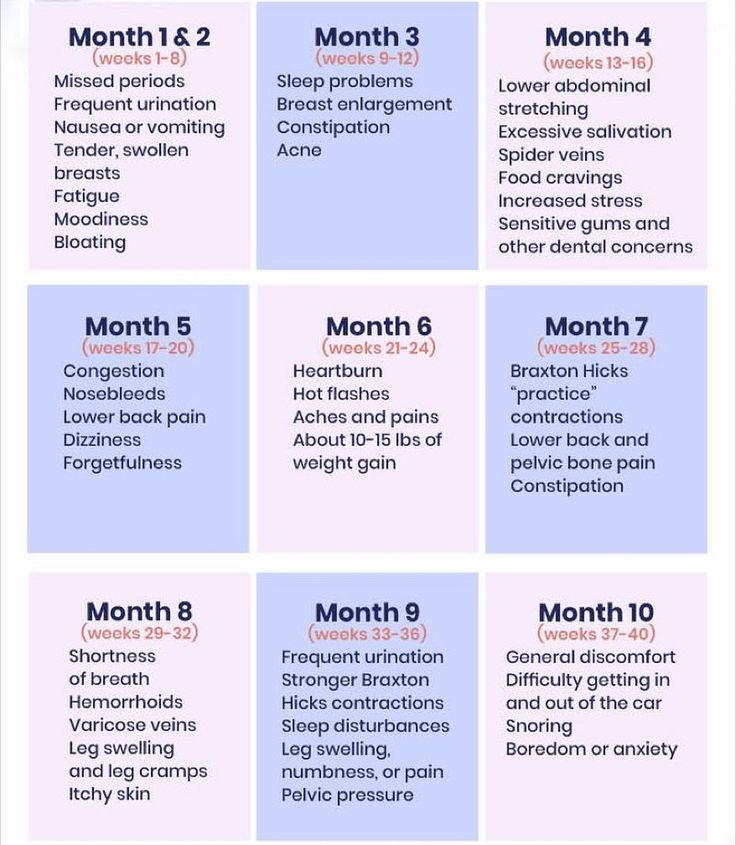
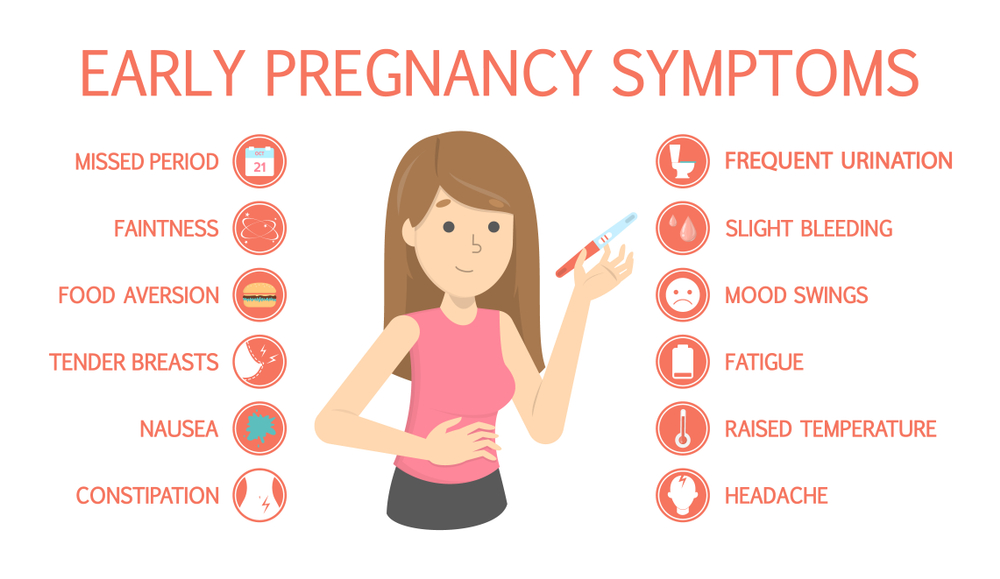
How to start the child custody process
What you can file to ask for a child custody and visitation order | California Courts
Index: All Pages
There are different types of cases and papers you can file to ask for a child custody and visitation (parenting time) order. Which type of case or papers you can file depends on your situation, like whether you and the other parent are married or you already filed a family law case.
If you have a family law case, you can file a
Request for Order in that caseIf there's already a family law case involving the child in California, then you can file a Request for Order (form FL-300) to ask the judge to make or change an order in that case about child custody and visitation (parenting time). Common family law cases are divorces or parentage (paternity) cases.
If you and the other parent agree about what orders you want, you can also ask the judge to make your agreement an order.
Generally, if there is a case in another State about custody of the child, you will need to file papers in that State to ask for custody orders. Talk to your court's Self-Help Center staff to find out your options, or talk to a lawyer for advice.
