Acid reflux during pregnancy remedies
Pregnancy Heartburn? 7 Ways to Get Relief
Keywords
Kathryn Walker, MD
Women and Newborn
Learn more about women and newborn services we offer.
Expectant mothers everywhere are aching to know one thing: “How can I get some relief from this awful pregnancy heartburn?”
To help ease your pain, here are some answers to your “burning” questions. (Pardon the pun.)
When you’re growing a human being, you don’t have time for that yucky acid reflux. But your usual go-to methods for treating it may not be safe for your unborn baby. (Remember Pepto Bismol? That’s on the No Fly List for moms-to-be, according to FDA recommendations.)
Instead, here are some of the safest and best ways to get rid of heartburn when you’re pregnant:
- Dip into some yogurt. Its probiotics and soothing texture make yogurt a great option for extinguishing heartburn – or at least dousing the flames a little.
- Drink milk with honey. According to the American Pregnancy Association, a tablespoon of honey mixed in a glass of warm milk may be just what you need to neutralize heartburn-causing acid.
- Snack on almonds. Munching on a handful of almonds may provide heartburn relief since these nuts have a lower acidity level than others.
- Eat pineapple or papaya.
 For some women, the digestive enzymes in pineapple and papaya have helped ease symptoms. Eating these fruits after your meals can aid digestion and reduce your chances of heartburn.
For some women, the digestive enzymes in pineapple and papaya have helped ease symptoms. Eating these fruits after your meals can aid digestion and reduce your chances of heartburn. - Try a little ginger. You probably knew ginger was a good remedy for an upset stomach. Well, that makes it a helpful candidate for fighting off heartburn, too. Among ginger’s many benefits, it can reduce inflammation and prevent stomach acid from traveling up the esophagus.
- Chew sugar-free gum. Another effective method for taming the burn is to chew some sugar-free gum. One study found that chewing sugar-free gum for 30 minutes after a meal can reduce acid reflux.
- Take (doctor-approved) medication. When all else fails, certain medications are considered safe to use for pregnancy heartburn relief. Just make sure you speak to your doctor or OB-GYN first. If your heartburn is severe, they may prescribe special medication to help control it.
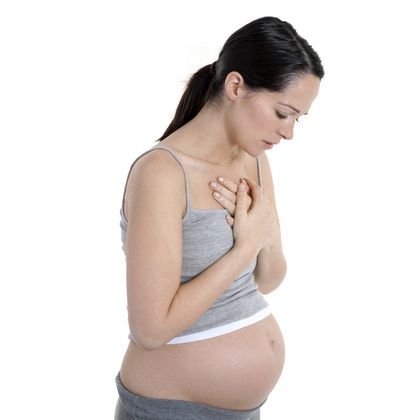

While not every tip mentioned above may work to ease your symptoms, you’ve got nine months to try them all and figure out what works.
It’s important to be extremely careful about the medications you take when pregnant.
For heartburn relief, over-the-counter antacids (such as Tums, Mylanta, Rolaids, and Maalox) are all considered safe medications to use during pregnancy.
As always, consult with your provider about any medications you’re taking – even if they’re considered safe. (This is especially true for high-risk pregnancies.)
If you experience any unusual symptoms while taking an over-the-counter medication, call your doctor immediately.
They say prevention is the best medicine, so knowing common heartburn triggers can help you keep the acid at bay.
Of course, pregnancy itself is a major trigger for heartburn. As your growing uterus puts pressure on your stomach, this pushes stomach acid up your throat.
