What does a cvs test for
Chorionic villus sampling - NHS
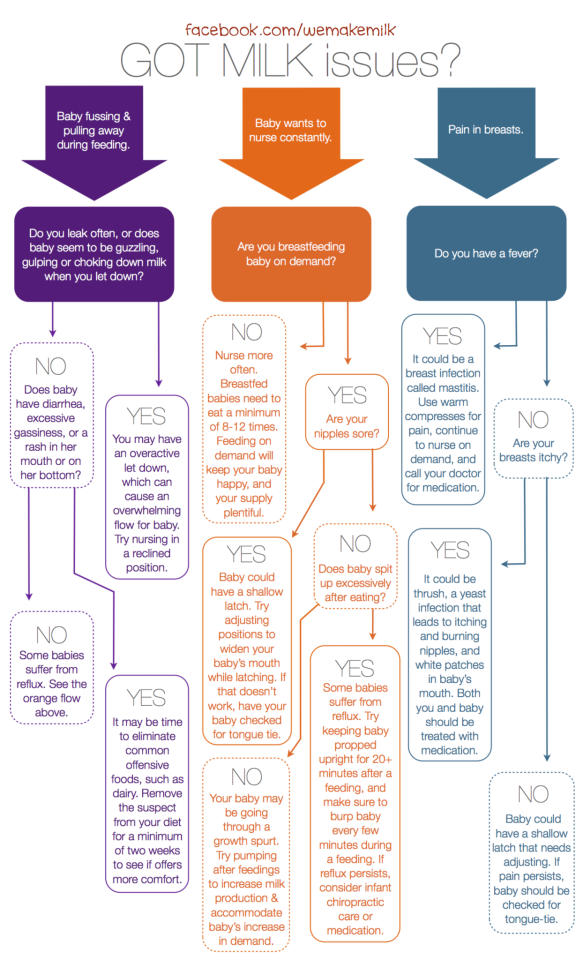
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a test you may be offered during pregnancy to check if your baby has a genetic or chromosomal condition, such as Down's syndrome, Edwards' syndrome or Patau's syndrome.
It involves removing and testing a small sample of cells from the placenta, the organ linking the mother's blood supply with the unborn baby's.
When CVS is offered
CVS is not routinely offered in pregnancy.
It's only offered if there's a high chance your baby could have a genetic or chromosomal condition.
This could be because:
- an antenatal screening test has suggested your baby may be born with a condition, such as Down's syndrome, Edwards' syndrome or Patau's syndrome
- you had a previous pregnancy affected by a genetic condition
- you have a family history of a genetic condition, such as sickle cell disease, thalassaemia, cystic fibrosis or muscular dystrophy
It's important to remember that you do not have to have CVS if it's offered. It's up to you to decide whether you want it.
A midwife or doctor will speak to you about what the test involves, and let you know what the possible benefits are, to help you make a decision.
Find out more about why CVS is offered and deciding whether to have it
How CVS is performed
CVS is usually carried out between the 11th and 14th weeks of pregnancy, although it's sometimes performed later than this if necessary.
During the test, a small sample of cells is removed from the placenta using 1 of 2 methods:
- transabdominal CVS – a needle is inserted through your tummy (this is the most common method used)
- transcervical CVS – a tube or small forceps (smooth metal instruments that look like tongs) are inserted through the cervix (the neck of the womb)
The test itself takes about 10 minutes, although the whole consultation may take about 30 minutes.
The CVS procedure is usually described as being uncomfortable rather than painful, although you may experience some cramps that are similar to period pains for a few hours afterwards.
Find out more about what happens during CVS
Getting your results
The first results of the test should be available within 3 working days and this will tell you if Down's syndrome, Edwards' syndrome or Patau's syndrome has been discovered.
If rarer conditions are also being tested for, it can take 2 to 3 weeks or more for the results to come back.
A specialist doctor (obstetrician) or midwife will explain what the screening results mean and talk to you about your options.
There's no cure for most of the conditions found by CVS, so you'll need to consider your options carefully.
You may decide to continue with your pregnancy while gathering information about the condition so you're fully prepared.
