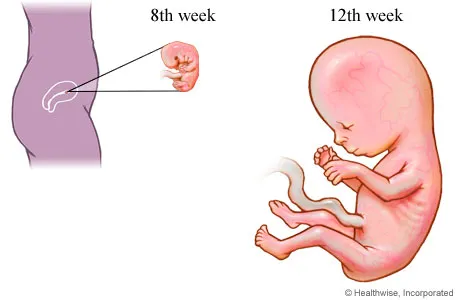
Not hungry during first trimester
Appetite changes and food aversions during pregnancy
Appetite changes and food aversions during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content6-minute read
Listen
Key facts
- Appetite changes are very common during pregnancy and may affect weight changes.
- A food aversion is an intense dislike of a specific food, together with unpleasant physical symptoms when you see or smell a particular food.
- Eating for 2 during pregnancy is a myth. It is the quality not quantity of food that matters.
- When you are pregnant, your body needs certain vitamins, minerals and nutrients, including iron, folate and iodine.
- If your nausea prevents you from getting enough nutrition, or if you are vomiting, not able to keep food or fluids down or losing weight, see your doctor or maternal health nurse.
What are food aversions, and why does appetite change during pregnancy?
A food aversion is an intense dislike of a specific food, together with unpleasant physical symptoms when you see or smell a particular food. These reactions are usually triggered by emotions associated with food rather than the food itself. You might also experience food cravings (an intense urge to eat a specific food). While these appetite changes are quite common, they can make healthy eating during pregnancy a challenge.
Is it normal for my appetite to change during pregnancy?
It is normal to experience either a loss of appetite or a change in food preferences during pregnancy. This may play a part in how much your weight changes during pregnancy.
Food aversions are common, and around 6 in 10 people experience a food aversion while pregnant.
When are food aversions likely to start and end?
You can experience food aversions resulting from generalised nausea (also known as 'morning sickness') at any time of day, and it tends to peak between week 6 and week 14 of pregnancy.
For this reason, if you've gone off certain foods that are important for your diet, you can try again later in your pregnancy to see if the aversion has passed. If your nausea prevents you from getting enough nutrition, or you are vomiting, not able to keep food or fluids down or losing weight, it's time to see your doctor.
What food aversions are common?
Common food aversions include:
- alcohol
- coffee / tea
- meat
- fatty food
- spicy food
- eggs
What causes food aversions?
While the cause of food aversions during pregnancy isn't clear, hormonal changes could affect the food you enjoy, particularly early in your pregnancy. For example, human gonadotropin (also known as hCG) is a hormone produced during pregnancy. It can cause feelings of nausea, appetite changes and food aversion. Pregnancy can also cause a greater sensitivity to smell and taste, which can influence the foods you prefer to eat.
More research is needed to better understand why food cravings and aversions occur. Some reasons may include hormonal balance or protecting the unborn baby from harmful substances and/or nutritional deficiencies. This is to encourage good nutrition and growth in the pregnancy.
Some reasons may include hormonal balance or protecting the unborn baby from harmful substances and/or nutritional deficiencies. This is to encourage good nutrition and growth in the pregnancy.
How can I eat well and have a healthy diet?
A healthy diet is important for both you and your baby. Eating for 2 during pregnancy is a myth. It is the quality not quantity of food that matters, and there is no need to eat twice as much. It is the quality not the quantity of food that matters most. Your diet should include a variety of the five food groups:
- vegetables and legumes
- breads and cereals
- milk, yoghurt and cheese
- meat, poultry, fish and alternatives
- fruit
During pregnancy, your body also needs plenty of water (8 to 10 glasses each day). You will also need extra vitamins, minerals, and nutrients to help your baby develop, including these:
- Folate (Folic acid) helps build your baby’s brain cells and prevents risk of the baby being born with a birth defect of the brain and/or spinal cord.
 This is especially important in the early stages of pregnancy. Folate-rich foods include green leafy vegetables, broccoli, legumes, oranges, avocado, or fortified breads and cereals.
This is especially important in the early stages of pregnancy. Folate-rich foods include green leafy vegetables, broccoli, legumes, oranges, avocado, or fortified breads and cereals. - Iodine is also important for your baby’s growth and development. Choose foods that are sources of iodine, such as low-fat milk products, eggs, cooked fish and seafood. Foods that contain seaweed, such as sushi, are also a good source of iodine, but if you’re pregnant only eat sushi without raw fish, cold meat or egg, and that is freshly prepared. If you add salt to your food or in cooking, choose iodised salt. If you have a thyroid condition, seek advice from your doctor before taking an iodine supplement.
- Iron-rich foods are recommended during pregnancy. These include red meat, poultry, tofu, and iron-fortified cereals. Eating foods high in vitamin C such as oranges, kiwi fruit, capsicum and broccoli can help iron absorption. Do not take an iron supplement during pregnancy without first checking with your doctor.
 Too much iron can pose health risks to you and your baby. A blood test will help your doctor know if you need to take iron tablets.
Too much iron can pose health risks to you and your baby. A blood test will help your doctor know if you need to take iron tablets.