Those lovely hormones are no help either.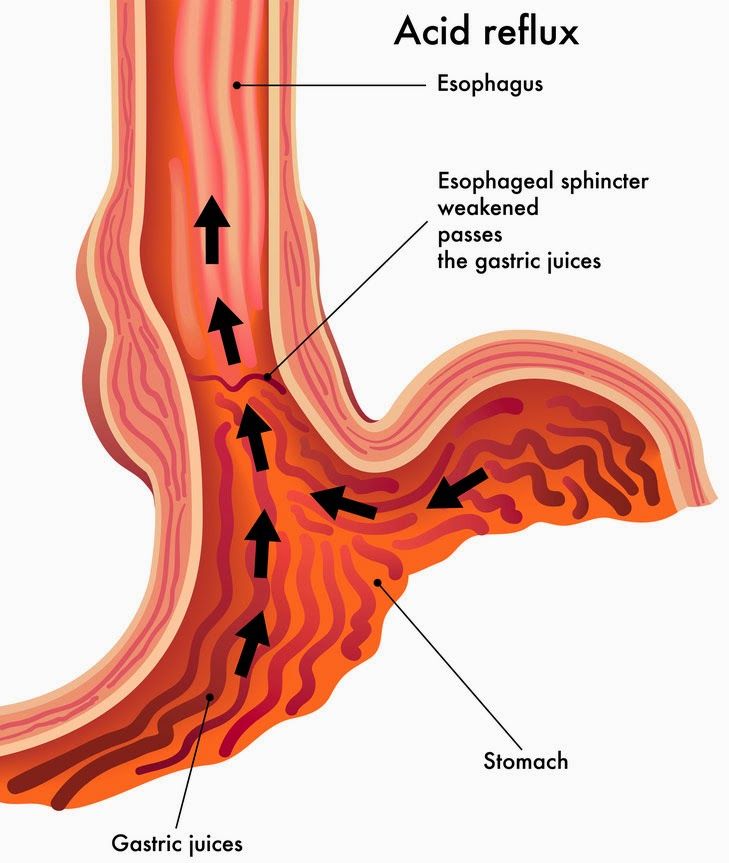 They tend to relax the valve between your stomach and esophagus, which makes it easier for acid to make its way upward.
They tend to relax the valve between your stomach and esophagus, which makes it easier for acid to make its way upward.
While there’s nothing you can do to stop this entirely, there are a few things that can help prevent heartburn from flaring up during pregnancy:
- Avoid lying down after eating. It may be tempting to take a post-meal nap, but if you want to prevent heartburn, don’t lie down after eating. Consider napping in an upright recliner instead.
- Prop yourself up at night. It’s hard enough to sleep well while pregnant without throwing acid reflux on top of everything. To prevent nighttime heartburn, try propping yourself up when you go to sleep to counteract the acid.
- Don’t eat before bedtime. In addition to propping yourself up at night, try not to eat anything within three hours of hitting the sack.
- Skip spicy, acidic, or fried foods. Ask yourself: Are those greasy chips worth being doubled over in pain later? (Probably not.
 ) If you want to avoid the risk, steer clear of any and all rich, fatty foods. Not only will this help prevent heartburn, but making more nutritious choices helps ensure that you your baby is getting the important vitamins and minerals that they need to stay healthy in utero.
) If you want to avoid the risk, steer clear of any and all rich, fatty foods. Not only will this help prevent heartburn, but making more nutritious choices helps ensure that you your baby is getting the important vitamins and minerals that they need to stay healthy in utero. - Eat small meals, but more frequently. Your pregnant tummy doesn’t love to be hit with large amounts of food to digest in one go. Make things easier on your gut by eating several small meals throughout the day instead of three large ones.
- Eat slowly. Wolfing down those small meals will defeat the purpose of spreading them out. Eating quickly increases the risk of acid reflux, so slow down and enjoy your food.
- Wear loose clothing. Tight-fitting clothes are not your stomach’s best friend when you’re trying to prevent heartburn – particularly during pregnancy. Wear clothing that offers support without being restrictive.
- Drink your liquids between meals.
 If you’re the type of person who likes to take a swig of their drink between each bite, it’s time to change course. Drinking liquids during meals can exacerbate heartburn symptoms, so take little sips if you’re thirsty at mealtime.
