1 week pregnant baby size
Pregnancy week-by-week | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Pregnancy week-by-week | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of contentPregnancy at weeks 1 to 4
When you conceive, your body’s hormone levels change, but you may not notice any signs that you’re pregnant yet.
Pregnancy at week 5
You may still wonder, at week 5, if you are pregnant, but you can do a pregnancy test the day after you miss a period.
Pregnancy at week 6
By week 6, your baby is growing quickly and you may notice the early signs of your pregnancy, such as feeling nauseous.
Pregnancy at week 7
Your baby is now about 1cm long and if you haven’t seen your doctor yet, now is a good time to start your antenatal care.
Pregnancy at week 8
By week 8, you might be experiencing morning sickness, need frequent trips to the toilet, and feel tired or moody.
Pregnancy at week 9
Your baby is now the size of a peanut. You won't be showing just yet, but you may have put on a little weight.
Pregnancy at week 10
Think about the prenatal screening tests you might have, and whether you want a dating scan to confirm your due date.
Pregnancy at week 11
During week 11, you might have your first ultrasound and see your baby for the first time.
Pregnancy at week 12
By week 12, your baby is the size of a plum but fully formed, with their organs, muscles, limbs and bones in place.
Pregnancy at week 13
At week 13 of pregnancy, you officially enter your second trimester and hopefully any morning sickness has eased off.
Pregnancy at week 14
By week 14, your baby’s organs have formed, their face is becoming more recognisable, and you may be feeling more energetic.
Pregnancy at week 15
By week 15, your baby may be able to respond to sound and light, while you are gaining weight and your skin and hair are changing.
Pregnancy at week 16
At week 16, you might begin to feel your baby moving, while hormonal changes may be affecting your libido.
Pregnancy at week 17
By week 17, you may want to start thinking about antenatal classes to help you and your partner prepare for the birth and beyond.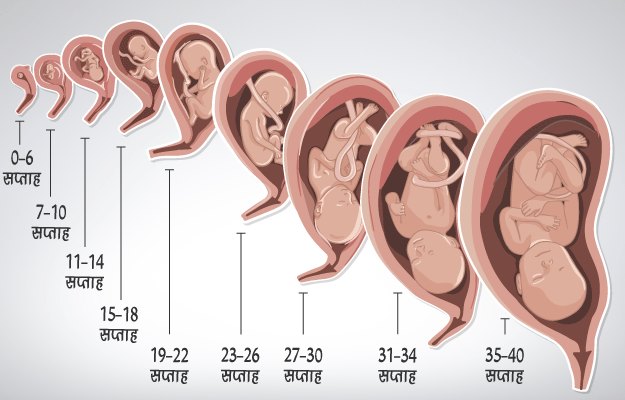
Pregnancy at week 18
By week 18, you may start to feel light-headed and dizzy, but you may also be able to find out whether you’re having a boy or a girl.
Pregnancy at week 19
By week 19, you will likely look very obviously pregnant, while your baby can now hear sounds from outside your body.
Pregnancy at week 20
By week 20, your baby is very active although you might feel breathless now and then and your back and hips may ache.
Pregnancy at week 21
At week 21, you should consider whether to do any travel since you may not be able to for much longer in your pregnancy.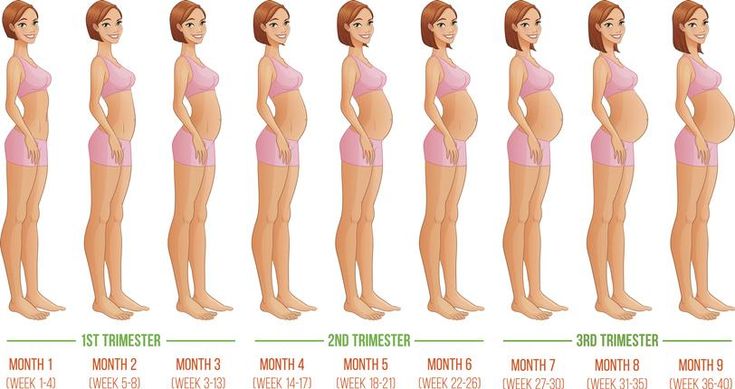
Pregnancy at week 22
By week 22, some parts of your baby’s body are fully formed, while some women experience Braxton Hicks contractions about now.
Pregnancy at week 23
By week 23, your baby is practising to breathe in the womb and you might be experiencing some incontinence.