If you develop an aversion to meat or another essential food, consider how you might substitute these for alternatives. For example, substitute meat for nuts.
It is also important to limit foods containing:
- saturated fats (biscuits, cakes, pies, butter and cream)
- added salt (processed meats, pickled fish, fast foods)
- added sugars (confectionary, sugar sweetened soft drinks, fruit juice and cordial)
Alcohol is not safe for developing babies, and not drinking alcohol is the safest option while you’re pregnant.
There are also certain foods you should avoid during pregnancy, so ask your doctor or maternal health nurse for more information.
Appetite changes during pregnancy are unlikely to harm you or your baby or significantly compromise your nutrition. If you are not sure which foods are most important for your diet, or you have no appetite for foods containing important nutrients, seek advice.
More information on changes in appetite
For more advice on food aversions or appetite loss in pregnancy speak to your:
- doctor
- midwife
- obstetrician
- accredited practising dietitian
Sources:
Epworth Hospital (Ask an Epworth midwife Your guide to early pregnancy), Royal Women Hospital Melbourne (Common concerns in early pregnancy), Queensland Health (During pregnancy), ACT Government (Good Nutrition in pregnancy), Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (Food Intolerance), University of Queensland (What the health: Why do women crave certain foods when they are pregnant), Australian Government (Healthy eating during your pregnancy), Science and Education Publishing (Psychological Factors in Food Aversions, Nausea, and Vomiting During Pregnancy), National Health and Medical Research Council (Australian guidelines to reduce health risks from drinking alcohol)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Foods to avoid when pregnant
- Food cravings during pregnancy
- Guide to a healthy pregnancy
Need more information?
Healthy diet during pregnancy
A healthy diet is an important part of a healthy lifestyle at any time, but especially vital if you're pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy health & wellbeing | Raising Children Network
Pregnant? Here’s all you need to stay healthy during pregnancy, including tips for healthy diet and lifestyle and a guide to pregnancy health care.
Read more on raisingchildren. net.au website
net.au website
Pregnancy and Healthy Eating
It’s especially important to eat healthy food during pregnancy and while breast feeding.
Read more on Healthy Eating Active Living NSW website
Healthy Eating When You’re Pregnant or Breastfeeding | Eat For Health
Eating well during pregancy and while breastfeeding has health benefits for you and your baby.
Read more on NHMRC – National Health and Medical Research Council website
Having a healthy pregnancy
Having a healthy pregnancy means following a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, knowing what to avoid and making sure your vaccinations are up to date. Find out more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Things to avoid during pregnancy
From hair dye to house paints, there are a few products or lifestyle habits pregnant women and their partners should be cautious of during pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Gi and Pregnancy | GI Foundation
Home / Gi Health Benefits / Gi and Pregnancy Gi and Pregnancy Following a healthy low Gi diet during pregnancy helps protect your child’s future health and improves health and wellbeing for lifelong benefits
Read more on Glycemic Index Foundation website
Healthy Weight During Pregnancy
Weight gain is a normal part of pregnancy. The amount of weight you put on partly depends on your weight before pregnancy.
Read more on SA Health website
Losing weight after birth safely
Tips for losing weight after birth, including how to enjoy a healthy lifestyle, setting realistic goals, breastfeeding and weight loss and when to seek help.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Guide to a healthy pregnancy
What you put in your body before falling pregnant, during your pregnancy and after the birth can effect your baby.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Pregnant Not Eating Food? 7 Appetite Loss Tips for Expecting Moms
Share with:
Pregnancy triggers ravenous hunger but not for everyone.
Having a bun in the oven usually leads to cravings and an increased appetite. Yet, some women feel turned off of food completely. Why? And what can you do about it?
In this article, we’re discussing why you might be pregnant, not eating, and experiencing a decreased appetite.
Most people know that pregnancy can make you furiously hungry, have weird cravings, and develop taste aversions. However, it can also impact your appetite in the opposite way. While many women experience a bigger appetite, some don’t change their eating patterns at all. Others feel their appetite has come to a sudden halt.
If you’re pregnant and not eating food, it may be concerning. When you should be eating more for the baby, why are you eating less?
Fortunately, losing your appetite can be normal during pregnancy. Although you need more nutrients for the baby, your body may go through changes while it adapts.
Your appetite will likely return. If it doesn’t or if you’re unable to eat, contact your doctor. Since your baby needs specific nutrients to develop, eating right during pregnancy is important.
Pregnant Not Eating Food: 7 CausesIf you’re pregnant, not eating food and have a reduced appetite, you’re probably wondering why. There’s a variety of reasons you may want to eat less—instead of more—during pregnancy. Scroll the list of possible causes below and see if you can relate to any.
There’s a variety of reasons you may want to eat less—instead of more—during pregnancy. Scroll the list of possible causes below and see if you can relate to any.
Whether triggered by taste or smell, an aversion is a food that completely turns you off. They’re one of the biggest reasons for decreased appetite. Between 50% and 90% of pregnant women experience cravings and aversions.
The most common aversions include:
- Caffeinated drinks
- Meats
- Fish
- Eggs
Research shows that changes to food cravings and aversions usually happen in the first and third trimesters.
