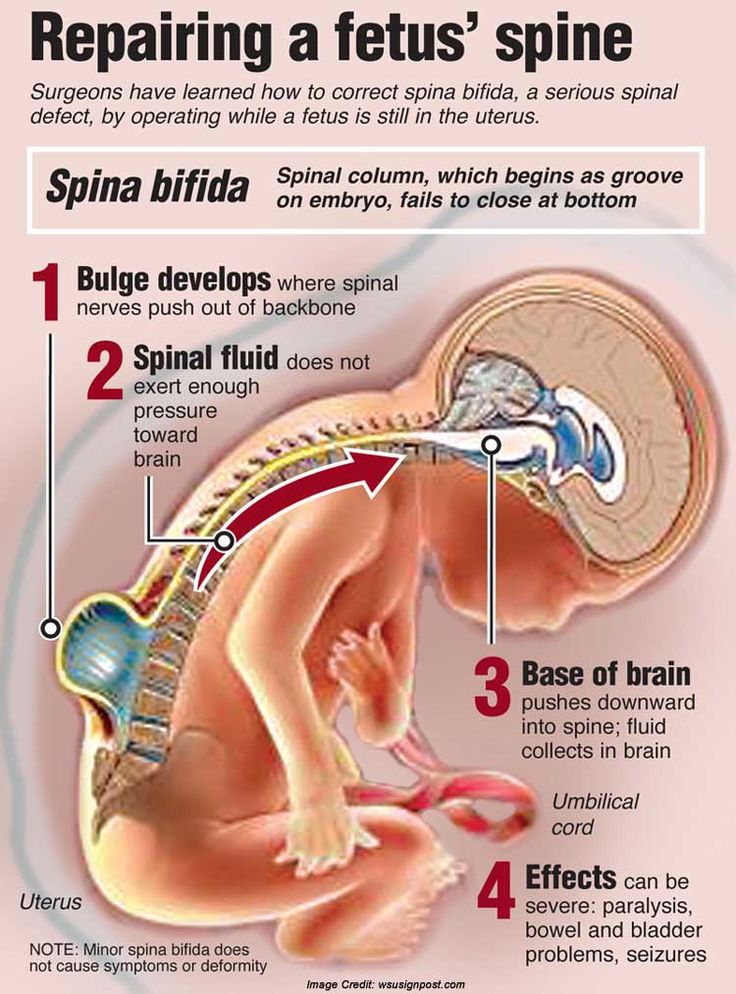
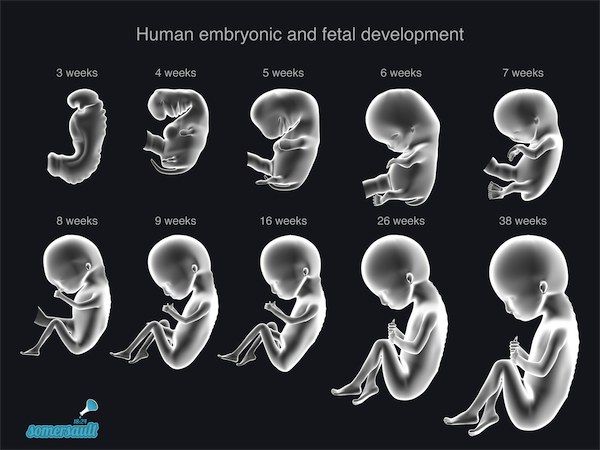
Yellow discharge after miscarriage
What happens after a loss?
Every person’s experience after a loss is different, physically and emotionally. This means that there’s no “one size fits all” explanation for your loss or for what comes afterwards, but we can tell you what you’re most likely to expect, mentally and physically, and how it will impact your Ovia account.
What happens to my Ovia account after a loss?
The experience is slightly different if you let us know in Ovia Pregnancy or Ovia Fertility.
Ovia Pregnancy
If you’ve reported a loss in Ovia Pregnancy, you will have the option to reset your account or start a new pregnancy. If you choose neither and tap the back arrow in the top left corner, your “Home” timeline will remain frozen on the day that you reported the loss, until you reset it. You will no longer receive updates or emails for this pregnancy.
Ovia Fertility
If you’ve reported a loss in Ovia Fertility, Ovia uses a combination of data logged in the past few months and new data to make future period projections — though you may or may not see a prediction for the next cycle depending on when you logged your last period. When you’re ready to start logging cycle data again, Ovia will use this information to make more accurate predictions. While past data will not be erased from your calendar, it will not be used to create future predictions.
In addition to reporting loss through the app (found in the “More” menu), you can add a Note to your Timeline with as much additional information as you’d like.
What happens to my body after a loss?
Some of the most common and normal physical changes you might experience include:
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting lasting for 1-3 weeks
- Brown or yellow cervical mucus
- Abdominal cramps and pain
- A decline in your hCG hormones (determined via lab work)
Normal physical changes you may experience a week or more afterwards include:
- A continued drop in your hCG hormones
- A delayed first period (you won’t menstruate until your hCG levels return to almost zero, which takes about 4-8 weeks depending on how far along you were).