Pregnancy at week 24
Your baby is continuing to grow rapidly and might respond to light and sound. You might also find their movements are getting stronger.
Pregnancy at week 25
As you are approaching the end of the second trimester, you might be starting to feel a bit uncomfortable as your baby continues to grow.
Pregnancy at week 26
Your baby is starting to put on fat and muscle and as your baby grows, your centre of gravity will shift, so you might find that you are starting to w...
Pregnancy at week 27
Your baby is growing fast and probably quite active now. You'll also be gaining more weight and might even be getting some stretch marks.
Pregnancy at week 28
You are now in the third trimester and you'll probably be feeling many of the common discomforts of pregnancy, like a sore back, swelling, heartburn o...
Pregnancy at week 29
Your baby should weigh about 1kg by now and as your uterus pushes against your diaphragm and lungs, you might be feeling quite breathless.
Pregnancy at week 30
Your baby's reflexes are developing, and they may even be sucking their thumb or fingers. You might be tired and sore, but try to exercise and get eno...
Pregnancy at week 31
Feeling tired and emotional during the third trimester is very common, but it's important to discuss these feelings with your doctor or midwife.
Pregnancy at week 32
Your baby doesn't have a lot of room, but they will still be moving. The extra weight might cause you some back and pelvic pain which can make it diff...
Pregnancy at week 33
Your baby's brain and nervous system are now fully developed, and the baby is continuing to gain weight. You'll probably also be feeling sore and tire...
You'll probably also be feeling sore and tire...
Pregnancy at week 34
As at the start of your pregnancy, you’re probably feeling tired and emotional. The baby doesn't have much room to move, but you might feel them kick ...
Pregnancy at week 35
You'll probably be having lots of Braxton Hicks contractions by now. It's your body's way of preparing for the birth. They should stop if you move pos...
Pregnancy at week 36
Your baby will by now be curled up and cramped inside your uterus and weigh about 2.5kg. Your bump may have moved down, putting pressure on your lower...
Pregnancy at week 37
By the end of week 37, your baby is considered full-term.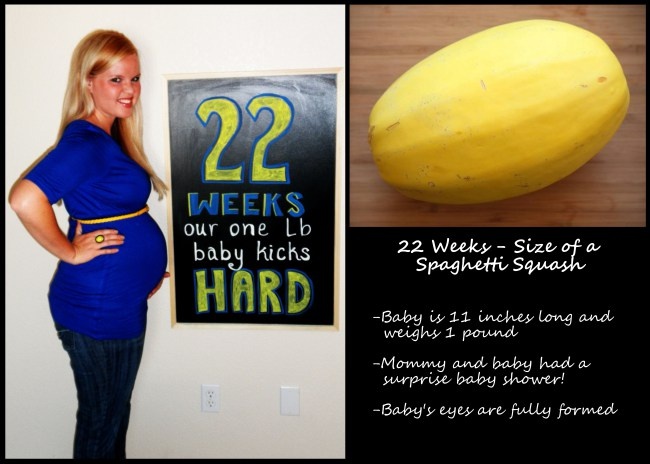 You'll probably be very tired because of the extra weight so try and get as much rest as you...
You'll probably be very tired because of the extra weight so try and get as much rest as you...
Pregnancy at week 38
Your baby is now ready to be born and you could go into labour at any time. Make sure you have you plan for getting to the hospital and you have every...
Pregnancy at week 39
Your baby's weight gain should slow down since they are now ready to be born. You might soon start to notice the early signs of labour.
