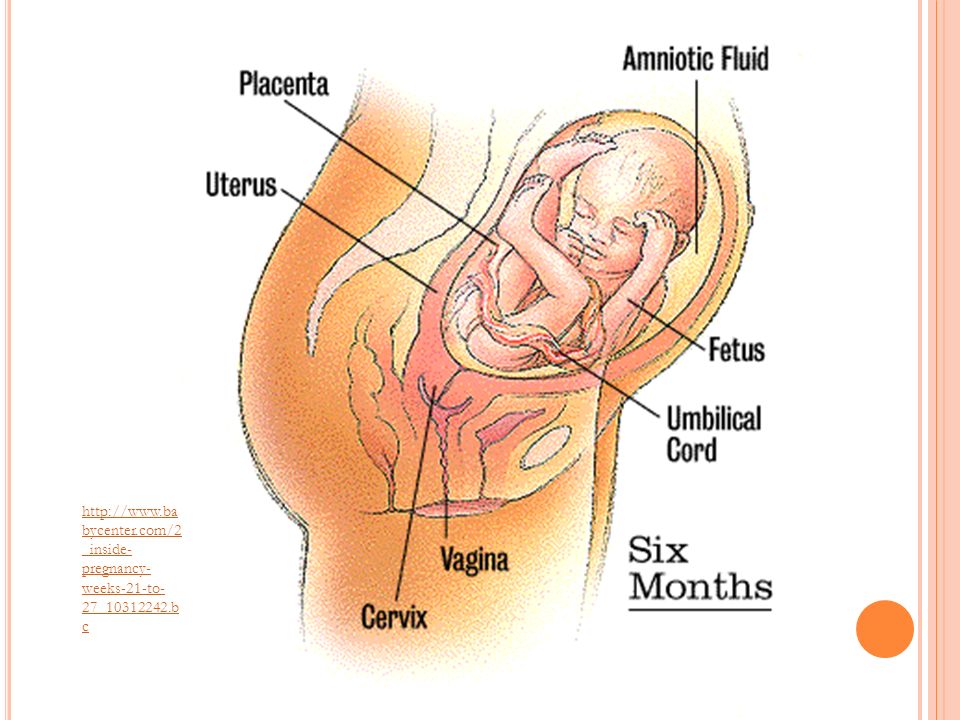
6 months old fetus pictures
Pictures of Fetal Development Month-by-Month
Reviewed by Amita Shroff, MD on February 24, 2021
You're pregnant. Congratulations! Are you curious how big your developing baby is, what your baby looks like as it grows inside you, and when you'll feel it move? Take a peek inside the womb to see how a baby develops from month to month.
Fertilization happens when a sperm meets and penetrates an egg. It's also called conception. At this moment, the genetic makeup is complete, including the sex of the baby. Within about three days after conception, the fertilized egg is dividing very fast into many cells. It passes through the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it attaches to the uterine wall. The placenta, which will nourish the baby, also starts to form.
At this point the baby is developing the structures that will eventually form their face and neck. The heart and blood vessels continue to develop. And the lungs, stomach, and liver start to develop. A home pregnancy test would show positive.
The baby is now a little over half an inch in size. Eyelids and ears are forming, and you can see the tip of the nose. The arms and legs are well formed. The fingers and toes grow longer and more distinct.
The baby measures about 2 inches and starts to make its own movements. You may start to feel the top of your uterus above your pubic bone. Your doctor may hear the baby's heartbeat with special instruments. The sex organs of the baby should start to become clear.
The baby now measures about 4.3 to 4.6 inches and weighs about 3.5 ounces. You should be able to feel the top of your uterus about 3 inches below your belly button. The baby's eyes can blink and the heart and blood vessels are fully formed. The baby's fingers and toes have fingerprints.
The baby weighs about 10 ounces and is a little more than 6 inches long. Your uterus should be at the level of your belly button. The baby can suck a thumb, yawn, stretch, and make faces. Soon -- if you haven't already -- you'll feel your baby move, which is called "quickening.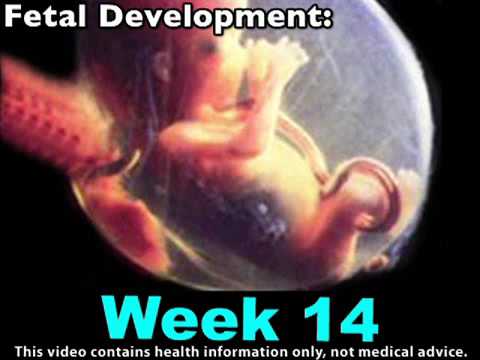 "
"
An ultrasound is usually done for all pregnant women at 20 weeks. During this ultrasound, the doctor will make sure that the placenta is healthy and attached normally and that your baby is growing properly. You can see the baby's heartbeat and movement of its body, arms, and legs on the ultrasound. You can usually find out whether it's a boy or a girl at 20 weeks.
Shown here is a 2D ultrasound (inset) contrasted with a 4D ultrasound, both at 20 weeks.
The baby weighs about 1.4 pounds now and responds to sounds by moving or increasing their pulse. You may notice jerking motions if they hiccup. With the inner ear fully developed, the baby may be able to sense being upside down in the womb.