How to Request an Order
If you do not have a family law case, you need to start one to ask for custody and visitation (parenting time) orders
You first need to start a family law case (like a divorce between you and the other parent or a parentage case). Then, you can ask in that case for child custody and visitation orders. Which type of case you start depends on your situation.
Typically, the child will need to have lived in California for the past 6 months (unless they are less than 6 months old) in order for a California judge to make a decision about custody. If the child has been living in another State for the past 6 months, then often you need to file a case where the child lives now. Ask your court's Self-Help Center staff or get legal advice if you aren't sure if California is the right state to file in.
If you and the other person . . . . . | You can file a . . . |
|---|---|
| Are married or in a domestic partnership and want to divorce or legally separate | Petition for divorce or legal separation |
| Are married or in a domestic partnership and do not want to divorce or legally separate | Petition for Custody and Support |
| Are not married or in a domestic partnership and you are not both the child's legal parent | Petition to Determine Parentage |
| Are not married or in a domestic partnership, but are both the child's legal parent (for example, you both signed a Voluntary Declaration of Parentage or legally adopted the child) | Petition for Custody and Support -or- Petition to Determine Parentage |
| Have a child together and you need protection from the other parent | Request for a Domestic Violence Restraining Order |
If you are not the child's parent but want custody of the child because the parents are not able to care for the child, find out more about guardianships. This is when the court orders someone other than a child's parent to have custody of the child.
This is when the court orders someone other than a child's parent to have custody of the child.
8 Steps to Final Orders
Litigating custody of a child in California consists of eight main steps. Some may be skipped or rearranged and others added, depending on your circumstances and county.
At any point, parents can agree on a plan and have a judge sign it. Then the custody process jumps to Step 8.
Private mediation, collaborative law and other alternative methods for deciding custody follow their own processes.
Bring calm to co‑parenting. Agree on a schedule and plan. Be prepared with everything documented.
Make My California Plan Now
Step 1: Preparation
Do your research and consider your options. Will you request sole or joint physical custody? What about legal custody? What does your ideal parenting schedule look like? Then, meet with a lawyer to come up with a legal strategy. Attorney representation is strongly recommended, but if you're not able to hire someone, you should at least do a free or low-cost consultation to hear the thoughts of a professional.
Step 2: Filing
Before you can request custody, you must open a family law case with your county's superior court; this can be a divorce, a request for a domestic violence restraining order, a paternity case or a custody case. Then you file a request for a custody order, which can be done by either parent. Once the other parent has been served with a copy of your court papers, they can file a response.
Possible: Emergency custody hearing
If a child is at risk of being harmed or removed from the state within the next few days, a parent can request an expedited hearing to determine if emergency temporary orders are necessary (also called ex parte orders). If a judge issues emergency orders, they stay in effect until the next hearing, when they can be terminated, replaced by temporary orders or extended.
Step 3: Orientation
Many counties in California require parents to complete a short orientation at the start of their custody-related case. Often times, it can be done online, such as in Los Angeles, Santa Clara and Napa counties. If your county doesn't require orientation, the video introduction to child custody mediation from California Courts can help you prepare for your next step.
Often times, it can be done online, such as in Los Angeles, Santa Clara and Napa counties. If your county doesn't require orientation, the video introduction to child custody mediation from California Courts can help you prepare for your next step.
Step 4: Court-ordered mediation
Parents are required by law to attend mediation before having a judge decide their custody or visitation arrangement. They will meet for free with a court-employed mediator for up to several hours, and lawyers will not be present.
The goal of mediation is to develop a detailed parenting plan the parents both support, which can be signed by a judge to become a final order. If mandatory mediation does not result in total agreement, some counties' mediators give recommendations to the court. In other counties, mediators simply report that an agreement was not reached.
Remember that anytime parents are able to agree on a parenting plan ― through mediation, informal negotiation or otherwise ― a judge can sign it, and the custody process jumps to Step 8.
Step 5: Hearing
If mediation did not result in a parenting agreement, it will be followed by a hearing. This is generally the first time the parties meet with a judge, though some counties require an initial hearing before court-ordered mediation.
After reviewing the facts of your case, the judge will do one or more of the following:
- Order a child custody evaluation if they want a mental health professional to weigh in
- Appoint child's counsel if they believe the child needs a lawyer
- Give temporary custody orders if the parties can't agree on a parenting arrangement for the duration of the custody proceedings
- Order another hearing or a trial
Hearings are opportunities for you to briefly present your argument and evidence to the judge so he or she can determine next steps. The parents and their lawyers typically all speak.
You may have as few as one hearing or as many as 10 hearings throughout your case, depending on your family's circumstances.
Step 6: Conferences
Conferences are essentially meetings with the judge, and they generally happen in the judge's chambers. Many times, parents who have lawyers send the lawyers in their places.
Different counties use different types of conferences.
A pretrial conference or trial setting conference makes sure both parents are ready for trial, estimates how long the trial is likely to take, sets ground rules and more.
In a settlement conference, the parents again come together to try to find common ground and avoid a trial. This time, the judge guides the parents toward a solution. Some counties do not require or offer this step, while others use multiple settlement conferences.
