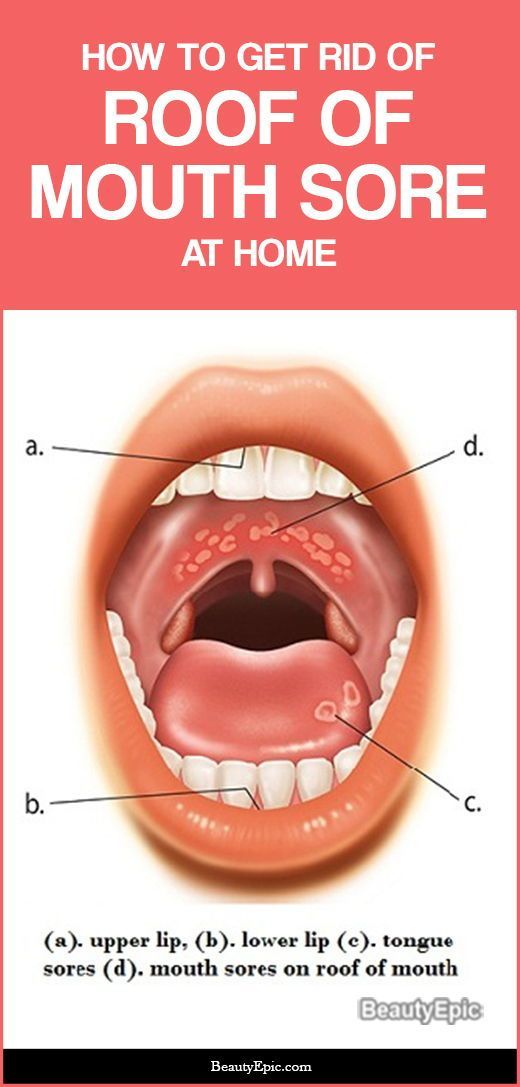
Yeast around the mouth
Oral thrush in adults - Illnesses & conditions
Oral thrush is a fungal infection of the mouth. It is not contagious and is usually successfully treated with antifungal medication.
It is also called oral candidosis (or candiasis) because it is caused by a group of yeasts called Candida.
Symptoms of oral thrush can include:
- white patches (plaques) in the mouth that can often be wiped off, leaving behind red areas that may bleed slightly
- loss of taste or an unpleasant taste in the mouth
- redness inside the mouth and throat
- cracks at the corners of the mouth
- a painful, burning sensation in the mouth
In some cases, the symptoms of oral thrush can make eating and drinking difficult.
When to seek medical advice
Speak to your GP if you develop symptoms of oral thrush. If left untreated, the symptoms will often persist and your mouth will continue to feel uncomfortable.
In severe cases that are left untreated, there is also a risk of the infection spreading further into your body, which can be serious.
Your GP will usually be able to diagnose oral thrush simply by examining your mouth. Sometimes they may also recommend blood tests to look for certain conditions associated with oral thrush, such as diabetes and nutritional deficiencies.
What causes oral thrush?
Low numbers of the fungus Candida are naturally found in the mouth and digestive system of most people. They don't usually cause any problems, but can lead to oral thrush if they multiply.
There are a number of reasons why this may happen, including:
- taking a course of antibiotics, particularly over a long period or at a high dose
- taking inhaled corticosteroid medication for asthma
- wearing dentures (false teeth), particularly if they don't fit properly
- having poor oral hygiene
- having a dry mouth, either because of a medical condition or a medication you are taking
- smoking
- having chemotherapy or radiotherapy to treat cancer
Babies, young children and elderly people are at a particularly high risk of developing oral thrush, as are people with certain underlying conditions, including diabetes, an iron deficiency or vitamin B12 deficiency, an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) and HIV.
As most people already have Candida fungi living in their mouth, oral thrush is not contagious. This means it cannot be passed to others.
Treating oral thrush
Oral thrush can usually be successfully treated with antifungal medicines. These usually come in the form of gels or liquid that you apply directly inside your mouth (topical medication), although tablets or capsules are sometimes used.
Topical medication will usually need to be used several times a day for around 7 to 14 days. Tablet or capsules are usually taken once daily.
These medications don't often have side effects, although some can cause nausea (feeling sick), vomiting, bloating, abdominal (tummy) pain and diarrhoea.
If antibiotics or corticosteroids are thought to be causing your oral thrush, the medicine – or the way it is delivered – may need to be changed or the dosage reduced.
Preventing oral thrush
There are a number of things you can do to reduce your chances of developing oral thrush, including:
- rinsing your mouth after meals
- brushing your teeth twice a day with a toothpaste that contains fluoride and interdental cleaning (flossing) regularly
- visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups, even if you wear dentures or have no natural teeth
- removing your dentures every night, cleaning them with paste or soap and water before soaking them in a solution of water and denture-cleaning tablets
- brushing your gums, tongue and inside your mouth with a soft brush twice a day if you wear dentures or have no or few natural teeth
- visiting your dentist if your dentures do not fit properly
- stopping smoking if you smoke
- rinsing your mouth with water and spitting it out after using a corticosteroid inhaler, and using a spacer (a plastic cylinder that attaches to the inhaler) when you take your medicine
- ensuring that any underlying condition you have, such as diabetes, is well controlled
If you have a condition or are receiving treatment that could put you at a high risk of developing oral thrush, your doctor may recommend taking a course of antifungal medication to prevent this happening.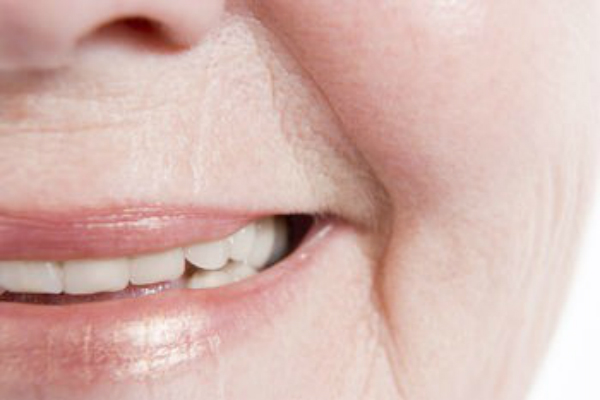
Read more about taking care of your oral health.
