Your not pregnant
How To Be Reasonably Certain a Woman Is Not Pregnant - US SPR
In most cases, a detailed history provides the most accurate assessment of pregnancy risk in a woman who is about to start using a contraceptive method. Several criteria for assessing pregnancy risk are listed in the recommendation that follows. These criteria are highly accurate (i.e., a negative predictive value of 99%–100%) in ruling out pregnancy among women who are not pregnant (16–19). Therefore, CDC recommends that health care providers use these criteria to assess pregnancy status in a woman who is about to start using contraceptives (Box 2). If a woman meets one of these criteria (and therefore the health care provider can be reasonably certain that she is not pregnant), a urine pregnancy test might be considered in addition to these criteria (based on clinical judgment), bearing in mind the limitations of the accuracy of pregnancy testing. If a woman does not meet any of these criteria, then the health care provider cannot be reasonably certain that she is not pregnant, even with a negative pregnancy test. Routine pregnancy testing for every woman is not necessary.
BOX 2. How to be reasonably certain that a woman is not pregnant
A health care provider can be reasonably certain that a woman is not pregnant if she has no symptoms or signs of pregnancy and meets any one of the following criteria:
- is ≤7 days after the start of normal menses
- has not had sexual intercourse since the start of last normal menses
- has been correctly and consistently using a reliable method of contraception
- is ≤7 days after spontaneous or induced abortion
- is within 4 weeks postpartum
- is fully or nearly fully breastfeeding (exclusively breastfeeding or the vast majority [≥85%] of feeds are breastfeeds), amenorrheic, and <6 months postpartum
On the basis of clinical judgment, health care providers might consider the addition of a urine pregnancy test; however, they should be aware of the limitations, including accuracy of the test relative to the time of last sexual intercourse, recent delivery, or spontaneous or induced abortion. Routine pregnancy testing for every woman is not necessary. If a woman has had recent (i.e., within the last 5 days) unprotected sexual intercourse, consider offering emergency contraception (either a Cu-IUD or ECPs), if pregnancy is not desired.
Routine pregnancy testing for every woman is not necessary. If a woman has had recent (i.e., within the last 5 days) unprotected sexual intercourse, consider offering emergency contraception (either a Cu-IUD or ECPs), if pregnancy is not desired.
Comments and Evidence Summary. The criteria for determining whether a woman is pregnant depend on the assurance that she has not ovulated within a certain amount of time after her last menses, spontaneous or induced abortion, or delivery. Among menstruating women, the timing of ovulation can vary widely. During an average 28-day cycle, ovulation generally occurs during days 9–20 (20). In addition, the likelihood of ovulation is low from days 1–7 of the menstrual cycle (21). After a spontaneous or an induced abortion, ovulation can occur within 2–3 weeks and has been found to occur as early as 8–13 days after the end of the pregnancy. Therefore, the likelihood of ovulation is low ≤7 days after an abortion (22–24). A systematic review reported that the mean day of first ovulation among postpartum nonlactating women occurred 45–94 days after delivery (25). In one study, the earliest ovulation was reported at 25 days after delivery. Among women who are within 6 months postpartum, are fully or nearly fully breastfeeding (exclusively breastfeeding or the vast majority [≥85%] of feeds are breastfeeds), and are amenorrheic, the risk for pregnancy is <2% (26,27).
A systematic review reported that the mean day of first ovulation among postpartum nonlactating women occurred 45–94 days after delivery (25). In one study, the earliest ovulation was reported at 25 days after delivery. Among women who are within 6 months postpartum, are fully or nearly fully breastfeeding (exclusively breastfeeding or the vast majority [≥85%] of feeds are breastfeeds), and are amenorrheic, the risk for pregnancy is <2% (26,27).