Pregnancy at week 40
Your baby will arrive very soon – if it hasn't already. Babies are rarely born on their due date and many go past 40 weeks.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.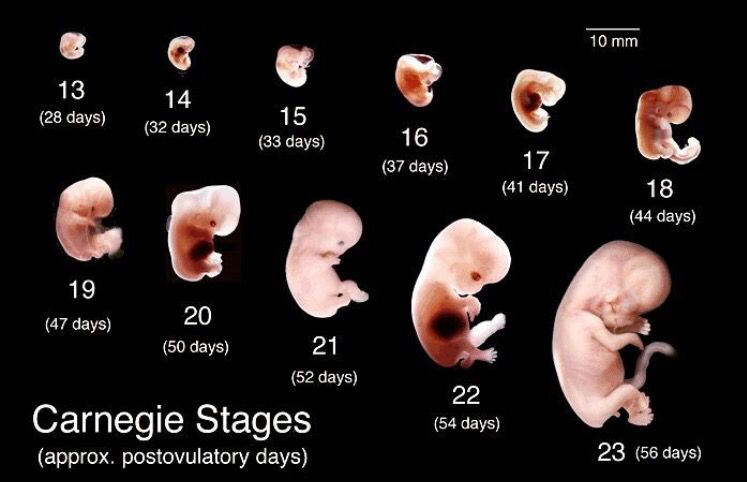
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Pregnancy at weeks 1 to 4
Pregnancy at weeks 1 to 4 | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
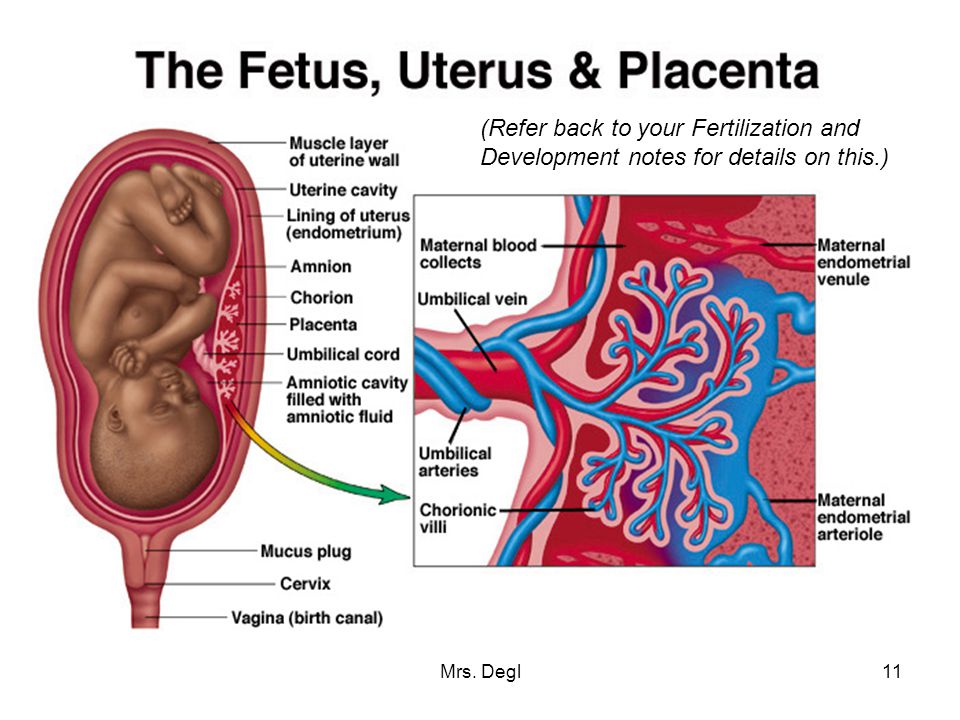
Your baby
Your pregnancy is calculated according to the first day of your last period. In the first week of your menstrual cycle, and in the second week your ovaries release an egg (called an ovum). This is fertilised by your partner’s sperm sometime in the third week.
In the first week of your menstrual cycle, and in the second week your ovaries release an egg (called an ovum). This is fertilised by your partner’s sperm sometime in the third week.
About 30 hours after conception, the fertilised egg divides into two. At this stage it is called a zygote. The cells keep dividing and multiplying in numbers and the zygote gradually moves down the fallopian tube towards the womb (uterus).
By the end of the fourth week, the egg implants itself into your uterus. It is now called a blastocyst. It is about 0.2mm wide and contains about 200 cells.
The blastocyst is made up of different layers of cells. The outer layer, called the ectoderm, will become the baby’s nervous system and brain. The middle layer, or mesoderm, will become the heart, blood vessels, muscles, and bones, and the inner layer, or endoderm will become the breathing and digestive systems. The outside of the blastocyst has small tentacles called chorionic villi, which will develop into the placenta.
Your baby at 1 to 4 weeks
| Length: | 0.2mm |
Your body
As soon as you conceive, the hormone levels in your body start to change. You produce more of the hormone progesterone, which prevents you from having a period, and there is an increase your levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This is the pregnancy hormone that is detected when you do a pregnancy test.
You probably won’t notice any signs that you’re pregnant just yet. The first sign for many women is that they miss their period at the end of week 4.
Things to remember
Your baby will have the best possible start in life if you make sure you are healthy when you conceive.