Step 7: Trial
If parents are unable to settle, they will ultimately end up in trial.
A trial is like an extended, more formal version of a hearing. Both parents get to present evidence and question witnesses in front of the judge so he or she can issue a ruling.
A trial can last hours, days, weeks or, in extremely complicated cases, months. Often there's a significant waiting period between the last hearing and the trial because court calendars fill up and lawyers need time to gather evidence.
At the end of the trial, the judge will announce their decision. Once signed, it is known as a final custody order.
Step 8: Final custody orders
To bring the custody process to a close, a judge will sign a final custody order. It lays out, in the form of a parenting plan, the legal terms all parties must abide by until each child involved turns 18 or is emancipated. The details are decided either by a judge after a trial or by the parents themselves, with the judge signing off.
If a parent has reason to contest a court's decision, they can appeal to a higher court and begin the legal process again. They can also file a motion to cancel the court order.
As children grow older and their lifestyles change, orders often need to be modified several times. Parents can develop a new parenting plan together or one can request that the court modify the existing plan.
Parents can develop a new parenting plan together or one can request that the court modify the existing plan.
If the other parent doesn't follow a court order, you should keep detailed notes of the violations. For serious or repeat violations, you can contact police or file for contempt with the court.
Throughout your case
During the custody process, you may need to create a parenting plan, draft custody schedules, track your time with your child, keep a log about interactions with the other parent, and more.
The Custody X Change app enables you to do all of this in one place.
With a parenting plan template, custody calendars, a digital journal and beyond, Custody X Change makes sure you're prepared for whatever arises in your journey to child custody.
Throughout your case, take advantage of our technology to stay on top of all the moving parts.
Bring calm to co‑parenting. Agree on a schedule and plan. Be prepared with everything documented.
Make My California Plan Now
Bring calm to co‑parenting. Agree on a schedule and plan. Be prepared with everything documented.
Make My PlanHow to take a child into custody in 2023: how to get guardianship
Lada Pozdeeva
talked to her mother-in-law about guardianship
Author profile
She became his guardian.
I learned from Svetlana how to take a child into custody, what is needed for this and what payments a guardian can receive from the state.
You will know
- How Svetlana made the decision
- What is custody
- The differences between guardianship and adoption
- School of adoptive parents
- Documents
- Housing Preparation
- Treaty with guardianship bodies
- Costs
- difficult. Psychological aspects of guardianship
How Svetlana made the decision
My mother-in-law has three daughters and one son. The children are already adults, and she rarely sees them. She meets with some of them only once a year.
The children are already adults, and she rarely sees them. She meets with some of them only once a year.
In 2012, Svetlana realized that her youngest daughter would also soon graduate from school and go to study in Syktyvkar. And it is 730 kilometers from their village.
At that time, my mother-in-law was 50 years old, and she did not want to stay with her common-law husband without children. It seemed to her that the big village house would be empty and lonely without them. For her, this was a reason to take a six-year-old boy from an orphanage under guardianship. The civil husband supported her.
Svetlana Pozdeeva - my mother-in-law, mother of four children and guardianBy law, guardianship is an arrangement for a family of children under 14 years of age. Guardians appointed by the guardianship and guardianship authorities are considered the legal representatives of the wards and act on their behalf and in their interests.
paragraph 1 of Art. 2 of the Federal Law "On guardianship and guardianship"
Guardianship is not adoption. They differ in their essence, in documents, in the form of state control and in the amount of payments.
They differ in their essence, in documents, in the form of state control and in the amount of payments.
Adoption is the adoption of a child into a family as a son or daughter. It entails irreversible legal consequences. For example, an adopted child is equated in property rights with a native: after the death of an adoptive parent, adopted children are considered heirs of the first stage. A child under guardianship does not have such rights.
Art. 137, 138 SK RF
Art. 1147 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
Svetlana did not consider adoption, because she understood that relations with a child from an orphanage might not work out.
Differences between guardianship and adoption
Paperwork. Fewer certificates are required to take a child into custody than to adopt one. For the mother-in-law, this also played an important role. She works as a social work specialist and initially understood that it was easier to get custody of a child than to collect documents for adoption.
Memo for candidates for adoptive parents
State control form. Social security checks come to the guardian more often than to the adoptive parent. For some people, this can cause psychological discomfort.
Amount of lump-sum payments. If a person adopts a child, he is entitled to a one-time payment from the region: 200,000 R for a healthy child and 250,000 R for a child with physical disabilities. These amounts of payments are valid in the Komi Republic. The adoptive parent also receives a one-time allowance - 22 909 R.
Law of the Republic of Komi on state support when transferring a child to a family
Benefits and payments to citizens with children
art. 12.2 of the Federal Law "On state benefits to citizens with children"
The guardian is not given such large amounts. He receives only an allowance - 22,909 R. Regions have the right to establish their own additional one-time payments, their amounts may vary.