Although pregnancy tests often are performed before initiating contraception, the accuracy of qualitative urine pregnancy tests varies depending on the timing of the test relative to missed menses, recent sexual intercourse, or recent pregnancy. The sensitivity of a pregnancy test is defined as the concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) at which 95% of tests are positive. Most qualitative pregnancy tests approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) report a sensitivity of 20–25 mIU/mL in urine (28–31). However, pregnancy detection rates can vary widely because of differences in test sensitivity and the timing of testing relative to missed menses (30,32). Some studies have shown that an additional 11 days past the day of expected menses are needed to detect 100% of pregnancies using qualitative tests (29). In addition, pregnancy tests cannot detect a pregnancy resulting from recent sexual intercourse. Qualitative tests also might have positive results for several weeks after termination of pregnancy because hCG can be present for several weeks after delivery or abortion (spontaneous or induced) (33–35).
However, pregnancy detection rates can vary widely because of differences in test sensitivity and the timing of testing relative to missed menses (30,32). Some studies have shown that an additional 11 days past the day of expected menses are needed to detect 100% of pregnancies using qualitative tests (29). In addition, pregnancy tests cannot detect a pregnancy resulting from recent sexual intercourse. Qualitative tests also might have positive results for several weeks after termination of pregnancy because hCG can be present for several weeks after delivery or abortion (spontaneous or induced) (33–35).
For contraceptive methods other than IUDs, the benefits of starting to use a contraceptive method likely exceed any risk, even in situations in which the health care provider is uncertain whether the woman is pregnant. Therefore, the health care provider can consider having patients start using contraceptive methods other than IUDs at any time, with a follow-up pregnancy test in 2–4 weeks. The risks of not starting to use contraception should be weighed against the risks of initiating contraception use in a woman who might be already pregnant. Most studies have shown no increased risk for adverse outcomes, including congenital anomalies or neonatal or infant death, among infants exposed in utero to COCs (36–38). Studies also have shown no increased risk for neonatal or infant death or developmental abnormalities among infants exposed in utero to DMPA (37,39,40).
The risks of not starting to use contraception should be weighed against the risks of initiating contraception use in a woman who might be already pregnant. Most studies have shown no increased risk for adverse outcomes, including congenital anomalies or neonatal or infant death, among infants exposed in utero to COCs (36–38). Studies also have shown no increased risk for neonatal or infant death or developmental abnormalities among infants exposed in utero to DMPA (37,39,40).
In contrast, for women who want to begin using an IUD (Cu-IUD or LNG-IUD), in situations in which the health care provider is uncertain whether the woman is pregnant, the woman should be provided with another contraceptive method to use until the health care provider is reasonably certain that she is not pregnant and can insert the IUD. Pregnancies among women with IUDs are at higher risk for complications such as spontaneous abortion, septic abortion, preterm delivery, and chorioamnionitis (41).
A systematic review identified four analyses of data from three diagnostic accuracy studies that evaluated the performance of the criteria listed above through use of a pregnancy checklist compared with a urine pregnancy test conducted concurrently (42). The performance of the checklist to diagnose or exclude pregnancy varied, with sensitivity of 55%–100% and specificity of 39%–89%. The negative predictive value was consistent across studies at 99%–100%; the pregnancy checklist correctly ruled out women who were not pregnant. One of the studies assessed the added usefulness of signs and symptoms of pregnancy and found that these criteria did not substantially improve the performance of the pregnancy checklist, although the number of women with signs and symptoms was small (16) (Level of evidence: Diagnostic accuracy studies, fair, direct).
Top of Page
False Pregnancy (Pseudocyesis): Causes, Symptoms, and Tests
Written by Stephanie Watson
In this Article
- What Causes False Pregnancy?
- Symptoms of False Pregnancy
- Tests for False Pregnancy
- Treating False Pregnancy
Pregnancy is usually an exciting time for expectant parents. But pregnancy doesn't always end with the anticipated baby. In rare cases, women (or even men) believe they are pregnant, only to find out that their symptoms were caused not by pregnancy, but by something else entirely.
But pregnancy doesn't always end with the anticipated baby. In rare cases, women (or even men) believe they are pregnant, only to find out that their symptoms were caused not by pregnancy, but by something else entirely.
