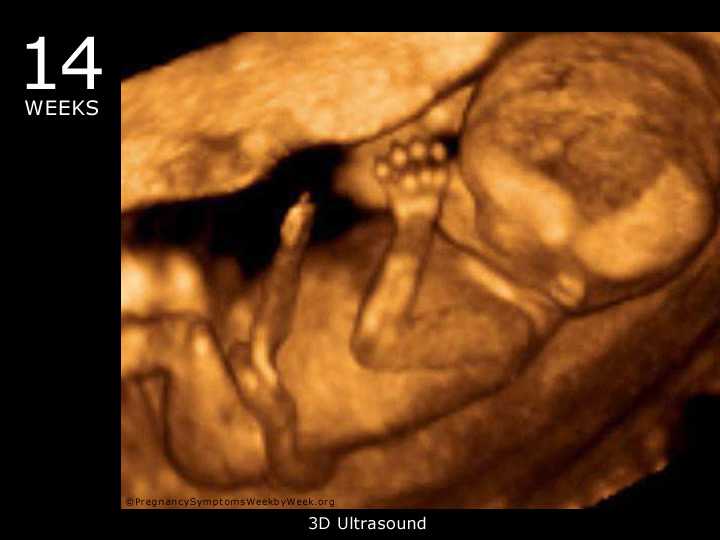
Pregnancy scan 12 weeks
12-week scan - NHS
If you're pregnant in England you'll be offered an ultrasound scan at around 10 to 14 weeks of pregnancy. This is called the dating scan. It's used to see how far along in your pregnancy you are and check your baby's development. The scan may also be part of a screening test for Down's syndrome.
Your midwife or doctor will book you a dating scan appointment. It will usually take place at your local hospital ultrasound department. Most scans are carried out by sonographers.
You may need to have a full bladder for this scan, as this makes the ultrasound image clearer. You can ask your midwife or doctor before the scan if this is the case. The dating scan usually takes about 20 minutes.
Find out more about what happens during a pregnancy ultrasound scan
Dating scan imageCredit:
Nic Cleave / Alamy Stock Photo https://www. alamy.com/stock-photo-12-twelve-week-ultrasound-scan-antenatal-photo-of-unborn-foetus-baby-18962836.html?pv=1&stamp=2&imageid=E0A8E3FE-D4B6-4EF5-9687-24C92C3FEA0F&p=74035&n=0&orientation=0&pn=1&searchtype=0&IsFromSearch=1&srch=foo%3dbar%26st%3d0%26pn%3d1%26ps%3d100%26sortby%3d2%26resultview%3dsortbyPopular%26npgs%3d0%26qt%3dB2RR84%26qt_raw%3dB2RR84%26lic%3d3%26mr%3d0%26pr%3d0%26ot%3d0%26creative%3d%26ag%3d0%26hc%3d0%26pc%3d%26blackwhite%3d%26cutout%3d%26tbar%3d1%26et%3d0x000000000000000000000%26vp%3d0%26loc%3d0%26imgt%3d0%26dtfr%3d%26dtto%3d%26size%3d0xFF%26archive%3d1%26groupid%3d%26pseudoid%3d788068%26a%3d%26cdid%3d%26cdsrt%3d%26name%3d%26qn%3d%26apalib%3d%26apalic%3d%26lightbox%3d%26gname%3d%26gtype%3d%26xstx%3d0%26simid%3d%26saveQry%3d%26editorial%3d1%26nu%3d%26t%3d%26edoptin%3d%26customgeoip%3d%26cap%3d1%26cbstore%3d1%26vd%3d0%26lb%3d%26fi%3d2%26edrf%3d0%26ispremium%3d1%26flip%3d0%26pl%3d
What is the purpose of the dating scan?
The purpose of the dating scan is to check:
- how many weeks pregnant you are and work out your due date (the estimated date of delivery, or EDD)
- whether you're expecting more than 1 baby
- that the baby is growing in the right place
- your baby's development
This scan can detect some health conditions, such as spina bifida.
Does screening for Down's syndrome happen at the dating scan?
This depends on whether you have agreed to have the screening and when the scan takes place. Screening for Down's syndrome will happen at the dating scan if:
- you have agreed to have screening for the condition
- the scan takes place between 10 and 14 weeks of pregnancy
The screening test for Down's syndrome used at this stage of pregnancy is called the combined test. It involves a blood test and measuring the fluid at the back of the baby's neck (nuchal translucency) with an ultrasound scan. This is sometimes called a nuchal translucency scan.
The nuchal translucency measurement can be taken during the dating scan. If you have agreed to have screening for Down's syndrome, the dating scan and the screening will usually happen at the same time.