If you’re the type of person who likes to take a swig of their drink between each bite, it’s time to change course. Drinking liquids during meals can exacerbate heartburn symptoms, so take little sips if you’re thirsty at mealtime.
Someday, scientists may very well invent a miracle medication that promises permanent pregnancy heartburn relief. Unfortunately, that hasn’t happened yet.
So, if you’re wondering how long you can expect to deal with heartburn while you’re pregnant, it will probably be throughout your entire pregnancy. (Now may be a good time to remind yourself that you get a cute little baby out of this when you’re done.)
However, just because there’s no cure, that doesn’t mean you can’t find some relief in the meantime.
If severe pregnancy heartburn is getting in the way of everyday life, it’s time to see a doctor.
Intermountain Healthcare offers individualized and compassionate pregnancy care for women of all ages and health needs.
To get the care you need, search for a provider or find an Intermountain Healthcare location near you.
Intermountain Moms Women's Health, Baby Your Baby, Pregnancy, Women and Newborn
Last Updated: 5/21/2021
-
Intermountain Moms
-
Intermountain Moms
Copyright ©2022, Intermountain Healthcare, All rights reserved.
Heartburn, Acid Reflux, and GERD During Pregnancy
It’s called heartburn, although that burning feeling in your chest has nothing to do with the heart. Uncomfortable and frustrating, it bothers many women, particularly during pregnancy.
The first question you may have is how to make it stop. You may also wonder if treatments are safe for your baby. Learn what causes heartburn during pregnancy and what you can do about it.
During normal digestion, food travels down the esophagus (the tube between your mouth and stomach), through a muscular valve called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), and into the stomach.
The LES is part of the doorway between your esophagus and your stomach. It opens to allow food through and closes to stop stomach acids from coming back up.
When you have heartburn, or acid reflux, the LES relaxes enough to allow stomach acid to rise up into the esophagus. This can cause pain and burning in the chest area.
During pregnancy, hormone changes can allow the muscles in the esophagus, including the LES, to relax more frequently. The result is that more acids may seep back up, particularly when you’re lying down or after you’ve eaten a large meal.
The result is that more acids may seep back up, particularly when you’re lying down or after you’ve eaten a large meal.
In addition, as your fetus grows during the second and third trimesters and your uterus expands to accommodate that growth, your stomach is under more pressure. This can also result in food and acid being pushed back up into your esophagus.
Heartburn is a common occurrence for most people at one time or another, but it doesn’t necessarily mean you’re pregnant. However, if you also experience other symptoms, such as a missed period or nausea, these could be signs that you need to take a pregnancy test.
Pregnancy increases your risk of heartburn or acid reflux. During the first trimester, muscles in your esophagus push food more slowly into the stomach and your stomach takes longer to empty.
This gives your body more time to absorb nutrients for the fetus, but it can also result in heartburn.
During the third trimester, the growth of your baby can push your stomach out of its normal position, which can lead to heartburn.
However, each woman is different. Being pregnant doesn’t necessarily mean you’ll have heartburn. It depends on many factors, including your physiology, diet, daily habits, and your pregnancy.
Relieving heartburn during pregnancy typically involves some trial and error. Lifestyle habits that can reduce heartburn are often the safest methods for mother and baby. The following tips may help relieve your heartburn:
- Eat smaller meals more frequently and avoid drinking while eating. Drink water in between meals instead.
- Eat slowly and chew every bite thoroughly.
- Avoid eating a few hours before bed.
- Avoid foods and beverages that trigger your heartburn. Typical culprits include chocolate, fatty foods, spicy foods, acidic foods like citrus fruits and tomato-based items, carbonated beverages, and caffeine.
- Stay upright for at least one hour after a meal. A leisurely walk may also encourage digestion.
- Wear comfortable rather than tight-fitting clothing.

- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Use pillows or wedges to elevate your upper body while sleeping.
- Sleep on your left side. Lying on your right side will position your stomach higher than your esophagus, which may lead to heartburn.