False pregnancy, clinically termed pseudocyesis, is the belief that you are expecting a baby when you are not really carrying a child. People with pseudocyesis have many, if not all, symptoms of pregnancy -- with the exception of an actual fetus. Some men experience a related phenomenon known as couvade, or sympathetic pregnancy. They will develop many of the same symptoms as their pregnant partners, including weight gain, nausea, and backache.
What Causes False Pregnancy?
Only recently have doctors begun to understand the psychological and physical issues that are at the root of pseudocyesis. Although the exact causes still aren't known, doctors suspect that psychological factors may trick the body into "thinking" that it's pregnant.
When a woman feels an intense desire to get pregnant, which may be because of infertility, repeat miscarriages, impending menopause, or a desire to get married, their body may produce some pregnancy signs (such as a swollen belly, enlarged breasts, and even the sensation of fetal movement). The woman's brain then misinterprets those signals as pregnancy, and triggers the release of hormones (such as estrogen and prolactin) that lead to actual pregnancy symptoms.
Some researchers have suggested that poverty, a lack of education, childhood sexual abuse, or relationship problems might play a role in triggering false pregnancy. Having a false pregnancy is not the same as claiming to be pregnant for a benefit (for example, to profit financially), or having delusions of pregnancy (such as in patients with schizophrenia).
Symptoms of False Pregnancy
Women with pseudocyesis have many of the same symptoms as those who are actually pregnant, including:
- Interruption of the menstrual period
- Swollen belly
- Enlarged and tender breasts, changes in the nipples, and possibly milk production
- Feeling of fetal movements
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weight gain
These symptoms can last for just a few weeks, for nine months, or even for several years.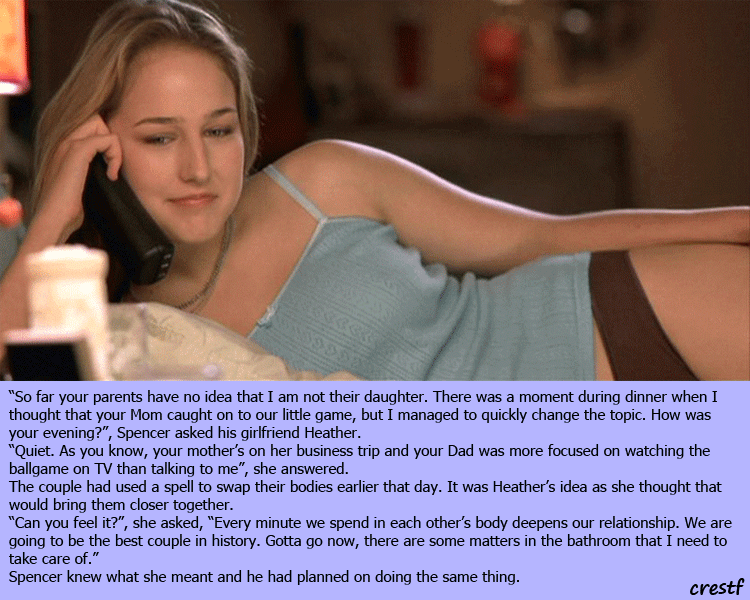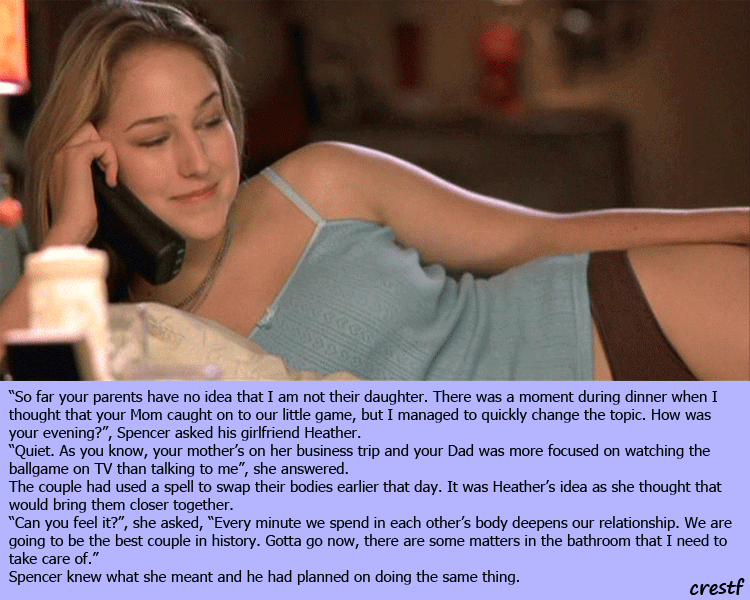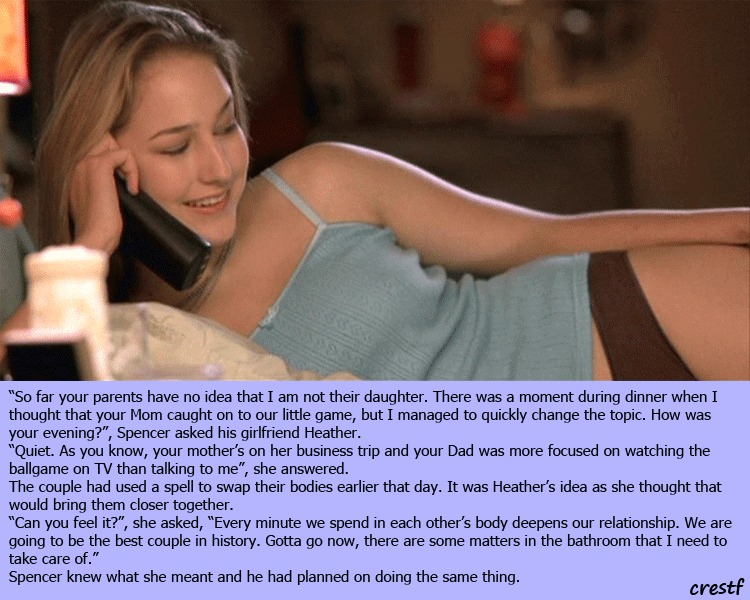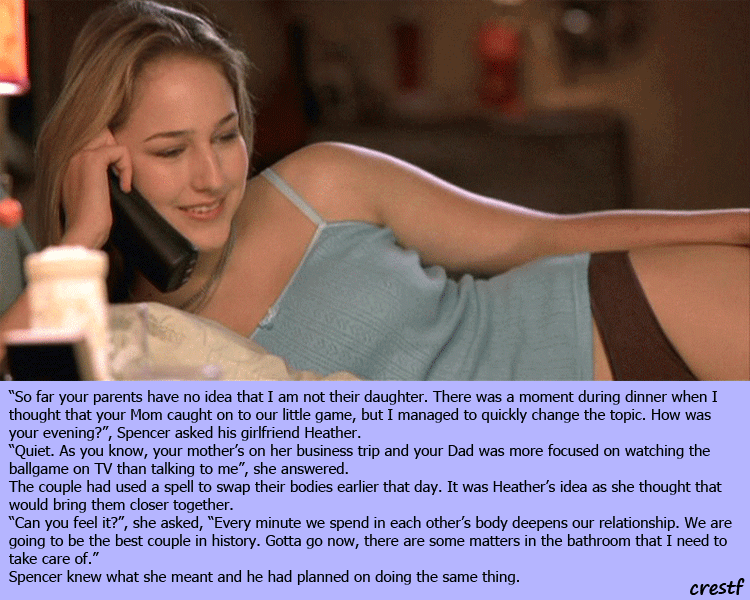 A very small percentage of patients with false pregnancy will arrive at the doctor's office or hospital with what feels like labor pains.
A very small percentage of patients with false pregnancy will arrive at the doctor's office or hospital with what feels like labor pains.
Tests for False Pregnancy
To determine whether a woman is experiencing a false pregnancy, the doctor will usually evaluate their symptoms, perform a pelvic exam and abdominal ultrasound -- the same tests used to feel and visualize the unborn baby during a normal pregnancy.