You might wonder why you’ve developed an aversion to a specific food. However, the answer isn’t clear. Some women believe their aversions or cravings are nature’s way of altering their diet, making it healthier for pregnancy. There is no evidence that’s true. You shouldn’t assume your diet is healthy just because you’ve listened to your aversions or cravings.
In fact, it’s possible your aversions could weaken your diet and affect your baby. For example, meats and eggs are a common aversion that can lower your protein intake. Low maternal protein can cause embryo loss, restriction of intrauterine growth, and reduced postnatal growth.
Experts say that a combination of factors likely causes your appetite and preferences to change. That could include biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
#2 Morning SicknessA second major reason why you might be pregnant not eating food is because of morning sickness. Up to 80% of women experience nausea and vomiting in the first trimester.
There’s a variety of reasons morning sickness may happen. Some experts believe hormones play a large role. For other women, food aversions can trigger vomiting.
In any case, if you feel sick when you eat, eating can become less appealing. If you’re afraid of vomiting, you might only eat when necessary.
#3 Decreased Food = Adjusted Feelings of FullnessFood aversions and morning sickness are normal. However, if eating less becomes a pattern, it can change your appetite in the long term.
However, if eating less becomes a pattern, it can change your appetite in the long term.
When you eat less food, your body will begin to adjust. Over time, it will take less food to make you feel full. Instead of feeling full after a meal, eating only half may leave you stuffed.
Many people attribute this change in appetite to their “stomach shrinking.” However, your stomach doesn’t actually shrink—it just gets more sensitive to small amounts of food. If this happens, you’ll probably notice a reduced appetite as your body learns to feel full from less food.
It’s important to recognize that even though you feel full, you might not be getting enough nutrients for the baby.
#4 ConstipationConstipation is another common pregnancy symptom that can affect your appetite. If you’re unable to pass stools normally, you might avoid eating in fear that the problem will worsen. You might also be afraid of the gas pains constipation can cause.
Another reason could be that constipation reduces your appetite. If food stays in your system longer, you might feel fuller longer. When there’s not much room for new food, your body won’t send hunger cues.
If food stays in your system longer, you might feel fuller longer. When there’s not much room for new food, your body won’t send hunger cues.
While you’re expecting, the extra acid in your stomach can create numerous problems. Most commonly, women experience heartburn, AKA acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It can also worsen nausea and vomiting. One lesser-known impact is that it can also decrease your appetite. The excess stomach acid could be making you feel full too quickly.
#6 Mental HealthWe’ve covered the physical reasons why you might lose your appetite while expecting. Next, we need to consider that mental health changes could be why you’re pregnant and not eating.
Research has shown that anxiety and depression can lead to appetite changes. Pregnancy can bring about a slew of new emotions. You might experience anxiety about your health, the baby, or upcoming life changes. Pregnancy depression can also reduce your appetite.
Pregnancy depression can also reduce your appetite.
Another psychological reason why you might be pregnant and not eating is because of body image concerns.
Most women gain weight during pregnancy; however, it might be difficult to accept. If you’ve experienced body image issues or disordered eating before, pregnancy can trigger these concerns or make them worse.
Knowingly or unknowingly, you may be reducing your food intake to try to limit weight gain.
7 Tips for Those Pregnant Not Eating FoodIf you’re pregnant and not eating food, try to pinpoint the cause. When you understand why your appetite has decreased, you can brainstorm possible solutions. Consider the suggestions below.
#1 Pinpoint Your AversionIf aversions are the reason you’re pregnant and not eating, get specific about the foods you don’t like. For example, maybe you loved spicy foods before but now anything with a kick kills your hunger. Pay attention to other types of aversions too. Perhaps a specific scent or the temperature of food is throwing you off.
Pay attention to other types of aversions too. Perhaps a specific scent or the temperature of food is throwing you off.
If the reason you’re pregnant and not eating food is because of morning sickness, explore your options.
After you’ve pinpointed your aversions using the tip above, brainstorm new snack ideas. When you discover foods that don’t turn you off, add them to your daily staples. Make sure to stock up and keep snacks in your purse to ensure you’re frequently eating.
Need ideas? Read 33 Satisfying Pregnancy Snacks Perfect for Morning Sickness
#3 Eat Frequent, Smaller MealsInstead of eating big meals, break it up into more frequent, smaller meals. This trick is helpful for those experiencing morning sickness or acid reflux.
#4 Take Steps to Reduce NauseaYou probably can’t fully rid yourself of nausea—but you can take steps to reduce the intensity of it. Try a few anti-morning sickness tricks and see what works for you:
Try a few anti-morning sickness tricks and see what works for you:
- Carry a pleasant scent to sniff when you smell something nauseating
- Stay hydrated
- Take B6 vitamin
- Reduce cybersickness before eating (scrolling through your phone or on the computer)
- Use deep breathing
- Take your prenatal vitamin at a different time of day
Read: 16 Best Morning Sickness Relievers to Ban Nausea
Try Our Acupressure Anti-Nausea Wristband to Alleviate Morning Sickness!