Find out more about the screening for Down's syndrome, Edwards' syndrome and Patau's syndrome
You will not be offered the combined screening test if your dating scan happens after 14 weeks. Instead, you'll be offered another blood test between 14 and 20 weeks of pregnancy to screen for your chance of having a baby with Down's syndrome. This test is not quite as accurate as the combined test.
Find out more about:
- the 20-week scan
- ultrasound scans in pregnancy
- GOV.UK: screening tests for you and your baby
Page last reviewed: 18 December 2020
Next review due: 18 December 2023
12-14 Week Scan - Women's Imaging
This scan should be ideally performed between 12 weeks 5 days and 13 weeks 6 days of your pregnancy. Women’s Imaging conducts a detailed risk assessment for your baby in accordance with the Fetal Medicine Foundation. As well as checking that your baby is growing well and confirming your due date the main aim of the scan includes:
Women’s Imaging conducts a detailed risk assessment for your baby in accordance with the Fetal Medicine Foundation. As well as checking that your baby is growing well and confirming your due date the main aim of the scan includes:
- To see if there are any structural abnormalities. Some can already be identified or suspected at this stage so a normal appearing scan is very reassuring for you.
- To check your uterus and ovaries to ensure they won’t be an issue during the pregnancy.
- To confirm the growth of the pregnancy and the due date.
- To check where the placenta is lying, where the umbilical cord is in relation to the placenta and if there is sufficient fluid around the baby.
Risks
Ultrasound is safe to use throughout your pregnancy.
Sometimes we need to do a vaginal scan. If you are allergic to latex prior to the vaginal scan or you don’t know then a latex-free cover will be used on the probe.
Occasionally there is some discomfort from probe pressure on a full bladder or from the vaginal probe manipulation. If this is extremely painful please let us know.
If this is extremely painful please let us know.
Benefits
You will be able to see all of your developing baby
We are able to take some important measurements which allows us to give you an accurate risk assessment for your baby.
You have the option of getting the results of the scan on the day by our consultant. Please let reception know at the time of booking.
What is an ultrasound?
An ultrasound scan uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of your body and baby. Sound waves are used instead of radiation which makes them safe.
What do I need to do to have a risk assessment for my baby?
You will need to have a blood test done before coming to Women’s Imaging for your ultrasound scan. Your doctor will organise this for you. Ideally you should have your 1st Trimester bloods/ Maternal Serum done at 11 weeks gestation. Your doctor will organise a form for you.
We like to scan you between 12. 5 and 13.6 weeks of pregnancy.
5 and 13.6 weeks of pregnancy.
Why is a 12-14 weeks scan different at Women’s Imaging?
We offer the most sensitive and comprehensive risk assessment for your baby between 12.5-13.6 weeks which includes pre-eclampsia and fetal growth restriction. We are currently the only practice in Tasmania that does this. Traditional chromosomal abnormalities such as Down’s Syndrome continue to be assessed. Our sonographers are trained to the highest standards to perform these specialist measurements of you and your baby. They hold Certificates in Competence from the Fetal Medicine Foundation which is recognised by the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists.
We measure:
- Your baby’s nasal bone
- The thin layer of fluid at the back of the baby’s neck (the nuchal translucency)
- Your blood pressure (we take 2 measurements from both arms)
- The blood flow between you and your baby
We also examine:
- Your blood results
- Your age
- Your weight
- Whether you have had any previous problems in pregnancies (if relevant).
When you choose to have your First Trimester scan with us, you can be confident that the risk assessment results you receive are the best available in obstetric scanning today.
Women’s Imaging provides a comforting and safe environment with the latest state of the art equipment to ensure that you have the best possible care and experience.
What happens on the day?
When you arrive for your scan you will be asked to fill out a form about your pregnancy to date.
You will then have your blood pressure taken on both arms and your height and weight will be measured if you are not sure. Sometimes your measurements are taken before you have your scan and sometimes after.
When the sonographer takes you through to the scanning room you will be asked to lie on the table and expose your tummy. A towel will be tucked into your pants to limit spread of the gel onto your clothes.
Clear gel is applied to your tummy and the sonographer moves the probe over your tummy recording images. The clear gel is water-soluble so it won’t stain your clothes. It’s just a little sticky!
The clear gel is water-soluble so it won’t stain your clothes. It’s just a little sticky!
Please come with a full bladder which will make it easier to obtain images of your baby. A full bladder pushes the uterus away from your lower pelvis thereby making it easier for us to see and scan your baby.
We will take measurements of your baby and check your placenta and ovaries.
Occasionally a vaginal scan is also performed to give us a better view of your baby. You will be able to watch the entire scan on our wall-mounted plasma screen monitors!
