How to determine blood type of child
Child Blood Type Calculator | Predict Your Baby Blood Group
Do you want to know your unborn baby’s blood group? Our blood type calculator can help you discover it!
A baby’s probable blood group is mainly determined by the mother and the father’s genes (1). While knowing the exact blood group of the unborn baby is not possible, this tool gives you a list of the blood types that baby likely to have.
Select the mother’s and the father’s blood type and you can find out the probable blood group of your child.
Mother's Blood Type
A+
B+
AB+
O+
A-
B-
AB-
O-
Father's Blood Type
A+
B+
AB+
O+
A-
B-
AB-
O-
Your child can have any of the possible blood types mentioned below:
Possible Blood Type:
Possible RH Type:
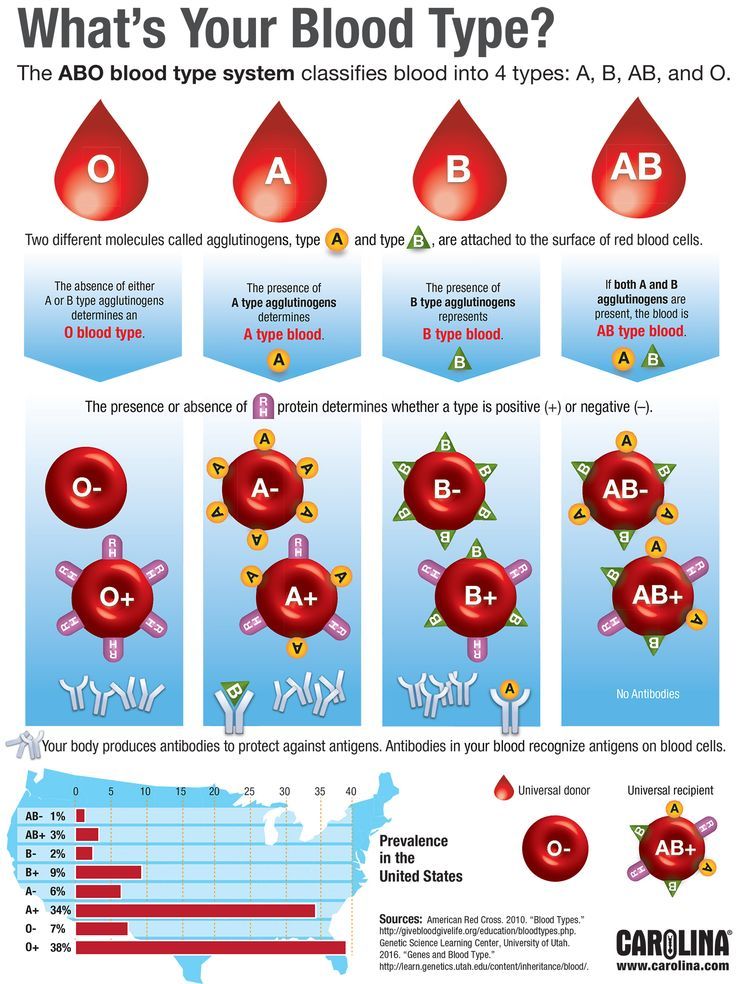
Blood Type DeterminationBlood groups were discovered in the 20th century when Karl Landsteiner observed that the red blood cells (RBCs) had specific substances on their surfaces, which were later used to create blood types. The two important blood group classifications in humans are the ABO and the Rh systems. The ABO system has four major blood groups – A, B, AB, and O.
Blood type A has the antigen A, blood type B has the B antigen, and O has no antigen on its surface (2). Each of these groups is either Rh positive (D) or Rh negative, which means there are eight major blood groups in all. Knowledge of both these systems is essential for medical reasons, especially blood transfusions.
The ABO Blood Group System:The gene, ABO, determines this blood group system. The four blood groups – A, B, AB, and O develop when the child inherits one or more of the alleles – A, B or O. The alleles A and B are considered codominant while O is considered to be the silent allele. Each parent gives one of their two ABO alleles to the child (3).
Sponsored
For instance –
- Mother with AB blood type can either pass the A or B allele to the baby.
 Likewise, a father with O blood type can only pass O allele to the baby.
Likewise, a father with O blood type can only pass O allele to the baby. - If both parents belong to the blood group O, the child will also belong to the O blood group.
