How many days can you ovulate
Calculating Your Monthly Fertility Window
Your fertility window is the time during your menstrual cycle when you’re most likely to get pregnant. For most people, it’s the five days leading up to ovulation, the day of ovulation and the day after ovulation. Calculating your monthly fertility window can help you target the optimal time to have sex if you’re trying to conceive. However, natural family planning is a less reliable form of contraception and does not protect against sexually transmitted infections.
Understanding Your Menstrual Cycle
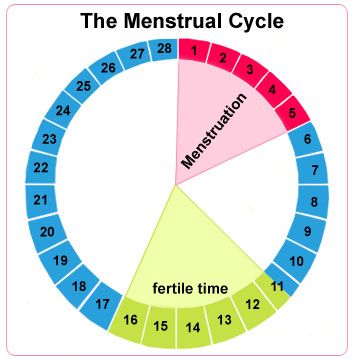
If you’re trying to get pregnant and want to track ovulation, you need to understand your menstrual cycle. Your menstrual cycle is your body’s way of preparing for pregnancy. It begins on the first day of your period and starts over when your next period begins. A typical menstrual cycle is 28 days, but cycles ranging from 21 to 35 days are considered normal.
Lots of changes happen in your body during the cycle, including hormone fluctuations. About halfway through, one of your ovaries releases a mature egg. The egg goes to one of your fallopian tubes, where it waits to be fertilized by sperm. The lining of your uterus gets thicker, too. This prepares the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg.
If you don’t get pregnant, it could mean that the egg didn’t fertilize, or that the embryo (fertilized egg) didn’t implant into the uterus. In those cases, the uterine lining sheds and you get your period.
When am I ovulating?
Knowing when you’re ovulating is key to tracking your fertility window and determining the best time to get pregnant. There are a few different fertility awareness methods, also called rhythm methods. It’s best to use all three methods if you’re doing natural family planning.
Calendar method
Use the calendar method to track the length of your menstrual cycle. Each month, mark the first day of your period on a calendar or in a period-tracking app. The number of days between the first day of consecutive periods is the length of your menstrual cycle. You should do this for at least six months to get good data.
You should do this for at least six months to get good data.
You ovulate about 12 to 14 days before the start of a new menstrual cycle. Your fertile window is the five days leading up to ovulation, plus the day of ovulation and the day after ovulation — so about seven days in total.
It’s important to note that if you have irregular periods and the length of your menstrual cycle varies from month to month, the calendar method won’t be accurate for you.
Cervical mucus method
Hormone fluctuations during your menstrual cycle change the amount and consistency of your vaginal mucus. You need to feel and look at your vaginal mucus each day and record the results on a chart. You’re likely ovulating (and most fertile) when the mucus is heavy, wet and slippery. It will have the consistency of raw egg whites.
You should chart your vaginal mucus for at least one menstrual cycle. It may be difficult at first to know what to look for, so talk to your provider if you want to try this method. He or she can explain how to chart and describe the mucus each day.
He or she can explain how to chart and describe the mucus each day.
Ovulation predictor kits
Ovulation predictor kits are an at-home tool to help predict your ovulation. These tests may be helpful if you have regular periods, but still aren’t quite sure if you are seeing natural signs of ovulation (cervical mucus or a rise in basal body temperature). Ovulation predictor kits test your urine for levels of luteinizing hormone. When the ovulation predictor test becomes positive, ovulation will typically occur within 24 hours, indicating that you’re fertile and should have sex. These kits might not be reliable if you have irregular periods due to polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Basal body temperature method
Also called the temperature method, you take your temperature each morning as soon as you wake up (before you get out of bed). You use a basal body thermometer, which may go in your mouth or your rectum. A basal thermometer is more sensitive than a regular thermometer.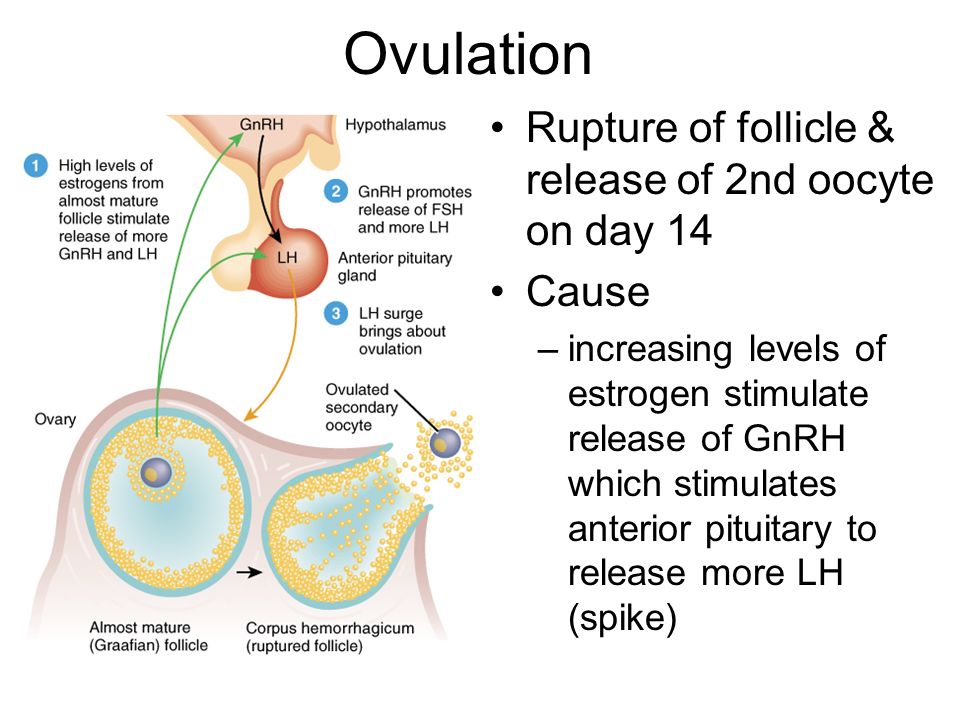 It measures body temperature to a tenth of a degree.
It measures body temperature to a tenth of a degree.
A woman’s basal body temperature rises slightly during ovulation (increases by 0.5 degrees Fahrenheit). If you track your temperatures leading up to ovulation, you should see a sustained rise in your basal body temperature after ovulation.
To help you plan, write your body temperature down each day on a tracking sheet. You should track your temperature for at least three months before using this method for family planning.
However, it’s important to note that the basal body temperature method is not good at predicting your ovulation when trying to conceive. Once you identify the rise in your temperature, you’ve already ovulated. However, this method is a good tool to monitor your pattern of ovulation.
Should I have sex before, during or after ovulation?
For the best chances of pregnancy, you should have sex every day or every other day during the:
- Five days leading up to ovulation
- Day of ovulation
- Day after ovulation
There’s a lot of information (and misinformation) about methods for having sex that could increase your chances of getting pregnant. There’s no specific sex position that increases your odds of conceiving. Some lubricants may negatively affect sperm and prevent them from reaching the egg. Talk to your health care provider about which lubricants to avoid.
There’s no specific sex position that increases your odds of conceiving. Some lubricants may negatively affect sperm and prevent them from reaching the egg. Talk to your health care provider about which lubricants to avoid.
What if I have irregular periods?
If you have irregular periods, meaning that your periods are outside of the 21–35-day window or if your cycle intervals vary by more than seven days each month (30-day interval one month, 23 days the next month), you should speak with your Gyn/OB or a fertility specialist. This irregularity may be due to a hormone imbalance and could make it more challenging to get pregnant using natural family planning methods.
How else can I prepare for pregnancy?
In addition to tracking your ovulation to determine your fertile window, it’s important to schedule preconception counseling with your doctor. There are a variety of screenings and lifestyle modifications that can help increase your chances of a successful planned pregnancy.
If you’re under 35 and have been trying to conceive for more than a year, or if you’re over 35 and have been trying for six months, it may be time to talk to your doctor about why you can’t get pregnant.
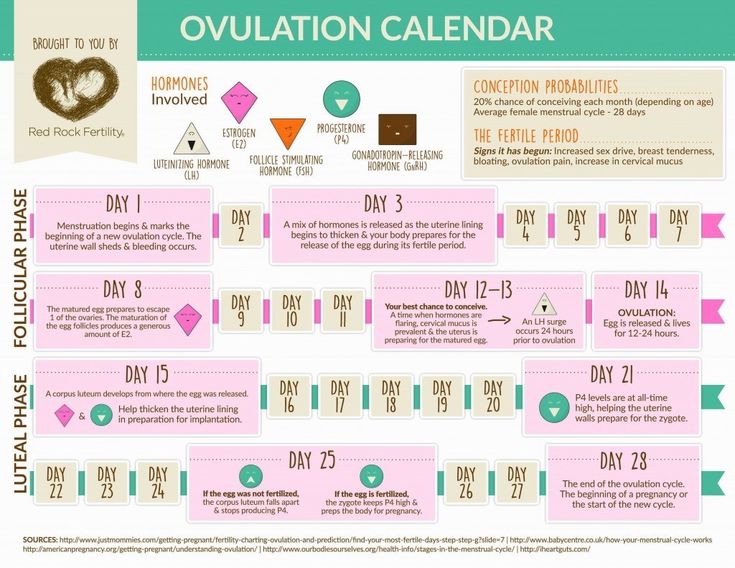
Right Time For Sex , When Do You Ovulate ?
When are you more likely to conceive?
We’re talking about the 'fertile window’ – the days in a woman’s menstrual cycle when pregnancy is possible. The ‘fertile window’ depends on the length of the menstrual cycle, which varies among women.
The ‘fertile window’ is the day an egg is released from the ovary (ovulation) and the five days beforehand. Having sex (intercourse) during this time gives you the best chance of getting pregnant.
Ovulation Calculator
What day did you your most recent period start?