In a case of false pregnancy, no baby will be seen on the ultrasound, and there won't be any heartbeat. Sometimes, however, the doctor will find some of the physical changes that occur during pregnancy, such as an enlarged uterus and softened cervix. Urine pregnancy tests will always be negative in these cases, with the exception of rare cancers that produce similar hormones to pregnancy.
Certain medical conditions can mimic the symptoms of pregnancy, including ectopic pregnancy, morbid obesity, and cancer. These conditions may need to be ruled out with tests.
Treating False Pregnancy
When women believe they are pregnant, especially for a period of several months, it can be very upsetting for them to learn that they are not. Doctors need to gently break the news, and provide psychological support, including therapy, to help the patient with pseudocyesis recover from their disappointment.
Which signs of pregnancy can be trusted and which can't?
You can listen to the short version of the article. If it's more convenient for you, turn on the podcast.
The most reliable signs of pregnancy are a positive blood test for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) and an ultrasound confirming the fact of conception. But sometimes you want to clarify the situation before going to the doctor or pharmacy. And this can really be done with high accuracy if you know which symptoms and in what period to pay attention.
At what time do the first signs of pregnancy appear
Let's say right away: stories like “I realized that I was pregnant the very next morning after a night of love!” or “we slept together, and after three days morning sickness appeared and everything became obvious” - this is something like an urban legend. They have nothing to do with science.
They have nothing to do with science.
The earliest signs of pregnancy appear at best 6 days after conception. And it's not for all women.
The reason is physiology. For a pregnancy to occur, the egg must meet with the sperm in the fallopian tube. This should happen within one or two days after ovulation - the maturation of the egg in the ovary. The fertilized egg then travels to the uterus to attach to it.
This process takes at least a few days - on average, from 6 to 10. Moreover, until the egg begins to fix itself in the endometrium lining the uterus, no changes in well-being can be noticed. Simply because they are not and cannot be.
Actually, it is the implantation (introduction) of the embryo into the wall of the uterus that doctors consider the beginning of pregnancy. And this is logical. If a woman is taking oral contraceptives or has an intrauterine device, implantation will not occur. Accordingly, pregnancy will not occur and will not be able to make itself felt with any symptoms.
Conclusion: it is useless to look for signs of pregnancy earlier than 6 days after unprotected intercourse. But after this period, you can already begin to listen to yourself.
Which Early Signs of Pregnancy You Can Trust
There are traditional signs of pregnancy related to well-being: morning sickness with or without vomiting, painful breasts, changes in taste… And most of them are really worthy of attention.
Patricia A. Yost
OB/GYN, MD
Even if you feel a little different than usual, it's enough to suggest pregnancy.
But at the same time, these symptoms may have other causes. The real signs of pregnancy manifest themselves in strictly defined terms - this is due to the physiology, which we talked about above.
Therefore, if any change in your health seems suspicious to you, be sure to check how much time has passed since the alleged conception (or the first day of the last menstruation - the so-called obstetric period is counted from it).
Here are the most common and reliable symptoms that you are pregnant. Not all of them may be present specifically for you. But the more of them, the higher the likelihood that you are in a position.
1. Mild cramps in the lower abdomen
- Onset : 6-12 days after conception (4-5 weeks from last period).
When a fertilized egg implants in the wall of the uterus, some women experience mild cramping pain in the lower abdomen. It can last 1-2 days until the implantation process is completed. These sensations are also enhanced by increased blood flow to the uterus.
However, pain in the lower abdomen often occurs before menstruation, when the uterus is preparing to reject the thickened endometrium that is not needed this time. If you are not pregnant, after a couple of days these cramps will end with menstruation. But if the stomach hurt and stopped and menstruation did not come, you should be wary.
2. Spotting spotting
- When appears: 6-12 days after the expected conception, that is, on the days of the expected menstruation (4-5th week from the beginning of the last menstruation).

The process of egg implantation in the uterine wall can be accompanied not only by pain, but also by the so-called implantation bleeding. It is small and usually consists of small, light red or brownish discharge that stops within a couple of days.
Sometimes women overlook this symptom, thinking it is simply too weak menstruation. But menstruation cannot be "too weak", this is important. If the monthly bleeding of your usual volumes did not come after the spotting discharge, you are most likely pregnant.