Oral thrush - Symptoms and causes
Overview
Oral thrush
Oral thrush
Oral thrush produces slightly raised, creamy white, sore patches in your mouth or on your tongue.
Oral thrush — also called oral candidiasis (kan-dih-DIE-uh-sis) — is a condition in which the fungus Candida albicans accumulates on the lining of your mouth. Candida is a normal organism in your mouth, but sometimes it can overgrow and cause symptoms.
Oral thrush causes creamy white lesions, usually on your tongue or inner cheeks. Sometimes oral thrush may spread to the roof of your mouth, your gums or tonsils, or the back of your throat.
Although oral thrush can affect anyone, it's more likely to occur in babies and older adults because they have reduced immunity; in other people with suppressed immune systems or certain health conditions; or people who take certain medications. Oral thrush is a minor problem if you're healthy, but if you have a weakened immune system, symptoms may be more severe and difficult to control.
Products & Services
- Book: Mayo Clinic Book of Home Remedies
Symptoms
Children and adults
Initially, you may not even notice symptoms of oral thrush. Signs and symptoms may include:
- Creamy white lesions on your tongue, inner cheeks, and sometimes on the roof of your mouth, gums and tonsils
- Slightly raised lesions with a cottage cheese-like appearance
- Redness, burning or soreness that may be severe enough to cause difficulty eating or swallowing
- Slight bleeding if the lesions are rubbed or scraped
- Cracking and redness at the corners of your mouth
- A cottony feeling in your mouth
- Loss of taste
- Redness, irritation and pain under dentures (denture stomatitis)
In severe cases, usually related to cancer or a weakened immune system from HIV/AIDS, the lesions may spread downward into your esophagus — the long, muscular tube stretching from the back of your mouth to your stomach (Candida esophagitis). If this occurs, you may experience difficulty swallowing and pain or feel as if food is getting stuck in your throat.
If this occurs, you may experience difficulty swallowing and pain or feel as if food is getting stuck in your throat.
Infants and breast-feeding mothers
In addition to the distinctive white mouth lesions, infants may have trouble feeding or be fussy and irritable. They can pass the infection to their mothers during breast-feeding. The infection may then pass back and forth between the mother's breasts and the baby's mouth.
Women whose breasts are infected with candida may experience these signs and symptoms:
- Unusually red, sensitive, cracked or itchy nipples
- Shiny or flaky skin on the darker, circular area around the nipple (areola)
- Unusual pain during nursing or painful nipples between feedings
- Stabbing pains deep within the breast
When to see a doctor
If you or your child develops white lesions inside the mouth, see your doctor or dentist.
Thrush is uncommon in healthy older children, teenagers and adults, so if thrush develops, see your doctor to determine if further evaluation is needed to check for an underlying medical condition or other cause.
Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free, and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips and current health topics, like COVID-19, plus expertise on managing health.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which
information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with
other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could
include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected
health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health
information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of
privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on
the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on
the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Causes
Normally, your immune system works to repel harmful invading organisms, such as viruses, bacteria and fungi, while maintaining a balance between "good" and "bad" microbes that normally inhabit your body. But sometimes these protective mechanisms fail, increasing the number of candida fungus and allowing an oral thrush infection to take hold.
The most common type of candida fungus is Candida albicans. Several factors, such as a weakened immune system, can increase your risk of oral thrush.
Risk factors
You may have an increased risk of oral thrush infection if any of these issues apply:
- Weakened immunity. Oral thrush is more likely to occur in infants and older adults due to reduced immunity. Some medical conditions and treatments can suppress your immune system, such as cancer and its treatments, organ transplantation and required drugs that suppress the immune system, and HIV/AIDS.

- Diabetes. If you have untreated diabetes or the disease isn't well-controlled, your saliva may contain large amounts of sugar, which encourages the growth of candida.
- Vaginal yeast infections. Vaginal yeast infections are caused by the same fungus that causes oral thrush. You can pass the infection to your baby.
- Medications. Drugs such as prednisone, inhaled corticosteroids, or antibiotics that disturb the natural balance of microorganisms in your body can increase your risk of oral thrush.
- Other oral conditions. Wearing dentures, especially upper dentures, or having conditions that cause dry mouth can increase the risk of oral thrush.
Complications
Oral thrush is seldom a problem for healthy children and adults.
For people with lowered immunity, such as from cancer treatment or HIV/AIDS, thrush can be more serious. Untreated oral thrush can lead to more-serious systemic candida infections. If you have a weakened immune system, thrush may spread to your esophagus or other parts of your body.
If you have a weakened immune system, thrush may spread to your esophagus or other parts of your body.
Prevention
These measures may help reduce your risk of developing candida infections:
- Rinse your mouth. If you need to use a corticosteroid inhaler, be sure to rinse your mouth with water or brush your teeth after taking your medication.