 You won’t ovulation during the first cycle following a miscarriage, even if you get a false reading with an ovulation test.
You won’t ovulation during the first cycle following a miscarriage, even if you get a false reading with an ovulation test. - An irregular period for up to 3 months
- Lingering pregnancy symptoms
- A partially dilated cervix, which can make you more susceptible to infection. Wait until after your first period to have sex, put anything in your vagina or go swimming.
Which symptoms are dangerous?
Any of the following post-miscarriage symptoms are considered serious. Contact your healthcare provider if you’re experiencing:
- Bleeding on and off for several weeks without fully stopping
- Heavy, severe bleeding, especially if it contains clots (i.e. ie soaking through a pad in an hour or less)
- Fever of 100.4F or higher, or other signs of infection
Most complications that arise after a loss are the result of tissue that hasn’t cleared your body yet and can cause infections or hemorrhaging.
Medical procedures associated with miscarriages
Many people who experience a miscarriage don’t have symptoms like heavy bleeding or cramping, and only find out they’re experiencing a loss at an appointment to check on their pregnancy. It can be shocking and difficult to process a silent miscarriage. Whether you had miscarriage symptoms or not, in addition to the emotion surrounding loss, you’ll be given options about how to proceed medically and physically. These options may include waiting until your body begins to miscarry on its own, taking medication to cause your body to miscarry without waiting, or having a surgical procedure to remove all pregnancy tissue. There are risks and benefits to each choice, and it is a highly personal medical decision.
It can be shocking and difficult to process a silent miscarriage. Whether you had miscarriage symptoms or not, in addition to the emotion surrounding loss, you’ll be given options about how to proceed medically and physically. These options may include waiting until your body begins to miscarry on its own, taking medication to cause your body to miscarry without waiting, or having a surgical procedure to remove all pregnancy tissue. There are risks and benefits to each choice, and it is a highly personal medical decision.
About half of those who experience pregnancy loss end up having one of two common procedures called a dilation and curettage (D&C) or a dilation and evacuation (D&E). Performed to stop bleeding and prevent infection, these procedures dilate your cervix and remove all of the pregnancy tissue from your uterus. The difference between them is typically the timing. A D&C is common in the first trimester, while a D&E is often needed for second trimester losses.
Either procedure typically takes about 20-30 minutes. You’ll receive pain medication or general anesthesia beforehand. If you need a D&E you may have medication placed in your cervix or given to you to take by mouth the night before. During the procedure, your doctor will remove the retained tissue from your uterus by passing through your dilated cervix with either a curette instrument or a suction tool. Most people are able to leave the hospital or surgery center the same day they receive the procedure.
Afterwards, you can expect cramps, spotting, and bleeding for up to two weeks. Avoid any vaginal penetration, including sex and tampons, or swimming during your recovery.
Can I get pregnant again?
A majority of those who suffer a miscarriage go on to have healthy pregnancies. Although some people may have hormonal imbalances or other conditions that heighten the likelihood of miscarriage, it appears that most miscarriages are independent events that happen randomly. According to the Mayo Clinic, less than 5% of pregnant people will experience two consecutive miscarriages, and only about 1% will suffer three. If you believe you’re prone to miscarriages, your doctor can perform genetic tests, blood tests, or ultrasounds that can help determine whether your miscarriage was the result of a specific condition.
According to the Mayo Clinic, less than 5% of pregnant people will experience two consecutive miscarriages, and only about 1% will suffer three. If you believe you’re prone to miscarriages, your doctor can perform genetic tests, blood tests, or ultrasounds that can help determine whether your miscarriage was the result of a specific condition.
Though some people may want to give it some time in between attempts because of the physical or emotional toll of miscarriage, there is no evidence that any waiting period is necessary before trying to conceive again. It’s really up to you, your partner, and your healthcare provider to decide if you’re ready.
Sources
- “Dilation and Curettage (D&C).” Mayo Clinic. Mayo Clinic, 2/15/2014. Web.
- Mayo Clinic Staff. “Micarriage.” Mayo Clinic. Mayo Clinic, 7/9/2013. Web.
- Leann Mikesh, PhD. “hCG Levels After a Miscarriage.” Livestrong. Livestrong, 4/16/2015. Web.
- “Miscarriage.
 ” Planned Parenthood. Planned Parenthood, n.d. Web.
” Planned Parenthood. Planned Parenthood, n.d. Web.
5 Most Common Questions Answered
What are the types of yellow discharge?
In order to know whether your discharge is considered normal, a few factors should be considered. There are many different types of vaginal discharge, and a quick assessment of the amount, color, consistency, phase of your menstrual cycle, and scent of your vaginal discharge can hint at whether you need to make an appointment with a gynecologist.
