At what trimester does the baby move
When Can You Feel Baby Move? Early Kicks, from the Outside, More
Feeling your baby’s first kick can be one of the most exciting milestones of pregnancy. Sometimes all it takes is that little movement to make everything seem more real and bring you closer to your baby.
But while you expect your baby to move at some point in your pregnancy, you may have questions about what’s normal and what’s not (the ongoing concern you’ll probably have in all things parenthood).
Well, we’ve got answers. But first off: Remember that every pregnancy is different, so your baby might move earlier or later than a friend’s baby (or that baby you read about on a mommy blog).
But if you’re looking for a general guide, here’s what you need to know about fetal movement at different stages.
Whether it’s your first, second, or third pregnancy, you’re probably eager to feel that first move or kick. Did I just feel a wiggle? Or was that gas? And if you haven’t felt anything yet, you may wonder just when it’s going to happen. Kid’s gotta stretch their legs at some point, right?
But the truth is, your baby’s been moving from the very beginning — you just haven’t felt it.
First trimester movement: Weeks 1–12
Given the teeny tiny size of your baby during early pregnancy, it’s unlikely that you’ll feel any type of fetal movement in your first trimester.
If you have an ultrasound later in this trimester — say, around week 12 or so — the person doing the scan may point out that your baby is already rockin’ and rollin’ to the beat of their own drum.
But without an ultrasound — or if baby isn’t active during the scan, which is also quite normal — you’ll be none the wiser, because you likely won’t feel a thing.
While the first three months of pregnancy will come and go with little to no perceivable action in your womb, your baby will more than make up for the lack of movement in your second and third trimesters.
Second trimester movement: Weeks 13–26
This will be an exciting trimester! Morning sickness might start to fade (thank goodness!), you’ll have a growing baby bump, and those baby kicks will become a bit more prominent.
The first movements (known as quickening) start in the second trimester. At first, you might not even recognize what’s happening. Your baby is still small, so the kicks aren’t going to be strong. Instead, you may feel a strange sensation that you can only describe as a flutter.
Imagine a tiny fish swimming in your stomach (or a bit lower, really) — odd as it may sound, this is likely what those first movements will feel like. It can start as early as 14 weeks, but 18 weeks is more of the average.
If you’ve been pregnant before, and kind of know what to expect, you might detect movement sooner — maybe even as early as 13 weeks.
What’s interesting, though, is that while carrying twins or triplets means there’s less space in your womb, you’re not likely to feel movement any earlier when pregnant with multiples. (But you can expect a wild, acrobatic ride later in the pregnancy!)
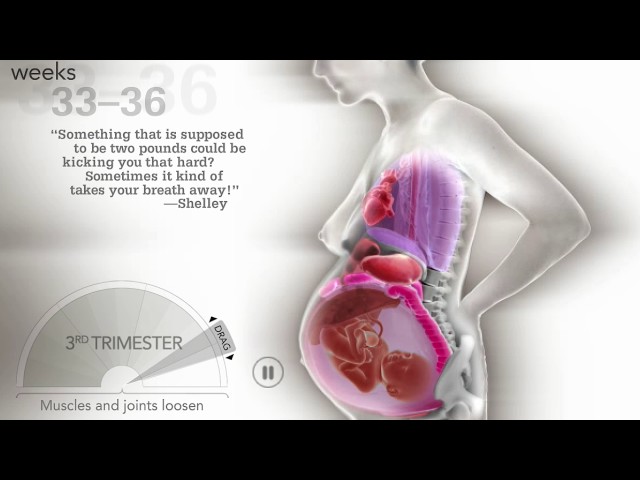
Third trimester movement: Weeks 27–40
This brings us to the third trimester, also known as the home stretch. Things are getting a little cramped. And with less room to stretch, your baby’s kicks, nudges, and punches are unmistakable.
Things are getting a little cramped. And with less room to stretch, your baby’s kicks, nudges, and punches are unmistakable.
Your baby is also stronger in the third trimester, so don’t be surprised if some of those kicks hurt or cause you to flinch. (Your precious babe hurting you? Inconceivable!)
As baby takes up more space, you can also expect movement be less dramatic as you get closer to your delivery date, but it shouldn’t be less frequent or come to a halt.
The joy of feeling your baby move is heightened when you can share it with your partner, or friend, or family members.
You’re carrying the baby, so naturally you’re able to notice movement sooner than others. But in most cases, your partner should be able to detect movement a few weeks after you.
If your partner places their hand on your stomach, they may feel the baby move as early as week 20. As your baby becomes bigger and stronger, your partner (or others you allow) will not only feel kicks, but also see kicks.
Your baby may even begin to respond to familiar voices around week 25, so speaking to your baby could prompt a kick or two.
While some of those earlier movements may feel like a wave or a fish swimming in your belly, movement can also mimic feelings of gas or hunger pangs. So you may think that you’re hungry or having digestion problems.
It’s not until the feeling becomes consistent and stronger that you realize it’s actually your baby exploring the environment!
Sometimes, your baby moving can feel like little ticks in your belly. In all likelihood, your baby has begun hiccuping, which is completely harmless.
It’s also important to keep in mind that the frequency of movement will change at different stages of your pregnancy.
Just because your baby starts moving in the second trimester doesn’t mean that it’ll happen all day. In fact, inconsistent movement is perfectly normal in this trimester. So even if you don’t feel any movement one day, don’t go into panic mode.
Remember, your baby is still tiny. It’s unlikely that you’ll feel every flip or roll. It’s not until your baby becomes bigger that you’ll start to feel something everyday. You might even begin to notice regular patterns of movement.
Your baby may be more active in the mornings, and calmer in the afternoons and evenings, or vice versa. It really depends on their sleep cycle.
Also, your own movements may lull the baby you’re carrying to sleep. This is also why you may notice more activity when you’re lying down — just as you’re trying to sleep, your soon-to-be newest addition wakes up.