Find out more about having a baby that might be born with a genetic condition
Or you may consider ending your pregnancy (having a termination).
Find out more about the results of CVS
Miscarriage and infections.
Before you decide to have CVS, the possible complications will be discussed with you.
CVS can cause miscarriage, the loss of the pregnancy in the first 23 weeks.
The chance of miscarrying after CVS is up to 1 in 100.
You might also get an infection, or need to have CVS again because it was not successful the first time.
Read more about the complications of CVS
What are the alternatives?
An alternative to CVS is a test called amniocentesis.
This is where a small sample of amniotic fluid, the fluid that surrounds the baby in the womb, is removed for testing.
It's usually carried out between the 15th and 18th week of pregnancy, although it can be performed later than this if necessary.
This test can also cause a miscarriage, but your pregnancy will be at a more advanced stage before you can get the results, so you'll have less time to consider your options.
If you're offered tests to look for a genetic or chromosomal condition in your baby, a specialist involved in carrying out the test will be able to discuss the different options with you and help you make a decision.
Page last reviewed: 20 July 2018
Next review due: 20 July 2021
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) | Johns Hopkins Medicine
What is chorionic villus sampling?
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS), or chorionic villus biopsy, is a prenatal test that involves taking a sample of tissue from the placenta to test for chromosomal abnormalities and certain other genetic problems.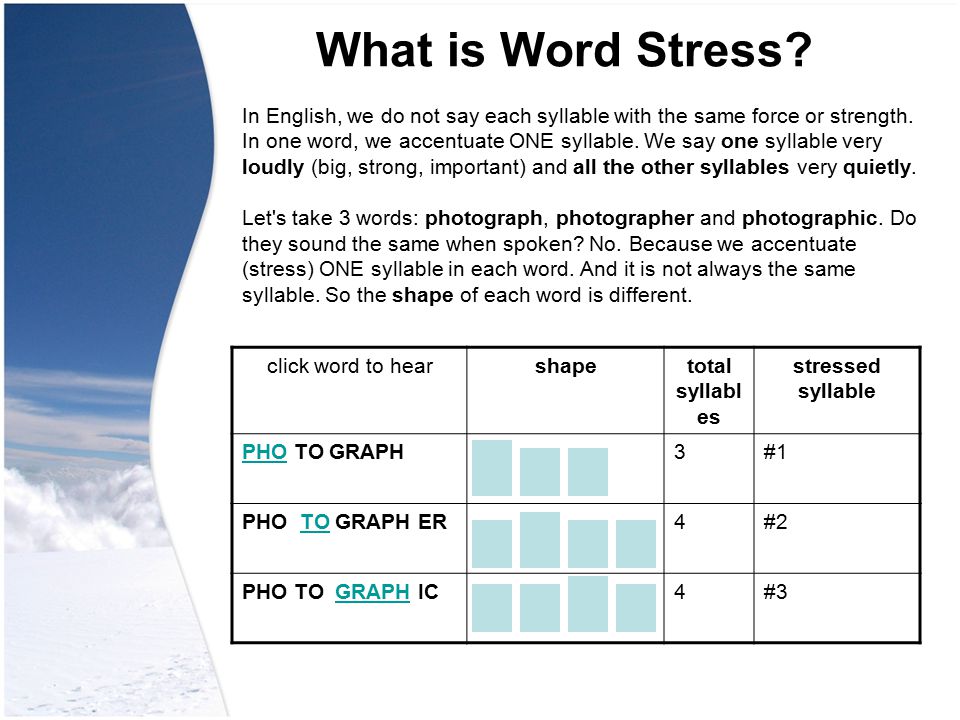 The placenta is a structure in the uterus that provides blood and nutrients from the mother to the fetus,
The placenta is a structure in the uterus that provides blood and nutrients from the mother to the fetus,
The chorionic villi are tiny projections of placental tissue that look like fingers and contain the same genetic material as the fetus. Testing may be available for other genetic defects and disorders depending on the family history and availability of lab testing at the time of the procedure.