- Two A blood group parents can give their child either A or O blood group.
- Two B blood group parents can give their child either B or O blood group.
- One parent with A and another with B will give their child either A, B, AB or O groups.
- One parent with A and another with AB will give their child either A, B or AB groups.
- One parent with A and another with O will give their child either A or O blood group.
Rhesus Blood Group System:
It is second most popular and also one of the complex blood types discovered by Landsteiner and Weiner in 1940. The research with rhesus monkeys on human blood led to the Rh factor, which can be either positive (+) or negative (-). With this blood grouping system, eight blood types were formed.
The Rh positive (Rh+) genotype masks the Rh negative (Rh-) gene.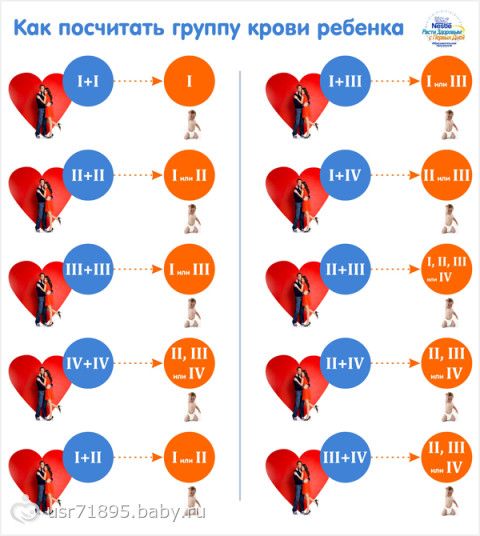 So even if you have an Rh+ blood type, you could possess an Rh- gene. Also, when both parents have the Rh+ gene, it is possible for the child to have Rh- blood type(4).
So even if you have an Rh+ blood type, you could possess an Rh- gene. Also, when both parents have the Rh+ gene, it is possible for the child to have Rh- blood type(4).
| Parental Rh type | Child's Rh type |
|---|---|
| + and + | + or - |
| + and - | + or - |
| - and - | - |
While blood groups are 100% genetically inherited, the environmental influences determine which groups are passed on more frequently to the next generations. According to the American Red Cross, B(-), AB(-) and O(-) are the rarest blood types and each account for less than 5% of global population.
Most Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can a child have different blood type than both parents ?
Yes, the child can have a blood type different from its parents. For instance, parents with blood types AB and O can give their children either A or B blood types, which are different from the parents’ blood groups.
2. Which parent determines the blood type of the child?
The blood type of a child depends on the blood type of both the parents. Each biological parent donates one of their two alleles to make up the child’s blood group. So the child’s blood type depends on the alleles that the parents carry(5).
For instance, if the mother has the blood type AO and father has blood type BO, the child can end up with any one of the blood groups: A (25%), B (25%), AB (25%) or O (50%).
3. What is the rarest blood type ?
AB negative is the rarest blood type according to the American Red Cross. It is found in 1% Caucasians. It is even rarer in African Americans. B negative and O negative are also rare blood types which are found in less than 5% of total world’s population (6).