#5 Improve Your DigestionIf you think constipation is affecting your appetite, take steps to get things moving again. You can free up space in your stomach and alleviate constipation by:
- Slowly increasing your fiber intake
- Drinking more water
- Exercising
- Using a poop stool (AKA squatty potty)
- Choosing the right iron supplement (or prenatal with iron)
For more tips on improving constipation, read Constipation in Pregnancy: 7 Fixes
#6 Address Your Mental Health
Pregnancy can be overwhelming and you don’t have to go through it alone. If you suspect you’re pregnant and not eating because of anxiety or depression, reach out for help. Your doctor can recommend a therapist, free community resources, or coping mechanisms.
If you suspect you’re pregnant and not eating because of anxiety or depression, reach out for help. Your doctor can recommend a therapist, free community resources, or coping mechanisms.
Also look at science-backed ways to improve your mental health, including:
- Exercise
- Journaling
- Meditation
- Self-guided workbooks
Read:
- 7 Actionable Tips to Manage Panic Attacks in Pregnancy
- What’s The Difference Between Postpartum Depression and Baby Blues?
- Pregnancy Worry: 10 Practical Remedies for Anxiety During Pregnancy
- How to Prevent Postpartum Depression Before Delivery: 8 Ways
- Pregnancy Mood Swings: 9 Powerful Remedies
Thoughts about your weight and body image may be affecting your appetite. Whether these are new or old patterns of thinking, pregnancy is a good time to tackle them.
If you’re pregnant and think you may be struggling with disordered eating, talk to your doctor. They can put you in touch with a counselor, nutritionist, and/or community resources.
They can put you in touch with a counselor, nutritionist, and/or community resources.
Talking about body image is difficult and being pregnant can double the shame. Try to remember that other women struggle with disordered eating when pregnant. Along with advice from your healthcare provider, consider joining a support group for moms-to-be with eating disorders.
Summary: Pregnant Not Eating FoodIf you’re pregnant, not eating food, and wondering why, there’s a few possible causes. Nausea, constipation, extra stomach acid, and mental health problems can all contribute to changes. To increase your appetite, use the tips above. If your appetite doesn’t go back to normal, contact your doctor. Remember that your baby needs nutrients to develop properly, so eating right is extra important during pregnancy.
P.S. If nausea is causing a lack of appetite, try an acupressure wristband. They’re designed to press your P6 acupressure point, alleviating feelings of sickness.
Is Morning Sickness Wrecking Your Appetite? Try Our Anti-Nausea Wristband!
Share with:
Diet in early pregnancy slows down fetal development
Diet in early pregnancy slows down fetal development - Gazeta.RuSwedish skier Grate said that he was afraid to communicate with Russian Zealous 23:47
The head of OPEC considered the decision to reduce oil production correct and timely 23:42
Head of RDIF: Sputnik V has become a springboard for the development of Russian drug exports 23:42
Khimki player Kukharchuk said that the club began to pay off debts... 23:40
An Angara-1.2 rocket with a military satellite was launched from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome 23:29
Wrestler Sadulaev turned to Makhachev before the fight against Oliveira 23:26
Khimki defender Danilkin on 12 games without a win: maybe... 23:19
The Minister of Economy of Bulgaria said that the country has resolved the gas issue for the year ahead 23:14
The German AfD called for the launch of Nord Stream 2 23:07
The Ministry of Internal Affairs of Moldova promised to “resolutely” stop violations during protests 23:05
Science
Malnutrition during pregnancy can slow down the development of fetal organs, particularly the brain. This, in turn, can have long-term consequences, such as lowering the IQ of the offspring, as well as the emergence of a predisposition to behavioral problems.
This, in turn, can have long-term consequences, such as lowering the IQ of the offspring, as well as the emergence of a predisposition to behavioral problems.
Smokers give birth to bandits
Women who smoke during pregnancy are more likely to have children with criminal tendencies...
January 22 18:44
Modern ladies who prefer to keep a good shape, that is, thinness, even during pregnancy (the most famous of them without five minutes is the mother of four children, Victoria Beckham), thus harming their unborn children, a study by American scientists has shown. The brain of the fetus, as it turned out, is sensitive to even a moderate lack of nutrition of the mother's body.
Thus, a diet in early pregnancy slows down the development of the brain in the fetus.
At least this is how the processes proceeded during the pregnancy of model organisms of primates - baboon monkeys, an article about the study of which physicians published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences .
Forced childbearing
Male domestic violence almost always coexists with forced conception of a child against the will of a woman...
January 25 11:34
Scientists observed pregnancy in two groups of female primates at a special nursery in San Antonio, Texas. One group of “ladies” was allowed to satisfy their appetite in the first trimester of pregnancy according to their needs, and the second group sat on a moderate diet: their diet was reduced by 30% - about how expectant mothers in the United States lose weight.
It turned out that maternal nutrition affects the fetus both at the cellular and molecular levels.
Diet results in dysregulation of hundreds of genes, many of which play a key role in regulating cell growth and development.
Thus, maternal nutrition is absolutely essential for the development of the fetus, as it regulates the basic foundations of cellular mechanisms.