Foster Parent School
The prospective guardian must be trained at a foster parent school and receive a course completion certificate.
While studying, future adoptive parents and guardians get acquainted with the regulations in the field of guardianship, as well as with the amounts of payments and benefits. Guardianship specialists psychologically prepare people for someone else's child in the family and discuss with them stressful situations that may arise.
Order of the Ministry of Education and Science on approval of the training program for guardians and foster parents
During the courses, future guardians are given tests, memos and information leaflets with tips on raising children and helpline numbers - the guardian can call there in emergency situations.
The guardianship authorities can meet the candidate halfway and allow him to study after he takes the child into custody. And some caregivers take these courses two or three times to learn how to get along with the child.
Documents
The future guardian must submit a package of documents to the guardianship department at the place of residence:
- Application for the desire to become a guardian.
- Certificate of no criminal record.
- Certificate of employment indicating the average salary or certificate of employment of the spouse of the person who has decided to become a guardian. You can also submit another document that confirms the income of the candidate or his spouse.
- A copy of the marriage certificate, if the guardian is one.
- Consent of adult family members to accept a child into the family.
- A copy of the guardian training certificate.
- Autobiography.
- Conclusion on the results of a medical examination.
clause 4 of the Rules for the selection of guardians
Application form of consent of adult family members living together to accept a child into the familyPDF, 212 KB
The candidate for guardianship will have to check whether he has any medical conditions that may prevent him from taking the child into care. For example, these include mental disorders and alcohol addiction. People with disabilities of the first group cannot take a child under guardianship.
For example, these include mental disorders and alcohol addiction. People with disabilities of the first group cannot take a child under guardianship.
List of diseases that may prevent you from becoming a guardian
All documents must be up to date. A certificate from the place of work is valid for a year, a health certificate - for 6 months.
Svetlana believes that her pedagogical education helped her to pass the selection process and become a guardian. She told about him in her autobiography. In the same place, she wrote that the common-law husband had been a cross-country skiing coach for many years and worked with children.
The guardianship authorities also asked Svetlana for a reference from work, although this document is not specified in the law. It was not difficult for Svetlana to obtain all these certificates, extracts and certificates. Instead of copies, you can bring original documents to the guardianship authorities. Specialists will make copies themselves.
Documents can be submitted via the Internet: on the website of public services or on the official website of the guardianship and guardianship authorities in your region. You can also do it at the nearest MFC.
clause 5 of the Rules for the selection of guardians
Guardianship authorities will verify the information within two business days from the date of submission of the application and documents.
Art. 146 SK RF
Preparation of housing
Having submitted documents to the guardianship authorities, the future guardian must prepare housing for inspection by specialists. Within three working days after the authorities confirm the information provided by the candidate, they will check the living conditions and draw up a special survey report.
clause 8 of the Rules for the selection of guardians
The guardian's house should be clean, a corner and a sleeping place should be equipped for the child, and toys should be bought. During the visit, specialists from the guardianship authorities will ask about the relationship between family members.
During the visit, specialists from the guardianship authorities will ask about the relationship between family members.
In some cases, guardianship officials may not inspect the candidate's house - for example, if a person has a positive reference from work.
When the act of examining housing conditions is ready, the guardianship authorities must make a decision on the candidate for guardians within 10 working days.
If the decision is positive, specialists will issue a conclusion on the person's ability to be a guardian - it is valid for two years.
paras. 9 and 11 of the Rules for the selection of guardians
Choice of the child
After receiving the opinion, the future guardian must select the child he wants to take into the family. First you need to decide on the age and gender, and then get to know the child in order to understand whether the guardian and the child can live together.
You can find a child in an orphanage or on special websites, such as "Orphans" or "Adoption in Russia".
About the database of children left without parental care
The Adoption in Russia website is a project of the Ministry of Education and one of the main resources for finding a child. There you can choose a ward or ward of a certain age. The site has a search for different regions.
More information about children who can be taken into the family is published by foundations and news sites. Each region has its own information sources where data on children left without parental care are posted.
Svetlana met the child in the office of the guardianship authority. She took a liking to the boy right away. With the consent of the guardianship specialists, she took him for the weekend. Since then, the child began to live with Svetlana, she decided not to give him away.
Svetlana immediately noticed that the boy is often overexcited. She believed that this was due to his difficult fate. The child also had psychological trauma and poor eyesight. This did not frighten the mother-in-law: she already had experience in raising difficult children.
Having taken the boy from the orphanage, Svetlana understood that she would have to take him to the republican hospital and bear the costs of treatment. But this is the choice of the mother-in-law - healthy children also live in shelters.
Agreement with guardianship authorities
Such an agreement is concluded if necessary, if it is in the interests of the ward. Child custody is by default free of charge. The guardian receives only child benefits, which he is obliged to spend strictly on the child. The amount of the allowance is established by regional legislation. But a guardian or candidate for guardianship may conclude an agreement with the guardianship authorities on the performance of all duties for a fee and receive additional cash payments. To do this, you need to write a special application.