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily or as often as your dentist recommends.
- Check your dentures. Remove your dentures at night. Make sure dentures fit properly and don't cause irritation. Clean your dentures daily. Ask your dentist for the best way to clean your type of dentures.
- See your dentist regularly, especially if you have diabetes or wear dentures. Ask your dentist how often you need to be seen.
- Watch what you eat. Try limiting the amount of sugar-containing foods you eat. These may encourage the growth of candida.

- Maintain good blood sugar control if you have diabetes. Well-controlled blood sugar can reduce the amount of sugar in your saliva, discouraging the growth of candida.
- Treat a vaginal yeast infection as soon as possible.
- Treat dry mouth. Ask your doctor about ways to avoid or treat your dry mouth.
By Mayo Clinic Staff
Related
Associated Procedures
Products & Services
Oral candidiasis: symptoms, features, diagnosis and treatment of the disease
Article content:
- What is candidiasis?
- Causes of oral candidiasis URL
- Symptoms and features of the course of candidiasis in children
- Symptoms of oral candidiasis in adults
- Diagnosis of oral candidiasis
- Treatment of candidiasis
The health of our body directly depends on the condition of the oral cavity. However, if you thought that only the integrity of the teeth affects the state of the oral cavity, this is not so. In addition to dental units, the oral mucosa has no less impact on human health, which is an ideal breeding ground for various bacteria that can both strengthen the immune system and adversely affect the general condition of the body, causing various diseases. One of these ailments is oral candidiasis, which has no age restrictions, and therefore occurs in people of any age.
However, if you thought that only the integrity of the teeth affects the state of the oral cavity, this is not so. In addition to dental units, the oral mucosa has no less impact on human health, which is an ideal breeding ground for various bacteria that can both strengthen the immune system and adversely affect the general condition of the body, causing various diseases. One of these ailments is oral candidiasis, which has no age restrictions, and therefore occurs in people of any age.
What is candidiasis?
Oral candidiasis (thrush) is a white cheesy plaque on the oral mucosa caused by a unicellular fungus of the genus Candida. Ideally, this organism is present in a small amount among the beneficial microflora of the intestines, vagina, nasopharynx or on the skin of 70-80% of people. This state of affairs in medicine is considered the norm, since in small quantities this type of fungus is completely harmless. However, under the influence of certain factors, the acidic environment in the human body can become less concentrated, which will lead to an increase in the pH level and the reproduction of a fungus such as Candida.
Most often, oral candidiasis occurs in children and the elderly, who are forced to wear a denture, under which an ideal environment for the reproduction of the fungus is formed. Adults, whose immunity has weakened for one reason or another, also suffer from candidiasis.
Causes of thrush in the oral cavity
The following circumstances can serve as reasons for the appearance and development of candidiasis:
- Weakened immunity. These may be age-related changes or a deficiency of immune cells as a consequence of an illness.
- Pregnancy. In women who are in an “interesting” position, the hormonal background changes, which leads to metabolic disorders and a weakened immune system. As a result, the body turns into a favorable environment for the development of a harmful fungus.
- Taking antibiotics. Antibiotics destroy many representatives of beneficial microflora, and fungi resistant to its effects, on the contrary, begin to multiply.

- Radiotherapy (radiotherapy). Exposure to radioactive rays not only kills cancer cells, but also disrupts the microflora of the body.
- Wearing a denture. Under the design of the prosthesis, an ideal environment for the reproduction of harmful candidiasis organisms develops.
- Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs).
- Microtrauma of the oral mucosa.
- Chronic dysbacteriosis. For some organisms, an imbalance in the representatives of the microflora is a common condition. In such patients, the disease may be mildly chronic.
Also, among the factors that can cause the development of candidiasis, include some diseases that significantly weaken the immune system: tuberculosis, HIV, diseases of the digestive tract and adrenal glands.
Symptoms and features of the course of the disease in children
Children belong to the risk category, which is more susceptible to the "attack" of white Candida than adults. According to statistics, 20% of infants under the age of 1 year and 5% of newborn babies carry thrush, having become infected from the mother or from the staff of the maternity hospital. The reason for infection and active reproduction of the fungus is the immaturity of the oral mucosa, weak immunity, as well as the instability of the microflora, which is the norm for children of this age.
According to statistics, 20% of infants under the age of 1 year and 5% of newborn babies carry thrush, having become infected from the mother or from the staff of the maternity hospital. The reason for infection and active reproduction of the fungus is the immaturity of the oral mucosa, weak immunity, as well as the instability of the microflora, which is the norm for children of this age.
Fungus usually grows on the inside of a baby's cheeks. But the tonsils, tongue, and pharynx may also be affected. As a rule, identifying thrush at an early stage in infants is quite difficult. A slightly reddened oral cavity, on which there is no sign of plaque, does not cause concern for mothers. However, after a few days, characteristic grains appear in the baby's mouth, which in appearance resemble particles of semolina. If at this stage the treatment of oral candidiasis is not started, then small “semolina” dots will gradually turn into large curd-like lumps, and in some places into white films. Both those and other manifestations of the disease are easily removed with a sterile swab. After removing plaque, pink spots remain in place of lumps and films, and sometimes even droplets of blood appear.
Both those and other manifestations of the disease are easily removed with a sterile swab. After removing plaque, pink spots remain in place of lumps and films, and sometimes even droplets of blood appear.