CVS is usually done between the 10th and 12th weeks of pregnancy. Unlike amniocentesis (another type of prenatal test), CVS does not provide information on neural tube defects, such as spina bifida. For this reason, women who undergo CVS also need a follow-up blood test between 16 to 18 weeks of their pregnancy to screen for neural tube defects.
There are two types of CVS procedures:
-
Transcervical. In this procedure, a catheter is inserted through the cervix into the placenta to obtain the tissue sample
-
Transabdominal. In this procedure, a needle is inserted through the abdomen and uterus into the placenta to obtain the tissue sample
Another related procedure that may be used to diagnose genetic and chromosomal defects is amniocentesis.
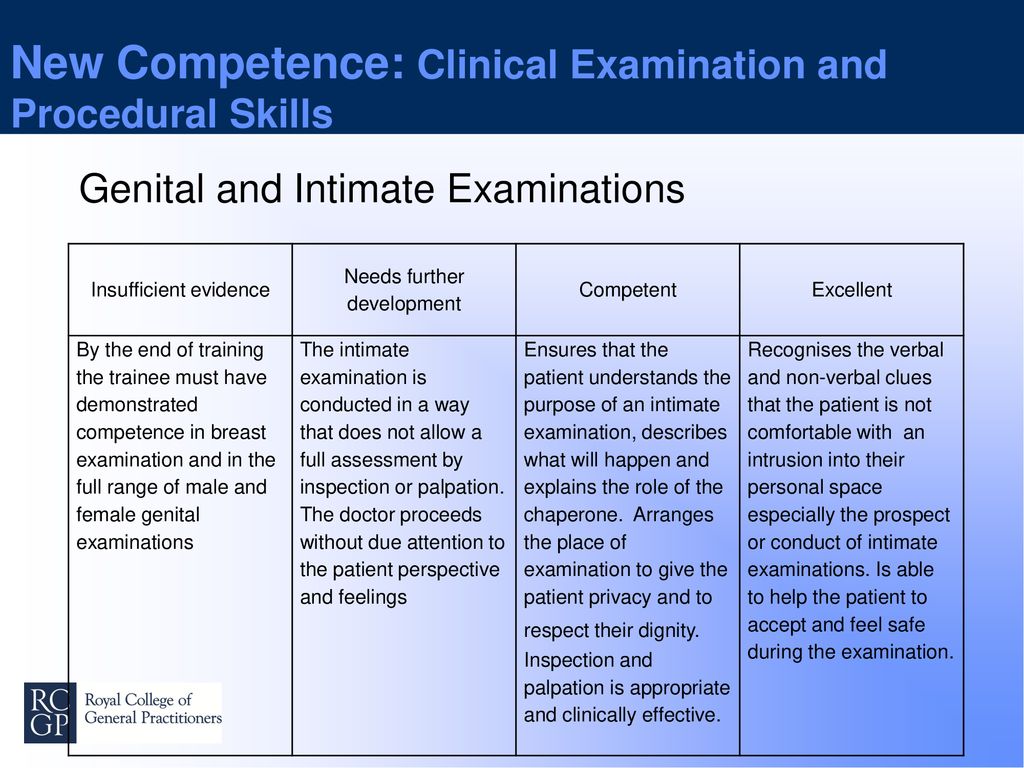
Anatomy of the fetus in utero
Click image to enlarge.
-
Amniotic sac. This is a thin-walled sac that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy. The sac is filled with amniotic fluid (liquid made by the fetus) and the amnion (the membrane that covers the fetal side of the placenta), which protects the fetus from injury and helps to regulate the temperature of the fetus.
-
Anus. This is the opening at the end of the anal canal.
-
Cervix. This is the lower part of the uterus that projects into the vagina. Made up of mostly fibrous tissue and muscle, the cervix is circular in shape.
-
Fetus. An unborn baby from the eighth week after fertilization until birth is called a fetus.
-
Placenta. This is an organ, shaped like a flat cake that only grows during pregnancy and provides a metabolic interchange between the fetus and mother.
 (The fetus takes in oxygen, food, and other substances and eliminates carbon dioxide and other wastes.)
