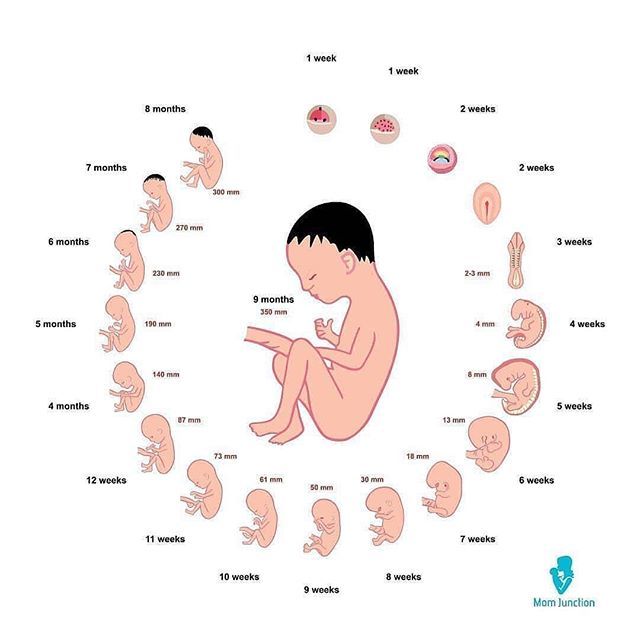
Average amount of weight gained during pregnancy
Weight Gain During Pregnancy: How Much Is Normal?
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- Where Does the Extra Weight Go During Pregnancy?
- Is It Safe to Lose Weight When Pregnant?
- How to Gain the Right Amount of Weight During Pregnancy
- What if You Gain Too Much Weight During Pregnancy?
- When to Call Your Doctor
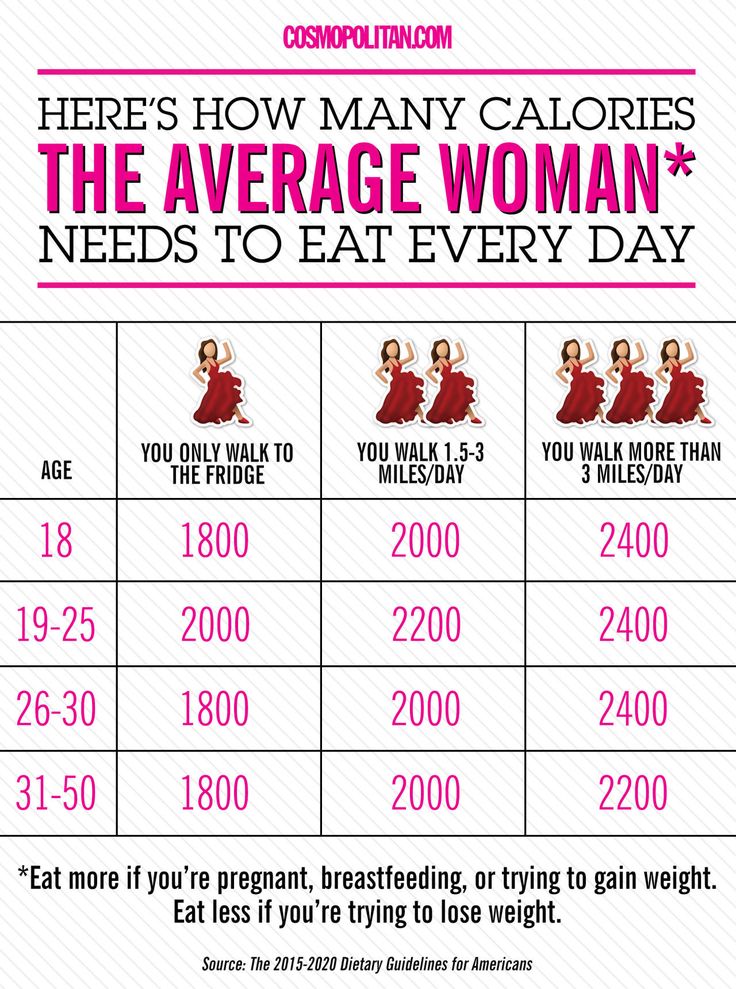
Eating a healthy, balanced diet will help your baby get the nutrients they need and grow at a healthy rate. But how many extra calories do you really need?
Though you do need some extra calories, it's not necessary to ''eat for two.'' The average pregnant woman needs only about 300 healthycalories more a day than they did before they were pregnant. This will help them gain the right amount of weight during pregnancy.
