How do you get a uti when pregnant
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI) During Pregnancy
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
Medically Reviewed by Nivin Todd, MD on September 04, 2022
In this Article
- UTI Symptoms
- Why Are UTIs More Common During Pregnancy?
- UTI Diagnosis
- UTI Treatment During Pregnancy
- UTI Complications During Pregnancy
- UTI Prevention
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection of some part of your body's urinary system, which includes your:
- Kidneys
- Ureters (tubes that carries urine from your kidneys to your bladder)
- Bladder
- Urethra (a short tube that carries urine from your bladder to outside your body)
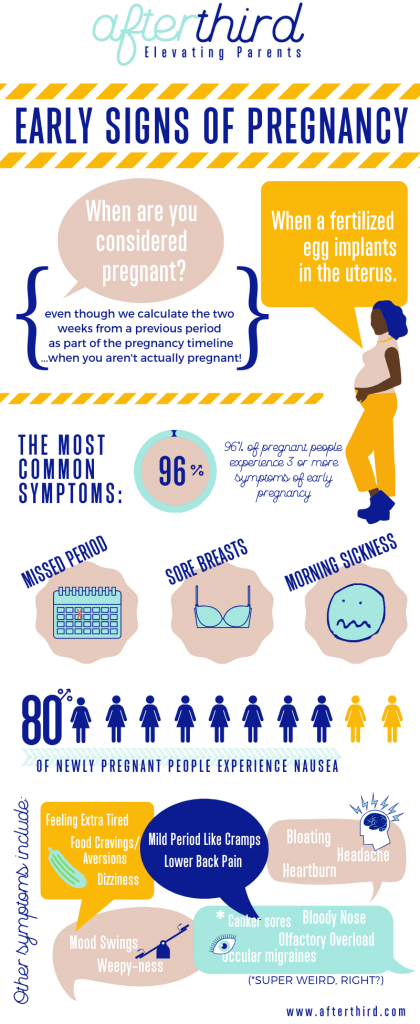
Bacteria cause most UTIs. Anyone can get one, but they're most common in women, and they can be extra concerning if you're pregnant.
If you think you might have a UTI, tell your doctor. With proper care, you and your baby should be fine.
Usually, these infections are in the bladder and urethra. But sometimes they can lead to kidney infections. If they do, UTIs may lead to preterm labor (giving birth too early) and low birth weight.
UTI Symptoms
If you have a UTI, you may have:
- An urgent need to pee, or peeing more often
- Trouble with peeing
- A burning sensation or cramps in your lower back or lower belly
- A burning feeling when you pee
- Urine that looks cloudy or has an odor
- Blood in your pee, which can turn it red, bright pink, or cola-colored
If you have a kidney infection, you may have:
- Fever
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Upper back pain, often on just one side
If you have symptoms of a kidney infection, see your doctor right away. Without treatment, the infection can spread into your bloodstream and cause life-threatening conditions.
Why Are UTIs More Common During Pregnancy?
Hormones are one reason. In pregnancy, they cause changes in the urinary tract, and that makes women more likely to get infections. Changes in hormones can also lead to vesicoureteral reflux, a condition in which your pee flows back up from your bladder to your kidneys. This can cause UTIs.
Changes in hormones can also lead to vesicoureteral reflux, a condition in which your pee flows back up from your bladder to your kidneys. This can cause UTIs.
When you’re pregnant, your pee has more sugar, protein, and hormones in it. These changes also put you at higher risk for a UTI.
Because you’re pregnant, your growing uterus presses on your bladder. That makes it hard for you to let out all the urine in your bladder. Leftover urine can be a source of infection.
Other causes of UTIs include:
Escherichia coli and other bacteria from your poop. E. Coli is the most common cause of UTIs and can move from your rectum to your urethra if you don’t wipe from front to back.
Sexual activity. Fingers, your partner’s penis, or devices can move bacteria near your vagina into your urethra.
Group B streptococcus. Many women have this bacteria in their colon and vagina. It can cause UTIs and women can pass it to their newborns. Your doctor will test you for this bacteria around weeks 36 to 37 of pregnancy. If you’re positive for group B strep, your doctor will give you IV antibiotics during labor.
Your doctor will test you for this bacteria around weeks 36 to 37 of pregnancy. If you’re positive for group B strep, your doctor will give you IV antibiotics during labor.