Disclaimer: The child blood type calculator is based on theoretical principles. The information should not be used to make any conclusions about your family’s blood grouping.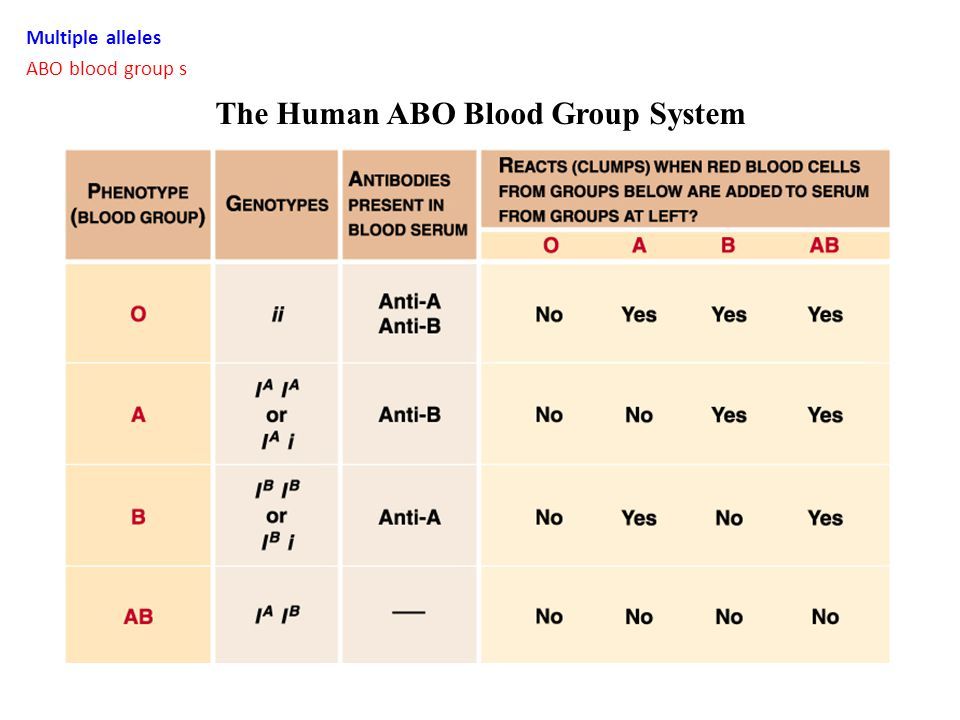 There is a chance that the blood type calculated here and the actual blood type of the baby are not the same. Therefore, we recommend that you check the baby’s blood type with a healthcare provider as well, instead of relying only on the calculator for determining blood type inheritance.
There is a chance that the blood type calculated here and the actual blood type of the baby are not the same. Therefore, we recommend that you check the baby’s blood type with a healthcare provider as well, instead of relying only on the calculator for determining blood type inheritance.
Blood Type Genetics and Compatibility
Your ABO blood type is based on the presence or absence of the A and B antigens on your red blood cells. The A blood type has only the A antigen and the B blood type has only the B antigen. The AB blood type has both A and B antigens, and the O blood type has neither A nor B antigen.
By the time you are 6 months old, you naturally develop antibodies against the antigens your red blood cells lack. For instance, a person with A blood type will have anti-B antibodies, and a person with B blood type will have anti-A antibodies. If you have type A blood, you cannot receive B blood because your body's anti-B antibodies will fight the B blood's B antigens.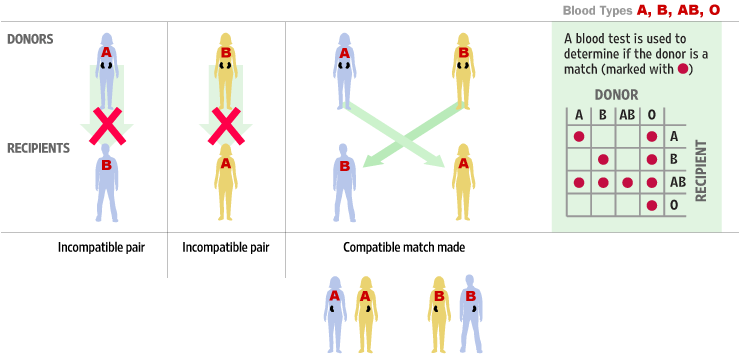 It is crucial we have all blood types available to our patients.
It is crucial we have all blood types available to our patients.
| Compatible Blood Type | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O- | O+ | B- | B+ | A- | A+ | AB- | AB+ | |
| O- | Yes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| O+ | Yes | Yes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| B- | Yes |
| Yes |
|
|
|
|
|
| B+ | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
|
|
| A- | Yes |
|
|
| Yes |
|
|
|
| A+ | Yes | Yes |
|
| Yes | Yes |
|
|
| AB- | Yes |
| Yes |
| Yes |
| Yes |
|
| AB+ | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Determination of blood group and Rh factor
What are blood groups?
Each person has one of the four blood groups according to the AB0 classification system. They differ depending on the presence or absence of certain proteins (alpha and beta agglutinins) in the blood, as well as the presence of specific antigens on the membrane of red blood cells, which are denoted by the letters A and B.
They differ depending on the presence or absence of certain proteins (alpha and beta agglutinins) in the blood, as well as the presence of specific antigens on the membrane of red blood cells, which are denoted by the letters A and B.
What are the blood types?