If you are trying for a baby, it’s a good idea to take 400 micrograms of folate every day to prevent neural tube defects such as spina bifida. If the baby is planned, you might consider seeing your doctor to talk about genetic screening or to be tested for any sexually transmitted infections before you fall pregnant.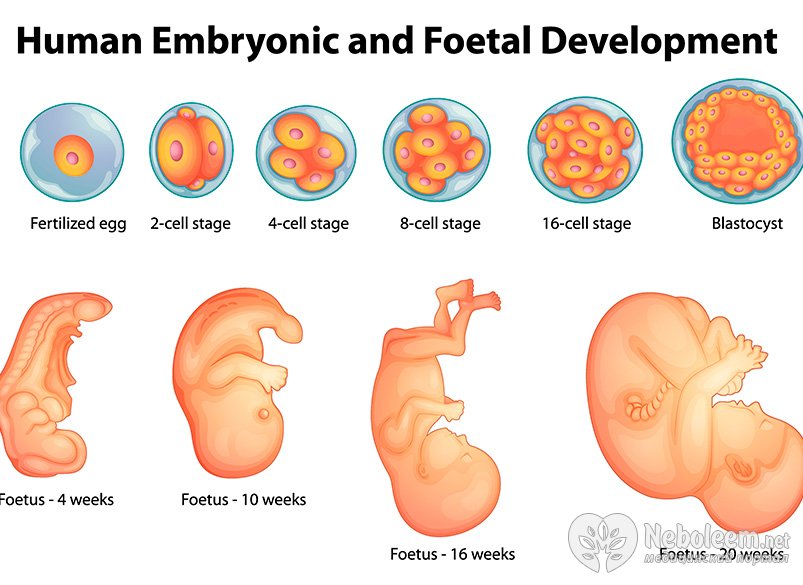
You should try to eat a healthy diet and make sure you’re not overweight when you’re trying to fall pregnant. Not drinking alcohol and giving up smoking are best for your baby.
Read more here about preconception health.
Read next
Your pregnancy at 5 weeks
Learn about your pregnancy journey and what is happening to you and your baby.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Raising Children Network (Pregnancy week-by-week), Embryology Education and Research (Carnegie stage 4), Better Health Channel (Pregnancy - week by week), MSD Manual (Stages of development of the fetus)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: August 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Pregnancy week-by-week
- Third trimester
- Second trimester
- First trimester
Need more information?
4 weeks pregnant: Key points
When you are 4 weeks pregnant your body and your new baby are undergoing rapid changes. The placenta forms and begins producing a hormone called human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), which is the substance a pregnancy test detects to confirm you are pregnant. The cells which are growing into your new baby establish membranes which connect them to the placenta and prepare themselves for differentiation into different types of cells, which will occur next week when you are 5 weeks pregnant. These developments may cause you to experience unusual emotions and also cause changes in your body such as darkening of the areolas of your nipples.
Read more on Parenthub website
5 weeks pregnant: Doctor appointments
Week 5 of pregnancy is the best time to have a pregnancy test. You can use a home pregnancy test but it’s still important to visit your doctor so that they can estimate your pregnancy due date. This may involve an early pregnancy ultrasound. You should also receive pregnancy health advice and discuss pregnancy folate supplements in the fifth week of pregnancy if you have not already done so. It’s also a good time to make sure you’re eating all the right pregnancy foods and start your pregnancy exercise routine.
Read more on Parenthub website
Week by week pregnancy- antenatal care at 7 weeks pregnant
Your doctor can look at your foetus’s features to determine how old they are – find out how. You need to talk to your doctor if you experience very severe morning sickness as you may not be getting all the nutrients you and your baby need or early pregnancy spotting (spot bleeding) as you may be at risk of miscarriage.
You need to talk to your doctor if you experience very severe morning sickness as you may not be getting all the nutrients you and your baby need or early pregnancy spotting (spot bleeding) as you may be at risk of miscarriage.
Read more on Parenthub website
Bleeding or pain in early pregnancy
One in 4 women will experience bleeding and/or pain during their first 12 weeks of pregnancy. Unfortunately half of these pregnancies may also end in miscarriage, which cannot be prevented.
Read more on WA Health website
Pregnancy at week 12
By week 12, your baby is the size of a plum but fully formed, with their organs, muscles, limbs and bones in place.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
8 weeks pregnant | Raising Children Network
8 weeks pregnant? In this pregnancy week by week guide, find out how your baby is growing, how your body is changing and how to look after yourself.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
2 weeks pregnant
When you are two weeks pregnant, your body is preparing for pregnancy but your egg has not yet been fertilised. Typically your egg will be released from your ovaries at the end of the second week of pregnancy and conception will occur on the first day of the third week of pregnancy. If you want to get pregnant, make sure you have plenty of sex this week so your partner’s sperm is ready and waiting to fertilise your egg.