Once the scan is completed the sonographer will leave the room. All of your measurements including your blood pressure and blood results will be reviewed by our radiologist or on-site obstetrician. Results will be sent to your referring doctor and they will give them to you at your next appointment.
You will be given your expected due date on the day and you will be given a online access card to view your images through our website.
How long will it take?
The 12-14 week scan takes approximately 45 minutes.
The 12-14 week scan and a consultation with our doctor on the day takes approximately 60 minutes.
(Please allow some extra time in your schedule when you come to see us for a 12-14 week scan. Occasionally we have to recalculate your measurements and this can take a few extra minutes)
Screening for the detection of congenital diseases of the fetus during pregnancy
Category: Reminders for the population .
Pregnancy screening is a whole range of studies that allows parents and doctors to get the most complete information about the health of an unborn baby. Screening reveals many congenital and physical characteristics. How and when is pregnancy screening done?
What is pregnancy screening and why is it done
Screening during pregnancy is a complex of examinations, which includes ultrasound and biochemical analysis of venous blood for hormones. As a rule, screening is carried out three times - in the first, second and third trimester.
As a rule, screening is carried out three times - in the first, second and third trimester.
Early detection of pathologies is very important. This makes it possible to start treating genetic diseases as early as possible and, if not completely cure them, then at least stop the symptoms as much as possible. If the doctor notices any abnormalities during the examination, the pregnancy is monitored especially carefully, which makes it possible to prevent the development of complications or premature birth. If the detected pathologies turn out to be too severe and incompatible with life, the doctor will refer the patient to terminate the pregnancy for medical reasons. nine0003
Pregnancy screening is harmless for both mother and baby. This is a fairly accurate study, although it should be clearly understood that it does not give a 100% guarantee. The accuracy of screening depends on many factors - the professionalism of the researchers, the woman's compliance with the rules for preparing for the examination, and other factors.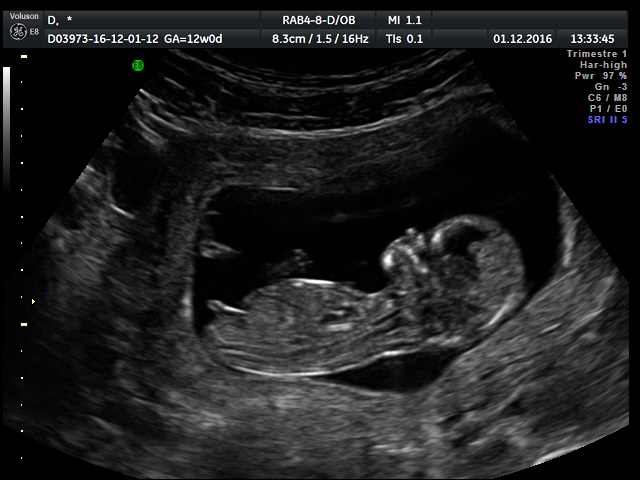
First pregnancy screening
The first screening during pregnancy is carried out between the 11th and 13th weeks. It makes no sense to undergo this examination earlier - before the 11th week of pregnancy, many indicators are practically indeterminate. nine0003
The study includes two medical tests - an ultrasound and a blood test.
ultrasound
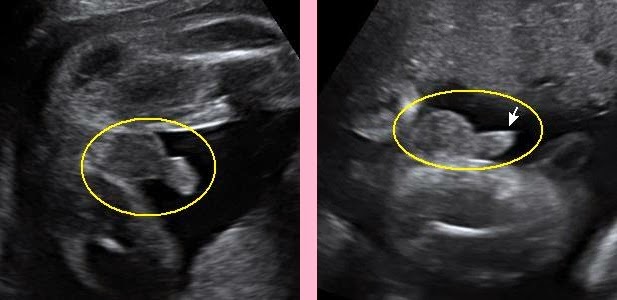
With the help of ultrasound, the doctor determines the exact gestational age, evaluates the baby's physique, its dimensions (head circumference, limb length, height), the work of the heart muscle, the symmetry of the brain, the volume of amniotic fluid, the structure and size of the placenta, as well as the condition and tone of the uterus. For each of these parameters, there are normal indicators with which the doctor will compare the results. For an 11-13 week pregnancy, these rates are:
- KTP (coccygeal-parietal size, that is, the length of the fetus from the crown to the tailbone) is 43–65 mm.