Toward the end of your third trimester, it’s also perfectly normal for movements to change slightly. This doesn’t mean that anything is wrong — it just means that your baby is running out of space to move.
Want to play a game with your baby?
As you enter the third trimester, your doctor may likely suggest kick counting as a fun and simple way to track your baby’s health during these final months.
The ideal is to count how many times your baby moves within a specific timeframe to get a baseline of what’s normal for them.
You’ll want to count kicks at the same time every day, if possible, and when your baby is the most active.
Sit with your feet up or lie on your side. Note the time on the clock, and then start counting the number of kicks, nudges, and punches you feel. Keep counting up to 10, and then write down how long it took to feel 10 movements.
It’s important that you do this every day, because a change in movement could indicate a problem. If it normally takes 45 minutes to count 10 kicks, and then one day it takes two hours to count 10 kicks, call your doctor.
To be abundantly clear, lack of movement doesn’t always indicate a problem. It could just mean that your baby is enjoying a nice long nap, or your baby’s in a position that makes it harder to feel movement.
You might also feel less movement (or feel those first kicks a bit later in your pregnancy) if you have an anterior placenta. This is perfectly normal.
This is perfectly normal.
And sometimes — like all of us — your baby needs a little snack to get going again. So eating something or drinking a glass of orange juice might encourage movement. All the same, your doctor can bring you in for monitoring.
You’re not likely to feel your baby move during true labor (and you’ll have a lot distracting you), but you may feel movement during Braxton-Hicks contractions.
These contractions happen during the third trimester, and it’s essentially your body’s way of preparing for labor and delivery. This is a tightening of your abdomen that comes and goes over a period of time.
Not only can you detect movement during these contractions, but your baby’s movements can even trigger Braxton-Hicks. Going for a walk or changing your position can help relieve these early contractions.
Feeling your baby move is one of the amazing joys of pregnancy, often allowing for an intense bond. So it’s pretty natural to feel worried if you think you haven’t felt movement often or early enough.
But some babies move more than others, and some pregnant women feel kicks sooner than others. Try not to worry. You’ll soon get a feel for your baby’s normal.
Call your doctor if you’re concerned about lack of movement or if you don’t feel 10 movements within a two-hour window in the third trimester.
Also, don’t hesitate to call your doctor or go to the hospital if you’re worried about your baby’s health, or if you can’t distinguish between Braxton-Hicks contractions and actual labor contractions.
Your doctor and clinic staff are your allies in this journey. You should never feel foolish for calling or going in — the precious cargo you’re carrying is worth checking on in the event of anything usual.
Fetal Movement - WebMD: When You Feel Baby Kick
Written by Stephanie Watson
In this Article
- When Will I Feel My Baby Kicking?
- What Does the Baby's Kicking Feel Like?
- How Often Should I Feel My Baby Moving?
- Should I Monitor My Baby's Kicking?
- If You Don't Feel Your Baby Moving
- Timeline of Baby Movement
One of the most exciting moments in your pregnancy is when you feel those first little flutters of your baby kicking. These tiny movements reassure you that your baby is developing and help you feel closer to the little life inside of you.
These tiny movements reassure you that your baby is developing and help you feel closer to the little life inside of you.
When Will I Feel My Baby Kicking?
You should feel your baby's first movements, called "quickening," between weeks 16 and 25 of your pregnancy. If this is your first pregnancy, you may not feel your baby move until closer to 25 weeks. By the second pregnancy, some women start to feel movements as early as 13 weeks. You're more likely to feel baby move when you're in a quiet position, either sitting or lying down.
What Does the Baby's Kicking Feel Like?
Pregnant women describe their baby's movements as butterflies, nervous twitches, or a tumbling motion. At first, it may be hard to tell whether your baby has moved. Second- and third-time moms are more adept at distinguishing those first baby movements from gas, hunger pangs, and other internal motions.
By your second and third trimesters, the movements should be more distinct, and you'll be able to feel your baby's kicks, jabs, and elbows.
How Often Should I Feel My Baby Moving?
Early in your pregnancy, you may just feel a few flutters every now and then. But as your baby grows -- usually by the end of the second trimester -- the kicks should grow stronger and more frequent. Studies show that by the third trimester, the baby moves about 30 times each hour.
Babies tend to move more at certain times of the day as they alternate between alertness and sleep. They are usually most active between 9 p.m. and 1 a.m., right as you're trying to get to sleep. This surge in activity is due to your changing blood sugar levels. Babies also can respond to sounds or touch, and may even kick your partner in the back if you snuggle too close in bed.
Should I Monitor My Baby's Kicking?
Once your baby's movements are well established (usually by week 28), some doctors recommend keeping track of all those little punches, jabs, and kicks to make sure your baby is still developing the way they should. This is known as a fetal movement assessment, fetal kick count, or fetal movement counting.
Obstetricians recommend moms do fetal movement counts. While reduced movements or counts done at home can be worrisome, they may not be reliable. If you feel your baby is moving or kicking less often than normal, contact your doctor.
Counting is a lot harder when you have twins. You may not be able to tell which baby is moving. Even so, many doctors recommend it as a way to keep track.
If you are counting, it helps to chart your baby's kicks so that you can keep track of your baby's normal patterns of movement. To count movements, pick a time when your baby is usually most active (often, this is right after you've eaten a meal). Get into a comfortable position either sitting down in a comfortable chair or lying on your side. If you lie down, lie on your left side, so your baby will have better circulation.
Opinion varies as to how to count your baby's movements, but the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends noting the time it takes for your baby to make 10 movements. You should feel at least 10 movements within a 2-hour period.
You should feel at least 10 movements within a 2-hour period.
If you can't feel 10 movements in 2 hours despite eating something and fully focusing on the baby's movements, call your doctor for advice on what to do next.
If You Don't Feel Your Baby Moving
If you haven't yet reached 25 weeks and don't feel your baby move, or you're not sure that what you're feeling is actually your baby, don't panic. As your baby grows, you'll be able to better distinguish their movements. You'll also figure out at what times of the day your baby is most active. Some babies just naturally move less often than others.