- Chew a piece of sugarless gum after meals. The increased saliva may neutralize any acid coming back up into the esophagus.
- Eat yogurt or drink a glass of milk to quell symptoms once they start.
Alternative medicine options include acupuncture and relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation, yoga, or guided imagery. Always check with your doctor before trying new treatments.
Over-the-counter antacids such as Tums, Rolaids, and Maalox may help you cope with occasional heartburn symptoms. Those made of calcium carbonate or magnesium are good options.
However, it may be best to avoid magnesium during the last trimester of pregnancy. Magnesium could interfere with contractions during labor.
Most doctors recommend avoiding antacids that contain high levels of sodium. These antacids can lead to a buildup of fluid in the tissues.
You should also avoid any antacids that list aluminum on the label, as in “aluminum hydroxide” or “aluminum carbonate”. These antacids can lead to constipation.
Finally, stay away from medications like Alka-Seltzer that may contain aspirin.
Ask your doctor for the best option. If you find yourself downing bottles of antacids, your heartburn may have progressed to gastroesophageal acid reflux disease (GERD). In that case, you may need a stronger treatment.
If you have heartburn that often wakes you up at night, returns as soon as your antacid wears off, or creates other symptoms (such as difficulty swallowing, coughing, weight loss, or black stools), you may have a more serious problem that requires attention.
Your doctor may diagnose you with GERD. This means that your heartburn needs to be controlled to protect you from complications such as damage to the esophagus.
Your doctor may prescribe certain acid-reducing medications to reduce your symptoms. Research indicates that medications called h3 blockers, which help block the production of acid, appear to be safe.
Another type of medication, called proton pump inhibitors, is used for people with heartburn that doesn’t respond to other treatments.
If you’re concerned about the effects of medications, be sure to talk to your doctor. Doctors can help you control your symptoms while keeping your unborn child safe.
Acid related diseases in pregnancy | Rassvet Clinic
Heartburn during pregnancy is a very common complaint. It is known that up to 80% of pregnant women experience symptoms characteristic of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) (heartburn, dysphagia, belching, and others), and the frequency of heartburn in the first trimester is 7.2%, in the second - 18.2%, in the third - 40%.
The main factors behind this high prevalence of GERD in pregnancy include hormonal changes such as hyperprogesteronemia (increased levels of the hormone progesterone) and hyperestrogenemia (increased levels of estrogen hormones), as well as increased intra-abdominal pressure due to uterine and fetal growth.
The action of gestational hormones in the first trimester of pregnancy is due to the fact that they, without affecting the basal tone of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), reduce the increase in pressure of this sphincter in response to a variety of physiological stimuli, including food intake. In the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, progesterone and estrogen reduce the basal tone of the LES to 50% of the initial level, the maximum decrease occurs at 36 weeks of gestation. After a successful delivery, the tone of the LES in women who did not suffer from GERD before pregnancy, as a rule, returns to normal - in connection with this, this condition is called "pregnancy heartburn."
Pregnancy heartburn usually does not lead to the development of esophagitis, complications of GERD (strictures, ulcers, bleeding) and does not require serious medical treatment.
If a woman had GERD before pregnancy, the complaints may worsen during pregnancy and require examination and medication.
The diagnosis of GERD during pregnancy is established primarily on the basis of complaints, anamnesis data and objective examination. X-ray examination in pregnant women - due to possible damaging effects on the fetus - is not used, pH-metry and manometry can be used, but the need for its use is doubtful.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is the method of choice for diagnosing GERD in pregnant women, but it should only be used for strict indications, such as a history of complications of GERD and the ineffectiveness of ongoing drug therapy.
Treatment of GERD in pregnant women should be based on changes in lifestyle and nutrition: exclusion of a horizontal position of the body immediately after meals, sleeping with the head end of the bed elevated (by 15 cm), exclusion of physical activity that increases intra-abdominal pressure (including wearing corsets, tight belts, bandages). The last meal should take place no later than 3 hours before bedtime, you need to eat in small portions, pay special attention to the normalization of the stool.