Ask your health care provider how much weight you should gain. A woman who was average weight before getting pregnant should gain 25 to 35 pounds after becoming pregnant. Underweight women should gain 28 to 40 pounds. And overweight women may need to gain only 15 to 25 pounds during pregnancy.
In general, you should gain about 2 to 4 pounds during the first 3 months you're pregnant and 1 pound a week during the rest of your pregnancy. If you are expecting twins you should gain 35 to 45 pounds during your pregnancy. This would be an average of 1 ½ pounds per week after the usual weight gain in the first 3 months.
It's especially important to gain the right amount of weight when you're expecting twins because your weight affects the babies' weight. And because twins are often born before the due date, a higher birth weight is important for their health. When carrying twins, you may need between 3,000 and 3,500 calories a day.
Where Does the Extra Weight Go During Pregnancy?
- Baby: 8 pounds
- Placenta: 2-3 pounds
- Amniotic fluid: 2-3 pounds
- Breast tissue: 2-3 pounds
- Blood supply: 4 pounds
- Stored fat for delivery and breastfeeding: 5-9 pounds
- Larger uterus: 2-5 pounds
- Total: 25-35 pounds
Is It Safe to Lose Weight When Pregnant?
If a woman is very overweight when they get pregnant, their doctor may want them to lose weight. They should only lose weight under their doctor's care. But in most cases, women should not try to lose weight or diet during pregnancy.
They should only lose weight under their doctor's care. But in most cases, women should not try to lose weight or diet during pregnancy.
How to Gain the Right Amount of Weight During Pregnancy
If your health care provider wants you to gain weight while you're pregnant, try these tips:
- Eat five to six small meals every day.
- Keep quick, easy snacks on hand, such as nuts, raisins, cheese and crackers, dried fruit, and ice cream or yogurt.
- Spread peanut butter on toast, crackers, apples, bananas, or celery. One tablespoon of creamy peanut butter gives you about 100 calories and 7 grams of protein.
- Add nonfat powdered milk to mashed potatoes, scrambled eggs, and hot cereal.
- Add extras to your meal, such as butter or margarine, cream cheese, gravy, sour cream, and cheese.
What if You Gain Too Much Weight During Pregnancy?
If you have gained more weight than your doctor recommended, talk to your doctor about it. In most cases, you'll want to wait until after delivery to lose weight.
Here are some tips to slow your weight gain:
- When eating fast food, choose lower-fat items such as broiled chicken breast sandwich with tomato and lettuce (no sauce or mayonnaise), side salad with low-fat dressing, plain bagels, or a plain baked potato. Avoid foods such as French fries, mozzarella sticks, or breaded chicken patties.
- Avoid whole milk products. You need at least four servings of milk products every day. However, using skim, 1%, or 2% milk will greatly reduce the amount of calories and fat you eat. Also, choose low-fat or fat-free cheese or yogurt.
- Limit sweet or sugary drinks. Sweetened drinks such as soft drinks, fruit punch, fruit drinks, iced tea, lemonade, or powdered drink mixes have lots of empty calories. Choose water, club soda, or mineral water to skip extra calories.
- Don't add salt to foods when cooking. Salt causes you to retain water.
- Limit sweets and high-calorie snacks. Cookies, candies, donuts, cakes, syrup, honey, and potato chips have a lot of calories and little nutrition.
 Try not to eat these foods every day. Instead, try fresh fruit, low-fat yogurt, angel food cake with strawberries, or pretzels as lower-calorie snack and dessert choices.
Try not to eat these foods every day. Instead, try fresh fruit, low-fat yogurt, angel food cake with strawberries, or pretzels as lower-calorie snack and dessert choices. - Use fats in moderation. Fats include cooking oils, margarine, butter, gravy, sauces, mayonnaise, regular salad dressings, sauces, lard, sour cream, and cream cheese. Try lower-fat alternatives.
- Cook food the healthy way. Frying foods in oil or butter will add calories and fat. Baking, broiling, grilling, and boiling are healthier preparation methods.
- Exercise. Moderate exercise can help burn excess calories. Walking or swimming is usually safe for pregnant women. Ask your health care provider what exercise would be right for you before getting started.
When to Call Your Doctor
Talk to your doctor if you:
- Want to know a good target weight gain for you
- Think you are gaining too much weight
- Are losing weight during the second or third trimester
- Have an eating disorder that is keeping you from eating a healthy amount of food
- Need help setting a good menu plan to gain a healthy amount of weight
- Gain weight rapidly.