A lack of movement also may mean that your baby is asleep. You may feel fewer kicks and jabs after the 32nd week as your baby gets bigger and has less room to move around in the uterus.
If your baby has started to move regularly and you don't feel at least 10 movements within a 2-hour period, or the movements have slowed significantly, it's time to call your doctor.
Timeline of Baby Movement
Here is a guide to your baby's possible movements.
Week 12: Your baby should start to move, but you probably won't be able to feel anything because the baby is still so small.
Week 16: Some pregnant women will start to feel tiny butterfly-like flutters. The feeling might just be gas, or it might be the baby moving.
Week 20: By this point in your baby's development, you may start to really feel your baby's first movements, called "quickening."
Week 24: The baby's movements are starting to become more established. You might also begin to feel slight twitches as your baby hiccups.
Week 28: Your baby is moving often now. Some of the kicks and jabs may take your breath away.
Week 36: Your uterus is getting crowded as the baby grows, and movements should slow down a bit. However, alert your doctor if you notice significant changes in your baby’s usual activity. You should feel consistent movement throughout the day.
Article "First movements"
The movements of the child are a way of his communication with his mother and with the outside world. In moments of excitement or joy, a woman often feels a more active movement of the baby.
The movements of the baby are not only an indicator of his condition, but also the unique sensations that the mother experiences during this happy period of her life, during pregnancy.
You have known for a long time that you are pregnant, mentally, and maybe talking out loud with the baby, but most mothers manage to really feel that the dearest little man in the world lives inside you only after his first pushes. nine0003
1. When the baby starts moving
Normally, the baby begins to move from the 8th week of pregnancy, when arms and legs appear. It’s just that its size is so small, and the blows are so weak that mom doesn’t feel it. The first movement of a child noticeable to a woman, as a rule, appears at 20-22 weeks of pregnancy, when the spinal cord and brain are formed in the crumbs, and its movements become regular. If a woman has already given birth, then her uterine muscles are more stretched and tremors can be felt earlier - starting from 16-18 weeks. In addition, she is already familiar with these sensations and can recognize them more quickly. nine0003
If a woman has already given birth, then her uterine muscles are more stretched and tremors can be felt earlier - starting from 16-18 weeks. In addition, she is already familiar with these sensations and can recognize them more quickly. nine0003
Future mothers describe the first tremors of the baby in different ways: someone compares them to the fluttering of a butterfly, someone feels wave-like movements, pulsation, slight tickling or seething in the intestines. As the baby grows, his movements become more recognizable. By 24 weeks of pregnancy, they already begin to resemble the movements of a newborn. It is from this age that the baby communicates with her mother in the language of movements and, with her movements, sensitively reacts to changes in her emotional state: when the mother is nervous, worried, or, conversely, rejoices and laughs, the baby can move more actively or calm down for a while nine0003
The baby moves most actively in the mother's stomach in the period from 24 to 32 weeks of pregnancy. By the time of childbirth, the motor activity of the crumbs decreases slightly, as it becomes crowded in the uterus.
By the time of childbirth, the motor activity of the crumbs decreases slightly, as it becomes crowded in the uterus.
An obstetrician-gynecologist will tell you how you can count the number of baby movements, and what number is considered normal. If you notice deviations from these indications, tell your doctor. Most likely, you will have to undergo additional examinations - listening to heart sounds, ultrasound or cardiotocography. nine0003
2. When not to worry
- still early . Some pregnant women start to panic when at 20 weeks they do not feel any movement inside them. If the last ultrasound did not reveal any abnormalities, there is no reason to worry. Wait: the baby can make itself felt at both 23 and 24 weeks. Some women, especially those who are expecting their first child, may only recognize movements at week 25, as they simply do not attach any importance to slight trembling or gurgling in the stomach. But in reality, you should listen to the stirring from the 30th week of pregnancy. nine0003
But in reality, you should listen to the stirring from the 30th week of pregnancy. nine0003
- baby sleeping . There is nothing surprising in the fact that you do not constantly feel fluttering inside the abdomen. The baby, like you, has its own regime, which provides for rest. It can calm down for 3-4 hours, and then make itself felt. And do not forget that all babies are different - some are active, others - behave calmer in their mother's tummy. If your belly is growing, and the obstetrician-gynecologist hears the baby's heartbeat during the examination, it means that the baby is growing and developing. nine0003
- all in mother . If the expectant mother leads an active lifestyle, works or plays sports, the child often adapts to this rhythm, which is why his tremors go unnoticed. Lie down and rest. You will see, the baby will immediately begin to kick.
For a period of 4-5 months, there are days when the baby has not made a single tangible push. In this case, its activity must be stimulated. Eat or drink a glass of milk, then lie down for an hour or two. The child will appreciate the calories offered and the calm state of the mother and, most likely, will begin to push. nine0019
In this case, its activity must be stimulated. Eat or drink a glass of milk, then lie down for an hour or two. The child will appreciate the calories offered and the calm state of the mother and, most likely, will begin to push. nine0019
Women with pronounced subcutaneous adipose tissue subjectively feel fetal movement to a lesser extent than thin women
3. What to look out for
- Jolts too weak . If earlier you regularly felt your baby, and now his tremors have become noticeably weaker or have completely stopped, this should alert you. An alarm signal is a complete cessation of motor activity for 12 hours or more. Seek immediate medical attention. nine0057
- Shocks too strong . If the baby kicks too violently, try changing the position in which you sit or lie - perhaps the baby is simply uncomfortable. If the baby does not let up and with its sharp and frequent movements causes you severe pain, consult a doctor.