First-line drugs for the treatment of GERD in pregnant women include antacids and alginates. With the ineffectiveness of these drugs, it is permissible to prescribe prokinetics (metoclopramide), blockers of histamine h3 receptors and (according to strict indications) proton pump inhibitors (PPIs).
H2-histamine blockers are the most commonly prescribed group of drugs for pregnant women. They are classified as risk category B by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) ( "drugs taken by a limited number of pregnant women without evidence of their effect on the incidence of congenital anomalies or damaging effects on the fetus") . In Russian instructions, only cimetidine and ranitidine are allowed with a caveat: use during pregnancy is possible only if the expected effect of therapy outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Famotidine and nizatidine in the Russian Federation are contraindicated for pregnant women.
Although most PPIs are also classified by the FDA as risk category B, in Russia there are more stringent restrictions on the use of this group of drugs in pregnant women. So, lansoprazole is contraindicated in the first trimester, in the second and third trimesters it can be used only if the expected benefit of therapy outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. The use of pantoprazole and esomeprazole is possible only under strict indications, when the benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Rabeprazole during pregnancy is contraindicated.
So, lansoprazole is contraindicated in the first trimester, in the second and third trimesters it can be used only if the expected benefit of therapy outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. The use of pantoprazole and esomeprazole is possible only under strict indications, when the benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Rabeprazole during pregnancy is contraindicated.
Pregnancy has a beneficial effect on the course of peptic ulcer disease: 75-80% of women experience remission of the disease, and it does not have a noticeable effect on its outcome. However, some patients may experience an exacerbation. This is most often observed in the first trimester of pregnancy (14.8%) and the third trimester (10.2%), as well as 2-4 weeks before the due date or in the early postpartum period. Uncomplicated peptic ulcer does not adversely affect the development of the fetus.
Treatment of peptic ulcer in pregnant women includes adherence to generally accepted "regime" measures and diet; taking in the usual therapeutic doses of non-absorbable antacids (1 sachet 3 times a day 1 hour after meals and adsorbents 1 sachet 3 times a day 1 hour after meals).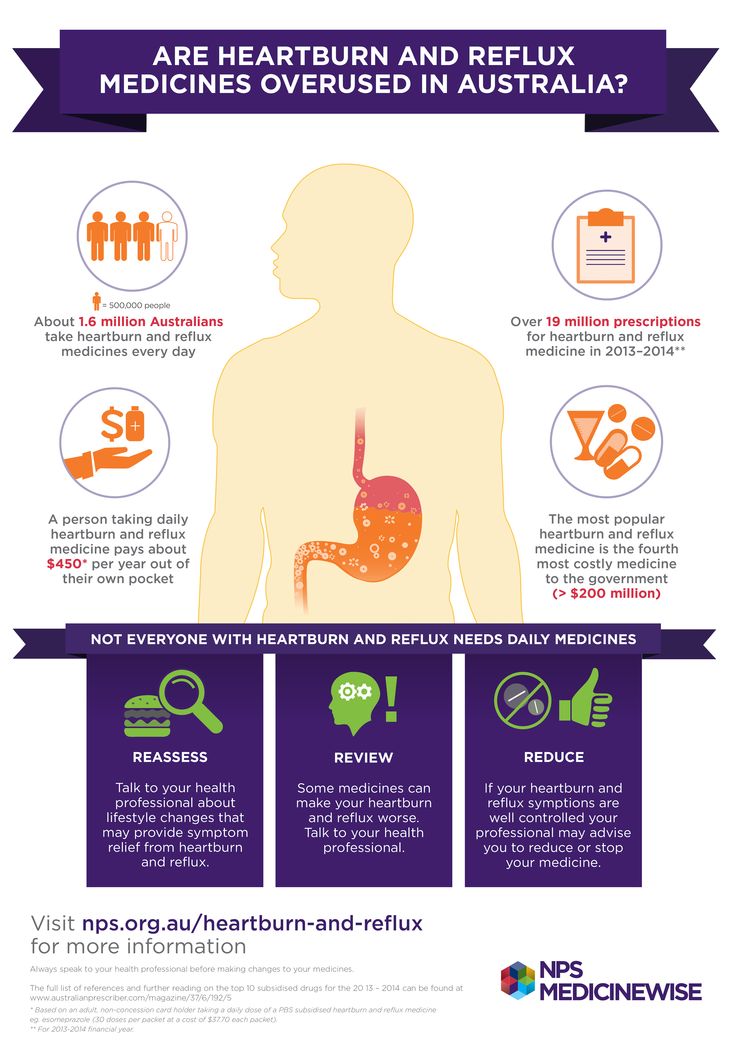 If there is no effect, h3-blockers are prescribed (ranitidine 150/300 mg once a night), in case of their insufficient effectiveness, as well as with the development of complications, we can take PPIs (omeprazole 20-40 mg, lansoprazole 30-60 mg, pantoprazole 40 mg). mg in the morning before the first meal). Bismuth preparations are contraindicated for pregnant women. Eradication therapy for H. pylori infection in pregnant women is not carried out.