3. Heavy, painful breasts
- When appears: 6-12 days after conception (4-5 weeks from the beginning of the last menstruation).
This is how the mammary glands react to hormonal changes in the body that begin after the implantation of the egg. This is a fairly common and characteristic symptom. According to a survey conducted by the American Pregnancy Association, for 17% of women, swollen breasts were the first sign of their new condition.
At the same time, breast enlargement and soreness can also be associated with approaching menstruation - the so-called premenstrual syndrome.
4. Unmotivated weakness, fatigue
- When appears: 6–12 days after the expected conception (4–5 weeks from the beginning of the last menstruation).
During and after the implantation of the egg, the body begins to produce progesterone, a hormone that helps maintain the pregnancy. A side effect of its increased level is sudden weakness, drowsiness, laziness, unwillingness to do anything. Later, when the female body adapts to the changed hormonal background, vigor will return. But at the very start of pregnancy, weakness is most noticeable.
However, concluding that you are pregnant just because you suddenly want to crawl under the covers and do nothing is not worth it. Unmotivated fatigue can have dozens of different reasons - from banal overwork or ordinary SARS to much more dangerous diseases. Keep monitoring your condition.
Keep monitoring your condition.
5. Delayed period
- When appears: about 14 days after conception (5-6 weeks from the beginning of the last menstruation) with a normal 28-day cycle.
Absence of menstruation is the key and most understandable sign of pregnancy. Nearly 30% of women surveyed by the American Pregnancy Association said it was what made them take the test.
Nevertheless, the delay in menstruation is still not an unambiguous sign. It can be related to a host of other factors besides pregnancy: stress, weight loss, exercising too intensely, jet lag, certain medications.
6. Nausea (early toxicosis)
- When appears: about 14 days after conception (weeks 5-6 from last period).
They like to show this sign in films so that the viewer understands that the heroine is pregnant. But nausea appears no earlier than 2 weeks after conception. Scientists do not fully understand what this process is connected with, however, they suggest that this is the body's reaction to a changed hormonal background.
If you feel sick 3-7 days after sexual intercourse, it is more likely to be digestive problems, rather than early toxicosis, because at this time the level of hormones does not change significantly.
7. Sensitivity to smells
- When appears: about 14 days after conception (5-6 weeks from the beginning of the last menstruation).
This symptom is caused by the same hormonal changes as nausea. Sometimes it appears even before the delay of menstruation. For example, you become unbearable smell from smoking colleagues. Or he begins to feel sick from the aroma of his favorite flowers, perfumes, dishes. This is a good reason to at least buy a pregnancy test.
8. Bloating and constipation
- When appears: 6-12 days after conception (4-5 weeks from the start of the last period).
Progesterone causes some muscle relaxation. This also applies to the muscles of the intestines. For this reason, the digestive process slows down, feces remain in the intestines longer. Which often causes a bursting sensation in the abdomen and constipation.
Which often causes a bursting sensation in the abdomen and constipation.
However, be aware that bloating and constipation can have dozens of other causes besides pregnancy. Therefore, it makes sense to consider this symptom only in combination with others.
9. Frequent urination
- When appears: 14-21 days after conception (5-6th week from the beginning of the last menstruation).
In the first weeks of pregnancy, the body actively produces the hormone hCG. It increases blood flow to the pelvis, causing women to run to the toilet more often.
10. Increased basal temperature
- When appears: 14-21 days after conception (5-6th week from the beginning of the last menstruation).
Basal body temperature is measured in the mouth, rectum or vagina. It rises during ovulation - that is, during the period when the egg leaves the ovary into the fallopian tube. During pregnancy, basal temperature can also increase. But this happens not earlier than the sixth obstetric week.
But this happens not earlier than the sixth obstetric week.
11. Mood swings
- When appears: 7-10 days after the start of the delay of menstruation (from the 6th week from the beginning of the last menstruation).
Mood swings are caused by hormonal changes that a pregnant woman goes through. However, these changes increase gradually and become significant after a delay in menstruation.