Number of days in your cycle Please select20 Days21 Days22 Days23 Days24 Days25 Days26 Days27 Days28 Days29 Days30 Days31 Days32 Days33 Days34 Days35 Days36 Days37 Days38 Days39 Days40 Days41 Days42 Days43 Days44 Days45 Days
Your ovulation day
Most fertile time
-
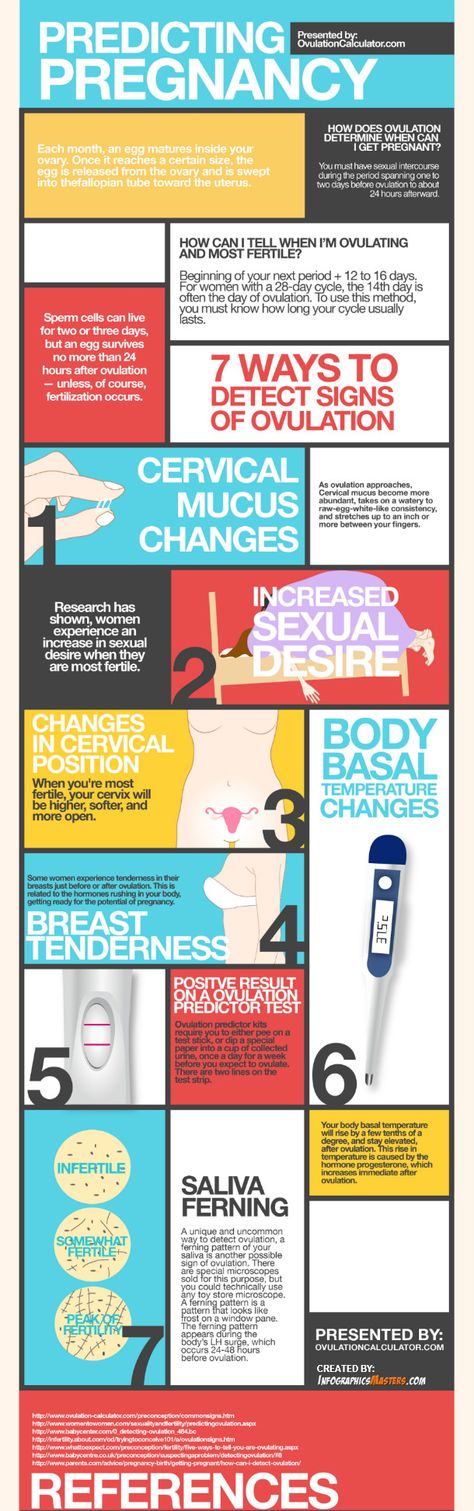
What is an ovulation calculator and how does it help you get pregnant?
This ovulation calculator or ovulation calendar can help you work out your most fertile time.
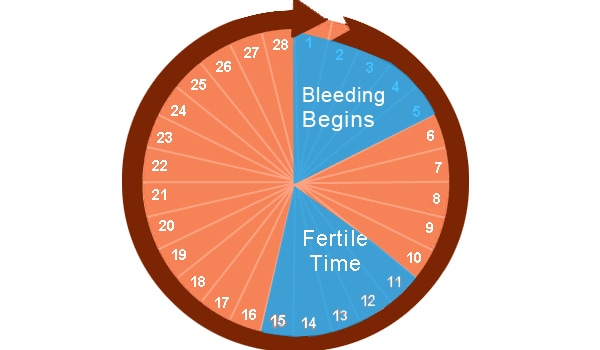 These are the days you are most likely to get pregnant.
These are the days you are most likely to get pregnant.It can also estimate your due date if you do become pregnant during your next fertile days.
Others ways to help you work out when you're ovulating:
- Notice changes in vaginal mucus
A few days before ovulation, you may notice your vaginal mucus becomes clear, slick and slippery, and feels a bit like egg white.
This is a sign that ovulation is about to happen. It’s the best time to have sex, as sperm travel more easily in this kind of mucus.
- Use an ovulation predictor kit
You can use a predictor kit from a supermarket or pharmacy, to test your urine for signs of ovulation. If you start testing your urine a few days before the day you next expect to ovulate, a positive result means you are going to ovulate within the next 24 to 36 hours (one to two days).
-
Facts about timing
Ovulation is when a mature egg is released from the ovary. The egg then moves down the fallopian tube where it can be fertilised. If sperm are in the fallopian tube when the egg is released, there is a good chance that the egg will be fertilised, creating an embryo, which can grow into a baby.
Pregnancy is technically only possible if you have sex during the five days before ovulation or on the day of ovulation. But the most fertile days are the three days leading up to and including ovulation. Having sex during this time gives you the best chance of getting pregnant.
By 12-24 hours after ovulation, a woman is no longer able to get pregnant during that menstrual cycle because the egg is no longer in the fallopian tube.
There’s almost no chance of getting pregnant if you have sex before or after the fertile window (but if you’re not trying to get pregnant, don’t rely on this – contraception is your best option!).

-
How to know when you’re ovulating
Knowing when you ovulate can help you plan for sex at the right time and improve your chance of getting pregnant. You can keep track of your menstrual cycles on a chart, in a diary, or on a free period-tracker app on your smartphone.
To work out the length of your menstrual cycle, record the first day you start bleeding (first day of your period). This is day 1. The last day of your cycle is the day before your next period begins.
- What is a ‘menstrual cycle’ and a ‘period’?
Some people think the ‘menstrual cycle’ and a ‘period’ are the same thing.
A period is when you bleed (or menstruate).

A menstrual cycle starts on the day when a period starts (day 1) and ends the day before the next period. A cycle’s length is considered normal if it’s between 21 and 35 days. They can vary between women and from one cycle to the next.
- Working out your ‘average’ menstrual cycle length
If your menstrual cycles are different lengths (most women’s cycles are) you can work out your average cycle length.
The number of days in a woman’s menstrual cycle can vary month to month. Periods are not always regular. It can be useful to work out an ‘average’ cycle length, based on the length of three menstrual cycles, to estimate when you’re most likely to be ovulating.
If you add the number of days in three cycles and divide the total number by three, it gives you your average cycle length.
Example
Sarah tracked her last three menstrual cycles by counting the time from the first day of one period, to the day before the next period.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24099629/Microsoft_Places__2_.jpg)
Cycle 1 was 28 days; Cycle 2 was 32 days; Cycle 3 was 27 days
28 + 32 + 27 = 87
87 divided by 3 = 29
So the average length of Sarah’s menstrual cycles is 29 days.
- Working out your most fertile days
When you know your average menstrual cycle length, you can work out when you ovulate.
Ovulation happens about 14 days before your period starts.
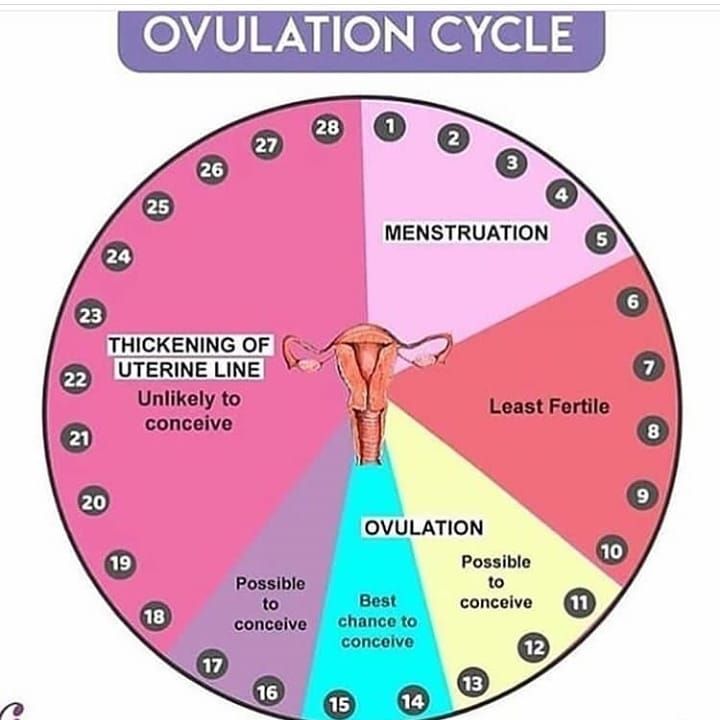
- If your average menstrual cycle is 28 days, you ovulate around day 14, and your most fertile days are days 12, 13 and 14.
- If your average menstrual cycle is 35 days ovulation happens around day 21 and your most fertile days are days 19,20 and 21.
- If you have shorter cycles, say 21 days, ovulation happens around day 7 and your most fertile days are days 5, 6 and 7.
Your most fertile days are the three days leading up to and including the day of ovulation.

Some women have very irregular cycles or find it difficult to work out an average cycle length. This can make it hard to work out when ovulation happens. If it’s all too hard, having sex every 2-3 days covers all bases and improves your chance of getting pregnant.
Myth busting
- MYTH
A woman can get pregnant any time of the month.
- FACT
A woman can only get pregnant on a few days during her menstrual cycle.
Why?
Because eggs and sperm only live for a short time:
- Sperm live for around five days.
- Eggs can only be fertilised for around 24 hours (one day) after being released from the ovary.
Eggs and sperm need to come together at the right time for fertilisation to happen to create an embryo.
Getting the timing right
If you're trying to get pregnant, timing is everything. Dr Karin Hammarberg explains how to work out when you are ovulating and the right time to have sex to improve your chance of pregnancy.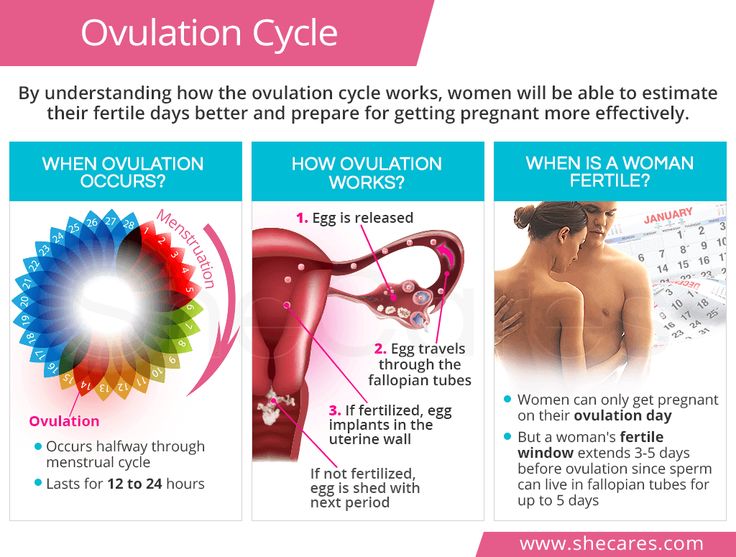
-
What are the chances?