The baby weighs about 2 pounds, 6 ounces, and changes position often at this point in pregnancy. If you had to deliver prematurely now, there is a good chance the baby would survive. Ask your doctor about preterm labor warning signs. Now is the time to register for birthing classes.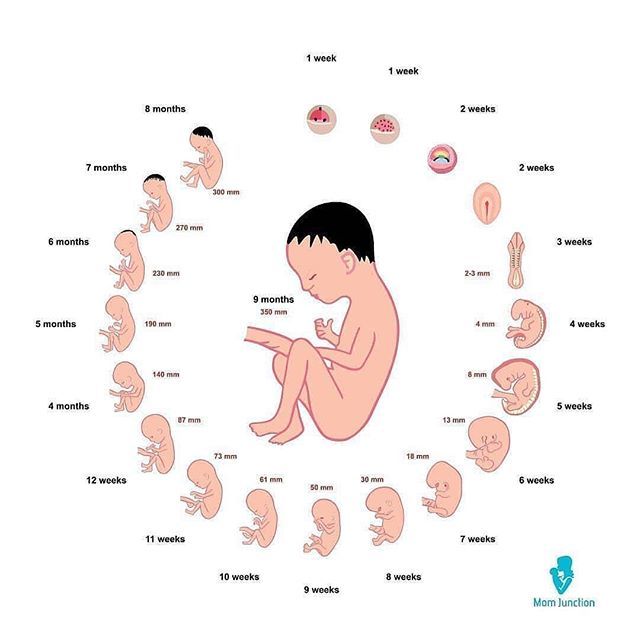 Birthing classes prepare you for many aspects of childbirth, including labor and delivery and taking care of your newborn.
Birthing classes prepare you for many aspects of childbirth, including labor and delivery and taking care of your newborn.
The baby weighs almost 4 pounds and is moving around often. The baby's skin has fewer wrinkles as a layer of fat starts to form under the skin. Between now and delivery, your baby will gain up to half their birth weight. Ask your doctor how to do a fetal movement chart. Think about breastfeeding. You may notice a yellowish fluid leaking from your breasts. That is colostrum, and it happens to get your breasts ready for making milk. Most women go to the doctor every two weeks at this stage of pregnancy.
Babies differ in size, depending on many factors, such as gender, the number of babies being carried, and size of the parents. So your baby's overall rate of growth is as important as the actual size. On average, a baby at this stage is about 18.5 inches and weighs close to 6 pounds. The brain has been developing rapidly. Lungs are nearly fully developed.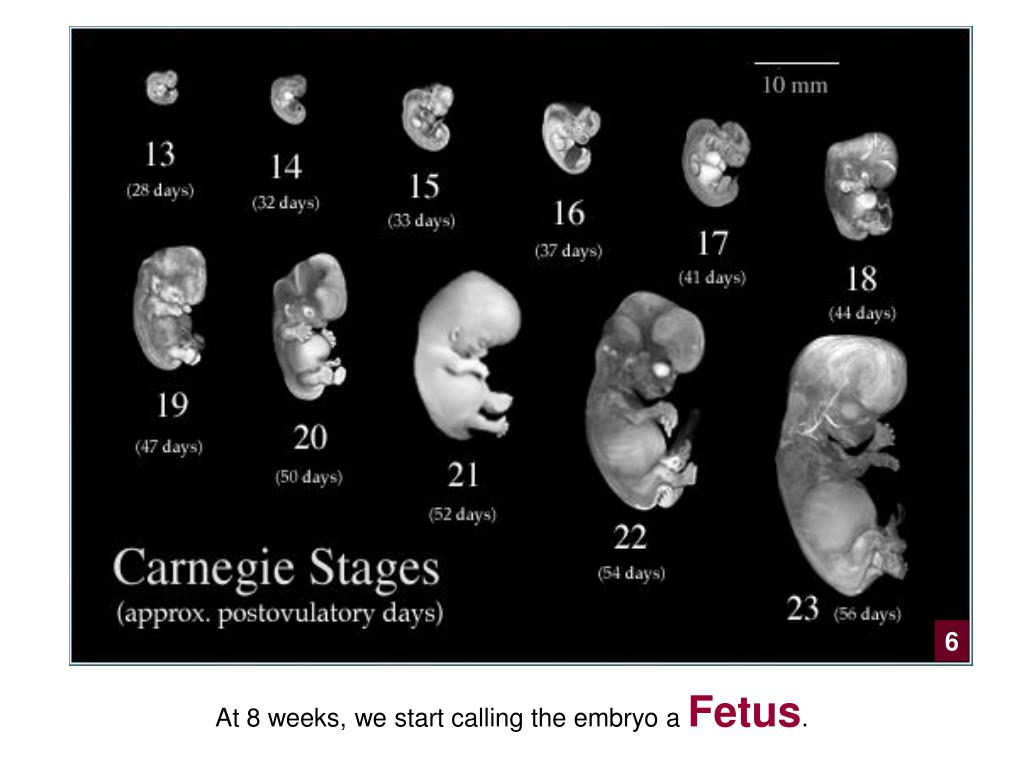 The head is usually positioned down into the pelvis by now. Your baby is considered at 'term' when they are 37 weeks. They are an early term baby if born between 37-39 weeks, at term, if they're 39-40 weeks and late term if they're 41-42 weeks.
The head is usually positioned down into the pelvis by now. Your baby is considered at 'term' when they are 37 weeks. They are an early term baby if born between 37-39 weeks, at term, if they're 39-40 weeks and late term if they're 41-42 weeks.
A mother's due date marks the end of their 40th week. The delivery date is calculated using the first day of their last period. Based on this, pregnancy can last between 38 and 42 weeks with a full-term delivery happening around 40 weeks. Some post-term pregnancies -- those lasting more than 42 weeks -- are not really late. The due date may just not be accurate. For safety reasons, most babies are delivered by 42 weeks. Sometimes the doctor may need to induce labor.
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
(1) Copyright © LookatSciences / Phototake – All rights reserved.
(2) Dr. David M. Phillips / Visuals Unlimited / Getty Images
(3) 3D4Medical.com / Getty Images
(4) Copyright © Scott Camazine / Phototake -- All rights reserved.