 It was previously thought that too active fetal movements could be a sign of hypoxia, but at the moment this diagnosis can only be made by a doctor. The causes of hypoxia are various diseases that complicate pregnancy (anemia, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, placental insufficiency, Rh conflict). nine0057
It was previously thought that too active fetal movements could be a sign of hypoxia, but at the moment this diagnosis can only be made by a doctor. The causes of hypoxia are various diseases that complicate pregnancy (anemia, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, placental insufficiency, Rh conflict). nine0057
Active movements of the baby may be associated with the position of the mother, which is uncomfortable for the child. It is not recommended to be in a state of lying on your back for a long time, as large vessels can be squeezed, which leads to impaired blood flow and the child reports this with increased motor activity. The most comfortable position for the mother is lying on her left side.
How to assess the condition of the baby?To assess the vital activity of the fetus, doctors use several methods: nine0003
-
non-stress test or cardiotocography (CTG). This is the most objective and informative method for assessing the condition of a growing baby.
 Routinely, it is performed at the 34th week of pregnancy, but if necessary, it can be performed earlier. In a normal pregnancy, the study is carried out once a week. CTG is a recording of the fetal heart rate using a device - a fetal monitor. To perform the test, an ultrasound probe is attached to the woman's abdomen, and the baby's heartbeat is recorded on paper tape for 30 minutes, after which the resulting curve is evaluated. The condition of the baby is determined by the frequency and rhythm of heart contractions and changes in heartbeat depending on the movements. Unfavorable signs are: the absence of a heartbeat response or its slowdown in response to the fetus's own movements, a monotonous rhythm and a decrease in the heart rate below 110 beats per minute. nine0003
Routinely, it is performed at the 34th week of pregnancy, but if necessary, it can be performed earlier. In a normal pregnancy, the study is carried out once a week. CTG is a recording of the fetal heart rate using a device - a fetal monitor. To perform the test, an ultrasound probe is attached to the woman's abdomen, and the baby's heartbeat is recorded on paper tape for 30 minutes, after which the resulting curve is evaluated. The condition of the baby is determined by the frequency and rhythm of heart contractions and changes in heartbeat depending on the movements. Unfavorable signs are: the absence of a heartbeat response or its slowdown in response to the fetus's own movements, a monotonous rhythm and a decrease in the heart rate below 110 beats per minute. nine0003 -
If CTG receives a low score, then for a more detailed clarification of the child's condition, starting from the 3rd trimester, a fetal biophysical profile (BFP) can be used , including ultrasound and CTG.
 The following parameters are evaluated: cardiac activity, respiratory movements of the chest, muscle tone and the amount of amniotic fluid. All this allows us to draw a conclusion about the reasons for reducing the movement of the baby. If a state of severe hypoxia is established, then an emergency caesarean section is performed. If there is no threat to the life of the child, then continue observation and repeated non-stress tests. nine0003
The following parameters are evaluated: cardiac activity, respiratory movements of the chest, muscle tone and the amount of amniotic fluid. All this allows us to draw a conclusion about the reasons for reducing the movement of the baby. If a state of severe hypoxia is established, then an emergency caesarean section is performed. If there is no threat to the life of the child, then continue observation and repeated non-stress tests. nine0003
Pearson Fetal Movement Test "Count to Ten"
Starting from the 28th week of pregnancy, on a special map, mark the number of perceptible movements of the baby every day. Start counting at 9 am and end at 9 pm. During these 12 hours, the baby must push you at least 10 times. It is this number of movements per day that is considered normal. In the map, you enter the time of the 10th perturbation. A small number of shocks - less than 10 per day - may indicate fetal oxygen deficiency and is a reason to see a doctor. nine0003
nine0003
Fetal movement - how and when it happens
- At what time does fetal movement begin
- Fetal movement rate
- Methods for assessing the "sufficiency" of fetal movements
- Changes in fetal activity
- Determining the condition of the fetus
“Dear patients, we are glad to welcome you to the website of the Fetal Medicine Center – a medical center of expert level in the field of modern prenatal medicine. nine0019
We see our mission in making the expectation of a child and its birth a happy, calm and most comfortable period for every woman. By providing professional medical support, we help couples plan pregnancy, control its harmonious course, conduct expert-level prenatal diagnostics, providing comprehensive care for the health of the expectant mother and baby.”
Roza Saidovna Bataeva
Head of the Fetal Medicine Center in Moscow
From the very beginning of pregnancy, every expectant mother begins to listen anxiously to the sensations inside her growing belly. Can't wait to feel your baby move. When does the fetus begin to move? At what time can a pregnant woman begin to listen carefully to herself, waiting for the first movements of her child? Should I be worried if they are not felt or the baby suddenly calmed down? And can movements carry any other information, besides communicating with mom? nine0019
Can't wait to feel your baby move. When does the fetus begin to move? At what time can a pregnant woman begin to listen carefully to herself, waiting for the first movements of her child? Should I be worried if they are not felt or the baby suddenly calmed down? And can movements carry any other information, besides communicating with mom? nine0019
At what time does the fetal movement begin
The first movements of the future baby begin early - as early as 7-8 weeks of pregnancy . It was at this time that the first muscles and the rudiments of the nervous system of the fetus are formed. Naturally, at this time, the movements of the embryo are still very primitive - these are muscle contractions in response to nerve impulses.