Having sex as close as possible to the time of ovulation increases the chance of pregnancy.
If a woman has sex six or more days before she ovulates, the chance she will get pregnant is virtually zero.
If she has sex five days before she ovulates, her probability of pregnancy is about 10 percent.
If she has sex on the day of ovulation, or the two days before, the chance of getting pregnant is around 30 percent.
These are average figures and depend on a woman’s age.
When does preconception health begin?
Professor Sarah Robertson, Director of Robinson Research Institute, University of Adelaide, highlights the key time before pregnancy that your health is most important to ensure your child has the best start to life.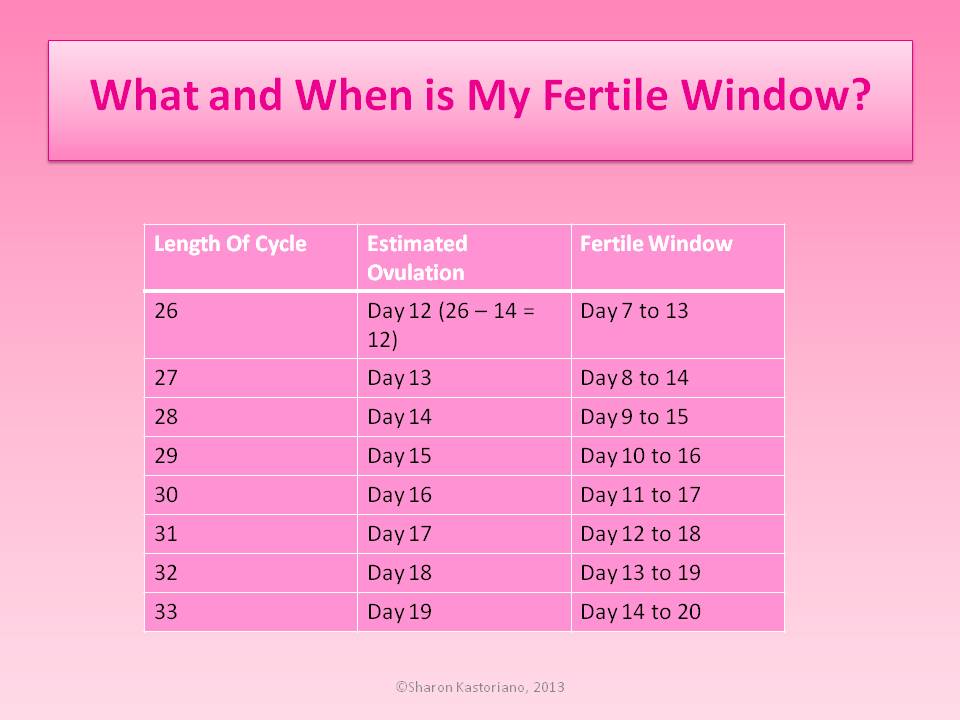
How to know you are ovulating
Kerry Hampton, a registered nurse and fertility specialist, discusses the importance of fertility awareness, and how to determine your fertile window to improve your chances of conceiving.
- References
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine, Optimizing natural fertility, https://www.reproductivefacts.org/news-and-publications/patient-fact-sheets-and-booklets/documents/fact-sheets-and-info-booklets/optimizing-natural-fertility/
- Berglund Scherwitzl, et al. (2015). Identification and prediction of the fertile window using Natural Cycles. The European Journal of Contraception and Reproductive Health Care, 20(5), 403-408. doi:10.3109/13625187.2014.988210
- Ecochard, R., et al. (2015). Self-identification of the clinical fertile window and the ovulation period.
 Fertility and Sterility, 103(5), 1319-1325.e1313. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.031
Fertility and Sterility, 103(5), 1319-1325.e1313. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.031 - Pfeifer, S., et al. (2017). Optimizing natural fertility: a committee opinion. Fertility and Sterility, 107(1), 52-58. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.09.029
- Stanford, J. B. (2015). Revisiting the fertile window. Fertility and Sterility, 103(5), 1152-1153. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.02.015
- Stanford, et al. (2002). Timing intercourse to achieve pregnancy: current evidence. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 100(6), 1333-1341.
- Stephenson, J., et al. (2018). Before the beginning: nutrition and lifestyle in the preconception period and its importance for future health. The Lancet, 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30311-8 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30311-8
- Vélez, M. Pet al. (2015). Female exposure to phenols and phthalates and time to pregnancy: the Maternal-Infant Research on Environmental Chemicals (MIREC) Study. Fertility and Sterility.
 doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.005
doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.005 - Verón, G. L., et al. (2018). Impact of age, clinical conditions, and lifestyle on routine semen parameters and sperm kinematics. Fertility and Sterility, 110(1), 68-75.e64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.03.016
- Waylen, A. Let al. (2009). Effects of cigarette smoking upon clinical outcomes of assisted reproduction: a meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update, 15(1), 31-44.
- Zenzes, M. T. (2000). Smoking and reproduction: gene damage to human gametes and embryos. Hum Reprod Update, 6(2), 122-131.
Page created on: 28/08/2018 | Last updated: 16/10/2022
| Author: http://www.jlady.ru/ |
| January 16, 2012 |
|
Everyone knows where the baby comes from, and this sperm has to meet the egg. The etymology of "ovulation" is "ovum", which means "egg" in Latin. Ovulation is the release of mature eggs that can be fertilized in the ovaries. The most important condition for pregnancy is the existence of good mature eggs, and doctors are interested in this problem in order to assess the general condition of the genitals. In women, there are quite a few causes of infertility, lack of ovulation, and abnormalities in various hormones. Ovulation TestsThe characteristic of ovulation is an isolated sign that feels uncomfortable with the lower abdomen in the middle of the menstrual cycle, and this period is the period of ovulation. On the same day, the genitals may cause bloody discharge or increase libido. However, to get more accurate results, it is better to use one of the following methods. Measurement of rectal temperature (basal body temperature) This method is one of the simplest methods that does not require any financial investment other than buying a thermometer. Ovulation test This is a method to more accurately measure the concentration of LH (hormone Lutea l-Formation), one of the gonadotropins to support the reproductive function of women. Before ovulation, the value of this hormone increases significantly, and as a result, the LH peak point before ovulation can be assumed to be a certain day of the menstrual cycle in the urine, and a special test strip is used for this. If it is a stable cycle, the luteal period will last from 12 to 16 days, so it is best to start the examination about 17 days before the next period. In the case of a total 2 8 day cycle, the test will start on day 1 1st and the 3 5 day cycle should be from day 1 8. If the test result is positive, ovulation will begin between 28 and 42 hours. Dynamic ultrasonic testing and progesterone measurement Ultrasound tests allow you to see the formation of mature missed follicles in the ovaries. After the eggs are released, luteins are formed in this place, producing progesterone, which contributes to the normal growth of the pregnancy. The value of this hormone allows you to get effective information about ovulation. Age and ovulation If you are a young woman with pregnancy, almost your entire menstrual cycle will be ovulated. In addition, they say that in 10-15% of the year there is no ovulation. The general trend is that the older women are, the lower the frequency of ovulation. If you can't get pregnantRegular sexual activity for 1 to 1.5 years is considered normal. If a young woman is of reproductive age and she does not become pregnant after the deadline, doctors will diagnose her couple as infertile. After that, it is recommended that both couples have a consultation to clarify that they can be considered not pregnant. It is recommended that women over 35 not become pregnant for six months after regular sexual activity. Such suggestions were made to avoid wasting time because ovarian function and egg quality decline with age. Factors that affect ovulation Whatever the cause, such as environment, difference in eating habits, and medication. Impractical use of weight loss and fasting often supports anorexia nervosa. For example, patients with anorexia nervosa will give up on their own and fall into extreme fatigue. When weighing less than 45 kg, the body clearly reacts to this and begins to suppress the normal functioning of the reproductive organ. These women stop menstruation and ovulation. Hormonal abnormalities also cause ovulation, most of which are due to genetic causes. Various diseases such as polycystic ovary syndrome, hyperprolactinemia, thyroid dysfunction, syndrome accompanied by an increase in male hormones and sexualization disorders can cause normal ovulation. Some of them can be expected to restore ovulation and pregnancy, while others completely eliminate the processes of ovulation. Ovulation is achieved by prescribing drugs that correct hormonal imbalances and promote ovulation. Many means are intended for this, ranging from tablets to injections. In recent years, new means of stimulating ovulation have appeared. It contains genetically modified gonadotropins and is guaranteed to be free of impurities. With the advent of such drugs, the effectiveness of the treatment of women with endocrine disorders has increased dramatically, both in terms of restoring ovulatory cycles and in terms of fertility. How ovulation affects the sex of the baby David Lowick and Lendran Shettles of Harvard have spent nearly half a century developing a method for planning intercourse based on known ovulation periods. Here's how. Empirically, it has been found that male Y-chromosome spermatozoa are more mobile than X-chromosome spermatozoa, so they can reach the egg first. Interestingly, there is a certain seasonality, which is confirmed by many observations. Girls are often born in early winter, spring, early summer, early autumn and late autumn.