If your yellow discharge is odorless, you probably don’t need to be concerned. Discharge with a smell may indicate an infection of some sort. If you have yellow discharge without odor, the color may be due to factors besides an infection.
Light-yellow or pale-yellow discharge without odor and other accompanying symptoms, such as vaginal burning or itching, may be considered normal.
Bright yellow discharge or thick yellow discharge — especially with an accompanying odor — is not considered normal. This usually indicates an infection.
This usually indicates an infection.
Is yellow discharge normal?
In certain circumstances, yellow discharge is considered normal. A few days before your period, you may notice a creamy or sticky, pale-yellow discharge.
Leading up to your period, the discharge may darken as a small amount of blood may mix with the discharge until it turns into the flow of your period.
As your period begins to lighten, the color of the blood will change from red to brown and eventually to a brownish-yellow. This yellow discharge that you’ll notice for a few days is just leftover menstrual fluid exiting your uterus.
Yellow discharge is not considered normal when it is accompanied by a bad smell, itchiness, soreness, pelvic pain, or pain when urinating.
What causes yellow discharge?
If you have yellow discharge and you’re pretty sure it isn’t related to your period, several other things could be causing it.
Yeast infection
The vagina needs to maintain a specific environment in order to stay healthy.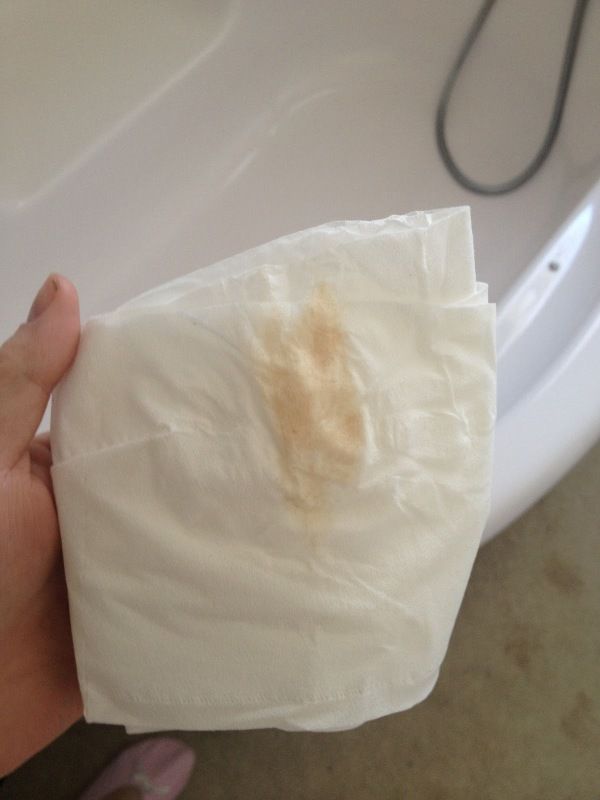 The pH, moisture level, and balance of bacteria all work together to create optimal conditions. When one of them varies for any reason, it can lead to an infection. Things like increased sexual activity, douching, taking antibiotics, and hormonal imbalances or changes can disrupt this delicate ecosystem and lead to an overgrowth of “bad” microbes.
The pH, moisture level, and balance of bacteria all work together to create optimal conditions. When one of them varies for any reason, it can lead to an infection. Things like increased sexual activity, douching, taking antibiotics, and hormonal imbalances or changes can disrupt this delicate ecosystem and lead to an overgrowth of “bad” microbes.
Vaginal yeast infection, also called candidiasis, is a common and treatable condition. It occurs when the vagina’s normal yeast multiply out of control.
The most common symptoms of a yeast infection are:
- Itching and irritation of the vulva and vagina
- Swelling and redness of the vulva
- Vaginal pain and soreness
- Pain during sex
- Pain, discomfort, or a burning sensation when urinating
- Clumpy discharge often described as looking like “cottage cheese”
If you notice these symptoms plus whitish-yellow discharge, you may have a yeast infection.
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis — sometimes called “trich” — is a common and treatable sexually transmitted infection (STI). Lots of people affected with trichomoniasis do not know they have it because many cases are asymptomatic.
Lots of people affected with trichomoniasis do not know they have it because many cases are asymptomatic.
The typical symptoms are:
- Green or yellow discharge that is frothy with an unpleasant smell
- Swelling and redness of the vulva and vagina
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Pain or discomfort during urination
- Pain or discomfort during sex
Trich is treated with antibiotics. A person who is diagnosed with trich should inform all of their sexual partners even if they do not have symptoms.