If left untreated, the child's mouth becomes covered with a uniform white coating that hides the inflamed mouth. The child becomes capricious, refuses food and breast. There may also be an increase in temperature up to 39C.
Symptoms of oral candidiasis in adults
Candidiasis in adults, like in children, does not appear immediately. Therefore, the symptoms of the disease at different stages will vary. However, with an increase in the number of bacteria on the surface of the mucosa, the signs of the disease become more and more obvious.
- Slight redness, swelling and dry mouth. These are signs of the initial stage, when the fungus is just beginning to "conquer" the territory. Candida penetrate the cells and, releasing enzymes, dissolve the tissues of the mucosa.
 As a result, the patient experiences mild discomfort (it can also be more or less noticeable painful sensations).
As a result, the patient experiences mild discomfort (it can also be more or less noticeable painful sensations). - Appearance of white cheesy plaque. First, small, barely noticeable white grains appear on the mucous surface of the cheeks, gums, palate or tongue, which subsequently turn into clearly visible lumps and merge together into white films. At this stage, the flakes are easily removed, and red spots with small drops of blood are found under them. Also at this stage, the patient may experience slight itching and burning.
- Severe itching and burning. These symptoms of candidiasis indicate deep tissue damage and allergies, with which the body reacts to the release of enzymes by fungal organisms. At this stage, not only the mucous membranes of the cheeks, gums, tongue and palate can be affected, but also the pharynx and even the surface of the lips. Also at this stage, an increase in temperature and the appearance of mycotic seizures in the corners of the mouth are possible.

The most severe stage of candidiasis is the complete poisoning of the body with white candida enzymes, and, as a result, a significant weakening of the immune system. However, such severe manifestations are now extremely rare, since most patients seek to cure oral candidiasis, the symptoms of which do not yet indicate extreme stages.
Diagnosis of oral thrush
In order to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor performs a visual examination of the oral cavity and listens to the patient's complaints. In addition, the patient will also have to pass some tests, which include:
- scraping from the outer mucosa;
- blood test for sugar;
- clinical blood test.
After receiving the results of the laboratory test, the doctor will be able to make the correct appointment. Indeed, often the disease is a side effect of diseases such as diabetes, leukemia and gastrointestinal diseases. Accordingly, without eliminating the listed diseases, you should not hope for getting rid of thrush.
Treatment of candidiasis
The treatment of the disease in each individual case will be prescribed on an individual basis. However, in any system there will be drugs such as:
- Antimycotics (polyene antibiotics and imidazoles). They destroy candida not only on the surface of the oral mucosa, but also in other organs, contributing to the restoration of damaged tissues.
- Vitamins (B2, B6, C and PP). Helps strengthen the immune system.
- Calcium gluconate and iron. Calcium will reduce the manifestation of an allergic reaction, and the constant intake of new doses of iron into the body will restore the iron metabolism, which is disturbed due to the reproduction of candida.
- Preparations for local action (iodine, lysozyme tablets, levorin ointment). Means have a local effect on the foci of thrush.
- Rinsing solutions. These can be disinfectants and alkaline solutions that rinse your mouth every 2-3 hours.
It is also recommended to follow a diet during therapy, during which you should limit the amount of confectionery, spicy and sour foods, focusing on warm and semi-liquid dishes with a neutral taste.
Contact us for more information
Yeast infection - all you need to know
Definition
A yeast infection is commonly referred to as candidiasis. This is a widespread infection caused by the yeast Candida Albicans. Fungal infections are common in warm, moist areas of the body, including the mouth, intestines, vagina, throat, and moist areas of the skin.
Candida usually causes no problems and can live inside the body. Normally, the body's immune system is actively working to balance the growth of fungi. If the immune system changes, you can get candidiasis. When Candida gets out of control, you may experience a number of problems. Thrush occurs due to the abundance of fungi in the mouth. If it forms in the vagina, it is called a vaginal yeast infection.
Candidiasis is more likely to occur as a secondary infection in immunocompromised people. Candidiasis, moniliosis and thrush are synonymous with candidiasis. These organisms can be found in the mouth, gastrointestinal tract, genitals, and other parts of the body.
Fungi become pathogenic only under certain conditions. They can affect the oral cavity, vaginal area, penis, and other parts of the body. Thrush is the name of a type of candidiasis that affects the oral cavity. Oral candidiasis can be pseudomembranous, erythematous, and chronic hyperplastic.
Candidiasis is common in chronically ill people and newborns. It most often appears as white, soft, slightly raised plaques on the tongue and oral mucosa. The plaques look like cottage cheese and are composed of matted masses of fungal hyphae, desquamated epithelium, necrotic debris, keratin, leukocytes, fibrin, and bacteria. When the white plaque is removed, an erythematous area remains.
Antibiotic pain in the mouth is another name for erythematous candidiasis. This occurs after the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics or corticosteroids. Lesions present as persistently painful erythematous patches on the tongue, as well as atrophy of the central papillae. When the palate is involved and erythema occurs as a result of contact with the tongue, this is called kissing injury.
Candidal leukoplakia, also known as chronic hyperplastic candidiasis, is characterized by hard, white, persistent plaques on the lips, tongue, and buccal mucosa. These plaques may be uniform or nodular and may persist for years. This may be a precancerous condition.
Epidemiology of thrush
Candidiasis is more common in the elderly and children. Thrush affects approximately 37% of newborns in the United States during the first few months of their lives. Oral candidiasis is more common in children who use inhaled steroids. Quite common in pregnant women. Thrush can be an early sign of HIV infection. Thrush occurs worldwide and is more common in those who are malnourished. Thrush affects both men and women.