Hysterectomy (or hysterectomy) is a fairly common operation. Its indications are varied, including uterine fibroids, various neoplasms and tumors (including postmenopausal ovarian cysts), endometriosis. The volume of surgical intervention is proposed when the preservation of the affected organ is impossible due to the high risk of complications (bleeding, malignancy, progression). Since this type of surgery has been around for about 100 years, a lot of experience has been accumulated in this area of gynecology. In addition, many clinical studies have been conducted, and now it is possible to draw certain conclusions about the outcome of the operation and the quality of life of the operated patient. In modern gynecological medicine, laparoscopic hysterectomy is possible as long as the size of the uterus allows, providing high accuracy during the operation and a quick recovery after the operation. However, most women who recommend hysterectomy are concerned about the outcome of the operation. However, in many cases, you need to worry about the status of an operation. How does life change? Do I need to make fundamental changes to remove important organs like the uterus and adapt to how my body works? How does this feature affect your sex life, and how should you build relationships with sexual partners? Does surgery change, such as weight gain, rapid skin decline, and black hair on the face and body? If you try to briefly answer these questions, the answer will be. “There are no sudden changes in lifestyle and appearance. And if you want more explanation, read on. Why do such questions arise?The stereotype works on a woman's heart. There is no uterus, no menstruation, no climax. Klimax = aging. Women are convinced that when the uterus is removed, the body is artificially reconstructed, aging is faster, sexual desire is reduced, and many functions are lost. In fact, this stereotype can be extremely easy to break by understanding the anatomical structure of a woman's body and understanding the purpose of the uterus, the occurrence of menstruation and menopause. We are going to help you The uterus and its functions (briefly about the main things) The uterus is an organ that has a specific function in a woman's body (see "Normal Anatomy of the Internal Pelvic Organs") and plays a role in the transfer of embryos for the development of the embryos. At birth, the uterus contracts and plays a very active role in fetal hatching. Among them, it is "supported" by a mucous membrane called the endometrium. The endometrium is saturated with blood vessels, and the blood supply is remarkable in the middle and late period of the menstrual cycle (the doctor says that "the endometrium is thickened"). The body needs the fertilized eggs to be fixed in the uterus and begin to grow. If fertilization is not established, the blood vessels will not reach the blood vessels, the top layer of the endometrium will be cut off and discharged outside the body. Menstruation begins. When the uterus is removed, menstruation does not exist, and because of the absence of the endometrium, there is nothing to excrete outside the body. However, this condition has a completely different character from menopause. This is called "surgical menopause". What is menopause The climax is the disappearance of ovarian function. The secretion of sex hormones (estrogen, testosterone, progesterone) is reduced and the eggs are not mature. Estrogen (female hormone) is very important in the condition of the skeleton and blood vessels, and a deficiency is often accompanied by muscle circulation and blood circulation. Reducing testosterone (male hormone) decreases leads to a decrease in libido (libido). It is the reconstruction of hormones that are actively carried out in the body, which causes external changes such as excess weight, aging skin and hair loss. Even if the uterus is removed, the ovaries continue to function and secrete sex hormones, so the hormones do not change. Clinical studies have proven that the ovaries work at the same time as genetically programmed in the body when the uterus is removed. Estrogen is generated independently of the uterus and continues to have positive effects on the skeletal and cardiovascular systems. Since testosterone is also generated, libido does not decrease and the quality of sex life does not change. In addition, those who are familiar with symptoms such as pre-menstrual syndrome (PMS) will continue. Approach to surgeryIf the doctor thinks the uterus needs to be removed, she does not remove the types of uterus (ovaries or testicular tubes). Modern thinking argues that the ovaries can be left in the cervix as well. It has also been confirmed that the risk of developing ovarian cancer after hysterectomy is reduced. It appears that the risk of ovarian cancer in women after hysterectomy is 1/300, and the risk for women after uterine preservation is 1/80. Psychological consequences of hysterectomy
The correct way to hold is healthy, the key to returning to daily life after surgery. For a good psychological state, you need to first trust your doctor and be convinced that your body will work as before (this is true). Positive attitude and support of important people is very important. Many women give the uterus some kind of symbolic and consider it super, which is important. Sexual life after hysterectomy
Sexual negotiations are prohibited for 1-1.5 months after removal of the uterus (as well as after another operation). This is basically the time it takes for the wound to heal. If you understand that your body is recovering and you can live a normal life again, there is no interference in sexual intercourse. The sensitive areas that give pleasure to women with sexual activity are not in the uterus, but in the vagina and vulva. Of course, the degree of rapport with your sexual partner plays a very important role here. Remember that your partner also needs reliable information. Feel free to discuss any questions or concerns he may have. If necessary, seek a joint consultation with a gynecologist. Perhaps your partner will take his words with more confidence. He must be sure that your sex appeal and feelings will not undergo major changes and that you can continue to be an attractive and voluptuous woman for him. like before. So you have to weigh the pros and cons. The results of a hysterectomy will not cause you any discomfort. You always have to choose between your health after the removal of a diseased organ and imaginary fears of changes in appearance and lifestyle. During the first phase of the menstrual cycle, a follicle, called the main follicle, develops and matures.
The corpus luteum functions for 10-12 days. If conception does not occur, the egg dies, the corpus luteum recedes, which leads to menstruation. Symptoms of ovulation
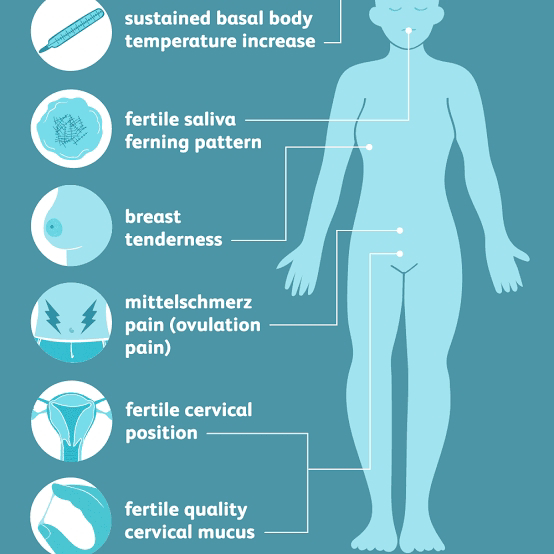
Most women ovulate completely asymptomatically, but some experience symptoms a few days before ovulation. During ovulation, women may experience pain in the lower abdomen. This can make a very strong impression. This disorder is called ovulatory syndrome. The discomfort lasts for several days. Women can change and become more viscous. During ovulation, her sex appeal increases. Egg maturity changes the number of days as follows.
Single cycle studies are considered inconsistent. The duration of the menstrual cycle directly depends on the rate of maturation of the egg in the first stage before ovulation. A typical classic version is 14 days, and the cycle is 28 days. After the release of the egg, the second phase of the cycle (luteal phase) begins, which in the same woman is constant from 12 to 16 days, but more often 14 days. Ultrasonic folliculometrySome ultrasounds with a vaginal probe can calculate a woman's ovulation and conception dates. Examinations in the ultrasound diagnostic room are carried out 3-4 times per cycle every 2-3 days. If you have an irregular cycle, you should visit your doctor 3-4 times every 2-3 days, starting on the 7th day after your period ends. If you have a regular cycle, you can have an ultrasound 2-3 days before delivery. With a 30-day cycle, ultrasound control begins 4-5 days before the middle of the monthly cycle, on days 10-11. The eggs are then checked with ultrasound every 2 days until the eggs are released. With the size of the follicle the day before from 20 to 24 mm and the beginning of the development of the corpus luteum, ultrasound diagnostics confirmed the beginning of the ovulation period.
Ovulation TestsOvulation tests can be done at home if the follicles can be seen with ultrasound. The mechanism is the following. 24-36 hours before the release of the egg from the ovary into the urine, the amount of luteinizing hormone (LH) rises sharply. A day or two before that, she, as it were, “pushes out” the egg from the wall of the ovary. Ovulation test strips determine if the amount of hormones is increasing. Fertile days can also be calculated. Test twice a day 5-6 days before your expected ovulation date.
Basal Temperature Method This method measures the temperature of the rectum (rectum). This is measured immediately after sleep during the cycle. To do this, use a thermometer. You need to knock at night before going to bed. The measurement is taken immediately after getting up in the morning. By correctly measuring your basal body temperature, you can determine whether a patient is ovulating normally, fast, or slow. Calendar method This ovulation judgment method is suitable for people with regular menstrual cycles. Full ovulation occurs 14 days before the start of a new cycle. To find out the number of days it is easy to get pregnant, you need to analyze the last three months. The first day of the menstrual cycle is the first day of menstruation. Cervical mucus assessment methodIn a woman's ovaries, estrogen is secreted just before ovulation. As a result, the number of vaginal cells and cervical mucosa will increase. This mucus is viscous and can be controlled by expanding a small amount of about 2 cm between the fingers. Why doesn't ovulation occur?There may be no ovulation for various reasons. It is divided into two types, normal and uncommon. In this case, you do not need to worry about not ovulating.
Oral contraceptives should not occur.
Early follicle rupture has the following causes.
Not everything, but the female body moves like clockwork. The case when there is no ovulation, although there is regular menstruation, is called the menstrual sutra. Don't worry if this phenomenon doesn't happen two or more times. Lack of ovulation with regular menstrual periods can only be assessed by observing the body for a long time (at least 3 months).