 If this figure is more than normal, then the child will be large. A downward deviation indicates slow development (the reason for this state of affairs is often a hormonal imbalance or infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother), genetic pathologies or fetal death (in this case, the heart will not be auscultated). However, this may also be due to a banal mistake in determining the timing of pregnancy. nine0030
If this figure is more than normal, then the child will be large. A downward deviation indicates slow development (the reason for this state of affairs is often a hormonal imbalance or infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother), genetic pathologies or fetal death (in this case, the heart will not be auscultated). However, this may also be due to a banal mistake in determining the timing of pregnancy. nine0030 - BDP (biparietal size, that is, the distance from the temple to the temple) - 17-24 mm. A high BDP means a large fetus, but only on the condition that all other indicators say the same. Otherwise, we can talk about a herniated brain or hydrocephalus. Low BDP indicates slow brain development.
- TVP (collar space thickness) - 1.6–1.7 mm. Deviation from this norm (TVP above 3 mm) is considered a sign of some severe chromosomal pathologies - Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc. However, one should not panic ahead of time - no one will make such a serious diagnosis only on the basis of TVP.
 To confirm, you need to take a blood test for hormones and take a biopsy of the outer dense shell of the embryo for further research. nine0030
To confirm, you need to take a blood test for hormones and take a biopsy of the outer dense shell of the embryo for further research. nine0030
The length of the nasal bone is 2–4.2 mm. Too small a nose bone can indicate pathology or simply that the baby's nose will be snub-nosed. HR (heart rate) - 140-160 beats per minute. A small (up to 40 beats per minute) deviation in one direction or another is considered a variant of the norm.
The size of the chorion, amnion and yolk sac. The chorion is the outer shell of the fetus, which will eventually become the placenta. If it is located on the lower wall of the uterus, they speak of chorion previa. This is a potentially dangerous situation, fraught with miscarriage, and in this case, bed rest is recommended for the pregnant woman. nine0003
The amnion is the inner membrane that holds the amniotic fluid. The normal volume of amniotic fluid at 11–13 weeks is 50–100 ml.
The yolk sac is an embryonic organ that, in the first weeks of a fetus's life, plays the role of some internal organs that will be formed later. By the time of the first screening, the yolk sac should practically disappear (then the examination form will indicate “not visualized”). If its size is about 6 mm, then the fetus may have certain pathologies. nine0003
By the time of the first screening, the yolk sac should practically disappear (then the examination form will indicate “not visualized”). If its size is about 6 mm, then the fetus may have certain pathologies. nine0003
Cervix. Normally, its length by the time of the first screening is 35–40 mm. A shorter cervix means a risk of preterm labor.
Ultrasound is performed in two ways - transabdominal, in which the sensor of the ultrasound machine is located on the abdomen, and transvaginal, in which it is inserted into the vagina. Transvaginal ultrasound provides more complete and accurate information, but it is usually performed only in the first trimester. This method is usually used when examining overweight women, since the fat layer in the abdomen does not allow the fetus and uterus to be examined in detail. nine0003
It is necessary to properly prepare for an ultrasound. Before a transabdominal ultrasound, it is advised to drink about a liter of water so that the bladder is full at the time of the examination - then the uterus will shift slightly towards the abdomen and the picture will be clearer. With transvaginal ultrasound, the degree of fullness of the bladder does not matter, however, before the examination, it is better to go to the toilet - it will be more comfortable. Before the examination, you need to take a shower or freshen up with wet wipes. The accumulation of gases can distort the results of ultrasound, no matter what method it is carried out. Therefore, expectant mothers suffering from flatulence are advised the day before the examination to take remedies for flatulence and not eat anything that produces gas. nine0003
With transvaginal ultrasound, the degree of fullness of the bladder does not matter, however, before the examination, it is better to go to the toilet - it will be more comfortable. Before the examination, you need to take a shower or freshen up with wet wipes. The accumulation of gases can distort the results of ultrasound, no matter what method it is carried out. Therefore, expectant mothers suffering from flatulence are advised the day before the examination to take remedies for flatulence and not eat anything that produces gas. nine0003
Blood test
Biochemical screening, also called a dual test, is done to determine the level of two hormones (hence the name) - free b-hCG and PAPP-A.
- b-hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) begins to be produced from the first days of pregnancy. Its amount gradually increases until about the 9th week, and then begins to gradually decrease. On average, for a period of 11–13 weeks, 50,000–55,000 mIU / ml is considered the norm.
 An elevated level of hCG may indicate a multiple pregnancy, or, in the worst case, genetic pathologies of the fetus or the presence of diabetes in the mother. Reduced hCG is typical of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, fetal death, or certain malformations (Patau syndrome and Edwards syndrome). nine0030
An elevated level of hCG may indicate a multiple pregnancy, or, in the worst case, genetic pathologies of the fetus or the presence of diabetes in the mother. Reduced hCG is typical of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, fetal death, or certain malformations (Patau syndrome and Edwards syndrome). nine0030 - PAPP-A is an A-plasma protein. The content rate for a period of 11–13 weeks is 0.79–6.01 mU / l. Low PAPP-A is a sign of chromosomal pathologies such as Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome, fetal death and miscarriage, fetal malnutrition (underweight) and preeclampsia.