(5) Copyright © LookatSciences / Phototake – All rights reserved.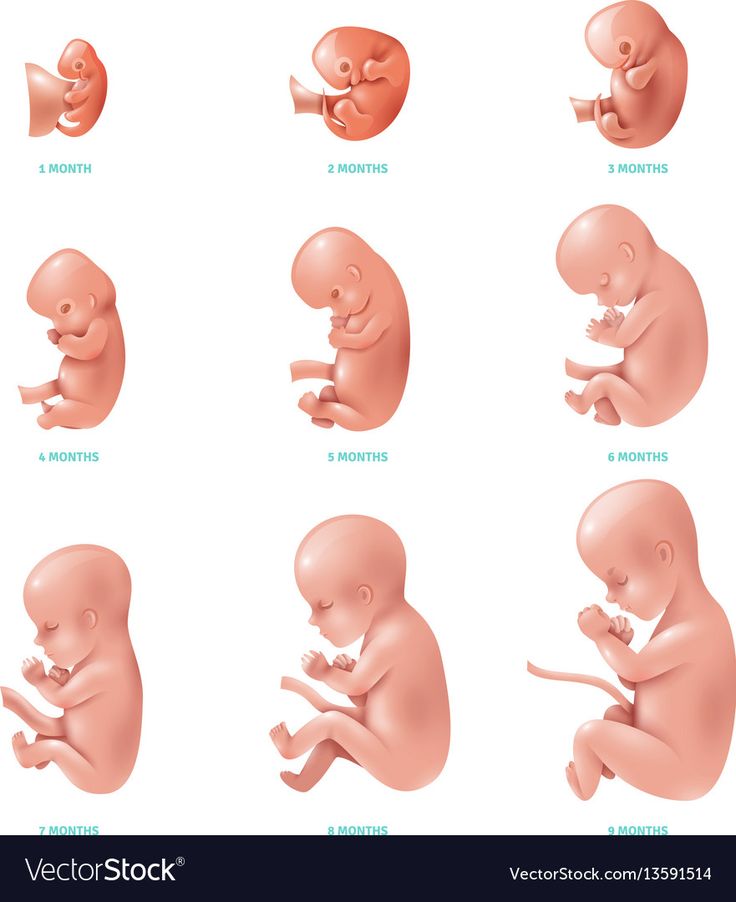
(6) Nestle / Petit Format / Photo Researchers, Inc.
(7) © Lennart Nilsson Photography AB. All rights reserved worldwide.
(8) a) Dr.Benoit/Mona Lisa. Copyright © LookatSciences / Phototake -- All rights reserved. b)Vincenzo Lombardo / Photographer's Choice / Getty Images
(9) Dr. Benoit/Mona Lisa. Copyright © LookatSciences / Phototake -- All rights reserved.
(10) © Lennart Nilsson Photography AB. All rights reserved worldwide.
(11) Jose Manuel Gelpi Diaz / iStockphoto
(12) © Lennart Nilsson Photography AB. All rights reserved worldwide.
(13) © Yoav Levy / Phototake -- All rights reserved.
SOURCES:
American Academy of Family Physicians.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: "How Your Baby Grows During Pregnancy."
KidsHealth.org: "Pregnancy Calendar."
March of Dimes: "Prenatal Care – Ultrasound."
US Department of Health and Human Services Office of Women’s Health: "Pregnancy: Breast Changes."
© 2021 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. View privacy policy and trust info
All rights reserved. View privacy policy and trust info
Five Photos You Must Take of Your Baby At 6 Months
At six months old your baby will have developed their own little personality. Around this time, they’ll learn to sit unaided and have lots of wonderful expressions to share.
This is a great time to capture a set of milestone photographs – pictures that capture all of those new skills your baby has developed and record how your baby has grown.
In this article I’m going to share five moments not to miss at 6 months. You can find my must-take baby photos for 3 month old babies here.
Sitting Up
Your baby’s favourite new trick will be sitting up unaided around this age. They may tire quickly at first, so set up your camera, and clear space where they can sit down beforehand. Then, when they’re well fed and rested sit your baby in the space you’ve created and snap away.
Do talk to your baby as you are photographing so that you can capture some of those gorgeous expressions they make.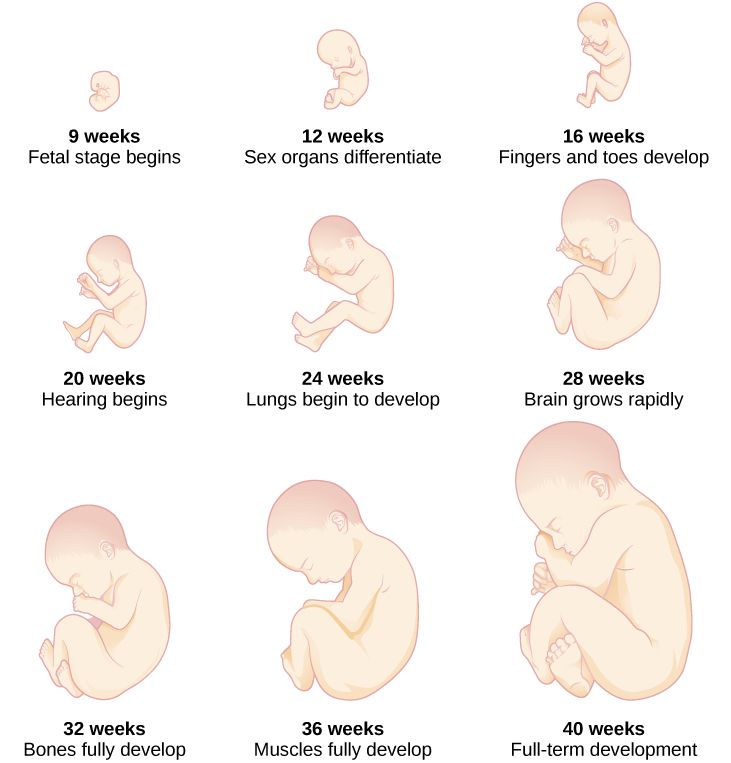
On Their Tummy
By now your baby will be pushing themselves up when they’re on their tummy and may even be trying to crawl! This is a great time to capture them as they experiment and explore their immediate surroundings.