UTI Diagnosis
You’ll take a urine test. Your doctor will test it for bacteria and red and white blood cells. A urine culture may also be checked. It shows what kind of bacteria are in the urine.
UTI Treatment During Pregnancy
You’ll take antibiotics for 3 to 7 days or as your doctor recommends. If your infection makes you feel uncomfortable, your doctor will probably start your treatment before you get your urine test results.
Your symptoms should go away in 3 days. Take all of your medication on schedule anyway. Don’t stop it early, even if your symptoms fade.
Many common antibiotics -- amoxicillin, erythromycin, and penicillin, for example -- are considered safe for pregnant women. Your doctor wouldn’t prescribe others, such as ciprofloxacin (Cipro), sulfamethoxazole, tetracycline, or trimethoprim (Primsol, Proloprim, Trimpex), that can affect your baby’s development.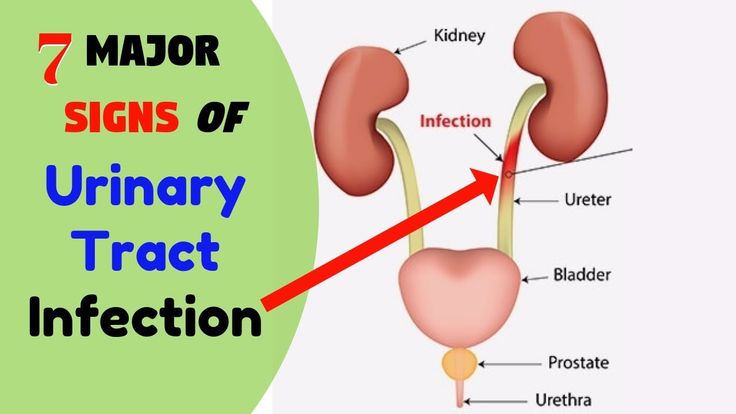
UTI Complications During Pregnancy
Pyelonephritis is a UTI that affects the kidneys. If you’re pregnant it can cause:
- Preterm labor
- Severe infection
- Adult respiratory distress syndrome
- Anemia
- Long-term infection
UTI Prevention
To try to avoid getting a UTI:
- Drink at least eight glasses of water a day.
- Wipe yourself from front to back when you go to the bathroom.
- Empty your bladder shortly before and after sex.
- If you need a lubricant when you have sex, choose a water-based one.
- Don't douche.
- Avoid strong feminine deodorants or soaps that cause irritation.
- Wash your genital area with warm water before sex.
- Wear cotton underwear.
- Take showers instead of baths.
- Don’t wear pants that are too tight.
- Pee often.
- Avoid alcohol, citrus juices, spicy food, and caffeinated drinks, which can irritate your bladder.
Women's Health Guide
- Screening & Tests
- Diet & Exercise
- Rest & Relaxation
- Reproductive Health
- Head to Toe
UTIs during pregnancy are common and treatable | Your Pregnancy Matters
×
What can we help you find?Refine your search: Find a Doctor Search Conditions & Treatments Find a Location
Appointment New Patient Appointment
or Call214-645-8300
MedBlog
Your Pregnancy Matters
September 20, 2021
Your Pregnancy Matters
Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M. D. Obstetrics and Gynecology
D. Obstetrics and Gynecology
As you adjust to new changes in your body during pregnancy, it can be easy to overlook symptoms of everyday health conditions, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs). UTIs are equally common in pregnant and non-pregnant patients and usually require medication to clear the infection.
But if left untreated during pregnancy, a UTI can progress to s serious infection that can lead to preterm labor, premature delivery, or even fetal loss.
UTIs occur when bacteria enter and grow in the urinary tract. During pregnancy, your bladder – which is in the lower part of your urinary tract – is less likely to empty entirely when you urinate, thanks to pressure from your expanding uterus and an increase in hormones that relax the muscles in your uterus. The longer urine stays in your body, the higher the chances that you’ll grow too much bacteria.
During pregnancy, your bladder – which is in the lower part of your urinary tract – is less likely to empty entirely when you urinate, thanks to pressure from your expanding uterus and an increase in hormones that relax the muscles in your uterus. The longer urine stays in your body, the higher the chances that you’ll grow too much bacteria.