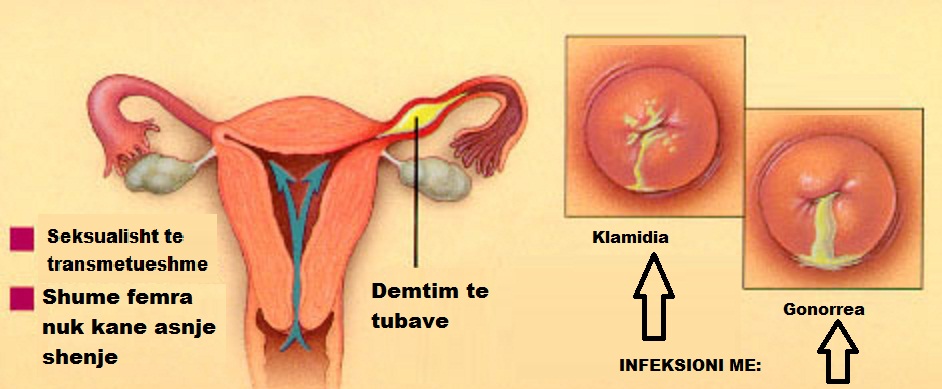
Chlamydia or gonorrhea
Chlamydia and gonorrhea are both STIs that are often asymptomatic. These common infections are easily treated with antibiotics. If left untreated for a long time, they can lead to complications like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain due to adhesions, infertility, complications in pregnancy, and more.
That’s why it’s a good idea to get tested for STIs frequently, especially if you’ve recently had sex with someone new or have multiple sexual partners.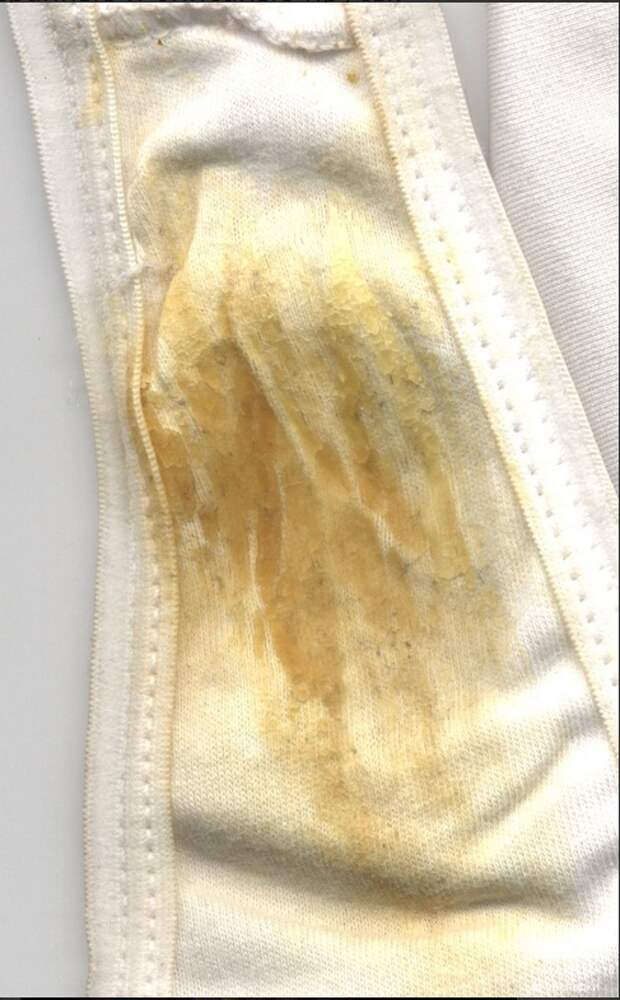
Common symptoms of chlamydia and gonorrhea include:
- Increased vaginal discharge
- Pain or burning during urination
- Pelvic pain
- Vaginal bleeding between periods
Pelvic inflammatory disease
When an infection like chlamydia or gonorrhea goes untreated, it can spread inside the pelvis to the uterus, uterine tubes, and ovaries, leading to a condition called pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Many different types of bacteria can cause PID. Left untreated, it can lead to a wide range of complications, including pregnancy complications like extrauterine pregnancy, miscarriage, or chronic pelvic pain.
It’s worth making note of the symptoms of PID, which include:
- Pain in the lower abdomen and pelvis
- Irregular periods
- Spotting or bleeding during or after intercourse or between menstrual cycles
- Green or yellow discharge that has a foul smell
- Painful sex
- Painful urination
- Fever, chills, or nausea accompanying these symptoms
What does yellow discharge mean during pregnancy?
Pregnancy comes with lots of changes and symptoms due to increased hormones. Many pregnant people will experience an increase in vaginal discharge during pregnancy because estrogen and progesterone levels, which affect vaginal discharge, are at an all-time high.
Many pregnant people will experience an increase in vaginal discharge during pregnancy because estrogen and progesterone levels, which affect vaginal discharge, are at an all-time high.
Normally, vaginal discharge during pregnancy — also called leukorrhea — is thin, white, and mild-smelling. Slightly yellow discharge without odor may also be perfectly normal.
However, if you notice green or yellow discharge that has a foul smell, it might signal a vaginal infection. One of the most common infections during pregnancy is a yeast infection. Yellow discharge should definitely be checked by a health care provider, especially if it is accompanied by itching, swelling, or pain in or outside the vagina.