How does a yeast infection occur?
Yeast infections can occur for a number of reasons. As a result of fluctuations in hormones in some women, they appear during the menstrual cycle or during pregnancy. Some birth control pills can also make you more likely to develop a yeast infection.
Candida (yeast) is a form of fungus that can survive almost anywhere. It is normally present in the body; however, the immune system prevents it from spreading out of reach. Thus, infection occurs as most of the yeast multiplies inside the vagina.
Thrush can occur due to an imbalance in the natural balance between yeast and bacteria in the vagina. For example, antibiotics used to treat any bacterial infection can also kill lactobacilli. These are beneficial bacteria found in the vagina that inhibit the growth of yeast.
Fungal infections can be exacerbated by conditions that compromise the immune system, including sexually transmitted diseases. Women with diabetes who do not control their blood sugar are also at greater risk. This is due to the fact that elevated sugar levels stimulate the growth of yeast.
Yeast infections can sometimes also occur on the scrotum and penis, although this is less common. They can cause inflammation and redness around the penis or scrotum.
Generally, yeast infections are not STDs. They are not contagious and cannot be transmitted during sexual intercourse. However, intercourse can sometimes lead to fungal infections. This is because the body can react negatively to someone else's natural genital yeast or bacteria, causing the yeast to develop.
Yeast infection risk factors
The following factors may increase your chances of getting a yeast infection;
Use of antibiotics. Yeast infections are common in women who take antibiotics frequently. Broad-spectrum antibiotics that kill all bacteria often kill the good bacteria in the vagina, leading to yeast overgrowth.
High estrogen levels. In most cases, yeast infections are more common in women with higher estrogen levels. This includes pregnant women or women taking high doses of birth control or estrogen hormones.
Uncontrolled diabetes. Most women with poorly controlled blood sugar levels are more prone to yeast infections than women with well controlled blood sugar levels.
Immune system dysfunction: Women with weakened immune systems, including those due to corticosteroid injections and HIV infection, are most likely to develop yeast infections.
Types of yeast infections
Thrush (oropharyngeal candidiasis):
Thrush is an infection that occurs when Candida is spread in the throat and mouth. It is more common in the elderly, newborns, and people with weakened immune systems.
Oral candidiasis is a fungus that affects the oral mucosa and is one of the most common fungal infections. These ulcers are caused by the yeast Candida albicans. Candida albicans is a common component of the normal oral microbiota, with 30 to 50 percent of people carrying the fungus. With the age of the patient, the frequency of carriage increases. Candida albicans is found on the lips in 60% of patients over 60 with dentures.
In addition, adults are more likely to get thrush if they;
- Under treatment for cancer
- Taking medications such as corticosteroids or broad-spectrum antibiotics.

- Have diabetes
- Wearing dentures
Thrush may not cause any symptoms in the early stages. However, as the infection worsens, you may develop one or more of the following signs and symptoms;
- White or yellow bumps around the tongue, cheeks, lips, tonsils or gums
- If the bumps of the yeast infection are scraped off, you may have some bleeding.
- Burning and sore mouth
- Cotton sensation in the mouth
- Cracked and dry skin around the corners of the mouth
- Problems with swallowing
- Having an unpleasant taste in the mouth
- Loss of taste
In some cases, thrush can also affect the esophagus, although this is rare. A similar fungus associated with oral thrush can also cause a yeast infection in another part of the body.
Yeast infection is contagious to people who are at increased risk. This includes people with compromised body immune systems or who use certain medications. The infection is rarely transmitted through kissing or other intimate contact in healthy people. In most cases, thrush is not contagious, but it can still spread.
The infection is rarely transmitted through kissing or other intimate contact in healthy people. In most cases, thrush is not contagious, but it can still spread.
If you are afraid of contracting thrush from an infected person, refrain from contact with his saliva. When you are in close proximity to a person with thrush, it is recommended that you wash your hands as often as possible.
- Difference between "oral yeast infection" and "strep" infection.
A bacterial infection of the throat causes soreness and inflammation of the throat. Oral candidiasis is an opportunistic oral infection that often co-occurs with staphylococcus or streptococcus bacteria.
- Oral Yeast Infection and Simple Tongue Ulcer
Ulcers are painful sores that develop in the inside of the mouth. Ulcers are caused by stress, minor trauma to the inside of the mouth, sour fruits and vegetables, and hot, spicy foods.
Genital yeast infection or genital candidiasis:
Approximately 3 out of every four adult women will develop a yeast infection at any time in their lives. This happens if there is so much yeast growing in the vagina. Genital yeast infections can also occur in men, but are much less common.
Thrush usually occurs when the vaginal balance changes. Diabetes, pregnancy, use of certain medications, spermicides, lubricants, or a weakened immune system can contribute to this. Sometimes the infection can be passed from one person to another during sexual intercourse.
A vaginal or genital yeast infection can be associated with numerous signs and symptoms:
- Itching sensation in the vagina and vulva.
- White and thick cheesy vaginal discharge.
- Swelling of the vulva and vagina.
- Small cracks and tiny cuts in the skin around the vulva due to looseness of the skin.
- Burning sensation in thrush, especially when urinating
- In some cases, pain during intercourse may be associated with a vaginal yeast infection.

Invasive candidiasis:
Candida yeast can spread to the heart, eyes, blood, bones and brain if it enters the bloodstream. This can happen through medical instruments or devices, resulting in a severe fatal infection.