Read more on Parenthub website
18-20 Week Screening Pregnancy Ultrasound - Consumers - InsideRadiology
An 18–20 week pregnancy screening ultrasound is part of the routine care during pregnancy. Screening is carried out at this stage in the pregnancy because the foetus
Read more on InsideRadiology website
Pregnancy at week 10
Think about the prenatal screening tests you might have, and whether you want a dating scan to confirm your due date.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 32
Your baby doesn't have a lot of room, but they will still be moving. The extra weight might cause you some back and pelvic pain which can make it difficult for you to move around.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Monthly development of the child - Geburtsinfo Wien
Child
When the ovum combines with the sperm in the fallopian tube, fertilization occurs. Within 6-10 days, a woman's fertilized egg enters the uterine cavity and implants into the wall. Until the end of the 4th week of pregnancy, the egg divides several times. The embryo is about the size of a grain of rice. The placenta is formed.
The embryo is about the size of a grain of rice. The placenta is formed.
Mother
Many women begin to experience the first discomfort, such as nausea, frequent urination, or increased fatigue. Pregnancy is not a disease, it does not mean a drastic change in lifestyle! This also applies to the field of sexual relations. In case of bleeding or pain, it is strongly recommended to consult a doctor.
Baby
At the seventh week the fetus is the size of a walnut. From now until 21 weeks it will grow very fast. nine0008
Mom
Do you experience joy that is suddenly replaced by sadness? Mood swings are completely normal and can accompany you throughout your pregnancy. This is due not only to the restructuring of the hormonal background. You need to mentally adjust to the new situation. If you're feeling sad or frustrated for a long time, or you're having marital or financial problems, seek professional help. During this difficult period, specialized antenatal clinics will help you. The good news: By the end of the third month, most pregnant women experience nausea. nine0008
During this difficult period, specialized antenatal clinics will help you. The good news: By the end of the third month, most pregnant women experience nausea. nine0008
Child
A face with auricles, nose and eyes is already very similar to human features. The little heart beats confidently. You will see this at the first ultrasound examination between the 8th and 12th weeks of pregnancy. During this period, vital organs also develop: the liver, kidneys, intestines, brain and lungs are already formed. At the end of 12 weeks, the fetus weighs 50 to 70 g with a height of 8 cm from head to toe.
Attention! nine0006 It is important that you complete your first mother and child passport examination before the end of the 16th week.
Mother
In many women, pregnancy becomes noticeable due to the growth of the belly. Rub the cream daily into the skin of the abdomen to prevent stretch marks. Stretch mark ointment can be purchased at a pharmacy or beauty supply store. You can also use regular olive oil.
You can also use regular olive oil.
Baby
Your baby's organs are all fully formed and just growing. Eyebrows and hair begin to grow. At the end of the month, the fruit reaches the size of an avocado. He is already very mobile and can suck his thumb. nine0008
Attention! Between the 18th and 22nd weeks of pregnancy, a second ultrasound examination is necessary. The doctor measures the size of the child and evaluates his development. In addition, the doctor can already determine the sex of your baby.
Mom
Between 18 and 20 weeks of pregnancy, you may first feel your baby pushing. Many women experience this as a gentle pat. Sometimes the muscles of the uterus can contract for a few seconds. The abdomen becomes hard. This is absolutely normal. nine0008
Baby
Your baby is already moving his arms, fingers, legs and feet, more and more purposefully each time. Every day he drinks about half a liter of amniotic fluid. In professional medical language, from this point on, the child is called a fetus.
Every day he drinks about half a liter of amniotic fluid. In professional medical language, from this point on, the child is called a fetus.
Mom
Physiological complaints (nausea, urge to urinate and fatigue) usually disappear by this time. Enjoy this time!
Baby
The fetus already looks like a “real” baby. He already hears, and his height is about 25 cm. Many babies begin to hiccup after drinking amniotic fluid. At the same time, your stomach makes short rhythmic movements.
Mother
Many women start to accumulate water in their bodies at this time. Leg cramps, hemorrhoids, varicose veins, and itching on the abdomen may also appear.
Baby
At the end of the seventh month, the baby measures between 35 and 38 cm from head to toes. He already knows how to open his eyes. If he notices a bright stream of light outside, then he turns his head in that direction. Your child is exercising his lungs with small breaths.