- A high PAPP-A is a sign of multiple pregnancies, large fetuses, or a low placenta.
In order for the blood test to give the most accurate information, it must be taken on an empty stomach, at least 8 hours after the last meal. 2-3 days before the analysis, you should refrain from fried, fatty, spicy, smoked foods, chocolate, nuts, seafood. It is also recommended not to have sexual intercourse.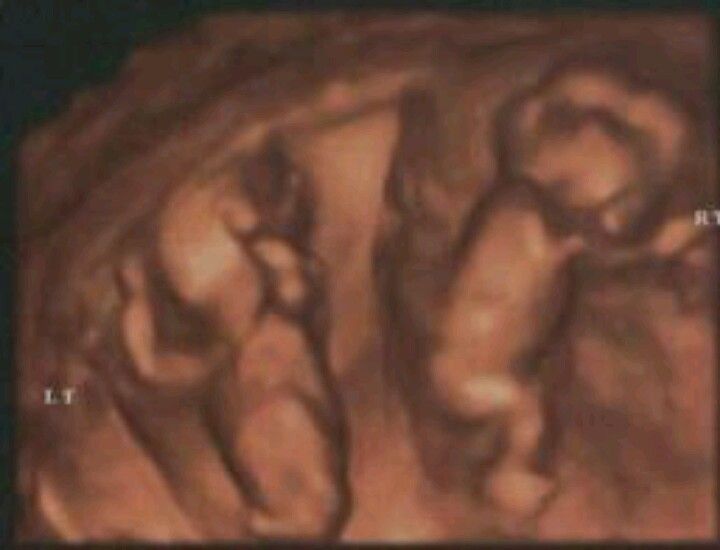 All this is not so significant, but it can affect the result in one way or another. nine0003
All this is not so significant, but it can affect the result in one way or another. nine0003
Second pregnancy screening
The second screening during pregnancy is carried out at 16-20 weeks. Like the first one, it consists of the same two stages - ultrasound and blood test.
ultrasound
This time, the doctor determines not only the size, but also the position of the fetus and its bone structure, the condition of the internal organs and the place of attachment of the umbilical cord, as well as the volume of amniotic fluid. Here are the approximate main indicators of the norm for a period of 16-20 weeks:
- BPR - 26–56 mm.
- DBK (length of the femur) - 13-38 mm.
- DPC (length of the humerus) - 13-36 mm.
- OG (head circumference) - 112-186 mm.
IAF (amniotic fluid index, that is, the volume of amniotic fluid) - 73-230 mm. Oligohydramnios can adversely affect the condition of the child's bone structure and the development of his nervous system.
Localization of the placenta. There is some risk only when the placenta is located on the anterior wall of the uterus - with such localization, detachment of the placenta is possible. nine0003
Umbilical cord. One of the most important parameters is the place of attachment of the umbilical cord. Marginal, split or sheath attachment is fraught with fetal hypoxia and difficulties during childbirth, often it becomes an indication for caesarean section. The umbilical cord is fed through 2 arteries and 1 vein, although sometimes only one artery is available. This can cause fetal hypoxia, heart disease, disorders in the child’s cardiovascular system, and cause a baby’s low body weight. However, if all other analyzes and examinations do not show deviations from the norm, you should not worry. nine0003
Cervix. The length of the cervix at this time should be 40–45 mm. A short cervix means a threatened miscarriage.
Visualization. Unsatisfactory visualization can be caused both by the peculiarities of the position of the fetus or the excess weight of the expectant mother, and by edema or hypertonicity of the uterus.
Blood test
As during the first screening, during the second, a blood test for b-hCG is taken, the level of free estriol and AFP is also checked. Here are the norms for their content at the 16th-20th weeks of pregnancy:
- b-hCG - 4.67-5-27 ng / ml.
- Free estriol is a hormone whose level can be used to judge the state of the placenta. The norm is 1.17–3.8 ng / ml. Elevated estriol is characteristic of multiple pregnancy or a large fetus. Reduced - for threatened miscarriage, placental insufficiency, anencephaly and Down's syndrome.
- AFP is a protein that is produced in the gastrointestinal tract of the fetus. Norm - 15-27 U / ml. A slightly lower AFP may mean that the gestational age was determined incorrectly (slightly underestimated). If the AFP is very low, the cause may be Edwards or Down syndrome, the threat of miscarriage or fetal death. High AFP is characteristic of neural tube pathologies, esophageal atresia, Meckel's syndrome.