This usually occurs in patients who have been hospitalized or live in a medical facility such as a nursing home. You are more likely to have invasive candidiasis, especially if you have a weakened immune system, diabetes, kidney disease, or are taking antibiotics.
Fever and chills are some of the signs and symptoms of invasive candidiasis. Although a person with this infection is likely to develop another disease, it can be difficult to diagnose.
Diaper rash due to yeast infection:
Diaper rash usually occurs when a wet or dirty diaper is left on the baby for an extended period of time. When a child's skin becomes irritated, infection becomes more likely. If the diaper rash persists, examine the child and check for reddened perineal skin. Also check for raised red borders on sores. If this is the case, ask the pediatrician to examine the child for candidiasis.
Also check for raised red borders on sores. If this is the case, ask the pediatrician to examine the child for candidiasis.
In general, the best way to avoid candidiasis and diaper rash is to keep your baby's bottom clean and dry at all times.
Yeast infection symptoms
Intense itching and irritation in the vagina and vulva, burning sensation when urinating, which can be mistaken for a urinary tract infection. Vaginal discomfort or pain, a dry, erythematous rash, and a thick, white, cheesy discharge are all symptoms of vulvovaginitis.
Candida can also cause thrush, which is characterized by a white or yellow rash on the tongue and mucous membranes of the mouth, and redness and cracking pain around the corners of the mouth. In this case, it spreads into the oropharynx, causing discomfort when swallowing. Infants, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems are all susceptible to candidiasis. Fever, chills, hypotension, and confusion are all symptoms of systemic candidemia.
Candidal infection of the larynx is rare. Women suffer the most. They often express dysphoria. It is closely related to gastric reflux or a history of inhaled corticosteroid use. The presence of leukoplastic lesions can lead to damage to the glottis.
Diagnosis of thrush
To effectively diagnose a yeast infection, a gynecologist or other healthcare professional may;
- Ask about your general medical history . This usually includes getting the necessary information about previous yeast infections and any STIs.
- Gynecological examination. During the diagnosis, the doctor will evaluate the external genitalia for signs of a yeast infection. After that, he or she may insert a device known as a speculum into the vagina to examine the cervix and vagina. The cervix is the lower and narrower region of the uterus.
- Examination of vaginal discharge. If necessary, the doctor may take a sample of vaginal secretions to analyze the types of fungus, which will further provoke infection.
 Determining the types of fungus allows a doctor to prescribe appropriate forms of treatment for recurrent yeast infections.
Determining the types of fungus allows a doctor to prescribe appropriate forms of treatment for recurrent yeast infections.
Yeast Infection Treatment
Yeast infection treatment usually depends on the type and nature of the infection, whether it is complex or uncomplicated.
For a less complex yeast infection, treatment includes two approaches including oral therapy and topical vaginal treatment. A short course of vaginal therapy is usually appropriate for treating an uncomplicated yeast infection.
Alternative medicine for yeast infection or over-the-counter yeast infection medications include butoconazole (ginazol-1), clotrimazole (gynelothrimine), miconazole (monistat 3) and terconazole (terazol 3). In addition, clotrimazole, monistat 3 and terciflunomide can be purchased online.
The effectiveness of oral and topical therapy is the same, although oral preparations are more expensive. Fluconazole should not be given during the first trimester of pregnancy. Fluconazole is taken on days 1, 4, and 7 for recurrent vaginal candida infection, and then monthly for six months.
Fluconazole is taken on days 1, 4, and 7 for recurrent vaginal candida infection, and then monthly for six months.
Oral thrush can similarly be treated with oral lozenges as a replacement dosage form. Oral or intravenous antifungals such as caspofungin, fluconazole, and amphotericin B are used to treat systemic candidiasis.
In the case of fungal stomatitis, the patient should stop using a denture for at least two weeks and apply topical antifungal drugs. Loss of vertical dimension of the jaw causes angular cheilitis. As a result, when the infection subsides, it is necessary to fabricate a new denture with suitable vertical dimensions. Probiotics may be used as an adjunct in the treatment of oral thrush.
Complex yeast infection:
Treatment of complex yeast infection will require long-term vaginal treatment or multi-dose oral formulas. Maintenance medications may be recommended. Such drugs are used daily to prevent the recurrence of the disease.
Long-term vaginal therapy consists of 7-14 days of complex treatment using tablets, vaginal cream, thrush suppositories or ointment. Instead of direct vaginal treatment, two or three oral doses of fluconazole can sometimes be given. When symptoms are severe, a doctor may recommend topical steroids for a few days to relieve symptoms until antifungal treatment is effective.
Check if fungal infections are causing symptoms before taking antifungals. This is because overuse of antifungal medications can increase the chance of yeast resistance. This means that drugs can no longer function in the body in the way that they will in the future.
When maintenance prescriptions are needed, they should begin after completion of one of the above forms of treatment. This may be weekly oral fluconazole therapy for six months or weekly vaginal therapy with clotrimazole.
If your partner is showing symptoms of a yeast infection, they should also be treated. In this case, it is often recommended to use a condom.
Yeast Infection Prevention
Although there is no sure way to avoid a Candida infection, there are certain things you can do to reduce your chance of getting a vaginal yeast infection. In most cases, women at risk are strongly advised to:
- Refrain from douching
- Avoid using feminine deodorants, tampons, or deodorant pads.
- Wear underwear made from cotton or other natural fabrics.
- Wear slightly loose and fitted trousers and skirts.