Your child is exercising his lungs with small breaths.
Attention! Starting from the third week of pregnancy, it is necessary to pass the third examination according to the passport of the mother and child.
Mother
Do you experience shortness of breath or other ailments? Many women find it difficult to breathe because the uterus almost reaches the level of the chest. If possible, do not lie on your back. The most comfortable position is lying on your side with a pillow between your thighs.
Baby
Your baby will usually turn head down into the presentation position. He weighs between 1.5 and 1.8 kg and is about 40 cm tall. He can no longer move freely as he becomes cramped. nine0008
Baby
Your baby's weight increases to 2.5 to 2.75 kg before 36 weeks. If your baby is head-up, this is called a breech presentation or breech presentation. Less common oblique or transverse presentation. This complicates childbirth. There are various techniques to get the baby to turn, such as acupuncture. Contact your gynecologist or obstetrician.
Less common oblique or transverse presentation. This complicates childbirth. There are various techniques to get the baby to turn, such as acupuncture. Contact your gynecologist or obstetrician.
Mother
The last days before childbirth can be very long. Do things that give you benefit or pleasure. After giving birth, it will be a long time before you can return to your previous activities
Child
Almost there! From two tiny cells a little man was formed. The big day is coming up very soon. Your child is gaining weight again. At birth, he will weigh from 2.5 to 4.5 kg with a height of 48 to 54 cm. He needs to take the maximum amount of nutrients from the womb of his mother, which was enough for him for some time after birth. Because it usually takes several days before you have enough milk to feed your baby. nine0008
Starting on your due date, you will need frequent regular check-ups with your doctor, who monitors your baby's heart sounds with a cardiotocograph.
Child development by weeks | Regional Perinatal Center
Expectant mothers are always curious about how the fetus develops at a time when it is awaited with such impatience. Let's talk and look at the photos and pictures of how the fetus grows and develops week by week.
What does the whole 9 stubbler domonths in mom's tummy? What does he feel, see and hear?
Let's start the story about the development of the fetus by weeks from the very beginning - from the moment of fertilization. A fetus up to 8 weeks old is called embryo , this occurs before the formation of all organ systems.
Embryo development: 1st week
The egg is fertilized and begins to actively split. The ovum travels to the uterus, getting rid of the membrane along the way.
On days 6-8, implantation egg - implantation in the uterus. The egg settles on the surface of the uterine mucosa and, using the chorionic villi, attaches to the uterine mucosa.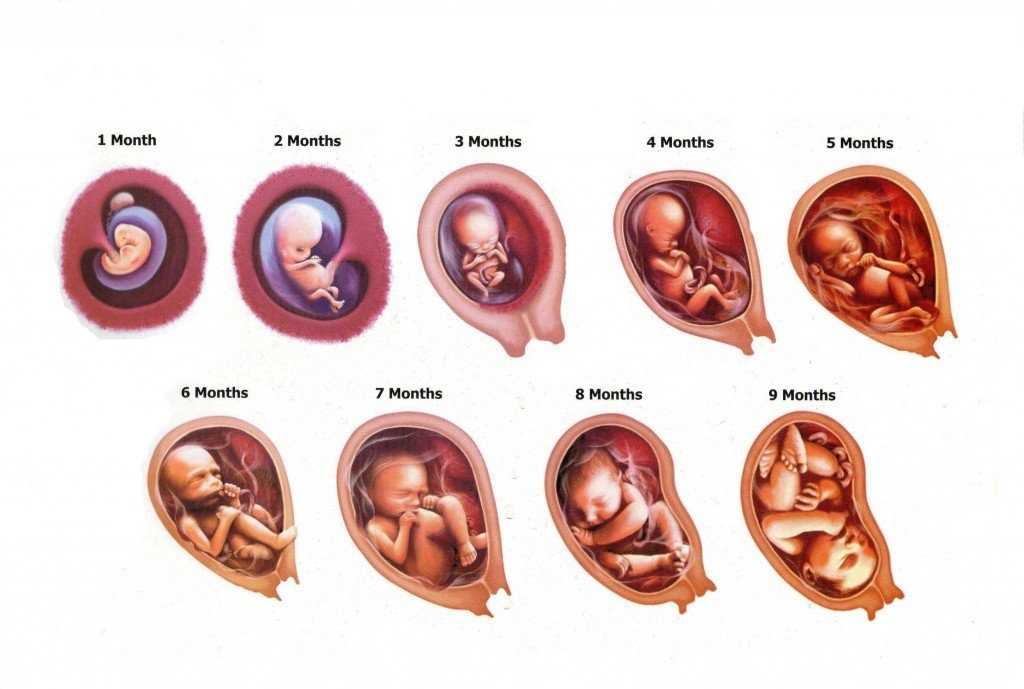
Embryo development: 2-3 weeks
Picture of embryo development at 3 weeks.