If you have a yeast infection, bacterial vaginosis, or an STI when you give birth, the baby could get exposed to infection. It’s important to visit a health care provider right away if you suspect an infection during pregnancy.
How is yellow discharge treated?
In order for your health care provider to treat yellow discharge, they must first diagnose you. If you have a yeast infection, a health care provider may prescribe an antifungal cream, ointment, tablet, or suppository. Your treatment plan will vary based on the severity of your symptoms.
If you have a yeast infection, a health care provider may prescribe an antifungal cream, ointment, tablet, or suppository. Your treatment plan will vary based on the severity of your symptoms.
Bacterial infections and STIs like the ones mentioned above are treated with antibiotics. Starting treatment as soon as possible can keep the infection from spreading and causing a more serious condition such as pelvic inflammatory disease.
Conclusion
If you have a vagina, you’re going to experience vaginal discharge. It’s important to know how to identify whether your discharge may be abnormal. Clear, white, or slightly yellow discharge that does not have an odor and accompanying symptoms is typically harmless. However, if your discharge is green or yellow and has a foul smell, you may have an infection.
If you think you may have a vaginal infection, see a health care provider soon so you can start treatment if it’s needed.
90,000 types, volumes, duration - discharge.
Table of Table of Contents
- 1 Types of miscarriages
- 2 DISCOUNTIONS AND EARE PACK
- 3 DISCOUNTIONS IN LATION OF
- 4 DISCOUNTIONS AFTER
- 5 Pathological discharge after a miscarriage of
- 9000 5.1 Dark is dark brown discharge
- 5.2 Yellow and green discharge
- 5.3 No discharge
A miscarriage is a huge stress not only for the psyche, but also for the body of a woman. The fetus spontaneously detaches from the walls of the placenta, rupturing the blood vessels and forming an open wound in the place where it was located. So discharge during a miscarriage is a completely normal and physiologically determined phenomenon! nine0003
Types of miscarriages
There are two types of miscarriages. The first classification is based on the timing of the miscarriage, and distinguishes the following subtypes of miscarriages:
- Early: occurs before 12 weeks;
- Late: occurs from 12 to 22 weeks inclusive.
Late spontaneous abortion is no longer considered a miscarriage: it is either premature or term birth. In the first case, the child is born prematurely, and in the second, his health is practically not in danger. nine0003
The second classification groups miscarriages into stages of passage. It has the following types:
- Incomplete: the fertilized egg remains in the uterus;
- Complete: fetus comes out without surgery;
- Missed miscarriage, also known as miscarriage.
In addition to these variants, there are also recurrent miscarriages and anembryos, but these conditions are rare and do not have unusual symptoms worth highlighting separately. nine0003
Distinguishing the types of miscarriages is extremely important: depending on the period and stage of discharge, they can have a different shade, volume, consistency and duration. For example, with an early miscarriage, the discharge lasts up to five days, with a late one - much longer, and with a missed pregnancy, there is no bleeding at all.
However, despite all their differences, all types of miscarriages begin in the same way: first there are severe spasmodic pains in the lower abdomen, and only after a couple of days bleeding begins. With timely diagnosis of the threat of miscarriage, it can be prevented, so contact the clinic as soon as you feel persistent pain that is not associated with the cycle. nine0003
Early miscarriage discharge
Early miscarriage often goes unnoticed. If a woman does not follow her cycle too closely, she may not even know she is pregnant until the twelfth week! In such a situation, bloody discharge with clots in which the fetus comes out is taken for untimely menstruation.
The symptoms of an early miscarriage are really like the onset of menstruation. It is characterized by severe spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen, the next day after which heavy, but short-lived bleeding begins. After two or three days, it turns into a scanty spotting of red, brown or pink. nine0003
nine0003
The appearance of blood clots in such a situation indicates that the fetus is gradually leaving the uterus. For the early terms, it is precisely this disposal of the embryo that is characteristic: it is easier for the body to bring the dead fetus out in parts rather than completely. Sometimes there are exceptions, and instead of clots, a small gray bubble comes out of the vagina. This is a fetal egg, and its appearance indicates that the bleeding will soon stop.
But it often happens that the bleeding does not stop and does not weaken for a long time: from five days or more. This condition is typical for an incomplete miscarriage, during which the fetus cannot leave the uterus on its own. The resulting wound does not heal and continues to bleed with the same force as on the first day, causing weakness, deterioration of health and severe blood loss. In such a situation, it is necessary to clean, and do it as soon as possible: if the fetus is not removed from the uterus, this is fraught with serious complications, including infertility. nine0003
nine0003
Discharge in late miscarriage
Late miscarriage is much less common, but never occurs as quietly and imperceptibly as in the case of early spontaneous abortion. The symptoms that occur during this process are much more pronounced after the twelfth week: the bleeding becomes profuse and long, the lower abdomen hurts unbearably, and weakness and dizziness often occur.