Art. 16 FZ "On guardianship and guardianship"
Sample agreement on a foster familyPDF, 98 KB
If you sign such an agreement, the guardian will be paid a fee for raising the child. There is no need to report to the state for this money. Svetlana is also a contractual guardian.
There is no need to report to the state for this money. Svetlana is also a contractual guardian.
clause 9 of the Rules for the selection of guardians
After collecting all the documents, submitting applications and choosing a child, specialists from the guardianship authorities draw up an act on the appointment of a person as a guardian.
Costs of care
The activities of the guardian and the quality of life of the child are constantly monitored by the guardianship and guardianship authorities. Svetlana lives in the Ust-Tsilemsky district of the Komi Republic and, as a guardian, is attached to the local center for social protection. Once every six months, she receives checks from the guardianship authorities. Specialists look at the appearance of the ward, whether he has clothes and shoes for the season. They also ask the guardian about how the child communicates with peers, with family members.
Art. 24 of the Federal Law "On guardianship and guardianship"
Specialists also control the conditions in which the child grows up. In order to maintain the conditions of his life at the proper level, constant costs are needed to update repairs, purchase books, toys.
In order to maintain the conditions of his life at the proper level, constant costs are needed to update repairs, purchase books, toys.
The child must live with a guardian
By law, the guardian and the child must live together. Separation is allowed only when the child is 16 years old. This is possible only with the consent of social workers.
st. 36 Civil Code of the Russian Federation
Guardians must notify the guardianship authorities of any change of residence.
Personal space. In an apartment or house for a child, there must be a separate bed and a play area. In the act of checking the living conditions of a minor ward, which is compiled at each check, there is even a corresponding line.
If the child does not have a furnished personal space, the guardian will be obliged to equip it.
Cleanliness and order. The house should be clean: the floor and dishes are washed, the dust is wiped off.
At the time of the check, the kitchen must have cooked food, and the refrigerator must have food supplies for at least two days. Some welfare officers even look into pots to find out what the child is being fed.
Svetlana's ward loves to play consoles. His favorite game is TanksRepair. Every year Svetlana makes cosmetic repairs in the child's room. For example, she paints the floor and windows, glues wallpaper. It takes 2500-3500 R per year.
It is necessary to make annual repairs because the guardianship authorities carefully ensure that the child lives in a clean and renovated room. And if in ordinary families the repair in the room can be done when the parents themselves want it, in the guardian family, the guardianship authorities will ensure that it is always fresh.
The amounts Svetlana spends on supporting her son vary from month to month.
At first, the boy had clothes left over from his life in his family. This helped the mother-in-law save money in the first months of guardianship. At the same time, specialists from the guardianship authorities advised Svetlana not to buy expensive toys for her son, because he quickly broke them. Instead, they offered to purchase inexpensive construction sets so that the child develops fine motor skills of the hands.
At the same time, specialists from the guardianship authorities advised Svetlana not to buy expensive toys for her son, because he quickly broke them. Instead, they offered to purchase inexpensive construction sets so that the child develops fine motor skills of the hands.
Svetlana regularly gives her ward something that goes beyond the budget. For example, over the past year, she bought him a smartphone, new clothes for school, as well as a jacket and trendy sneakers.
On the wall in Svetlana's house there is a daily routine of her ward. Warm clothes and shoes for a child are one of Svetlana's most significant expenses. She lives in the north, so she has to be responsible in the choice of children's winter clothesHow much does guardianship cost
| Already purchased | |
|---|---|
| Clothing and footwear | 7000 R |
| Desk | 4000 R |
| Toys and books | 3000 R |
| Bed | 2000 R |
| Chair | 1500 Р |
| Total | 17 500 Р |
Already purchased
Clothing and footwear
7000 R
desk
4000 4000 R toys and books
3000 3000 R
bed
200002 SELE
1500 R
CON Had to spendI had to spend
trips to the guardianship authorities and hospital
2000 R
Paid physical examination
1500 R
toys and books
1000 r 9000
1000 R0003
Total
5500 R
| Expenses | Per month | per year |
|---|---|---|
| Home and school meals | 8000 P | 96 000 Р |
| Transport and medicine | 3000 R | 36 000 R |
| Unexpected expenses | 2500 R | 30,000 R |
| Clothes and toys | 2000 R | 24 000 Р |
| Large purchases | - | 15 000 R |
| Room renovation | - | 3000 R |
| Total | 15 500 R | 204 000 Р |
Costs
per month
per year
Power supply house and at school
8000 R
96 000 R
Transport and Medicine
3000 3000 r
36 000 R
Unexpected expenses
2500 R
30 000 000 000 0002 Clothing and toys
20000 2 24 000 2 24 000 R
Large purchases
-
15 000 R
Repair in the room
-
3000 R
Total
15 500 R
204 000 R
Payments for a child under guardianship of
First, guardianship authorities give the guardian a single payment. In 2012, when the child was transferred to the family, Svetlana received about 14,000 R. The region also transferred 10,89 monthly9 R - this money must be spent on a child and accountable for them to the state. Every other month, Svetlana was given 1410 R to repair the house.