 High AFP is also possible in women who have had an infectious disease during pregnancy. nine0030
High AFP is also possible in women who have had an infectious disease during pregnancy. nine0030
Third pregnancy screening
The third screening during pregnancy is carried out at the 30th-43rd week. Based on the results of this screening, the doctor decides on the need for a caesarean section or the possibility of a natural birth. The basis of the third screening is the same ultrasound. Sometimes dopplerography is prescribed - a study of the work of blood vessels. Here are the approximate norms for a given gestational age:
ultrasound
nine0028 The thickness of the placenta is 23.9–43.8. Too thin placenta is not a particularly dangerous deviation from the norm. The reason may be the miniature physique of a woman, her infectious diseases, hypertension. An excessively thick placenta is a sign of anemia, diabetes, Rh conflict. Such an indicator as the degree of maturity of the placenta is also taken into account - at a period of 30–35 weeks, the 1st degree of maturity is considered normal. With too rapid thickening and aging of the placenta, premature birth, fetal hypoxia and its slow development are possible. nine0003
An excessively thick placenta is a sign of anemia, diabetes, Rh conflict. Such an indicator as the degree of maturity of the placenta is also taken into account - at a period of 30–35 weeks, the 1st degree of maturity is considered normal. With too rapid thickening and aging of the placenta, premature birth, fetal hypoxia and its slow development are possible. nine0003
Prenatal screening is very important and should not be neglected. Timely detected pathologies and deviations from the norm can save the life and health of your child. This is worth remembering, especially for those parents who refuse to be examined out of fear of learning that the development of the baby is not going according to plan.
prices for tests for pregnant women
During the development of the fetus, ultrasound is one of the key methods of examination. There is no exact schedule for ultrasound, so the doctor focuses primarily on the condition of the patient, the condition of the fetus, the presence of somatic pathology.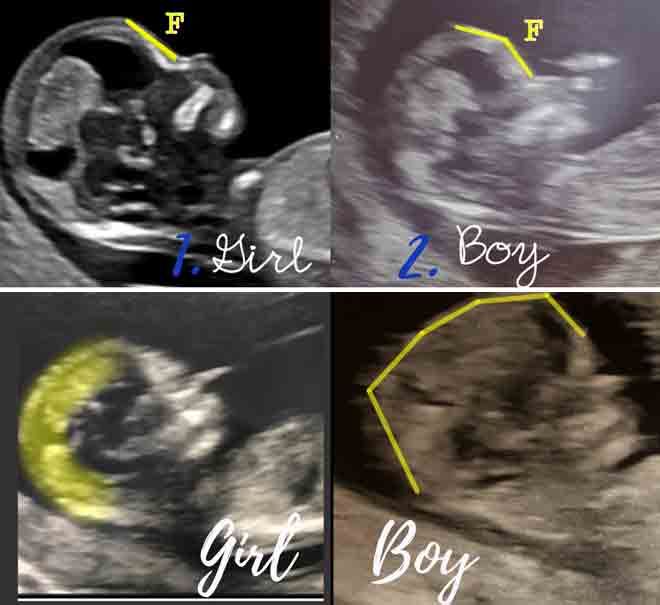 If we take a physiologically occurring pregnancy, then ultrasound is performed in each of the trimesters. nine0003
If we take a physiologically occurring pregnancy, then ultrasound is performed in each of the trimesters. nine0003
Ultrasound at 8 weeks is the first time this test is recommended. The eighth week is the first critical period, therefore, it is most rational to carry out diagnostics during this period.
Since it is the 8th week of pregnancy, a transvaginal examination is performed more often, which is more reliable. At this time, transabdominal ultrasound is used less and less. The transvaginal method does not pose any threat to either the mother or the fetus.
Ultrasound at 8 weeks can confirm
- Normal uterine pregnancy;
- Dimensions of the gestational sac;
- Whether the pregnancy is multiple;
- Place of attachment of fetus;
- Rule out malformations;
- Exclude various obstetric complications.