(The fetus takes in oxygen, food, and other substances and eliminates carbon dioxide and other wastes.) -
Umbilical cord. This is a rope-like cord connecting the fetus to the placenta. The umbilical cord contains 2 arteries and a vein, which carry oxygen and nutrients to the fetus and waste products away from the fetus.
-
Uterine wall. This is the wall of the uterus.
-
Uterus (also called the womb). The uterus is a hollow, pear-shaped organ located in a woman's lower abdomen, between the bladder and the rectum. It sheds its lining each month during menstruation and in which a fertilized egg (ovum) becomes implanted and the fetus develops.
-
Vagina. This is part of the female genitals sits behind the bladder and in front of the rectum. It forms a canal extending from the uterus to the vulva.
Reasons for the procedure
Chorionic villus sampling may be used for genetic and chromosome testing in the first trimester of pregnancy . Here are some reasons that a woman might elect to undergo CVS:
Here are some reasons that a woman might elect to undergo CVS:
-
Previously affected child or a family history of a genetic disease, chromosomal abnormalities, or metabolic disorder
-
Maternal age over 35 years by the pregnancy due date
-
Risk of a sex-linked genetic disease
-
Previous ultrasound with questionable or abnormal findings
-
Abnormal cell-free DNA test
There may be other reasons for your doctor to recommend a chorionic villus sampling.
Risks of the procedure
As with any invasive procedure, complications may occur. Some possible complications may include, but are not limited to, the following:
-
Cramping, bleeding, or leaking of amniotic fluid (water breaking)
-
Infection
-
Miscarriage
-
Preterm labor
-
Limb defects in infants, especially in CVS procedures done before 9 weeks (rare)
People who are allergic to or sensitive to medications or latex should notify their doctor.
Women with twins or other multiples will need sampling from each placenta in order to study each baby.
There may be other risks depending upon your specific medical condition. Be sure to discuss any concerns with your doctor prior to the procedure.
Certain factors or conditions may interfere with CVS. These factors include, but are not limited to, the following:
-
Pregnancy earlier than seven weeks or later than 13 weeks
-
Position of the baby, placenta, amount of amniotic fluid, or mother's anatomy
-
Vaginal or cervical infection
-
Samples that are inadequate for testing, or that may contain maternal tissue
Before the procedure
-
The doctor will explain the procedure to you and offer you the opportunity to ask any questions that you might have about the procedure.
-
You will be asked to sign a consent form that gives your permission to do the procedure.
 Read the form carefully and ask questions if something is not clear.
Read the form carefully and ask questions if something is not clear. -
Generally, there is no special restriction on diet or activity prior to chorionic villus sampling.
-
Tell your doctor if you are sensitive to or are allergic to any medications, latex, iodine, tape, and anesthetic agents (local and general).
-
Tell your doctor of all medications (prescribed and over-the-counter) and herbal supplements that you are taking.
-
Tell your doctor if you have a history of bleeding disorders or if you are taking any anticoagulant (blood-thinning) medications, aspirin, or any other medications that may affect blood clotting. It may be necessary for you to stop these medications prior to the procedure.
-
Tell your doctor if you are Rh negative. During the CVS procedure, blood cells from the mother and fetus can mix. This may lead to Rh sensitization and breaking down of fetal red blood cells.
 In most cases, prenatal blood tests will have determined whether you are Rh negative. You may be asked to provide these lab results before the procedure.
In most cases, prenatal blood tests will have determined whether you are Rh negative. You may be asked to provide these lab results before the procedure. -
You may or may not be asked to have a full bladder right before the procedure. Depending on the position of the uterus and placenta, a full or empty bladder may help move the uterus into a better position for the procedure.
-
Based upon your medical condition, your doctor may request other specific preparation.
During the procedure
Click image to enlarge.
A CVS procedure may be done on an outpatient basis, or as part of your stay in a hospital. Procedures may vary depending on your condition and your doctor’s practices.
Generally, a CVS procedure follows this process:
-
You will be asked to undress completely, or from the waist down, and put on a hospital gown.