If you want a boy, eat
Now we know what boys are made of. For the birth of a boy to women before conception ...
For the birth of a boy to women before conception ...
12 May 10:31
The dangers of a sharp lack of nutrition (hunger) for the development of the fetal brain have been known for a long time, but the new work is the first scientifically substantiated confirmation that even a moderate diet does not go unnoticed for the development of the fetus.
Partially similar to diets and malnutrition are teen pregnancies: in their case, the fetus receives insufficient nutrition, as the still growing mother's body needs it. In late pregnancies, the fetus also suffers from malnutrition, but for other reasons: the maternal arteries become harder, and this disrupts the blood supply to the uterus, inevitably disrupting the fetal diet. A similar effect occurs with preeclampsia (late toxicosis of pregnant women) - here the fetus is “malnourished” due to dysfunction of the placenta.
"Starving fetus" lags behind in the formation of intercellular connections, cell division and the volume of growth factors - hormones that stimulate growth.
Lose weight to get pregnant
Extra pounds seriously reduce a woman's chances of getting pregnant. The more extra...
September 22 14:36
It is in the first half of pregnancy that nerve cells are formed - the neurons of the brain, as well as all the auxiliary brain cells necessary for their work. Malnutrition during this period affects directly this process.
“Our study is further evidence of the importance of good maternal nutrition and health. Malnutrition during pregnancy can slow the development of fetal organs (we see this in the brain), and this, in turn, can have long-term consequences - a decrease in the IQ of the offspring, as well as a predisposition to behavioral problems, ”says Dr. Thomas McDonald, who led work.
Scientists urge mothers to eat well and be aware of the dangers of malnutrition for their unborn children. They emphasize that the study is quite reliable, since model primates provide a very high-quality imitation of processes in the human body.
Much of this research has previously been done in rats.
Subscribe to Gazeta.Ru in News, Zen and Telegram.
To report a bug, select the text and press Ctrl+Enter
News
Zen
Telegram
Picture of the day
The Ministry of Defense reported a terrorist attack at a training ground in the Belgorod Region
Russian military operation in Ukraine. Day 234
Online broadcast of the military special operation of the Russian Federation in Ukraine - 234th day
"To hell with it": Musk changed his mind about turning off free internet in Ukraine
Musk promised to continue funding Starlink in Ukraine
Zelensky called the situation in the Artyomovsk direction "difficult"
An explosion occurred in Iran's largest prison
The German AfD called for the launch of Nord Stream 2
The Minister of Economy of Bulgaria said that the country has resolved the gas issue for the year ahead
News and materials
Swedish skier Grate said he was afraid to communicate with Russian Zealous
The head of OPEC considered the decision to reduce oil production correct and timely
Head of RDIF: Sputnik V has become a springboard for the development of Russian drug exports
Khimki player Kukharchuk said that the club began to pay wage arrears
An Angara-1. 2 rocket with a military satellite
2 rocket with a military satellite
Wrestler Sadulaev turned to Makhachev before the fight against Oliveira
Khimki defender Danilkin on 12 games without a win: maybe the team has a psychological hole
The Ministry of Internal Affairs of Moldova promised to "resolutely" stop violations during the protests
Kadyrov promised to do everything possible to release the captured soldiers
Coach Gadzhiev about Abaskal: his training process is thoroughly staged
RIA Novosti: an eyewitness said that the Armed Forces of Ukraine are shelling residents being evacuated from Artemovsk
Chelsea legend Drogba: in the era of Abramovich, the club had class, today it is lacking
In the Czech Republic, an unscheduled disconnection from the power grid of one of the units of the Dukovany NPP occurred
Alexander Emelianenko: my wife and I do not drink, we are preparing to give birth to children
Axios: White House 'disappointed' with Abbas's words about losing confidence in the US in a conversation with Putin
About 100 cubic meters of oil leaked due to an oil pipeline accident in Komi
A criminal case has been opened against Manchester United striker Greenwood
Head of Defense Lecornu: the transfer of Caesar to Kyiv could complicate the training of French artillerymen
All news
APU fired at the Belgorod region. Oil depot caught fire
Oil depot caught fire
Belgorod governor Gladkov: fire at oil depot in Belgorod region extinguished
German Chancellor called for enlargement of the EU and depriving countries of the right to veto
Scholz advocated reforming the EU and abolishing the unanimity principle
"The meeting was unexpectedly warm." Echelons with Russian military arrived in Belarus
The Ministry of Defense of Belarus announced the arrival of the first echelons with Russian military
The first season of The Lord of the Rings is everything. The series has never been more expensive, but is it really that good?