 This could be a sign of preeclampsia, pregnancy-related high blood pressure, a serious health issue
This could be a sign of preeclampsia, pregnancy-related high blood pressure, a serious health issue
Health & Pregnancy Guide
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor and Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Guide Topics
Managing your weight gain during pregnancy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
Most women should gain somewhere between 25 and 35 pounds (11.5 to 16 kilograms) during pregnancy. Most will gain 2 to 4 pounds (1 to 2 kilograms) during the first trimester, and then 1 pound (0.5 kilogram) a week for the rest of the pregnancy. The amount of weight gain depends on your situation.
- Overweight women need to gain less (15 to 25 pounds or 7 to 11 kilograms or less, depending on their pre-pregnancy weight).
- Underweight women will need to gain more (28 to 40 pounds or 13 to 18 kilograms).

- You should gain more weight if you are having more than 1 baby. Women having twins need to gain 37 to 54 pounds (16.5 to 24.5 kilograms).
A balanced, nutrient-rich diet, along with exercise, is the basis for a healthy pregnancy. For most pregnant women, the right amount of calories is:
- 1,800 calories per day in the 1st trimester
- 2,200 calories per day in the 2nd trimester
- 2,400 calories per day in the 3rd trimester
Much of the weight that you gain during pregnancy is not fat, but is related to the baby. Here is a breakdown of how 35 pounds (16 kilograms) adds up:
- Baby: 8 pounds (3.5 kilograms)
- Placenta: 2 to 3 pounds (1 to 1.5 kilograms)
- Amniotic fluid: 2 to 3 pounds (1 to 1.5 kilograms)
- Breast tissue: 2 to 3 pounds (1 to 1.5 kilograms)
- Blood supply: 4 pounds (2 kilograms)
- Fat stores: 5 to 9 pounds (2.5 to 4 kilograms)
- Uterus growth: 2 to 5 pounds (1 to 2.5 kilograms)
Some women are already overweight when they get pregnant. Other women gain weight too quickly during their pregnancy. Either way, a pregnant woman should not go on a diet or try to lose weight during pregnancy.
Other women gain weight too quickly during their pregnancy. Either way, a pregnant woman should not go on a diet or try to lose weight during pregnancy.
It is better to focus on eating the right foods and staying active. If you do not gain enough weight during pregnancy, you and your baby may have problems.
Still, you can make changes in your diet to get the nutrients you need without gaining too much weight. Talk to your health care provider to get help with planning a healthy diet.
Below are some healthy eating tips to help you get started.
Healthy choices:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables make good snacks. They are full of vitamins and low in calories and fat.
- Eat breads, crackers, and cereals made with whole grains.
- Choose reduced-fat dairy products. You need at least 4 servings of milk products every day. However, using skim, 1%, or 2% milk will greatly reduce the amount of calories and fat you eat. Also choose low-fat or fat-free cheese or yogurt.
Foods to avoid:
- Naturally sweetened is better than foods and drinks with added sugar or artificial sweeteners.
- Food and drinks that list sugar or corn syrup as one of the first ingredients are not good choices.
- Many sweetened drinks are high in calories. Read the label and watch out for drinks that are high in sugar. Substitute water for sodas and fruit drinks.
- Avoid junk-food snacks, such as chips, candy, cake, cookies, and ice cream. The best way to keep from eating junk food or other unhealthy snacks is to not have these foods in your house.
- Go light on fats. Fats include cooking oils, margarine, butter, gravy, sauces, mayonnaise, regular salad dressings, lard, sour cream, and cream cheese. Try the lower-fat versions of these foods.
Eating out:
- Knowing the amount of calories, fat, and salt in your food can help you eat healthier.
- Most restaurants have menus and nutrition facts on their websites. Use these to plan ahead.

- In general, eat at places that offer salads, soups, and vegetables.
- Avoid fast food.
Cooking at home:
- Prepare meals using low-fat cooking methods.
- Avoid fried foods. Frying foods in oil or butter will increase the calories and fat of the meal.
- Baking, broiling, grilling, and boiling are healthier, lower-fat methods of cooking.
Exercise:
- Moderate exercise, as recommended by your provider, can help burn extra calories.
- Walking and swimming are generally safe, effective exercises for pregnant women.
- Be sure to talk to your provider before starting an exercise program.
If you have struggled with your weight in the past, it may be hard to accept that it is OK to gain weight now. It is normal to feel anxious as the numbers on the scale edge up.