Approximately from 10 weeks of pregnancy the fetus begins to move more actively in the uterus, and, encountering an obstacle on its way (walls of the uterus), change the trajectory of movements. However, the baby is still very small and the impacts on the uterine wall are very weak, the expectant mother cannot yet feel them.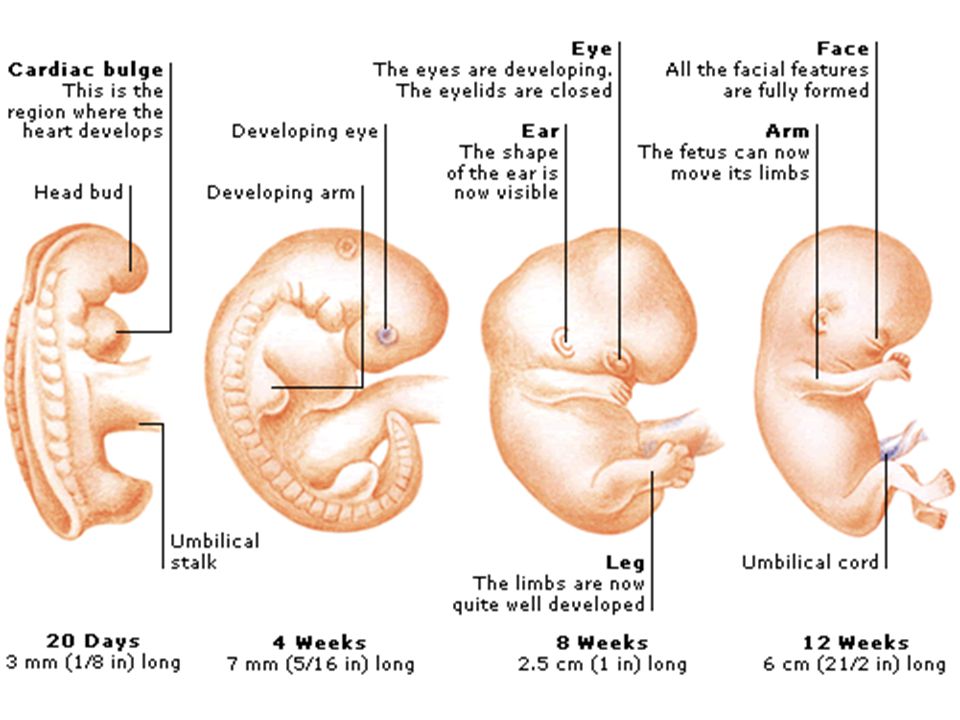 At 11-12 weeks of intrauterine life, a little man already knows how to clench his fists, grimace, frown, by 16 weeks of pregnancy he begins to react to loud, sharp sounds with increased motor activity, at 17 weeks the first facial expressions appear, and at 18 weeks he covers his face with his hands and plays with the umbilical cord, compresses and unclenches the fingers of the hands. nine0003
At 11-12 weeks of intrauterine life, a little man already knows how to clench his fists, grimace, frown, by 16 weeks of pregnancy he begins to react to loud, sharp sounds with increased motor activity, at 17 weeks the first facial expressions appear, and at 18 weeks he covers his face with his hands and plays with the umbilical cord, compresses and unclenches the fingers of the hands. nine0003
Gradually, with increasing gestational age, movements become more coordinated and more like conscious. When the baby grows up, the pregnant woman begins to feel his movements.
When does the fetal movement begin during the first and subsequent pregnancies
It is generally accepted that during the first pregnancy, the expectant mother feels the first fetal movements at 20 weeks of pregnancy, with repeated pregnancies - at 18 weeks. This is not entirely true. A mother who is expecting her first child, indeed, most often begins to feel the movements of the fetus a little later than a multiparous woman. This is due to the fact that "experienced" mothers know how the movements of the crumbs are felt at first and what they should feel. Some primigravidas perceive the first movements of the fetus as an increase in intestinal peristalsis, “gaziki”. Many women describe the first movements of the fetus as a feeling of fluid transfusion in the abdomen, "fluttering butterflies" or "swimming fish." nine0003
This is due to the fact that "experienced" mothers know how the movements of the crumbs are felt at first and what they should feel. Some primigravidas perceive the first movements of the fetus as an increase in intestinal peristalsis, “gaziki”. Many women describe the first movements of the fetus as a feeling of fluid transfusion in the abdomen, "fluttering butterflies" or "swimming fish." nine0003
The first movements are usually rare and irregular. The time of the first sensations of fetal movements naturally depends on the individual sensitivity of the woman. Some future mothers feel the first movements as early as 15-16 weeks, and someone only after 20. Slender women, as a rule, begin to feel movements earlier than full ones. Women who lead an active lifestyle, work hard, usually feel the movements of the fetus later.
By 20 weeks, due to the formation of the spinal cord and brain, as well as the accumulation of a certain amount of muscle mass in the fetus, movements become more regular and noticeable .
From 24 weeks of pregnancy, the movements of the fetus are already reminiscent of the movements of a newborn - the expectant mother feels how the fetus changes position, moves its arms and legs. The motor activity of the fetus increases gradually and its peak falls on the period from the 24th to the 32nd week of pregnancy. At this time, the activity of the baby's movements becomes one of the indicators of its normal development. After 24 weeks, the child begins to "communicate" with the mother with the help of movements, respond to the sounds of voice, music, and the emotional state of the mother. With an increase in the gestational age of more than 32 weeks, the motor activity of the fetus gradually decreases due to the fact that the baby is growing up and he simply does not have enough space for active movements. This becomes especially noticeable at the time of childbirth. By the end of the third trimester of pregnancy, the number of fetal movements may decrease somewhat, but their intensity and strength remain the same or increase. nine0003
nine0003
Fetal movement rate
The baby in the mother's belly moves almost constantly. At the 20th week of pregnancy, the fetus makes about 200 movements per day, and between the 28th and 32nd weeks, the number of movements reaches 600 per day. Naturally, a pregnant woman does not feel all the movements of the fetus, but only a small part of them. So, after 28 weeks, the frequency of fetal movement, according to the sensations of a woman, is usually 4 to 8 times per hour, with the exception of periods of fetal sleep (3-4 hours in a row). nine0003