Warsaw
Class Noopris Nensekaya
Asano
This question worries women who dream of children and those who want to protect themselves from unwanted pregnancies. This time, together with the Health Clinic, we will clarify what kind of ovulation occurs from a physiological point of view and how to catch it. Ovulation is the short period of a woman's menstrual cycle when pregnancy is at its strongest. Ovulation lasts from 12 to 24 hours and traditionally occurs in the middle of the 11-21 day cycle, depending on its length. Only women with an ideal menstrual cycle can accurately calculate ovulation using a calendar. Most women should see a gynecologist or try to determine ovulation by a set of symptoms specific to this time of year. Fortunately, we live in the 21st century and we have several ways to determine when we are ovulating. Methods for determining ovulation1. Calendar method This method is very popular but has poor accuracy. As I wrote above, using the calendar, only women who do not have disruptions in the menstrual cycle can determine ovulation. For example, if you have 29- the daily menstrual cycle, menstruation comes on time, and reproductive health is normal, then the calendar method is a good choice. Of course, it should be used by those who want to conceive a child. Otherwise, it will be more reliable to protect yourself, regardless of the day of the cycle. 2. Spawn test Ovulation test is available at any pharmacy and is now available to all women in developed countries. Such tests should be used from the 11th day of the cycle, not earlier. However, this test only detects the luteinizing hormone peak that promotes the distribution of the follicular capsule. This does not guarantee 100% ovulation. Even in perfectly healthy women, the probability of conception on the day of ovulation rarely exceeds 40%. In addition, if the dominant follicle has not matured for some reason, the probability will be completely zero. 3. Follicle Modern and accurate method for determining ovulation. During the operation, a special sensor is inserted during crushing, and the doctor evaluates the condition of each ovarian follicle. From the moment of ovulation, the dominant follicle matures and reaches 20 mm, the optimal time for conception. This procedure should be carried out at least 3 times per cycle on the first day, 11-12 days and 24-25 days after the end of menstruation. The first ultrasound will assess the condition of the ovaries and the number of follicles, the second ultrasound will assess the likelihood and timing of ovulation, and the third ultrasound will assess the chances of pregnancy. In any case, a gynecologist should be consulted before the ultrasound. Doctors give clear instructions and recommendations. 4. Symptoms of ovulation The effect is not confirmed, but it is a popular method for women. In the days leading up to ovulation and during the ovulation period, you will experience various symptoms that indicate a favorable time for conception. There are nuances here. Some women have severe symptoms, while others hardly notice them. But we will talk about them in the next part. Symptoms of ovulationSo what should we be afraid of? Basal body temperature (lowest body temperature after sleep). On the day of ovulation, the temperature drops sharply by about 0.5 ° C, the next day it rises sharply and continues to rise until the 23-27th day of the cycle. To calculate the exact date of ovulation, you need to take your temperature immediately after waking up every day of your cycle and plot it on the change curve. Temperature is taken rectally by inserting the thermometer into the rectum. Changes in cervical mucus. During the fertile period (4-6 days), the mucus is almost transparent, watery and slippery, like egg white, but at the same time thick and elastic. If you pay attention to such changes, your chances of conception will increase significantly. breast swelling; The breasts may become swollen and painful, and the nipples may become tender. Increased libido A few days before ovulation, a woman's attraction to a partner increases. Some women report that their skin and hair have improved and they are more confident. Pain and unpleasant twitching in the lower abdomen on the side of the ovary where the egg has matured. Keeps no more than 5 days. To keep track of all these symptoms, a woman must make an effort to monitor her body throughout the cycle for several months. Symptoms of the end of ovulation There are also symptoms indicating that ovulation has ended.
How to accurately determine the days of ovulation?Currently, only a folliculometer can accurately determine the date of ovulation and the possibility of pregnancy. This is because ultrasound can confirm and evaluate the condition of the follicles before and after ovulation. For example, during the second phase of the cycle, follicles can be reborn and turn into cysts. Ovulation may not occur for a variety of reasons, including stress in a woman's life, rapid weight loss, climate change, and hormonal imbalances. Is it possible to get pregnant not on ovulation, but on other days of the cycle? Yes, I can. It is said that from 6 days before ovulation to 2 days after ovulation, the chance of pregnancy is 16-30%. Since every living being has its own biorhythm, no one will tell you the exact number. The female body is not a clockwork mechanism that works according to medical books. Ovulation may occur later than expected or may occur earlier. You can solve it yourself, but it will take time and energy. If you are thinking about getting pregnant or want to protect yourself from an unwanted pregnancy, please contact us. This increases the chances of success for both the first and second attempts. Version of the site for the visually impaired |
How to independently determine the beginning of ovulation and not make a mistake
Ovulation is the release of an egg from the follicle. It can be tracked with an ultrasound. Or you can do an ovulation test. But some women claim that they feel it without any auxiliary means. Are you one of those?
Ovulation formula
Knowing when ovulation occurs is important for solving two questions: if a woman wants to become pregnant or if a woman chooses a calendar method of contraception.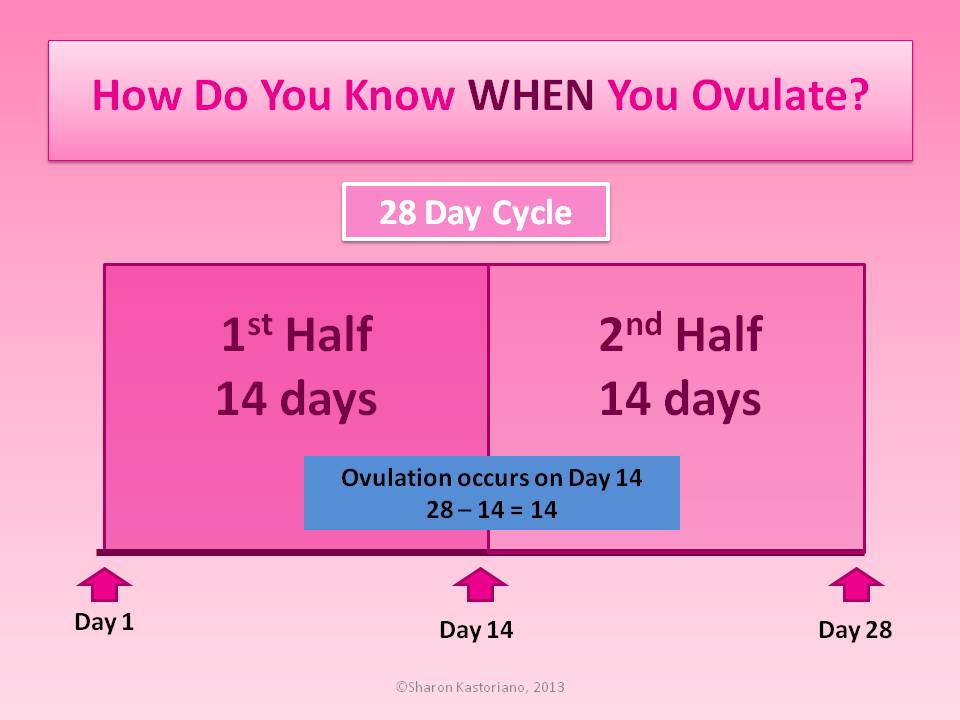 The fertile period - the period when fertilization can occur - lasts approximately six days: five days before ovulation and the day of ovulation. The highest probability of conception is within two days before and on the day of ovulation.
The fertile period - the period when fertilization can occur - lasts approximately six days: five days before ovulation and the day of ovulation. The highest probability of conception is within two days before and on the day of ovulation.
Calculating the day of ovulation mathematically makes sense if you have a very clear and stable menstrual cycle. The length of the first phase of the cycle varies. The second phase is more stable and lasts 14 days. Accordingly, to calculate the day of ovulation, it is necessary to subtract 14 from the cycle length. In an ideal 28-day cycle, ovulation occurs exactly in the middle: 28-14 = 14. In a short cycle, it will occur earlier: for example, with a cycle length of 24 days, ovulation will have to around day 10. In the long - later: 33-14 \u003d 19. For women whose menstrual cycle fluctuates by several days, the formula becomes more complicated: you need to take into account the duration of both the shortest and longest cycles, calculate the average.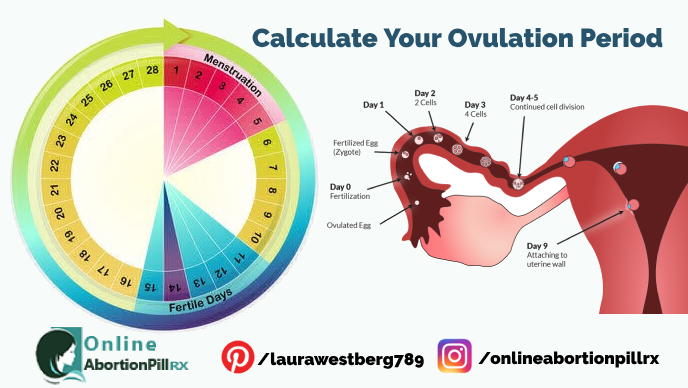 Still, the figure will only be approximate.
Still, the figure will only be approximate.
A woman can determine the days favorable for conception if she pays attention to the changes that occur to her on certain days of the cycle. These changes are most noticeable in the uterine mucosa and cervix.
Mucus
Cervical glands produce mucus. Usually it is thick: a real cork that closes the cervical canal and prevents infections from passing into the uterus. In such thick mucus, sperm cells quickly lose their mobility, and it is difficult for them to rise into the uterine cavity. But the main (dominant) follicle growing in the ovary, from which the egg will be released, produces the hormone estradiol. The more estradiol, the more cervical mucus becomes and the thinner it is. On the eve of ovulation, it becomes extensible, like egg white. In some women, this viscous transparent discharge in the middle of the cycle is very noticeable. For some - a few days before ovulation, for others - only on the day of ovulation itself.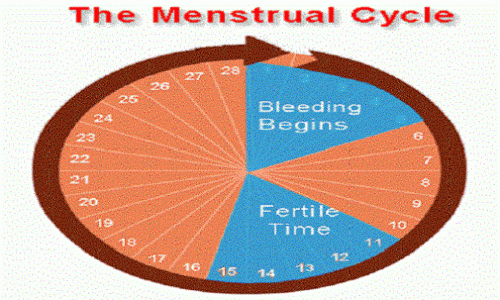 This is individual.
This is individual.
Pain
Ovulation may be indicated by pain in the lower abdomen on the days of the cycle, not associated with menstrual bleeding. The pain can be in the lower abdomen in the center or on the right / left - depending on which ovary the dominant follicle matures. The pain is often of a pulling nature. It may be accompanied by slight bloating or a feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen. At first, the pain is slight, but within a couple of days it can intensify. These pains are associated with an increase in the level of biologically active substances in the body of a woman before ovulation - prostaglandins. Prostaglandins dissolve the wall of the follicle and ovarian tissue so that the egg can be released into the abdominal cavity, and from there into the fallopian tube. The "side effect" of prostaglandins is pain. Just like a change in the nature of cervical mucus, pain associated with ovulation may occur only on the day of ovulation itself or be noted on the eve of ovulation and even a day or two after it.
How to understand that pain is associated with ovulation
It is important to understand that pain in the lower abdomen can be associated with much less pleasant causes than ovulation.
How to understand that this is exactly “it”.
- The pain lasts 1-3 days and goes away on its own.
- Pain recurs in several cycles.
- Approximately 14 days after such pain comes the next menstruation.