Keep in mind that you need to gain weight for a healthy pregnancy. The extra pounds will come off after you have had your baby. However, if you gain a lot more weight than is recommended, your baby will also be bigger. That can sometimes lead to problems with delivery. A healthy diet and regular exercise are your best ways to ensure a healthy pregnancy and baby.
That can sometimes lead to problems with delivery. A healthy diet and regular exercise are your best ways to ensure a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Prenatal care - managing your weight
Berger DS, West EH. Nutrition during pregnancy. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe’s Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 6.
Bodnar LM, Himes KP. Maternal nutrition. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 12.
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Center for Fertility, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Browse the Encyclopedia
Pregnancy weight gain - What is BMI?
- Contents
Every woman gains a certain amount of weight during pregnancy. But in this case, it cannot be called superfluous, since each kilogram appears for a reason. You should not be afraid of such weight gain, because often after childbirth, most women manage to quickly return to their usual form. However, one should not “launch” oneself either - too rapid weight gain at each stage of pregnancy can have negative consequences. Everything should be in moderation, and in order to control it, you need to know in advance what should be the rate of weight gain during pregnancy. nine0008
But in this case, it cannot be called superfluous, since each kilogram appears for a reason. You should not be afraid of such weight gain, because often after childbirth, most women manage to quickly return to their usual form. However, one should not “launch” oneself either - too rapid weight gain at each stage of pregnancy can have negative consequences. Everything should be in moderation, and in order to control it, you need to know in advance what should be the rate of weight gain during pregnancy. nine0008
What is the normal weight gain during pregnancy?
This indicator is individual. Some gain only 5-6 kg, feeling fine, having no problems with bearing a child. There are those who gain more than 20 kg, also without complaints and complications. However, in most cases, the rate of weight gain during pregnancy is average between these values - 9-14 kg when carrying one child and 16-21 kg if the pregnancy is multiple.
It is also important to remember that during the first trimester a pregnant woman may not notice weight gain.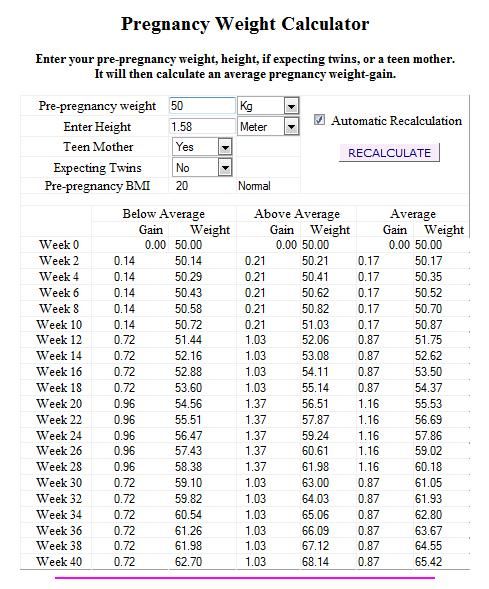 Firstly, the fetus is just being formed, and it is too early to talk about its growth. Secondly, many during this period have severe toxicosis, accompanied by a deterioration in appetite and vomiting. As a result of such conditions, a woman can, on the contrary, lose a couple of kilograms. Starting from the second trimester, weight gain becomes more noticeable. Usually it is about 1 kg per month. The sharpest jump can be seen in recent months - then a woman can recover more than 400 g per week. nine0008
Firstly, the fetus is just being formed, and it is too early to talk about its growth. Secondly, many during this period have severe toxicosis, accompanied by a deterioration in appetite and vomiting. As a result of such conditions, a woman can, on the contrary, lose a couple of kilograms. Starting from the second trimester, weight gain becomes more noticeable. Usually it is about 1 kg per month. The sharpest jump can be seen in recent months - then a woman can recover more than 400 g per week. nine0008
It should be borne in mind that these are only generalized data, and they should not be taken as a rigid norm of weight gain during pregnancy. Only a doctor can determine whether this or that weight gain is acceptable for a woman and her fetus. This is especially true in cases where a pregnant woman has concomitant health problems, or she bears more than three children.
Due to what the weight of the pregnant woman increases?
So that a pregnant woman is not afraid of the fact that she is gaining kilograms, she needs to understand where they come from. nine0020 The main sources of weight gain are:
nine0020 The main sources of weight gain are:
- Fetal weight. The child in the womb is getting bigger every day, respectively, this affects the weight indicator, adding up to 3-4 kg.
- Enlarged uterus and amniotic fluid. Usually, at their expense, a pregnant woman gains up to 2 kg before giving birth.