- Wash underwear at high temperatures
- Refrain from wearing tight underwear or tights
- Eat a balanced, varied diet
- Change wet clothing, such as bathing suits, as soon as possible.
- Avoid hot tubs and hot tubs if possible.
Health care providers may recommend oral or intravaginal probiotics for women with more than three infections per year. Also, if you notice or suspect any symptoms and signs of a yeast infection, talk to your doctor right away about a proper diagnosis.
Differential
Pustular psoriasis, subcorneal pustulosis, and acute generalized basal pustulosis can all cause a spongy rash. To exclude the fungal etiology of psoriasis, certain dyes should be applied.
Impetigo is also spongy. Gram stain can be used to detect bacterial colonies in impetigo, although GMS and PAS stains do not stain fungal forms.
Tinea cruris and corporis are known for their spongy shape. Without developing candida yeast, special staining reveals septate hyphae. Sometimes it can be difficult to tell the difference. Candida infiltrates the keratinized epithelium, while dermatophytosis more often affects the stratum corneum.
It is difficult for an otolaryngologist to make a correct diagnosis of laryngeal candidiasis, a high degree of alertness is required. Patients with predisposed characteristics who present with a suspected lesion should include the disease in the differential diagnosis.
Prognosis
Although the most common candidal infections are localized, vaginal and skin infections are also common.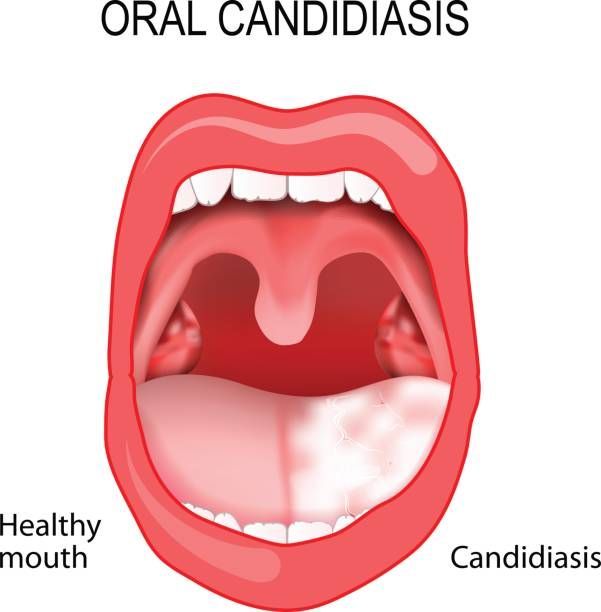 As a result, antifungal drugs can be used to treat them, resulting in complete recovery and excellent prognosis and outcomes. Candida infection, if left untreated, can spread to other organs and cause systemic disease.
As a result, antifungal drugs can be used to treat them, resulting in complete recovery and excellent prognosis and outcomes. Candida infection, if left untreated, can spread to other organs and cause systemic disease.
The extent and location of the Candida infection, the general health of the victim, and the timing of diagnosis and treatment all play a role in the long-term prognosis of systemic candidiasis.
Nearly a third of patients with candidemia develop septic shock as a result of host characteristics, including age and source of infection, rather than virulence characteristics of the organisms.
Complications of yeast infections
Complications of a yeast infection can occur in the following cases:
- If there are extreme signs and symptoms, including widespread redness, itching, and swelling that cause cracks, tears, and sores.
- Four or more episodes of yeast infections within one year
- Infection due to less common forms of fungus.

- Pregnancy
- Compromised body immune system due to certain medications or health conditions such as HIV infection.
- Uncontrolled diabetes
Is thrush contagious?
Although yeast infections are not classified as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), they are still contagious. Thrush can be transmitted through oral and vaginal sex. Also, a yeast infection is spread through sex toys or kissing someone who has oral candidiasis.
A baby may develop a fungal diaper rash during childbirth if the mother had vaginal thrush during childbirth. Also, if you have a Candida overgrowth around your breast area, you can pass the disease on to your baby by mouth while breastfeeding.
Although a yeast infection can be passed from one person to another, it is not contagious like other diseases. Therefore, you will not get an infection through the air or from sharing a shower with someone who has it.
Yeast infections in men
Yeast infections in men can develop and affect the penis. When this happens, the condition is called a penile yeast infection. Candida is in all organs, not only in women. Yeast infection can result from overgrowth of this fungus. Due to moisture and skin folds, the groin area is particularly vulnerable to Candida overgrowth.
When this happens, the condition is called a penile yeast infection. Candida is in all organs, not only in women. Yeast infection can result from overgrowth of this fungus. Due to moisture and skin folds, the groin area is particularly vulnerable to Candida overgrowth.
Yeast infections in women
Yeast infections in women are common. According to studies, three out of four women may have more than two vaginal yeast infections in their lifetime. Despite their widespread occurrence, it is extremely important to treat vaginal yeast infections as soon as possible. You will not only be able to relieve unpleasant symptoms, but you will also be able to minimize the possibility of the spread of the disease in the body.
Yeast infections in children
Yeast infections are usually associated with vaginal infections, but they can also affect children. Diaper rash is the most common yeast infection in children. However, not all diaper rash is caused by yeast overgrowth.
Sometimes your baby's skin becomes excessively red and blotchy around the diaper or in the groin area even after diaper rash cream is applied. With this, you will be able to determine if the disorder is more than a typical diaper rash. In other cases, a yeast infection may also occur in other skin folds, including under the armpits.