If the doctor confirms a physiologically proceeding pregnancy on an ultrasound examination, does not reveal any complications, the fetus develops according to age norms, then the next ultrasound is prescribed at 12 weeks.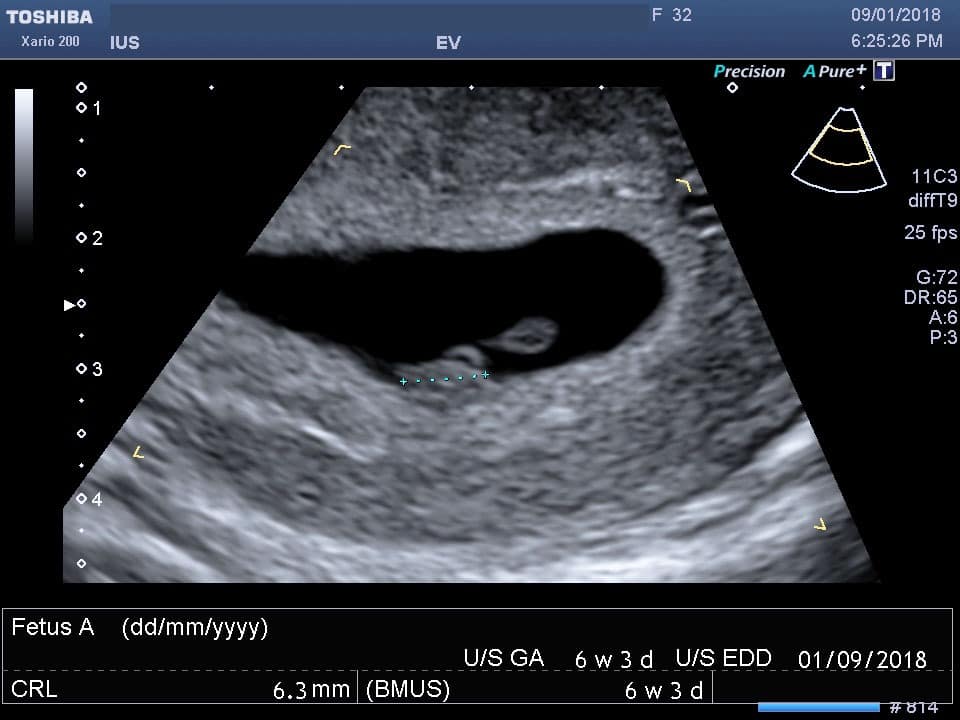 This period is another critical period when it is necessary to assess the condition of the woman and the unborn baby. nine0003
This period is another critical period when it is necessary to assess the condition of the woman and the unborn baby. nine0003
If the first two critical periods are mainly related to hormonal changes, then the next period - 22 weeks, is most often associated with sexual infections. Therefore, we also perform an ultrasound at 22 weeks. Pregnancy can provoke the development of latent infections, which, in turn, can lead to certain complications.
Tests at 8 weeks of pregnancy
There are no exact recommendations for registering pregnant women, but doctors recommend starting monitoring at the antenatal clinic before 12 weeks. There is a mandatory list of tests in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, and an additional one, which is appointed by the gynecologist individually. nine0003
Tests at 8 weeks of gestation:
- CBC;
- OAM;
- Swab;
- Determination of blood group and Rh factor;
- Tests for major venereal diseases.
In addition, the 8th week of pregnancy is the period of visiting the following doctors:
- Therapist;
- Optometrist;
- ENT;
- Dentist.
Accordingly, if any pathology is detected, any of these specialists has the right to prescribe an additional analysis in their direction. If this pregnancy proceeds with complications, or if there are previous complications in the anamnesis, then the laboratory and instrumental complex may expand. nine0003
You will have to take tests regularly, so you should prepare in advance for the next tests at week 12.
Ultrasound at 12 weeks pregnant
As we mentioned earlier, the next critical period is the 12th week of pregnancy. Therefore, the next ultrasound is performed at this time. Here we are not talking about a simple study, but about screening, which allows you to identify intrauterine malformations of the fetus.
In contrast to the ultrasound at 8 weeks, this is predominantly a transabdominal examination. Transvaginal ultrasound is performed only for certain indications:
Transvaginal ultrasound is performed only for certain indications:
- Low insertion of the placenta;
- Presence of isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- Pelvic inflammation;
- Atypical location of myomatous nodes;
- Malposition of the fetus, in which transabdominal ultrasound at 12 weeks of gestation is uninformative.
So, what information does an ultrasound give a gynecologist?
- Identification of deviations in the growth and development of the fetus; nine0030
- Possibility to suspect congenital anomalies;
- Exact gestational age;
- Palpitation;
- Cord entanglement;
- Characteristics of amniotic fluid;
- Condition of the placenta.
It must be clearly understood that ultrasound during pregnancy is only one of the methods of examination, therefore, if there are any deviations in the indicators, one should not panic, it is necessary to consult a specialist.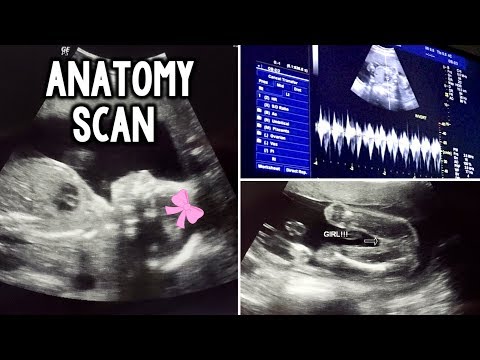 The doctor, interpreting the results, always relies on many factors, which allows him to adequately assess the true state of the future mother and fetus. nine0003
The doctor, interpreting the results, always relies on many factors, which allows him to adequately assess the true state of the future mother and fetus. nine0003
Even if deviations in some indicators are confirmed, doctors still only talk about a certain probability of developing a particular pathology. In this case, a second screening may be prescribed, or a similar study is carried out at a later date. In any case, the final decision regarding the continuation of the pregnancy is made exclusively by a specialist.