- 0 (I) - 1st blood group: no antigens in blood cells. The plasma contains alpha and beta agglutinins. nine0010
- A (II) - 2nd blood group: the most common. Group A antibodies are present in the shell of blood cells, and only beta-agglutinin is present in the plasma itself.
- B (III) - 3rd blood group: erythrocytes contain antigen B, and only alpha-antibody is present in plasma.
- AB (IV) - 4th blood group: blood cells in their shell contain antigens of both groups (A and B), but there are no agglutinins in the plasma.
In addition, the blood of people differs in the Rh factor (Rh). This is a special antigen (protein) that is located on the membrane of red blood cells. Approximately 80-85% of people have it and, accordingly, are Rh-positive (Rh +), the rest are Rh-negative (Rh-). The blood type and Rh factor are determined in the child in the womb and are inherited in a complex system. nine0005
The blood type and Rh factor are determined in the child in the womb and are inherited in a complex system. nine0005
The child will not necessarily inherit the blood type of the father or mother. Only if both have 0 (I) group, the child will also have this group. Blood group and Rh factor do not change during life. To learn them, it is enough to donate blood from a vein or a finger. The result becomes known within 5-10 minutes.
When transfusing blood, it is important to observe the compatibility of the group and Rh. People with a zero group are considered universal donors. Their blood suits everyone. Any group is suitable for representatives of the 4th group - they are considered universal recipients. Rh+ and Rh- blood are suitable for Rh positive patients, while Rh- blood can only be infused for a Rh-negative person. nine0005
If the pregnant woman is Rh-, it is important to know what Rh factor the child's father has. If it is positive, and if the fetus has inherited Rh+ from the father, if this protein enters the mother's blood during childbirth, the body of a woman with a negative Rh factor will develop antibodies to it.
Therefore, knowledge of blood type and Rh factor can be vital. But the definition of character and diet by blood group have no scientific basis.
A little about us
Eurpomed Kids are two children's clinics (in the north and south of the city), each of which employs all the necessary specialists, including pediatric dentists, as well as their own laboratories and pediatric outreach service . In order for children to grow up healthy, we work seven days a week from 9until 22:00! Read more about why Euromed Kids clinics are the best here 🙂
To take a blood test, you must come to the clinic on an empty stomach:
- at the clinic at 1st Nikitinskaya, 30, lit.
 A from 8:30 to 18:00;
A from 8:30 to 18:00; - to the clinic on Varshavskaya, 61k1 from 9:00 to 18:00.
And if you want to arrive at a certain time, just call us on +7 812 331 00 00.
How is blood type inherited? - American Medical Clinic
Blood consists of a liquid part - plasma and various blood cells (shaped elements). Plasma contains proteins, minerals. The formed elements of blood are erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets. The volume of blood is 6-8% of body weight - about 5 liters. Blood performs a number of important functions: transports oxygen, carbon dioxide and nutrients; distributes heat throughout the body; provides water-salt exchange; delivers hormones and other regulatory substances to various organs; has a protective (immune) function. nine0005
Differences between people in terms of blood types are differences in the composition of certain antigens and antibodies.
The existence of blood groups became known only at the beginning of the last century, in 1900-1902, when the Austrian scientist Karl Landsteiner found that when the blood of two different people is mixed, in some cases, red blood cells stick together, in others they do not. This means that not everyone has the same blood, and there are compatible and incompatible blood types. This discovery was of great importance, as it suggested a way to safely transfuse blood: you just need to determine its compatibility. nine0005
This means that not everyone has the same blood, and there are compatible and incompatible blood types. This discovery was of great importance, as it suggested a way to safely transfuse blood: you just need to determine its compatibility. nine0005
More than 20 years later, it became known that blood types are inherited and that inheritance occurs in strict accordance with the laws of genetics.
Any hereditary trait is controlled by at least a couple of genes, one of which the child receives from the mother, the other from the father. And in this case, too, parents pass on to the child not a “ready-made” blood type, but one gene responsible for its formation. It depends on the interaction of these genes what kind of blood type the child will have: the same as that of the father, the same as that of the mother, or as a result of a combination of genes, a third variant will arise. nine0005
Studying the structure of red blood cells, Landsteiner discovered special substances. He divided them into two categories, A and B, highlighting the third, where he took the cells in which they were not. Later, his students discovered erythrocytes containing A- and B-type markers at the same time.