In the third trimester, a pregnant woman may notice that her baby has regular sleep and wake cycles. Children are usually most active from 19:00 to 4:00 in the morning, and the period of "rest" occurs more often from 4 to 9:00 in the morning. Of course, the movements of the fetus depend on the mood of the mother, if the mother is worried or happy, the baby can move more actively, or vice versa, calm down. The fact is that when a mother rejoices, her body significantly increases the amount of hormones of joy - endorphins, which regulate the work of the heart and blood vessels, including the vessels of the placenta. During stress or pronounced negative emotions, biologically active substances are also produced - stress hormones, they also affect the work of the heart and blood vessels. It is thanks to this biological interaction between the organisms of mother and baby that the fetus feels the state of the mother. When the expectant mother is resting, the baby usually becomes more active, if the pregnant woman is active, busy with some kind of work, the child most often calms down. The movements also change depending on the satiety of the expectant mother. Usually the baby begins to move actively after the mother eats, especially something sweet. At the same time, the level of glucose in the blood increases sharply, which causes the fetus to be more active. nine0003
During stress or pronounced negative emotions, biologically active substances are also produced - stress hormones, they also affect the work of the heart and blood vessels. It is thanks to this biological interaction between the organisms of mother and baby that the fetus feels the state of the mother. When the expectant mother is resting, the baby usually becomes more active, if the pregnant woman is active, busy with some kind of work, the child most often calms down. The movements also change depending on the satiety of the expectant mother. Usually the baby begins to move actively after the mother eats, especially something sweet. At the same time, the level of glucose in the blood increases sharply, which causes the fetus to be more active. nine0003
Fetal movements are the language in which the unborn child speaks to the mother. Naturally, a pregnant woman should listen to the movements, because in some cases, changes in the movements of the fetus may indicate a violation of its intrauterine state and a not entirely successful pregnancy.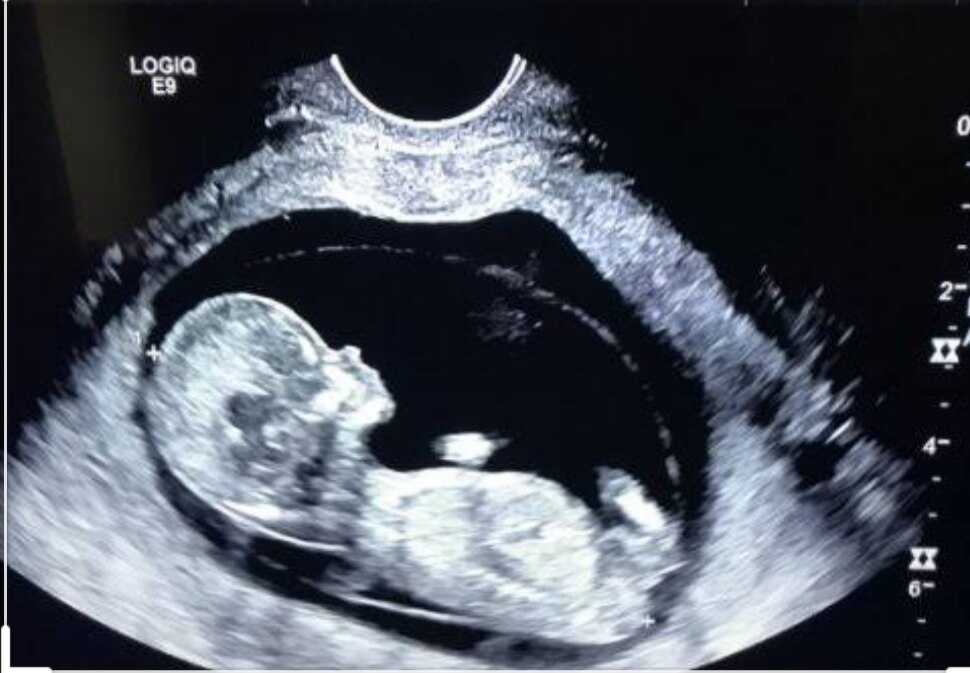
If, after 20 weeks of pregnancy, the expectant mother does not feel fetal movement, it may be worthwhile to see a doctor and make sure that everything is in order with the baby.
Methods for assessing the "sufficiency" of fetal movements
Counting the number of movements
The easiest way to assess fetal movements is to count the number of movements of the pregnant woman herself. Self-assessment methods are very easy to use, do not require additional equipment, the presence of a doctor and are easily reproducible by any woman. Their disadvantages are that each woman has different thresholds of susceptibility.
Count to ten
The most common method for assessing fetal movements is called count to ten . It can be carried out after 28 weeks of pregnancy, when the fetus is mature enough for active movements. Its essence lies in the fact that the expectant mother counts the movements of the fetus for a 12-hour time interval, for example, from 9 am to 9 pm. The time when a pregnant woman catches the tenth movement is recorded on a tablet. If the fetus makes less than 10 movements in 12 hours, this is a reason to consult a doctor for an additional examination.
The time when a pregnant woman catches the tenth movement is recorded on a tablet. If the fetus makes less than 10 movements in 12 hours, this is a reason to consult a doctor for an additional examination.
Sadowski method
In the evening after dinner (approximately between 19until 11 p.m.), the woman lies on her left side and counts the movements of the fetus. At the same time, everything is considered, even the smallest movements. If 10 or more movements are noted within an hour, this indicates that the baby is moving quite actively and feels good. If the fetus moved less than 10 times in an hour, then the movements are counted for the next hour. Evening time for this assessment method was not chosen by chance. It is in the evening hours, especially after dinner and the associated increase in glucose, that the greatest activity of the fetus is noted. If the number of fetal movements during this test is less than 10 per two hours, this should be considered as a sign of a violation of his condition and additional studies should be carried out. nine0003
nine0003
For an obstetrician-gynecologist, fetal movements are also an important diagnostic criterion for some deviations in the course of pregnancy from the norm. Too active, violent, painful fetal movement or weak, rare movements may indicate its unfavorable condition.