How many days the discharge should go during a late miscarriage depends solely on the body of a particular woman, the period and general history. Most often, bleeding lasts from five to ten days, and then turns into a spotting brown discharge, which soon stops completely. With repeated miscarriage and some diseases, the duration of bleeding can reach two weeks. nine0003
If the discharge after a miscarriage without cleaning lasts more than two weeks, and also does not hurry to subside, this is an incomplete spontaneous abortion. This condition is characterized by weakness and dizziness, severe incessant pain in the lower abdomen and a general deterioration in well-being. Contacting a doctor in this situation should be immediate - such profuse blood loss is very dangerous for the body.
Contacting a doctor in this situation should be immediate - such profuse blood loss is very dangerous for the body.
A late miscarriage is a much more serious blow to the body than a spontaneous abortion that occurs before twelve weeks. That is why this condition requires a gynecological examination and the right treatment: if you engage in amateur activities or do nothing at all, the likelihood of a repeated miscarriage or infertility increases several times. nine0003
Discharge after cleansing
Cleaning for incomplete abortion may be medical or surgical. In the first case, tablets are used, after which the fetus leaves the body on its own, without surgical intervention. The discharge after cleaning the drug type lasts a long time and is quite plentiful, but this condition no longer poses a danger to the body.
Surgical cleaning, also known as scraping, is a much less pleasant process. The fetal egg and everything related to it is removed surgically, which provokes severe pain and heavy bleeding. Already after 4-5 days, it is replaced by brownish or pink discharge of a smearing type, which soon stops. nine0003
Already after 4-5 days, it is replaced by brownish or pink discharge of a smearing type, which soon stops. nine0003
After cleansing, the body must begin to restore the reproductive system. This process should take place under the full control of a gynecologist so that possible complications are treated and prevented even before they occur. Usually, recovery takes up to two months, and at least half of this period should pass without sex, heavy sports activities and carrying weights.
Pathological discharge after a miscarriage
Abnormal discharge after spontaneous abortion is considered to be both too long, profuse and unremitting bleeding, as well as discharge of other shades and consistency, uncharacteristic of a miscarriage. It has already been said about the normal timing and amount of blood released, but what do the discharges of other colors mean? nine0003
Dark brown discharge
The appearance of dark brown discharge, close to black, indicates serious complications in the body: it can be a polyp, endometritis, endometriosis or hyperplasia. They differ from normal brown secretions in a darker color, severe incessant pain in the lower abdomen, and in the case of endometritis, also in an unpleasant pungent odor.
They differ from normal brown secretions in a darker color, severe incessant pain in the lower abdomen, and in the case of endometritis, also in an unpleasant pungent odor.
Yellow and green discharge
Yellow or green discharge that occurs after a miscarriage indicates an inflammatory process that has begun in the genitourinary system of a woman. Most often, this condition occurs after scraping, however, even in the absence of cleaning, it is also not uncommon: the fetal egg remaining in the body disrupts the microflora and provokes infectious diseases.
No discharge
This symptom can be diagnosed after cleansing. If bleeding does not occur after drug delivery from the fetus or curettage, this means that blood accumulates inside the body. This condition is very dangerous and requires prompt examination and treatment! nine0003
Whatever type of miscarriage you have, it requires a mandatory examination and consultation with a gynecologist. This is a strong and dangerous shock for the body, which must be treated correctly and in a timely manner in order to avoid a similar problem in the future.
This is a strong and dangerous shock for the body, which must be treated correctly and in a timely manner in order to avoid a similar problem in the future.
Summary
what is the discharge during an early miscarriage, without cleaning, brown
Contents
According to statistics, 15 to 20% of pregnancies end in spontaneous termination. The causes of the tragedy may be different. But the consequences in the form of discharge after a miscarriage are a natural pattern of this process. nine0003
What are the discharges during miscarriage and its threat?
Miscarriage in medicine is called spontaneous abortion. This is how pregnancy is terminated before 22 weeks. From 2 to 12 weeks is classified as an early miscarriage, from 12 to 22 - late. Everything that happens after, refers to premature birth. Vaginal discharge is the main symptom by which this pathology can be determined.
With the onset of uterine bleeding, gradually increasing secretions are indicated. nine0144 Their color varies from pinkish to dark brown, unpleasant sensations are felt in the form of spasms and pulling pain in the lower abdomen. Which then appears, then disappears along with dizziness and nausea. If such symptoms appear, it means that a threat has arisen over the fetus and you should immediately call emergency care. In some cases, a quick visit to the doctor makes it possible to save the pregnancy. How the discharge looks like during a miscarriage, look at the photo:
nine0144 Their color varies from pinkish to dark brown, unpleasant sensations are felt in the form of spasms and pulling pain in the lower abdomen. Which then appears, then disappears along with dizziness and nausea. If such symptoms appear, it means that a threat has arisen over the fetus and you should immediately call emergency care. In some cases, a quick visit to the doctor makes it possible to save the pregnancy. How the discharge looks like during a miscarriage, look at the photo:
When a miscarriage occurs, the fetus completely leaves the uterus in the form of a dark bubble.