Tests at 12 weeks of pregnancy
As we have already said, 12 weeks is the time for screening. For this, an ultrasound examination is prescribed, the external indicators of the woman are evaluated, and a blood test is performed. nine0003
Particular attention is paid to two coefficients: β-hCG and PAPP-A. It is believed that in the presence of deviations according to these parameters, one can judge the presence of fetal pathologies. According to the level of hCG, doctors predict the further management of pregnancy and the possibility of miscarriage or premature birth.
Accordingly, according to the screening results, it is possible to identify:
- The baby has Down syndrome;
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Specify term; nine0029 Detect toxicosis;
- Determine the risk of miscarriage;
- Check for other chromosomal abnormalities.
Thus, tests at the 12th week of pregnancy are decisive for solving a number of issues related to the further development of the fetus. It should be clearly understood that screening is not 100% reliable, therefore, if you receive any deviations from normal results, you should immediately contact a specialist who can correctly assess such changes in indicators. nine0003
Ultrasound at 22 weeks gestation
The next scheduled ultrasound is performed at 22 weeks of gestation. Here, for the doctor, it is not the condition of the mother or the size of the fetus that is important, but the assessment of the formation of various organs and systems, as well as bones.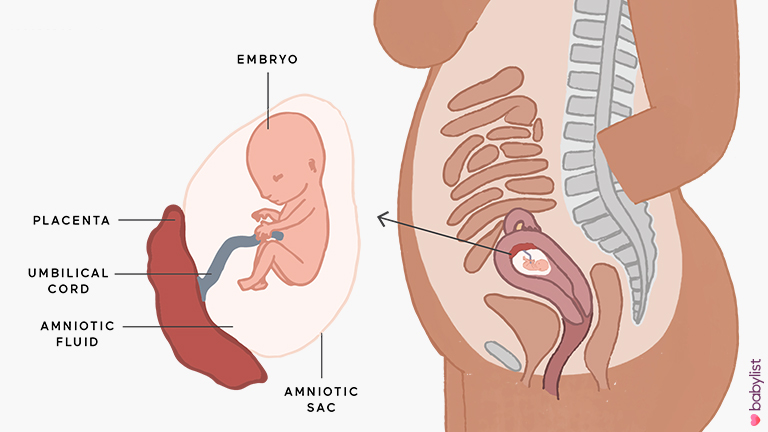
So, the 22nd week - the fetus has already formed all the main organs and systems, and on the monitor screen the child acquires the outlines familiar to future parents. Accordingly, the following indicators come to the fore:
- All internal organs should form. During an ultrasound, the doctor evaluates their location, how they function;
- The spine is also studied, the presence of bones and their sizes are determined;
- Assessing the brain and its activity;
- The condition of the placenta, umbilical cord vessels is assessed;
- Composition of amniotic fluid;
- Condition of the cervix.
Unlike ultrasound at 8 weeks, ultrasound at this time is performed transabdominally. 22 weeks is already the second trimester, and right now the question is being decided whether there are serious deviations in the development of the fetus, and further actions of obstetricians. The question of whether to continue a further pregnancy is decided not by one doctor, but by a whole council, based on numerous research results. nine0003
nine0003
Tests at 22 weeks pregnant
Week 22 is when the second screening is more common. This analysis is prescribed in the period from 18 to 24 weeks, but this time is considered optimal. Accordingly, during repeated screening, the doctor already makes final conclusions about the condition and development of the fetus, the presence of deviations.
In addition to ultrasound, the doctor prescribes mandatory tests to monitor the woman's health. The expectant mother again takes a general blood and urine test, where the most important are a number of indicators: hemoglobin, erythrocytes, leukocytes, ESR, protein in the urine. nine0003
During the examination, the gynecologist necessarily measures the woman's height, weight, blood pressure level, and measures the abdomen. Tests at 22 weeks of gestation are designed to assess the likelihood of developing preeclampsia. Here, the role is played not by hormonal changes, but by the exacerbation of chronic pathology. Therefore, timely screening and assessment of the woman's condition allows you to plan further tactics for managing pregnancy.