- Increased blood volume in the body. This indicator can vary greatly, but usually about 1.5 kg is assigned to it.
- The appearance of additional fluid in the body. Its weight can be from 1.5 to 3 kg. nine0005
Do not forget that in the last weeks before childbirth, a woman's mammary glands begin to increase - milk accumulates in them. This process increases the total weight by about 0.5 kg.
Regardless of how a woman eats during pregnancy, avoiding the accumulation of body fat is extremely rare. The norm can be considered a situation when their weight does not exceed 3-4 kg. This indicator can be considered the most unstable. If a woman was actively involved in sports before pregnancy, she may gain less. If a pregnant woman allows herself to eat too much, or takes hormonal drugs to preserve the fetus, this can lead to a significant increase in this indicator. nine0008
If a woman was actively involved in sports before pregnancy, she may gain less. If a pregnant woman allows herself to eat too much, or takes hormonal drugs to preserve the fetus, this can lead to a significant increase in this indicator. nine0008
What factors influence weight gain during pregnancy?
Although the sources of weight gain are clearly identified, there are internal and external factors that can affect the amount of weight gained.
The main ones are:
- Woman's reference weight. Of course, this factor cannot be considered decisive, but it shows that usually thin women gain more extra pounds during pregnancy than obese women.
- Growth of a pregnant woman. Tall women tend to gain more kg. nine0005
- Tendency to be overweight. If a woman has such a predisposition, she needs to be especially careful, because during pregnancy she can gain a lot of extra pounds.
- Great increase in appetite. This factor is not common to everyone, but to the majority.
 Feeling a sharp increase in appetite, women can succumb to it, or vice versa - try to restrain themselves, controlling weight gain in themselves and in the fetus.
Feeling a sharp increase in appetite, women can succumb to it, or vice versa - try to restrain themselves, controlling weight gain in themselves and in the fetus. - The presence of toxicosis. If such conditions are frequent and severe, it can lead to weight loss, which is highly undesirable during pregnancy. nine0005
- Presence of comorbidities, such as diabetes mellitus. In this case, a violation of metabolic processes is possible, which will cause weight gain.
It is worth remembering that age can also affect the rate of weight gain. The older a woman is, the more difficult it is for her to control her weight gain during pregnancy. Therefore, for those who give birth in adulthood, it is important to pay special attention to this issue.
Body mass index when calculating weight gain
BMI is one of the basic concepts, using which you can control the process of weight gain during pregnancy. This indicator is calculated quite simply - according to the formula: the usual weight of a person must be divided by his height (m) squared.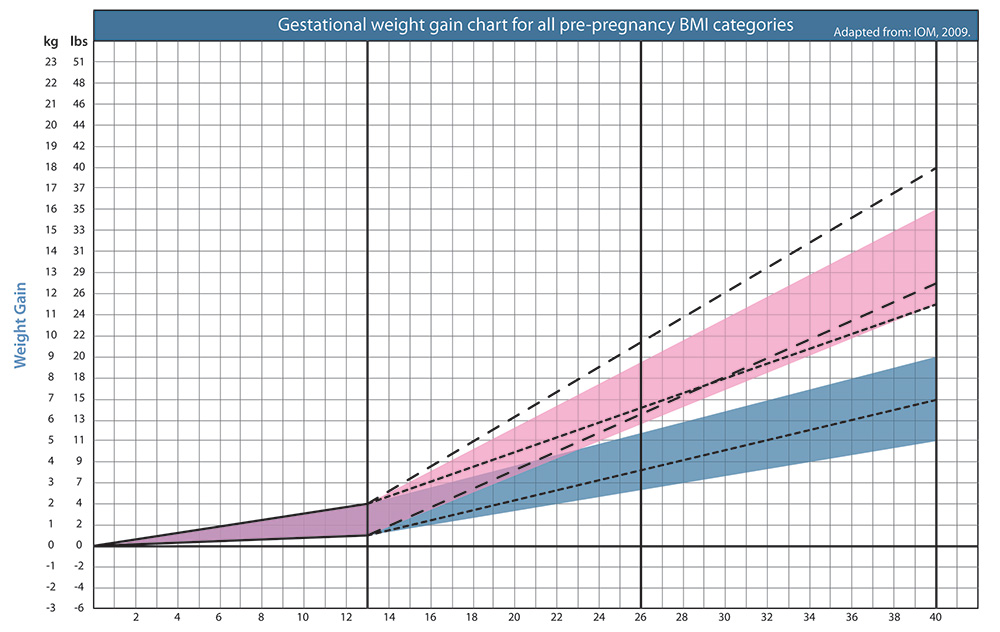
The resulting figure can be attributed to 3 types of figures:
- up to 19.8 (group 1) - the thinnest women
- 19.8-26 (group 2) - women with an average build
- from 26 (group 3) - obese women
For example
With a height of 1.75 m, a woman weighs 65 kg.