-
You will be asked to lie down on an exam table and place your hands behind your head.
-
Your vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing rate) will be checked.
-
An ultrasound will be performed to check the fetal heart rate, and the position of the placenta, fetus, and umbilical cord.
-
Based on the location of the placenta, the CVS procedure will be performed through your cervix (transcervical) or through your abdominal wall (transabdominal).
For a transcervical CVS procedure:
-
The doctor will insert an instrument called a speculum into your vagina so that he or she can see your cervix.
-
Your vagina and cervix will be cleansed with an antiseptic solution.
-
Using ultrasound guidance, a thin tube will be guided through the cervix to the chorionic villi.
-
Cells will be gently suctioned through the tube into a syringe. You may feel a twinge or slight cramping.
 More than one sample may be needed to obtain enough tissue for testing.
More than one sample may be needed to obtain enough tissue for testing. -
The tube will then be removed.
For a transabdominal CVS procedure:
-
For an abdominal CVS, your abdomen will be cleansed with an antiseptic. You will be instructed not to touch the sterile area on your abdomen during the procedure.
-
The doctor may inject a local anesthetic to numb the skin. If a local anesthetic is used, you will feel a needle stick when the anesthetic is injected. This may cause a brief stinging sensation.
-
Ultrasound will be used to help guide a long, thin, hollow needle through your abdomen and into the uterus and placenta. This may be slightly painful, and you may feel a cramp as the needle enters the uterus.
-
Cells will be gently suctioned into a syringe. More than one sample may be needed to obtain enough tissue for testing.
-
The needle will then be removed.
 An adhesive bandage will be placed over the abdominal needle insertion site.
An adhesive bandage will be placed over the abdominal needle insertion site.
Procedure completion, both methods:
-
The fetus’ heart rate and your vital signs will be reassessed.
-
If you are Rh negative, you may be given Rho(D) immune globulin. This is a specially developed blood product that can prevent an Rh negative mother's antibodies from reacting to Rh positive fetal cells.
-
The chorionic villus tissue will be sent to the lab.
After the procedure
You and your fetus will be monitored for a while after the procedure. Your vital signs and the fetal heart rate will be checked periodically for an hour or longer.
The CVS tissue will be sent to a specialty genetics lab for analysis. Counseling with a genetics specialist may be recommended depending on the test results.
You may experience some slight cramping and light spotting for a few hours after CVS.
You should rest at home and avoid strenuous activities for at least 24 hours. You should not douche or have sexual intercourse for 2 weeks, or until directed by your doctor.
Tell your doctor to report any of the following:
If a transabdominal procedure was performed, check the bandaged needle site on your abdomen for any bleeding or drainage of fluid.
Your doctor may give you additional or alternate instructions after the procedure, depending on your particular situation.
VLIS - an ecosystem for business: accounting, management and communications
VK_37992622
Exchange documents and set tasks in VLIS, manage accounting and finance, automate purchases and warehouse, move the client along the funnel in CRM.
Select personnel, calculate salaries, keep personnel records, motivate through KPIs, badges and ratings. Here you can also hold meetings and webinars, communicate with colleagues and partners.
From the dry corporate structure VLSI forms a live social network with chats, groups, news. nine0003
nine0003
Reporting in the Federal Tax Service, PF, FSS
Electronic agreements
Monething
Financial analysis
Search tenders
Houses for housing and communal services
Catalog of master data
Restaurant
Product store
Reporting to the Federal Tax Service, Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund
Electronic contracts
Labeling of medicines
Financial analysis
Search for tenders
Checks for utilities and services
Catalog of master data
Restaurant
Analysis and optimization of taxes
Campaign for perfumes
Management of a restaurant network
Reporting in FSRAR
Organization of purchases
Management of KKT
Park and consistent of prices
Beauty Salon Salon Salon.