Changes in fetal activity
Changes in fetal activity may be associated with external influences. For example, if a pregnant woman lies on her back for a long time, then the enlarged uterus compresses a large vessel - the inferior vena cava, the blood flow to the fetus is disrupted, which immediately causes its violent reaction - active movements. The same changes in the activity of the baby can occur in any other uncomfortable position of the mother - if she leans forward, squeezing her stomach, sits with her legs crossed, the child forces her mother to change her position with her activity. A similar situation occurs if the baby himself squeezes or presses the loops of the umbilical cord, limiting the flow of blood through it. He begins to move more actively, changes his position and relieves pressure on the umbilical cord. However, in some cases, an increase or vice versa, a subsidence of fetal movements can be a sign of a serious pathology. nine0003
He begins to move more actively, changes his position and relieves pressure on the umbilical cord. However, in some cases, an increase or vice versa, a subsidence of fetal movements can be a sign of a serious pathology. nine0003
After 28 weeks of pregnancy, if your baby does not let you know for 3-4 hours, he may just be sleeping. In this case, the expectant mother needs to eat something sweet and lie down on her left side for half an hour. If these simple manipulations do not lead to a result, it is worth repeating them again after 2-3 hours. If this time the baby does not make itself felt, this is an occasion to consult a doctor. Rare and weak movements can also indicate a fetal problem, most often a lack of oxygen for the baby, that is, fetal hypoxia. nine0003
Determining the condition of the fetus
To determine the condition of the fetus, the doctor conducts a series of examinations:
Auscultation (listening)
The simplest is auscultation (listening) with a special wooden tube (obstetric stethoscope) or a special apparatus that captures the fetal heartbeat, doctor listens to the baby's heartbeat.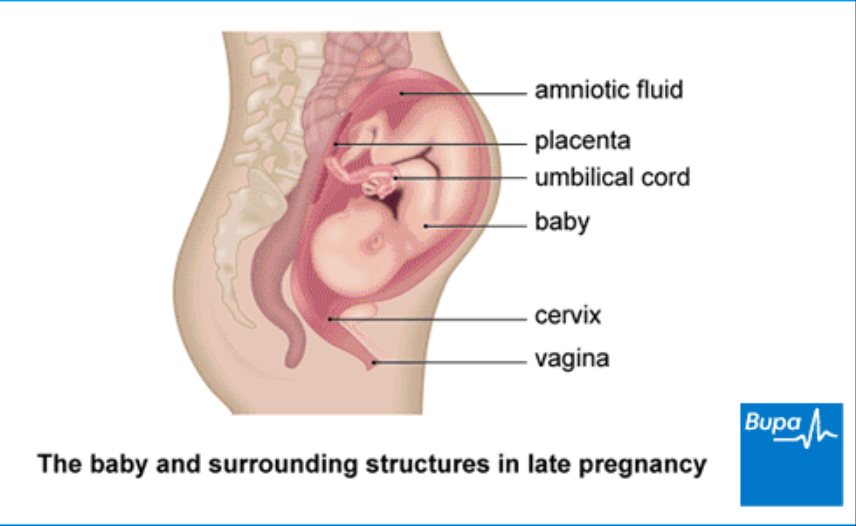 Normally, it is about 120-160 beats per minute. A decrease in heart rate less than 120 or an increase of more than 160 indicates intrauterine suffering of the child. nine0003
Normally, it is about 120-160 beats per minute. A decrease in heart rate less than 120 or an increase of more than 160 indicates intrauterine suffering of the child. nine0003
Ultrasound and dopplerometry
During ultrasound, the doctor visually assesses the size of the fetus, the correspondence of the development of the fetus to the gestational age, because with oxygen starvation, the growth rate of the fetus slows down and its size lags behind the norm for each period of pregnancy. Also important is the structure of the placenta, the presence of signs of aging in it, as a result of which the function of transferring blood, oxygen and nutrients to the fetus usually worsens. During ultrasound, the amount and type of amniotic fluid is assessed, which can also change with intrauterine fetal suffering. Dopplerometry of the vessels of the placenta and umbilical cord is a method for studying blood flow velocities in these vessels. With a decrease in the speed of blood flow in any vessel, one can speak of fetal malnutrition of varying severity. nine0003
nine0003
Learn more about the services:
- Pregnancy ultrasound
- Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy
- Make KTG
- Perform fetal echocardiography
Cardiotocography (CTG)
This is an important method for assessing the condition of the fetus. CTG is performed at a gestational age of 33 weeks or more, since only in this period of intrauterine development of the baby is a full-fledged regulation of the activity of the cardiovascular system of the fetus by the centers of the spinal cord and brain. Recording of fetal heartbeats is carried out for at least 40 minutes, and if necessary, the study can be extended up to one and a half hours. The device registers and records the baby's heart rate. For example, with a decrease in the concentration of oxygen in the blood of the fetus, the supply of oxygen to the cells of the nervous system decreases, which in turn affects the heart rate, especially during the period of wakefulness of the child.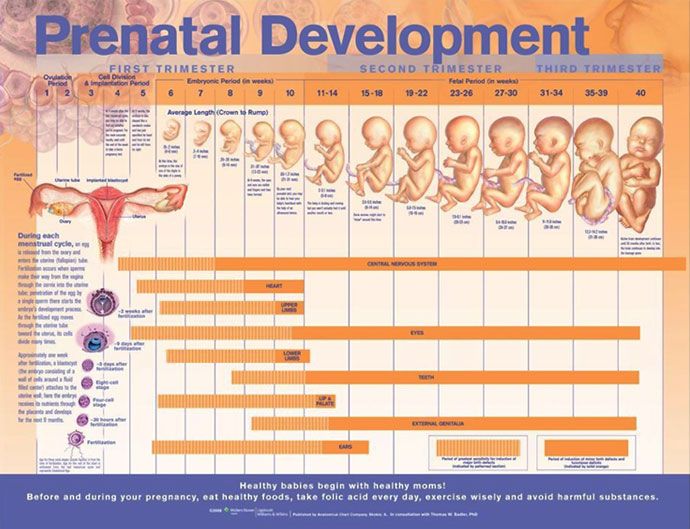 The obstetrician-gynecologist evaluates the heartbeat recording curve, episodes of slowing down and a sharp increase in the fetal heart rate, and based on these data, makes a conclusion about how comfortable the baby feels in the mother's stomach. nine0003
The obstetrician-gynecologist evaluates the heartbeat recording curve, episodes of slowing down and a sharp increase in the fetal heart rate, and based on these data, makes a conclusion about how comfortable the baby feels in the mother's stomach. nine0003
If during additional methods for assessing the condition of the fetus, initial disturbances in the supply of oxygen to the baby are detected, drug treatment is carried out aimed at increasing the access of blood and oxygen through the placenta and mandatory control examinations against the background of ongoing therapy. If the changes are profound and the baby experiences a pronounced deficiency of oxygen and nutrients, his condition suffers, an emergency delivery of such a patient is performed.