As you photograph your baby on their tummy do try experimenting with angles to capture different perspectives – the photograph you take when you’re down at their level will be very different to one you take from above.
On Their Back
Babies are great fun to watch when they’re lying on their backs at this age. Almost all of them will end up playing with their feet, which is wonderful to capture!
Sit back quietly and see what your baby does and how they entertain themselves. It should make for some lovely photographs.
The Tiny Details
As I discussed in my post about must take photographs at 3-months old, the tiny details such as baby’s hands and feet are also wonderful to capture. And you’ll be able to see just how much your baby has grown when you compare the photographs of their feet and hands from 3 months to 6 months.
Favourite Toys and Books
As at 6-months, capturing your baby with their favourite toys and books will create a wonderful memory of what they enjoyed at this age. If you capture these photographs regularly you’ll have a record of what your baby enjoyed through their first year, Perhaps it’s the book you always read at bedtime, a favourite teddy or both.
Over to You
I hope that these tips help you to capture some gorgeous photographs of your 6 month old baby.
If you’d prefer to invest in some professional baby photographs, now is the ideal time to do it. Between 6 and 10 months of age, when your baby can confidently sit up but isn’t yet crawling is one of the best times for a baby photo shoot. Your baby will happily engage with the camera, show us all of the gorgeous expressions, but won’t get frustrated because they want to crawl away. You can find out about my photo shoots for babies here.
Related Links
4 Must Take Photos of Your 3 Month Old Baby
What is the best age for baby photos?
Child development by week | Regional Perinatal Center
Expectant mothers are always curious about how the fetus develops at a time when it is awaited with such impatience.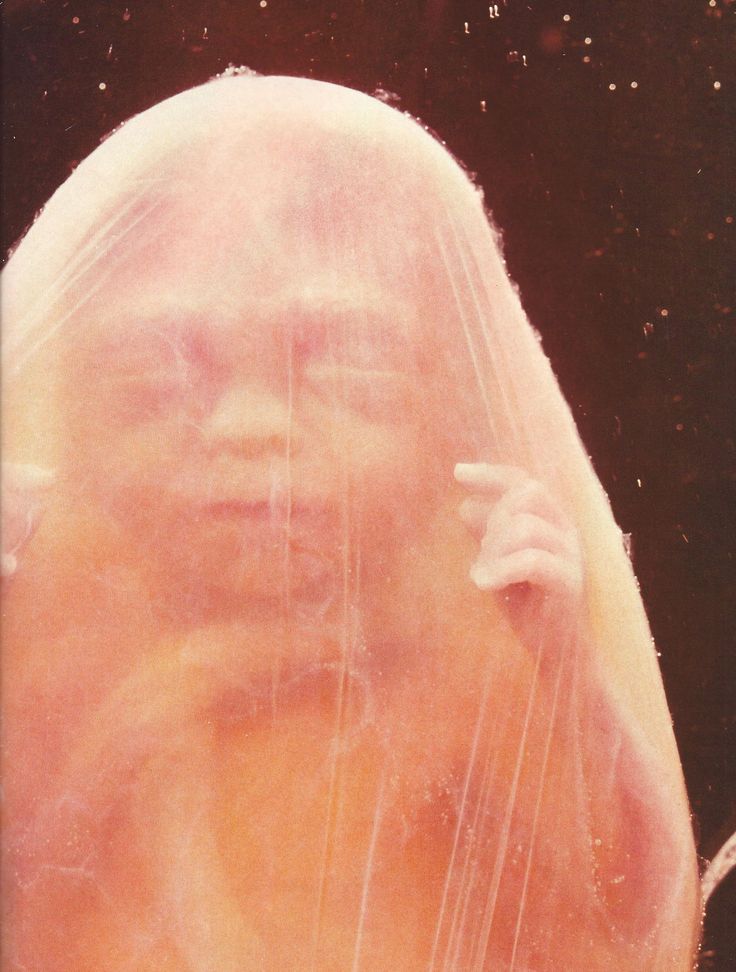 Let's talk and look at the photos and pictures of how the fetus grows and develops week by week.
Let's talk and look at the photos and pictures of how the fetus grows and develops week by week.
What does the puffer do for 9 whole months in mom's tummy? What does he feel, see and hear?
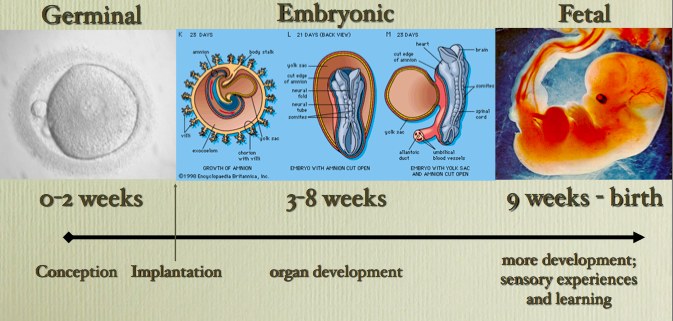
Let's start the story about the development of the fetus by weeks from the very beginning - from the moment of fertilization. A fetus up to 8 weeks old is called embryo , this occurs before the formation of all organ systems.
Embryo development: 1st week
The egg is fertilized and begins to actively split. The ovum travels to the uterus, getting rid of the membrane along the way.
On the 6th-8th days, implantation of eggs is carried out - implantation into the uterus. The egg settles on the surface of the uterine mucosa and, using the chorionic villi, attaches to the uterine mucosa.
Embryo development: 2-3 weeks
Picture of embryo development at 3 weeks.
The embryo is actively developing, starting to separate from the membranes. At this stage, the beginnings of the muscular, skeletal and nervous systems are formed. Therefore, this period of pregnancy is considered important.
At this stage, the beginnings of the muscular, skeletal and nervous systems are formed. Therefore, this period of pregnancy is considered important.