The embryo is actively developing, starting to separate from the membranes. At this stage, the beginnings of the muscular, skeletal and nervous systems are formed. Therefore, this period of pregnancy is considered important.
Embryo development: 4-7 weeks
Development of the fetus in weeks in pictures: Week 4
Development of the fetus for weeks: Week 4
Embrion photos until the 6th week of pregnancy.
The heart, head, arms, legs and tail are formed in the embryo :) . Gill slit is defined. The length of the embryo at the fifth week reaches 6 mm.
Fetal development by week photo: week 5
At the 7th week, the rudiments of the eyes, abdomen and chest are determined, and fingers appear on the handles. The baby already has a sense organ - the vestibular apparatus. The length of the embryo is up to 12 mm.
The baby already has a sense organ - the vestibular apparatus. The length of the embryo is up to 12 mm.
Fetal development: 8th week
Fetal development by weeks photo: weeks 7-8
The face of the fetus can be distinguished, the mouth, nose, and auricles can be distinguished. The head of the embryo is large and its length corresponds to the length of the body; the fetal body is formed. All significant, but not yet fully formed, elements of the baby's body already exist. The nervous system, muscles, skeleton continue to improve. nine0008
Development of the fetus in the photo already sensitive arms and legs: week 8
The fetus developed skin sensitivity in the mouth area (preparation for the sucking reflex), in the area of the palm and hand.
At this stage of pregnancy, the genitals are already visible. Gill slits die. The fruit reaches 20 mm in length.
Fetal development: 9-10 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 9
Fingers and toes are already nailed. The fetus begins to move in the pregnant woman's stomach, but the mother does not feel it yet. With a special stethoscope, you can hear the baby's heartbeat. Muscles continue to develop.
The fetus begins to move in the pregnant woman's stomach, but the mother does not feel it yet. With a special stethoscope, you can hear the baby's heartbeat. Muscles continue to develop.
Weekly development of the fetus photo: week 10
The entire surface of the fetal body is sensitive and the baby develops tactile sensations with pleasure, touching his own body, the walls of the fetal bladder and the umbilical cord. It is very curious to observe this on ultrasound. By the way, the baby first moves away from the ultrasound sensor (of course, because it is cold and unusual!), And then puts his hands and heels trying to touch the sensor. nine0008
Surprisingly, when a mother puts her hand on her stomach, the baby tries to master the world and tries to touch with his pen “from the back”.
fetal development: 11–14 weeks
9000 child).
The fetus begins to swallow, and if something is not to its taste, for example, if something bitter got into the amniotic fluid (mother ate something), then the baby will begin to frown and stick out his tongue, making less swallowing movements.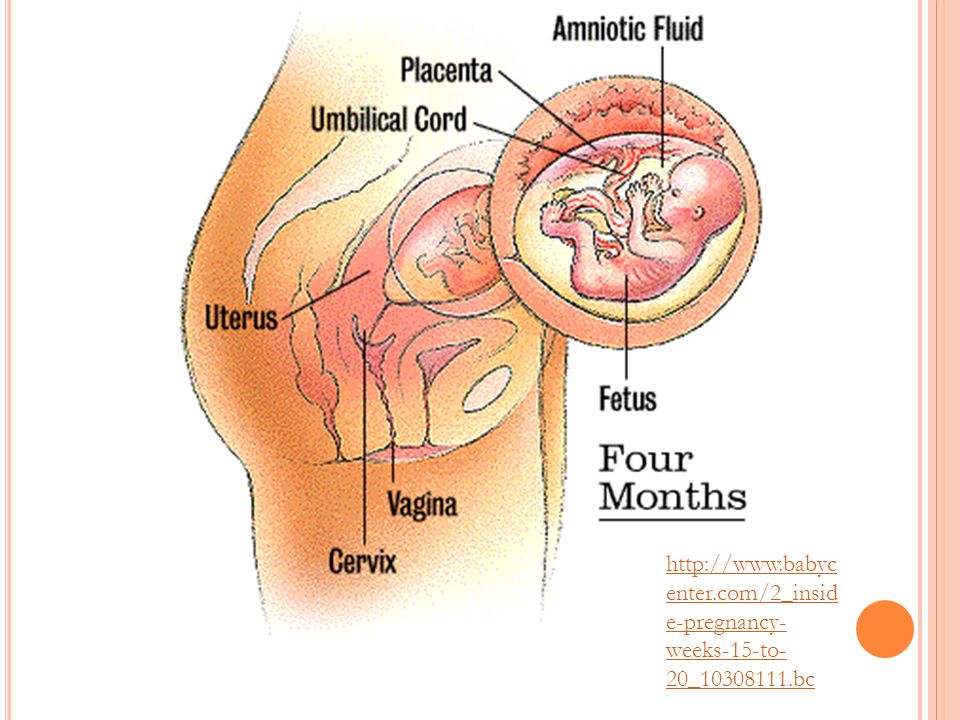 nine0008
nine0008 Fruit skin looks translucent.