He divided them into two categories, A and B, highlighting the third, where he took the cells in which they were not. Later, his students discovered erythrocytes containing A- and B-type markers at the same time.
As a result of research, a system of division into blood groups arose, which was called ABO (read a, b, zero), in which four groups are distinguished. We are still using this system.
- I (0) - blood group is characterized by the absence of antigens A and B;
- II (A) - is established in the presence of antigen A;
- III (B) - is established in the presence of antigens B;
- IV (AB) - is established in the presence of antigens A and B.
Group I is called zero and is designated as 00, which indicates the presence of two identical genes that determined the sign of the group - one zero was received from the father, the other from the mother. nine0005
If a child has I blood type, this means that both the father and mother necessarily have gene 0, but it does not mean at all that they also have group I, since their second genes could be different.
The gene of group II is denoted by the letter A. And if a child receives such a gene from both parents, then, of course, he will have blood group II (AA). But he will have the same group and if he receives gene 0 from one of the parents, and A from the other, since gene 0 has one feature - it cannot manifest itself in the presence of gene A.
The gene of the III blood group is denoted by the letter B. This group is also formed in those who received from their parents two identical BB genes or two different ones - B and 0, because gene 0 does not manifest itself in this combination either.
What happens if a child inherits gene A from one parent and gene B from the other? In relation to each other, they are tolerant, one does not suppress the other, and their combination leads to the appearance of a new sign - blood group IV (AB).
Table of inheritance of the blood type of the child depending on the blood types of the father and mother
| Mom + Dad | Child's blood group: Options (in %) | |||
| I+ I | I (100%) | - | - | - |
| nine0021 I + II | I (50%) | II (50%) | - | - |
| I + III | I (50%) | - | III (50%) | nine0021 - |
| I + IV | - | II (50%) | III (50%) | - |
| II + II | I (25%) | II (75%) | nine0021 - | - |
| II + III | I (25%) | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| II + IV | - | nine0021 II (50%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| III + III | I (25%) | - | III (75%) | - |
| III + IV | nine0106 -II (25%) | III (50%) | IV (25%) | |
| IV + IV | - | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (50%) |
Rh factor inheritance
The birth of a child with a negative Rh factor in a family with Rh-positive parents causes deep bewilderment at best, distrust at worst.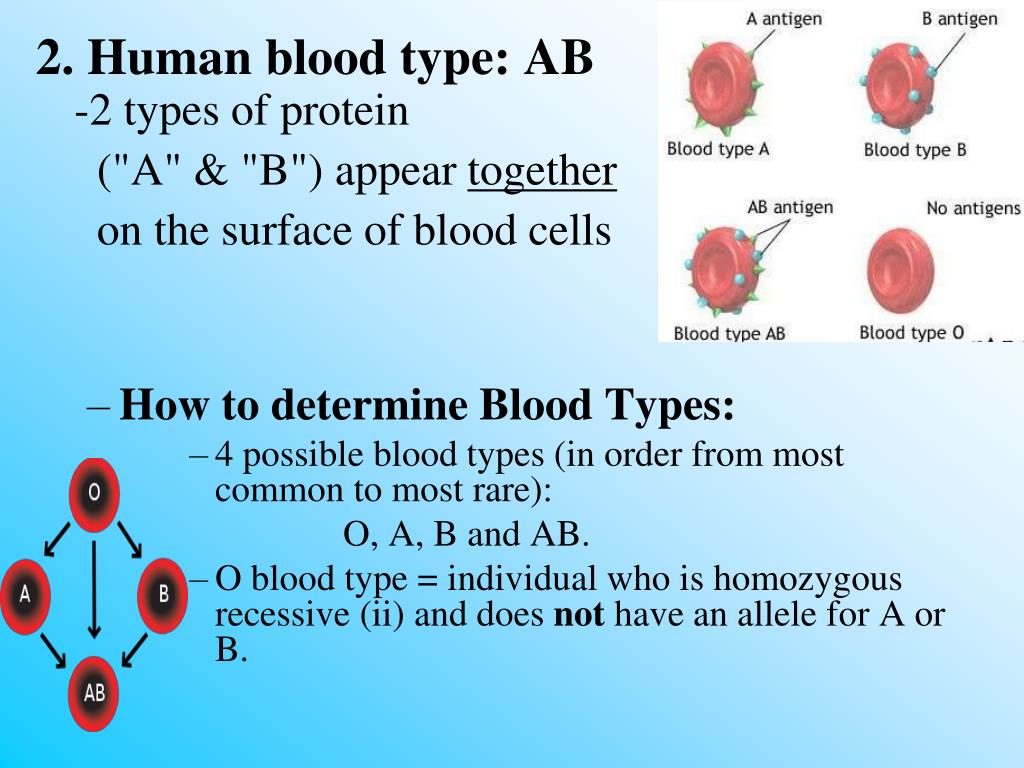 Reproaches and doubts about the fidelity of the spouse. Oddly enough, there is nothing exceptional in this situation. There is a simple explanation for such a delicate problem.