1.75*1.75≈3.
65:3=21.6
It is the body mass index that is used in calculating the rate of weight gain during pregnancy by trimester or week. The easiest way to do this is to use a weight gain calculator.
Risk of being underweight during pregnancy
Severe weight loss during pregnancy or simply lack of body weight can adversely affect the health of both the woman and the child. nine0020 Possible risks are:
- premature birth, which may be of great danger to both mother and child
- too low birth weight, which can cause health problems
- asthenia and slow weight gain of the baby in the first months after birth
To exclude the possibility of such unpleasant situations, it is important to notice the underweight in time and determine its cause. It may consist in malnutrition, severe toxicosis, etc. Usually, such conditions can be successfully corrected by taking special medications or diets. nine0008
It may consist in malnutrition, severe toxicosis, etc. Usually, such conditions can be successfully corrected by taking special medications or diets. nine0008
Why is too rapid weight gain during pregnancy dangerous?
Rapid weight gain during pregnancy, as well as its reduction, is fraught with the following pathologies:
- development of gestational diabetes mellitus
- increase in blood pressure
- risk of preeclampsia - severe deterioration of the pregnant woman in the last weeks before delivery
- persistent headaches
- premature aging of the placenta
- metabolic disorder
It is important to remember that if the expectant mother recovers rapidly, the same happens to the fetus. Its large weight can complicate the process of natural childbirth, because of which you will have to do a caesarean. It also increases the risk of preterm birth with complications.
How to maintain a correct BMI during pregnancy: nutritional advice
No matter how fast a woman gains weight during pregnancy, it is important for her to follow a healthy diet. In addition to the ability to maintain normal weight, it will also help maintain the health of the pregnant woman and the child. nine0020 The following recommendations can be considered universal:
In addition to the ability to maintain normal weight, it will also help maintain the health of the pregnant woman and the child. nine0020 The following recommendations can be considered universal:
- Exclusion from the diet of a large number of sweet foods, primarily flour.
- The use of fermented milk products in sufficient quantities (they will help improve metabolic processes).
- Selection of foods that contain folic acid. If this is not possible, you can take the appropriate drugs.
- Refusal of fatty, fried and smoked foods - such food can not only cause weight gain, but also adversely affect the health of the fetus, as it worsens the quality of the blood. nine0005
- Emphasis on fresh fruits and vegetables - they will improve digestion, provide the bodies of a pregnant woman and a child with the necessary vitamins.
It is also important to ensure that the diet is balanced in terms of protein, fat and carbohydrates. If it is not possible to independently develop the correct nutrition schedule, then it is better to consult a doctor who will suggest the optimal diet. To do this, you can visit the Ivimed reproductive health clinic. Thanks to this, the norm of weight during pregnancy will be observed. nine0008
If it is not possible to independently develop the correct nutrition schedule, then it is better to consult a doctor who will suggest the optimal diet. To do this, you can visit the Ivimed reproductive health clinic. Thanks to this, the norm of weight during pregnancy will be observed. nine0008
How does weight change during pregnancy?