Embryo development: 4–7 weeks
Fetal development by week in pictures: week 4
Fetal development by week photo: week 4
Photo of an embryo before the 6th week of pregnancy.
The heart, head, arms, legs and tail are formed in the embryo :) . Gill slit is defined. The length of the embryo at the fifth week reaches 6 mm.
Fetal development by week photo: week 5
At the 7th week, the rudiments of the eyes, stomach and chest are determined, and fingers appear on the handles. The baby already has a sense organ - the vestibular apparatus. The length of the embryo is up to 12 mm.
Fetal development: 8th week
Fetal development by week photo: week 7-8
The face of the fetus can be identified, the mouth, nose, and auricles can be distinguished.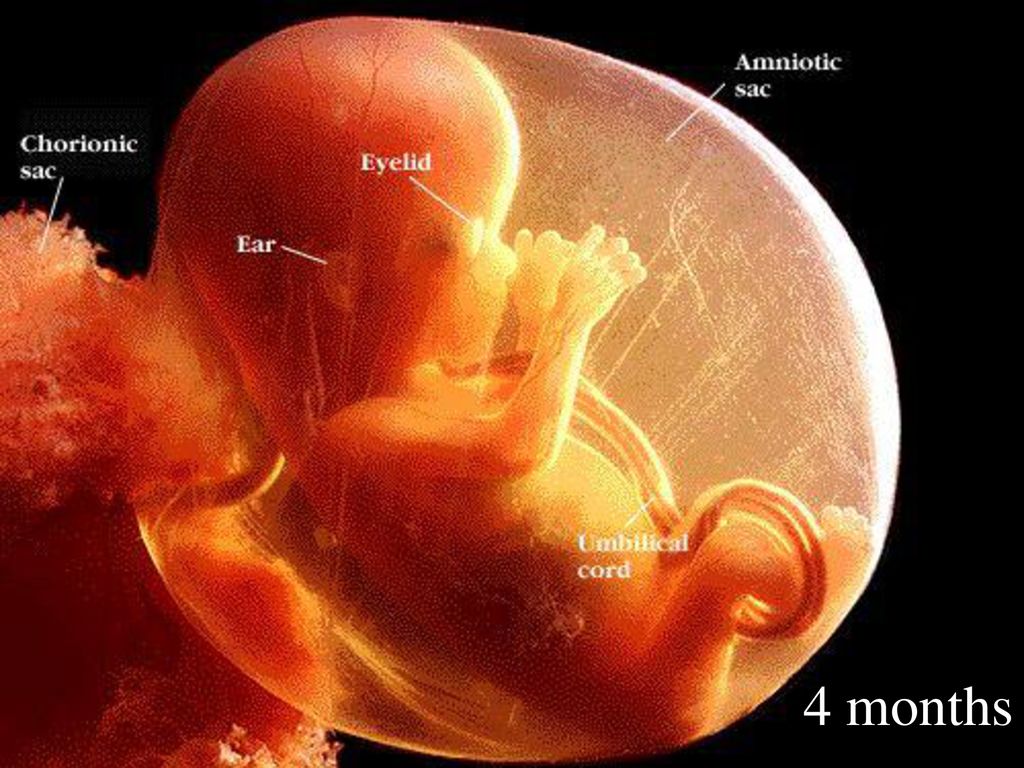 The head of the embryo is large and its length corresponds to the length of the body; the fetal body is formed. All significant, but not yet fully formed, elements of the baby's body already exist. The nervous system, muscles, skeleton continue to improve.
The head of the embryo is large and its length corresponds to the length of the body; the fetal body is formed. All significant, but not yet fully formed, elements of the baby's body already exist. The nervous system, muscles, skeleton continue to improve.
Fetal development in the photo already sensitive arms and legs: week 8
The fetus developed skin sensitivity in the mouth (preparation for the sucking reflex), and later in the face and palms.
At this stage of pregnancy, the genitals are already visible. Gill slits die. The fruit reaches 20 mm in length.
Fetal development: 9–10 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 9
Fingers and toes already with nails. The fetus begins to move in the pregnant woman's stomach, but the mother does not feel it yet. With a special stethoscope, you can hear the baby's heartbeat. Muscles continue to develop.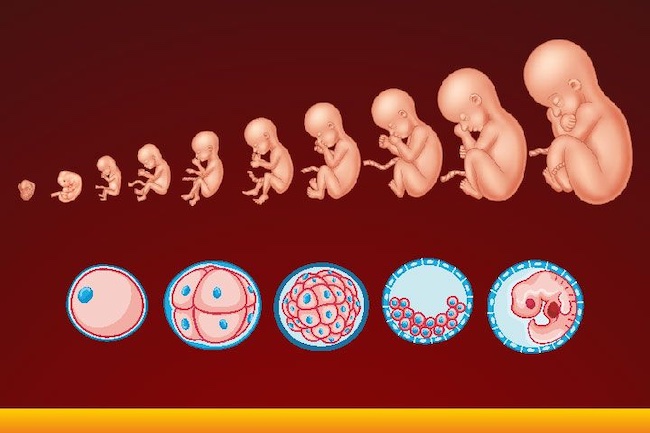
Weekly development of the fetus photo: week 10
The entire surface of the fetal body is sensitive and the baby develops tactile sensations with pleasure, touching his own body, the walls of the fetal bladder and the umbilical cord. It is very curious to observe this on ultrasound. By the way, the baby first moves away from the ultrasound sensor (of course, because it is cold and unusual!), And then puts his hands and heels trying to touch the sensor.
It's amazing when a mother puts her hand to her stomach, the baby tries to master the world and tries to touch with his pen "from the back".