Reproaches and doubts about the fidelity of the spouse. Oddly enough, there is nothing exceptional in this situation. There is a simple explanation for such a delicate problem.
The Rh factor is an antigen (protein) found on the surface of red blood cells (erythrocytes). It was discovered at 1919 g in the blood of monkeys, and later in humans. Approximately 80-85% of people have it and are accordingly Rh-positive. Those who do not have it (the remaining 15%) are Rh-negative. It is also taken into account in blood transfusion.
These indicators are denoted by the Latin letters Rh with a plus or minus sign, respectively.
The inheritance of blood type and Rh factor occur independently of each other. If both parents are Rh positive, the child will be positive. If both parents are negative. - the child inherits more often - negative. If one of the parents is Rh-positive and the other is Rh-negative, then the probability of the baby's Rh-affiliation is determined by 50% to 50%. There is a possibility of Rhesus inheritance after several generations (the case when the father and mother have a positive Rh, and the born child has a negative Rh). Therefore, when planning a family, parental compatibility studies are mandatory - it is necessary to determine blood groups and blood rhesus. Women with Rh-negative blood are at risk. nine0005
There is a possibility of Rhesus inheritance after several generations (the case when the father and mother have a positive Rh, and the born child has a negative Rh). Therefore, when planning a family, parental compatibility studies are mandatory - it is necessary to determine blood groups and blood rhesus. Women with Rh-negative blood are at risk. nine0005
A positive Rh factor in a woman and a negative one in a man do not represent any cause for concern. If a woman has Rh-negative blood, and her husband has Rh-positive blood, then Rh conflict may develop during pregnancy, so a woman is recommended to do a blood test for antibodies to the Rh factor before pregnancy. The fact is that if a woman has undergone a surgical operation (including abortion) or a blood transfusion before pregnancy, or if the pregnancy is not the first, then there is a possibility of formation of specific antibodies in her blood. In a Rh-negative woman with a Rh-positive fetus, immune complications (hemolytic disease of the newborn, etc.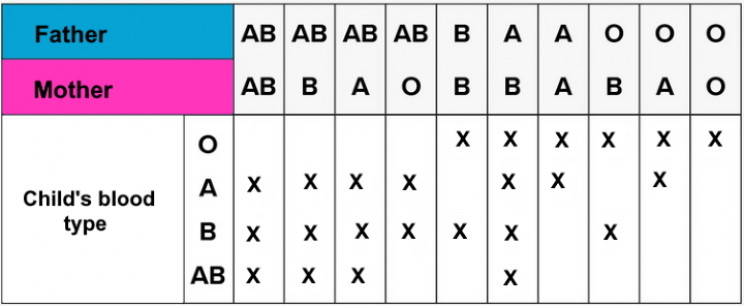 ) are possible, and especially from the second or third pregnancy. To prevent complications, anti-Rhesus gamma globulin is administered. It is necessary to regularly examine the blood for Rh antibodies in dynamics. nine0005
) are possible, and especially from the second or third pregnancy. To prevent complications, anti-Rhesus gamma globulin is administered. It is necessary to regularly examine the blood for Rh antibodies in dynamics. nine0005
Character inheritance
For centuries, parents only wondered what their child would be like. Today there is an opportunity to look into the beautiful far away. Thanks to ultrasound, you can find out the sex and some features of the anatomy and physiology of the baby.
