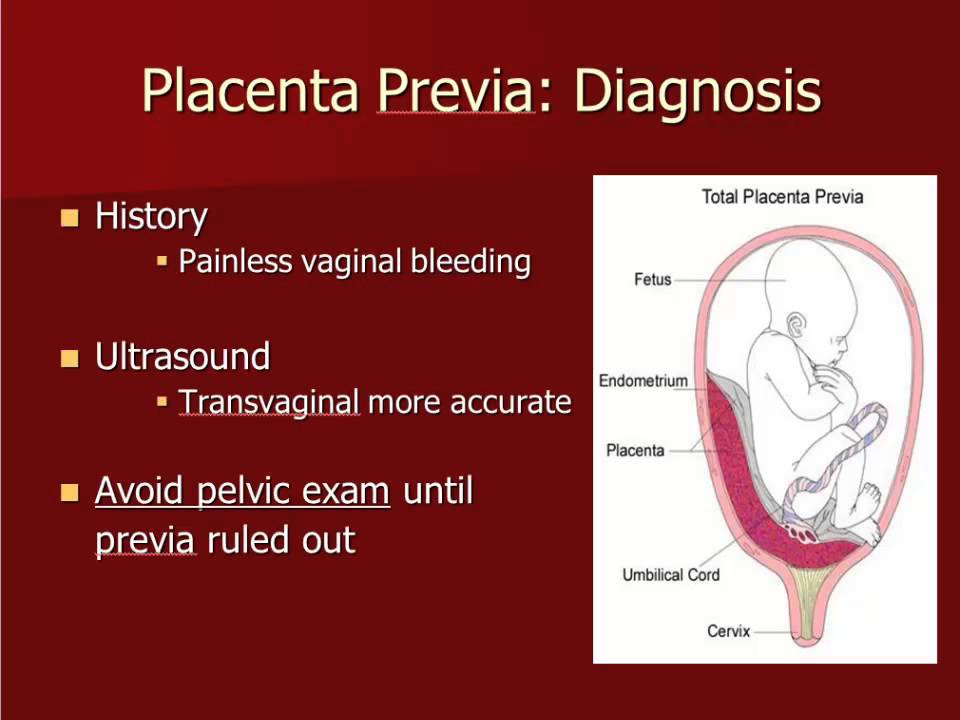 Her cauterization is carried out after childbirth. Bleeding during pregnancy against the background of the threat of miscarriage and placenta previa requires immediate hospitalization in an obstetric hospital, followed by the appointment of drug treatment. To reduce uterine tone, sedatives, tocolytics are used. Pregnancy management in this case requires careful monitoring by a specialist.
Her cauterization is carried out after childbirth. Bleeding during pregnancy against the background of the threat of miscarriage and placenta previa requires immediate hospitalization in an obstetric hospital, followed by the appointment of drug treatment. To reduce uterine tone, sedatives, tocolytics are used. Pregnancy management in this case requires careful monitoring by a specialist.
Bleeding during pregnancy caused by ectopic attachment of the ovum, scar rupture, or completed spontaneous abortion requires hospitalization and surgical treatment. After removal of the remnants of fetal tissues or emergency delivery, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. In this case, stopping bleeding during pregnancy is carried out in different ways, depending on its intensity, often ligation of the uterine arteries is performed. With premature detachment of the placenta, an emergency caesarean section is indicated.
Prognosis and prevention of bleeding during pregnancy
Bleeding during pregnancy is usually accompanied by a favorable prognosis. Timely medical care can save the life of the fetus and the woman. Lethal outcome is extremely rare. Prevention of bleeding during pregnancy consists in the early detection of benign neoplasms and their treatment even before conception. To prevent the development of a pathological symptom, you should register as soon as possible, take all the necessary tests, and if any violations occur, immediately seek advice from an obstetrician-gynecologist. Prevention of bleeding during pregnancy also consists in avoiding stress, physical exertion, violent sexual contacts.
Timely medical care can save the life of the fetus and the woman. Lethal outcome is extremely rare. Prevention of bleeding during pregnancy consists in the early detection of benign neoplasms and their treatment even before conception. To prevent the development of a pathological symptom, you should register as soon as possible, take all the necessary tests, and if any violations occur, immediately seek advice from an obstetrician-gynecologist. Prevention of bleeding during pregnancy also consists in avoiding stress, physical exertion, violent sexual contacts.
You can share your medical history, what helped you in the treatment of bleeding during pregnancy.
Sources
- In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy ᐈ Blood during early pregnancy
Seeing bloody discharge, a pregnant woman is always frightened.
 They are considered a symptom of miscarriage and other equally serious pathologies. At the same time, in some cases, the appearance of a small amount of blood is considered the norm and does not pose a threat to the life and health of the fetus or the expectant mother.
They are considered a symptom of miscarriage and other equally serious pathologies. At the same time, in some cases, the appearance of a small amount of blood is considered the norm and does not pose a threat to the life and health of the fetus or the expectant mother. In early pregnancy, bloody discharge occurs in 25% of women. In most cases, they are associated with the implantation of the fetal egg to the wall of the uterus. Also, scanty spotting may appear on the dates of the expected menstruation. If they end quickly, are not accompanied by pain, and the woman has not had miscarriages or pregnancy complications before, most likely she has nothing to worry about. However, it is necessary to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Why bloody discharge can appear and when it is dangerous, said Elena Petrovna Domnich, obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound specialist of the ADONIS medical center.
Elena Nikolaevna, tell me, can a woman have periods during pregnancy?- Sometimes during pregnancy, a woman may experience spotting, but this should not be interpreted as menstruation. Menstruation occurs at the end of the menstrual cycle, during which the endometrium changes, first proliferative, then secretory. During the cycle, the endometrium prepares for pregnancy, and if it does not occur, then menstruation begins.
In the event of pregnancy, menstruation is not possible, although bleeding may occur at the expected time. Because of this, some women do not immediately know that they are pregnant. However, when the obstetrician-gynecologist at the reception asks them about the nature of the discharge, it always turns out that they are different from menstrual. As a rule, they are more scarce, pass faster and are not accompanied by other symptoms. Sometimes a woman says that her period was very recent, but at the time of examination and examination, we find that she is already 8 or 12 weeks pregnant.

How often does this happen? Is spotting during pregnancy an exception or a fairly common occurrence?- Bloody discharge is rare in pregnant women, but still it cannot be said that these are exceptional cases.
Tell me, if a woman is planning to conceive a child, and during the expected period she has unusual discharge, should she take a pregnancy test?– Yes, but it is better to visit an obstetrician-gynecologist. There are cases when a woman is pregnant, but the test strip shows a negative result. To accurately determine whether there is a pregnancy, allows a blood test for the level of hCG.
So bleeding during pregnancy is not menstruation, but bleeding? Why can it appear and why is it dangerous?- Yes, that's right. This is bleeding, not menstruation. It can be a symptom of a miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or other pathology.
 For diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
For diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
Tell me more, if a woman has a discharge and thinks she is menstruating, but a previous pregnancy test came back positive, could it be wrong?- A pregnancy test is sometimes positive even if it is not. This happens if a woman has formed luteal cysts or developed a thyroid disease.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy requires contacting the antenatal clinic or the medical center where the woman was registered for pregnancy management. Sometimes they may not be dangerous, but without diagnosis, it cannot be ruled out that this is a symptom of a serious disorder.
Bleeding may occur with:
- threatened miscarriage;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- infectious diseases of the reproductive system;
- cysts;
- myomas;
- cervical erosion;
- placental abruption;
- threatened preterm birth.
You can watch the video version of Elena Petrovna Domnich's interview here.