We watch for three types of UTIs during pregnancy:
- Asymptomatic: Approximately 7% of pregnant women may have a UTI that doesn’t cause symptoms. An untreated asymptomatic infection has a 25% chance of advancing to the next level of UTI – your bladder and then your kidney.
- Cystitis: Localized to the bladder, this infection will cause symptoms typically associated with UTIs, such as frequent but small amounts of urine, painful urination, and strong urges to urinate immediately.
- Pyelonephritis: This kidney infection can lead to serious issues such as septic shock, anemia, excess lung fluid, and pre-term labor.
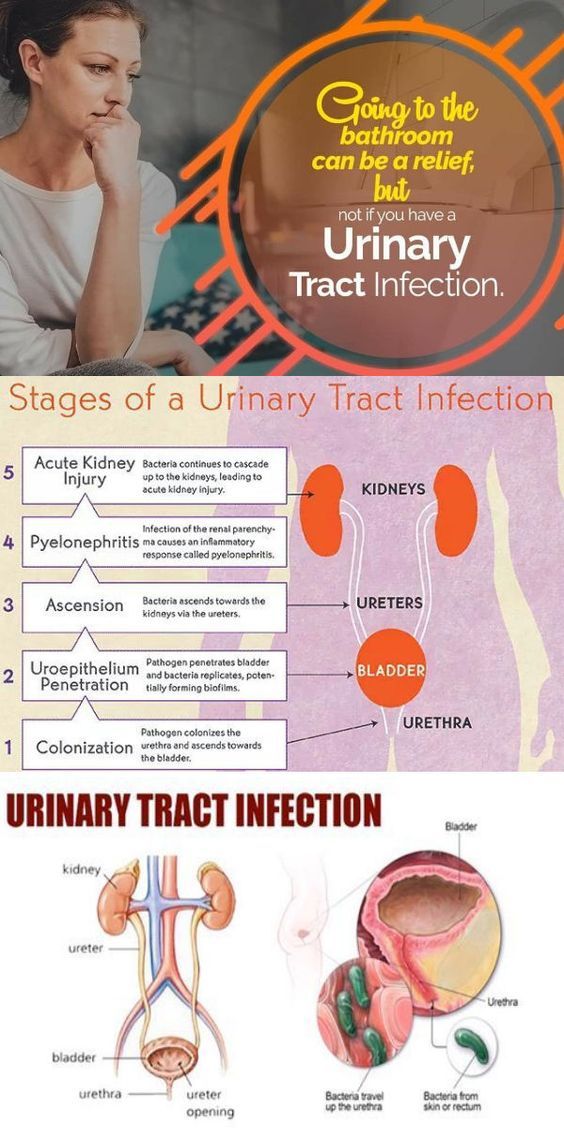 It typically includes the symptoms of cystitis, plus nausea, fever, chills, and pain in your lower back and sides.
It typically includes the symptoms of cystitis, plus nausea, fever, chills, and pain in your lower back and sides.
Because UTIs are prevalent during pregnancy, we request a urine sample to conduct a culture test as part of your prenatal care. The test looks for specific types of bacteria in your urine that can cause an infection.
We will likely test your urine multiple times throughout your pregnancy. But don’t assume we’re looking for a UTI every time; this is a common misconception. It’s important to talk with your doctor if you experience UTI symptoms to make sure you get the right test. The earlier we diagnose a UTI, the sooner we can treat you and prevent a more dangerous condition.
UTI treatment: What to expect
UTI treatments during pregnancy are safe and easy, usually involving a short course (3-7 days) of oral antibiotics. There are two exceptions:
- If you continue to have UTIs after we treat the first one, we may recommend suppressive therapy.
 You will take a lower dose of antibiotics every day of your pregnancy instead of larger doses for just a few days.
You will take a lower dose of antibiotics every day of your pregnancy instead of larger doses for just a few days. - If you have pyelonephritis (kidney infection), you will need to receive antibiotics through an IV at a hospital.
For most patients, receiving antibiotic treatment is much safer than risking a kidney infection. We will discuss all your health conditions and pregnancy symptoms to determine the best type of antibiotic for you, depending on what will work effectively against the bacteria in your urine.