Your child's pediatrician will likely recommend a topical antifungal cream to help fight fungal skin infections. If a child has oral candidiasis or a yeast infection in the mouth, oral treatment may be needed. While a yeast infection rash in children is usually harmless, it can be more serious if left untreated.
Thrush and intercourse
Fungal infection is not sexually transmitted. However, infection is possible after sexual intercourse. On the other hand, other factors can upset the balance of Candida in the vagina. The bacteria can be transmitted through vaginal intercourse, fingers, and sex toys.
Another risk is vaginal intercourse with a partner who has a penile yeast infection. A man can also get a penile yeast infection from a partner with a vaginal yeast infection. In addition, bacteria in the mouth, vaginal area, and also in the penis area can be destroyed by oral sex.
A man can also get a penile yeast infection from a partner with a vaginal yeast infection. In addition, bacteria in the mouth, vaginal area, and also in the penis area can be destroyed by oral sex.
It is also likely that a yeast infection after sex is not associated with other symptoms. Sexual intercourse is just one of the major risk factors for a yeast infection.
Fungal infection and urinary tract infection (UTI)
UTI is one of the most common infections affecting most women. While it is possible to get one or both diseases at the same time, yeast infections and UTIs are two different diseases.
A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection that develops in the urinary system. The urethra, bladder and kidneys are part of this complex structure. UTIs can also occur due to a variety of factors, including sexual intercourse, STIs, and lack of regular urination.
Signs and symptoms of a UTI are different from those of a yeast infection. As long as there is no visible discharge from a yeast infection, you may notice a small trace of blood in your urine. In addition to regular urination, a UTI can cause pain in the pelvis as well as in the abdomen.
As long as there is no visible discharge from a yeast infection, you may notice a small trace of blood in your urine. In addition to regular urination, a UTI can cause pain in the pelvis as well as in the abdomen.
A UTI can cause serious kidney problems if left untreated. Antibiotics must be obtained from a doctor. Also, ask your doctor about the differences between a yeast infection and a urinary tract infection.
How do you tell a "yeast infection" from a "chlamydia" infection?
Yeast infections cause thick, white, cottage cheese-like discharge, while chlamydia can cause white, green, or yellow discharge. Gonorrhea discharge is white or green.
Thrush and menstrual periods
Having a yeast infection and menstruating at the same time can seem like a disaster. This, however, is rare. Yeast infections are common in women in the last days before menstruation.
Hormonal fluctuations are believed to be the cause of thrush before menstruation.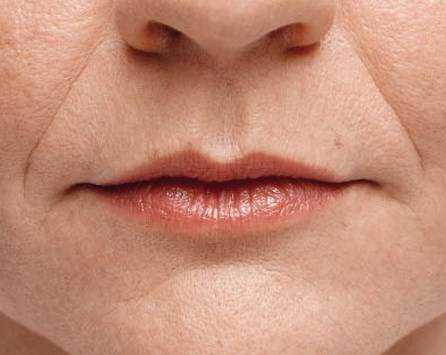 This creates an imbalance of good bacteria in the vagina.
This creates an imbalance of good bacteria in the vagina.
If you have white or yellow discharge about a week before your cycle, it may not always be due to a yeast infection. What matters is whether you already have these tell-tale signs, including redness, itching, or burning.
Although it may be uncomfortable, early treatment can clear up the yeast infection before your next period. Check with your doctor if signs of a yeast infection persist after a cycle is completed. You may also notice them if you continue to get thrush every month before your period.
Yeast infection during pregnancy
Due to the hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy, yeast infections are normal. If you are pregnant and think you have a yeast infection, you should consult your doctor and get a proper diagnosis.
Thrush during pregnancy is not treated in the same way as in non-pregnant women. Because of the potential risk of birth defects in the fetus, you will not be able to use oral antifungals. Doctors often recommend using topical antifungals during pregnancy.
Doctors often recommend using topical antifungals during pregnancy.
Although yeast infections will not harm the baby, Candida can be passed at birth. Therefore, as a result of this, the child may develop diaper rash or stomatitis. Therefore, it is very important to treat a yeast infection as soon as possible during pregnancy to avoid complications.
Yeast infection of the gut
In immunocompromised individuals, fungal infections are one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality. Invasive fungal infections, especially those of the gastrointestinal tract, have become more common as the number of immunocompromised people has grown.
Mushroom growth in the intestines is also possible. As a result, candida may appear in your stool. When patients develop symptoms of colon inflammation, especially if they are immunosuppressed, doctors should be aware of the possibility of this fungal disease.
Yeast Infection Diet
It is possible that the foods you eat are contributing to the development of a yeast infection. Sugar is the favorite of yeast. Avoiding the foods listed below (sometimes called the Candida diet) will help you control the development of yeast in your body:
Sugar is the favorite of yeast. Avoiding the foods listed below (sometimes called the Candida diet) will help you control the development of yeast in your body:
- White flour and rice
- Foods or drinks fermented with yeast
- Products consisting of simple sugars
While avoiding certain foods can help you avoid a yeast infection, sticking to this diet can be difficult. Fortunately, you may not need to completely avoid these foods to reduce the frequency or severity of yeast infections. It may be helpful to simply reduce the amount of these foods.
It may also be helpful to increase your intake of healthy proteins and fats, as well as low starch fruits and vegetables. You don't have to starve on a low sugar diet; you just need to consume more from other food categories.
When to see a doctor?
You should contact your doctor immediately if;
- You are experiencing signs and symptoms of a yeast infection for the first time
- You are not sure if you have a yeast infection.