Ovulation pain is moderate and does not require pain medication. Severe pain indicates a health problem. If the pain on the days of the alleged ovulation is severe, you need to contact a gynecologist. Other alarming symptoms accompanying pain in the lower abdomen and which may indicate a problem with the uterus and appendages: fever, increased discharge (leucorrhoea) from the genital tract, discoloration of the leucorrhoea from transparent or white to yellow-green, spotting. By the way, taking painkillers and NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) on the days of expected ovulation or shortly before ovulation can reduce the chances of conception.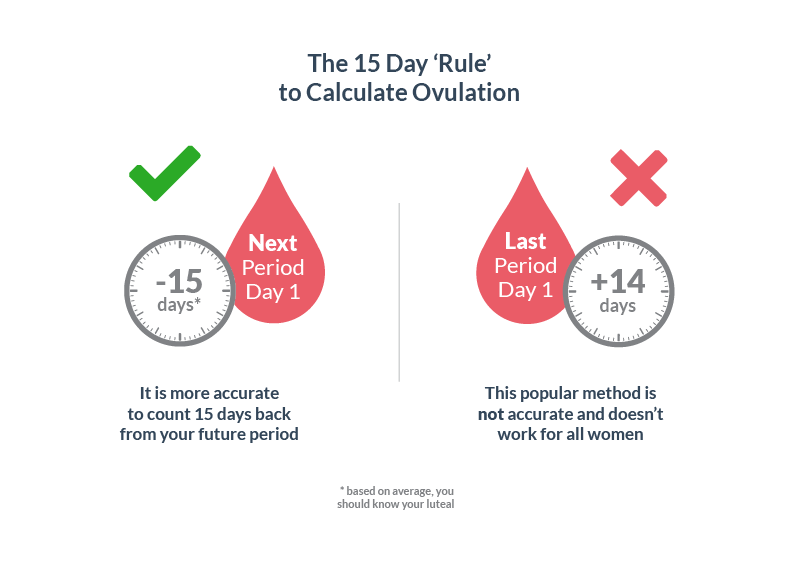
Technical aids
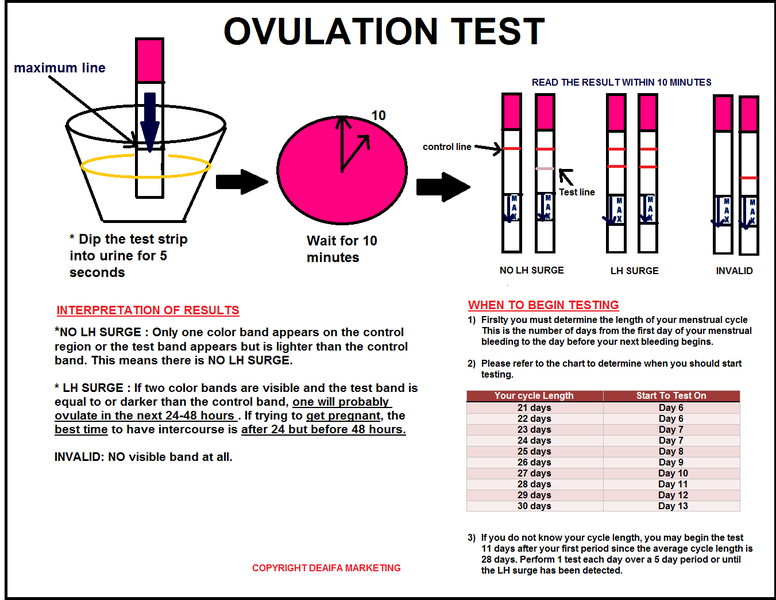
Home test
Ovulation can be determined with a home test available from a pharmacy. The principle of the study is based on determining the concentration of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the urine. The level of LH in women fluctuates depending on the period of the menstrual cycle. Just before ovulation, it reaches its maximum values. The ovulation test makes it possible to register the peak of LH release into the blood. After the maximum LH surge, ovulation occurs within the next 36 hours. Therefore, with a positive ovulation test, this and the following days are most favorable for conception.
Folliculometry
This is a series of ultrasound examinations carried out during one or more menstrual cycles. During folliculometry, the growth of follicles and changes in the endometrium are assessed according to the day of the menstrual cycle, and the fact of ovulation is also ascertained. The average size of the dominant follicle, at which ovulation can occur, is 18-25 mm.
 Therefore, the period that can become pregnant due to defenseless intercourse is six days after ovulation to two to three days after ovulation.
Therefore, the period that can become pregnant due to defenseless intercourse is six days after ovulation to two to three days after ovulation. 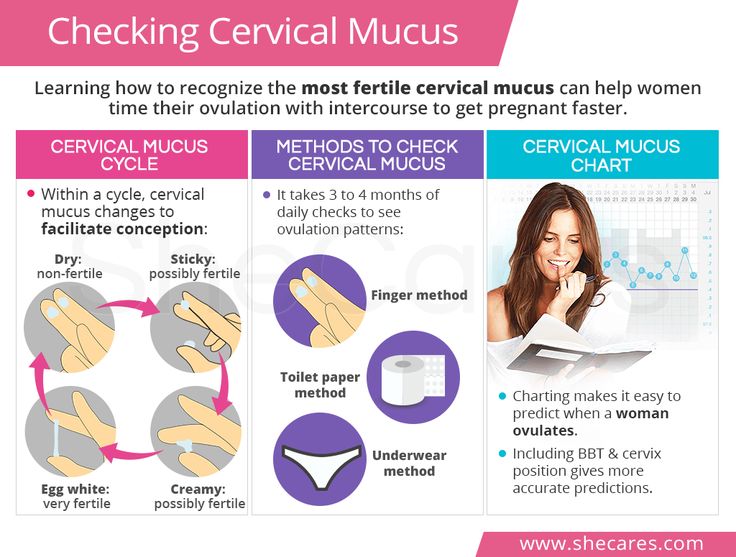
 5 days. It is necessary to check every day until a positive reaction is four days before the expected date of ovulation. Drawback - There is the possibility of a false positive.
5 days. It is necessary to check every day until a positive reaction is four days before the expected date of ovulation. Drawback - There is the possibility of a false positive. 
 However, in order to realize this meeting, more active sperm must be "coming" to the final line, eggs must be mature and follicles.
However, in order to realize this meeting, more active sperm must be "coming" to the final line, eggs must be mature and follicles. 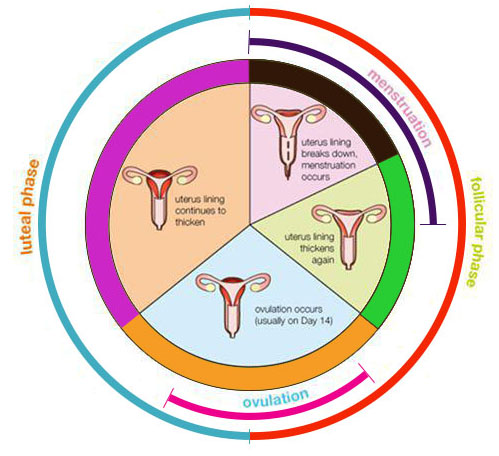 However, it is impossible to completely accurately measure many conditions, such as regular sleep for a long time, measure body temperature at the same time without getting out of bed in the morning. Take the temperature in the rectum. Body temperature information is graphed by taking the menstrual cycle on the horizontal axis and body temperature on the vertical axis. A menstrual cycle can be considered an ovulation period if the temperature difference between the first and second phase is 0.3°C or higher. The first stage is the period before ovulation, the classic normal cycle is 28 days, and the period is 14 days. In the second stage, the remaining two weeks will be a cycle.
However, it is impossible to completely accurately measure many conditions, such as regular sleep for a long time, measure body temperature at the same time without getting out of bed in the morning. Take the temperature in the rectum. Body temperature information is graphed by taking the menstrual cycle on the horizontal axis and body temperature on the vertical axis. A menstrual cycle can be considered an ovulation period if the temperature difference between the first and second phase is 0.3°C or higher. The first stage is the period before ovulation, the classic normal cycle is 28 days, and the period is 14 days. In the second stage, the remaining two weeks will be a cycle. 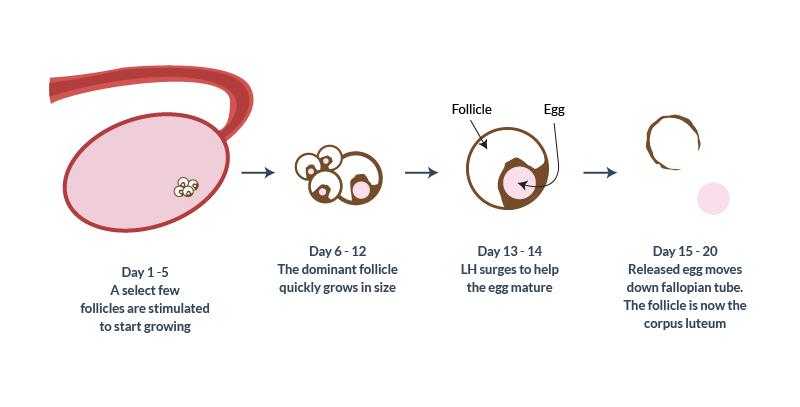 He was. Questionnaire
He was. Questionnaire  At age 40, ovulation does not occur more than six times a year. However, this is not only ovulation. For women over 40, it not only decreases in the ovulation cycle, but also reduces the chance of pregnancy and due to the degradation of egg quality. As a result, it affects the likelihood of pregnancy, normal growth and quality of the embryos.
At age 40, ovulation does not occur more than six times a year. However, this is not only ovulation. For women over 40, it not only decreases in the ovulation cycle, but also reduces the chance of pregnancy and due to the degradation of egg quality. As a result, it affects the likelihood of pregnancy, normal growth and quality of the embryos. 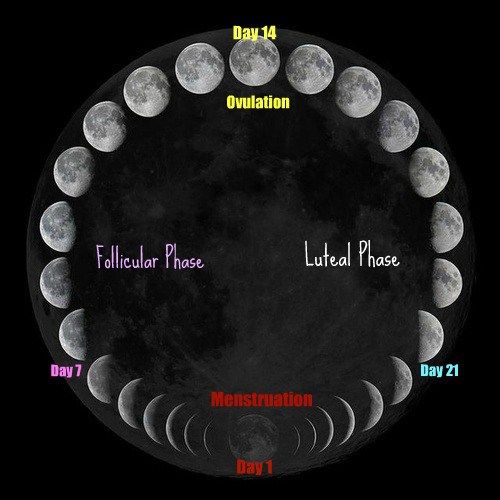 All this causes a hormonal imbalance, which leads to the occurrence of ovulation. These factors, such as constantly changing time zones, long flights, and normal climate changes, can be stressful for the body and cause the reproductive organ to have a normal rhythm. However, these enzymes are usually transient.