Development of the fetus: 9000 urine. Blood forms inside the bones. And hairs begin to grow on the head. Moves more coordinated.
Fetal development: 15-18 weeks
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 15
The skin turns pink, the ears and other parts of the body, including the face, are already visible. Imagine, a child can already open his mouth and blink, as well as make grasping movements. The fetus begins to actively push in the mother's tummy. The sex of the fetus can be determined by ultrasound.
Fetal development: 19-23 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 19
Baby sucks his thumb, becomes more energetic. Pseudo-feces are formed in the intestines of the fetus - meconium , kidneys begin to work. During this period, the brain develops very actively.
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 20
The auditory ossicles become stiff and now they are able to conduct sounds, the baby hears his mother - heartbeat, breathing, voice. The fetus intensively gains weight, fat deposits are formed. The weight of the fetus reaches 650 g, and the length is 300 mm.
The fetus intensively gains weight, fat deposits are formed. The weight of the fetus reaches 650 g, and the length is 300 mm.
The lungs at this stage of fetal development are so developed that the baby can survive in the artificial conditions of the intensive care unit. nine0008
Fetal development: 24-27 weeks
Lungs continue to develop. Now the baby is already falling asleep and waking up. Downy hairs appear on the skin, the skin becomes wrinkled and covered with grease. The cartilage of the ears and nose is still soft.
Fetal development by week photo: week 27
Lips and mouth become more sensitive. The eyes develop, open slightly and can perceive light and squint from direct sunlight. In girls, the labia majora do not yet cover the small ones, and in boys, the testicles have not yet descended into the scrotum. Fetal weight reaches 900–1200 g, and the length is 350 mm.
9 out of 10 children born at this term survive.
Fetal development: 28-32 weeks
The lungs are now adapted to breathe normal air. Breathing is rhythmic and body temperature is controlled by the CNS. The baby can cry and responds to external sounds.
Child opens eyes while awake and closes during sleep.
The skin becomes thicker, smoother and pinkish. Starting from this period, the fetus will actively gain weight and grow rapidly. Almost all babies born prematurely at this time are viable. The weight of the fetus reaches 2500 g, and the length is 450 mm. nine0008
Fetal development: 33–37 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 36
The fetus reacts to a light source. Muscle tone increases and the baby can turn and raise his head. On which, the hairs become silky. The child develops a grasping reflex. The lungs are fully developed.
Fetal development: 38-42 weeks
The fetus is quite developed, prepared for birth and considered mature. The baby has mastered over 70 different reflex movements. Due to the subcutaneous fatty tissue, the baby's skin is pale pink. The head is covered with hairs up to 3 cm.
The baby has mastered over 70 different reflex movements. Due to the subcutaneous fatty tissue, the baby's skin is pale pink. The head is covered with hairs up to 3 cm.
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 40
The baby perfectly mastered the movements of his mother , knows when she is calm, excited, upset and reacts to this with her movements. During the intrauterine period, the fetus gets used to moving in space, which is why babies love it so much when they are carried in their arms or rolled in a stroller. For a baby, this is a completely natural state, so he will calm down and fall asleep when he is rocked.
The nails protrude beyond the tips of the fingers, the cartilages of the ears and nose are elastic. In boys, the testicles have descended into the scrotum, and in girls, the large labia cover the small ones. The weight of the fetus reaches 3200-3600 g, and the length is 480-520 mm. nine0008
After being born, the baby yearns for touching his body, because at first he cannot feel himself - the arms and legs do not obey the child as confidently as it was in the amniotic fluid.![]()