Not all urine tests are the same
In the third trimester, we’ll likely test your urine for the presence of protein or glucose, which can indicate high blood pressure or gestational diabetes. Around this time, we also test urine for sexually transmittable diseases such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, which can be transferred to your baby.
Neither of these tests will tell us whether you have a UTI. If you’re experiencing UTI symptoms, please tell us so we can perform the appropriate test and begin treatment.
What increases or reduces risk of UTIs during pregnancy?
Women who have or carry the trait for sickle cell disease are at increased risk for UTIs. We test these patients monthly to ensure we detect an infection as soon as possible.
If you have diabetes, you’re also at a higher risk. We might not test you as frequently, but we will consistently look for symptoms. Both conditions make it harder for the body to fight infections.
Just as when you’re not pregnant, you can take specific actions to lower your chances of getting a UTI, such as:
- Wiping front to back in the bathroom
- Urinating before and after sex
- Wearing cotton underwear
- Avoiding tight and wet clothing
- Drinking more water
Prepare for possible postpartum UTIs
In some cases, the risks of developing a UTI increase after you give birth.
Patients who have a C-section or receive an epidural during labor have a catheter inserted into their bladder. This ensures a safer delivery by keeping your bladder empty. But a catheter increases your risk of infection the longer it stays in your body, and its placement provides the perfect track for bacteria to enter your bladder.
This ensures a safer delivery by keeping your bladder empty. But a catheter increases your risk of infection the longer it stays in your body, and its placement provides the perfect track for bacteria to enter your bladder.
To decrease your UTI risk, our goal is to remove your catheter no more than six to eight hours after surgery and even sooner after an epidural. An infection can take days to appear, so watch for symptoms after you leave the hospital and tell your doctor right away if you experience them. We don’t perform routine UTI tests after delivery, so it’s important to alert us to abnormal pain or discomfort.
Related reading: Tips to prevent involuntary urine leakage (incontinence) during and after pregnancy
With so many new tasks to complete and emotions to experience after bringing your newborn home, it can feel overwhelming to keep track of one more thing – but your health remains a priority after the birth of your baby. The more you tell us about how you feel, the more we can do to help you stay healthy.
To visit with an Ob/Gyn, call 214-645-8300 or request an appointment online.
More in: Your Pregnancy Matters
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
October 11, 2022
Prevention; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.
 D.
D.
October 4, 2022
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Meitra Doty, M.D.
September 27, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.
 D.
D.
September 20, 2022
Men's Health; Women's Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Yair Lotan, M.D.
September 6, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
August 29, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Patricia Santiago-Munoz, M.
 D.
D.
August 23, 2022
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
August 11, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Emily Adhikari, M.D.
August 2, 2022
More Articles
Increased tone of the uterus during pregnancy
Nicotine constricts the blood vessels of the expectant mother, as well as the vessels of the placenta and umbilical cord, through which the fetus is nourished. Of course, smoking by itself is unlikely to lead to hypertonicity, but in combination with other factors, it may well
Of course, smoking by itself is unlikely to lead to hypertonicity, but in combination with other factors, it may well
If the work is associated with constant stress, it has harmful effects or it is physically difficult, give it up as soon as possible. If this is not possible, use your rights, which are enshrined in the labor legislation of the Russian Federation
Hypertonicity must be distinguished from Braxton-Hicks contractions: it lasts much longer than these training contractions and usually does not go away on its own (or goes away only after a long time)
what is hypertonicity
, - muscle, and according to the laws of physiology, muscle tissue is reduced under the influence of any factor. Slightly the uterus contracts in women every month during menstruation, much stronger during labor pains. The uterus can also contract during pregnancy, doctors call this condition hypertonicity. What it looks like: suddenly, at some point, a woman feels that her stomach is tense, becomes hard, as if “hardening”. This state lasts for a long time - half an hour, an hour, half a day or even all day. Additionally, discomfort (or pain) in the lower back or sacrum may also appear. It is clear that such tension in the abdomen worries the mother, because since the uterus is contracting, then perhaps there is a threat of termination of pregnancy. But here it all depends on how much and how often the stomach tenses.
This state lasts for a long time - half an hour, an hour, half a day or even all day. Additionally, discomfort (or pain) in the lower back or sacrum may also appear. It is clear that such tension in the abdomen worries the mother, because since the uterus is contracting, then perhaps there is a threat of termination of pregnancy. But here it all depends on how much and how often the stomach tenses.