In 2012, when the child was transferred to the family, Svetlana received about 14,000 R. The region also transferred 10,89 monthly9 R - this money must be spent on a child and accountable for them to the state. Every other month, Svetlana was given 1410 R to repair the house.
Art. 12.2 of the Federal Law "On state benefits to citizens with children"
Art. 37 Civil Code of the Russian Federation
art. 3 Law of the Republic of Komi on state support when transferring a child to a family
Every year, the amounts of payments are indexed: for example, from February 1, 2023, a one-time payment to a guardian is 22,909 R. The amounts of other payments depend on the region and the age of the child under guardianship.
In addition, the boy's bank account receives alimony from his own father. But this money cannot be used without the knowledge of the guardianship authorities. Svetlana once removed alimony to buy clothes and a bicycle for her son.
At first, Svetlana was a guardian for free and did not receive monthly payments.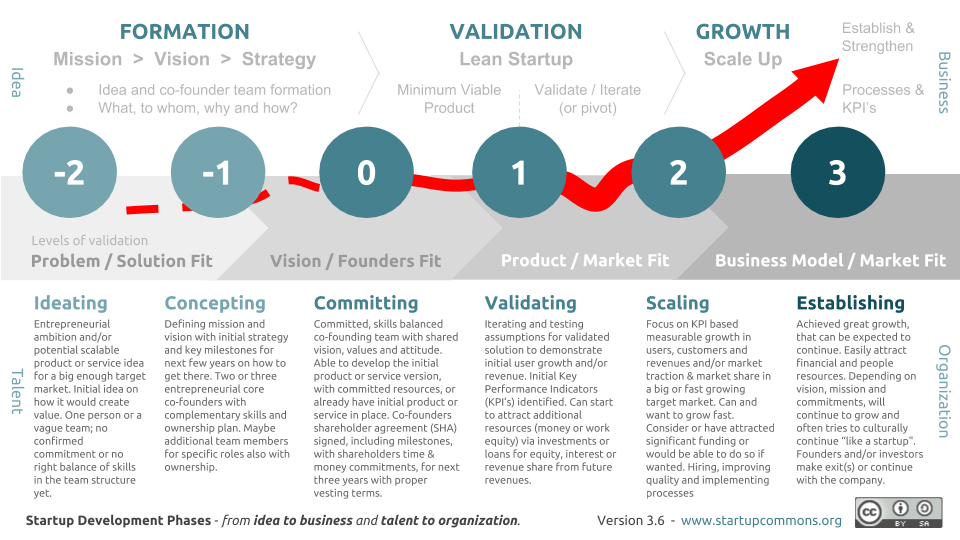 In 2014, social security specialists offered her to conclude an agreement on paid guardianship: she went with her son to doctors in Syktyvkar several times a year and spent a lot of money on it. Svetlana agreed to such help. After that, according to the agreement, she, as a guardian, began to receive about 8,000 RUR from the region every month. This money does not have to be spent only on a child.
In 2014, social security specialists offered her to conclude an agreement on paid guardianship: she went with her son to doctors in Syktyvkar several times a year and spent a lot of money on it. Svetlana agreed to such help. After that, according to the agreement, she, as a guardian, began to receive about 8,000 RUR from the region every month. This money does not have to be spent only on a child.
Art. 16 of the Federal Law "On guardianship and guardianship"
paragraph 6 of the letter of the Ministry of Education and Science No. 06-364
Svetlana also enjoys benefits for the rest of the ward. For example, she sent him to a camp and a sanatorium on discounted vouchers. The boy went to the camp from school as a child from a foster family, and to the sanatorium from the hospital on the testimony of a doctor.
Decree of the Government of the Republic of Komi on the development of a system for the rehabilitation and recreation of children
Every year, no later than February 1, the guardian submits to the guardianship and guardianship authorities a written report on the expenses for the child on a special form.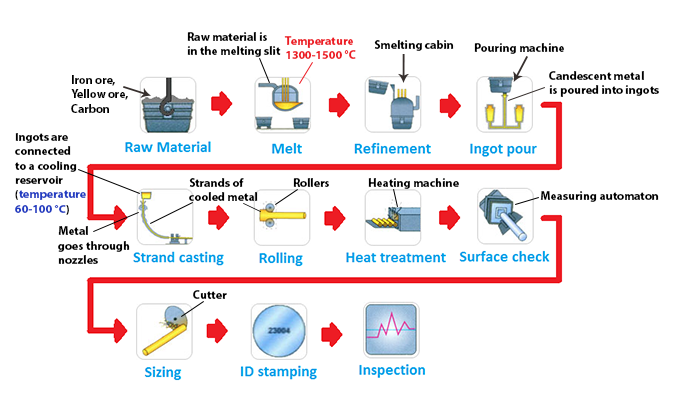 It reflects how the guardian used the state allowance and disposed of the property of the ward.