Natural weight gain during pregnancy is absolutely normal, read about the rate of weight gain in each trimester
Many women constantly monitor their weight and during pregnancy begin to worry about the weight gained. Natural weight gain "in position" is absolutely normal. Expectant mothers should know more about the rate of weight gain in each trimester. nine0008
It is worth noting that the number of overweight women during pregnancy is growing every year 1 . Excessive weight negatively affects the well-being of a pregnant woman, contributes to the appearance of edema, complicates the course of pregnancy and the birth itself.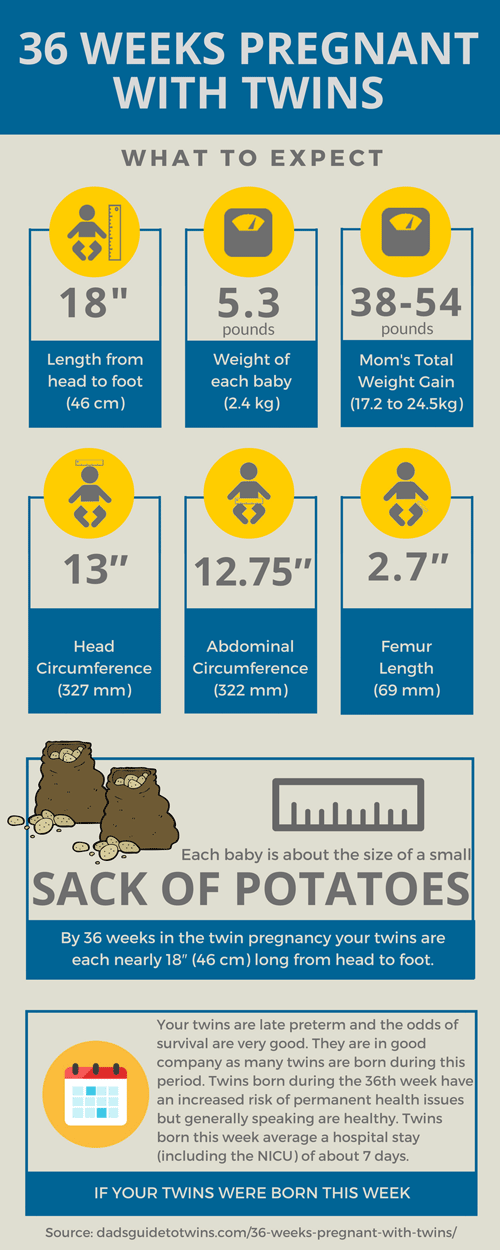 The risks of complications for expectant mothers are growing with every kilogram gained in excess of the norm.
The risks of complications for expectant mothers are growing with every kilogram gained in excess of the norm.
Below are the average gains, which may vary up or down. In order not to be disappointed by the numbers you see on the scales, you should weigh yourself correctly. It is better to do this in the morning, before breakfast, preferably always in the same clothes or naked. It is also worth observing the weighing interval, so it will be easier to keep statistics. The optimal interval is a week. nine0008
In addition to home weight checks, each expectant mother is weighed monthly, without fail, during examinations at the antenatal clinic. In the third trimester, the procedure is already carried out twice a month.
Norm of weight gain in different trimesters
It is believed that the allowable weight gain during pregnancy should be calculated individually. The value of the increase can be influenced by the initial weight and age, bad habits, and even belonging to a certain race.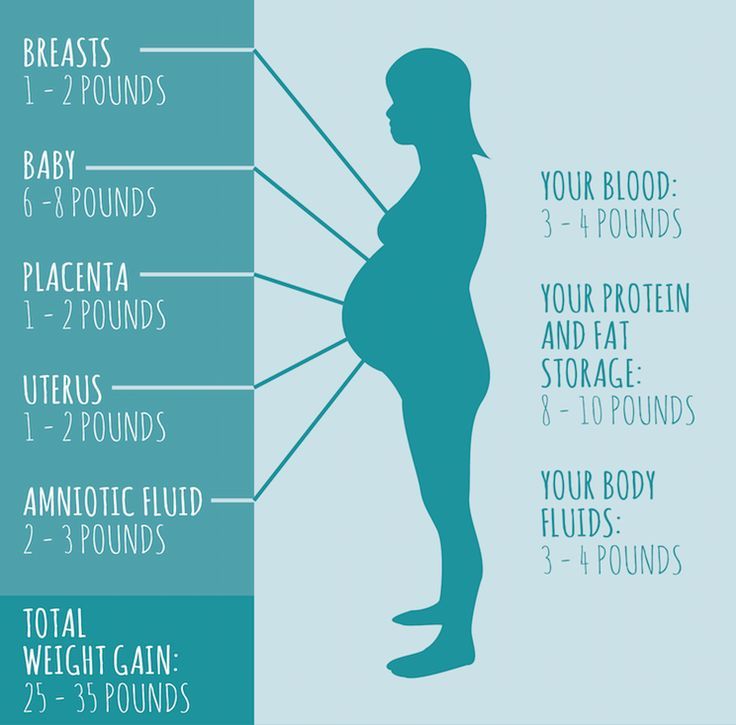 Usually, the average value is an increase of 9up to 11 kg. More accurate values of the recommended weight gain can only be given by a doctor, taking into account the characteristics of the body of a pregnant woman and the body mass index (BMI) 1 .
Usually, the average value is an increase of 9up to 11 kg. More accurate values of the recommended weight gain can only be given by a doctor, taking into account the characteristics of the body of a pregnant woman and the body mass index (BMI) 1 .
- The first trimester is characterized by a slight weight gain. Some women may even lose weight, which is associated with toxicosis. The norm is an increase in weight of 1-2 kilograms.