The first season of The Lord of the Rings: Rings of Power ended
This Weekend Detective: "Karen Peary" on Case 1996, which is revealed because of the podcast
Karen Peary detective series review
Iraq, Semak and shawarma: interview about the first private football club in the USSR
Director Nikola Prorokov about the documentary "Asmaral"
Best photos of the week
180 thousand for deferment from mobilization. The prosecutor's office checks the largest private university in Russia
The prosecutor's office checks the largest private university in Russia
Synergy University is being checked in the case of the sale of certificates for deferment from mobilization
"We want to be respected." The President of Tajikistan appealed to Putin
Rahmon urged Putin not to treat Central Asia as the former USSR
Our end, the western one has not yet arrived: what is the state of Ukraine's air defense
Will Western deliveries be able to qualitatively strengthen Ukraine's air defense
Test: Guess the name of the girl from the USSR cartoon
Remember the name of this young heroine from the Soviet cartoon
"Self-medication exacerbates the problem": trichologists about dandruff in men and women in the autumn-winter period
Bazyleva's trichologist: men suffer from dandruff more often than women due to the activity of the sebaceous glands
A substation caught fire in Belgorod. What is known about new attacks
What is known about new attacks
Belgorod authorities reported on the elimination of the fire at the substation after the shelling of the APU
Dmitry Vodennikov
People with especially sensitive skin
About the writer who built the labyrinth
Dmitry Samoilov
The smoke will clear
About fierce discussions on the net
Marina Yardaeva
Don't leave me, my love
Contradictory female reaction to mobilization
Vitaly Tuzov
Increase and not lose
About what to invest in this fall
Alexey Mukhin
Do not hit!
Why nuclear conflict is impossible
-->
See also
Error found?
Close
Thank you for your message, we will fix it soon.
Continue reading
Screening for the detection of congenital fetal diseases during pregnancy
Category: Reminders for the population .
Screening during pregnancy is a whole range of studies that allows parents and doctors to get the most complete information about the health of an unborn baby. Screening reveals many congenital and physical characteristics. How and when is pregnancy screening done
What is pregnancy screening and why is it done
Screening during pregnancy is a complex of examinations, which includes ultrasound and biochemical analysis of venous blood for hormones. As a rule, screening is carried out three times - in the first, second and third trimester.
As a rule, screening is carried out three times - in the first, second and third trimester.
Early detection of pathologies is very important. This makes it possible to start treating genetic diseases as early as possible and, if not completely cure them, then at least stop the symptoms as much as possible. If the doctor notices any abnormalities during the examination, the pregnancy is monitored especially carefully, which makes it possible to prevent the development of complications or premature birth. If the detected pathologies turn out to be too severe and incompatible with life, the doctor will refer the patient to terminate the pregnancy for medical reasons.
Pregnancy screening is harmless for both mother and baby. This is a fairly accurate study, although it should be clearly understood that it does not give a 100% guarantee. The accuracy of screening depends on many factors - the professionalism of the researchers, the woman's compliance with the rules for preparing for the examination, and other factors.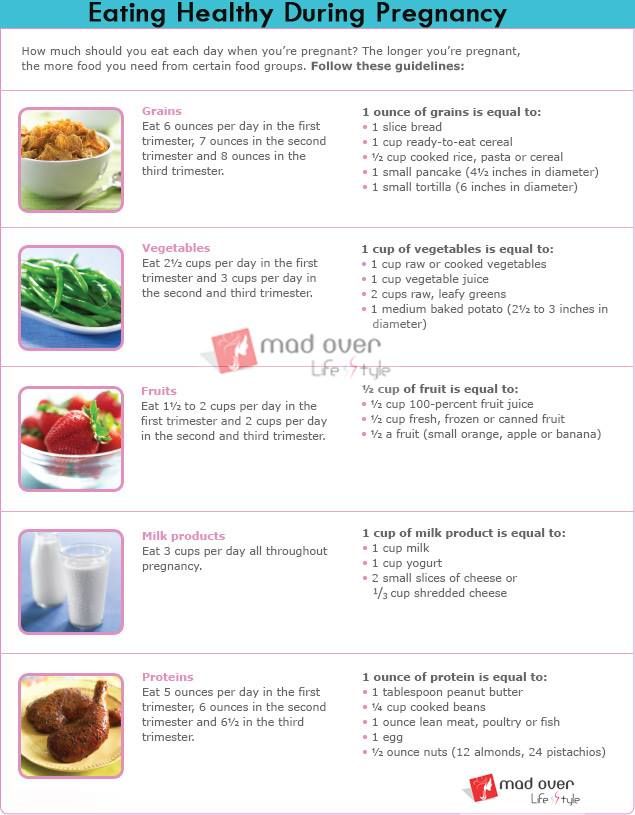
First pregnancy screening
The first screening during pregnancy is carried out between the 11th and 13th weeks. It makes no sense to undergo this examination earlier - before the 11th week of pregnancy, many indicators are practically indeterminate.
The study includes two medical tests - an ultrasound and a blood test.
ultrasound
With the help of ultrasound, the doctor determines the exact gestational age, evaluates the baby's physique, its dimensions (head circumference, limb length, height), the work of the heart muscle, the symmetry of the brain, the volume of amniotic fluid, the structure and size of the placenta, as well as the condition and tone of the uterus. For each of these parameters, there are normal indicators with which the doctor will compare the results. For an 11-13 week pregnancy, these rates are:
- KTP (coccygeal-parietal size, that is, the length of the fetus from the crown to the tailbone) is 43–65 mm.