It reflects how the guardian used the state allowance and disposed of the property of the ward.
Art. 25 of the Federal Law "On guardianship and guardianship"
It also records how much money the guardian spent on the treatment of the child and on durable goods. The report is accompanied by checks that confirm the costs.
paragraph 1 of Art. 148 SK RF
Svetlana lives in a village, and some stores there simply don't issue checks. But especially for the report, she asks the sellers for them. Checks are not needed just for food, basic necessities, and household items such as soap, toothpaste, and brushes.
The report of the guardian is kept in the personal file of the ward.
Svetlana keeps a notebook where she writes down the expenses for clothes, toys and other things for the ward. Sometimes the guardianship authorities require such notebooks as additional evidence of how she spent the allowance on her son. The annual amount of expenses for a child must not be lower than the amount of payments received for himDifficulties
If the guardian does not pass one of the regular social security checks or shows himself on a negative side, the guardianship authorities can take the child.
Art. 148.1, 65 SK RF
art. 36 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
The following situations are also unacceptable for a guardian:
- The child is systematically left at home without adult supervision.
- No food at home.
- The guardian abuses alcohol, and this was recorded by social workers or confirmed by witnesses.
- A child comes to kindergarten or school dirty, in torn clothes.
- The child himself complained to the guardianship authorities about the guardian.
To raise a child, a caregiver must lead a healthy lifestyle and be positive in every way.
Svetlana's ward has problems with studies. Guardianship specialists know that the boy is not doing well in some subjects. They are periodically interested in whether there are improvements in the development of the school curriculum and why difficulties arise. Svetlana has to constantly motivate her ward to study well so that the family does not have problems with guardianship authorities.
Psychological moments of guardianship
At the beginning of guardianship, Svetlana did not bring guests to the house. It was the advice of the guardianship authorities - so that the child quickly adapts to the new environment. The future guardian must be ready to temporarily limit ties with the outside world and fully devote himself to the child being cared for.
Svetlana sometimes quarrels with the ward and takes the boy's pranks and misdeeds very close to her heart, which makes her very nervous. But when everything is fine, Svetlana is happy. Most of their life passes in mutual understanding. The boy calls Svetlana mom.
Svetlana's own children accepted her choice: to raise a child from an orphanage. They communicate with the boy on an equal footing and do not focus on the fact that he was not born in their family. This is important for both the guardian and the ward.
This is important for both the guardian and the ward.
Remember
- Child custody is a big responsibility. Especially if the ward has health problems. The guardian needs to be ready to take the child to doctors, take him to other cities for examinations and send him to sanatoriums.
- Being a guardian is not a way to earn money. Rather, on the contrary, state payments for the maintenance of a child are not always enough.
- The guardian needs to find out from the guardianship authorities and the school about all possible types of social assistance for the child - preferential vouchers and additional payments. This will help reduce family expenses.
How do I get custody of a child, elderly or disabled person?
What is guardianship?
In Russia, citizens who need guardianship include minors, that is, children under 14, as well as persons recognized by the court as incompetent. We are talking about people who, due to a mental disorder, cannot understand the meaning of their actions or control them.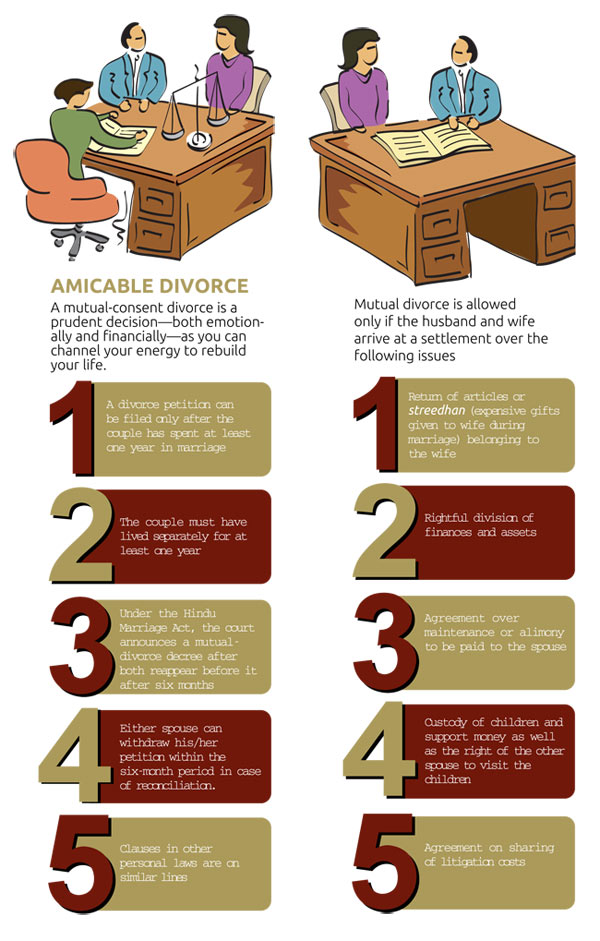 This is stated by the Federal Law "On guardianship and guardianship". Based on the document, citizens appointed by the body of guardianship and guardianship "are the legal representatives of the wards, and perform on their behalf and in their interests all legally significant actions."