Personnel accounting
Corporate certification center
Tax analysis and optimization
Perfume labeling
Restaurant chain management
Reporting in the FSRAR
Purchasing and trading organization
Management of the KKT Park
Price and approval of prices
Beauty Salon
Reporting in the UFMS
Electronic labor books
Automation of shopping centers 9000
Field Worker Management
Delivery Automation
API Company Data
Asset Accounting
CALL-center
Reporting in the Federal Mediconest factoring
Information about counterparties
Control of the sales department
Beer labeling
Recruitment
Control of traveling employees
Electronic reconciliation of settlements
CRM and accounting of customers
Video and glider
VAT
Electronic factoring
Information about contractors
Control of the
Personnel Marking Delight. traveling employees
traveling employees
Electronic reconciliation of settlements
Reporting to Rosprirodnadzor
Monitoring of points of sale
Personnel training
Pharmacy
Calculation of salaries
Work and vacations
Calculations with accountable persons
Corporate telephone network
Work with EGAIS and FSRAR
Diningrian reporting in Rosprirodnadzor
Monitoring
Staff training
Pharmacy
Payroll
Work and vacation schedules
Settlements with accountable persons
Corporate telephone network
Audit and reporting consolidation
Electronic invoices
Verification of partners
Analysis of sales and assortment
Social network of personnel
Electronic passing
Accounting
9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 Milk labelingAudit and consolidation of reporting
Electronic invoices
Partner verification
Analysis of sales and assortment
Social network of the company
Management of personnel
Electronic passage
Accounting
reconciliation of settlements with a budget of
GOOSORGANS
Retail store
Motivation
Everything for remote work
Webinars
Tobacco marking
Electronic signature of documents
reconciliation of settlements with a budget of
Documents transfer to government agencies
Retail store
Employees
Financial planning
Commission Trade
All for "Raring"
Webinars
Work with Mercury and VSD
Transfer of documents courts
Retail network management
Fast food
Service center
Electronic document archive
ES on your website
Designer of the Communist Party, contracts, accounts
Purchasing Organization
Competitive intelligence
Work with Mercury and VSD
Documents Transfer of
Retail network
Fastfood
Electronic archive of documents
EP on EP on your site
Designer of commercial proposals, contracts, invoices
Shoe labeling
Warehouse accounting
Company valuation
Accounting for working hours
Corporate portal
Cloud telephony
EDI and logistics
Construction store
Electronic sick leave
Fiscal data operator
Shoe marking
Warehouse accounting
9000Corporate Portal
Cloud Telephony
EDI and Logistics
Hardware Store
more than 4,500,000 companies
different sizes and lines of business —
from sole proprietors to transnational corporations, from Sakhalin to Kaliningrad, from churches to casinos, from kindergartens to ministries. VLSI perfectly solves the problems of everyone.
VLSI perfectly solves the problems of everyone.
Factoring
Oil & Gas
Pharmaceuticals
Manufacturing
Construction
Medium Companies
Federal Companies
Catering Companies
Small Catering Companies
0003
Consumer goods
State institutions
Services
Energy and housing and communal services
Autoprom
RESTEL
International companies
Entertainment
Trade
IT
Logistics
9000 ="/cdn/SbisRuCDN/1.0.6/video/Slider/cola.mp4" type="video/mp4" //> Your browser does not support the video tag. WatchPhone and Internet - all you need to work in VLSI anywhere in the world. Messages, tasks, documents, reports... and this is not all that is in the mobile version of VLSI. nine0003
🤰 CVS TEST - PREPARATION, PROCEDURE, RISKS AND RESULTS
Contents:
In this article
- What is a Chorionic Villus Sampler?
- Is the CVS test applicable to all pregnant women?
- How to prepare for the
- test How is the CVS test done?
- Is the CVS test painful?
- When is the right time for a chorionic villus test?
- When do you get your CVS test results? nine0399
- Problems you may encounter after the test
- Possible risks associated with CVS
- What does the result of a CVS pregnancy test mean?
- What if the CVS test shows an abnormality?
- What are the alternatives for the CVS test?