 If this figure is more than normal, then the child will be large. A downward deviation indicates slow development (the reason for this state of affairs is often a hormonal imbalance or infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother), genetic pathologies or fetal death (in this case, the heart will not be auscultated). However, this may also be due to a banal mistake in determining the timing of pregnancy.
If this figure is more than normal, then the child will be large. A downward deviation indicates slow development (the reason for this state of affairs is often a hormonal imbalance or infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother), genetic pathologies or fetal death (in this case, the heart will not be auscultated). However, this may also be due to a banal mistake in determining the timing of pregnancy. - BDP (biparietal size, that is, the distance from the temple to the temple) - 17-24 mm. A high BDP means a large fetus, but only on the condition that all other indicators say the same. Otherwise, we can talk about a herniated brain or hydrocephalus. Low BDP indicates slow brain development.
- TVP (collar space thickness) - 1.6–1.7 mm. Deviation from this norm (TVP above 3 mm) is considered a sign of some severe chromosomal pathologies - Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc. However, one should not panic ahead of time - no one will make such a serious diagnosis only on the basis of TVP.
 To confirm, you need to take a blood test for hormones and take a biopsy of the outer dense shell of the embryo for further research.
To confirm, you need to take a blood test for hormones and take a biopsy of the outer dense shell of the embryo for further research.
The length of the nasal bone is 2–4.2 mm. Too small a nose bone can indicate pathology or simply that the baby's nose will be snub-nosed. HR (heart rate) - 140-160 beats per minute. A small (up to 40 beats per minute) deviation in one direction or another is considered a variant of the norm.
The size of the chorion, amnion and yolk sac. The chorion is the outer shell of the fetus, which will eventually become the placenta. If it is located on the lower wall of the uterus, they speak of chorion previa. This is a potentially dangerous situation, fraught with miscarriage, and in this case, bed rest is recommended for the pregnant woman.
The amnion is the inner membrane that holds the amniotic fluid. The normal volume of amniotic fluid at 11–13 weeks is 50–100 ml.
The yolk sac is an embryonic organ that, in the first weeks of a fetus's life, plays the role of some internal organs that will be formed later. By the time of the first screening, the yolk sac should practically disappear (then the examination form will indicate “not visualized”). If its size is about 6 mm, then the fetus may have certain pathologies.
By the time of the first screening, the yolk sac should practically disappear (then the examination form will indicate “not visualized”). If its size is about 6 mm, then the fetus may have certain pathologies.
Cervix. Normally, its length by the time of the first screening is 35–40 mm. A shorter cervix means a risk of preterm labor.
Ultrasound is performed in two ways - transabdominal, in which the sensor of the ultrasound machine is located on the abdomen, and transvaginal, in which it is inserted into the vagina. Transvaginal ultrasound provides more complete and accurate information, but it is usually performed only in the first trimester. This method is usually used when examining overweight women, since the fat layer in the abdomen does not allow the fetus and uterus to be examined in detail.
It is necessary to properly prepare for an ultrasound. Before a transabdominal ultrasound, it is advised to drink about a liter of water so that the bladder is full at the time of the examination - then the uterus will shift slightly towards the abdomen and the picture will be clearer. With transvaginal ultrasound, the degree of fullness of the bladder does not matter, however, before the examination, it is better to go to the toilet - it will be more comfortable. Before the examination, you need to take a shower or freshen up with wet wipes. The accumulation of gases can distort the results of ultrasound, no matter what method it is carried out. Therefore, expectant mothers suffering from flatulence are advised the day before the examination to take remedies for flatulence and not eat anything that produces gas.
With transvaginal ultrasound, the degree of fullness of the bladder does not matter, however, before the examination, it is better to go to the toilet - it will be more comfortable. Before the examination, you need to take a shower or freshen up with wet wipes. The accumulation of gases can distort the results of ultrasound, no matter what method it is carried out. Therefore, expectant mothers suffering from flatulence are advised the day before the examination to take remedies for flatulence and not eat anything that produces gas.
Blood test
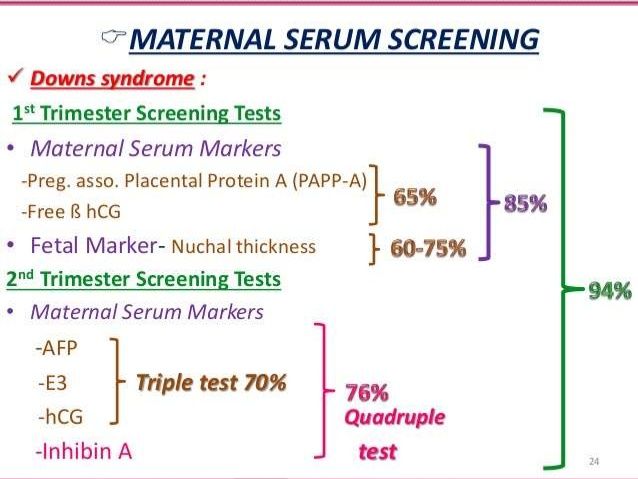
Biochemical screening, also called a dual test, is done to determine the level of two hormones (hence the name) - free b-hCG and PAPP-A.