If irritability, anxiety, tearfulness occur much earlier, most likely, it is not about pregnancy, but about banal PMS or stress.
12. Dizziness
- When appears: from 14-21 days after conception (from 5-6 weeks from the beginning of the last menstruation).
In the early stages of pregnancy, blood pressure often drops. This is due to the fact that the uterus requires more blood supply, the blood vessels dilate to provide the necessary blood flow, and the heart is not yet ready to pump the required volumes. The pressure decreases, this process is accompanied by dizziness.
The pressure decreases, this process is accompanied by dizziness.
However, dizziness can have other causes, including dangerous ones. If you begin to regularly “sickness”, consult a general practitioner or (if pregnancy has already been established) a gynecologist.
13. Accelerated pulse
- When appears: from the 8th to 10th week from the beginning of the last menstruation.
During pregnancy, the heart has to pump more blood to keep the growing uterus and fetus healthy. Therefore, it begins to work more actively. An increased heart rate is a common symptom in pregnant women, but it occurs already at those times when pregnancy is in most cases obvious.
But again, keep in mind that an accelerated heartbeat (tachycardia) can also occur for other reasons - for example, with cardiovascular diseases. In any case, such conditions, if they began to manifest themselves regularly, require consultation with a general practitioner, gynecologist or cardiologist.
14. Pimples
- When appears: as a rule, not earlier than the 11th week from the beginning of the last menstruation.
Increased blood volume and increased hormone levels increase blood flow. This leads to the fact that the sebaceous glands of the body begin to work more actively than usual. Acne is often a side effect of this activity.
However, acne has many other causes, so do not rush to write off pimples for pregnancy. You may be able to quickly get rid of them if you make small changes in your lifestyle.
Signs of pregnancy to avoid
1. Diarrhea
Liquid, watery stools are also sometimes considered a sign of pregnancy. But it's not. On the contrary, you are more likely to become constipated in the early stages of pregnancy. Exclusively for hormonal reasons, which we wrote about above.
If you do develop diarrhea, it is likely caused by other factors: you may have eaten something that was not right, or you may have contracted a rotavirus infection.
2. Sudden changes in taste preferences
There are legends about the love of pregnant women for peaches with herring or strawberries with soy sauce. But there is little convincing scientific evidence that women experience cravings for unusual flavor combinations during pregnancy.
Rather, we are talking about some changes in appetite associated with early toxicosis and sensitivity to smells. So, you may want to give up your usual coffee or fried foods - simply because their pungent smell will become disgusting.
However, there is still a craving for non-standard dishes. As a rule, it is associated with the fact that the body of a pregnant woman is deficient in certain essential vitamins and minerals. And he tries to cover their shortage by making the hostess want chalk (this may be a sign of iron deficiency) or, for example, pickles (deficiency of some salts) with raspberry jam (vitamin C deficiency). But such food perversions occur at solid terms of pregnancy, when it is already obvious.
3. Dreams about fish and other signs
But these options have nothing to do with evidence-based medicine at all, no matter at what moment they appear. Also, do not try to detect pregnancy with the help of fortune-telling and waving a ring on a string.
How to establish pregnancy for sure
To begin with, listen to yourself, but don't go crazy. If you have a couple of reliable signs, invest in a quality pharmacy test. With its help, you can determine pregnancy as early as 10–12 days after fertilization.
If you want to clarify earlier, take a blood test for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). It can be done in any certified medical laboratory, and the results will be ready within a few hours.
Lia Moss
Nurse Midwife at Northwestern University School of Medicine
An hCG blood test can detect pregnancy as early as 7 to 10 days after conception. But be aware: too early testing can give a false positive result.
If the test is positive, go to the gynecologist. The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe a follow-up ultrasound to confirm your new position.
The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe a follow-up ultrasound to confirm your new position.
If the tests are negative, but the symptoms of pregnancy seem obvious to you, repeat the test in 1-2 days. And if necessary - again after the same period of time.