Genetics allows you to determine the likely color of the eyes and hair, and even the presence of an ear for music in a baby. All these traits are inherited according to the laws of Mendel and are divided into dominant and recessive. The dominant gene is indicated by a capital letter of the Latin alphabet, and in its presence, the recessive gene, as a rule, does not show its properties. The recessive gene is indicated by a capital letter of the Latin alphabet. If, for some trait, an organism contains two identical genes (two recessive or two dominant), then it is called homozygous for this trait.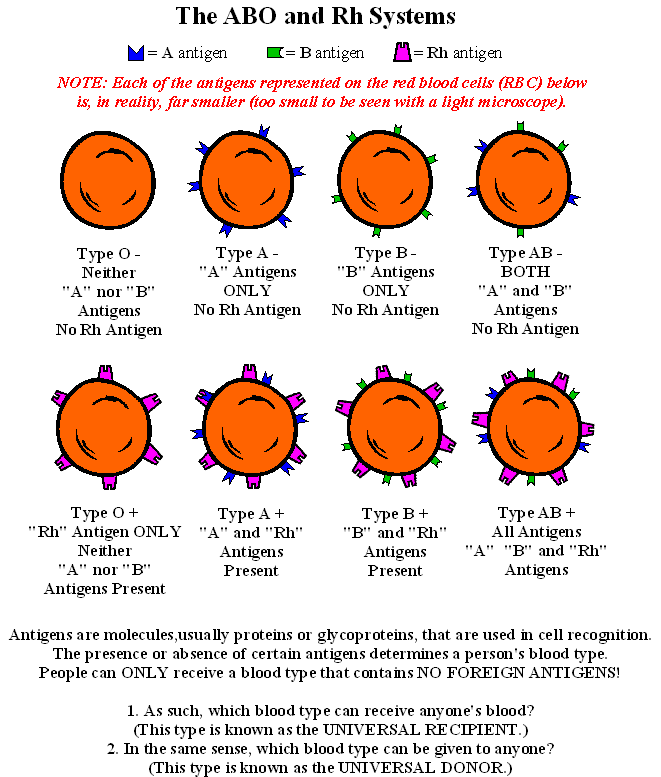 If the organism contains one dominant and one recessive gene, then it is called heterozygous for this trait, and at the same time, those properties of the trait that are encoded by the dominant gene are manifested. nine0005
If the organism contains one dominant and one recessive gene, then it is called heterozygous for this trait, and at the same time, those properties of the trait that are encoded by the dominant gene are manifested. nine0005
For example,
A is a dominant gene that determines brown eye color
a - recessive gene that determines blue eyes
Possible variants of the genotype:
AA - homozygous, brown eyes
Aa - heterozygote, brown eyes
aa - homozygous, blue eyes
Brown eyes, hair with small curls, and even the ability to roll the tongue into a tube are dominant signs. Most likely, the child will inherit them. nine0005
Unfortunately, the dominant features also include a tendency to early baldness and graying, myopia and a gap between the front teeth.
Gray and blue eyes, straight hair, fair skin, mediocre ear for music are considered recessive. These symptoms are less likely to occur.
Blood type and risk of certain diseases
There is a pattern between blood type and the risk of developing certain diseases (predisposition). Australian scientists have found that people with blood type 0 (I) are much less likely to suffer from schizophrenia. People with type B (III) blood have a higher risk than others of a severe disease of the nervous system - Parkinson's disease. Of course, the blood type itself does not mean that a person will necessarily suffer from a "characteristic" disease for her. There are many factors involved, and blood type is just one of them. nine0005
Australian scientists have found that people with blood type 0 (I) are much less likely to suffer from schizophrenia. People with type B (III) blood have a higher risk than others of a severe disease of the nervous system - Parkinson's disease. Of course, the blood type itself does not mean that a person will necessarily suffer from a "characteristic" disease for her. There are many factors involved, and blood type is just one of them. nine0005
Blood group and personality
Blood type 0 (I). Energetic, sociable, good health, strong will. Striving for leadership. Fussy, ambitious.
Blood group A (II). Diligent and committed. They love harmony and order. Their weakness is stubbornness.
Blood group B (III). Delicate, impressionable, calm. Increased demands on themselves and others. Individualists. Easy to adapt to everything. Powerful and creative personalities. nine0005
Blood group AB (IV). Emotions and feelings take precedence over common sense and calculation.