- b-hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) begins to be produced from the first days of pregnancy. Its amount gradually increases until about the 9th week, and then begins to gradually decrease. On average, for a period of 11–13 weeks, 50,000–55,000 mIU / ml is considered the norm.
 An elevated level of hCG may indicate a multiple pregnancy, or, in the worst case, genetic pathologies of the fetus or the presence of diabetes in the mother. Reduced hCG is typical of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, fetal death, or certain malformations (Patau syndrome and Edwards syndrome).
An elevated level of hCG may indicate a multiple pregnancy, or, in the worst case, genetic pathologies of the fetus or the presence of diabetes in the mother. Reduced hCG is typical of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, fetal death, or certain malformations (Patau syndrome and Edwards syndrome). - PAPP-A is an A-plasma protein. The content rate for a period of 11–13 weeks is 0.79–6.01 mU / l. Low PAPP-A is a sign of chromosomal pathologies such as Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome, fetal death and miscarriage, fetal malnutrition (underweight) and preeclampsia.
- A high PAPP-A is a sign of multiple pregnancies, large fetuses, or a low placenta.
In order for the blood test to give the most accurate information, it must be taken on an empty stomach, at least 8 hours after the last meal. 2-3 days before the analysis, you should refrain from fried, fatty, spicy, smoked foods, chocolate, nuts, seafood. It is also recommended not to have sexual intercourse. All this is not so significant, but it can affect the result in one way or another.
All this is not so significant, but it can affect the result in one way or another.
Second pregnancy screening
The second screening during pregnancy is carried out at 16-20 weeks. Like the first one, it consists of the same two stages - ultrasound and blood test.
ultrasound
This time, the doctor determines not only the size, but also the position of the fetus and its bone structure, the condition of the internal organs and the place of attachment of the umbilical cord, as well as the volume of amniotic fluid. Here are the approximate main indicators of the norm for a period of 16-20 weeks:
- BPR - 26–56 mm.
- DBK (length of the femur) - 13-38 mm.
- DPC (length of the humerus) - 13-36 mm.
- OG (head circumference) - 112-186 mm.
IAF (amniotic fluid index, that is, the volume of amniotic fluid) - 73-230 mm. Oligohydramnios can adversely affect the condition of the child's bone structure and the development of his nervous system.
Localization of the placenta. There is some risk only when the placenta is located on the anterior wall of the uterus - with such localization, detachment of the placenta is possible.
Umbilical cord. One of the most important parameters is the place of attachment of the umbilical cord. Marginal, split or sheath attachment is fraught with fetal hypoxia and difficulties during childbirth, often it becomes an indication for caesarean section. The umbilical cord is fed through 2 arteries and 1 vein, although sometimes only one artery is available. This can cause fetal hypoxia, heart disease, disorders in the child’s cardiovascular system, and cause a baby’s low body weight. However, if all other analyzes and examinations do not show deviations from the norm, you should not worry.
Cervix. The length of the cervix at this time should be 40–45 mm. A short cervix means a threatened miscarriage.
Visualization. Unsatisfactory visualization can be caused both by the peculiarities of the position of the fetus or the excess weight of the expectant mother, and by edema or hypertonicity of the uterus.
Blood test
As during the first screening, during the second, a blood test for b-hCG is taken, the level of free estriol and AFP is also checked. Here are the norms for their content at the 16th-20th weeks of pregnancy:
- b-hCG - 4.67-5-27 ng / ml.
- Free estriol is a hormone whose level can be used to judge the state of the placenta. The norm is 1.17–3.8 ng / ml. Elevated estriol is characteristic of multiple pregnancy or a large fetus. Reduced - for threatened miscarriage, placental insufficiency, anencephaly and Down's syndrome.
- AFP is a protein that is produced in the gastrointestinal tract of the fetus. Norm - 15-27 U / ml. A slightly lower AFP may mean that the gestational age was determined incorrectly (slightly underestimated). If the AFP is very low, the cause may be Edwards or Down syndrome, the threat of miscarriage or fetal death. High AFP is characteristic of neural tube pathologies, esophageal atresia, Meckel's syndrome.
 High AFP is also possible in women who have had an infectious disease during pregnancy.
High AFP is also possible in women who have had an infectious disease during pregnancy.
Third pregnancy screening
The third screening during pregnancy is carried out at the 30th-43rd week. Based on the results of this screening, the doctor decides on the need for a caesarean section or the possibility of a natural birth. The basis of the third screening is the same ultrasound. Sometimes dopplerography is prescribed - a study of the work of blood vessels. Here are the approximate norms for a given gestational age:
ultrasound
- BPR - 67-91 mm
- DBK - 47-71 mm
- WPC - 44-63 mm
- Exhaust - 238-336 mm
- IAG — 82- 278 mm
The thickness of the placenta is 23.9–43.8. Too thin placenta is not a particularly dangerous deviation from the norm. The reason may be the miniature physique of a woman, her infectious diseases, hypertension. An excessively thick placenta is a sign of anemia, diabetes, Rh conflict.