All this causes a hormonal imbalance, which leads to the occurrence of ovulation. These factors, such as constantly changing time zones, long flights, and normal climate changes, can be stressful for the body and cause the reproductive organ to have a normal rhythm. However, these enzymes are usually transient. 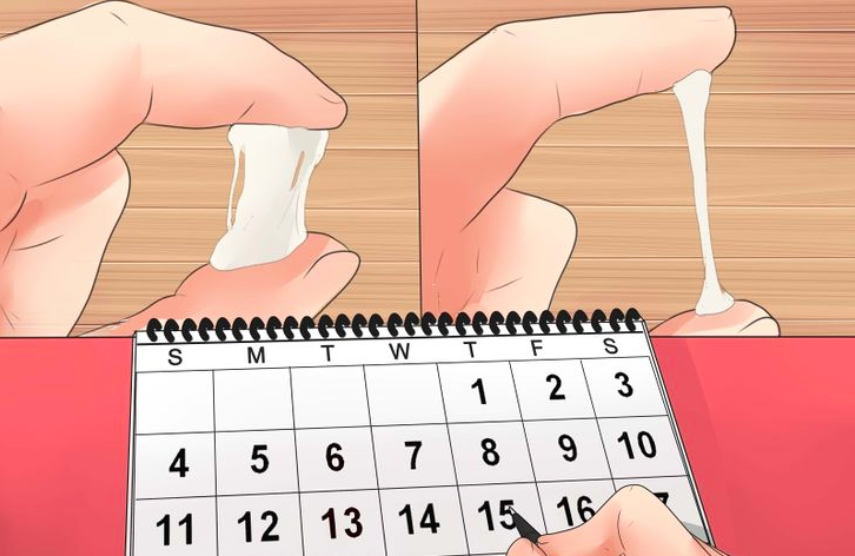 Therefore, the problem of treating hormonal abnormalities and choosing medications should be left to the physician's decision.
Therefore, the problem of treating hormonal abnormalities and choosing medications should be left to the physician's decision.  When exposed to the acidic environment of the vagina, Y-spermatozoa quickly die, becoming less active and giving way to slower, but more viable X-spermatozoa. Scientists believed that X-chromosome sperm could survive in the womb for several days in anticipation of ovulation, unlike Y-chromosome sperm, which could not. As the day of ovulation approaches, the vaginal secretions become more alkaline, which increases the chances of survival of sperm carrying the Y chromosome. If the exact date of ovulation is known, it is possible to plan the sex of the unborn child, making it more likely that certain sperm will participate in the fertilization process. To increase your chances of having a girl, have sex 2-3 days before ovulation. If you want a boy, you should avoid intercourse the week before ovulation until the day of ovulation.
When exposed to the acidic environment of the vagina, Y-spermatozoa quickly die, becoming less active and giving way to slower, but more viable X-spermatozoa. Scientists believed that X-chromosome sperm could survive in the womb for several days in anticipation of ovulation, unlike Y-chromosome sperm, which could not. As the day of ovulation approaches, the vaginal secretions become more alkaline, which increases the chances of survival of sperm carrying the Y chromosome. If the exact date of ovulation is known, it is possible to plan the sex of the unborn child, making it more likely that certain sperm will participate in the fertilization process. To increase your chances of having a girl, have sex 2-3 days before ovulation. If you want a boy, you should avoid intercourse the week before ovulation until the day of ovulation.  Boys are often born in the first two months of winter, in early or late spring, late summer or mid-autumn. With these observations, you will be able to plan the timing of conception and increase your chances of having a gender-differentiated child.
Boys are often born in the first two months of winter, in early or late spring, late summer or mid-autumn. With these observations, you will be able to plan the timing of conception and increase your chances of having a gender-differentiated child. 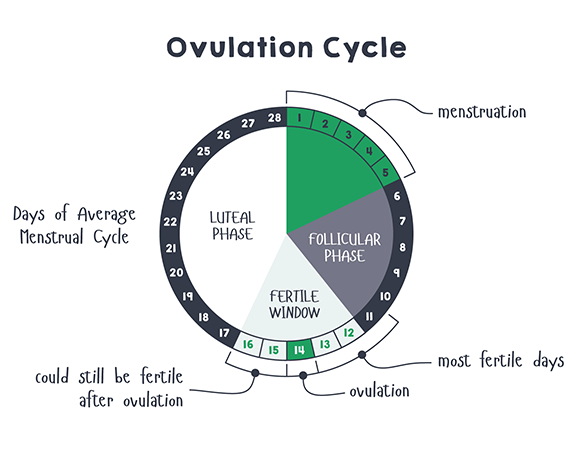
 There is a problem with health and happiness, you will be depressed and you will have irrational fatigue, and as a result it will affect relationships with others, especially relationships with your lover. Psychological problems may be replaced by physiological problems, and family understanding and trust cannot be established. As a result, it causes sad situations such as early, loneliness, fast quality of life, as well as guilt and inferiority.
There is a problem with health and happiness, you will be depressed and you will have irrational fatigue, and as a result it will affect relationships with others, especially relationships with your lover. Psychological problems may be replaced by physiological problems, and family understanding and trust cannot be established. As a result, it causes sad situations such as early, loneliness, fast quality of life, as well as guilt and inferiority. 
 Pre-menstrual syndrome is due to periodic ovarian function.
Pre-menstrual syndrome is due to periodic ovarian function.  In their minds, the womb is assimilated into the essence of women. The fact that the situation is different, as described above. If you emphasize the opinions of others and want to protect yourself from psychological adverse effects, you do not need to explain the details of the operation (including a close relative other than your husband). That's what lies saves." In this case, remember that your most important thing is your health. Both physically and mentally.
In their minds, the womb is assimilated into the essence of women. The fact that the situation is different, as described above. If you emphasize the opinions of others and want to protect yourself from psychological adverse effects, you do not need to explain the details of the operation (including a close relative other than your husband). That's what lies saves." In this case, remember that your most important thing is your health. Both physically and mentally. 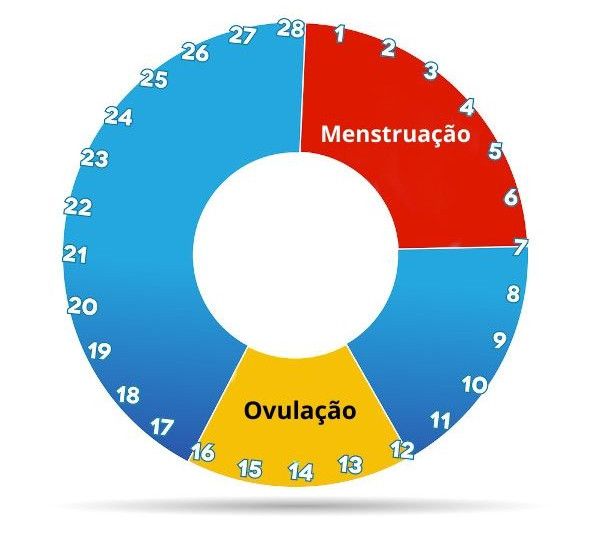 He feels cramped and anxious, tries to adapt to your new state, is afraid of sudden movements, experiences a general fear. In addition, his feelings will be determined solely by your feelings. He will take your situation positively and take everything very seriously.
He feels cramped and anxious, tries to adapt to your new state, is afraid of sudden movements, experiences a general fear. In addition, his feelings will be determined solely by your feelings. He will take your situation positively and take everything very seriously.  Ovulation occurs when the dominant follicle breaks its wall and comes out. enter the fallopian tubes. You can fertilize throughout the day. The dominant follicle of the second cycle turns into a corpus luteum and its main function is the synthesis of progesterone.
Ovulation occurs when the dominant follicle breaks its wall and comes out. enter the fallopian tubes. You can fertilize throughout the day. The dominant follicle of the second cycle turns into a corpus luteum and its main function is the synthesis of progesterone. 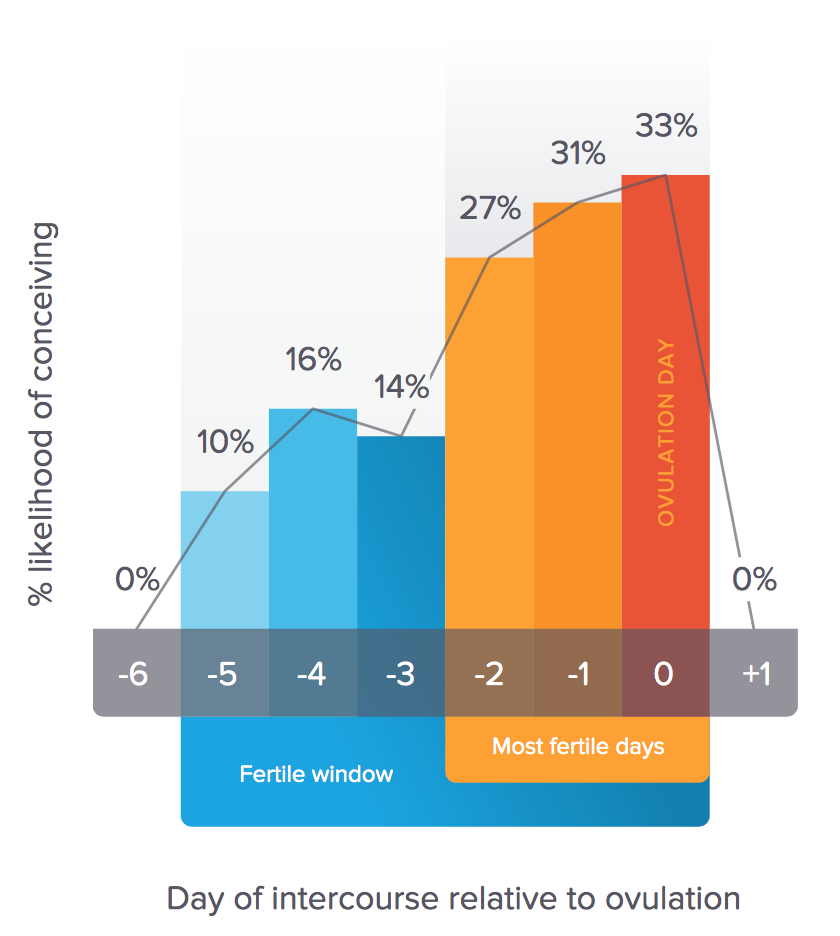
 In a long cycle, the egg matures longer than usual and ovulates later. For example, in a woman with a 32-35-day cycle, the release of the egg occurs at 18-21 DC, two weeks before the start of the next menstruation, and not in the middle of the cycle, as many believe.