The development of the fetus: 11–14 weeks
Development of the fetus in the photo of the legs: weeks 11
The baby, legs and eyelids are formed, and the genitals become distinguishable (you can find out the gender (you can find out the gender child).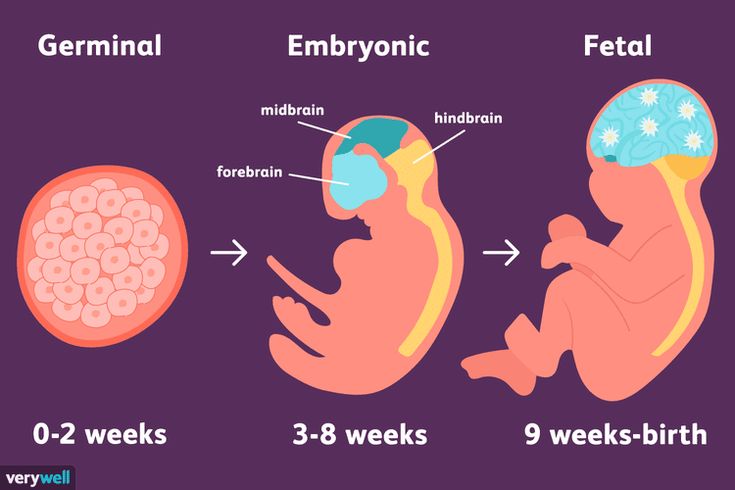 The fetus begins to swallow, and if something is not to its taste, for example, if something bitter got into the amniotic fluid (mother ate something), then the baby will begin to frown and stick out his tongue, making less swallowing movements.
The fetus begins to swallow, and if something is not to its taste, for example, if something bitter got into the amniotic fluid (mother ate something), then the baby will begin to frown and stick out his tongue, making less swallowing movements.
Fruit skin appears translucent.
Fruit development: Week 12
Photo of the fetus 12 weeks per 3D Uzi
buds are responsible for production for production urine. Blood forms inside the bones. And hairs begin to grow on the head. Moves more coordinated. The skin turns pink, the ears and other parts of the body, including the face, are already visible. Imagine, a child can already open his mouth and blink, as well as make grasping movements. Baby sucks his thumb, becomes more energetic. Pseudo-feces are formed in the intestines of the fetus - meconium , kidneys begin to work. During this period, the brain develops very actively. The auditory ossicles become stiff and now they are able to conduct sounds, the baby hears his mother - heartbeat, breathing, voice. The fetus intensively gains weight, fat deposits are formed. The weight of the fetus reaches 650 g, and the length is 300 mm. The lungs at this stage of fetal development are so developed that the baby can survive in the artificial conditions of the intensive care unit. Lungs continue to develop. Lips and mouth become more sensitive. The eyes develop, open slightly and can perceive light and squint from direct sunlight. In girls, the labia majora do not yet cover the small ones, and in boys, the testicles have not yet descended into the scrotum. Fetal weight reaches 900–1200 g, and the length is 350 mm. 9 out of 10 children born at this term survive. The lungs are now adapted to breathe normal air. Breathing is rhythmic and body temperature is controlled by the CNS. The baby can cry and responds to external sounds. Child opens eyes while awake and closes during sleep. The skin becomes thicker, smoother and pinkish. Starting from this period, the fetus will actively gain weight and grow rapidly. The fetus reacts to a light source. Muscle tone increases and the baby can turn and raise his head. On which, the hairs become silky. The child develops a grasping reflex. The lungs are fully developed. The fetus is quite developed, prepared for birth and considered mature. The baby has mastered over 70 different reflex movements. Due to the subcutaneous fatty tissue, the baby's skin is pale pink. The head is covered with hairs up to 3 cm. The baby perfectly mastered the movements of his mother , knows when she is calm, excited, upset and reacts to this with her movements. During the intrauterine period, the fetus gets used to moving in space, which is why babies love it so much when they are carried in their arms or rolled in a stroller. The nails protrude beyond the tips of the fingers, the cartilages of the ears and nose are elastic. In boys, the testicles have descended into the scrotum, and in girls, the large labia cover the small ones. The weight of the fetus reaches 3200-3600 g, and the length is 480-520 mm. After the birth, the baby longs for touching his body, because at first he cannot feel himself - the arms and legs do not obey the child as confidently as it was in the amniotic fluid. Therefore, so that your baby does not feel lonely, it is advisable to carry him in your arms, press him to you while stroking his body. And one more thing, the baby remembers the rhythm and sound of your heart very well . Therefore, you can comfort the baby in this way - take him in your arms, put him on the left side and your miracle will calm down, stop crying and fall asleep. The earliest period at which a fetal egg in the uterine cavity can be seen using transvaginal ultrasound is the 30th day of gestation, or 4-5 obstetric weeks of pregnancy. The level of hCG blood in this case should be at least 1000 mU / ml. At this time, neither the embryo nor the yolk sac is visible. When visualizing two fetal eggs, it can be argued that this is a dichorionic multiple pregnancy. When visualizing one fetal egg, it can be argued that this is a monochorionic pregnancy. But at this time, we still cannot say how many embryos are in each fetal egg. In addition, during a single ultrasound, we still cannot tell if this pregnancy is progressing, since the embryo does not yet have a heartbeat. The average inner diameter (SID) of the fetal egg at this time is 2-10 mm. The conclusion will indicate: Uterine pregnancy of a short term. Learn more about ultrasound in early pregnancy At this time, a white ring appears inside the fetal egg - this is the yolk sac. Foci of erythropoiesis form in the wall of the yolk sac, which form a capillary network, supplying erythroblasts (nuclear erythrocytes) to the primary circulatory system of the fetus. The yolk sac is a source of primary germ cells that migrate from its wall to the anlage of the gonads of the embryo. Until the 6th week after fertilization, the