Miscarriage Discharge with clots
Why does the fetus reject?
The cause of spontaneous abortion is associated with many factors:
- Hormonal disorders in the body. When there is a deficiency of female progesterone or an excess of male androgen, then the expectant mother is prescribed hormonal drugs that minimize the risk of losing a child.

- Genetic disorders of the embryo. nine0006
- Stress, weakened immune system.
- Wrong way of life.
- Concomitant diseases, in particular from the field of gynecology.
- Injuries, physical and psychological stress.
In case of fetal freezing or incomplete delivery, uterine curettage is used.
Find out when your period comes after a miscarriage in one of our articles.
How long does the discharge last after a miscarriage and what is its nature without cleaning? nine0029
Blood discharge is a normal phenomenon that accompanies this pathology.
First of all, they are explained by the fact that during rejection, the embryo is detached from the walls of the uterus, as a result of which its tissues and blood vessels are injured. It turns out an open wound that causes bleeding.
During pregnancy, the size of the uterus increases several times, its walls are stretched. After a miscarriage, the muscles and tissues of this organ begin to contract intensively in order to return to their previous shape, which is accompanied by blood loss and rejection of the remaining particles of the embryo. nine0144 During this period, cramps and aching in the lower abdomen may be felt. In the early stages, the uterus is slightly enlarged, respectively, the fetus leaves a smaller wound and a cavity inside the organ, and therefore the discharge is moderate and ends, as a rule, faster, accompanied by minor discomfort.
nine0144 During this period, cramps and aching in the lower abdomen may be felt. In the early stages, the uterus is slightly enlarged, respectively, the fetus leaves a smaller wound and a cavity inside the organ, and therefore the discharge is moderate and ends, as a rule, faster, accompanied by minor discomfort.
The intensity and nature of bleeding depends on the duration of the fetus, the general condition of the woman, concomitant diseases and proper care during the recovery period, as well as whether cleaning was used. nine0003
How much is the average blood loss? Provided that there are no complications, the period of discharge after a miscarriage without cleaning ranges from 5 to 10 days. If they drag on for more than two weeks, it is worth contacting a specialist, as we can talk about an inflammatory process or incomplete removal of the embryo.
Discharge after miscarriage with purge
Sometimes the discharge may be in the form of large dark clots.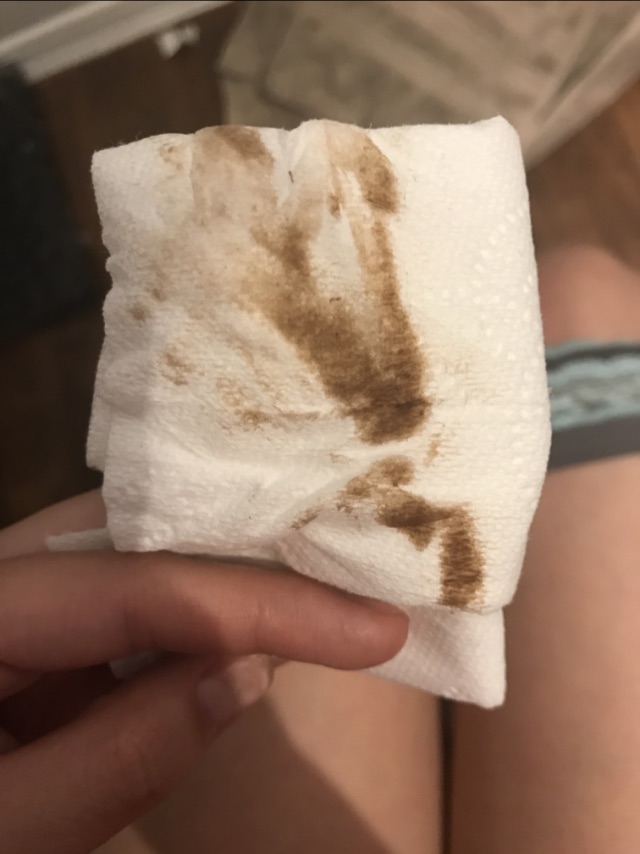 This is explained by the incomplete rejection of the fetus. Then the remains of the embryo are scraped, which affects the inner layer of the uterus - the endometrium. Surgical intervention and violation of the integrity of the tissue is not complete without bleeding. nine0143 If the miscarriage was cleaned in the second trimester, bleeding can last up to 14–20 days, as a large area of the endometrium and blood vessels is affected, and the uterus contracts longer and stronger. That is why in the second case the pains and spasms are felt more intensely. If the blood loss continues for more than the specified period, we are talking about a complication. The menstrual cycle is restored within a month, but the first 3-4 cycles are often delayed menstruation. Read about discharge after abortive curettage in more detail in the article at the link. nine0003
This is explained by the incomplete rejection of the fetus. Then the remains of the embryo are scraped, which affects the inner layer of the uterus - the endometrium. Surgical intervention and violation of the integrity of the tissue is not complete without bleeding. nine0143 If the miscarriage was cleaned in the second trimester, bleeding can last up to 14–20 days, as a large area of the endometrium and blood vessels is affected, and the uterus contracts longer and stronger. That is why in the second case the pains and spasms are felt more intensely. If the blood loss continues for more than the specified period, we are talking about a complication. The menstrual cycle is restored within a month, but the first 3-4 cycles are often delayed menstruation. Read about discharge after abortive curettage in more detail in the article at the link. nine0003
Pathological discharge
Normal discharge after spontaneous abortion is pink, scarlet, brown, and small dark clots may be observed in the first days. If no purge has been used, up to 10 days of bleeding is acceptable when it occurs, then up to 20 days is not to worry. Immediately after the termination of pregnancy, lingering pains, weakness can be felt, but over time, the discomfort subsides.