By the way, a negative result in this case will also be a result. If the signs of pregnancy persist or increase, and the test claims that there is no embryo in your body, this is a serious reason to see a gynecologist again. There are hormonal diseases that give symptoms similar to pregnancy. And it's important not to miss them.
Read also 🤱👶🧒
- To have time before 35: is it really necessary to give birth before a certain age
- How to conceive a girl or a boy: only scientific methods
- When and what causes a miscarriage
- Pregnancy planning: 12 things the right parents do
- What is the danger of an ectopic pregnancy and how to recognize it in time
How to determine pregnancy without a test
How to determine pregnancy without a test and what signs indirectly indicate that your beloved baby will be born soon? Of course, only a blood test can give a 100% guarantee, but the presence of certain signs may indicate its possible onset.
Classic signs of pregnancy
Most common early signs and symptoms may include
- Delayed menses. Problems with the regularity of the menstrual cycle may be associated with hormonal imbalance in the body. But if the delay arose for the first time, and before that the cycle was as accurate as a clock, then it is likely that you are pregnant.
- Early toxicosis with severe nausea and vomiting is the most common sign of an interesting situation, but it does not occur in every woman.
- Pain in both breasts or their enlargement. Nipples may become very sensitive and change color. Sometimes in the early stages, colostrum is released from them with slight pressure.
- Pain in the pelvic region, similar to menstruation. But this sign can also indicate such a serious pathology as an ectopic pregnancy.
- Increased amount of discharge from the genitals.
 This can usually be observed during ovulation. Normal discharge is clear and odorless. When a whitish tint or a curdled structure appears, thrush can also be assumed, which is a common problem for expectant mothers. But in this case, you can not do without treatment. During the period of bearing a child, it is necessary to protect your body as much as possible from any, even such a safe disease.
This can usually be observed during ovulation. Normal discharge is clear and odorless. When a whitish tint or a curdled structure appears, thrush can also be assumed, which is a common problem for expectant mothers. But in this case, you can not do without treatment. During the period of bearing a child, it is necessary to protect your body as much as possible from any, even such a safe disease. - Increased or vice versa reduced libido. Every woman experiences jumps in sexual desire in one direction or the other due to hormonal changes occurring in the body. Therefore, men should treat this with understanding, knowing that they have not become less loved, but these are just signs of pregnancy.
- Frequent urination, despite the fact that you do not drink more often and there are no inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. A similar phenomenon is associated with a slight relaxation of the sphincter of the bladder due to hormonal processes.
 And with the growth of the uterus and, accordingly, with the increase in pressure on the bladder, going to the toilet will become even more frequent.
And with the growth of the uterus and, accordingly, with the increase in pressure on the bladder, going to the toilet will become even more frequent.
Additional symptoms of pregnancy
There are less obvious signs that may occur during the first trimester. These include:
- Strange Desires . For example, at night I sharply wanted chocolate, and during the day - salted fish. Such desires may not be mere whims. If you want sour, then perhaps there is not enough vitamin C in the body. You want to gnaw on the wall with calcium deficiency, and sniff gasoline - with a lack of iron, anemia.
- Constant irritability, tearfulness. The flow of hormones in a woman's body in the early stages can make her unusually emotional. So-called mood swings can be a clear sign of pregnancy.
- Bloating . Hormonal changes can cause feelings of fullness in the abdomen, as at the beginning of the menstrual cycle.

- Bloody discharge pale pink. This symptom is called implantation bleeding. This happens when a fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus, about 10 to 14 days after conception. Usually occurs during the normal periods of the menstrual period. But not all women have such bleeding is a sign of a normal pregnancy. Therefore, in case of detection of deviations from the normal cycle, consult a gynecologist.
- Chair problems . Hormonal changes cause the digestive system to slow down, which can lead to constipation.
- Food aversions . When you are pregnant, you may become more sensitive to certain smells and your sense of taste may change. Like most other symptoms, these eating habits can be attributed to hormonal changes.
- Nasal congestion . An increase in hormone levels and blood production can lead to swelling of the nasal mucosa. This can cause congestion or runny nose, nosebleeds.