yolk sac, playing the role of the "primary liver", produces many important proteins for the embryo - alpha-fetoprotein, transferrins, alpha2-microglobulin. By the end of the first trimester of pregnancy, this provisional organ ceases to function and is reduced. The normal size of the yolk sac is 2-6 mm. If two yolk sacs are visualized in the fetal egg, then this is a monochorionic multiple pregnancy. But if one yolk sac is visible inside the fetal egg, and the embryo is not yet clearly visualized, then this may still be monochorionic monoamniotic twins. At the beginning of the 5th week, the embryo is practically indistinguishable on the wall of the yolk sac, but by the end of the week, the coccyx-parietal size (CTE) of the embryo reaches 3 mm. SVD of the ovum 11-16 mm. Read also: Is ultrasound harmful during pregnancy? Is ultrasound dangerous? How often can an ultrasound be done? Inside the fetal egg, we see a "ringlet with a precious stone" :) - this is the yolk sac and already a well-defined embryo, located nearby. The heart of the embryo begins to beat at the beginning of the 6th obstetric week of pregnancy. It is the presence of a heart pulsation that is a reliable ultrasound sign of a progressing pregnancy. With CTE ≥6 mm and the absence of heart pulsation, a conclusion is made about stopping the development of this embryo. Normal heart rate (HR) of the embryo at the very beginning of the 6th week 70-90 beats per minute, but by the end of the week it becomes more than 100 beats. The presence of one yolk sac, one embryo and one pulsating heart in most cases indicates a singleton pregnancy. But in very rare cases, it may later turn out to be unseparated twins. SVD of the ovum 13-23 mm. Embryo KTR 4-9 mm. Read also: "I don't want an ultrasound, I want a baby!". Why is ultrasound during pregnancy necessary? The distance between the embryo and the yolk sac gradually increases and the yolk duct (ductus vitellinus), which connects the yolk sac and the intestines of the embryo, becomes clearly visible. Until this time, the chorion has an annular shape, surrounds the fetal egg from all sides, and it is still impossible to say which wall of the uterus the embryo has attached to. In the case of monochorionic twins, no amniotic membranes are yet visible, and in the presence of two yolk sacs, it is still impossible to tell whether this pregnancy is mono or diamniotic. If the gestational sac contains two yolk sacs and two fetuses with cardiac activity, the subsequent number of amniotic cavities may be greater than the number of placentas (monochorial diamniotic) or the same (monochorial monoamniotic). In this case, it is possible to accurately determine amnionality after 8 weeks, when the amniotic membranes begin to be clearly visualized. Embryo heart rate 130-160 beats per minute. SVD of the ovum 24-30 mm, CTE of the embryo 9-15 mm. During the ultrasound of the embryo, it is already possible to clearly distinguish individual segments - the head, trunk, limbs. The first movement appears. The amniotic membranes become clearly visible and we can already talk about the number of amniotic sacs in multiple pregnancies. The chorion is differentiated into a smooth one, facing the uterine cavity, and a branched one, from which the placenta will subsequently form, so that we can already talk about the predominant location of the chorion along the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus. The heart rate of the embryo increases to 160-180 beats per minute. SVD of the ovum 31-37 mm. Embryo KTR 16-22 mm. The development of the embryo continues. The handles of the legs are already clearly visible, and on a good device, sometimes you can even see the fingers and toes.
Development of the fetus for weeks: Week 14 9000 9000 Fetal development: 15-18 weeks
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 15  The fetus begins to actively push in the mother's tummy. The sex of the fetus can be determined by ultrasound.
The fetus begins to actively push in the mother's tummy. The sex of the fetus can be determined by ultrasound. Fetal development: 19-23 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 19
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 20 Fetal development: 24-27 weeks
 Now the baby is already falling asleep and waking up. Downy hairs appear on the skin, the skin becomes wrinkled and covered with grease. The cartilage of the ears and nose is still soft.
Now the baby is already falling asleep and waking up. Downy hairs appear on the skin, the skin becomes wrinkled and covered with grease. The cartilage of the ears and nose is still soft.
Fetal development by week photo: week 27 Fetal development: 28-32 weeks
 Almost all babies born prematurely at this time are viable. The weight of the fetus reaches 2500 g, and the length is 450 mm.
Almost all babies born prematurely at this time are viable. The weight of the fetus reaches 2500 g, and the length is 450 mm. Fetal development: 33-37 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 36 Fetal development: 38-42 weeks
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 40 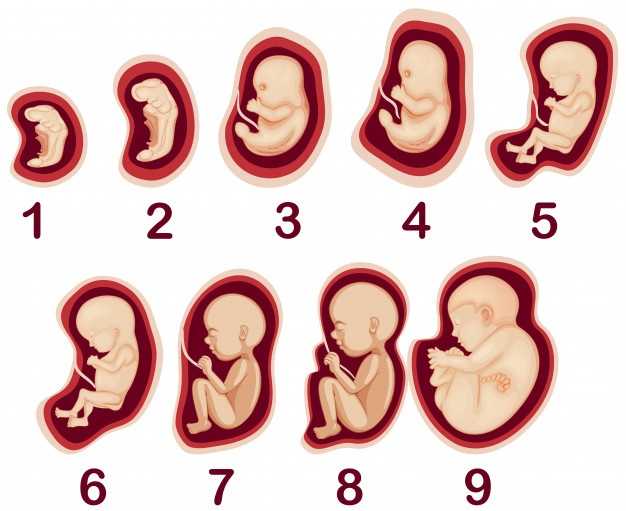 For a baby, this is a completely natural state, so he will calm down and fall asleep when he is shaken.
For a baby, this is a completely natural state, so he will calm down and fall asleep when he is shaken. 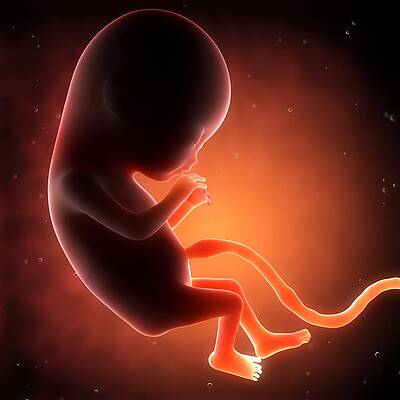 And for you, finally, the time of bliss will come :) .