- What to consider
Scientific developments have made it possible to detect unfavorable health conditions of the baby even before the baby is born. There are a number of tests that are done during pregnancy to determine if the baby is suffering from any disease or disease. Early detection of an adverse medical condition in a baby can allow doctors to take the necessary corrective action to ensure that the baby is born healthy and free from life-threatening conditions. nine0003
There are a number of tests that are done during pregnancy to determine if the baby is suffering from any disease or disease. Early detection of an adverse medical condition in a baby can allow doctors to take the necessary corrective action to ensure that the baby is born healthy and free from life-threatening conditions. nine0003
What is a Chorionic Villus Sampler?
The chorionic villous sampler is a prenatal test that is performed to diagnose whether a baby has a specific genetic disorder such as Down's syndrome or inherited conditions such as thalassemia and sickle cell anemia. Chorionic villi are tiny finger-like growths found in the placenta that share the same genetic material as the baby's cells. The CVS pregnancy test is done during early pregnancy, usually between 10 and 13 weeks. nine0003
Is the CVS test applicable to all pregnant women?
The CVS prenatal test is not a routine test and is suggested for the following conditions:
- Abnormal prenatal screening test results: If the first trimester screening result is positive or abnormal, the doctor may recommend a CVS to ensure the duration of the medical problem in child.

- Chromosomal abnormality in a previous pregnancy. nine0391 If you had a chromosomal abnormality in a previous pregnancy or have a child with Down syndrome, you will be offered this test.
- Family medical history indicates increased health risk: CVS testing may be recommended if there is a family history of a genetic disorder.
CVS is not recommended for women who have an active sexually transmitted infection, who are carrying twins, or who have experienced vaginal bleeding during pregnancy. nine0003
How to prepare for the test
Your healthcare provider will explain the entire test procedure in detail and ask you to sign a consent form prior to the test. The health care provider will use ultrasound to determine the position of the baby and the position of the placenta. Drink plenty of water leading up to the test as the ultrasound will require a full bladder.
How is the CVS test done?
The CVS early pregnancy test is done by taking a sample of cells called chorionic villus cells from a pregnant woman's placenta. The cell sample can be taken from the abdomen or from the cervix. nine0003
The cell sample can be taken from the abdomen or from the cervix. nine0003
A long, thin needle is inserted through the abdominal wall into the uterus, and a tissue sample is withdrawn from the placenta into a syringe. The needle does not enter the amniotic sac and does not pass near the baby, and the procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
Cervical specimen
A thin, hollow tube is inserted into the cervix through the vagina. When the catheter reaches the placenta, gentle suction will be used to remove the tissue sample.
After treatment
The procedure takes about 10 minutes. After the test is completed, you will be monitored for an hour in case of any side effects such as heavy bleeding, surface appearance and the need for immediate intervention. After completing the formalities, you can go home and rest.
Is the CVS test painful?
The CVS test is usually described as unpleasant rather than painful. You may experience tingling and cramping during and after the test, and you may have an inflamed stomach afterwards. Usually, local anesthesia is given before the test is performed in the area where the needle is inserted. nine0003
You may experience tingling and cramping during and after the test, and you may have an inflamed stomach afterwards. Usually, local anesthesia is given before the test is performed in the area where the needle is inserted. nine0003
When is the best time to do a chorionic villus test?
CVS testing should be performed between 10 and 13 weeks of gestation. In some cases, testing may be done later in the pregnancy. However, the test should not be performed before 10- and weeks, as the risk of cardiovascular disease causing complications such as birth defects or miscarriage is higher during this period.
When do you receive your CVS test results? nine0428
After CVS testing, two laboratory tests are carried out on specimens taken from the placenta. The first result is available within a few days and reports any serious chromosomal problems. Full results highlighting smaller and rarer conditions can take two to three weeks. If the test was done to identify a specific disorder, the results may take up to a month.
Problems you may encounter after the test
CVS testing involves the use of needles and suction tubes that enter the body and can lead to side effects after the procedure is completed. Following are some of the problems that may occur after the test: nine0399
Possible risks associated with CVS
CVS testing is an invasive procedure that comes with several risks. It is important to weigh the risks against the benefits before agreeing to a CVS procedure. The following are some of the common risks of doing the test:
Bleeding and cramps:
The test procedure may cause severe vaginal bleeding or spotting and cramps that are similar to menstrual cramps. nine0003
Infectious disease:
An infection of the uterus may occur after the test. Although the situation is rare.