Braxton-Hicks contractions
It turns out that the stomach can tense up not only when there is a threat of miscarriage. Starting from the end of the second trimester, the expectant mother can feel the so-called training contractions (Brexton-Hicks contractions) - the stomach also tenses with them for a while, as if “hardening”, - in general, the sensations are the same as with hypertonicity. But the main difference between such contractions and hypertonicity is that they last for a very short time (a few seconds - a couple of minutes) and pass by themselves, as well as if you change the position of the body or take a shower. Braxton-Hicks contractions occur up to about ten times a day, and by the end of pregnancy they appear even more often. These contractions are completely normal during pregnancy, and they do not indicate any threat of interruption. It’s just that with their help, the uterus, as it were, prepares (trains) for childbirth.
Braxton-Hicks contractions occur up to about ten times a day, and by the end of pregnancy they appear even more often. These contractions are completely normal during pregnancy, and they do not indicate any threat of interruption. It’s just that with their help, the uterus, as it were, prepares (trains) for childbirth.
where does hypertonicity come from
Hypertonicity can appear in any trimester of pregnancy. In the early stages, it occurs more often due to the fact that there is not enough progesterone, a hormone that is needed for the normal course of pregnancy. Another cause of hypertonicity is some changes in the uterine wall, for example, fibroids (a knot of uterine muscle tissue), endometriosis (growth of the uterine mucosa into the thickness of the wall), and inflammatory diseases. In these situations, the wall of the uterus is not able to stretch as it should. At later dates, hypertonicity can develop, on the contrary, with overstretching of the uterus (with polyhydramnios, large fetuses, multiple pregnancies). Very often, hypertonicity is provoked by some kind of physical activity too strong for a woman, for example, if, in a fit of “nesting”, the mother suddenly began to move and rearrange something in the apartment herself, or she simply moved for a very long time without resting. Someone hypertonicity occurs after psychological overstrain.
Very often, hypertonicity is provoked by some kind of physical activity too strong for a woman, for example, if, in a fit of “nesting”, the mother suddenly began to move and rearrange something in the apartment herself, or she simply moved for a very long time without resting. Someone hypertonicity occurs after psychological overstrain.
how to recognize hypertonicity
Hypertonicity must be distinguished from Braxton-Hicks contractions - as mentioned earlier, it lasts much longer than these training contractions and usually does not go away on its own (or goes away only after some long time). But if the mother cannot understand whether she has hypertension or not, you should consult a doctor. If there is still an increased tone of the uterus, the doctor, simply by placing his hand on his stomach, will feel a seal, tension, up to the feeling of a stone at hand. In addition, you can always do an ultrasound, on which, with hypertonicity, areas of local thickening of the muscular layer of the uterus are visible, and also look at the cervix, by the state of which you can also judge whether there is a threat of abortion or not.
what to do in case of hypertonicity
If it appears, the first thing you need to do is:
1. Calm down and lie down if possible. Do not panic, extra stress will not bring any benefits, especially since without consulting a doctor it is still not clear whether there is hypertonicity and how pronounced it is. Or maybe it's a false alarm? In addition, you can use relaxation techniques (breathing, auto-training, etc.).
2. Call your doctor. Of course, the doctor will not make a diagnosis in absentia, but since he knows the history of the expectant mother, her real or possible problems, he will be able to give the right direction for further action.
3. If it is not possible to contact your doctor, you can contact any clinic or antenatal clinic where pregnant women are treated. If medical institutions are already closed (late evening, at night), you can call an ambulance - she will take you to the nearest hospital or maternity hospital (you can also get there by taxi).
4. Hypertonicity is well eliminated by special medicines that relax the uterus (tocolytics), and if the doctor has prescribed them, then you should not be afraid to take them: they help quickly enough and do not harm the child.
how to prevent hypertonicity
There are simple rules that can prevent hypertonicity or reduce the risk of its occurrence:
1. Quit smoking, watch your weight, do not eat surrogate foods. No matter how trite it may sound, but it is a healthy lifestyle that is the basis of our well-being.
2. Distribute your forces correctly. Laundry, cooking can wait if the expectant mother suddenly feels that she needs a rest. If any activities require physical or psychological stress, cancel them for a while. Do not attend events or places where you may feel uncomfortable, reduce communication with people that are unpleasant for you.