- The second trimester will not go unnoticed, the increase will be obvious. Toxicosis and constant fatigue cease to torment, certain preferences in food appear. The addition of 1 kg per month during this period is considered the norm. nine0005
- Just before the birth, the expectant mother can see that she has grown by 11-16 kg. These numbers are considered normal. If a woman is expecting twins, the figure can increase to 21 kg.
Alarming signals during pregnancy are a rapid jump in weight (a sharp set) or a complete lack of gain. Weight loss in the second or third trimester carries risks to the health of the mother and fetus. During this period, the baby growing in the womb simply needs nutrients, and their lack can lead to pathologies and underweight. nine0008
Weight loss in the second or third trimester carries risks to the health of the mother and fetus. During this period, the baby growing in the womb simply needs nutrients, and their lack can lead to pathologies and underweight. nine0008
What makes up the weight gained during pregnancy
The bulk of the weight gain comes from the baby's weight. On average, the fetus weighs from 3.2 to 3.6 kilograms. But in addition to the weight of the child, the increase is calculated from the following 1 :
- The increase in blood volume is about 1.3-1.8 kg.
- Body fluid weight increases by 0.9-1.3 kg.
- Another 2.7-3.6 kg is the necessary body fat. nine0005
- 0.9-1.3 kg accounts for a significant increase in the mammary glands.
- The placenta weighs 0.7 kg.
- The uterus increases in weight by 0.9 kg.
As already mentioned, weight gain up to 16 kg is the norm and should not cause concern to the expectant mother.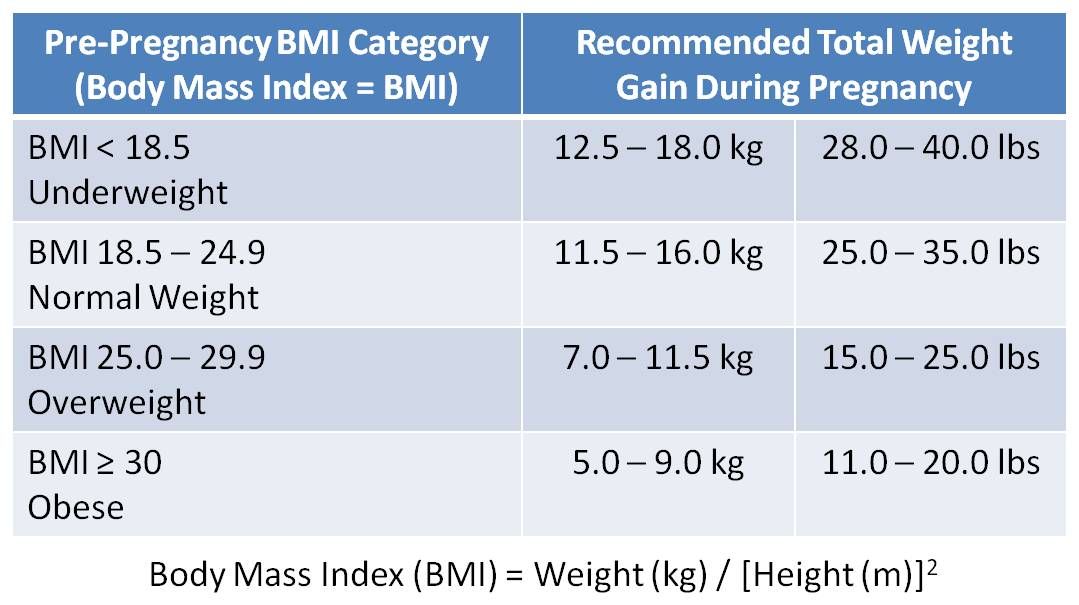
Helpful Hints
Many women, having learned about pregnancy, decide to eat "for two." This is a clear fallacy. You need to eat not “for”, but “for” two. It is better to give preference to the quality of products than their quantity. They should be rich in vitamins, trace elements and nutrients. It is better to abandon the constant use of fried, smoked, too salty and peppery. This will avoid problems with metabolism and the appearance of extra kilos. nine0008
Of course, you should not ignore the strong desire to eat something delicious. Sending a husband in the middle of the night for goodies is an important rite, but you should not abuse it. We recommend that you look at recommendations for healthy eating during pregnancy.
Pregnancy imposes a lot of responsibility on the expectant mother and weight control is an important component of the successful bearing of the baby!
The material is for information and reference purposes and does not replace expert advice or a visit to your doctor.