Rh sensitization:
CVS testing can cause small amounts of your baby's blood to enter your bloodstream, which can cause complications such as Rh sensitivity, especially if you are Rh negative.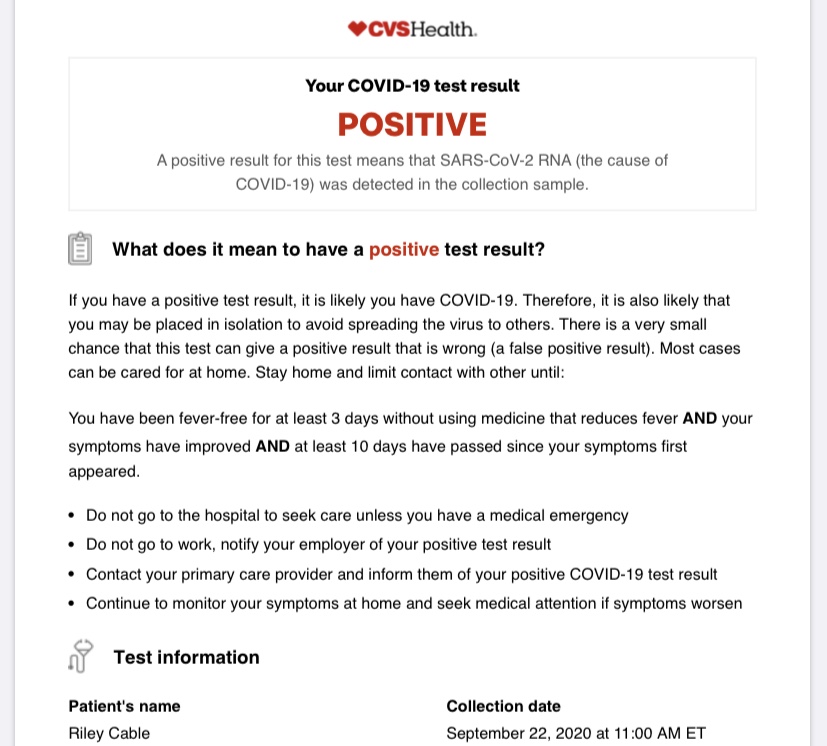
Accidental abortion or miscarriage:
CVS testing may also lead to a risk of accidental abortion or miscarriage. The risk of miscarriage with CVS is in addition to the risk of miscarriage that all women face in early pregnancy due to natural causes. One or two out of every hundred women who opt for CVS experience a miscarriage. nine0003
Fetal limb deformities:
The CVS test may also cause your child to have missing toes or fingers. However, this risk usually exists when testing occurs before 10- weeks of gestation.
What does the CVS pregnancy test result mean?
The CVS test scores 99% with a very small margin of error. While CVS can be used to test for specific genetic disorders, it cannot test for every birth defect. A CVS pregnancy will either be normal (i.e. negative) or abnormal (i.e. positive). nine0003
Normal results:
If the test results show no defects or deficiencies, the report is normal or negative. While the report may be missing any defects, it is possible that the baby could be born with the condition that was tested or with a different genetic condition.
While the report may be missing any defects, it is possible that the baby could be born with the condition that was tested or with a different genetic condition.
Abnormal results:
If the report shows "positive" results, your child has a condition that was being tested. There is no cure for most chromosomal conditions and hence the implications for such a disorder will be fully discussed with you. nine0003
What if the CVS test shows an abnormality?
The consequences of an abnormal result will be discussed with you and options for correction will be considered. Since most genetic conditions are not treatable, you may have the following options:
- To continue the pregnancy and be ready to care for the baby after delivery
- To terminate the pregnancy, in which case you will need to discuss with your doctor the appropriateness of this. nine0399
What are the alternatives for the CVS test?
Amniocentesis is an alternative to the CVS test, in which a sample of the mother's amniotic fluid is taken for testing.