3. Follow your doctor's recommendations: if he recommends any examination or treatment, do not neglect them.
Listen to your body, follow the doctor's advice, tune in to the positive - this is the key to a successful pregnancy. And then no hypertonicity is terrible for you!
Pregnancy - from the first days
With the onset of pregnancy, a woman's body immediately begins to rebuild in work and prepare for bearing a baby. After all, a young mother has a journey of 40 weeks, when she will carry a baby in herself, and her body will create all the most favorable conditions for this, provide the baby not only with a small, cozy apartment, but also with nutrition and oxygen. A woman who has received a long-awaited pregnancy treats all changes in her body with special attention, listens to every new sensation!
And how should a woman feel at the very beginning of pregnancy?
The first sign of an "interesting" situation, of course, menstruation did not start on time . Already on the first day of delay, you can do a urinary pregnancy test, with a high probability it will show the true result. More informative and important for an obstetrician-gynecologist will be the value of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, determined by the blood of a pregnant woman, this is a hormone that is produced by the future placenta, it appears in the woman's body from the first hours of pregnancy and actively increases in the future. By the amount of this hormone, the doctor will judge the gestational age, the absence of pathological conditions and the developmental norms of this pregnancy and will guide you on the most optimal terms for ultrasound examination.
More informative and important for an obstetrician-gynecologist will be the value of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, determined by the blood of a pregnant woman, this is a hormone that is produced by the future placenta, it appears in the woman's body from the first hours of pregnancy and actively increases in the future. By the amount of this hormone, the doctor will judge the gestational age, the absence of pathological conditions and the developmental norms of this pregnancy and will guide you on the most optimal terms for ultrasound examination.
Breast engorgement and enlargement. Gradually appearing symptom. If a woman has examined her breasts during the last year, was examined by a mammologist, underwent an ultrasound examination of the mammary glands, and received a conclusion from the doctor - she is healthy, there is nothing to worry about! The mammary glands enter a new phase of development and prepare for the upcoming feeding of the child. If the mammary glands have not been examined for more than a year, it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound scan to exclude possible pathology, especially since the obstetrician-gynecologist will need this examination to register for pregnancy.
Drawing pains in the lower abdomen. Can be normal only if they occur no more than 1-2 times a day, and go away on their own after a few minutes. In other cases, pain in the lower abdomen, of course, is not an indicator of a pathological or complicated course of pregnancy, but it is still necessary to consult a doctor. The gynecologist will determine the cause of the pain and give recommendations on the regimen, permissible loads and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
Nausea and vomiting. Not the most pleasant, but almost inevitable signs of pregnancy. If nausea occurs predominantly in the morning, try to fight it with food. Before going to bed, prepare for yourself a piece of an apple or a banana, you can have a cracker or a biscuit cookie, even a cracker will do. In the morning after waking up, without getting out of bed, enjoy the "piece" waiting for you, very often this is what saves you from an attack of morning sickness. A small spoonful of honey helps. Drink more liquids, mineral water, juices, tea. Ginger tea fights toxicosis well. Eat small meals. At least 5-7 times a day. Food should not be fatty or spicy. Avoid stuffy rooms. Walk outdoors more. Daytime naps are recommended. If vomiting occurs, especially more than 1-2 times a day, you should consult a doctor. Additional examination and more serious treatment may be required.
Drink more liquids, mineral water, juices, tea. Ginger tea fights toxicosis well. Eat small meals. At least 5-7 times a day. Food should not be fatty or spicy. Avoid stuffy rooms. Walk outdoors more. Daytime naps are recommended. If vomiting occurs, especially more than 1-2 times a day, you should consult a doctor. Additional examination and more serious treatment may be required.
Discharge from the genital tract becomes more profuse during pregnancy. Normally, this is a clear, odorless mucous discharge. If there is “something wrong” in the discharge, it is better to consult a doctor. They will take a swab from you to determine the degree of purity of the vagina, see why the discharge has changed its character, and whether it needs treatment. Since during pregnancy the woman's body is in an immunosuppressive state, that is, the mother's immunity is reduced, inflammatory changes in the vagina may occur, which during pregnancy is very important to treat in a timely manner.