This is stated by the Federal Law "On guardianship and guardianship". Based on the document, citizens appointed by the body of guardianship and guardianship "are the legal representatives of the wards, and perform on their behalf and in their interests all legally significant actions."
Guardianship is aimed at protecting the interests of the listed categories of citizens, as well as the very possibility of declaring a citizen legally incompetent. This was also emphasized by the Constitutional Court in the framework of Resolution No. 15-P dated June 27, 2012 “On the case of checking the constitutionality of paragraphs 1 and 2 of Article 29, paragraph 2 of Article 31 and Article 32 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in connection with the complaint of citizen I.B. Business".
How is guardianship different from guardianship?
In addition to guardianship, there is also guardianship, under which adolescents aged 14 to 18, as well as persons with limited legal capacity, can fall. Such people cannot be fully responsible for their actions. This category has more rights than minors and the incapacitated. For example, they can independently perform small everyday transactions and actions provided for by law (dispose of their own income, etc.). However, in other cases, they are obliged to assist the trustee.
Such people cannot be fully responsible for their actions. This category has more rights than minors and the incapacitated. For example, they can independently perform small everyday transactions and actions provided for by law (dispose of their own income, etc.). However, in other cases, they are obliged to assist the trustee.
It turns out that the guardian has more rights and obligations than the guardian, and therefore a greater responsibility falls on him.
Who can become a guardian or custodian?
The main requirement for a candidate is full legal capacity. And since it comes from the age of 18, the guardian must be of age. The law also establishes a list of restrictions. Guardianship cannot be issued by persons:
- deprived of parental rights;
- having an unexpunged or outstanding conviction for an intentional crime against life or health;
- who did not agree to become a guardian.
When it comes to guardianship of young children (under 14), additional restrictions are set. Future guardians must undergo special psychological, pedagogical and legal training, as well as prove that they are in a bisexual marriage. Those who have registered a same-sex marriage in the territory of another state will not be able to arrange guardianship.
Future guardians must undergo special psychological, pedagogical and legal training, as well as prove that they are in a bisexual marriage. Those who have registered a same-sex marriage in the territory of another state will not be able to arrange guardianship.
Arranging child custody
This process is supervised by guardianship authorities. To find out all the details of the procedure, you must contact the district office. The state is interested in ensuring that children are not left unattended, are not placed in orphanages and boarding schools, and therefore, most likely, those who wish to arrange guardianship will be met halfway and will be helped in every possible way.
The candidate needs to write an application, collect documents confirming, among other things, the passage of special training, and in case of a positive answer, sign an agreement.
How can I get guardianship of an elderly incapacitated person?
The algorithm is the same as for children - the guardianship and guardianship authority will also deal with the issue of guardianship. However, there are also differences. Thus, custody of an elderly or adult person does not always involve the joint residence of the guardian and his ward. This issue is decided individually, but cohabitation, of course, is welcome. It is much easier for a guardian to fulfill his duties and provide supervision, especially when it comes to a pensioner who, most likely, has a sufficient number of health problems.
However, there are also differences. Thus, custody of an elderly or adult person does not always involve the joint residence of the guardian and his ward. This issue is decided individually, but cohabitation, of course, is welcome. It is much easier for a guardian to fulfill his duties and provide supervision, especially when it comes to a pensioner who, most likely, has a sufficient number of health problems.
If cohabitation is intended, consent must be obtained from all family members of the guardian living in the same dwelling, including children aged 10 and over.
How to get paid guardianship?
There are two types of guardianship:
- gratuitous;
- paid.
In the first case, nothing is paid to the guardian. Paid guardianship can have quite flexible conditions, which are fixed by the contract. In accordance with Article 16 of the Federal Law “On Custody and Custody”, remuneration can also be paid at the expense of third parties, from the income from the property of the ward (no more than 5% and only if he is already an adult), as well as from the budget .
Features of the legal status
The guardian has an unlimited range of powers - he represents the interests of the ward in any relationship, no matter what is discussed. Moreover, this rule applies even when registering custody of a minor with living parents. If the ward is a child, then the guardian acts as a father or mother. However, in some cases notification of guardianship authorities is required. They can also establish restrictions on the actions of the guardian or, conversely, oblige him to perform any actions. All this is recorded in the act on the appointment of a guardian or custodian, or in an agreement on the implementation of guardianship or guardianship.
What documents are required for registration of guardianship?
- Written statement of consent to the establishment of guardianship.
- Documents of the guardian: proof of identity, proof of income, no criminal record, state of health (medical certificate in the form established for persons wishing to obtain guardianship), marital status and the right to use the living quarters.