And for you, finally, the time of bliss will come :) . Pregnancy Ultrasound Photo, Pregnancy Ultrasound Fetal Photo
4-5 weeks
Photo ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy 4-5 weeks 
5-6 weeks
Photo ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy 5-6 weeks 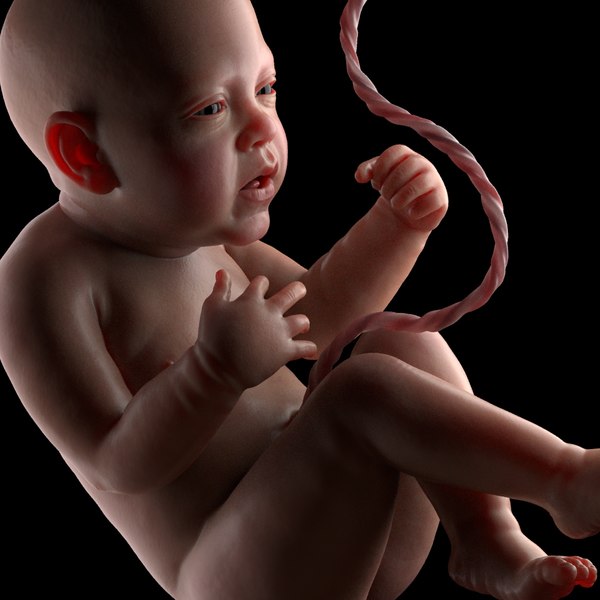
6 - 7 weeks
Photo ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy 6-7 weeks  in min. In the early stages of pregnancy, it is not the heart rate that matters, but the presence or absence of heart contractions as such. Sometimes, with a non-developing pregnancy, you can see the reflection of the pulsation of the mother's vessels inside the embryo and take them for the baby's heartbeat. But in this case, the pulsation frequency will be identical to the mother's heart rate.
in min. In the early stages of pregnancy, it is not the heart rate that matters, but the presence or absence of heart contractions as such. Sometimes, with a non-developing pregnancy, you can see the reflection of the pulsation of the mother's vessels inside the embryo and take them for the baby's heartbeat. But in this case, the pulsation frequency will be identical to the mother's heart rate. 7 - 8 weeks
Photo ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy 7-8 weeks 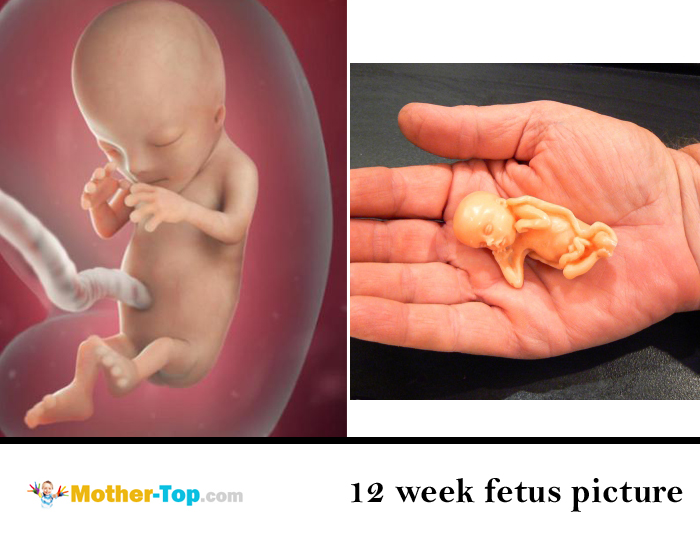 Just like the yolk sac, the duct becomes empty and resolves at a later date, but if this does not happen for some reason, then a blind protrusion of the ileum wall is formed in a person - Meckel's diverticulum.
Just like the yolk sac, the duct becomes empty and resolves at a later date, but if this does not happen for some reason, then a blind protrusion of the ileum wall is formed in a person - Meckel's diverticulum. 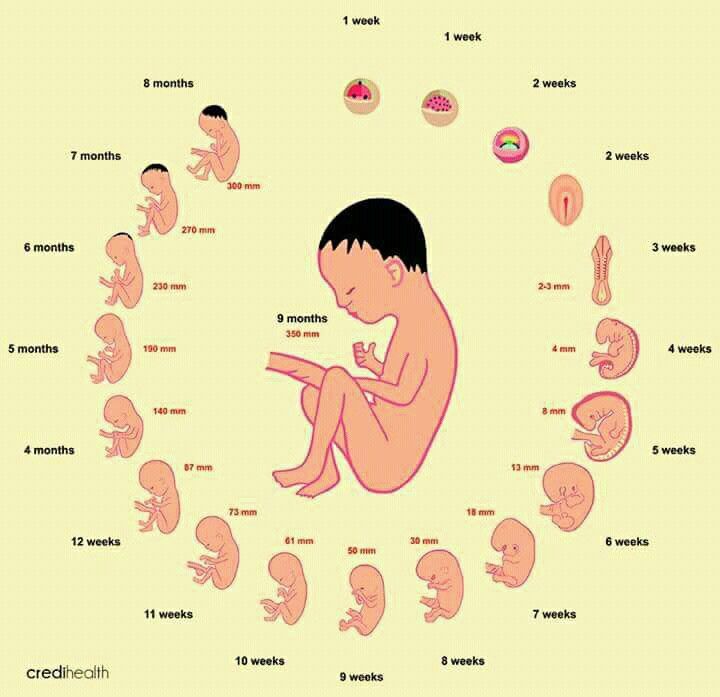
8 - 9 weeks
Photo ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy 8-9 weeks 9 - 10 weeks
Photo ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy 9-10 weeks