If no purge has been used, up to 10 days of bleeding is acceptable when it occurs, then up to 20 days is not to worry. Immediately after the termination of pregnancy, lingering pains, weakness can be felt, but over time, the discomfort subsides.
If, due to the rejection of the embryo, the discharge does not stop over the designated period and they do not decrease, but, on the contrary, their number increases, the painful sensations do not recede, then you are dealing with a complication or pathology. nine0003
Incomplete curettage
It is not uncommon for the embryo to be hatched incompletely and the cleaning was not effective. The remaining particles and cells of the embryo die off and rot in the womb. This process affects the internal tissues of the uterus, and sometimes it is transmitted to neighboring organs.
Inflammation and infection is a dangerous phenomenon for the health and even life of a woman. A prolonged rehabilitation period is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. This kind of complication will be indicated by pain transmitted from the lower abdomen to the side and back, fever, chills, dizziness, and even loss of consciousness. If measures are not taken in time, the next pregnancy will end in the same way or infertility will occur, but the most dangerous thing is the existence of a threat to the life of a woman. nine0003
This kind of complication will be indicated by pain transmitted from the lower abdomen to the side and back, fever, chills, dizziness, and even loss of consciousness. If measures are not taken in time, the next pregnancy will end in the same way or infertility will occur, but the most dangerous thing is the existence of a threat to the life of a woman. nine0003
Infections and bacteria
After a miscarriage, especially when a cleansing was used, an open wound remains in the uterine cavity. At this point, the body is especially vulnerable to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. Weakened immunity, abrupt hormonal changes make it unable to resist bacteria, infections and viruses. Therefore, the risk of developing inflammatory processes and gynecological ailments is high.
If the color of the secreted mucus has changed to white, green, yellow, an unpleasant smell of pus, rotten meat or cottage cheese has been added, itching and burning, then this indicates infectious diseases.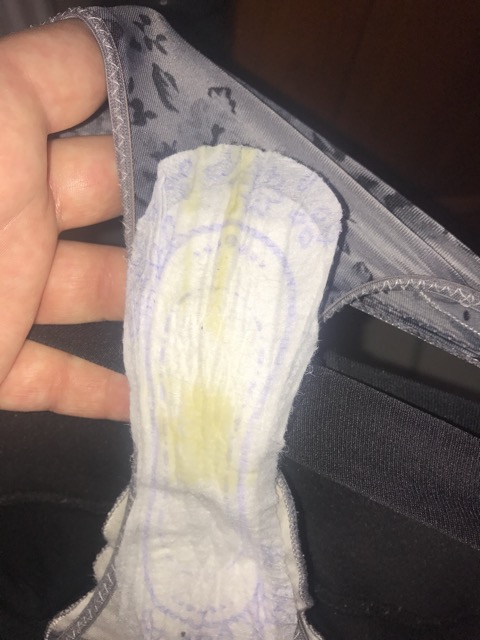 White clots of a curdled consistency with a sour-milk smell indicate the development of Candidiasis (thrush in everyday life). This ailment from a number of fungal infections is often exacerbated due to the growth of existing opportunistic particles in the microflora of the genital mucosa. This phenomenon occurs against the background of taking antibiotics, a weakened body and stress. nine0003
White clots of a curdled consistency with a sour-milk smell indicate the development of Candidiasis (thrush in everyday life). This ailment from a number of fungal infections is often exacerbated due to the growth of existing opportunistic particles in the microflora of the genital mucosa. This phenomenon occurs against the background of taking antibiotics, a weakened body and stress. nine0003
Bloody discharge with yellow or dirty white lumps with the smell of rotten fish is a symptom of bacterial vaginosis, provoked by the same bacteria in the microflora, reinforced from the outside by pathological microorganisms.
Recommendations during the rehabilitation period
To avoid complications, follow these simple rules:
- Avoid physical and emotional stress.
- Stay in bed for at least 5-7 days. nine0006
- Take all anti-inflammatory and restorative medicines prescribed by your doctor.
- Combine antibiotics with microflora balancers.
- Give up sexual activity for a while.