Fetal movements are not only an indicator of his condition, it is a way of communication between the baby and parents. The movements of the crumbs in the mother's tummy are unforgettable sensations that a woman can experience only in this short, but such a happy period of her life.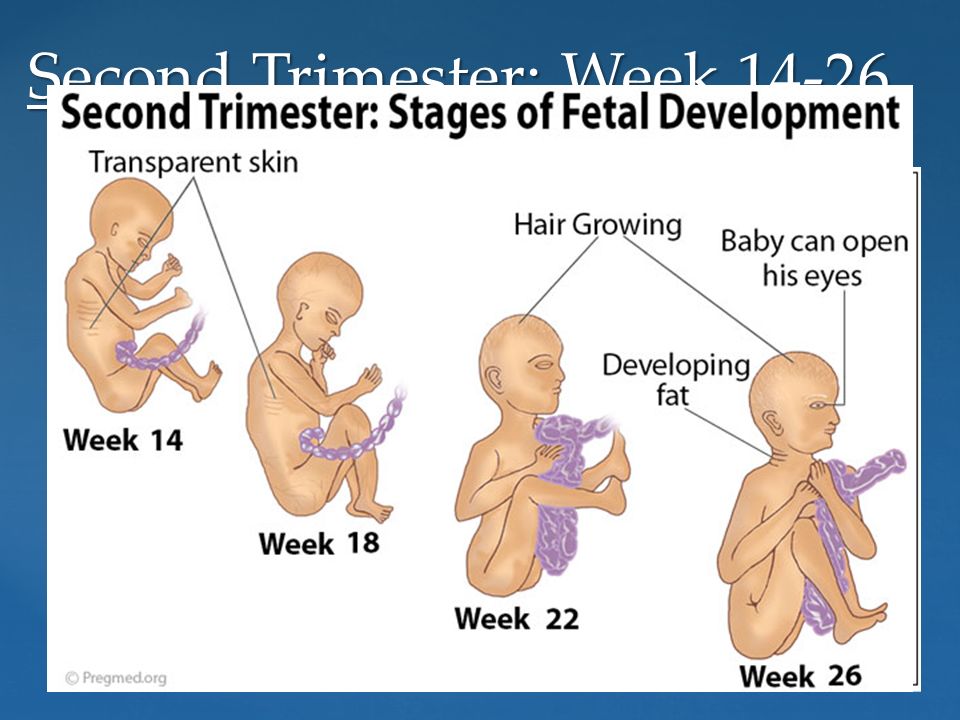 nine0003
nine0003
Center for Fetal Medicine in Moscow:
The main activities of our center are the early detection of congenital malformations in the fetus, prenatal screening for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, as well as pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia, fetal growth retardation and threatened abortion.
Our center is organized in such a way that the whole range of services is concentrated in one place, where a woman receives the results of various types of examinations, including ultrasound, biochemical, and specialist consultation within 1-1.5 hours. In the presence of a high risk for chromosomal diseases in the fetus, invasive diagnostics and genetics consultation are carried out here in the center. nine0003
Fetal echocardiography is given special attention in our center, since congenital heart defects in the fetus are increasingly common today, but, unfortunately, are often missed during ultrasound during pregnancy.
In view of the ever-increasing number of multiple pregnancies, which requires more time and a special approach, the observation of women with multiple pregnancies has been allocated to us in a separate clinic for multiple pregnancies.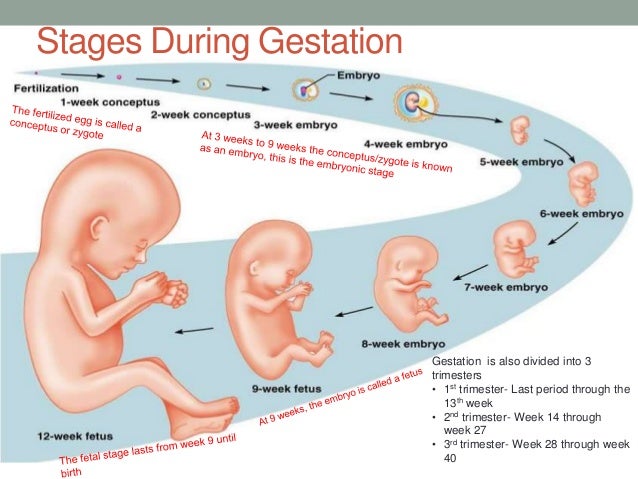
All examinations in the center are carried out according to the international standards FMF (Fetal Medicine Foundation) and ISUOG (International Society for Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology). In complex clinical cases, we can consult with specialists from King's College Hospital, King's College Hospital (London, UK). nine0003
The team is a special pride of the center. Our doctors are not only one of the leading specialists, professors, doctors and candidates of medical sciences, doctors of the highest categories, they are also a team of like-minded people and real enthusiasts in their field. All ultrasound diagnostic doctors in our center have international FMF certificates. Having extensive experience in prenatal diagnostics, we share our knowledge with our colleagues by conducting training courses.
The Center is equipped with the most modern diagnostic equipment: these are the latest generation ultrasound machines, GE Voluson E8 Expert, with a complete set of modern technologies, including three-dimensional ones, this is a biochemical analyzer, Delfia Xpress, these are workplaces with professional computer programs.