In a long cycle, the egg matures longer than usual and ovulates later. For example, in a woman with a 32-35-day cycle, the release of the egg occurs at 18-21 DC, two weeks before the start of the next menstruation, and not in the middle of the cycle, as many believe. 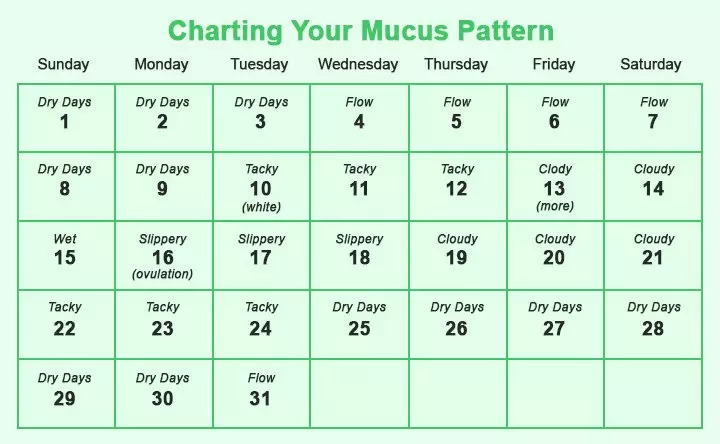 This operation can be performed through the vagina or through the abdominal wall. Vaginal examination does not require prior preparation and is primarily associated with the emptying of the cyst. Abdominal examination is traditionally performed from the side of the abdominal wall. For three days prior to the study, anything that can cause flatulence or bloating should be avoided, and on the day of the study, you should not eat or drink at least 1 liter of water.
This operation can be performed through the vagina or through the abdominal wall. Vaginal examination does not require prior preparation and is primarily associated with the emptying of the cyst. Abdominal examination is traditionally performed from the side of the abdominal wall. For three days prior to the study, anything that can cause flatulence or bloating should be avoided, and on the day of the study, you should not eat or drink at least 1 liter of water. 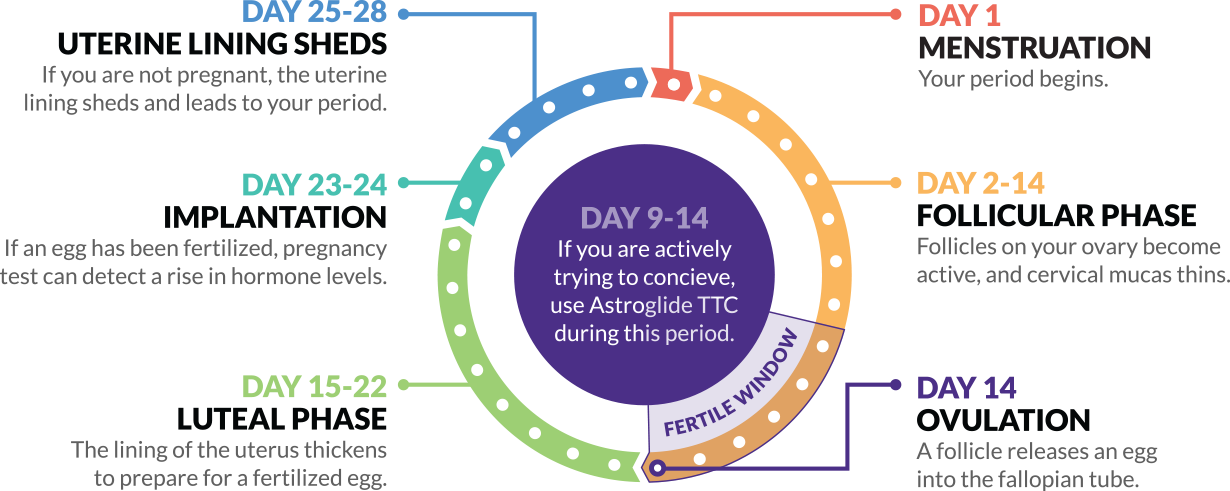 Since we are interested in ovulation in a 30-day cycle, it is recommended to start measuring around the 13th day. If ovulation is not observed, the second strip will be absent. However, the day before and on the 15th day, the test line had the same brightness as the control line. Similar signs indicate that ovulation is expected in the next 24 hours. It should be placed in a container of fresh urine for a few seconds, placed on a dry surface and the result read after about 5 minutes. This test is carried out by analogy with the test for detecting conception.
Since we are interested in ovulation in a 30-day cycle, it is recommended to start measuring around the 13th day. If ovulation is not observed, the second strip will be absent. However, the day before and on the 15th day, the test line had the same brightness as the control line. Similar signs indicate that ovulation is expected in the next 24 hours. It should be placed in a container of fresh urine for a few seconds, placed on a dry surface and the result read after about 5 minutes. This test is carried out by analogy with the test for detecting conception. 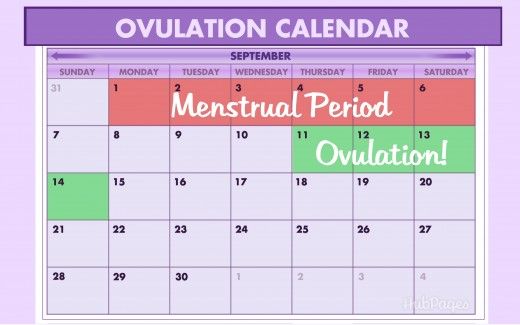 This is one of the easiest ways to appreciate a day when it's easy to get pregnant. It's a good idea to do this after waking up in the morning without getting out of bed. Now, as soon as I woke up, I was next to the thermometer. All results must be carefully noted with special graphics. At the end of the cycle, all points with measurement results are associated with broken programs. It cannot be measured during menstruation. On the first day of the cycle, the temperature reaches 36.9° C. A few days before ovulation, it can be 36.2 ° C-36.4 ° C. An increase in temperature to 37 ° C indicates that 37.4 ° C has ovulated. If the body temperature after the increase in ovulation, probably pregnant.
This is one of the easiest ways to appreciate a day when it's easy to get pregnant. It's a good idea to do this after waking up in the morning without getting out of bed. Now, as soon as I woke up, I was next to the thermometer. All results must be carefully noted with special graphics. At the end of the cycle, all points with measurement results are associated with broken programs. It cannot be measured during menstruation. On the first day of the cycle, the temperature reaches 36.9° C. A few days before ovulation, it can be 36.2 ° C-36.4 ° C. An increase in temperature to 37 ° C indicates that 37.4 ° C has ovulated. If the body temperature after the increase in ovulation, probably pregnant. 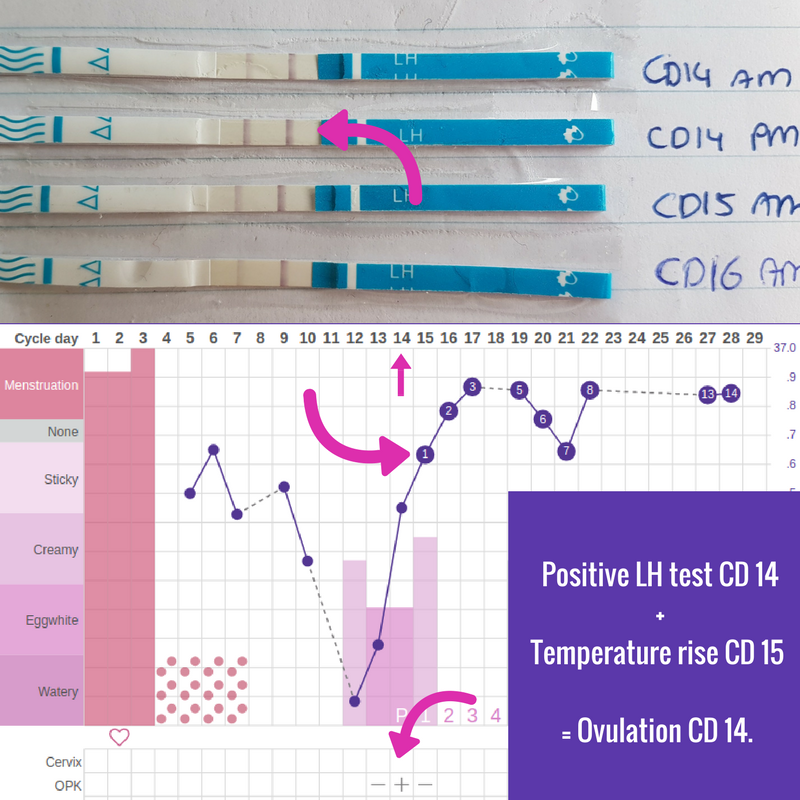 Fully ovulation occurs 12-14 days before the start of a new cycle. The cycle also changes due to various factors such as health, nervousness, stress, physical activity and changes in climate while driving.
Fully ovulation occurs 12-14 days before the start of a new cycle. The cycle also changes due to various factors such as health, nervousness, stress, physical activity and changes in climate while driving. 

 It is noteworthy that they are few.
It is noteworthy that they are few.  Two days before ovulation, both test and control strips will become lighter, signaling the start of the fertile period.
Two days before ovulation, both test and control strips will become lighter, signaling the start of the fertile period. 
 However, it is good to remember that there is no day in the cycle when the chances of conception are zero. Even during menstruation.
However, it is good to remember that there is no day in the cycle when the chances of conception are zero. Even during menstruation.