If there is no effect, h3-blockers are prescribed (ranitidine 150/300 mg once a night), in case of their insufficient effectiveness, as well as with the development of complications, we can take PPIs (omeprazole 20-40 mg, lansoprazole 30-60 mg, pantoprazole 40 mg). mg in the morning before the first meal). Bismuth preparations are contraindicated for pregnant women. Eradication therapy for H. pylori infection in pregnant women is not carried out.
Author:
Kaibysheva Valeria Olegovna
Gastroenterologist Ph.D.
Ayurvedic medicines, causes and symptoms
What is acid reflux
Acid reflux is a disease that causes a burning sensation (heartburn) in the lower part of the chest. In this case, there is a reverse outflow of acid from the stomach into the esophagus. When acid reflux is diagnosed as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) after two weeks.
Acid reflux according to Ayurveda
According to Ayurveda, acid reflux occurs due to exacerbation of Pitta and Vata dosha of the body. Increased Pitta causes a burning sensation, and increased Vata causes acid to move up the esophagus.
Increased Pitta causes a burning sensation, and increased Vata causes acid to move up the esophagus.
Causes of acid reflux
Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid backs up into the esophagus, causing heartburn. This condition occurs when the abdomen and upper body move above the diaphragm. The diaphragm is the muscle that separates the stomach from the chest and keeps the acid in the stomach. However, due to diaphragmatic disorders, acid can move up into the esophagus, which causes acid reflux symptoms. Common hiatal hernia is considered as the main possible cause of acid reflux.
Risk factors for acid reflux
It affects people of all ages, sometimes regardless of the cause. Lifestyle factors such as:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Eating before bed
- Insufficient or low levels of physical activity
- Certain medications such as calcium channel blockers, pain relievers, antihistamines, and sedatives and asthma medications.

- Drinking beverages such as alcohol, coffee, tea, carbonated drinks, etc.
Symptoms of acid reflux
Symptoms that commonly occur during acid reflux include:
- Heartburn
- Belching
9 Other symptoms include:
- Gas, bloating
- Bloody or black stools
- Hematemesis
- Belching and hiccups
- Dysphagia i.e. difficulty swallowing
- Nausea
- Unexpected weight loss
- wheezing (sound of piercing whistle when breathing)
- Dry cough
- Single -fingers or chronic sore throat
Contributed with acid reflux
As mentioned above, as it said, more than the above, acidic reflux is preserved. two weeks, it can be called GERD, and further complications of GERD are esophagitis, Barrett's esophagus, esophageal cancer and heart disease.
How to diagnose acid reflux
The appearance of heartburn-like symptoms is the key to the diagnosis of acid reflux.